
Kingdom of Sardinia
Encyclopedia
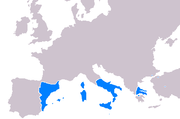
The Kingdom of Sardinia consisted of the island of Sardinia
first as a part of the Crown of Aragon
and subsequently the Spanish Empire
(1297–1720), and second as a part of the composite state of the House of Savoy
(1720–1861). Its capital was originally Cagliari
, in the south of the island, and later Turin
, on the mainland. The kingdom was formed by Pope Boniface VIII
from a papal claim to the islands of Corsica
and Sardinia in 1297 and bestowed, as a vassal
of the Holy See, on James II of Aragon
. It was not until 1324 that James launched a military campaign to take control of his kingdom, and not until 1410 that the last native resisters fell. In 1416 the first of a long line of viceroys was appointed, and in 1420 the last competing claim to the island was bought out.
From 1516 the Aragonese and by extension the Sardinian crown were in personal union with the Kingdom of Castile
and thus formed a part of the much larger Spanish Empire
. During this period the Spanish language
was introduced for administration. In 1713, following the War of the Spanish Succession
, the Kingdom of Sardinia was ceded to the Habsburgs
by the Treaty of Utrecht
, effectively a consolation prize for the loss of their Spanish kingdoms. By the same treaty Victor Amadeus II, Duke of Savoy, received the Kingdom of Sicily
, supplying him with the coveted royal rank. By 1720 the balance of power had shifted again and the House of Savoy
was forced to exchange Sicily with the Habsburgs for Sardinia (Treaty of The Hague
). At that time the Kingdom of Sardinia refers to the states
of the House of Savoy
from 1720 or 1723 onwards (also known as Piedmont-Sardinia
), following the award of the crown of Sardinia
to King Victor Amadeus II of Savoy
under the Treaty of The Hague (1720)
.
After 1720 the kingdom became a composite state and besides Sardinia included Duchy of Savoy
, Piedmont, Nice
, Duchy of Aosta
, Duchy of Monferrato, Vercelli
and Asti
, the Marquisate of Saluzzo
and part of the Duchy of Milan
; Ligurian Republic
, including Genoa
, was added by the Congress of Vienna
in 1815. Officially, the nation's name was Kingdom of Sardinia; the House of Savoy maintaining a national claim to the thrones of Cyprus
and Jerusalem
, although both had long been under Ottoman
rule and never conquered (the title was merely a formal title). In 1860, Nice and Savoy were ceded to France in return for French consent and assistance in Italian unification. In 1861, the Kingdom of Sardinia became the founding state of the new Kingdom of Italy, annexing
all other Italian states. The Kingdom thus continued in legal continuity with the actual Italian state, to which it transferred all its institutions first to Kingdom of Italy (1861–1946)
and after to Italian Republic.
, intervening between the Houses of Anjou
and Aragon
in the war called Sicilian Vespers
, established on paper a Regnum Sardiniae et Corsicae that would be a fief of the Papacy (in the island, however, already existed native state entities). Then the Pope offered his newly-invented fief to James II
of Aragon
, promising him papal support should he wish to conquer Pisan Sardinia in exchange for Sicily. In 1323 James II formed an alliance with Hugh II of Arborea
and, following a military campaign which lasted a year or so, occupied the Pisan territories of Cagliari
and Gallura
along with Sassari
, claiming the territory as the Kingdom of Sardinia and Corsica.
 In 1347 Aragon made war on Genoa
In 1347 Aragon made war on Genoa
(who owned large areas of the Logudoro
) then, starting from 1353, fought with the arborean leader Marianus IV
, of the Cappai de Bas
family, but did not reduce the last of the autochthonous
giudicati
(indigenous kingdoms of Sardinia) until 1409 when the Sardinian hopes of expel the Aragonese from the island vanished due to the heavy defeat at the Battle of Sanluri
. In 1420, after the exstintion of the Giudicato of Arborea, the Aragonese conquest of Sardinia was completed and the royal territory for the first time after almost a century of wars, coincided with that of the entire island. The Kingdom of Sardinia and Corsica retained its separate character as part of the Crown of Aragon and was not merely incorporated into the Kingdom of Aragon. At the time of his struggles with Arborea, Peter IV of Aragon
granted an autonomous legislature to the Kingdom, which had one of Europe's most advanced legal traditions. The Kingdom was governed in the king's name by a viceroy. When in 1409, Martin the Younger, king of Sicily and heir to Aragon, defeated the last Sardinian giudicato but then died in Cagliari of malaria, without issue, Sardinia passed with the Crown of Aragon to a united Spain. Corsica, which had never been conquered, was dropped from the formal title.
The loss of the autochthonous' independence, the firm Aragonese (later Spanish) rule, with the introduction of a sterile feudalism
, as well as the discovery of the Americas
, provoked an unstoppable decline of Kingdom of Sardinia. A short period of resurgence occurred under the local noble Leonardo de Alagon, marquess of Oristano
, who managed to defeat the viceroy's army in the 1470s but was later crushed at the Battle of Macomer (1478), ending any further hope of independence for the island.
and a series of plagues (from 1582, 1652 and 1655) worsened the situation on the island early in the reign of the Catholic Monarchs
.
. By the Treaty of Utrecht
of 1713, Spain
's European empire was divided: Savoy
received Sicily
and parts of the Duchy of Milan
, while Charles VI
(the Holy Roman Emperor
and Archduke of Austria), received the Spanish Netherlands, the Kingdom of Naples
, Sardinia
, and the bulk of the Duchy of Milan
. In 1718, by the Treaty of London
among the great powers, Victor Amadeus II, duke of Savoy and sovereign of Piedmont, was forced to yield Sicily to the Austrian Habsburgs and in exchange received Sardinia. Two years later, on Aug. 24, 1720, he formally took possession of the island.
 The Spanish domination of Sardinia ended at the beginning of the 18th century, as a result of War of the Spanish succession
The Spanish domination of Sardinia ended at the beginning of the 18th century, as a result of War of the Spanish succession
. By the Treaty of Utrecht
of 1713, Spain
's European empire was divided: Savoy
received Sicily
and parts of the Duchy of Milan
, while Charles VI
(the Holy Roman Emperor
and Archduke of Austria), received the Spanish Netherlands, the Kingdom of Naples
, Sardinia
, and the bulk of the Duchy of Milan
.
During the War of the Quadruple Alliance
, Victor Amadeus II, duke of Savoy and sovereign of Piedmont, had to agree to yield Sicily to the Austrian Habsburgs and receive Sardinia in exchange. The exchange was formally ratified in the Treaty of The Hague
of February 17, 1720. Because a kingdom of Sardinia had existed since the 14th century, the exchange allowed Victor Amadeus to retain the title of king in spite of the loss of Sicily. Victor Amadeus initially resisted the exchange, and until 1723 continued to style himself King of Sicily rather than King of Sardinia.

tribes such as the Taurini
and the Salassi
. They later submitted to the Romans
(c. 220 BC
), who founded several colonies there including Augusta Taurinorum (Turin) and Eporedia (Ivrea
). After the fall of the Western Roman Empire
, the region was repeatedly invaded by the Burgundians
, the Goths
(5th century), Byzantines
, Lombards
(6th century), Franks
(773). In the 9th-10th centuries there were further incursions by the Magyars and Saracens. At the time Piedmont, as part of the Kingdom of Italy
within the Holy Roman Empire
, was subdivided into several marks and counties.
In 1046, Oddo of Savoy added Piedmont to their main segment of Savoy
, with a capital at Chambéry
(now in France
). Other areas remained independent, such as the powerful communes of Asti
and Alessandria
and the marquisates of Saluzzo
and Montferrat. The County of Savoy was elevated to a duke in 1416, and Duke Emanuele Filiberto moved the seat to Turin
in 1563.

against the French First Republic
, but was beaten in 1796 by Napoleon and forced to conclude the disadvantageous Treaty of Paris (1796)
, giving the French army free passage through Piedmont. On December 6, 1798 Joubert
occupied Turin and forced Charles Emmanuel IV
to abdicate and leave for the island of Sardinia. The provisionary government voted to unite Piedmont with France. In 1799 the Austro-Russians briefly occupied the city, but with the Battle of Marengo (1800), the French regained control. The island of Sardinia stayed out of the reach of the French for the rest of the war.
In 1814 the kingdom was restored and enlarged with the addition of the former Republic of Genoa
, now a duchy, and it served as a buffer state
against France
. This was confirmed by the Congress of Vienna
.
