.gif)
John Dickinson (delegate)
Encyclopedia
John Dickinson was an American lawyer and politician from Philadelphia, Pennsylvania
and Wilmington, Delaware
. He was a militia officer during the American Revolution
, a Continental Congressman from Pennsylvania and Delaware, a delegate to the U.S. Constitutional Convention of 1787, President of Delaware and President of Pennsylvania. Among the wealthiest men in the British American colonies, he is known as the "Penman of the Revolution" for his Letters from a Farmer in Pennsylvania
; upon receiving news of his death, President Thomas Jefferson
recognized him as being "among the first of the advocates for the rights of his country when assailed by Great Britain" whose "name will be consecrated in history as one of the great worthies of the revolution." He is the namesake of Dickinson College
and Penn State University's Dickinson School of Law
.
. He was the great grandson of Walter Dickinson who emigrated from England to Virginia in 1654 and, having joined the Society of Friends
, came with several co-religionists to Talbot County on the Eastern Shore of the Chesapeake Bay
in 1659. There, with 400 acres (1.6 km²) on the banks of the Choptank River
Walter began a plantation, Croisadore, meaning "cross of gold." Walter also bought 800 acres (3.2 km²) on St. Jones Neck in what became Kent County, Delaware
.
Croisadore passed through Walter's son, William, to his grandson, Samuel, the father of John Dickinson. Each generation increased the landholdings, so that Samuel inherited 2500 acres (1,011.7 ha) on five farms in three Maryland counties and over his lifetime increased that to 9000 acres (3,642.2 ha). He also bought the Kent County
property from his cousin and expanded it to about 3000 acres (1,214.1 ha), stretching along the St. Jones River
from Dover to the Delaware Bay
. There he began another plantation and called it “Poplar Hall
.” These plantations were large, profitable agricultural enterprises worked by slave labor, until 1777 when John Dickinson freed the enslaved of Poplar Hall.
Samuel Dickinson first married Judith Troth on 11 April 1710. They had nine children; William, Walter, Samuel, Elizabeth, Henry, Elizabeth "Betsy," Rebecca and Rachel. The three eldest sons died of smallpox while in London seeking their education. Widowed, with two young children, Henry and Betsy, Samuel married Mary Cadwalader in 1731. She was the daughter of Martha Jones (Grand daughter of Dr. Thomas Wynne) and the prominent Quaker, John Cadwalader who was also grandfather of General John Cadwalader
of Philadelphia. Their sons, John, Thomas and Philemon
were born in the next few years.
For three generations the Dickinson family had been members of the Third Haven Friends Meeting in Talbot County and the Cadwaladers were members of the Meeting in Philadelphia. But in 1739, John Dickinson's half-sister, Betsy, was married in an Anglican church to Charles Goldsborough in what was called a "disorderly marriage" by the Meeting. The couple would be the grandparents of Maryland governor Charles Goldsborough
.
Leaving Croisadore to elder son Henry Dickinson, Samuel moved to Poplar Hall, where he had already taken a leading role in the community as Judge of the Court of Common Pleas of Kent County. The move also placed Mary nearer her Philadelphia relations.
Poplar Hall was situated on a now-straightened bend of the St. Jones River
. There was plenty of activity delivering the necessities, and shipping the agricultural products produced. Much of this product was wheat that along with other wheat from the region, was milled into a “superfine” flour. Most people at this plantation were servants and slaves of the Dickinsons.
, who later established New London Academy in Chester County, Pennsylvania
. Most important was William Killen, who became a life-long friend, and himself had a distinguished career as Delaware’s first Chief Justice and Chancellor. Dickinson was precocious and energetic, and in spite of his love of Poplar Hall and his family, was drawn to Philadelphia.
At 18 he began studying the law under John Moland
in Philadelphia. There he made friends with fellow students George Read
and Samuel Wharton
, among others. By 1753 John went to London for three years of study at the Middle Temple
. He spent those years studying the works of Edward Coke
and Francis Bacon
at the Inns of Court
following in the footsteps of his lifelong friend, Pennsylvania Attorney General Benjamin Chew
, and in 1757 was admitted to the Pennsylvania Bar beginning his career as barrister and solicitor.
