
Konkani language
Encyclopedia
KonkaniKonkani is a name given to a group of several cognate dialects spoken along the narrow strip of land called Konkan, on the west coast of India. This is, however, somewhat an over-generalisation. Geographically, Konkan is defined roughly as the area between the river Damanganga to the north and river Kali to the south; the north-south length being approx. 650 km. and east-west breadth about 50 km., going unto 96 km. in some places. A major part of Konkan is in Maharashtra most people in the area speak some dialects of Marathi. The dialect spoken in Goa and further south in coastal Karnataka and in some parts of northern Kerala has its distinct features, and is rightly identified as a separate language called Konkani and is hence is within the purview of this article. (Devanāgarī
: , , Roman script
: , , Kannada script
: , , Malayalam script
: ) is an Indo-Aryan language
belonging to the Indo-European
family of languages and is spoken on the western coast of India. It has approximately 3.6 million speakers. It is one of the official languages of India and is the official language of the Indian state of Goa
. It is a minority language in Karnataka
and northern Kerala
(Kasaragod district
).
Konkani is classified as a southern Indo-Aryan language along with Kadodi and Marathi
.
 The Proto-Australoids also known as Shabars who are believed to have come from the west, once formed the aboriginal population of Goa and Konkan. Gaudes, Kunbis, Mahars of Konkan today are supposed to be the modern representatives of Proto-Australoids. Many Konkani words related to agriculture find their roots in Proto-Australoid dialects, e.g.: kumeri, mer, zonn, khazzan.
The Proto-Australoids also known as Shabars who are believed to have come from the west, once formed the aboriginal population of Goa and Konkan. Gaudes, Kunbis, Mahars of Konkan today are supposed to be the modern representatives of Proto-Australoids. Many Konkani words related to agriculture find their roots in Proto-Australoid dialects, e.g.: kumeri, mer, zonn, khazzan.
The later settlers of Goa viz. the Mediterraneans also exerted an impact on this language. Some of their people can be collectively called the Dravidians. Words like tandul, narikel or naall, dholl, madval and others have Dravidian origin.
Subsequently, waves of Indo-Aryan dialect speakers have occurred in the history of the Indian west coast. Around 2400 BC the first wave of Indo-Aryans dialect speakers might have occurred, and the second wave in the period 1000-700 BC came and settled in the west coast. Most of them spoke Indo-Aryan Prakrit
vernacular languages, akin to Vedic Sanskrit
. Thus Konkani was born as a confluence of the Indo-Aryan dialects while accepting many words from the proto-Australoid speech. Proto-Konkani born out of Shauraseni vernacular Prakrit at the earlier stage of the evolution and later Maharashtri
prakrit, commonly spoken until 875 CE at its later phase ultimately developed into Apabhramsha which could be called as predecessor old Konkani.
Goa was ruled by the Mauryas and the Bhoja
a, as a result numerous migrations occurred from North-east and Western India. Immigrants spoke various vernaculars,which led to an admixture of features of Eastern and Western Prakrits. The Sumer
ians had trade contacts with India dating from 2100 BC. Many Sumerians settled in Goa and Konkan, arriving by sea. The period of Sumerian migration started about 2000 BC, after the first wave of Indo-Aryan speakers settled in Goa. Sumerian cuneiform
inscriptions have been found in Goa. Dhume gives many examples of how Sumerian language influenced the native Goan tongue and how the language still retains many Sumerian features and words.
It was substantially influenced later by Magadhi Prakrit and the overtones of Pali (the liturgical language of the Buddhists) that played a very important role in development of Konkani Apabhramsha grammar and vocabulary. A major number of linguistic innovations in Konkani are shared with Eastern Indo-Aryan languages like Bengali
, Oriya
which have its roots in Magadhi.
Maharashtri was the official language of the Satavahana Empire that ruled Goa and Konkan in the early centuries of the Common Era. Under the patronage of the Satavahana Empire, Maharashtri became the most widespread Prakrit of its time.
Studying early Maharashtri compilations many linguists have called Konkani as the first-born daughter of Maharashtri. This old language that was prevalent contemporary to old Marathi is found to be distinct from its counterpart.
The Sauraseni impact on Konkani is not so prominent than that of Maharashtri. Very few Konkani words are found to follow the Sauraseni pattern. Konkani forms are rather more akin to Pali than the corresponding Sauraseni forms. The major Sauraseni influence on Konkani, is the ao sound found at the end of many nouns in Sauraseni, which becomes o or u in Konkani, e.g.: dando, suno, raakhano and dukh, rukhu, manisu from prakrit dandao, sunnao, rakkhakao, dukkhao, vukkhao or vrukkhao, mannisso respectively. Another example could be the sound of ण in the beginning of the words, is still retained in many Konkani words as in archaic Shauraseni. E.g.: णव nine.
This form of old Konkani is referred to as Paishachi apabhramsha
by some linguists. This progenitor of Konkani or Paishachi apabhramsha has preserved an older form of phonetic and grammatic development showing greater variety of verbal forms found in Sanskrit and larger number of grammatical forms that are not found in Marathi, examples of which are found in many works like Dnyaneshwari
, and Leela Charitra.
The language is endowed with overall Sanskrit complexity and grammatical structure, that developed a lexical fund of its own.
Though it belongs to Indo-Aryan group, Konkani was influenced by Kannada, a member of Dravidian family. The Kadambas
who ruled Goa for a long period had their roots in Karnataka
Konkani was never used for official purposes. Another reason Kannada influence on Konkani is proximity of original Konkani speaking territory to Karnataka.
Old Konkani documents show considerable Kannada influence on grammar as well as the vocabulary. Like southern Dravidian languages Konkani has prothetic glides
y- and w-. Kannada influence is more evident in Konkani syntax. The question markers in yes/no questions and the negative marker are sentence final. Copula deletion in Konkani is remarkably similar to Kannada.
Phrasal verbs are not so commonly used in Indo-Aryan languages, Konkani spoken in Dravidian regions has however borrowed numerous phrasal verb patterns.
The table below illustrates some phrasal verbs used in Konkani:
It is said that Gujarat has got many historical ties with the port of Goa, mainly because of trade, and it is also said that many people have migrated to Goa via the port of Dwaraka
.
The Kols, Kharwas, Yadavas, and the Lothal
migrants settled in Goa during the pre-historic and the later period. Chavada, a tribe of warriors (now known as Chaddi or Chaddo), migrated to Goa from Saurashtra,during 7th and 8th century CE, after their kingdom was destroyed by the Arab
s in 740 AD. Royal matrimonial relationships between the two states, and the trade relationships had a major impact on Goan society which greatly influenced the language as a whole.
Goa being a major centre for trade was visited by Arabs, Turks since early times. Thus many Arabic and Persian words infiltrated into Konkani language. A large number of Arabic and Persian words form an integral part of Konkani vocabulary now and commonly used in day to day life by its speakers.e.g.;dukan(shop),karz(debt),fakt(only),dusman(enemy),barik(thin) etc. Single and compound words are found herein the original meaning is changed or distorted;mustaiki,(from Arabic Mustaid meaning ready),kapan khairo-eater of one's own shroud/miser and so on.
Most of the old Konkani Hindu literature does not show any influence of the Portuguese language. Even the spoken dialects by the majority of Goan Hindus has a very limited Portuguese influence. On the other hand, the spoken dialects of the Catholics from Goa (as well as the Canara to some extent), and their religious literature shows a strong Portuguese influence. They contain a number Portuguese lexical items but these are almost all religious terms. Even in the context of religious terminology, the missionaries adapted native terms associated with Hindu religious concepts. (For example Krupa for grace, Yamakuna for hell, Vaikuntha for paradise and so on). The syntax used by Goan Catholics in their literature shows a prominent Portuguese influence. As a result, many Portuguese loanwords are now commonly found in vernacular Konkani speech.
period in Brahmi
script, ascribed to the 2nd Century AD. It reads śacipurācyā śirāsi (on the top of Shachipura) in the late Brahmi script. Another inscription in Nāgarī
, of Shilahara King Aaparditya of the year 1166 AD says: ātā̃ jō kōṇṇuyirē śāsanō̃ḷapī̃ tēcyā vēḍhyāta dēvācī bhāla saktumbī āpaḍē̃ tēcī mā̃ya gāḍhavē̃. An inscription at the foot of the colossal Jain monolith Gomaṭēśvara (Bāhubali) Konkani: gomṭo – pretty masc., īśvar – God at Shravanabelagola of 981 CE reads "śrīcāvuṇḍarājē̃ kara viyālē̃, śrīgaṅgārājē̃ suttālē̃ kara viyālē̃" (Chavundaraya
got it done, Gangaraya got the surroundings done).Chavundaraya
was the military chief of the Ganga dynasty King Gangaraya. This inscription on the Bahubali statue draws attention to a Basadi (Jain Temple) initially built by him and then modified by Gangaraya in the 12th century CE Ref: S. Settar in Adiga (2006), p256
Stone and copper-plate inscriptions found in Goa and Konkan are written in an amalgam of Konkani and old-Marathi, written in Nāgarī
as well as Goykanadi
script. The grammar and the base of such texts is in Konkani, whereas very few verbs are in Marathi. One such stone inscription or shilalekh is found at the Nageshi temple in Goa (dating back to the year 1463 AD) mentions that the (then) ruler of Goa, Devaraja Gominam, had gifted land to the Nagueshi
Maharudra temple when Nanjanna Gosavi was the religious head or the Pratihasta of the state. It mentions words like, kullgga,kulaagra, naralel, tambavem, tilel.
The above inscription has been quite controversial, and touted as being old-Marathi. But the distinctive instrumental viyalem ending of the verb is the hallmark of Konkani language, and the verb sutatale or sutatalap is not prevalent in Marathi. So linguists and historians such as S.B. Kulkarni of Nagpur University, Dr V.P. Chavan (former vice-president of the Anthropological society of Mumbai), and others have thus concluded that it is Konkani.
 A piece of hymn dedicated to lord Narayana
A piece of hymn dedicated to lord Narayana
attributed to 12th century AD goes "jaṇẽ rasataḷavāntũ matsyarūpē̃ vēda āṇiyēlē̃. manuśivāka vāṇiyēlē̃. to saṁsārasāgara tāraṇu. mōhō to rākho nārāyāṇu". (The one who brought the Vedas up from the ocean in the form of a fish, from the bottoms of the water and offered it to Manu
, he is the one Saviour of the world, that is Narayana my God.). A hymn from later 16th century goes vaikuṇṭhācē̃ jhāḍa tu gē phaḷa amṛtācē̃, jīvita rākhilē̃ tuvē̃ manasakuḷācē̃.
Early Konkani was marked by the use of pronouns like dzo / jī / jẽ . This is replaced in contemporary Konkani by koṇa . The conjunctions yedō..tedō.. (when..then...) which were user in early Konkani are no longer in use. The use of "-viyalẽ'"' has been replaced by " -aylẽ". The pronoun moho, which is similar to the Brijbhasha word mōhē has been replaced by mākā.
(today's coastal Karnaraka) and Cochin.
These events caused the Konkani language to evolve into multiple dialects. The exodus to coastal Karnataka and Kerala required Konkani speakers in these regions to learn the local languages and hence this caused penetration of local words into the dialects of Konkani spoken by these speakers. e.g. the word dār (door) gave way to the word bāgil .
The phoneme "a" in the Salcette dialect was replaced by the phoneme "o"
Other Konkani communities came into being with their own dialects of Konkani. The Konkani Muslim
communities of Ratnagiri
and Bhatkal
came about due to a mixture of intermarriage of Arab seafarers and locals as well as conversions of Hindus to Islam. Another migrant community that picked up Konkani was the Siddis who were sailor-warriors from Ethiopia.
. This consists of the Konkan
division of Maharashtra
, the state of Goa
, and the Uttara Kannada
(formerly North Canara), Udupi
and Dakshina Kannada
(formerly South Canara) districts of Karnataka, together with many districts in Kerala(Kasargod, Kochi, Alappuzha, Trivandrum, Kottayam etc.). Each region has a different dialect
, pronunciation
style, vocabulary, tone and sometimes, significant differences in grammar.
The Census Department of India, 1991 figures put the number of Konkani speakers in India as 1,760,607 making up 0.21% of India's population. Out of these, 602,606 were in Goa
, 706,397 in Karnataka
, 312,618 in Maharashtra
and 64,008 in Kerala
. It ranks 15th in the list of Scheduled Languages by strength. According to the 2001 estimates of The Census Department of India, there are 2,489,015 Konkani speakers in India. A very large number of Konkanis live outside India, either as expatriates or citizens of other countries (NRIs). Determining their numbers is difficult.
Ethnologue
puts the number of Konkani speakers at 3.6 million in 2000.
A significant number of Konkani speakers are found in Kenya
and Uganda
, Pakistan
, Persian Gulf
and Portugal
. During Portuguese rule many Goans had migrated to these countries. Many families still continue to speak different dialects that their ancestors spoke, which are now highly influenced by the native languages.
. His death anniversary, 9 April, is celebrated as World Konkani Day (Viswa Konknni Dis).
Madhav Manjunath Shanbhag, an advocate by profession from Karwar, who with a few like-minded companions travelled in all the Konkani speaking areas, seeking to unite the fragmented Konkani community under the banner of "one language, one script, one literature". He succeeded in organizing the first All India Konkani Parishad
in Karwar in 1939 Successive Adhiveshans of All India Konkani Parishad held at various places in the following years. 27 Annual Adhiveshans of All India Konkani Parishad
have been held so far.
