
Karl Friedrich Mohr
Encyclopedia

Germany
Germany , officially the Federal Republic of Germany , is a federal parliamentary republic in Europe. The country consists of 16 states while the capital and largest city is Berlin. Germany covers an area of 357,021 km2 and has a largely temperate seasonal climate...
chemist
Chemist
A chemist is a scientist trained in the study of chemistry. Chemists study the composition of matter and its properties such as density and acidity. Chemists carefully describe the properties they study in terms of quantities, with detail on the level of molecules and their component atoms...
famous for his early statement of the principle of the conservation of energy
Conservation of energy
The nineteenth century law of conservation of energy is a law of physics. It states that the total amount of energy in an isolated system remains constant over time. The total energy is said to be conserved over time...
. Ammonium iron(II) sulfate
Mohr's salt
Ammonium iron sulfate, or Mohr's Salt, is the inorganic compound with the formula 2Fe2·6H2O. Containing two different cations, Fe2+ and NH4+, it is classified as a double salt of ferrous sulfate and ammonium sulfate. It is a common laboratory reagent...
, (NH4)2Fe(SO4)2.6H2O, is named Mohr's salt
Mohr's salt
Ammonium iron sulfate, or Mohr's Salt, is the inorganic compound with the formula 2Fe2·6H2O. Containing two different cations, Fe2+ and NH4+, it is classified as a double salt of ferrous sulfate and ammonium sulfate. It is a common laboratory reagent...
after him.
Life
Mohr was born in 1806 into the family of a prosperous druggist in KoblenzKoblenz
Koblenz is a German city situated on both banks of the Rhine at its confluence with the Moselle, where the Deutsches Eck and its monument are situated.As Koblenz was one of the military posts established by Drusus about 8 BC, the...
. Being a delicate child, the young Mohr received much of his early education at home, a great part of it in his father's laboratory. This experience may be responsible for much of the skill Mohr later showed in devising instruments and methods of chemical analysis. At the age of twenty-one he began to study chemistry under Leopold Gmelin
Leopold Gmelin
Leopold Gmelin was a German chemist.Gmelin was the son of Johann Friedrich Gmelin. He studied medicine and chemistry at Göttingen, Tübingen and Vienna, and in 1813 began to lecture on chemistry at Heidelberg, where in 1814 he was appointed extraordinary-, and in 1817 ordinary-, professor of...
, and, after five years in Heidelberg
Heidelberg
-Early history:Between 600,000 and 200,000 years ago, "Heidelberg Man" died at nearby Mauer. His jaw bone was discovered in 1907; with scientific dating, his remains were determined to be the earliest evidence of human life in Europe. In the 5th century BC, a Celtic fortress of refuge and place of...
, Berlin
Berlin
Berlin is the capital city of Germany and is one of the 16 states of Germany. With a population of 3.45 million people, Berlin is Germany's largest city. It is the second most populous city proper and the seventh most populous urban area in the European Union...
and Bonn
Bonn
Bonn is the 19th largest city in Germany. Located in the Cologne/Bonn Region, about 25 kilometres south of Cologne on the river Rhine in the State of North Rhine-Westphalia, it was the capital of West Germany from 1949 to 1990 and the official seat of government of united Germany from 1990 to 1999....
, he returned with the degree of Ph.D.
Ph.D.
A Ph.D. is a Doctor of Philosophy, an academic degree.Ph.D. may also refer to:* Ph.D. , a 1980s British group*Piled Higher and Deeper, a web comic strip*PhD: Phantasy Degree, a Korean comic series* PhD Docbook renderer, an XML renderer...
to join his father's establishment.
Mohr's father died during 1840 at which time Mohr assumed control of the family business. He retired from it for a life of scientific leisure in 1857, but at the age of fifty-seven some serious financial losses caused him to become a privatdozent
Privatdozent
Privatdozent or Private lecturer is a title conferred in some European university systems, especially in German-speaking countries, for someone who pursues an academic career and holds all formal qualifications to become a tenured university professor...
in Bonn. In 1867 he was appointed, by the direct influence of the government, extraordinary professor of pharmacy
Pharmacy
Pharmacy is the health profession that links the health sciences with the chemical sciences and it is charged with ensuring the safe and effective use of pharmaceutical drugs...
.
Work
Germany
Germany , officially the Federal Republic of Germany , is a federal parliamentary republic in Europe. The country consists of 16 states while the capital and largest city is Berlin. Germany covers an area of 357,021 km2 and has a largely temperate seasonal climate...
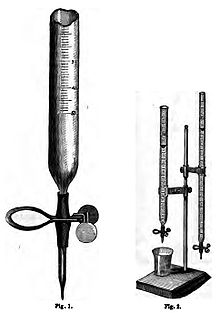
, and the inventor of many improvements in analytical methodology. He invented an improved burette
Burette
A burette is a vertical cylindrical piece of laboratory glassware with a volumetric graduation on its full length and a precision tap, or stopcock, on the bottom. It is used to dispense known amounts of a liquid reagent in experiments for which such precision is necessary, such as a titration...
which had a tip at the bottom and a clamp, which made it much easier to use than its predecessors, which were more similar to a graduated cylinder. His methods of volumetric analysis were expounded in his Lehrbuch der chemisch-analytischen Titrir-methode (1855) (Instructional Book of Titration Methods in Analytical Chemistry), which won special commendation from Liebig and ran to many editions. His Geschichie der Erde, eine Geologic auf neuer Grundlage (1866), was also widely circulated.
In a paper Über die Natur der Wärme (1837), Mohr gave one of the earliest general statements of the doctrine of the conservation of energy
Conservation of energy
The nineteenth century law of conservation of energy is a law of physics. It states that the total amount of energy in an isolated system remains constant over time. The total energy is said to be conserved over time...
:
- "besides the 54 known chemical elements there is in the physical world one agent only, and this is called Kraft (energy). It may appear, according to circumstances, as motion, chemical affinity, cohesion, electricity, light and magnetism; and from any one of these forms it can be transformed into any of the others."
Further reading
- Mohr, K. F. (1837) "Ansichten über die Natur der Wärme." Ann. der Pharm., 24, pp. 141–147.
- Mohr, K. F. (1876) (trans. P. G. TaitPeter Guthrie TaitPeter Guthrie Tait FRSE was a Scottish mathematical physicist, best known for the seminal energy physics textbook Treatise on Natural Philosophy, which he co-wrote with Kelvin, and his early investigations into knot theory, which contributed to the eventual formation of topology as a mathematical...
) "Views of the nature of heat." Philosophical MagazinePhilosophical MagazineThe Philosophical Magazine is one of the oldest scientific journals published in English. Initiated by Alexander Tilloch in 1798, in 1822 Richard Taylor became joint editor and it has been published continuously by Taylor & Francis ever since; it was the journal of choice for such luminaries as...
2 110-14. - See also this site for a different photograph of Mohr