On July 19, 1770, Dickinson married Mary Norris, known as Polly, the daughter of a wealthy Philadelphia Quaker, and Speaker of the Pennsylvania General Assembly, Isaac Norris
. They had five children, but only two survived to adulthood: Sarah Norris "Sally" Dickinson and Maria Mary Dickinson. Dickinson never formally joined the Quaker Meeting, because, as he explained, he believed in the "lawfulness of defensive war."
Already wealthy his marriage increased his wealth. In Philadelphia, he lived at the family estate of his wife, Fairhill, near Germantown
. Meanwhile he built an elegant mansion on Chestnut Street but never lived there as it was confiscated and turned into a hospital during his 1776-77 absence in Delaware. It then became the residence of the French ambassador and still later the home of his brother, Philemon Dickinson. Fairhill was burned by the British during the Battle of Germantown
. While in Philadelphia as State President, he lived at the confiscated mansion of Joseph Galloway
at Sixth and Market Streets, now established as the State Presidential mansion.
Dickinson lived at Poplar Hall, for extended periods only in 1776-77 and 1781-82. In August 1781 it was sacked by Loyalists
and was badly burned in 1804. This home is now owned by the State of Delaware and is open to the public. After his service as President of Pennsylvania, he returned to live in Wilmington, Delaware in 1785 and built a mansion at the northwest corner of 8th and Market Streets.
in 1774 and the Second Continental Congress
in 1775 and 1776. In support of the cause, he continued to contribute declarations in the name of the Congress. Among the most famous is one written with Thomas Jefferson
, a Declaration of the Causes and Necessity of Taking Up Arms
, with Dickinson’s conclusion that Americans were "resolved to die free men rather than live slaves." Another was the Olive Branch Petition
, a last ditch appeal to King George III to resolve the dispute. But through it all, agreeing with New Castle County
's George Read
and many others in Philadelphia and the Lower Counties
, Dickinson's object was reconciliation, not independence and revolution. He was a proud devotee of the British Constitution and felt the dispute was with Parliament only.
When the Continental Congress began the debate on the Declaration of Independence on July 1, 1776, Dickinson reiterated his opposition to declaring independence at that time. Dickinson believed that Congress should complete the Articles of Confederation
and secure a foreign alliance before issuing a declaration. He abstained or absented himself from the votes on July 2 that declared independence and absented himself again from voting on the wording of the formal Declaration on July 4. Dickinson understood the implications of his refusal to vote stating, "My conduct this day, I expect will give the finishing blow to my once too great and, my integrity considered, now too diminished popularity." Dickinson refused to sign the Declaration and since a proposal had been brought forth and carried that stated, "for our mutual security and protection," no man could remain in Congress without signing, Dickinson voluntarily left and joined the Pennsylvania militia.
Following the Declaration of Independence
Dickinson was given the rank of brigadier general in the Pennsylvania militia, known as the Associators. He led some 10,000 soldiers to Elizabeth, New Jersey
to protect that area against British attack from Staten Island
. But because of his unpopular opinion on independence two junior officers were promoted above him.
tried to appoint him as their delegate to the Continental Congress in 1777, but he refused. In August 1777 he served as a private with the Kent county Militia at Middletown
, Delaware under General Caesar Rodney
to help delay General William Howe
's march to Philadelphia. In October 1777, Dickinson's friend, Thomas McKean
, appointed him Brigadier General of the Delaware Militia, but again Dickinson declined the appointment. Shortly afterwards he learned that the British had burned down his Fairhill property during the Battle of Germantown.
These years were not without accomplishment however. In 1777, Dickinson, Delaware's wealthiest farmer and largest slaveholder, decided to free his slaves. While Kent County was not a large slave-holding area, like farther south in Virginia, and even though Dickinson had only 37 slaves, this was an action of some considerable courage. Undoubtedly the strongly abolitionist Quaker influences around them had their effect, and the action was all the easier because his farm had moved away from tobacco to the less labor intensive crops like wheat and barley. Furthermore manumission
was a multi-year process and many of the workers remained obligated to service for a considerable additional time.
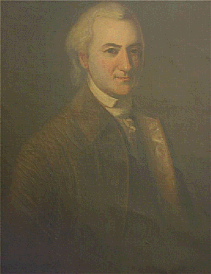 On January 18, 1779, Dickinson was appointed to be a delegate for Delaware to the Continental Congress. During this term he signed the Articles of Confederation, having in 1776 authored their first draft while serving in the Continental Congress as a delegate from Pennsylvania. In August 1781, while still a delegate in Philadelphia he learned that Poplar Hall had been severely damaged by a Loyalist raid. Dickinson returned to the property to investigate the damage and once again stayed for several months.