Late Pandu Putti Kolambkar an eminient Social Worker of Kodibag, Karwar Strived a lot for the Upliftment of Konkani in Karwar (North Kanara) & The Konkan.
However, with the reorganization of states along linguistic lines, and growing calls from Maharashtra, as well as Marathis in Goa for the merger of Goa into Maharashtra, an intense debate was started in Goa. The main issues discussed were the status of Konkani as an independent language and Goa's future as a part of Maharashtra or as an independent state. A plebiscite retained Goa as an independent state in 1967. However, English, Hindi and Marathi continued to be the preferred languages for official communication, while Konkani was sidelined.
. Suniti Kumar Chatterji
, the president of the Akademi appointed a Committee of linguistic experts to settle the dispute. On February 26, 1975, the Committee after due deliberation, came to the conclusion that Konkani was indeed an independent and literary language with it being classified as an Indo-European language which in its present state is heavily influenced by the Portuguese language.
Konkani was included in the Eight Schedule of the Constitution of India, as per the Seventy-First Amendment on 20 August 1992, adding it to the list of National Languages.
s. Like the other Indo-Aryan languages
, it has both long and short vowels and syllables with long vowels may appear to be stressed. Different types of nasal vowels are a special feature of the Konkani language.
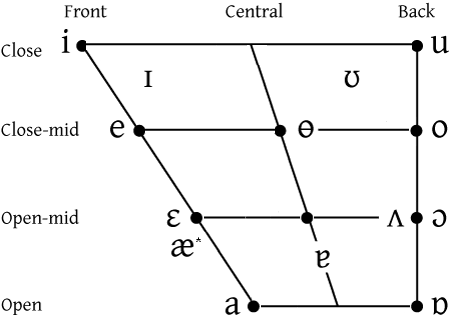 One of the most distinguishing features of Konkani phonology is the use of ɵ, the close-mid central vowel, instead of the schwa
One of the most distinguishing features of Konkani phonology is the use of ɵ, the close-mid central vowel, instead of the schwa
as used in Hindi
and Marathi
.
Whereas most Indian languages use only one of the three front vowels, represented by the Devanagari grapheme ए (IPA:e), Konkani uses three: e, ɛ and æ.
Nasalizations exist for all vowels except for ʌ.
The consonants in Konkani are similar to those in Marathi
.
Like most of the Indo-Aryan languages Konkani is an SOV
language, meaning among other things that not only is the verb found at the end of the clause but also modifiers and complements tend to precede the head and postpositions are far more common than prepositions. In terms of syntax Konknai is a head-last language unlike English which is an SVO
language.
The following table illustrates this:
>
e.g.: I eat and I am eating sound similar in Goan Konkani, due to loss of auxiliary in colloquial speech. hāv khātā corresponds to I am eating. On the other hand in Karnataka Konkani hāv khātā corresponds to I eat, and hāv khātoāsā or hāv khāter āsā means I am eating
, but it still retains Prakrit
and apabhramsha structure, verbal forms and vocabulary. Though Goan Hindu dialect is highly Prakritsed, numerous Sanskrit loan words are found unlike the Catholic dialect which was influenced by Portuguese as they got converted in early 16th century. The catholic literary dialect has now adopted Sanskrit vocabulary again, the Catholic Church has also adopted Sanskritisation policy. Even though recently introduced Sanskritic vocabulary is difficult and unfamiliar to the new catholic generations, they have not revolted. On the other hand, southern Konkani dialects, having been influenced by Kannada, which is one of the most sanskritised language of Dravidian origin, have undergone re-sanskritisation in the due course of time.
was originally used but fell into disuse.
A script called as Kandevi or Goykandi was used in Goa since the times of the Kadambas, although it lost its popularity after 17th century. Kandevi/Goykandi is very different from the Halekannada script, with strikingly similar features. Unlike Halekannada, Kandevi/Goykandi letters were usually written with a distinctive horizontal bar, like the Nagari scripts. This script may have been evolved out of Kadamba script
which was extensively used in Goa and Konkan. The earliest documents written in this script is found in a petition addressed by Ravala Śeṭī; most probably a Gaunkar of Caraim in the islands of Goa, to the king of Portugal
. This 15th century document bears signature in Konkani which says: Ravala Śeṭī baraha ( Translation: writing of Ravala Śeṭī). The earliest known inscription in Devanagari dates back to 1187 A.D. The Roman script has the oldest preserved and protected literary tradition beginning from the 16th century.
, Roman
, Kannada
, Malayalam
and Perso-Arabic
. The Goan Hindus use the Devanagari
script in their writings while the Goan Catholics use the Roman script
. The Saraswats of Karnataka
use the Devanagari script in the North Kanara district, but those in Udupi and South Kanara use the Kannada script
. The Karnataka Christians also use the Kannada script. Malayalam script
was used by the Konkani community in Kerala, but now there is a move to use the Devanagari script. Konkani Muslims around Bhatkal taluka of Karnataka use Arabic script to write Konkani.
s. The dialect tree structure of Konkani can easily be classified according to the region, religion, caste and local tongue influence.
Other researchers have classified the dialects differently.
Kalelkar classification
Based on the historical events and cultural ties of the speakers, N. G. Kalelkar
has broadly classified the dialects into three main groups:
Ethnologue (ISO) classification
Ethnologue assigns two ISO 639-3
codes to varieties of Konkani, which it labels a 'macrolanguage
' with the code :
Both languages are referred to as Konkani by their respective speakers.
Efforts have been made to stop this downward trend of usage of Konkani, starting with Shenoi Goembab's
efforts to revive Konkani. There has been a renewed interest in Konkani Literature. The recognition granted by Sahitya Akademi
to Konkani and the institution of an annual award for Konkani literature has helped.
Some organisations such as the Konkan Daiz Yatra, organised by Konkani Bhasha Mandal, Mumbai since 1939 and the newer Vishwa Konkani Parishad have laid great stress on uniting all factions of Konkanis.
. In the 1991 census, as compared to the national average of 19.44% for bilingualism and 7.26% for trilingualism; Konkani speakers scored 74.20% and 44.68% respectively. This makes Konkanis the most multilingual community of India.
This has been due to the fact that in most areas where Konkanis have settled, they seldom form a majority of the population and have to interact with others in the local tongue. Another reason for bilingualism has been the lack of schools teaching Konkani as a primary or secondary language.
While bilingualism is not by itself a bad thing, it has been misinterpreted as a sign that Konkani is not a developed language. The bilingualism of Konkanis with Marathi in Goa and Maharashtra has been a source of great discontent because it has led to the belief that Konkani is a dialect of Marathi and hence had a bearing on the future of Goa.
and Maharashtra
, the strong Marathi influence on Konkani dialects spoken in Maharashtra (such as Malwani), a supposed lack of literature in Konkani and a great degree of bilingualism of Konkani Hindus with respect to Marathi.
José Pereira, in his 1971 work “Konkani – A Language: A History of the Konkani Marathi Controversy”, pointed to an essay on Indian languages written by John Leyden in 1807 wherein Konkani is called a “dialect of Maharashtra” as an origin of the language controversy.
Another linguist to whom the error is attributed is Grierson
. Grierson's work on the languages of India: The Linguistic Survey of India was regarded as an important reference by other linguists. In his book, Grierson had distinguished between the Konkani spoken in costal Maharashtra (then, part of Bombay Presidency) and the Konkani spoken in Goa as being two different languages. He regarded the Konkani spoken in costal Maharashtra as a dialect of Marathi and not as a dialect of Goan Konkani itself. But, in his opinion, Goan Konkani was also to be considered a dialect of Marathi because the religious literature used by the Hindus in Goa was not in Konkani itself, but in Marathi. Grierson's opinion about Goan Konkani was not based on its linguistics but on the diglossic situation in Goa.
S. M. Katre's 1966 work, The Formation of Konkani, which utilized the instruments of modern historical and comparative linguistics across six typical Konkani dialects, showed the formation of Konkani to be distinct from that of Marathi. Shenoi Goembab
, who played a pivotal role in the Konkani revival movement, rallied against the pre-eminence of Marathi over Konkani amongst Hindus and Portuguese amongst Christians.
Goa's accession to India in 1961 came at a time when Indian states were being reorganized along linguistic lines. There were demands to merge Goa with Maharashtra state. This was because Goa had a sizeable population of Marathi speakers and Konkani was also considered to be a dialect of Marathi by many. Konkani Goans were opposed to the move. The status of Konkani as an independent language or as a dialect of Marathi had a great political bearing on Goa's merger, which was settled by a plebiscite in 1967.
The Sahitya Akademi
(a prominent literary organization in India) recognized it as an independent language in 1975, and subsequently Konkani (in Devanagari
script) was made the official language of Goa in 1987.
In Karnataka, which has the largest number of Konkanis, leading organisations and activists have similarly demanded that Kannada script be made the medium of instruction for Konkani in local schools instead of Devanagari. Government of Karnataka has given its approval for teaching of Konkani as an optional third language from 6th to 10th standard students either in Kannada or Devanagari script.
 There are organisations working for Konkani but, primarily, these were restricted to individual communities. The All India Konkani Parishad
There are organisations working for Konkani but, primarily, these were restricted to individual communities. The All India Konkani Parishad
founded on 8 July 1939 served the purpose of providing a common ground for Konkani people from all the regions. A new organisation known as Vishwa Konkani Parishad, which aims to be an all-inclusive and pluralistic umbrella organization for Konkanis around the world, was founded on 11 September 2005.
Mandd Sobhann is the premier organization which is striving hard to preserve, promote, propagate and enrich Konkani language and culture.
The Konkan Daiz Yatra, started in 1939 in Mumbai
, is the oldest Konkani organisation. The Konkani Bhasha Mandal was born in Mumbai on April 5, 1942 during the Third Adhiveshan of All India Konkani Parishad
. On December 28, 1984, Goa Konkani Akademi
(GKA) was founded by the Government of Goa to promote Konkani language, literature and culture. The Thomas Stephens Konknni Kendr (TSKK)
is a popular research institute based in the Goa
n capital Panaji, which works on issues related to the Konkani language, literature, culture and education. The Dalgado Konkani Academy is a popular Konkani organisation based in Panaji.
The Konkani Triveni Kala Sangam is one more famed Konkani organisation in Mumbai
, which is engaged in the vocation of patronizing Konkani language through theatre movement. The Government of Karnataka
established the Karnataka Konkani Sahitya Akademy on 20 April 1994. The Konkani Ekvott is an umbrella organisation of the Konkani bodies in Goa.
The First World Konkani Convention
was held in Mangalore in December 1995. The Konkani Language and Cultural Foundation came into being immediately after the World Konkani Convention in 1995.
The World Konkani Centre
built on a three-acre plot called Konkani Gaon (Konkani Village) at Shakti Nagar, Mangalore
was inaugurated on 17 January 2009 “to serve as a nodal agency for the preservation and overall development of Konkani language, art and culture involving all the Konkani people the world over.”
It is probable that valuable non-religious literature dealing with art, literature, sciences, etc. were destroyed indiscriminately as a consequence. For instance, even before the inquisition orders, in a letter dated 24 November 1548, Fr. Joao de Albuquerque proudly reports his achievement in this direction.
started broadcasting Konkani news and other services. Radio Goa Panjim started Konkani broadcast in 1945. AIR Mumbai and Dharwad later started it in the years 1952 and 1965 respectively. Portuguese Radio, Lisbon started services in 1955 for India, East Africa and Portuguese. Similarly Trivandrum, Alleppey, Trichur and Calicut AIR centers started Konkani broadcasts.
Devanagari
Devanagari |deva]]" and "nāgarī" ), also called Nagari , is an abugida alphabet of India and Nepal...
: , , Roman script
Latin alphabet
The Latin alphabet, also called the Roman alphabet, is the most recognized alphabet used in the world today. It evolved from a western variety of the Greek alphabet called the Cumaean alphabet, which was adopted and modified by the Etruscans who ruled early Rome...
: , , Kannada script
Kannada script
The Kannada script is an alphasyllabary of the Brahmic family, used primarily to write the Kannada language, one of the Dravidian languages of southern India and also Sanskrit in the past. The Telugu script is derived from Old Kannada, and resembles Kannada script...
: , , Malayalam script
Malayalam script
The Malayalam script is a Brahmic script used commonly to write the Malayalam language—which is the principal language of the Indian state of Kerala, spoken by 36 million people in the world. Like many other Indic scripts, it is an abugida, or a writing system that is partially “alphabetic” and...
: ) is an Indo-Aryan language
Indo-Aryan languages
The Indo-Aryan languages constitutes a branch of the Indo-Iranian languages, itself a branch of the Indo-European language family...
belonging to the Indo-European
Indo-European languages
The Indo-European languages are a family of several hundred related languages and dialects, including most major current languages of Europe, the Iranian plateau, and South Asia and also historically predominant in Anatolia...
family of languages and is spoken on the western coast of India. It has approximately 3.6 million speakers. It is one of the official languages of India and is the official language of the Indian state of Goa
Goa
Goa , a former Portuguese colony, is India's smallest state by area and the fourth smallest by population. Located in South West India in the region known as the Konkan, it is bounded by the state of Maharashtra to the north, and by Karnataka to the east and south, while the Arabian Sea forms its...