In the reaction after Napoleon, the country was ruled by conservative monarchs: Victor Emmanuel I
(1802–21), Charles Felix
(1821–31) and Charles Albert (1831–49), who fought at the head of a contingent of his own troops at the Battle of Trocadero
, which set the reactionary Ferdinand VII on the Spanish throne. Victor Emanuel I disbanded the entire Code Napoléon and returned the lands and power to the nobility and the Church. This reactionary policy went as far as discouraging the use of roads built by the French. These changes typified Piedmont.
The Kingdom of Sardinia industrialized from 1830 onward. A constitution, the Statuto Albertino
, was enacted in the year of revolutions, 1848
, under liberal pressure, and under the same pressure Charles Albert declared war on Austria. After initial success the war took a turn for the worse and Charles Albert was defeated by Marshal Radetzky at Custozza.

.
In 1852 a liberal ministry under Count Camillo Benso di Cavour was installed, and the Kingdom of Sardinia became the engine driving the Italian Unification
. The Kingdom of Sardinia (Piedmont) took part in the Crimean War
, allied with the Ottoman Empire
, Britain
, and France
, and fighting against Russia
.
In 1859 France sided with the Kingdom of Sardinia in a war against Austria
, the Austro-Sardinian War. Napoleon III didn't keep his promises to Cavour to fight until all of the Kingdom of Lombardy-Venetia had been conquered. Following the bloody battles of Magenta
and Solferino
, both French victories, Napoleon thought the war too costly to continue and made a separate peace behind Cavour's back in which only Lombardy would be ceded. Due to the Austrian government's refusal to cede any lands to the Kingdom of Sardinia, they agreed to cede Lombardy
to Napoleon who in turn then ceded the territory to the Kingdom of Sardinia to avoid 'embarrassing' the defeated Austrians. Cavour angrily resigned from office when it became clear that Victor Emmanuel would accept the deal.

, Tuscany
, Modena
, and Romagna
voted in referendum
s to join the Kingdom of Sardinia. This alarmed Napoleon who feared a strong Savoyard state on his southeastern border and he insisted that if the Kingdom of Sardinia were to keep the new acquisitions they would have to cede Savoy and Nice to France. This was done after dubious referendums showed over 99.5% majorities in both areas in favour of joining France.
In 1860 Giuseppe Garibaldi
started his campaign to conquer southern Italy in the name of the Kingdom of Sardinia. He quickly toppled the Kingdom of the Two Sicilies
and marched to Gaeta
. Cavour was actually the most satisfied with the unification while Garibaldi wanted to conquer Rome. Garibaldi was too revolutionary for the king and his prime minister.
s of all other Italian states to Piedmont. The institutions and laws of the Kingdom were quickly extended to all Italy, brutally abolishing the administrations of the other regions. Piedmont would become the most dominant and wealthiest region in Italy and the capital of Piedmont, Turin, would remain the Italian capital until 1865 when the capital was moved to Florence
; but in contrast, many revolts exploded through the peninsula, especially in Southern Italy
. The House of Savoy
would rule Italy until 1946 when Italy was declared a republic
.


 Dynasty of the Counts of Barcelona:
Dynasty of the Counts of Barcelona:
Dynasty of the Trastámara of Castile
:
Dynasty of the Habsburgs of Spain
:
Dynasty of the Bourbons
of Spain:
Dynasty of the Habsburgs of Spain
Dynasty of Savoy
:
was add into Kingdom of Sicily in 1713 and Kingdom of Sardinia in 1723, it maintained its traditional flag depicting a white cross on a red field. But a problem arose: if the Duchy owned the small harbour of Nice
only, the union with Sicily and then Sardinia gave to the Kingdom a quite big fleet, which had the same flag of Malta
. To disambiguate the ships of the two different States, the House of Savoy added a blue border to its flag, and then it reduced the cross in a single quarter.
The flag had following minor changes until 1848, when a revolution happened: to follow the liberal revolutions which were exploding in all Europe, King Charles Albert adopted the Napoleonic Italian tricolour, surmonted by the Savoyard shield, as national flag. This flag became the flag of Italy until 1946.
Sardinia
Sardinia is the second-largest island in the Mediterranean Sea . It is an autonomous region of Italy, and the nearest land masses are the French island of Corsica, the Italian Peninsula, Sicily, Tunisia and the Spanish Balearic Islands.The name Sardinia is from the pre-Roman noun *sard[],...
first as a part of the Crown of Aragon
Crown of Aragon
The Crown of Aragon Corona d'Aragón Corona d'Aragó Corona Aragonum controlling a large portion of the present-day eastern Spain and southeastern France, as well as some of the major islands and mainland possessions stretching across the Mediterranean as far as Greece...
and subsequently the Spanish Empire
Spanish Empire
The Spanish Empire comprised territories and colonies administered directly by Spain in Europe, in America, Africa, Asia and Oceania. It originated during the Age of Exploration and was therefore one of the first global empires. At the time of Habsburgs, Spain reached the peak of its world power....
(1297–1720), and second as a part of the composite state of the House of Savoy
House of Savoy
The House of Savoy was formed in the early 11th century in the historical Savoy region. Through gradual expansion, it grew from ruling a small county in that region to eventually rule the Kingdom of Italy from 1861 until the end of World War II, king of Croatia and King of Armenia...
(1720–1861). Its capital was originally Cagliari
Cagliari
Cagliari is the capital of the island of Sardinia, a region of Italy. Cagliari's Sardinian name Casteddu literally means castle. It has about 156,000 inhabitants, or about 480,000 including the outlying townships : Elmas, Assemini, Capoterra, Selargius, Sestu, Monserrato, Quartucciu, Quartu...
, in the south of the island, and later Turin
Turin
Turin is a city and major business and cultural centre in northern Italy, capital of the Piedmont region, located mainly on the left bank of the Po River and surrounded by the Alpine arch. The population of the city proper is 909,193 while the population of the urban area is estimated by Eurostat...
, on the mainland. The kingdom was formed by Pope Boniface VIII
Pope Boniface VIII
Pope Boniface VIII , born Benedetto Gaetani, was Pope of the Catholic Church from 1294 to 1303. Today, Boniface VIII is probably best remembered for his feuds with Dante, who placed him in the Eighth circle of Hell in his Divina Commedia, among the Simonists.- Biography :Gaetani was born in 1235 in...
from a papal claim to the islands of Corsica
Corsica
Corsica is an island in the Mediterranean Sea. It is located west of Italy, southeast of the French mainland, and north of the island of Sardinia....
and Sardinia in 1297 and bestowed, as a vassal
Vassal
A vassal or feudatory is a person who has entered into a mutual obligation to a lord or monarch in the context of the feudal system in medieval Europe. The obligations often included military support and mutual protection, in exchange for certain privileges, usually including the grant of land held...
of the Holy See, on James II of Aragon
James II of Aragon
James II , called the Just was the King of Sicily from 1285 to 1296 and King of Aragon and Valencia and Count of Barcelona from 1291 to 1327. In 1297 he was granted the Kingdom of Sardinia and Corsica...
. It was not until 1324 that James launched a military campaign to take control of his kingdom, and not until 1410 that the last native resisters fell. In 1416 the first of a long line of viceroys was appointed, and in 1420 the last competing claim to the island was bought out.
From 1516 the Aragonese and by extension the Sardinian crown were in personal union with the Kingdom of Castile
Kingdom of Castile
Kingdom of Castile was one of the medieval kingdoms of the Iberian Peninsula. It emerged as a political autonomous entity in the 9th century. It was called County of Castile and was held in vassalage from the Kingdom of León. Its name comes from the host of castles constructed in the region...
and thus formed a part of the much larger Spanish Empire
Spanish Empire
The Spanish Empire comprised territories and colonies administered directly by Spain in Europe, in America, Africa, Asia and Oceania. It originated during the Age of Exploration and was therefore one of the first global empires. At the time of Habsburgs, Spain reached the peak of its world power....
. During this period the Spanish language
Spanish language
Spanish , also known as Castilian , is a Romance language in the Ibero-Romance group that evolved from several languages and dialects in central-northern Iberia around the 9th century and gradually spread with the expansion of the Kingdom of Castile into central and southern Iberia during the...
was introduced for administration. In 1713, following the War of the Spanish Succession
War of the Spanish Succession
The War of the Spanish Succession was fought among several European powers, including a divided Spain, over the possible unification of the Kingdoms of Spain and France under one Bourbon monarch. As France and Spain were among the most powerful states of Europe, such a unification would have...