On January 18, 1779, Dickinson was appointed to be a delegate for Delaware to the Continental Congress. During this term he signed the Articles of Confederation, having in 1776 authored their first draft while serving in the Continental Congress as a delegate from Pennsylvania. In August 1781, while still a delegate in Philadelphia he learned that Poplar Hall had been severely damaged by a Loyalist raid. Dickinson returned to the property to investigate the damage and once again stayed for several months.
While there, in October 1781, Dickinson was elected to represent Kent County in the State Senate, and shortly afterwards the Delaware General Assembly elected him the President of Delaware. The General Assembly's vote was nearly unanimous, the only dissenting vote having been cast by Dickinson himself. Dickinson took office on November 13, 1781 and served until November 7, 1782. Beginning his term with a "Proclamation against Vice and Immorality," he sought ways to bring an end to the disorder of the days of the Revolution. It was a popular position and enhanced his reputation both in Delaware and Pennsylvania. Dickinson then successfully challenged the Delaware General Assembly to address lagging militia enlistments and to properly fund the state’s assessment to the Confederation government. And recognizing the delicate negotiations then underway to end the American Revolution
, Dickinson secured the Assembly's continued endorsement of the French alliance, with no agreement on a separate peace treaty with Great Britain. He also introduced the first census.
However, as before, the lure of Pennsylvania politics was too great. On October 10, 1782, Dickinson was elected to the Supreme Executive Council of Pennsylvania. On November 7, 1782 a joint ballot by the Council and the Pennsylvania General Assembly elected him as president of the Council and thereby President of Pennsylvania. But he did not actually resign as State President of Delaware. Even though Pennsylvania and Delaware had shared the same governor until very recently, attitudes had changed, and many in Delaware were upset at seemingly being cast aside so readily, particularly after the Philadelphia newspapers began criticizing the state for allowing the practice of multiple and non resident office holding. Dickinson’s constitutional successor, John Cook
, was considered too weak in his support of the Revolution, and it was not until January 12, 1783, when Cook called for a new election to choose a replacement, that Dickinson formally resigned.
{|class=wikitable style="width: 94%" style="text-align: center;" align="center"
|-bgcolor=#cccccc
!colspan=12 style="background: #ccccff;" |Delaware General Assembly
(sessions while President)
|-
!Year
!Assembly
!
!Senate Majority
!Speaker
!
!House Majority
!Speaker
|-
|1781/82
|6th
|
| |non-partisan
| |Thomas Collins
|
| |non-partisan
| |Simon Kollock
|-
|1782/83
|7th
|
| |non-partisan
| |Thomas Collins
|
| |non-partisan
| |Nicholas Van Dyke
who later became Federalists, and Radicals or Constitutionalists. The old Pennsylvania General Assembly was dominated by the Loyalists and Moderates and, like Dickinson, did little to support the burgeoning Revolution or independence, except protest. The Radicals took matters into their own hands, using irregular means to write the Pennsylvania Constitution of 1776, which by law excluded from the franchise anyone who would not swear loyalty to the document or the Christian Holy Trinity. In this way all Loyalists, Moderate Whigs, and Quakers were kept out of government. This peremptory action seemed appropriate to many during the crises of 1777 and 1778, but less so in the later years of the Revolution, and the Moderate Whigs gradually became the majority.
Dickinson's election to the Supreme Executive Council was the beginning of a counterrevolution against the Constitutionalists. He was elected President of Pennsylvania on November 7, 1782, garnering 41 votes to James Potter
's 32. As president he presided over the intentionally weak executive authority of the state, and was its chief officer, but always required the agreement of a majority to act. He was re-elected twice and served the constitutional maximum of three years; his election on November 6, 1783 was unanimous. On November 6, 1784 he defeated John Neville, who also lost the election for Vice-President the same day. Working with only the smallest of majorities in the General Assembly in his first two years and with the Constitutionalists in the majority in his last year, all issues were contentious. At first he endured withering attacks from his opponents for his alleged failure to fully support the new government in large and small ways. He responded ably and survived the attacks. He managed to settle quickly the old boundary dispute with Virginia in southwestern Pennsylvania, but was never able to satisfactorily disentangle disputed titles in the Wyoming Valley resulting from prior claims of Connecticut to those lands. An exhausted Dickinson left office October 18, 1785. On that day a special election was held in which Benjamin Franklin
was unanimously elected to serve the ten days left in Dickinson's term.