. It is a minority language in Karnataka
Karnataka Konkani
Karnataka Konkani refers to the various dialects of Konkani language spoken in the state of Karnataka,and some parts of Kerala.Konkani is spoken by a remarkable number of Goan migrants who have settled in North Kanara, Udupi, South Kanara and many other places in North and south Karnataka for the...
and northern Kerala
Kerala
or Keralam is an Indian state located on the Malabar coast of south-west India. It was created on 1 November 1956 by the States Reorganisation Act by combining various Malayalam speaking regions....
(Kasaragod district
Kasaragod district
Kasaragod District is one of the districts of the Indian state of Kerala. Kasaragod District was organised as a separate district on 24 May 1984...
).
Konkani is classified as a southern Indo-Aryan language along with Kadodi and Marathi
Marathi language
Marathi is an Indo-Aryan language spoken by the Marathi people of western and central India. It is the official language of the state of Maharashtra. There are over 68 million fluent speakers worldwide. Marathi has the fourth largest number of native speakers in India and is the fifteenth most...
.
Exonyms
- Konkani was commonly referred to as lingua canarim by the Portuguese.
- It was also known as lingua brahmana by the Catholic missionaries.
- Portuguese later started referring to Konkani as Lingua Concanim.
Etymology
There are different views as to the origin of the word Konkan and hence Konkani- The word Konkan comes from the Kukkana tribe, who were the original inhabitants of the land Konkani originated from.
- According to some HinduHinduHindu refers to an identity associated with the philosophical, religious and cultural systems that are indigenous to the Indian subcontinent. As used in the Constitution of India, the word "Hindu" is also attributed to all persons professing any Indian religion...
legends, ParashuramaParashuramaParashurama , is the sixth avatar of Vishnu and belongs to the treta yuga, and is the son of a Brahmin father Jamadagni and mother Renuka. He is considered one of the seven immortal human. He received an axe after undertaking a terrible penance to please Shiva, from whom he learned the methods of...
shot his arrow into the sea and commanded the Sea God to recede up to the point where his arrow landed. The new piece of land thus recovered came to be known as KonkanKonkanThe Konkan also called the Konkan Coast or Karavali is a rugged section of the western coastline of India from Raigad to Mangalore...
meaning piece of earth or corner of earth,kōṇa (corner)+ kaṇa (piece).This legend has been mentioned in SahyadrikhandaSahyadrikhandaSahyādrikhaṇḍa or Sahyadri Khand, written in Sanskrit, is claimed as a part of Skandapurāṇa. From the old records it can be seen that Sahyādrikhaṇḍa is a later inclusion in the original Skandapurāṇa...
of the Skanda PuranaSkanda PuranaThe Skanda Purana is the largest Mahapurana, a genre of eighteen Hindu religious texts. The text is devoted mainly to the lilas of Kartikeya , a son of Shiva and Parvati. It also contains a number of legends about Shiva, and the holy places associated with him...
.
Roots
The roots of the Konkani language lie in the Indo-Aryan language of the Kukna tribals called Kokni, Kukni or Kukna. They are now concentrated in Nasik, Thane and Dhule. In Gujarat, their major concentration is in Valsad and Dang districts. In Dadra and Nagar Haveli, the Kokna are distributed in 60 villages. It is possible that their ancestors were the first settlers of the Konkan and most probably the seeds of the modern Konkani language are hidden in their ancient speech.
The later settlers of Goa viz. the Mediterraneans also exerted an impact on this language. Some of their people can be collectively called the Dravidians. Words like tandul, narikel or naall, dholl, madval and others have Dravidian origin.
Subsequently, waves of Indo-Aryan dialect speakers have occurred in the history of the Indian west coast. Around 2400 BC the first wave of Indo-Aryans dialect speakers might have occurred, and the second wave in the period 1000-700 BC came and settled in the west coast. Most of them spoke Indo-Aryan Prakrit
Prakrit
Prakrit is the name for a group of Middle Indic, Indo-Aryan languages, derived from Old Indic dialects. The word itself has a flexible definition, being defined sometimes as, "original, natural, artless, normal, ordinary, usual", or "vernacular", in contrast to the literary and religious...
vernacular languages, akin to Vedic Sanskrit
Vedic Sanskrit
Vedic Sanskrit is an old Indo-Aryan language. It is an archaic form of Sanskrit, an early descendant of Proto-Indo-Iranian. It is closely related to Avestan, the oldest preserved Iranian language...
. Thus Konkani was born as a confluence of the Indo-Aryan dialects while accepting many words from the proto-Australoid speech. Proto-Konkani born out of Shauraseni vernacular Prakrit at the earlier stage of the evolution and later Maharashtri
Maharashtri
Maharastri or Maharastri Prakrit, SIL: Mahārāṣṭri Prākrit , is a language of ancient and medieval India which is the ancestor of Marathi, Konkani, Sinhala and the Maldivian language as well. It is one of the many languages of a complex called Prakrit, and the chief Dramatic Prakrit...
prakrit, commonly spoken until 875 CE at its later phase ultimately developed into Apabhramsha which could be called as predecessor old Konkani.
Goa was ruled by the Mauryas and the Bhoja
Bhoja
Bhoja was a philosopher king and polymath of medieval India, who ruled the kingdom of Malwa in central India from about 1000 to 1050 CE. Also known as Raja Bhoja Of Dhar, he belonged to the Paramara dynasty...
a, as a result numerous migrations occurred from North-east and Western India. Immigrants spoke various vernaculars,which led to an admixture of features of Eastern and Western Prakrits. The Sumer
Sumer
Sumer was a civilization and historical region in southern Mesopotamia, modern Iraq during the Chalcolithic and Early Bronze Age....
ians had trade contacts with India dating from 2100 BC. Many Sumerians settled in Goa and Konkan, arriving by sea. The period of Sumerian migration started about 2000 BC, after the first wave of Indo-Aryan speakers settled in Goa. Sumerian cuneiform
Cuneiform
Cuneiform can refer to:*Cuneiform script, an ancient writing system originating in Mesopotamia in the 4th millennium BC*Cuneiform , three bones in the human foot*Cuneiform Records, a music record label...
inscriptions have been found in Goa. Dhume gives many examples of how Sumerian language influenced the native Goan tongue and how the language still retains many Sumerian features and words.
It was substantially influenced later by Magadhi Prakrit and the overtones of Pali (the liturgical language of the Buddhists) that played a very important role in development of Konkani Apabhramsha grammar and vocabulary. A major number of linguistic innovations in Konkani are shared with Eastern Indo-Aryan languages like Bengali
Bengali language
Bengali or Bangla is an eastern Indo-Aryan language. It is native to the region of eastern South Asia known as Bengal, which comprises present day Bangladesh, the Indian state of West Bengal, and parts of the Indian states of Tripura and Assam. It is written with the Bengali script...
, Oriya
Oriya language
Oriya , officially Odia from November, 2011, is an Indian language, belonging to the Indo-Aryan branch of the Indo-European language family. It is mainly spoken in the Indian states of Orissa and West Bengal...
which have its roots in Magadhi.
Maharashtri was the official language of the Satavahana Empire that ruled Goa and Konkan in the early centuries of the Common Era. Under the patronage of the Satavahana Empire, Maharashtri became the most widespread Prakrit of its time.
Studying early Maharashtri compilations many linguists have called Konkani as the first-born daughter of Maharashtri. This old language that was prevalent contemporary to old Marathi is found to be distinct from its counterpart.
The Sauraseni impact on Konkani is not so prominent than that of Maharashtri. Very few Konkani words are found to follow the Sauraseni pattern. Konkani forms are rather more akin to Pali than the corresponding Sauraseni forms. The major Sauraseni influence on Konkani, is the ao sound found at the end of many nouns in Sauraseni, which becomes o or u in Konkani, e.g.: dando, suno, raakhano and dukh, rukhu, manisu from prakrit dandao, sunnao, rakkhakao, dukkhao, vukkhao or vrukkhao, mannisso respectively. Another example could be the sound of ण in the beginning of the words, is still retained in many Konkani words as in archaic Shauraseni. E.g.: णव nine.
This form of old Konkani is referred to as Paishachi apabhramsha
Paisaci
Paisaci, also known as Paisachi, or Paishachi, is an extinct language of classical India, mentioned as a medium of debate and literary expression in various Theravada Buddhist sources, and in Prakrit and Sanskrit grammars of antiquity...
by some linguists. This progenitor of Konkani or Paishachi apabhramsha has preserved an older form of phonetic and grammatic development showing greater variety of verbal forms found in Sanskrit and larger number of grammatical forms that are not found in Marathi, examples of which are found in many works like Dnyaneshwari
Dnyaneshwari
The Dnyaneshwari is the commentary on Bhagavad Gita written by Marathi saint and poet Dnyaneshwar during the 13th century at age 16...
, and Leela Charitra.
The language is endowed with overall Sanskrit complexity and grammatical structure, that developed a lexical fund of its own.
Kannada Influence
Though it belongs to Indo-Aryan group, Konkani was influenced by Kannada, a member of Dravidian family. The Kadambas
Kadambas
The Kadamba Dynasty was an ancient royal family of Karnataka that ruled from Banavasi in present day Uttara Kannada district. The dynasty later continued to rule as a feudatory of larger Kannada empires, the Chalukya and the Rashtrakuta empires for over five hundred years during which time they...
who ruled Goa for a long period had their roots in Karnataka
Karnataka
Karnataka , the land of the Kannadigas, is a state in South West India. It was created on 1 November 1956, with the passing of the States Reorganisation Act and this day is annually celebrated as Karnataka Rajyotsava...
Konkani was never used for official purposes. Another reason Kannada influence on Konkani is proximity of original Konkani speaking territory to Karnataka.
Old Konkani documents show considerable Kannada influence on grammar as well as the vocabulary. Like southern Dravidian languages Konkani has prothetic glides
Prosthesis (linguistics)
In linguistics, prosthesis is the addition of a sound or syllable at the beginning of a word without changing the word's meaning or the rest of its structure. The alternative spelling prothesis was first used in post-classical Latin, based on Greek próthesis "placing before" or "in public"...
y- and w-. Kannada influence is more evident in Konkani syntax. The question markers in yes/no questions and the negative marker are sentence final. Copula deletion in Konkani is remarkably similar to Kannada.
Phrasal verbs are not so commonly used in Indo-Aryan languages, Konkani spoken in Dravidian regions has however borrowed numerous phrasal verb patterns.
The table below illustrates some phrasal verbs used in Konkani:
| Konkani in Goa and North Karnataka | Konkani in South Karnataka | Meaning |
|---|---|---|
| bas or basun sod | baisa | sit down |
| randh or randhun ghe | randhun sodi | cook |
| karun ghe | kornu dhi | to get something done |
Konkani and Gujarati
It is said that Gujarat has got many historical ties with the port of Goa, mainly because of trade, and it is also said that many people have migrated to Goa via the port of Dwaraka
Dwarka
Dwarka also spelled Dvarka, Dwaraka, and Dvaraka, is a city and a municipality of Jamnagar district in the Gujarat state in India. Dwarka , also known as Dwarawati in Sanskrit literature is rated as one of the seven most ancient cities in the country...
.
The Kols, Kharwas, Yadavas, and the Lothal
Lothal
Lothal is one of the most prominent cities of the ancient Indus valley civilization. Located in Bhāl region of the modern state of Gujarāt and dating from 2400 BCE. Discovered in 1954, Lothal was excavated from February 13, 1955 to May 19, 1960 by the Archaeological Survey of India...
migrants settled in Goa during the pre-historic and the later period. Chavada, a tribe of warriors (now known as Chaddi or Chaddo), migrated to Goa from Saurashtra,during 7th and 8th century CE, after their kingdom was destroyed by the Arab
Arab
Arab people, also known as Arabs , are a panethnicity primarily living in the Arab world, which is located in Western Asia and North Africa. They are identified as such on one or more of genealogical, linguistic, or cultural grounds, with tribal affiliations, and intra-tribal relationships playing...
s in 740 AD. Royal matrimonial relationships between the two states, and the trade relationships had a major impact on Goan society which greatly influenced the language as a whole.
- Konkani and Gujarati have many words in common, not found in Marathi.
- Konkani O (as opposed to Marathi A which is of different Prakrit origin), is similar to that in Gujarati.
- The case terminations in Konkani lo, li, le, and Gujarati no, ni, ne have same Prakrit roots.
- In both the languages the present indicativePresent IndicativePresent Indicative is a 1972 Hungarian drama film directed by Péter Bacsó. The film was selected as the Hungarian entry for the Best Foreign Language Film at the 45th Academy Awards, but was not accepted as a nominee.-Cast:...
s have no gender, unlike Marathi.
Other foreign languages
Goa being a major centre for trade was visited by Arabs, Turks since early times. Thus many Arabic and Persian words infiltrated into Konkani language. A large number of Arabic and Persian words form an integral part of Konkani vocabulary now and commonly used in day to day life by its speakers.e.g.;dukan(shop),karz(debt),fakt(only),dusman(enemy),barik(thin) etc. Single and compound words are found herein the original meaning is changed or distorted;mustaiki,(from Arabic Mustaid meaning ready),kapan khairo-eater of one's own shroud/miser and so on.
