Juno clump
Encyclopedia
The Juno clump is a probable asteroid family
in the vicinity of 3 Juno
.
 3 Juno
3 Juno
is a large asteroid with a mean diameter of about 235 km, but the remaining bodies are all small. , the brightest of those clearly in the visible clump would have a diameter of about 6 km, given the same albedo as 3 Juno
. This indicates that it is probably a so-called cratering family composed of ejecta from impacts on 3 Juno.
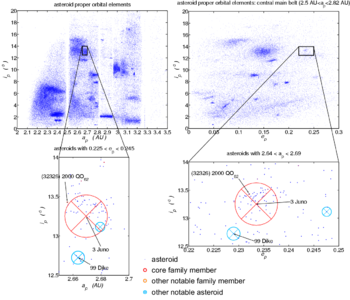
The HCM analysis by (Zappalà 1995) determined several likely core members, whose proper elements lie in the approximate ranges
! !! ap
!! ep !! ip
>
min
2.64 AU
0.226
13.3°
max
2.68 AU
0.240
13.9°
At the present epoch
, the range of osculating
orbital elements
of these core members is
Asteroid family
An asteroid family is a population of asteroids that share similar proper orbital elements, such as semimajor axis, eccentricity, and orbital inclination. The members of the families are thought to be fragments of past asteroid collisions...
in the vicinity of 3 Juno
3 Juno
Juno , formal designation 3 Juno in the Minor Planet Center catalogue system, was the third asteroid to be discovered and is one of the larger main-belt asteroids, being one of the two largest stony asteroids, along with 15 Eunomia. Juno is estimated to contain 1% of the total mass of the asteroid...
.

3 Juno
Juno , formal designation 3 Juno in the Minor Planet Center catalogue system, was the third asteroid to be discovered and is one of the larger main-belt asteroids, being one of the two largest stony asteroids, along with 15 Eunomia. Juno is estimated to contain 1% of the total mass of the asteroid...
is a large asteroid with a mean diameter of about 235 km, but the remaining bodies are all small. , the brightest of those clearly in the visible clump would have a diameter of about 6 km, given the same albedo as 3 Juno
3 Juno
Juno , formal designation 3 Juno in the Minor Planet Center catalogue system, was the third asteroid to be discovered and is one of the larger main-belt asteroids, being one of the two largest stony asteroids, along with 15 Eunomia. Juno is estimated to contain 1% of the total mass of the asteroid...
. This indicates that it is probably a so-called cratering family composed of ejecta from impacts on 3 Juno.
The HCM analysis by (Zappalà 1995) determined several likely core members, whose proper elements lie in the approximate ranges
Semi-major axis
The major axis of an ellipse is its longest diameter, a line that runs through the centre and both foci, its ends being at the widest points of the shape...
!! ep !! ip
Inclination
Inclination in general is the angle between a reference plane and another plane or axis of direction.-Orbits:The inclination is one of the six orbital parameters describing the shape and orientation of a celestial orbit...
>
Astronomical unit
An astronomical unit is a unit of length equal to about or approximately the mean Earth–Sun distance....
At the present epoch
Epoch (astronomy)
In astronomy, an epoch is a moment in time used as a reference point for some time-varying astronomical quantity, such as celestial coordinates, or elliptical orbital elements of a celestial body, where these are subject to perturbations and vary with time...
, the range of osculating
Osculating orbit
In astronomy, and in particular in astrodynamics, the osculating orbit of an object in space is the gravitational Kepler orbit In astronomy, and in particular in astrodynamics, the osculating orbit of an object in space (at a given moment of time) is the gravitational Kepler orbit In astronomy,...
orbital elements
Orbital elements
Orbital elements are the parameters required to uniquely identify a specific orbit. In celestial mechanics these elements are generally considered in classical two-body systems, where a Kepler orbit is used...
of these core members is
| a Semi-major axis The major axis of an ellipse is its longest diameter, a line that runs through the centre and both foci, its ends being at the widest points of the shape... | e | i Inclination Inclination in general is the angle between a reference plane and another plane or axis of direction.-Orbits:The inclination is one of the six orbital parameters describing the shape and orientation of a celestial orbit... |
|
|---|---|---|---|
| min | 2.64 AU Astronomical unit An astronomical unit is a unit of length equal to about or approximately the mean Earth–Sun distance.... |
0.238 | 11.8° |
| max | 2.68 AU | 0.274 | 14.6° |