, the Kingdom of Sardinia was ceded to the Habsburgs
Habsburg Monarchy
The Habsburg Monarchy covered the territories ruled by the junior Austrian branch of the House of Habsburg , and then by the successor House of Habsburg-Lorraine , between 1526 and 1867/1918. The Imperial capital was Vienna, except from 1583 to 1611, when it was moved to Prague...
by the Treaty of Utrecht
Treaty of Utrecht
The Treaty of Utrecht, which established the Peace of Utrecht, comprises a series of individual peace treaties, rather than a single document, signed by the belligerents in the War of Spanish Succession, in the Dutch city of Utrecht in March and April 1713...
, effectively a consolation prize for the loss of their Spanish kingdoms. By the same treaty Victor Amadeus II, Duke of Savoy, received the Kingdom of Sicily
Kingdom of Sicily
The Kingdom of Sicily was a state that existed in the south of Italy from its founding by Roger II in 1130 until 1816. It was a successor state of the County of Sicily, which had been founded in 1071 during the Norman conquest of southern Italy...
, supplying him with the coveted royal rank. By 1720 the balance of power had shifted again and the House of Savoy
House of Savoy
The House of Savoy was formed in the early 11th century in the historical Savoy region. Through gradual expansion, it grew from ruling a small county in that region to eventually rule the Kingdom of Italy from 1861 until the end of World War II, king of Croatia and King of Armenia...
was forced to exchange Sicily with the Habsburgs for Sardinia (Treaty of The Hague
Treaty of The Hague (1720)
The Treaty of The Hague was signed on February 17, 1720. The treaty ended the War of the Quadruple Alliance, a conflict that arose between King Philip V of Spain and an alliance of Great Britain, France, Austria and the Dutch Republic.Philip was confirmed king of Spain by the Treaty of Utrecht in...
). At that time the Kingdom of Sardinia refers to the states
State (polity)
A state is an organized political community, living under a government. States may be sovereign and may enjoy a monopoly on the legal initiation of force and are not dependent on, or subject to any other power or state. Many states are federated states which participate in a federal union...
of the House of Savoy
House of Savoy
The House of Savoy was formed in the early 11th century in the historical Savoy region. Through gradual expansion, it grew from ruling a small county in that region to eventually rule the Kingdom of Italy from 1861 until the end of World War II, king of Croatia and King of Armenia...
from 1720 or 1723 onwards (also known as Piedmont-Sardinia
Piedmont-Sardinia
Kingdom of Sardinia or Sardinia, also Piedmont-Sardinia, Sardinia-Piedmont or Piemonte, refers to the states of the House of Savoy from 1720 or 1723 onwards, following the award of the crown of Sardinia to King Victor Amadeus II of Savoy under the Treaty of The Hague...
), following the award of the crown of Sardinia
Sardinia
Sardinia is the second-largest island in the Mediterranean Sea . It is an autonomous region of Italy, and the nearest land masses are the French island of Corsica, the Italian Peninsula, Sicily, Tunisia and the Spanish Balearic Islands.The name Sardinia is from the pre-Roman noun *sard[],...
to King Victor Amadeus II of Savoy
Victor Amadeus II of Sardinia
Victor Amadeus II was Duke of Savoy from 1675 to 1730. He also held the titles of marquis of Saluzzo, duke of Montferrat, prince of Piedmont, count of Aosta, Moriana and Nizza. Louis XIV organised his marriage in order to maintain French influence in the Duchy but Victor Amadeus soon broke away...
under the Treaty of The Hague (1720)
Treaty of The Hague (1720)
The Treaty of The Hague was signed on February 17, 1720. The treaty ended the War of the Quadruple Alliance, a conflict that arose between King Philip V of Spain and an alliance of Great Britain, France, Austria and the Dutch Republic.Philip was confirmed king of Spain by the Treaty of Utrecht in...
.
After 1720 the kingdom became a composite state and besides Sardinia included Duchy of Savoy
Duchy of Savoy
From 1416 to 1847, the House of Savoy ruled the eponymous Duchy of Savoy . The Duchy was a state in the northern part of the Italian Peninsula, with some territories that are now in France. It was a continuation of the County of Savoy...
, Piedmont, Nice
County of Nice
The County of Nice or Niçard Country is a historical region of France, located in the south-eastern part, around the city of Nice.-History:Its territory lies between the Mediterranean Sea , Var River and the southernmost crest of the...
, Duchy of Aosta
Duchy of Aosta
The Duchy of Aosta, originally the County of Aosta, was a state ruled by the House of Savoy from the early 11th century until the late 18th, when its independent institutions were aligned with those of the Principality of Piedmont. The title "Duke of Aosta" continued to be used by the second sons...
, Duchy of Monferrato, Vercelli
Vercelli
Vercelli is a city and comune of about 47,000 inhabitants in the Province of Vercelli, Piedmont, northern Italy. One of the oldest urban sites in northern Italy, it was founded, according to most historians, around the year 600 BC.The city is situated on the river Sesia in the plain of the river...
and Asti
Asti
Asti is a city and comune of about 75,000 inhabitants located in the Piedmont region of northwestern Italy, about 55 kilometres east of Turin in the plain of the Tanaro River...
, the Marquisate of Saluzzo
Marquisate of Saluzzo
The Marquisate of Saluzzo was an historical Italian state that included French and Piedmont territories on the Alps.-Marquisate territories:The Marquisate of Saluzzo occupied parts of the provinces of Cuneo and Turin, and at times areas now under French control. However, Saluzzo was historically...
and part of the Duchy of Milan
Duchy of Milan
The Duchy of Milan , was created on the 1st of may 1395, when Gian Galeazzo Visconti, Lord of Milan, purchased a diploma for 100,000 Florins from King Wenceslaus. It was this diploma that installed, Gian Galeazzo as Duke of Milan and Count of Pavia...
; Ligurian Republic
Ligurian Republic
The Ligurian Republic was a short-lived French client republic formed by Napoleon on 14 June 1797. It consisted of the old Republic of Genoa which covered most of the Ligurian region of Northwest Italy, and the small Imperial fiefs owned by the House of Savoy inside its territory...
, including Genoa
Genoa
Genoa |Ligurian]] Zena ; Latin and, archaically, English Genua) is a city and an important seaport in northern Italy, the capital of the Province of Genoa and of the region of Liguria....
, was added by the Congress of Vienna
Congress of Vienna
The Congress of Vienna was a conference of ambassadors of European states chaired by Klemens Wenzel von Metternich, and held in Vienna from September, 1814 to June, 1815. The objective of the Congress was to settle the many issues arising from the French Revolutionary Wars, the Napoleonic Wars,...
in 1815. Officially, the nation's name was Kingdom of Sardinia; the House of Savoy maintaining a national claim to the thrones of Cyprus
Kingdom of Cyprus
The Kingdom of Cyprus was a Crusader kingdom on the island of Cyprus in the high and late Middle Ages, between 1192 and 1489. It was ruled by the French House of Lusignan.-History:...
and Jerusalem
Kingdom of Jerusalem
The Kingdom of Jerusalem was a Catholic kingdom established in the Levant in 1099 after the First Crusade. The kingdom lasted nearly two hundred years, from 1099 until 1291 when the last remaining possession, Acre, was destroyed by the Mamluks, but its history is divided into two distinct periods....
, although both had long been under Ottoman
Ottoman Empire
The Ottoman EmpireIt was usually referred to as the "Ottoman Empire", the "Turkish Empire", the "Ottoman Caliphate" or more commonly "Turkey" by its contemporaries...
rule and never conquered (the title was merely a formal title). In 1860, Nice and Savoy were ceded to France in return for French consent and assistance in Italian unification. In 1861, the Kingdom of Sardinia became the founding state of the new Kingdom of Italy, annexing
Annexation
Annexation is the de jure incorporation of some territory into another geo-political entity . Usually, it is implied that the territory and population being annexed is the smaller, more peripheral, and weaker of the two merging entities, barring physical size...
all other Italian states. The Kingdom thus continued in legal continuity with the actual Italian state, to which it transferred all its institutions first to Kingdom of Italy (1861–1946)
Kingdom of Italy (1861–1946)
The Kingdom of Italy was a state forged in 1861 by the unification of Italy under the influence of the Kingdom of Sardinia, which was its legal predecessor state...
and after to Italian Republic.
Crown of Aragon (1297–1479)
In 1297, Pope Boniface VIIIPope Boniface VIII
Pope Boniface VIII , born Benedetto Gaetani, was Pope of the Catholic Church from 1294 to 1303. Today, Boniface VIII is probably best remembered for his feuds with Dante, who placed him in the Eighth circle of Hell in his Divina Commedia, among the Simonists.- Biography :Gaetani was born in 1235 in...