Perhaps the most significant decision of his term was his patient, peaceful management of the Pennsylvania Mutiny of 1783
. This was a violent protest of Pennsylvania veterans who marched on the Continental Congress demanding their pay before being discharged from the army. Somewhat sympathizing with their case, Dickinson refused Congress's request to bring full military action against them, causing Congress to vote to remove themselves to Princeton
, New Jersey. And when the new Congress agreed to return in 1790, it was to be for only 10 years, until a permanent capital was found elsewhere.
While serving this term he donated 500 acres (2 km²) to Dickinson College
in Carlisle, Pennsylvania, an educational institution founded in 1783 by his friend Benjamin Rush
.
{|class=wikitable style="width: 94%" style="text-align: center;" align="center"
|-bgcolor=#cccccc
!colspan=12 style="background: #ccccff;" |Pennsylvania General Assembly
(sessions while President)
|-
!Year
!Assembly
!
!Majority
!Speaker
|-
|1782/83
|7th
|
| |Republican
| |Frederick A. C. Muhlenberg
|-
|1783/84
|8th
|
| |Republican
| |George Gray
|-
|1784/85
|9th
|
| |Constitutional
| |John Bubenheim Bayard
 After his service in Pennsylvania, Dickinson returned to Delaware, and lived in Wilmington. He was quickly appointed to represent Delaware at the Annapolis Convention
After his service in Pennsylvania, Dickinson returned to Delaware, and lived in Wilmington. He was quickly appointed to represent Delaware at the Annapolis Convention
, where he served as its President. In 1787, Delaware sent him as one of its delegates to the Constitutional Convention of 1787
, along with Gunning Bedford, Jr.
, Richard Bassett
, George Read
, and Jacob Broom
, There, he supported the effort to create a strong central government, but only after the Great Compromise assured that each state, regardless of size, would have an equal vote in the future United States Senate
. Following the Convention
he promoted the resulting Constitution in a series of nine essays, written under the pen name, Fabius.
In 1791, Delaware convened a convention to revise its existing Constitution
, which had been hastily drafted in 1776. Dickinson was elected president of this convention, and although he resigned the chair after most of the work was complete, he remained highly influential in the content of the final document. Major changes included the establishment of a separate Chancery Court and the expansion of the franchise to include all taxpayers, except blacks and women. Dickinson remained neutral in an attempt to include a prohibition of slavery in the document, believing the General Assembly was the proper place to decide that issue. The new Constitution
was approved June 12, 1792.
Once more Dickinson was returned to the State Senate for the 1793 session, but served for just one year before resigning due to his declining health. In his final years he worked to further the abolition movement, donated a considerable amount of his wealth to the "relief of the unhappy." In 1801 he published two volumes of his collected works on politics.
.
In an original copy of a letter discovered November 2009 from Thomas Jefferson to Joseph Bringhurst, caretaker of Dickinson in his later years, Jefferson responded to news of Dickinson's death:
"A more estimable man, or truer patriot, could not have left us. Among the first of the advocates for the rights of his country when assailed by Great Britain, he continued to the last the orthodox advocate of the true principles of our new government and his name will be consecrated in history as one of the great worthies of the revolution.".
He shares with Thomas McKean the distinction of serving as Chief Executive of both Delaware and Pennsylvania after the Declaration of Independence. Dickinson College
and Dickinson School of Law
, separate institutions both located in Carlisle, Pennsylvania
, were named after him. And along with his Letters from a Farmer in Pennsylvania
, Dickinson also authored The Liberty Song
.
Dickinson Street in Madison, Wisconsin
is named in his honor.
Pennsylvania elections were held in October as well. Assemblymen had a one-year term. The Pennsylvania Supreme Executive Council was created in 1776, and counsellors were popularly elected for three-year terms. A joint ballot of the Pennsylvania General Assembly and the Council chose the President from among the twelve Counsellors for a one-year term. Both Assemblies chose the Continental Congressmen for a one-year term as well as the delegates to the U.S. Constitution Convention.