Portuguese influence
Most of the old Konkani Hindu literature does not show any influence of the Portuguese language. Even the spoken dialects by the majority of Goan Hindus has a very limited Portuguese influence. On the other hand, the spoken dialects of the Catholics from Goa (as well as the Canara to some extent), and their religious literature shows a strong Portuguese influence. They contain a number Portuguese lexical items but these are almost all religious terms. Even in the context of religious terminology, the missionaries adapted native terms associated with Hindu religious concepts. (For example Krupa for grace, Yamakuna for hell, Vaikuntha for paradise and so on). The syntax used by Goan Catholics in their literature shows a prominent Portuguese influence. As a result, many Portuguese loanwords are now commonly found in vernacular Konkani speech.
Early Konkani
The earliest inscription in Konkani found in the village of Aravalem, in Goa dated back in the GuptaGupta
Gupta is a common surname of Indian origin.According to some academicians, the name Gupta is derived from Sanskrit goptri, meaning military governor. A more direct translation of the Sanskrit word gupta is 'secret' or 'hidden'. According to prominent historian R. C...
period in Brahmi
Brāhmī script
Brāhmī is the modern name given to the oldest members of the Brahmic family of scripts. The best-known Brāhmī inscriptions are the rock-cut edicts of Ashoka in north-central India, dated to the 3rd century BCE. These are traditionally considered to be early known examples of Brāhmī writing...
script, ascribed to the 2nd Century AD. It reads śacipurācyā śirāsi (on the top of Shachipura) in the late Brahmi script. Another inscription in Nāgarī
Nagari script
The Nāgarī script is the ancestor of Devanagari, Assamese, Bengali and other variants, and was first used to write Prakrit and Sanskrit. It was in vogue from before the 10th century...
, of Shilahara King Aaparditya of the year 1166 AD says: ātā̃ jō kōṇṇuyirē śāsanō̃ḷapī̃ tēcyā vēḍhyāta dēvācī bhāla saktumbī āpaḍē̃ tēcī mā̃ya gāḍhavē̃. An inscription at the foot of the colossal Jain monolith Gomaṭēśvara (Bāhubali) Konkani: gomṭo – pretty masc., īśvar – God at Shravanabelagola of 981 CE reads "śrīcāvuṇḍarājē̃ kara viyālē̃, śrīgaṅgārājē̃ suttālē̃ kara viyālē̃" (Chavundaraya
Chavundaraya
Chavundraya was a military commander, poet and a minister in the court of the Western Ganga Dynasty of Talakad . A person of many talents, in 982 he commissioned the Gomateshwara, a monolithic sculpture in Shravanabelagola, an important place of pilgrimage for Jains...
got it done, Gangaraya got the surroundings done).Chavundaraya
Chavundaraya
Chavundraya was a military commander, poet and a minister in the court of the Western Ganga Dynasty of Talakad . A person of many talents, in 982 he commissioned the Gomateshwara, a monolithic sculpture in Shravanabelagola, an important place of pilgrimage for Jains...
was the military chief of the Ganga dynasty King Gangaraya. This inscription on the Bahubali statue draws attention to a Basadi (Jain Temple) initially built by him and then modified by Gangaraya in the 12th century CE Ref: S. Settar in Adiga (2006), p256
Stone and copper-plate inscriptions found in Goa and Konkan are written in an amalgam of Konkani and old-Marathi, written in Nāgarī
Nagari script
The Nāgarī script is the ancestor of Devanagari, Assamese, Bengali and other variants, and was first used to write Prakrit and Sanskrit. It was in vogue from before the 10th century...
as well as Goykanadi
Goykanadi
' is an extinct script used in the territory of Goa .This script was also called as and .This script was similar to the Halekannada and Kadamba script and was extensively used to write Konkani and sometimes Marathi. Similarly this was used by the trading Saraswat and Daivajna families along with...
script. The grammar and the base of such texts is in Konkani, whereas very few verbs are in Marathi. One such stone inscription or shilalekh is found at the Nageshi temple in Goa (dating back to the year 1463 AD) mentions that the (then) ruler of Goa, Devaraja Gominam, had gifted land to the Nagueshi
Nagueshi
Nagueshi or Nagesh is a form of Lord Shiva worshipped by Hindu Goans in India. The temple lies in verdant surroundings in the Ponda district of Goa. Unlike many other Hindu temples of Goa which were shifted out of the Velha Conquistas the Nagueshi Temple is at its original place. It has, however,...
Maharudra temple when Nanjanna Gosavi was the religious head or the Pratihasta of the state. It mentions words like, kullgga,kulaagra, naralel, tambavem, tilel.
The above inscription has been quite controversial, and touted as being old-Marathi. But the distinctive instrumental viyalem ending of the verb is the hallmark of Konkani language, and the verb sutatale or sutatalap is not prevalent in Marathi. So linguists and historians such as S.B. Kulkarni of Nagpur University, Dr V.P. Chavan (former vice-president of the Anthropological society of Mumbai), and others have thus concluded that it is Konkani.

Narayana
Narayana or Narayan or Naraina is an important Sanskrit name for Vishnu, and in many contemporary vernaculars a common Indian name. Narayana is also identified as the original man, Purusha. The Puranas present divergent views on Narayana...
attributed to 12th century AD goes "jaṇẽ rasataḷavāntũ matsyarūpē̃ vēda āṇiyēlē̃. manuśivāka vāṇiyēlē̃. to saṁsārasāgara tāraṇu. mōhō to rākho nārāyāṇu". (The one who brought the Vedas up from the ocean in the form of a fish, from the bottoms of the water and offered it to Manu
Manu
-Geography:*Manú Province, a province of Peru, in the Madre de Dios Region*Manú National Park, Peru*Manú River, in southeastern Peru*Manu River, Tripura, which originates in India and flows into Bangladesh...
, he is the one Saviour of the world, that is Narayana my God.). A hymn from later 16th century goes vaikuṇṭhācē̃ jhāḍa tu gē phaḷa amṛtācē̃, jīvita rākhilē̃ tuvē̃ manasakuḷācē̃.
Early Konkani was marked by the use of pronouns like dzo / jī / jẽ . This is replaced in contemporary Konkani by koṇa . The conjunctions yedō..tedō.. (when..then...) which were user in early Konkani are no longer in use. The use of "-viyalẽ'"' has been replaced by " -aylẽ". The pronoun moho, which is similar to the Brijbhasha word mōhē has been replaced by mākā.
Medieval Konkani
This era was marked by the invasion of Goa and subsequent exodus to Marhatta territory and CanaraCanara
Canara can refer to:* Kanara – a region in Karnataka, India* Ovidiu – a town in Constanţa County, Romania...
(today's coastal Karnaraka) and Cochin.
- Hindu exodus ( between 1312–1327 when General Malik KafurMalik KafurMalik Kafur, General , or Chand Ram as his name was originally, was a slave who became a head general in the army of Alauddin Khilji, ruler of the Delhi sultanate from 1296 to 1316 AD. He was originally seized by Alauddin's army after the army conquered the city of Khambhat...
of the Delhi SultansDelhi SultanateThe Delhi Sultanate is a term used to cover five short-lived, Delhi based kingdoms or sultanates, of Turkic origin in medieval India. The sultanates ruled from Delhi between 1206 and 1526, when the last was replaced by the Mughal dynasty...
Alauddin KhiljiAlauddin KhiljiAli Gurshap Khan better known by his titular name as Sultan Ala-ud-din Khilji was the second ruler of the Turko-Afghan Khilji dynasty in India.He was a well and capable ruler. He belonged to the Afghanized Turkic tribe of the Khiljis...
and Muhammed bin TughlaqMuhammad bin TughluqMuhammad bin Tughluq was the Turkic Sultan of Delhi from 1325 to 1351. He was the eldest son of Ghiyas-ud-din Tughlaq.He was born in Kotla Tolay Khan in Multan. His wife was daughter of the raja of Dipalpur...
destroyed Govepuri and the KadambasKadambasThe Kadamba Dynasty was an ancient royal family of Karnataka that ruled from Banavasi in present day Uttara Kannada district. The dynasty later continued to rule as a feudatory of larger Kannada empires, the Chalukya and the Rashtrakuta empires for over five hundred years during which time they... - Hindu exodus subsequent to 1470 when the Bahamani kingdom captured Goa, and subsequently in 1492 by Sultan Yusuf Adil ShahYusuf Adil ShahYusuf Adil Shah , referred as Adil Khan or Hidalcão by the Portuguese, was the founder of the Adil Shahi dynasty that ruled the Sultanate of Bijapur for nearly two centuries...
of Bijapur - Hindu exodus due to persecutionPersecution of HindusPersecution of Hindus refers to the religious persecution inflicted upon Hindus. Hindus have been historically persecuted during Islamic rule of the Indian subcontinent and during the Goa Inquisition...
and proselytisationChristianization of GoaThe indigenous population of the erstwhile Portuguese colony of Goa underwent a large-scale conversion to Christianity after its conquest and occupation by the Portuguese Empire, which was led by the voyager and adventurer Afonso de Albuquerque in 1510. After conversion to Roman Catholicism, they...
of Hindus by Portuguese Jesuit and FranciscanFranciscanMost Franciscans are members of Roman Catholic religious orders founded by Saint Francis of Assisi. Besides Roman Catholic communities, there are also Old Catholic, Anglican, Lutheran, ecumenical and Non-denominational Franciscan communities....
missionaries subsequent to 1500 - Hindu, Muslim and Neo-Catholic Christian exodus during the InquisitionGoa InquisitionThe Goa Inquisition was the office of the Inquisition acting in the Indian state of Goa and the rest of the Portuguese empire in Asia. It was established in 1560, briefly suppressed from 1774–1778, and finally abolished in 1812. The Goan Inquisition is considered a blot on the history of...
ordered by St. Francis Xavier which was established in 1560 and abolished in 1812.
These events caused the Konkani language to evolve into multiple dialects. The exodus to coastal Karnataka and Kerala required Konkani speakers in these regions to learn the local languages and hence this caused penetration of local words into the dialects of Konkani spoken by these speakers. e.g. the word dār (door) gave way to the word bāgil .
The phoneme "a" in the Salcette dialect was replaced by the phoneme "o"
Other Konkani communities came into being with their own dialects of Konkani. The Konkani Muslim
Konkani Muslims
Konkani / Kokani Muslims is a Muslim sub-ethnic group of Maharashtrian Muslims living in the Konkan region of India. They speak the Konkani language. A good number of them live in Mumbai...
communities of Ratnagiri
Ratnagiri
Ratnāgiri is a port city on the Arabian Sea coast in Ratnagiri district in the southwestern part of Maharashtra, India. The district is a part of Konkan.The Sahyadri mountains border Ratnagiri to the east...
and Bhatkal
Bhatkal
Bhatkal is also known as Batecala in some historical text especially in Portuguese history.Once ruled by Jain King Bhattakalanka and thus the name. Bhatkal is a port town in Uttara Kannada district of Karnataka, India 126 km from Karwar. The town lies on NH-17 running between Mumbai and Mangalore...
came about due to a mixture of intermarriage of Arab seafarers and locals as well as conversions of Hindus to Islam. Another migrant community that picked up Konkani was the Siddis who were sailor-warriors from Ethiopia.
Contemporary Konkani
Contemporary Konkani is written in the Devanagari, Kannada, Malayalam, Persian and Roman scripts. It is written by speakers in their native dialects. However, the Goan Antruz dialect in the Devanagari script has been promulgated Standard Konkani.Geographical distribution
The Konkani language is spoken widely in the Western Coastal region of India known as KonkanKonkan
The Konkan also called the Konkan Coast or Karavali is a rugged section of the western coastline of India from Raigad to Mangalore...
. This consists of the Konkan
Konkan
The Konkan also called the Konkan Coast or Karavali is a rugged section of the western coastline of India from Raigad to Mangalore...
division of Maharashtra
Maharashtra
Maharashtra is a state located in India. It is the second most populous after Uttar Pradesh and third largest state by area in India...
, the state of Goa
Goa
Goa , a former Portuguese colony, is India's smallest state by area and the fourth smallest by population. Located in South West India in the region known as the Konkan, it is bounded by the state of Maharashtra to the north, and by Karnataka to the east and south, while the Arabian Sea forms its...
, and the Uttara Kannada
Uttara Kannada
Uttara Kannada also known as North Canara or North Kanara, is a district in the southern Indian state of Karnataka. It is bordered by the state of Goa and Belgaum District to the north, Dharwad District and Haveri District to the east, Shimoga District and Udupi District to the south and the...
(formerly North Canara), Udupi
Udupi district
Udupi district , ಉಡುಪಿ ಜಿಲ್ಲೆ) in the Karnataka state of India was created in August 1997. The three northern taluks, Udupi, Kundapur and Karkal, were separated from Dakshina Kannada District to form Udupi district. Udupi district is surrounded by Uttara Kannada district in north, Dakshina Kannada...
and Dakshina Kannada
Dakshina Kannada
- Geography :The district geography consists of sea shore in the west and Western Ghats in the east. The major rivers are Netravathi, Kumaradhara, Phalguni, Shambhavi, Nandini or Pavanje and Payaswini which all join Arabian sea. Vast areas of evergreen forests which once covered this district, have...