, intervening between the Houses of Anjou
Capetian House of Anjou
The Capetian House of Anjou, also known as the House of Anjou-Sicily and House of Anjou-Naples, was a royal house and cadet branch of the direct House of Capet. Founded by Charles I of Sicily, a son of Louis VIII of France, the Capetian king first ruled the Kingdom of Sicily during the 13th century...
and Aragon
House of Barcelona
The House of Barcelona was a medieval dynasty that ruled the County of Barcelona continuously from 878 and the Crown of Aragon from 1137 . From the male part they descend from the Bellonids, the descendants of Wifred the Hairy...
in the war called Sicilian Vespers
Sicilian Vespers
The Sicilian Vespers is the name given to the successful rebellion on the island of Sicily that broke out on the Easter of 1282 against the rule of the French/Angevin king Charles I, who had ruled the Kingdom of Sicily since 1266. Within six weeks three thousand French men and women were slain by...
, established on paper a Regnum Sardiniae et Corsicae that would be a fief of the Papacy (in the island, however, already existed native state entities). Then the Pope offered his newly-invented fief to James II
James II of Aragon
James II , called the Just was the King of Sicily from 1285 to 1296 and King of Aragon and Valencia and Count of Barcelona from 1291 to 1327. In 1297 he was granted the Kingdom of Sardinia and Corsica...
of Aragon
Crown of Aragon
The Crown of Aragon Corona d'Aragón Corona d'Aragó Corona Aragonum controlling a large portion of the present-day eastern Spain and southeastern France, as well as some of the major islands and mainland possessions stretching across the Mediterranean as far as Greece...
, promising him papal support should he wish to conquer Pisan Sardinia in exchange for Sicily. In 1323 James II formed an alliance with Hugh II of Arborea
Hugh II of Arborea
Hugh II was Giudice of Arborea, reigning from 1321 CE until his death in 1336 CE. He was the illegitimate son of Marianus III of Arborea and Paulesa de Serra....
and, following a military campaign which lasted a year or so, occupied the Pisan territories of Cagliari
Cagliari
Cagliari is the capital of the island of Sardinia, a region of Italy. Cagliari's Sardinian name Casteddu literally means castle. It has about 156,000 inhabitants, or about 480,000 including the outlying townships : Elmas, Assemini, Capoterra, Selargius, Sestu, Monserrato, Quartucciu, Quartu...
and Gallura
Gallura
Gallura is a region of northern Sardinia, Italy.The name Gallùra means "area located on high ground".-Geography:...
along with Sassari
Sassari
Sassari is an Italian city. It is the second-largest city of Sardinia in terms of population with about 130,000 inhabitants, or about 300,000 including the greater metropolitan area...
, claiming the territory as the Kingdom of Sardinia and Corsica.

Republic of Genoa
The Most Serene Republic of Genoa |Ligurian]]: Repúbrica de Zêna) was an independent state from 1005 to 1797 in Liguria on the northwestern Italian coast, as well as Corsica from 1347 to 1768, and numerous other territories throughout the Mediterranean....
(who owned large areas of the Logudoro
Logudoro
The Logudoro is a large traditional region in central-northern Sardinia, Italy. The local dialect is known as Logudorese.Mostly composed of soft volcanic terrains, it is the most fertile area of the island. For this reason it was settled since early Prehistoric times, as shown by the presence of...
) then, starting from 1353, fought with the arborean leader Marianus IV
Marianus IV of Arborea
Marianus IV , called the Great, was the Giudice of Arborea from 1347 to his death. He was, as his nickname indicates, the greatest sovereign of Arborea. He was a legislator and a warrior whose reign saw the commencement of massive codification of the laws of his realm and incessant warfare with the...
, of the Cappai de Bas
Cappai de Bas
Cappai des Baux, originally Çapay viscounts of Bas , is the name of an old Aragonese noble family who came to Sardinia in the 14th century with the king James II of Aragon during his campaign to conquer the island...
family, but did not reduce the last of the autochthonous
Indigenous peoples
Indigenous peoples are ethnic groups that are defined as indigenous according to one of the various definitions of the term, there is no universally accepted definition but most of which carry connotations of being the "original inhabitants" of a territory....
giudicati
Giudicati
The giudicati were the indigenous kingdoms of Sardinia from about 900 until 1410, when the last fell to the Aragonese. The rulers of the giudicati were giudici , from the Latin iudice , often translates as "judge". The Latin for giudicato was iudicatus The giudicati (singular giudicato) were the...
(indigenous kingdoms of Sardinia) until 1409 when the Sardinian hopes of expel the Aragonese from the island vanished due to the heavy defeat at the Battle of Sanluri
Battle of Sanluri
The Battle of Sanluri was fought on June 30, 1409 between the armies of the Giudicato of Arborea and the Catalan-Sicilian army of King Martin I of Sicily....
. In 1420, after the exstintion of the Giudicato of Arborea, the Aragonese conquest of Sardinia was completed and the royal territory for the first time after almost a century of wars, coincided with that of the entire island. The Kingdom of Sardinia and Corsica retained its separate character as part of the Crown of Aragon and was not merely incorporated into the Kingdom of Aragon. At the time of his struggles with Arborea, Peter IV of Aragon
Peter IV of Aragon
Peter IV, , called el Cerimoniós or el del punyalet , was the King of Aragon, King of Sardinia and Corsica , King of Valencia , and Count of Barcelona Peter IV, (Balaguer, September 5, 1319 – Barcelona, January 6, 1387), called el Cerimoniós ("the Ceremonious") or el del punyalet ("the one...
granted an autonomous legislature to the Kingdom, which had one of Europe's most advanced legal traditions. The Kingdom was governed in the king's name by a viceroy. When in 1409, Martin the Younger, king of Sicily and heir to Aragon, defeated the last Sardinian giudicato but then died in Cagliari of malaria, without issue, Sardinia passed with the Crown of Aragon to a united Spain. Corsica, which had never been conquered, was dropped from the formal title.
The loss of the autochthonous' independence, the firm Aragonese (later Spanish) rule, with the introduction of a sterile feudalism
Feudalism
Feudalism was a set of legal and military customs in medieval Europe that flourished between the 9th and 15th centuries, which, broadly defined, was a system for ordering society around relationships derived from the holding of land in exchange for service or labour.Although derived from the...
, as well as the discovery of the Americas
Americas
The Americas, or America , are lands in the Western hemisphere, also known as the New World. In English, the plural form the Americas is often used to refer to the landmasses of North America and South America with their associated islands and regions, while the singular form America is primarily...
, provoked an unstoppable decline of Kingdom of Sardinia. A short period of resurgence occurred under the local noble Leonardo de Alagon, marquess of Oristano
Oristano
Oristano is a town and comune, capital of the Province of Oristano, on the island of Sardinia, Italy. It has approximately 32,500 inhabitants.Its economy is mainly based on fishing, agriculture and, to a certain extent, tourism.-History:...
, who managed to defeat the viceroy's army in the 1470s but was later crushed at the Battle of Macomer (1478), ending any further hope of independence for the island.
Spanish Empire (1479–1700)
Unceasing attacks from North African piratesBerber people
Berbers are the indigenous peoples of North Africa west of the Nile Valley. They are continuously distributed from the Atlantic to the Siwa oasis, in Egypt, and from the Mediterranean to the Niger River. Historically they spoke the Berber language or varieties of it, which together form a branch...
and a series of plagues (from 1582, 1652 and 1655) worsened the situation on the island early in the reign of the Catholic Monarchs
Catholic Monarchs
The Catholic Monarchs is the collective title used in history for Queen Isabella I of Castile and King Ferdinand II of Aragon. They were both from the House of Trastámara and were second cousins, being both descended from John I of Castile; they were given a papal dispensation to deal with...
.
Sardinia between two powers (1700–1720)
The Spanish domination of Sardinia ended at the beginning of the 18th century, as a result of War of the Spanish successionWar of the Spanish Succession
The War of the Spanish Succession was fought among several European powers, including a divided Spain, over the possible unification of the Kingdoms of Spain and France under one Bourbon monarch. As France and Spain were among the most powerful states of Europe, such a unification would have...
. By the Treaty of Utrecht
Treaty of Utrecht
The Treaty of Utrecht, which established the Peace of Utrecht, comprises a series of individual peace treaties, rather than a single document, signed by the belligerents in the War of Spanish Succession, in the Dutch city of Utrecht in March and April 1713...
of 1713, Spain
Spain
Spain , officially the Kingdom of Spain languages]] under the European Charter for Regional or Minority Languages. In each of these, Spain's official name is as follows:;;;;;;), is a country and member state of the European Union located in southwestern Europe on the Iberian Peninsula...