{|class=wikitable style="width: 94%" style="text-align: center;" align="center"
|-bgcolor=#cccccc
!colspan=8 style="background: #ccccff;" | Public Offices
|-
! Office
! State
! Type
! Location
! Began office
! Ended office
! notes
|-
|Assemblyman
|Lower Counties
|Legislature
|New Castle
|October 20, 1759
|October 20, 1760
|
|-
|Assemblyman
|Lower Counties
|Legislature
|New Castle
|October 20, 1760
|October 20, 1761
|
|-
|Assemblyman
|Pennsylvania
|Legislature
|Philadelphia
|October 1762
|October 1763
|
|-
|Assemblyman
|Pennsylvania
|Legislature
|Philadelphia
|October 1763
|October 1764
|
|-
|Delegate
|Pennsylvania
|Legislature
|New York
|October 7, 1765
|October 19, 1765
|Stamp Act Congress
|-
|Delegate
|Pennsylvania
|Legislature
|Philadelphia
|August 2, 1774
|October 26, 1774
|Continental Congress
|-
|Delegate
|Pennsylvania
|Legislature
|Philadelphia
|March 16, 1775
|October 21, 1775
|Continental Congress
|-
|Delegate
|Pennsylvania
|Legislature
|Philadelphia
|October 21, 1775
|November 7, 1776
|Continental Congress
|-
|Delegate
|Delaware
|Legislature
|Philadelphia
|January 18, 1779
|December 22, 1779
|Continental Congress
|-
|Delegate
|Delaware
|Legislature
|Philadelphia
|December 22, 1779
|February 10, 1781
|Continental Congress
|-
|Councilman
|Delaware
|Legislature
|Dover
|October 20, 1781
|November 13, 1781
|
|-
|State President
|Delaware
|Executive
|Dover
|November 13, 1781
|November 7, 1782
|Executive Council
|-
|State President
|Pennsylvania
|Executive
|Philadelphia
|November 4, 1782
|October 18, 1785
|
|-
|Delegate
|Delaware
|Convention
|Philadelphia
|May 14, 1787
|September 17, 1787
|U.S. Constitution
|-
|Delegate
|Delaware
|Convention
|Dover
|November 29, 1791
|June 12, 1792
|State Constitution
|-
|State Senator
|Delaware
|Legislature
|Dover
|January 6, 1793
|January 6, 1794
|
{|class=wikitable style="width: 94%" style="text-align: center;" align="center"
|-bgcolor=#cccccc
!colspan=7 style="background: #ccccff;" |Delaware General Assembly service
|-
! Dates
! Assembly
! Chamber
! Majority
! Governor
! Committees
! District
|-
|1781/82
|6th
|State House
|non-partisan
|Caesar Rodney
|
|Kent at-large
|-
|1793
|17th
|State Senate
|Republican
|Joshua Clayton
|
|New Castle at-large
, billed third after the parts of Adams and Franklin. He was originally portrayed on stage by Paul Hecht
, and in the 1972 film adaptation by Donald Madden
. Michael Cumpsty
portrayed him in the 1997 revival. His portrayal in this musical differs from reality: instead of abstaining from voting and debating, he acts as John Adams' primary antagonist in the debates over independence, to the point where the two men come to blows. His motivation in the musical is to convince the delegates to come to peace terms with the mother country.
In Part II of the 2008 HBO series John Adams
, based on the book by David McCullough
, the part of Dickinson is played by Zeljko Ivanek
.
Places with more information
Philadelphia, Pennsylvania
Philadelphia is the largest city in the Commonwealth of Pennsylvania and the county seat of Philadelphia County, with which it is coterminous. The city is located in the Northeastern United States along the Delaware and Schuylkill rivers. It is the fifth-most-populous city in the United States,...
and Wilmington, Delaware
Wilmington, Delaware
Wilmington is the largest city in the state of Delaware, United States, and is located at the confluence of the Christina River and Brandywine Creek, near where the Christina flows into the Delaware River. It is the county seat of New Castle County and one of the major cities in the Delaware Valley...
. He was a militia officer during the American Revolution
American Revolution
The American Revolution was the political upheaval during the last half of the 18th century in which thirteen colonies in North America joined together to break free from the British Empire, combining to become the United States of America...