(formerly South Canara) districts of Karnataka, together with many districts in Kerala(Kasargod, Kochi, Alappuzha, Trivandrum, Kottayam etc.). Each region has a different dialect
Dialect
The term dialect is used in two distinct ways, even by linguists. One usage refers to a variety of a language that is a characteristic of a particular group of the language's speakers. The term is applied most often to regional speech patterns, but a dialect may also be defined by other factors,...
, pronunciation
Pronunciation
Pronunciation refers to the way a word or a language is spoken, or the manner in which someone utters a word. If one is said to have "correct pronunciation", then it refers to both within a particular dialect....
style, vocabulary, tone and sometimes, significant differences in grammar.
The Census Department of India, 1991 figures put the number of Konkani speakers in India as 1,760,607 making up 0.21% of India's population. Out of these, 602,606 were in Goa
Goa
Goa , a former Portuguese colony, is India's smallest state by area and the fourth smallest by population. Located in South West India in the region known as the Konkan, it is bounded by the state of Maharashtra to the north, and by Karnataka to the east and south, while the Arabian Sea forms its...
, 706,397 in Karnataka
Karnataka
Karnataka , the land of the Kannadigas, is a state in South West India. It was created on 1 November 1956, with the passing of the States Reorganisation Act and this day is annually celebrated as Karnataka Rajyotsava...
, 312,618 in Maharashtra
Maharashtra
Maharashtra is a state located in India. It is the second most populous after Uttar Pradesh and third largest state by area in India...
and 64,008 in Kerala
Kerala
or Keralam is an Indian state located on the Malabar coast of south-west India. It was created on 1 November 1956 by the States Reorganisation Act by combining various Malayalam speaking regions....
. It ranks 15th in the list of Scheduled Languages by strength. According to the 2001 estimates of The Census Department of India, there are 2,489,015 Konkani speakers in India. A very large number of Konkanis live outside India, either as expatriates or citizens of other countries (NRIs). Determining their numbers is difficult.
Ethnologue
Ethnologue
Ethnologue: Languages of the World is a web and print publication of SIL International , a Christian linguistic service organization, which studies lesser-known languages, to provide the speakers with Bibles in their native language and support their efforts in language development.The Ethnologue...
puts the number of Konkani speakers at 3.6 million in 2000.
A significant number of Konkani speakers are found in Kenya
Kenya
Kenya , officially known as the Republic of Kenya, is a country in East Africa that lies on the equator, with the Indian Ocean to its south-east...
and Uganda
Uganda
Uganda , officially the Republic of Uganda, is a landlocked country in East Africa. Uganda is also known as the "Pearl of Africa". It is bordered on the east by Kenya, on the north by South Sudan, on the west by the Democratic Republic of the Congo, on the southwest by Rwanda, and on the south by...
, Pakistan
Pakistan
Pakistan , officially the Islamic Republic of Pakistan is a sovereign state in South Asia. It has a coastline along the Arabian Sea and the Gulf of Oman in the south and is bordered by Afghanistan and Iran in the west, India in the east and China in the far northeast. In the north, Tajikistan...
, Persian Gulf
Persian Gulf
The Persian Gulf, in Southwest Asia, is an extension of the Indian Ocean located between Iran and the Arabian Peninsula.The Persian Gulf was the focus of the 1980–1988 Iran-Iraq War, in which each side attacked the other's oil tankers...
and Portugal
Portugal
Portugal , officially the Portuguese Republic is a country situated in southwestern Europe on the Iberian Peninsula. Portugal is the westernmost country of Europe, and is bordered by the Atlantic Ocean to the West and South and by Spain to the North and East. The Atlantic archipelagos of the...
. During Portuguese rule many Goans had migrated to these countries. Many families still continue to speak different dialects that their ancestors spoke, which are now highly influenced by the native languages.
Konkani revival
Konkani was in a sorry state, due to the use of Portuguese as the official and social language among the Christians; the predominance of Marathi over Konkani among Hindus and the Konkani Christian-Hindu divide. Seeing this Vaman Raghunath Varde Valaulikar set about on a mission to unite all Konkanis, Hindus as well as Christians, regardless of caste or religion. He saw this movement not just as a nationalistic movement against Portuguese rule, but also against the pre-eminence of Marathi over Konkani. Almost single handedly he crusaded, writing a number of works in Konkani. He is regarded as the pioneer of modern Konkani literature and affectionately remembered as Shenoi GoembabShenoi Goembab
Waman Raghunath Shennoi Varde Valaulikar known popularly as Shenoi Goembab was a noted Konkani writer and activist.-Education:...
. His death anniversary, 9 April, is celebrated as World Konkani Day (Viswa Konknni Dis).
Madhav Manjunath Shanbhag, an advocate by profession from Karwar, who with a few like-minded companions travelled in all the Konkani speaking areas, seeking to unite the fragmented Konkani community under the banner of "one language, one script, one literature". He succeeded in organizing the first All India Konkani Parishad
All India Konkani Parishad
The All India Konkani Parishad was founded in 1939 in its first Adhiveshan on 8 July 1939 at Karwar, Karnataka.Madhav Manjunath Shanbhag an advocate by profession from Karwar, who with a few like-minded companions travelled in all the Konkani speaking areas, seeking to unite the fragmented Konkani...
in Karwar in 1939 Successive Adhiveshans of All India Konkani Parishad held at various places in the following years. 27 Annual Adhiveshans of All India Konkani Parishad
All India Konkani Parishad
The All India Konkani Parishad was founded in 1939 in its first Adhiveshan on 8 July 1939 at Karwar, Karnataka.Madhav Manjunath Shanbhag an advocate by profession from Karwar, who with a few like-minded companions travelled in all the Konkani speaking areas, seeking to unite the fragmented Konkani...
have been held so far.
Late Pandu Putti Kolambkar an eminient Social Worker of Kodibag, Karwar Strived a lot for the Upliftment of Konkani in Karwar (North Kanara) & The Konkan.
Post-independence period
Following India's independence and its subsequent annexation of Goa in 1961, Goa was absorbed into the Indian Union as a Union Territory, directly under central administration.However, with the reorganization of states along linguistic lines, and growing calls from Maharashtra, as well as Marathis in Goa for the merger of Goa into Maharashtra, an intense debate was started in Goa. The main issues discussed were the status of Konkani as an independent language and Goa's future as a part of Maharashtra or as an independent state. A plebiscite retained Goa as an independent state in 1967. However, English, Hindi and Marathi continued to be the preferred languages for official communication, while Konkani was sidelined.
Recognition as an independent language
With the continued insistence of some Marathis that Konkani was a dialect of Marathi and not an independent language, the matter was finally placed before the Sahitya AkademiSahitya Akademi
The Sahitya Akademi ', India's National Academy of Letters, is an organisation dedicated to the promotion of literature in the languages of India...
. Suniti Kumar Chatterji
Suniti Kumar Chatterji
Suniti Kumar Chatterji was an Indian linguist, educationist and litterateur. He was born on 26 November 1890 at Shibpur in Howrah...
, the president of the Akademi appointed a Committee of linguistic experts to settle the dispute. On February 26, 1975, the Committee after due deliberation, came to the conclusion that Konkani was indeed an independent and literary language with it being classified as an Indo-European language which in its present state is heavily influenced by the Portuguese language.
Official language status
All this did not change anything in Goa. Finally fed up with the delay, Konkani lovers launched an agitation demanding official status to Konkani in 1986. The agitation turned violent in various places, resulting in the death of six agitators from Catholic Community, Mr. Floriano Vaz from Gogal Margao, Aldrin Fernandes, Mathew Faria, C. J. Dias, John Fernandes and Joaquim Pereira all from Agacaim. Finally, on 4 February 1987, the Goa Legislative Assembly passed the Official Language Bill making Konkani the Official Language of Goa.Konkani was included in the Eight Schedule of the Constitution of India, as per the Seventy-First Amendment on 20 August 1992, adding it to the list of National Languages.
Phonology
The Konkani language has 16 basic vowels (excluding equal number of long vowels), 36 consonants, 5 semi-vowels, 3 sibilants, 1 aspirate and many diphthongDiphthong
A diphthong , also known as a gliding vowel, refers to two adjacent vowel sounds occurring within the same syllable. Technically, a diphthong is a vowel with two different targets: That is, the tongue moves during the pronunciation of the vowel...
s. Like the other Indo-Aryan languages
Indo-Aryan languages
The Indo-Aryan languages constitutes a branch of the Indo-Iranian languages, itself a branch of the Indo-European language family...
, it has both long and short vowels and syllables with long vowels may appear to be stressed. Different types of nasal vowels are a special feature of the Konkani language.
- The palatal and alveolar stops are affricates. The palatal glides are truly palatal but other the consonants in the palatal column are alveopalatal.
- The voiced/voicelessVoice (phonetics)Voice or voicing is a term used in phonetics and phonology to characterize speech sounds, with sounds described as either voiceless or voiced. The term, however, is used to refer to two separate concepts. Voicing can refer to the articulatory process in which the vocal cords vibrate...
contrasts is found only in the stops and affricates. The affricates are all voiceless and the sonorants are all voiced. - The initial vowel-syllable is shortened after the aspiratesAspiration (phonetics)In phonetics, aspiration is the strong burst of air that accompanies either the release or, in the case of preaspiration, the closure of some obstruents. To feel or see the difference between aspirated and unaspirated sounds, one can put a hand or a lit candle in front of one's mouth, and say pin ...
and the fricatives. Many speakers substitute unaspirated consonants for aspirates. - Aspirates in non-initial position are rare and only occur in careful speech. Palatalisation/non palatisation is found in all ObstruentObstruentAn obstruent is a consonant sound formed by obstructing airflow, causing increased air pressure in the vocal tract, such as [k], [d͡ʒ] and [f]. In phonetics, articulation may be divided into two large classes: obstruents and sonorants....
s, except for palatal and alveolars. Where a palatalised alveolar is expected, a palatal is found instead. In case of sonorants, only unaspirated consonants show this contrast, and among the glides only labeo-velar glides exhibit this. Vowels show a contrast between oral and nasal ones
Vowels

Schwa
In linguistics, specifically phonetics and phonology, schwa can mean the following:*An unstressed and toneless neutral vowel sound in some languages, often but not necessarily a mid-central vowel...
as used in Hindi
Hindi
Standard Hindi, or more precisely Modern Standard Hindi, also known as Manak Hindi , High Hindi, Nagari Hindi, and Literary Hindi, is a standardized and sanskritized register of the Hindustani language derived from the Khariboli dialect of Delhi...
and Marathi
Marathi language
Marathi is an Indo-Aryan language spoken by the Marathi people of western and central India. It is the official language of the state of Maharashtra. There are over 68 million fluent speakers worldwide. Marathi has the fourth largest number of native speakers in India and is the fifteenth most...
.
Whereas most Indian languages use only one of the three front vowels, represented by the Devanagari grapheme ए (IPA:e), Konkani uses three: e, ɛ and æ.
Nasalizations exist for all vowels except for ʌ.
Consonants
| Labial | Dental | Alveolar | Retroflex | Alveopalatal | Velar | Glottal | |
| Voiceless stops |
p pʰ |
t̪ t̪ʰ |
ʈ ʈʰ |
cɕ cɕʰ |
k kʰ |
||
| Voiced stops |
b bʱ |
d̪ d̪ʱ |
ɖ ɖʱ |
ɟʝ ɟʝʱ |
ɡ ɡʱ |
||
| Voiceless fricatives |
s | ɕ | h | ||||
| Nasals | m mʱ |
n̪ n̪ʱ |
ɳ ɳʱ |
ɲ | ŋ | ||
| Liquids | ʋ ʋʱ |
l ɾ lʱ ɾʱ |
|ɭ ɽ | j |
The consonants in Konkani are similar to those in Marathi
Marathi language
Marathi is an Indo-Aryan language spoken by the Marathi people of western and central India. It is the official language of the state of Maharashtra. There are over 68 million fluent speakers worldwide. Marathi has the fourth largest number of native speakers in India and is the fifteenth most...
.
Grammar
Konkani grammar has an overall Sanskrit structure and is similar to other Indo-Aryan languages. Notably Konkani grammar is also influenced by Dravidian languages. Konkani is a language rich in morphology and syntax. It cannot be described as a stress language nor as a tone language.- Speech can be classified in any of the following parts:
- naam (nounNounIn linguistics, a noun is a member of a large, open lexical category whose members can occur as the main word in the subject of a clause, the object of a verb, or the object of a preposition .Lexical categories are defined in terms of how their members combine with other kinds of...
) - sarvanaam (pronounPronounIn linguistics and grammar, a pronoun is a pro-form that substitutes for a noun , such as, in English, the words it and he...
) - visheshan (adjectiveAdjectiveIn grammar, an adjective is a 'describing' word; the main syntactic role of which is to qualify a noun or noun phrase, giving more information about the object signified....
) - kriyapad (verbVerbA verb, from the Latin verbum meaning word, is a word that in syntax conveys an action , or a state of being . In the usual description of English, the basic form, with or without the particle to, is the infinitive...
) - kriyavisheshana (adverbAdverbAn adverb is a part of speech that modifies verbs or any part of speech other than a noun . Adverbs can modify verbs, adjectives , clauses, sentences, and other adverbs....