's European empire was divided: Savoy
House of Savoy
The House of Savoy was formed in the early 11th century in the historical Savoy region. Through gradual expansion, it grew from ruling a small county in that region to eventually rule the Kingdom of Italy from 1861 until the end of World War II, king of Croatia and King of Armenia...
received Sicily
Sicily
Sicily is a region of Italy, and is the largest island in the Mediterranean Sea. Along with the surrounding minor islands, it constitutes an autonomous region of Italy, the Regione Autonoma Siciliana Sicily has a rich and unique culture, especially with regard to the arts, music, literature,...
and parts of the Duchy of Milan
Duchy of Milan
The Duchy of Milan , was created on the 1st of may 1395, when Gian Galeazzo Visconti, Lord of Milan, purchased a diploma for 100,000 Florins from King Wenceslaus. It was this diploma that installed, Gian Galeazzo as Duke of Milan and Count of Pavia...
, while Charles VI
Charles VI, Holy Roman Emperor
Charles VI was the penultimate Habsburg sovereign of the Habsburg Empire. He succeeded his elder brother, Joseph I, as Holy Roman Emperor, King of Bohemia , Hungary and Croatia , Archduke of Austria, etc., in 1711...
(the Holy Roman Emperor
Holy Roman Emperor
The Holy Roman Emperor is a term used by historians to denote a medieval ruler who, as German King, had also received the title of "Emperor of the Romans" from the Pope...
and Archduke of Austria), received the Spanish Netherlands, the Kingdom of Naples
Kingdom of Naples
The Kingdom of Naples, comprising the southern part of the Italian peninsula, was the remainder of the old Kingdom of Sicily after secession of the island of Sicily as a result of the Sicilian Vespers rebellion of 1282. Known to contemporaries as the Kingdom of Sicily, it is dubbed Kingdom of...
, Sardinia
Sardinia
Sardinia is the second-largest island in the Mediterranean Sea . It is an autonomous region of Italy, and the nearest land masses are the French island of Corsica, the Italian Peninsula, Sicily, Tunisia and the Spanish Balearic Islands.The name Sardinia is from the pre-Roman noun *sard[],...
, and the bulk of the Duchy of Milan
Duchy of Milan
The Duchy of Milan , was created on the 1st of may 1395, when Gian Galeazzo Visconti, Lord of Milan, purchased a diploma for 100,000 Florins from King Wenceslaus. It was this diploma that installed, Gian Galeazzo as Duke of Milan and Count of Pavia...
. In 1718, by the Treaty of London
Treaty of London
The Treaty of London may refer to:* Treaty of London , which ceded western France to England, repudiated by the Estates-General in Paris on 19 May 1359* Treaty of London , a non-aggression pact between the major European nations...
among the great powers, Victor Amadeus II, duke of Savoy and sovereign of Piedmont, was forced to yield Sicily to the Austrian Habsburgs and in exchange received Sardinia. Two years later, on Aug. 24, 1720, he formally took possession of the island.

War of the Spanish Succession
The War of the Spanish Succession was fought among several European powers, including a divided Spain, over the possible unification of the Kingdoms of Spain and France under one Bourbon monarch. As France and Spain were among the most powerful states of Europe, such a unification would have...
. By the Treaty of Utrecht
Treaty of Utrecht
The Treaty of Utrecht, which established the Peace of Utrecht, comprises a series of individual peace treaties, rather than a single document, signed by the belligerents in the War of Spanish Succession, in the Dutch city of Utrecht in March and April 1713...
of 1713, Spain
Spain
Spain , officially the Kingdom of Spain languages]] under the European Charter for Regional or Minority Languages. In each of these, Spain's official name is as follows:;;;;;;), is a country and member state of the European Union located in southwestern Europe on the Iberian Peninsula...
's European empire was divided: Savoy
House of Savoy
The House of Savoy was formed in the early 11th century in the historical Savoy region. Through gradual expansion, it grew from ruling a small county in that region to eventually rule the Kingdom of Italy from 1861 until the end of World War II, king of Croatia and King of Armenia...
received Sicily
Sicily
Sicily is a region of Italy, and is the largest island in the Mediterranean Sea. Along with the surrounding minor islands, it constitutes an autonomous region of Italy, the Regione Autonoma Siciliana Sicily has a rich and unique culture, especially with regard to the arts, music, literature,...
and parts of the Duchy of Milan
Duchy of Milan
The Duchy of Milan , was created on the 1st of may 1395, when Gian Galeazzo Visconti, Lord of Milan, purchased a diploma for 100,000 Florins from King Wenceslaus. It was this diploma that installed, Gian Galeazzo as Duke of Milan and Count of Pavia...
, while Charles VI
Charles VI, Holy Roman Emperor
Charles VI was the penultimate Habsburg sovereign of the Habsburg Empire. He succeeded his elder brother, Joseph I, as Holy Roman Emperor, King of Bohemia , Hungary and Croatia , Archduke of Austria, etc., in 1711...
(the Holy Roman Emperor
Holy Roman Emperor
The Holy Roman Emperor is a term used by historians to denote a medieval ruler who, as German King, had also received the title of "Emperor of the Romans" from the Pope...
and Archduke of Austria), received the Spanish Netherlands, the Kingdom of Naples
Kingdom of Naples
The Kingdom of Naples, comprising the southern part of the Italian peninsula, was the remainder of the old Kingdom of Sicily after secession of the island of Sicily as a result of the Sicilian Vespers rebellion of 1282. Known to contemporaries as the Kingdom of Sicily, it is dubbed Kingdom of...
, Sardinia
Sardinia
Sardinia is the second-largest island in the Mediterranean Sea . It is an autonomous region of Italy, and the nearest land masses are the French island of Corsica, the Italian Peninsula, Sicily, Tunisia and the Spanish Balearic Islands.The name Sardinia is from the pre-Roman noun *sard[],...
, and the bulk of the Duchy of Milan
Duchy of Milan
The Duchy of Milan , was created on the 1st of may 1395, when Gian Galeazzo Visconti, Lord of Milan, purchased a diploma for 100,000 Florins from King Wenceslaus. It was this diploma that installed, Gian Galeazzo as Duke of Milan and Count of Pavia...
.
During the War of the Quadruple Alliance
War of the Quadruple Alliance
The War of the Quadruple Alliance was a result of the ambitions of King Philip V of Spain, his wife, Elisabeth Farnese, and his chief minister Giulio Alberoni to retake territories in Italy and to claim the French throne. It saw the defeat of Spain by an alliance of Britain, France, Austria , and...
, Victor Amadeus II, duke of Savoy and sovereign of Piedmont, had to agree to yield Sicily to the Austrian Habsburgs and receive Sardinia in exchange. The exchange was formally ratified in the Treaty of The Hague
Treaty of The Hague (1720)
The Treaty of The Hague was signed on February 17, 1720. The treaty ended the War of the Quadruple Alliance, a conflict that arose between King Philip V of Spain and an alliance of Great Britain, France, Austria and the Dutch Republic.Philip was confirmed king of Spain by the Treaty of Utrecht in...
of February 17, 1720. Because a kingdom of Sardinia had existed since the 14th century, the exchange allowed Victor Amadeus to retain the title of king in spite of the loss of Sicily. Victor Amadeus initially resisted the exchange, and until 1723 continued to style himself King of Sicily rather than King of Sardinia.

Early history of Piedmont
Piedmont was inhabited in early historic times by Celtic-LigurianLigurian
Ligurian may mean:* Ligurian, pertaining to modern Liguria* Ligurian, pertaining to the ancient Ligures* Ligurian , a modern language spoken in parts of Italy, France, Monaco and Argentina...
tribes such as the Taurini
Taurini
The Taurini were an ancient Celto-Ligurian Alpine people, who occupied the upper valley of the river Po, in the centre of modern Piedmont.In 218 BC, they were attacked by Hannibal since his allies were the Insubres. The Taurini and the Insubres had a long-standing feud. Their chief town was...
and the Salassi
Salassi
The Salassi were an Alpine tribe whose lands lay on the Italian side of the Little St Bernard Pass across the Graian Alps to Lyons, and the Great St Bernard Pass over the Pennine Alps...
. They later submitted to the Romans
Ancient Rome
Ancient Rome was a thriving civilization that grew on the Italian Peninsula as early as the 8th century BC. Located along the Mediterranean Sea and centered on the city of Rome, it expanded to one of the largest empires in the ancient world....