, a Continental Congressman from Pennsylvania and Delaware, a delegate to the U.S. Constitutional Convention of 1787, President of Delaware and President of Pennsylvania. Among the wealthiest men in the British American colonies, he is known as the "Penman of the Revolution" for his Letters from a Farmer in Pennsylvania
Letters from a Farmer in Pennsylvania
Letters from a Farmer in Pennsylvania is a series of essays written by the Pennsylvania lawyer and legislator John Dickinson and published under the name "A Farmer" from 1767 to 1768. The twelve letters were widely read and reprinted throughout the thirteen colonies, and were important in uniting...
; upon receiving news of his death, President Thomas Jefferson
Thomas Jefferson
Thomas Jefferson was the principal author of the United States Declaration of Independence and the Statute of Virginia for Religious Freedom , the third President of the United States and founder of the University of Virginia...
recognized him as being "among the first of the advocates for the rights of his country when assailed by Great Britain" whose "name will be consecrated in history as one of the great worthies of the revolution." He is the namesake of Dickinson College
Dickinson College
Dickinson College is a private, residential liberal arts college in Carlisle, Pennsylvania. Originally established as a Grammar School in 1773, Dickinson was chartered September 9, 1783, five days after the signing of the Treaty of Paris, making it the first college to be founded in the newly...
and Penn State University's Dickinson School of Law
Dickinson School of Law
Penn State University Dickinson School of Law is the law school of The Pennsylvania State University...
.
Family history
Dickinson was born at Croisadore his family's tobacco plantation near the village of Trappe in Talbot County, MarylandTalbot County, Maryland
-2010:Whereas according to the 2010 U.S. Census Bureau:*81.4% White*12.8% Black*0.2% Native American*1.2% Asian*0.1% Native Hawaiian or Pacific Islander*1.6% Two or more races*2.7% Other races*5.5% Hispanic or Latino -2000:...
. He was the great grandson of Walter Dickinson who emigrated from England to Virginia in 1654 and, having joined the Society of Friends
Religious Society of Friends
The Religious Society of Friends, or Friends Church, is a Christian movement which stresses the doctrine of the priesthood of all believers. Members are known as Friends, or popularly as Quakers. It is made of independent organisations, which have split from one another due to doctrinal differences...
, came with several co-religionists to Talbot County on the Eastern Shore of the Chesapeake Bay
Chesapeake Bay
The Chesapeake Bay is the largest estuary in the United States. It lies off the Atlantic Ocean, surrounded by Maryland and Virginia. The Chesapeake Bay's drainage basin covers in the District of Columbia and parts of six states: New York, Pennsylvania, Delaware, Maryland, Virginia, and West...
in 1659. There, with 400 acres (1.6 km²) on the banks of the Choptank River
Choptank River
The Choptank River is a major tributary of the Chesapeake Bay on the Delmarva Peninsula. Running for , it rises in Kent County, Delaware, runs through Caroline County, Maryland and forms much of the border between Talbot County, Maryland on the north, and Caroline County and Dorchester County on...
Walter began a plantation, Croisadore, meaning "cross of gold." Walter also bought 800 acres (3.2 km²) on St. Jones Neck in what became Kent County, Delaware
Kent County, Delaware
Kent County is a county located in the central part of the U.S. state of Delaware. It is coextensive with the Dover, Delaware, Metropolitan Statistical Area. As of 2010 the population was 162,310, a 28.1% increase over the previous decade. The county seat is Dover, the state capital...
.
Croisadore passed through Walter's son, William, to his grandson, Samuel, the father of John Dickinson. Each generation increased the landholdings, so that Samuel inherited 2500 acres (1,011.7 ha) on five farms in three Maryland counties and over his lifetime increased that to 9000 acres (3,642.2 ha). He also bought the Kent County
Kent County, Delaware
Kent County is a county located in the central part of the U.S. state of Delaware. It is coextensive with the Dover, Delaware, Metropolitan Statistical Area. As of 2010 the population was 162,310, a 28.1% increase over the previous decade. The county seat is Dover, the state capital...
property from his cousin and expanded it to about 3000 acres (1,214.1 ha), stretching along the St. Jones River
St. Jones River
The St. Jones River is a river flowing to Delaware Bay in central Delaware in the United States. It is long and drains an area of on the Atlantic Coastal Plain. The river is believed to have been named either for Robert Jones, an early European property owner in the region, or for "St. Jone",...
from Dover to the Delaware Bay
Delaware Bay
Delaware Bay is a major estuary outlet of the Delaware River on the Northeast seaboard of the United States whose fresh water mixes for many miles with the waters of the Atlantic Ocean. It is in area. The bay is bordered by the State of New Jersey and the State of Delaware...