) - ubhayanvayi avyaya
- shabdayogi avyaya
- kevalaprayogi avyaya
Like most of the Indo-Aryan languages Konkani is an SOV
SOV
SOV is an acronym for several terms:in organizations*Same Old Vanderbilt, usually refers to Vanderbilt Commodores football by their fans due to lack of success over the years*Stade Olympique Voironnais, a French rugby union club...
language, meaning among other things that not only is the verb found at the end of the clause but also modifiers and complements tend to precede the head and postpositions are far more common than prepositions. In terms of syntax Konknai is a head-last language unlike English which is an SVO
SVO
SVO is an acronym for several terms:* Mustang SVO, a car developed by Ford Motor Company* Saturn Valley Online, an EarthBound MMORPG.* Sheremetyevo International Airport in Moscow, Russia, IATA Airport Code...
language.
- Almost all the verbs, adverbs, adjectives and the avyayas are either tatsama or tadbhava.
The following table illustrates this:
| Konkani verbs | Sanskrit/Prakrit Root | Translation | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| वाच vaach (tatsama) | वच् vach | read | ||
| आफय, आपय aafay, aapay (tatsama) | आव्हय् aavhay | call, summon | ||
| रांध raandh (tatsama) | रांध् raandh | cook | ||
| बरय baray (tadbhav) | वर्णय् varnay | write | ||
| व्हर vhar (tadbhav) | हर har | take away | ||
| भक bhak (tadbhav) | भक्ष् bhaksh | eat | ||
| हेड hedd (tadbhav) | अट् att | roam | ||
| ल्हेव lhev (tadbhav) | लेह् leh | lick | ||
| शीन sheen (tadbhav) | छिन्न chinna | cut | ||
| Source:Koṅkaṇî Dhatukosh | ||||
- Present indefinite of the auxiliary is fused with present participle of the primary verb, and the auxiliary is partially dropped. The southern dialects when came in contact with Dravidian languages this difference became more prominent in dialects spoken in KarnatakaKarnataka KonkaniKarnataka Konkani refers to the various dialects of Konkani language spoken in the state of Karnataka,and some parts of Kerala.Konkani is spoken by a remarkable number of Goan migrants who have settled in North Kanara, Udupi, South Kanara and many other places in North and south Karnataka for the...
whereas Goan Konkani still retains the original form.
e.g.: I eat and I am eating sound similar in Goan Konkani, due to loss of auxiliary in colloquial speech. hāv khātā corresponds to I am eating. On the other hand in Karnataka Konkani hāv khātā corresponds to I eat, and hāv khātoāsā or hāv khāter āsā means I am eating
- Out of eight grammatical casess, Konkani has totally lost the dativeDative caseThe dative case is a grammatical case generally used to indicate the noun to whom something is given, as in "George gave Jamie a drink"....
, the locativeLocative caseLocative is a grammatical case which indicates a location. It corresponds vaguely to the English prepositions "in", "on", "at", and "by"...
and the ablativeAblative caseIn linguistics, ablative case is a name given to cases in various languages whose common characteristic is that they mark motion away from something, though the details in each language may differ...
. It has partially lost the accusativeAccusative caseThe accusative case of a noun is the grammatical case used to mark the direct object of a transitive verb. The same case is used in many languages for the objects of prepositions...
and the instrumental caseInstrumental caseThe instrumental case is a grammatical case used to indicate that a noun is the instrument or means by or with which the subject achieves or accomplishes an action...
s too. So the preserved cases are: the nominativeNominative caseThe nominative case is one of the grammatical cases of a noun or other part of speech, which generally marks the subject of a verb or the predicate noun or predicate adjective, as opposed to its object or other verb arguments...
, the genitiveGenitive caseIn grammar, genitive is the grammatical case that marks a noun as modifying another noun...
and the vocative caseVocative caseThe vocative case is the case used for a noun identifying the person being addressed and/or occasionally the determiners of that noun. A vocative expression is an expression of direct address, wherein the identity of the party being spoken to is set forth expressly within a sentence...
.
Some Konkani Apabhramsha rules
- Like other languages the konkani language has has three genders.Use of the neuter gender is quite unique in Konkani. During the Middle Ages most of the Indo-Aryan languages lost their neuter gender, except Maharashtri, which is retained much more in Konkani than Marathi. Gender in Konkani is purely grammatical and unconnected to sex.
- Unlike Sanskrit anusvaraAnusvaraAnusvara is the diacritic used to mark a type of nasalization used in a number of Indic languages. Depending on the location of the anusvara in the word and the language within which it is used, its exact pronunciation can vary greatly....
has great importance in Konkani. A characteristic of Middle Indo-Aryan dialects, Konkani still retains the anusvara on the initial or the final syllable. Similarly visargaVisargaVisarga is a Sanskrit word meaning "sending forth, discharge". In Sanskrit phonology , is the name of a phone, , written as IAST , Harvard-Kyoto , Devanagari . Visarga is an allophone of and in pausa...
, is totally lost and is assimilated with उ and/or ओ; e.g. Sanskrit दीपः becomes दिवो and दुःख becomes दुख . - Konkani retains the pitch accent which is a direct derivative of Vedic accent which probabaly would account for nasalism in Konkani.Breathed accent is retained in most of the tatsamas than the tadbhavas.DeclensionDeclensionIn linguistics, declension is the inflection of nouns, pronouns, adjectives, and articles to indicate number , case , and gender...
also affects the accent. - Konkani has lost passive voice and now the transitive verbs in their perfects are equivalent to passives.
- Konkani has rejected ऋ, ॠ, ऌ, ॡ, ष, क्ष and are assimilated with र, ख, ह, श and स.
- Sanskrit compound letters are avoided in Konkani; e.g. Sanskrit द्वे, प्राय, गृहस्थ, उद्योत become बे, पिराय, गिरेस्त, उज्जो respectively in Konkani.
Vocabulary
The vocabulary from Konkani comes from a number of sources.The main source is Prakrits.There are many indications that Konkani is more closer to Sanskrit than any other widely spoken Indian languages.So Sanskrit as a whole has played a very important part in Konkani vocabulary.Konkani vocabulary is made of tatsama (Sanskrit words without change), tadhbhava (adapted Sanskrit words), deshya (indigenous words) and antardeshya or foreign words.Other sources of vocabulary are Arabic,Persian and Turkish.Finally Kannada,Marathi and Portuguese have enriched its lexical content.Sanskritisation
Konkani is not highly Sanskritised like MarathiMarathi language
Marathi is an Indo-Aryan language spoken by the Marathi people of western and central India. It is the official language of the state of Maharashtra. There are over 68 million fluent speakers worldwide. Marathi has the fourth largest number of native speakers in India and is the fifteenth most...
, but it still retains Prakrit
Prakrit
Prakrit is the name for a group of Middle Indic, Indo-Aryan languages, derived from Old Indic dialects. The word itself has a flexible definition, being defined sometimes as, "original, natural, artless, normal, ordinary, usual", or "vernacular", in contrast to the literary and religious...
and apabhramsha structure, verbal forms and vocabulary. Though Goan Hindu dialect is highly Prakritsed, numerous Sanskrit loan words are found unlike the Catholic dialect which was influenced by Portuguese as they got converted in early 16th century. The catholic literary dialect has now adopted Sanskrit vocabulary again, the Catholic Church has also adopted Sanskritisation policy. Even though recently introduced Sanskritic vocabulary is difficult and unfamiliar to the new catholic generations, they have not revolted. On the other hand, southern Konkani dialects, having been influenced by Kannada, which is one of the most sanskritised language of Dravidian origin, have undergone re-sanskritisation in the due course of time.
Past
Brahmi scriptBrāhmī script
Brāhmī is the modern name given to the oldest members of the Brahmic family of scripts. The best-known Brāhmī inscriptions are the rock-cut edicts of Ashoka in north-central India, dated to the 3rd century BCE. These are traditionally considered to be early known examples of Brāhmī writing...
was originally used but fell into disuse.
A script called as Kandevi or Goykandi was used in Goa since the times of the Kadambas, although it lost its popularity after 17th century. Kandevi/Goykandi is very different from the Halekannada script, with strikingly similar features. Unlike Halekannada, Kandevi/Goykandi letters were usually written with a distinctive horizontal bar, like the Nagari scripts. This script may have been evolved out of Kadamba script
Kadamba script
The Kadamba script marks the birth of a dedicated Kannada script that was used for Kannada language. It is a descendant of the Brahmi script. The Kadamba script was developed during the reign of the Kadambas in the 4th - 6th centuries. The Kadamba script is also known as Pre-Old-Kannada script...
which was extensively used in Goa and Konkan. The earliest documents written in this script is found in a petition addressed by Ravala Śeṭī; most probably a Gaunkar of Caraim in the islands of Goa, to the king of Portugal
Portugal
Portugal , officially the Portuguese Republic is a country situated in southwestern Europe on the Iberian Peninsula. Portugal is the westernmost country of Europe, and is bordered by the Atlantic Ocean to the West and South and by Spain to the North and East. The Atlantic archipelagos of the...
. This 15th century document bears signature in Konkani which says: Ravala Śeṭī baraha ( Translation: writing of Ravala Śeṭī). The earliest known inscription in Devanagari dates back to 1187 A.D. The Roman script has the oldest preserved and protected literary tradition beginning from the 16th century.
Present
Konkani is today written in five scripts – DevanagariDevanagari
Devanagari |deva]]" and "nāgarī" ), also called Nagari , is an abugida alphabet of India and Nepal...
, Roman
Latin alphabet
The Latin alphabet, also called the Roman alphabet, is the most recognized alphabet used in the world today. It evolved from a western variety of the Greek alphabet called the Cumaean alphabet, which was adopted and modified by the Etruscans who ruled early Rome...
, Kannada
Kannada script
The Kannada script is an alphasyllabary of the Brahmic family, used primarily to write the Kannada language, one of the Dravidian languages of southern India and also Sanskrit in the past. The Telugu script is derived from Old Kannada, and resembles Kannada script...
, Malayalam
Malayalam script
The Malayalam script is a Brahmic script used commonly to write the Malayalam language—which is the principal language of the Indian state of Kerala, spoken by 36 million people in the world. Like many other Indic scripts, it is an abugida, or a writing system that is partially “alphabetic” and...
and Perso-Arabic
Perso-Arabic script
The Persian or Perso-Arabic alphabet is a writing system based on the Arabic script. Originally used exclusively for the Arabic language, the Arabic alphabet was adapted to the Persian language, adding four letters: , , , and . Many languages which use the Perso-Arabic script add other letters...
. The Goan Hindus use the Devanagari
Devanagari
Devanagari |deva]]" and "nāgarī" ), also called Nagari , is an abugida alphabet of India and Nepal...
script in their writings while the Goan Catholics use the Roman script
Konkani in the Roman script
Konkani is a language that is spoken by 3.6 million speakers mostly on the western coast of the Indian states of Maharashtra, Goa, Karnataka and Kerala. Konkani is written in five scripts – Devanagari, Roman, Kannada, Malayalam and Perso-Arabic. Of these, the Roman script has the oldest preserved ...
. The Saraswats of Karnataka
Karnataka
Karnataka , the land of the Kannadigas, is a state in South West India. It was created on 1 November 1956, with the passing of the States Reorganisation Act and this day is annually celebrated as Karnataka Rajyotsava...
use the Devanagari script in the North Kanara district, but those in Udupi and South Kanara use the Kannada script
Kannada script
The Kannada script is an alphasyllabary of the Brahmic family, used primarily to write the Kannada language, one of the Dravidian languages of southern India and also Sanskrit in the past. The Telugu script is derived from Old Kannada, and resembles Kannada script...
. The Karnataka Christians also use the Kannada script. Malayalam script
Malayalam script
The Malayalam script is a Brahmic script used commonly to write the Malayalam language—which is the principal language of the Indian state of Kerala, spoken by 36 million people in the world. Like many other Indic scripts, it is an abugida, or a writing system that is partially “alphabetic” and...
was used by the Konkani community in Kerala, but now there is a move to use the Devanagari script. Konkani Muslims around Bhatkal taluka of Karnataka use Arabic script to write Konkani.
Alphabet or the Varṇamāḷha
The vowels,consonants and their arrangement are:| अ | /ɐ/ |
आ | /ɑː/ |
इ | /i/ |
ई | /iː/ |
उ | /u/ |
ऊ | /uː/ |
ए | /eː/ |
ऐ | /aːi/ |
ओ | /oː/ |
औ | /aːu/ |
अं | /ⁿ/ |
अः | /h/ |
| क | /k/ |
ख | /kʰ/ |
ग | /ɡ/ |
घ | /ɡʱ/ |
ङ | /ŋ/ |
| च | /c, t͡ʃ/ |
छ | /cʰ, t͡ʃʰ/ |
ज | /ɟ, d͡ʒ/ |
झ | /ɟʱ, d͡ʒʱ/ |
ञ | /ɲ/ |
| ट | /ʈ/ |
ठ | /ʈʰ/ |
ड | /ɖ/ |
ढ | /ɖʱ/ |
ण | /ɳ/ |
| त | /t̪/ |
थ | /t̪ʰ/ |
द | /d̪/ |
ध | /d̪ʱ/ |
न | /n/ |
| प | /p/ |
फ | /pʰ/ |
ब | /b/ |
भ | /bʱ/ |
म | /m/ |
| य | /j/ |
र | /r/ |
ल | /l/ |
व | /ʋ/ |
||
| ष | /ʂ/ |
श | /ɕ, ʃ/ |
स | /s/ |
ह | /ɦ/ |
||
| ळ | //ɭʱ// |
क्ष | /kʃ/ |
ज्ञ | /ɟʝɲ/ |
Dialects
Konkani, despite having a small population shows a very high number of dialectDialect
The term dialect is used in two distinct ways, even by linguists. One usage refers to a variety of a language that is a characteristic of a particular group of the language's speakers. The term is applied most often to regional speech patterns, but a dialect may also be defined by other factors,...
s. The dialect tree structure of Konkani can easily be classified according to the region, religion, caste and local tongue influence.