(c. 220 BC
220 BC
Year 220 BC was a year of the pre-Julian Roman calendar. At the time it was known as the Year of the Consulship of Laevinus/Catulus and Scaevola/Philo...
), who founded several colonies there including Augusta Taurinorum (Turin) and Eporedia (Ivrea
Ivrea
Ivrea is a town and comune of the province of Turin in the Piedmont region of northwestern Italy. Situated on the road leading to the Aosta Valley , it straddles the Dora Baltea and is regarded as the centre of the Canavese area. Ivrea lies in a basin that, in prehistoric times, formed a great lake...
). After the fall of the Western Roman Empire
Western Roman Empire
The Western Roman Empire was the western half of the Roman Empire after its division by Diocletian in 285; the other half of the Roman Empire was the Eastern Roman Empire, commonly referred to today as the Byzantine Empire....
, the region was repeatedly invaded by the Burgundians
Burgundians
The Burgundians were an East Germanic tribe which may have emigrated from mainland Scandinavia to the island of Bornholm, whose old form in Old Norse still was Burgundarholmr , and from there to mainland Europe...
, the Goths
Goths
The Goths were an East Germanic tribe of Scandinavian origin whose two branches, the Visigoths and the Ostrogoths, played an important role in the fall of the Roman Empire and the emergence of Medieval Europe....
(5th century), Byzantines
Byzantine Empire
The Byzantine Empire was the Eastern Roman Empire during the periods of Late Antiquity and the Middle Ages, centred on the capital of Constantinople. Known simply as the Roman Empire or Romania to its inhabitants and neighbours, the Empire was the direct continuation of the Ancient Roman State...
, Lombards
Lombards
The Lombards , also referred to as Longobards, were a Germanic tribe of Scandinavian origin, who from 568 to 774 ruled a Kingdom in Italy...
(6th century), Franks
Franks
The Franks were a confederation of Germanic tribes first attested in the third century AD as living north and east of the Lower Rhine River. From the third to fifth centuries some Franks raided Roman territory while other Franks joined the Roman troops in Gaul. Only the Salian Franks formed a...
(773). In the 9th-10th centuries there were further incursions by the Magyars and Saracens. At the time Piedmont, as part of the Kingdom of Italy
Kingdom of Italy (1861–1946)
The Kingdom of Italy was a state forged in 1861 by the unification of Italy under the influence of the Kingdom of Sardinia, which was its legal predecessor state...
within the Holy Roman Empire
Holy Roman Empire
The Holy Roman Empire was a realm that existed from 962 to 1806 in Central Europe.It was ruled by the Holy Roman Emperor. Its character changed during the Middle Ages and the Early Modern period, when the power of the emperor gradually weakened in favour of the princes...
, was subdivided into several marks and counties.
In 1046, Oddo of Savoy added Piedmont to their main segment of Savoy
Savoy
Savoy is a region of France. It comprises roughly the territory of the Western Alps situated between Lake Geneva in the north and Monaco and the Mediterranean coast in the south....
, with a capital at Chambéry
Chambéry
Chambéry is a city in the department of Savoie, located in the Rhône-Alpes region in southeastern France.It is the capital of the department and has been the historical capital of the Savoy region since the 13th century, when Amadeus V of Savoy made the city his seat of power.-Geography:Chambéry...
(now in France
France
The French Republic , The French Republic , The French Republic , (commonly known as France , is a unitary semi-presidential republic in Western Europe with several overseas territories and islands located on other continents and in the Indian, Pacific, and Atlantic oceans. Metropolitan France...
). Other areas remained independent, such as the powerful communes of Asti
Asti
Asti is a city and comune of about 75,000 inhabitants located in the Piedmont region of northwestern Italy, about 55 kilometres east of Turin in the plain of the Tanaro River...
and Alessandria
Alessandria
-Monuments:* The Citadel * The church of Santa Maria di Castello * The church of Santa Maria del Carmine * Palazzo Ghilini * Università del Piemonte Orientale-Museums:* The Marengo Battle Museum...
and the marquisates of Saluzzo
Marquisate of Saluzzo
The Marquisate of Saluzzo was an historical Italian state that included French and Piedmont territories on the Alps.-Marquisate territories:The Marquisate of Saluzzo occupied parts of the provinces of Cuneo and Turin, and at times areas now under French control. However, Saluzzo was historically...
and Montferrat. The County of Savoy was elevated to a duke in 1416, and Duke Emanuele Filiberto moved the seat to Turin
Turin
Turin is a city and major business and cultural centre in northern Italy, capital of the Piedmont region, located mainly on the left bank of the Po River and surrounded by the Alpine arch. The population of the city proper is 909,193 while the population of the urban area is estimated by Eurostat...
in 1563.

Napoleonic Wars and the Congress of Vienna
In 1792 Piedmont-Sardinia joined the First CoalitionFirst Coalition
The War of the First Coalition was the first major effort of multiple European monarchies to contain Revolutionary France. France declared war on the Habsburg monarchy of Austria on 20 April 1792, and the Kingdom of Prussia joined the Austrian side a few weeks later.These powers initiated a series...
against the French First Republic
French First Republic
The French First Republic was founded on 22 September 1792, by the newly established National Convention. The First Republic lasted until the declaration of the First French Empire in 1804 under Napoleon I...
, but was beaten in 1796 by Napoleon and forced to conclude the disadvantageous Treaty of Paris (1796)
Treaty of Paris (1796)
The Treaty of Paris of May 15, 1796 was a treaty between the French Republic and the Kingdom of Piedmont-Sardinia during the War of the First Coalition....
, giving the French army free passage through Piedmont. On December 6, 1798 Joubert
Barthélemy Catherine Joubert
Barthélemy Catherine Joubert was a French general. He joined the royal French army in 1784 and rose rapidly in rank during the French Revolutionary Wars. Napoleon Bonaparte recognized his talents and gave him increased responsibilities...
occupied Turin and forced Charles Emmanuel IV
Charles Emmanuel IV of Sardinia
Charles Emmanuel IV was King of Sardinia from 1796 to 1802. He abdicated in favour of his brother Victor Emmanuel I...
to abdicate and leave for the island of Sardinia. The provisionary government voted to unite Piedmont with France. In 1799 the Austro-Russians briefly occupied the city, but with the Battle of Marengo (1800), the French regained control. The island of Sardinia stayed out of the reach of the French for the rest of the war.
In 1814 the kingdom was restored and enlarged with the addition of the former Republic of Genoa
Republic of Genoa
The Most Serene Republic of Genoa |Ligurian]]: Repúbrica de Zêna) was an independent state from 1005 to 1797 in Liguria on the northwestern Italian coast, as well as Corsica from 1347 to 1768, and numerous other territories throughout the Mediterranean....
, now a duchy, and it served as a buffer state
Buffer state
A buffer state is a country lying between two rival or potentially hostile greater powers, which by its sheer existence is thought to prevent conflict between them. Buffer states, when authentically independent, typically pursue a neutralist foreign policy, which distinguishes them from satellite...
against France
France
The French Republic , The French Republic , The French Republic , (commonly known as France , is a unitary semi-presidential republic in Western Europe with several overseas territories and islands located on other continents and in the Indian, Pacific, and Atlantic oceans. Metropolitan France...
. This was confirmed by the Congress of Vienna
Congress of Vienna
The Congress of Vienna was a conference of ambassadors of European states chaired by Klemens Wenzel von Metternich, and held in Vienna from September, 1814 to June, 1815. The objective of the Congress was to settle the many issues arising from the French Revolutionary Wars, the Napoleonic Wars,...
.
In the reaction after Napoleon, the country was ruled by conservative monarchs: Victor Emmanuel I
Victor Emmanuel I of Sardinia
Victor Emmanuel I was the Duke of Savoy and King of Sardinia from 1802 to 1821, and Jacobite Pretender from 1819 until his death.-Biography:...
(1802–21), Charles Felix
Charles Felix of Sardinia
Charles Felix was the Duke of Savoy, Piedmont, Aosta and King of Sardinia from 1821 to 1831.-Early life:...
(1821–31) and Charles Albert (1831–49), who fought at the head of a contingent of his own troops at the Battle of Trocadero
Battle of Trocadero
The Battle of Trocadero, fought on 31 August 1823, was the only significant battle in the French invasion of Spain when French forces defeated the Spanish liberal forces and restored the absolute rule of King Ferdinand VII.-Prelude:...
, which set the reactionary Ferdinand VII on the Spanish throne. Victor Emanuel I disbanded the entire Code Napoléon and returned the lands and power to the nobility and the Church. This reactionary policy went as far as discouraging the use of roads built by the French. These changes typified Piedmont.