. There he began another plantation and called it “Poplar Hall
John Dickinson House
The John Dickinson House, generally known as Poplar Hall, is located on the John Dickinson Plantation, a property owned by the State of Delaware and open to the public as a museum by the Delaware Division of Historical and Cultural Affairs...
.” These plantations were large, profitable agricultural enterprises worked by slave labor, until 1777 when John Dickinson freed the enslaved of Poplar Hall.
Samuel Dickinson first married Judith Troth on 11 April 1710. They had nine children; William, Walter, Samuel, Elizabeth, Henry, Elizabeth "Betsy," Rebecca and Rachel. The three eldest sons died of smallpox while in London seeking their education. Widowed, with two young children, Henry and Betsy, Samuel married Mary Cadwalader in 1731. She was the daughter of Martha Jones (Grand daughter of Dr. Thomas Wynne) and the prominent Quaker, John Cadwalader who was also grandfather of General John Cadwalader
John Cadwalader (general)
John Cadwalader was a commander of Pennsylvania troops during the American Revolutionary War.-Early life:...
of Philadelphia. Their sons, John, Thomas and Philemon
Philemon Dickinson
Philemon Dickinson was an American lawyer and politician from Trenton, New Jersey. As a brigadier general of the New Jersey militia, he was one of the most effective militia officers of the American Revolutionary War. He was also a Continental Congressman from Delaware and a United States Senator...
were born in the next few years.
For three generations the Dickinson family had been members of the Third Haven Friends Meeting in Talbot County and the Cadwaladers were members of the Meeting in Philadelphia. But in 1739, John Dickinson's half-sister, Betsy, was married in an Anglican church to Charles Goldsborough in what was called a "disorderly marriage" by the Meeting. The couple would be the grandparents of Maryland governor Charles Goldsborough
Charles Goldsborough
Charles Goldsborough served as the 16th Governor of the state of Maryland in the United States in 1819.Goldsborough was born at "Hunting Creek", near Cambridge, Maryland, and pursued an academic course. He graduated from the University of Pennsylvania at Philadelphia in 1784 and began to study law...
.
Leaving Croisadore to elder son Henry Dickinson, Samuel moved to Poplar Hall, where he had already taken a leading role in the community as Judge of the Court of Common Pleas of Kent County. The move also placed Mary nearer her Philadelphia relations.
Poplar Hall was situated on a now-straightened bend of the St. Jones River
St. Jones River
The St. Jones River is a river flowing to Delaware Bay in central Delaware in the United States. It is long and drains an area of on the Atlantic Coastal Plain. The river is believed to have been named either for Robert Jones, an early European property owner in the region, or for "St. Jone",...
. There was plenty of activity delivering the necessities, and shipping the agricultural products produced. Much of this product was wheat that along with other wheat from the region, was milled into a “superfine” flour. Most people at this plantation were servants and slaves of the Dickinsons.
Early life and family
Dickinson was educated at home, by his parents and by recent immigrants employed for that purpose. Included among them was the Presbyterian minister Francis AlisonFrancis Alison
Francis Alison was a leading minister in the Synod of Philadelphia during The Old Side-New Side Controversy-Early life and education:...
, who later established New London Academy in Chester County, Pennsylvania
Chester County, Pennsylvania
-State parks:*French Creek State Park*Marsh Creek State Park*White Clay Creek Preserve-Demographics:As of the 2010 census, the county was 85.5% White, 6.1% Black or African American, 0.2% Native American or Alaskan Native, 3.9% Asian, 0.0% Native Hawaiian, 1.8% were two or more races, and 2.4% were...
. Most important was William Killen, who became a life-long friend, and himself had a distinguished career as Delaware’s first Chief Justice and Chancellor. Dickinson was precocious and energetic, and in spite of his love of Poplar Hall and his family, was drawn to Philadelphia.