Other researchers have classified the dialects differently.
Kalelkar classification
Based on the historical events and cultural ties of the speakers, N. G. Kalelkar
Narayan Govind Kalelkar
Narayan Govind Kalelkar was a linguist from Maharashtra, India.He was born in the village of Bambuli in Ratnagiri District. He received his early college education in Baroda and Mumbai with specialization in French language, and a D.Lit...
has broadly classified the dialects into three main groups:
- Northern Konkani: Dialects spoken in the Ratnagiri district of Maharashtra with strong cultural ties to Marathi; i.e. Malvani
- Central Konkani: Dialects in Goa and Northern Karnataka, where Konkani came in close contact with Portuguese language and culture.
- Southern Konkani: Dialects spoken in the Canara region(Mangalore & Udupi) of Karnataka which came in close contact with TuluTulu languageThe Tulu language |?]]]) is a Dravidian language spoken by 1.95 million native speakers mainly in the southwest part of Indian state Karnataka known as Tulu Nadu. In India, 1.72 million people speak it as their mother tongue , increased by 10 percent over the 1991 census...
and Kannada.
Ethnologue (ISO) classification
Ethnologue assigns two ISO 639-3
ISO 639-3
ISO 639-3:2007, Codes for the representation of names of languages — Part 3: Alpha-3 code for comprehensive coverage of languages, is an international standard for language codes in the ISO 639 series. The standard describes three‐letter codes for identifying languages. It extends the ISO 639-2...
codes to varieties of Konkani, which it labels a 'macrolanguage
ISO 639 macrolanguage
ISO 639-3 is an international standard for language codes. In defining some of its language codes, some are defined as macrolanguages covering either borderline cases between strongly divergent dialects and very closely related languages , or speech varieties that are considered to be either the...
' with the code :
- Goan Konkani – official recognition as an independent language
- Maharashtrian KonkaniMaharashtrian KonkaniMaharashtrian Konkani refers to a group of dialects spoken in the Konkan region. It is often mistakenly extended to cover Goan Konkani which is an independent language since the speakers of both Goan Konkani and Maharashtrian Konkani refer to their language as Konkani...
– no official recognition, treated by some linguists as a dialect of Marathi
Both languages are referred to as Konkani by their respective speakers.
Problems/issues
The Konkani language has been in danger of dying out primarily due to:- The fragmentation of Konkani into various, sometimes mutually unintelligible dialects.
- The PortuguesePortugalPortugal , officially the Portuguese Republic is a country situated in southwestern Europe on the Iberian Peninsula. Portugal is the westernmost country of Europe, and is bordered by the Atlantic Ocean to the West and South and by Spain to the North and East. The Atlantic archipelagos of the...
influence in Goa, especially on Catholics. - Strong degree of bilingualism of Konkani Hindus in Goa and coastal Maharashtra with Marathi
- Progressive inroads made by Urdu into the Muslim communities.
- Mutual animosity among various religious and caste groups; including a secondary status of Konkani culture to religion.
- Migration of Konkanis to various parts of India and around the world.
- Lack of opportunities to study Konkani in schools and colleges. Even till recently there were few Konkani schools in Goa. Populations outside the native Konkani areas have absolutely no access to Konkani education, even informally.
- Preference among Konkani parents to speak to their children in “Potaachi Bhas” (language of the stomach) over “Maaim Bhas”(mother tongue) Konkani; primarily in English to help their children gain a grip over English in schools.
Efforts have been made to stop this downward trend of usage of Konkani, starting with Shenoi Goembab's
Shenoi Goembab
Waman Raghunath Shennoi Varde Valaulikar known popularly as Shenoi Goembab was a noted Konkani writer and activist.-Education:...
efforts to revive Konkani. There has been a renewed interest in Konkani Literature. The recognition granted by Sahitya Akademi
Sahitya Akademi
The Sahitya Akademi ', India's National Academy of Letters, is an organisation dedicated to the promotion of literature in the languages of India...
to Konkani and the institution of an annual award for Konkani literature has helped.
Some organisations such as the Konkan Daiz Yatra, organised by Konkani Bhasha Mandal, Mumbai since 1939 and the newer Vishwa Konkani Parishad have laid great stress on uniting all factions of Konkanis.
Multilingualism
According to the Census Department of India, Konkani speakers show a very high degree of multilingualismMultilingualism
Multilingualism is the act of using, or promoting the use of, multiple languages, either by an individual speaker or by a community of speakers. Multilingual speakers outnumber monolingual speakers in the world's population. Multilingualism is becoming a social phenomenon governed by the needs of...
. In the 1991 census, as compared to the national average of 19.44% for bilingualism and 7.26% for trilingualism; Konkani speakers scored 74.20% and 44.68% respectively. This makes Konkanis the most multilingual community of India.
This has been due to the fact that in most areas where Konkanis have settled, they seldom form a majority of the population and have to interact with others in the local tongue. Another reason for bilingualism has been the lack of schools teaching Konkani as a primary or secondary language.
While bilingualism is not by itself a bad thing, it has been misinterpreted as a sign that Konkani is not a developed language. The bilingualism of Konkanis with Marathi in Goa and Maharashtra has been a source of great discontent because it has led to the belief that Konkani is a dialect of Marathi and hence had a bearing on the future of Goa.
Konkani–Marathi dispute
It has been claimed by some quarters that Konkani is a dialect of Marathi and not an independent language. This has been attributed to several historical reasons (outlined in the History section), the close similarities between Marathi and Konkani, the geographical proximity between GoaGoa
Goa , a former Portuguese colony, is India's smallest state by area and the fourth smallest by population. Located in South West India in the region known as the Konkan, it is bounded by the state of Maharashtra to the north, and by Karnataka to the east and south, while the Arabian Sea forms its...
and Maharashtra
Maharashtra
Maharashtra is a state located in India. It is the second most populous after Uttar Pradesh and third largest state by area in India...
, the strong Marathi influence on Konkani dialects spoken in Maharashtra (such as Malwani), a supposed lack of literature in Konkani and a great degree of bilingualism of Konkani Hindus with respect to Marathi.
José Pereira, in his 1971 work “Konkani – A Language: A History of the Konkani Marathi Controversy”, pointed to an essay on Indian languages written by John Leyden in 1807 wherein Konkani is called a “dialect of Maharashtra” as an origin of the language controversy.
Another linguist to whom the error is attributed is Grierson
George Abraham Grierson
Sir George Abraham Grierson OM KCIE was born to a prominent Dublin family in 1851. His father and grandfather, both also named George, were well-known printers and publishers.-Biography:Educated at St...
. Grierson's work on the languages of India: The Linguistic Survey of India was regarded as an important reference by other linguists. In his book, Grierson had distinguished between the Konkani spoken in costal Maharashtra (then, part of Bombay Presidency) and the Konkani spoken in Goa as being two different languages. He regarded the Konkani spoken in costal Maharashtra as a dialect of Marathi and not as a dialect of Goan Konkani itself. But, in his opinion, Goan Konkani was also to be considered a dialect of Marathi because the religious literature used by the Hindus in Goa was not in Konkani itself, but in Marathi. Grierson's opinion about Goan Konkani was not based on its linguistics but on the diglossic situation in Goa.
S. M. Katre's 1966 work, The Formation of Konkani, which utilized the instruments of modern historical and comparative linguistics across six typical Konkani dialects, showed the formation of Konkani to be distinct from that of Marathi. Shenoi Goembab
Shenoi Goembab
Waman Raghunath Shennoi Varde Valaulikar known popularly as Shenoi Goembab was a noted Konkani writer and activist.-Education:...
, who played a pivotal role in the Konkani revival movement, rallied against the pre-eminence of Marathi over Konkani amongst Hindus and Portuguese amongst Christians.
Goa's accession to India in 1961 came at a time when Indian states were being reorganized along linguistic lines. There were demands to merge Goa with Maharashtra state. This was because Goa had a sizeable population of Marathi speakers and Konkani was also considered to be a dialect of Marathi by many. Konkani Goans were opposed to the move. The status of Konkani as an independent language or as a dialect of Marathi had a great political bearing on Goa's merger, which was settled by a plebiscite in 1967.
The Sahitya Akademi
Sahitya Akademi
The Sahitya Akademi ', India's National Academy of Letters, is an organisation dedicated to the promotion of literature in the languages of India...
(a prominent literary organization in India) recognized it as an independent language in 1975, and subsequently Konkani (in Devanagari
Devanagari
Devanagari |deva]]" and "nāgarī" ), also called Nagari , is an abugida alphabet of India and Nepal...
script) was made the official language of Goa in 1987.
Script and dialect issues
The problems posed by multiple scripts and varying dialects have come as an impediment in the efforts to unite Konkanis. The decision to use Devanagari as official script and Antruz dialect has met with opposition both within Goa and outside it. The critics contend that Antruz dialect is unintelligible to most Goans, let alone other Konkanis, and that Devanagari is used very little as compared to Roman script in Goa or Kannada script in coastal Karnataka Prominent among the critics are Konkani Catholics in Goa, who have been at the forefront of the Konkani agitation in 1986–87 and have for long used the Roman script including producing literature in Roman script. They are demanding that Roman script be given equal status to Devanagari.In Karnataka, which has the largest number of Konkanis, leading organisations and activists have similarly demanded that Kannada script be made the medium of instruction for Konkani in local schools instead of Devanagari. Government of Karnataka has given its approval for teaching of Konkani as an optional third language from 6th to 10th standard students either in Kannada or Devanagari script.
Organisations

All India Konkani Parishad
The All India Konkani Parishad was founded in 1939 in its first Adhiveshan on 8 July 1939 at Karwar, Karnataka.Madhav Manjunath Shanbhag an advocate by profession from Karwar, who with a few like-minded companions travelled in all the Konkani speaking areas, seeking to unite the fragmented Konkani...
founded on 8 July 1939 served the purpose of providing a common ground for Konkani people from all the regions. A new organisation known as Vishwa Konkani Parishad, which aims to be an all-inclusive and pluralistic umbrella organization for Konkanis around the world, was founded on 11 September 2005.
Mandd Sobhann is the premier organization which is striving hard to preserve, promote, propagate and enrich Konkani language and culture.
The Konkan Daiz Yatra, started in 1939 in Mumbai
Mumbai
Mumbai , formerly known as Bombay in English, is the capital of the Indian state of Maharashtra. It is the most populous city in India, and the fourth most populous city in the world, with a total metropolitan area population of approximately 20.5 million...
, is the oldest Konkani organisation. The Konkani Bhasha Mandal was born in Mumbai on April 5, 1942 during the Third Adhiveshan of All India Konkani Parishad
All India Konkani Parishad
The All India Konkani Parishad was founded in 1939 in its first Adhiveshan on 8 July 1939 at Karwar, Karnataka.Madhav Manjunath Shanbhag an advocate by profession from Karwar, who with a few like-minded companions travelled in all the Konkani speaking areas, seeking to unite the fragmented Konkani...
. On December 28, 1984, Goa Konkani Akademi
Goa Konkani Akademi
The Goa Konkani Akademi is an organization set up by the Government of Goa in 1986 to promote Konkani in Goa. Its stated aim is to accelerate the pace of development of Konkani by encouraging writers, researchers, etc. and to bring Konkanis from all areas together.-Nature:The Goa Konkani Akademi...
(GKA) was founded by the Government of Goa to promote Konkani language, literature and culture. The Thomas Stephens Konknni Kendr (TSKK)
Thomas Stephens Konkkni Kendr
Thomas Stephens Konknni Kendr is a Jesuit-run research-institute working on issues related to the Konkani language, literature, culture and education. It is based in Alto Porvorim, on the outskirts of the state capital of Goa, India.-Aim:...
is a popular research institute based in the Goa
Goa
Goa , a former Portuguese colony, is India's smallest state by area and the fourth smallest by population. Located in South West India in the region known as the Konkan, it is bounded by the state of Maharashtra to the north, and by Karnataka to the east and south, while the Arabian Sea forms its...
n capital Panaji, which works on issues related to the Konkani language, literature, culture and education. The Dalgado Konkani Academy is a popular Konkani organisation based in Panaji.
The Konkani Triveni Kala Sangam is one more famed Konkani organisation in Mumbai
Mumbai
Mumbai , formerly known as Bombay in English, is the capital of the Indian state of Maharashtra. It is the most populous city in India, and the fourth most populous city in the world, with a total metropolitan area population of approximately 20.5 million...
, which is engaged in the vocation of patronizing Konkani language through theatre movement. The Government of Karnataka
Government of Karnataka
The Government of Karnataka is a democratically elected body with the Governor as the constitutional head. The Governor who is appointed for a period of five years appoints the Chief Minister and his council of ministers...
established the Karnataka Konkani Sahitya Akademy on 20 April 1994. The Konkani Ekvott is an umbrella organisation of the Konkani bodies in Goa.