The Kingdom of Sardinia industrialized from 1830 onward. A constitution, the Statuto Albertino
Statuto Albertino
The Statuto Albertino or Albertine Statute was the constitution that King Charles Albert conceded to the Kingdom of Piedmont-Sardinia in Italy on 4 March 1848...
, was enacted in the year of revolutions, 1848
Revolutions of 1848
The European Revolutions of 1848, known in some countries as the Spring of Nations, Springtime of the Peoples or the Year of Revolution, were a series of political upheavals throughout Europe in 1848. It was the first Europe-wide collapse of traditional authority, but within a year reactionary...
, under liberal pressure, and under the same pressure Charles Albert declared war on Austria. After initial success the war took a turn for the worse and Charles Albert was defeated by Marshal Radetzky at Custozza.

Risorgimento
Like all of Italy, the Kingdom of Sardinia was troubled with political instability, under alternating governments. After a very short and disastrous renewal of the war with Austria in 1849, Charles Albert abdicated on March 23, 1849, in favour of his son Victor Emmanuel IIVictor Emmanuel II of Italy
Victor Emanuel II was king of Sardinia from 1849 and, on 17 March 1861, he assumed the title King of Italy to become the first king of a united Italy since the 6th century, a title he held until his death in 1878...
.
In 1852 a liberal ministry under Count Camillo Benso di Cavour was installed, and the Kingdom of Sardinia became the engine driving the Italian Unification
Italian unification
Italian unification was the political and social movement that agglomerated different states of the Italian peninsula into the single state of Italy in the 19th century...
. The Kingdom of Sardinia (Piedmont) took part in the Crimean War
Crimean War
The Crimean War was a conflict fought between the Russian Empire and an alliance of the French Empire, the British Empire, the Ottoman Empire, and the Kingdom of Sardinia. The war was part of a long-running contest between the major European powers for influence over territories of the declining...
, allied with the Ottoman Empire
Ottoman Empire
The Ottoman EmpireIt was usually referred to as the "Ottoman Empire", the "Turkish Empire", the "Ottoman Caliphate" or more commonly "Turkey" by its contemporaries...
, Britain
United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland
The United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland was the formal name of the United Kingdom during the period when what is now the Republic of Ireland formed a part of it....
, and France
France
The French Republic , The French Republic , The French Republic , (commonly known as France , is a unitary semi-presidential republic in Western Europe with several overseas territories and islands located on other continents and in the Indian, Pacific, and Atlantic oceans. Metropolitan France...
, and fighting against Russia
Russia
Russia or , officially known as both Russia and the Russian Federation , is a country in northern Eurasia. It is a federal semi-presidential republic, comprising 83 federal subjects...
.
In 1859 France sided with the Kingdom of Sardinia in a war against Austria
Austrian Empire
The Austrian Empire was a modern era successor empire, which was centered on what is today's Austria and which officially lasted from 1804 to 1867. It was followed by the Empire of Austria-Hungary, whose proclamation was a diplomatic move that elevated Hungary's status within the Austrian Empire...
, the Austro-Sardinian War. Napoleon III didn't keep his promises to Cavour to fight until all of the Kingdom of Lombardy-Venetia had been conquered. Following the bloody battles of Magenta
Battle of Magenta
The Battle of Magenta was fought on June 4, 1859 during the Second Italian War of Independence, resulting in a French-Sardinian victory under Napoleon III against the Austrians under Marshal Ferencz Gyulai....
and Solferino
Battle of Solferino
The Battle of Solferino, , was fought on June 24, 1859 and resulted in the victory of the allied French Army under Napoleon III and Sardinian Army under Victor Emmanuel II against the Austrian Army under Emperor Franz Joseph I; it was the last major battle in world...
, both French victories, Napoleon thought the war too costly to continue and made a separate peace behind Cavour's back in which only Lombardy would be ceded. Due to the Austrian government's refusal to cede any lands to the Kingdom of Sardinia, they agreed to cede Lombardy
Lombardy
Lombardy is one of the 20 regions of Italy. The capital is Milan. One-sixth of Italy's population lives in Lombardy and about one fifth of Italy's GDP is produced in this region, making it the most populous and richest region in the country and one of the richest in the whole of Europe...
to Napoleon who in turn then ceded the territory to the Kingdom of Sardinia to avoid 'embarrassing' the defeated Austrians. Cavour angrily resigned from office when it became clear that Victor Emmanuel would accept the deal.

Garibaldi and the Thousand
On March 5, 1860 ParmaParma
Parma is a city in the Italian region of Emilia-Romagna famous for its ham, its cheese, its architecture and the fine countryside around it. This is the home of the University of Parma, one of the oldest universities in the world....
, Tuscany
Tuscany
Tuscany is a region in Italy. It has an area of about 23,000 square kilometres and a population of about 3.75 million inhabitants. The regional capital is Florence ....
, Modena
Modena
Modena is a city and comune on the south side of the Po Valley, in the Province of Modena in the Emilia-Romagna region of Italy....
, and Romagna
Romagna
Romagna is an Italian historical region that approximately corresponds to the south-eastern portion of present-day Emilia-Romagna. Traditionally, it is limited by the Apennines to the south-west, the Adriatic to the east, and the rivers Reno and Sillaro to the north and west...
voted in referendum
Referendum
A referendum is a direct vote in which an entire electorate is asked to either accept or reject a particular proposal. This may result in the adoption of a new constitution, a constitutional amendment, a law, the recall of an elected official or simply a specific government policy. It is a form of...
s to join the Kingdom of Sardinia. This alarmed Napoleon who feared a strong Savoyard state on his southeastern border and he insisted that if the Kingdom of Sardinia were to keep the new acquisitions they would have to cede Savoy and Nice to France. This was done after dubious referendums showed over 99.5% majorities in both areas in favour of joining France.
In 1860 Giuseppe Garibaldi
Giuseppe Garibaldi
Giuseppe Garibaldi was an Italian military and political figure. In his twenties, he joined the Carbonari Italian patriot revolutionaries, and fled Italy after a failed insurrection. Garibaldi took part in the War of the Farrapos and the Uruguayan Civil War leading the Italian Legion, and...
started his campaign to conquer southern Italy in the name of the Kingdom of Sardinia. He quickly toppled the Kingdom of the Two Sicilies
Kingdom of the Two Sicilies
The Kingdom of the Two Sicilies, commonly known as the Two Sicilies even before formally coming into being, was the largest and wealthiest of the Italian states before Italian unification...
and marched to Gaeta
Gaeta
Gaeta is a city and comune in the province of Latina, in Lazio, central Italy. Set on a promontory stretching towards the Gulf of Gaeta, it is 120 km from Rome and 80 km from Naples....
. Cavour was actually the most satisfied with the unification while Garibaldi wanted to conquer Rome. Garibaldi was too revolutionary for the king and his prime minister.
Towards Kingdom of Italy
On March 17, 1861 the Kingdom of Italy was proclaimed by the Parliament, so ratifying the annexationAnnexation
Annexation is the de jure incorporation of some territory into another geo-political entity . Usually, it is implied that the territory and population being annexed is the smaller, more peripheral, and weaker of the two merging entities, barring physical size...
s of all other Italian states to Piedmont. The institutions and laws of the Kingdom were quickly extended to all Italy, brutally abolishing the administrations of the other regions. Piedmont would become the most dominant and wealthiest region in Italy and the capital of Piedmont, Turin, would remain the Italian capital until 1865 when the capital was moved to Florence
Florence
Florence is the capital city of the Italian region of Tuscany and of the province of Florence. It is the most populous city in Tuscany, with approximately 370,000 inhabitants, expanding to over 1.5 million in the metropolitan area....
; but in contrast, many revolts exploded through the peninsula, especially in Southern Italy
Brigandage in the Two Sicilies
Brigandage in the Two Sicilies had existed in some form since ancient times, however its origins as outlaws targeting random travellers would evolve vastly later on in the form of the political resistance movement form of brigandage in the Two Sicilies...
. The House of Savoy
House of Savoy
The House of Savoy was formed in the early 11th century in the historical Savoy region. Through gradual expansion, it grew from ruling a small county in that region to eventually rule the Kingdom of Italy from 1861 until the end of World War II, king of Croatia and King of Armenia...
would rule Italy until 1946 when Italy was declared a republic
Italy
Italy , officially the Italian Republic languages]] under the European Charter for Regional or Minority Languages. In each of these, Italy's official name is as follows:;;;;;;;;), is a unitary parliamentary republic in South-Central Europe. To the north it borders France, Switzerland, Austria and...