The First World Konkani Convention
First World Konkani Convention
The First World Konkani Convention was held in Mangalore, Karnataka, India, from December 16 to 22, 1995.In 1995 from December 16 to 22, First World Konkani Convention was held in Mangalore under the auspice of Konkani Bhasha Mandal Karnatak, Konkani Activist and organiser Basti Vaman Shenoy was...
was held in Mangalore in December 1995. The Konkani Language and Cultural Foundation came into being immediately after the World Konkani Convention in 1995.
The World Konkani Centre
World Konkani Centre
World Konkani Centre Konkani: विश्व कोंकणी केंद्र Kannada:ವಿಶ್ವ ಕೊಂಕಣಿ ಕೇಂದ್ರ was founded by Konkani Bhas Ani Sanskriti Prathistan Konkani: कोंकणी भास आनी संस्कृति प्रतिष्टान/ಕೊಂಕಣಿ ಭಾಸ್ ಆನಿ ಸಂಸ್ಕೃತಿ ಪ್ರತಿಷ್ಟಾನ್ at Konkani Gaon, Shakti Nagar, Mangalore "to serve as a nodal agency for the...
built on a three-acre plot called Konkani Gaon (Konkani Village) at Shakti Nagar, Mangalore
Mangalore
Mangalore is the chief port city of the Indian state of Karnataka. It is located about west of the state capital, Bangalore. Mangalore lies between the Arabian Sea and the Western Ghat mountain ranges, and is the administrative headquarters of the Dakshina Kannada district in south western...
was inaugurated on 17 January 2009 “to serve as a nodal agency for the preservation and overall development of Konkani language, art and culture involving all the Konkani people the world over.”
Literature
The inquisition of Goa is seen as a blot in the history of the Konkani language. According to the orders of the Goan inquisition, it was an offense to remain in possession of books in local languages. All books, whatever their subject matter, written in Konkani, Marathi, or Sanskrit, were seized by the inquisition and burnt on the suspicion that they might deal with idolatry.It is probable that valuable non-religious literature dealing with art, literature, sciences, etc. were destroyed indiscriminately as a consequence. For instance, even before the inquisition orders, in a letter dated 24 November 1548, Fr. Joao de Albuquerque proudly reports his achievement in this direction.
- The first writer in the history of Konkani language known to us today is Shamaraja; he was also known as Krishnadas Shama as he was an ardent devotee of Lord KrishnaKrishnaKrishna is a central figure of Hinduism and is traditionally attributed the authorship of the Bhagavad Gita. He is the supreme Being and considered in some monotheistic traditions as an Avatar of Vishnu...
. He was born in the 15th century CE in the village of QuellosimQuellosimQuellosim is a village in Salcette Taluk, South Goa, India.This village was known as Kardalipura in ancient times and had wonderful temple dedicated to the mother-goddess Shantadurga which was shifted to Kavale when the Portuguese demolished the shrine as apart of inquisition. Prior to the...
in Goa. As per the date mentioned in his Shrikrishnacharitrakatha, he began writing his book on 13th of the Vaishakha month of the Hindu lunar calender, which is 25 April 1526 according to the Gregorian calender. He authored Ramayana, Mahabharata and Krishnacharitrakatha in proseProseProse is the most typical form of written language, applying ordinary grammatical structure and natural flow of speech rather than rhythmic structure...
style. The manuscripts have not been found, though transliterations in Roman script are found in BragaBragaBraga , a city in the Braga Municipality in northwestern Portugal, is the capital of the Braga District, the oldest archdiocese and the third major city of the country. Braga is the oldest Portuguese city and one of the oldest Christian cities in the World...
in Portugal. The script used by him for his work still remains a mystery. - Vishnudas Nama who also takes pen-names like Vaishampayana and Parameshvaraco sharanagat nama, authored Bhishmaparva and Adiparva, transliterations of which are found in Public library of Braga in northern Portugal.
- Another copy of Ramayana does not bear any author's name, although the name of a certain Sadashiva has been mentioned.
- The first known printed book in Konkani was written by an EnglishEnglish peopleThe English are a nation and ethnic group native to England, who speak English. The English identity is of early mediaeval origin, when they were known in Old English as the Anglecynn. England is now a country of the United Kingdom, and the majority of English people in England are British Citizens...
Jesuit priest, Fr. Thomas Stephens in 1622, and entitled Dovtrina Cristam Em Lingoa Brahmana Canarim (Old Portuguese for: Christian Doctrine in the Canarese Brahman Language). - The first book exclusively on Konkani Grammar, Arte da lingoa Canarim, was printed in 1640 by Father Stephens in Portuguese. Similarly, a book named A Konkani grammar, was printed in the year 1882 in MangaloreMangaloreMangalore is the chief port city of the Indian state of Karnataka. It is located about west of the state capital, Bangalore. Mangalore lies between the Arabian Sea and the Western Ghat mountain ranges, and is the administrative headquarters of the Dakshina Kannada district in south western...
by Angelo Francesco Saverio Maffei, and describes Canara Konkani grammar.
Radio
All India RadioAll India Radio
All India Radio , officially known since 1956 as Akashvani , is the radio broadcaster of India and a division of Prasar Bharati. Established in 1936, it is the sister service of Prasar Bharati's Doordarshan, the national television broadcaster. All India Radio is one of the largest radio networks...
started broadcasting Konkani news and other services. Radio Goa Panjim started Konkani broadcast in 1945. AIR Mumbai and Dharwad later started it in the years 1952 and 1965 respectively. Portuguese Radio, Lisbon started services in 1955 for India, East Africa and Portuguese. Similarly Trivandrum, Alleppey, Trichur and Calicut AIR centers started Konkani broadcasts.
Miscellanea
- There is some disagreement about whether the name “Konkani” was always the accepted name for the language. The earliest reference to the Konkani language comes in a devotional poem by Sant NamdevNamdevSant Namdeo or Bhagat Namdeo was born on October 29, 1270 in the state of Maharashtra village of Narasi-Bamani, in Hingoli district . His father, a calico printer/tailor, was named Damshet and his mother's name was Gonabai...
(c.1270–c.1350 CE) where he has written a stanza in Konkani. - An international ad campaign by NikeNike, Inc.Nike, Inc. is a major publicly traded sportswear and equipment supplier based in the United States. The company is headquartered near Beaverton, Oregon, which is part of the Portland metropolitan area...
for the 2007 Cricket World Cup2007 Cricket World CupThe 2007 ICC Cricket World Cup was the ninth edition of the ICC Cricket World Cup tournament that took place in the West Indies from 13 March to 28 April 2007, using the sport's One Day International format...
featured a Konkani song Rav Patrao Rav as the background theme. It was based on the tune of an older song BebdoBebdo"Bebdo" is a traditional Goan Konkani song composed by Chris Perry and sung by Lorna. It was a part of the album Lorna - Unforgettable Hits. The song is about a drunkard husband who troubles his wife.-Nike ad:...
, composed by Chris PerryChris Perry (musician)Chris Perry , born Pereira was a Goan musician, composer, songwriter and film producer.Chris Perry was an exceptionally gifted trumpeter, but he was also at ease with blowing instruments as saxophone, trumpet and flute as well as finger instruments like keyboard, piano and guitar. He learnt to...
and sung by LornaLorna CordeiroLorna Cordeiro popularly known as Lorna, is a popular Konkani language singer and tiatrist from the state of Goa, India.-Early life:Lorna was born in Mumbai on 9 August 1946 to Cecelia Cordeiro and Theophilus Cordeiro and was brought up there. She belongs to the Goan Catholic community, a prominent...
. The new lyrics written by Agnello Dias (who worked in the ad agency that made the ad), recomposed by Ram Sampat and sung by Ella Castellino. - A Konkani cultural event Konkani Nirantari held in MangaloreMangaloreMangalore is the chief port city of the Indian state of Karnataka. It is located about west of the state capital, Bangalore. Mangalore lies between the Arabian Sea and the Western Ghat mountain ranges, and is the administrative headquarters of the Dakshina Kannada district in south western...
on 26 and 27 January 2008; has entered the Guinness Book of World RecordsGuinness World RecordsGuinness World Records, known until 2000 as The Guinness Book of Records , is a reference book published annually, containing a collection of world records, both human achievements and the extremes of the natural world...
for holding a 40-hour-long non-stop musical singing marathon by beating the Brazilian musical troupe who had previously held the record of singing non-stop for 36 hours. - A Konkani film Paltadacho Munis, or The Man Beyond the BridgeThe Man Beyond the BridgeThe Man Beyond the Bridge is an Indian film in Konkani language directed by Laxmikant Shetgaonkar. A multilayered tale of a lonely forest guard in a dwindling forest strikes a perfect balance between the personal and the political. Laxmikant’s cinema is rich in metaphors, remarkable in its...
was selected in the Toronto International Film FestivalToronto International Film FestivalThe Toronto International Film Festival is a publicly-attended film festival held each September in Toronto, Ontario, Canada. In 2010, 339 films from 59 countries were screened at 32 screens in downtown Toronto venues...
(TIFF) among 300 films being played there.
See also
- Konkani languages
- Konkani ScriptKonkani scriptThe Konkani alphabet may be any one of three alphabets currently used to write the Konkani language....
- Konkani in the Roman scriptKonkani in the Roman scriptKonkani is a language that is spoken by 3.6 million speakers mostly on the western coast of the Indian states of Maharashtra, Goa, Karnataka and Kerala. Konkani is written in five scripts – Devanagari, Roman, Kannada, Malayalam and Perso-Arabic. Of these, the Roman script has the oldest preserved ...
- Konkani PhonologyKonkani phonologyKonkani'Disambiguation: Konkani is a name given to a group of several cognate dialects spoken along the narrow strip of land called Konkan, on the west coast of India. This is, however, somewhat an over-generalisation. Geographically, Konkan is defined roughly as the area between the river...
- Sahitya Akademi Award to Konkani Writers
- Canara Konkani
- Konkani Language AgitationKonkani language agitationThe Konkani language agitations were a series of agitations that happened in the Indian state of Goa during the post-Independence period...
- World Konkani Hall Of FameWorld Konkani Hall Of FameThe World Konkani Hall of Fame is a shrine to great Konkani Men and Women who have rendered commendable service aimed at the betterment of the society in various fields such as art, folklore, literature, education, science, technology, banking, politics and administration etc.The Hall of Fame is...
- World Konkani CentreWorld Konkani CentreWorld Konkani Centre Konkani: विश्व कोंकणी केंद्र Kannada:ವಿಶ್ವ ಕೊಂಕಣಿ ಕೇಂದ್ರ was founded by Konkani Bhas Ani Sanskriti Prathistan Konkani: कोंकणी भास आनी संस्कृति प्रतिष्टान/ಕೊಂಕಣಿ ಭಾಸ್ ಆನಿ ಸಂಸ್ಕೃತಿ ಪ್ರತಿಷ್ಟಾನ್ at Konkani Gaon, Shakti Nagar, Mangalore "to serve as a nodal agency for the...
- MalvaniMalvaniMalvani is a dialect of Konkani with significant Marathi influences and loanwords. Some define it as a Creole between Konkani and Marathi. Though Malvani does not have a unique script, scripts of the other languages native to the regions its speakers inhabit are used. Devanagari is used by most of...
- MaharashtriMaharashtriMaharastri or Maharastri Prakrit, SIL: Mahārāṣṭri Prākrit , is a language of ancient and medieval India which is the ancestor of Marathi, Konkani, Sinhala and the Maldivian language as well. It is one of the many languages of a complex called Prakrit, and the chief Dramatic Prakrit...
- PaisaciPaisaciPaisaci, also known as Paisachi, or Paishachi, is an extinct language of classical India, mentioned as a medium of debate and literary expression in various Theravada Buddhist sources, and in Prakrit and Sanskrit grammars of antiquity...
- Konkani peopleKonkani peopleKonkani people , form a group of people mainly found in the Konkan Coast of western India whose mother-tongue is the Konkani language....
- Malvani peopleMalvani peopleMalvani people or Malvanis are an ethnic group from the Malvan region speaking the Malvani language. Malvani people are mostly of the Konkani or Marathi ethnicities. It may also refer to the residents of Malvan.-External links:**...
- Konkani words from other languagesKonkani words from other languagesKonkani, the language of Goa and of many diaspora on the western coast of India, has come into contact with many local languages and incorporated words from these languages in it....
- Languages of IndiaLanguages of IndiaThe languages of India belong to several language families, the major ones being the Indo-European languages—Indo-Aryan and the Dravidian languages...
- Languages with official status in India
- Linguistic issues in GoaLinguistic issues in Goa-Problems/Issues:The Konkani language has been in danger of dying out primarily due to# The fragmentation of Konkani into various, sometimes mutually unintelligible dialects.# The Portuguese influence in Goa, especially on Catholics....
- List of Indian languages by total speakers
External links
- Konkani Phrasebook at Wikitravel
- Learn Goan Konkani online
- Learn Mangalorean GSB Konkani online
- Learn Mangalorean Catholic Konkani online
- The Origins of the Konkani Language
- An excellent article on Konkani history and literature by Goa Konkani Academi
- Online Manglorean Konkani Dictionary Project
- Online Konkani (GSB) dictionary
- World Konkani Centre, Mangalore