.
Kings of Sardinia (1297–1861)



- James II of AragonJames II of AragonJames II , called the Just was the King of Sicily from 1285 to 1296 and King of Aragon and Valencia and Count of Barcelona from 1291 to 1327. In 1297 he was granted the Kingdom of Sardinia and Corsica...
(1324–1327) - Alfonso IV of AragonAlfonso IV of AragonAlfonso IV, called the Kind was the King of Aragon and Count of Barcelona from 1327 to his death. He was the second son of James II and Blanche of Anjou...
(1327–1336) - Peter IV of AragonPeter IV of AragonPeter IV, , called el Cerimoniós or el del punyalet , was the King of Aragon, King of Sardinia and Corsica , King of Valencia , and Count of Barcelona Peter IV, (Balaguer, September 5, 1319 – Barcelona, January 6, 1387), called el Cerimoniós ("the Ceremonious") or el del punyalet ("the one...
(1336–1387) - John I of AragonJohn I of AragonJohn I , called by posterity the Hunter or the Lover of Elegance , but the Abandoned in his lifetime, was the King of...
(1387–1396) - Martin of Aragon (1396–1410)
Dynasty of the Trastámara of Castile
Castile (historical region)
A former kingdom, Castile gradually merged with its neighbours to become the Crown of Castile and later the Kingdom of Spain when united with the Crown of Aragon and the Kingdom of Navarre...
:
- Ferdinand I of AragonFerdinand I of AragonFerdinand I called of Antequera and also the Just or the Honest) was king of Aragon, Valencia, Majorca, Sardinia and Corsica and king of Sicily, duke of Athens and Neopatria, and count of Barcelona, Roussillon and Cerdanya...
(1412–1416) - Alfonso I of Aragon (1416–1458)
- John II of AragonJohn II of AragonJohn II the Faithless, also known as the Great was the King of Aragon from 1458 until 1479, and jure uxoris King of Navarre from 1425 until his death. He was the son of Ferdinand I and his wife Eleanor of Alburquerque...
(1458–1479) - Ferdinand II of AragonFerdinand II of AragonFerdinand the Catholic was King of Aragon , Sicily , Naples , Valencia, Sardinia, and Navarre, Count of Barcelona, jure uxoris King of Castile and then regent of that country also from 1508 to his death, in the name of...
(1479–1516)
Dynasty of the Habsburgs of Spain
Spanish Empire
The Spanish Empire comprised territories and colonies administered directly by Spain in Europe, in America, Africa, Asia and Oceania. It originated during the Age of Exploration and was therefore one of the first global empires. At the time of Habsburgs, Spain reached the peak of its world power....
:
- Charles V, Holy Roman EmperorCharles V, Holy Roman EmperorCharles V was ruler of the Holy Roman Empire from 1519 and, as Charles I, of the Spanish Empire from 1516 until his voluntary retirement and abdication in favor of his younger brother Ferdinand I and his son Philip II in 1556.As...
(1516–1556) - Philip II of SpainPhilip II of SpainPhilip II was King of Spain, Portugal, Naples, Sicily, and, while married to Mary I, King of England and Ireland. He was lord of the Seventeen Provinces from 1556 until 1581, holding various titles for the individual territories such as duke or count....
(1556–1598) - Philip III of SpainPhilip III of SpainPhilip III , also known as Philip the Pious, was the King of Spain and King of Portugal and the Algarves, where he ruled as Philip II , from 1598 until his death...
(1598–1621) - Philip IV of SpainPhilip IV of SpainPhilip IV was King of Spain between 1621 and 1665, sovereign of the Spanish Netherlands, and King of Portugal until 1640...
(1621–1665) - Charles II of SpainCharles II of SpainCharles II was the last Habsburg King of Spain and the ruler of large parts of Italy, the Spanish territories in the Southern Low Countries, and Spain's overseas Empire, stretching from the Americas to the Spanish East Indies...
(1665–1700)
Dynasty of the Bourbons
House of Bourbon
The House of Bourbon is a European royal house, a branch of the Capetian dynasty . Bourbon kings first ruled Navarre and France in the 16th century. By the 18th century, members of the Bourbon dynasty also held thrones in Spain, Naples, Sicily, and Parma...
of Spain:
- Philip V of SpainPhilip V of SpainPhilip V was King of Spain from 15 November 1700 to 15 January 1724, when he abdicated in favor of his son Louis, and from 6 September 1724, when he assumed the throne again upon his son's death, to his death.Before his reign, Philip occupied an exalted place in the royal family of France as a...
(1700–1713)
Dynasty of the Habsburgs of Spain
- Charles VI, Holy Roman EmperorCharles VI, Holy Roman EmperorCharles VI was the penultimate Habsburg sovereign of the Habsburg Empire. He succeeded his elder brother, Joseph I, as Holy Roman Emperor, King of Bohemia , Hungary and Croatia , Archduke of Austria, etc., in 1711...
(1713–1720)
Dynasty of Savoy
House of Savoy
The House of Savoy was formed in the early 11th century in the historical Savoy region. Through gradual expansion, it grew from ruling a small county in that region to eventually rule the Kingdom of Italy from 1861 until the end of World War II, king of Croatia and King of Armenia...
:
- Victor Amadeus II of SardiniaVictor Amadeus II of SardiniaVictor Amadeus II was Duke of Savoy from 1675 to 1730. He also held the titles of marquis of Saluzzo, duke of Montferrat, prince of Piedmont, count of Aosta, Moriana and Nizza. Louis XIV organised his marriage in order to maintain French influence in the Duchy but Victor Amadeus soon broke away...
(1720–1730) - Charles Emmanuel III of SardiniaCharles Emmanuel III of SardiniaCharles Emmanuel III was the Duke of Savoy and King of Sardinia from 1730 until his death.-Biography:...
(1730–1773) - Victor Amadeus III of SardiniaVictor Amadeus III of SardiniaVictor Amadeus III was King of Sardinia from 1773 until his death. Although he was politically conservative, he carried out numerous administrative reforms until declaring war on revolutionary France in 1792...
(1773–1796) - Charles Emmanuel IV of SardiniaCharles Emmanuel IV of SardiniaCharles Emmanuel IV was King of Sardinia from 1796 to 1802. He abdicated in favour of his brother Victor Emmanuel I...
(1796–1802) - Victor Emmanuel I of SardiniaVictor Emmanuel I of SardiniaVictor Emmanuel I was the Duke of Savoy and King of Sardinia from 1802 to 1821, and Jacobite Pretender from 1819 until his death.-Biography:...
(1802–1821) - Charles Felix of SardiniaCharles Felix of SardiniaCharles Felix was the Duke of Savoy, Piedmont, Aosta and King of Sardinia from 1821 to 1831.-Early life:...
(1821–1831) - Charles Albert of SardiniaCharles Albert of SardiniaCharles Albert was the King of Piedmont-Sardinia from 1831 to 1849. He succeeded his distant cousin Charles Felix, and his name is bound with the first Italian statute and the First War of Independence...
(1831–1849) - Victor Emmanuel II of Sardinia (1849–1861)
Flags
When the Duchy of SavoyDuchy of Savoy
From 1416 to 1847, the House of Savoy ruled the eponymous Duchy of Savoy . The Duchy was a state in the northern part of the Italian Peninsula, with some territories that are now in France. It was a continuation of the County of Savoy...
was add into Kingdom of Sicily in 1713 and Kingdom of Sardinia in 1723, it maintained its traditional flag depicting a white cross on a red field. But a problem arose: if the Duchy owned the small harbour of Nice
Nice
Nice is the fifth most populous city in France, after Paris, Marseille, Lyon and Toulouse, with a population of 348,721 within its administrative limits on a land area of . The urban area of Nice extends beyond the administrative city limits with a population of more than 955,000 on an area of...
only, the union with Sicily and then Sardinia gave to the Kingdom a quite big fleet, which had the same flag of Malta
Malta
Malta , officially known as the Republic of Malta , is a Southern European country consisting of an archipelago situated in the centre of the Mediterranean, south of Sicily, east of Tunisia and north of Libya, with Gibraltar to the west and Alexandria to the east.Malta covers just over in...
. To disambiguate the ships of the two different States, the House of Savoy added a blue border to its flag, and then it reduced the cross in a single quarter.
The flag had following minor changes until 1848, when a revolution happened: to follow the liberal revolutions which were exploding in all Europe, King Charles Albert adopted the Napoleonic Italian tricolour, surmonted by the Savoyard shield, as national flag. This flag became the flag of Italy until 1946.