At 18 he began studying the law under John Moland
John Moland
John Moland was born around 1700 in London.He studied law at the Inner Temple, where his name was recorded as John Morland and a note says that he was commissioned King’s Attorney in Pennsylvania...
in Philadelphia. There he made friends with fellow students George Read
George Read (signer)
George Read was an American lawyer and politician from New Castle in New Castle County, Delaware. He was a signer of the Declaration of Independence, a Continental Congressman from Delaware, a delegate to the U.S. Constitutional Convention of 1787, President of Delaware, and a member of the...
and Samuel Wharton
Samuel Wharton
Samuel Wharton was a merchant, land speculator, and politician from Dover in Kent County, Delaware. John Bayton, George Morgan, and George Croghan, deputy superintendent of Indian affairs, joined in a partnership on the Ohio country and Indian Trade after 1763...
, among others. By 1753 John went to London for three years of study at the Middle Temple
Middle Temple
The Honourable Society of the Middle Temple, commonly known as Middle Temple, is one of the four Inns of Court exclusively entitled to call their members to the English Bar as barristers; the others being the Inner Temple, Gray's Inn and Lincoln's Inn...
. He spent those years studying the works of Edward Coke
Edward Coke
Sir Edward Coke SL PC was an English barrister, judge and politician considered to be the greatest jurist of the Elizabethan and Jacobean eras. Born into a middle class family, Coke was educated at Trinity College, Cambridge before leaving to study at the Inner Temple, where he was called to the...
and Francis Bacon
Francis Bacon
Francis Bacon, 1st Viscount St Albans, KC was an English philosopher, statesman, scientist, lawyer, jurist, author and pioneer of the scientific method. He served both as Attorney General and Lord Chancellor of England...
at the Inns of Court
Inns of Court
The Inns of Court in London are the professional associations for barristers in England and Wales. All such barristers must belong to one such association. They have supervisory and disciplinary functions over their members. The Inns also provide libraries, dining facilities and professional...
following in the footsteps of his lifelong friend, Pennsylvania Attorney General Benjamin Chew
Benjamin Chew
Benjamin Chew was a third-generation American, a Quaker-born legal scholar, a prominent and successful Philadelphia lawyer, head of the Pennsylvania Judiciary System under both Colony and Commonwealth, and Chief Justice of the Supreme Court of the Province of Pennsylvania...
, and in 1757 was admitted to the Pennsylvania Bar beginning his career as barrister and solicitor.
On July 19, 1770, Dickinson married Mary Norris, known as Polly, the daughter of a wealthy Philadelphia Quaker, and Speaker of the Pennsylvania General Assembly, Isaac Norris
Isaac Norris (II)
Isaac Norris was a merchant and statesman in provincial Pennsylvania.-Early life and education:Isaac Norris was born in Philadelphia in 1701, the son of Isaac Norris, a prosperous Quaker merchant and original participant in William Penn's establishment of the colony of Pennsylvania...
. They had five children, but only two survived to adulthood: Sarah Norris "Sally" Dickinson and Maria Mary Dickinson. Dickinson never formally joined the Quaker Meeting, because, as he explained, he believed in the "lawfulness of defensive war."
Already wealthy his marriage increased his wealth. In Philadelphia, he lived at the family estate of his wife, Fairhill, near Germantown
Germantown, Philadelphia, Pennsylvania
Germantown is a neighborhood in the northwest section of the city of Philadelphia, Pennsylvania, United States, about 7–8 miles northwest from the center of the city...
. Meanwhile he built an elegant mansion on Chestnut Street but never lived there as it was confiscated and turned into a hospital during his 1776-77 absence in Delaware. It then became the residence of the French ambassador and still later the home of his brother, Philemon Dickinson. Fairhill was burned by the British during the Battle of Germantown
Battle of Germantown
The Battle of Germantown, a battle in the Philadelphia campaign of the American Revolutionary War, was fought on October 4, 1777, at Germantown, Pennsylvania between the British army led by Sir William Howe and the American army under George Washington...
. While in Philadelphia as State President, he lived at the confiscated mansion of Joseph Galloway
Joseph Galloway
Joseph Galloway was an American Loyalist during the American Revolution, after serving as delegate to the First Continental Congress from Pennsylvania.-Early life:...
at Sixth and Market Streets, now established as the State Presidential mansion.
Dickinson lived at Poplar Hall, for extended periods only in 1776-77 and 1781-82. In August 1781 it was sacked by Loyalists
Loyalist (American Revolution)
Loyalists were American colonists who remained loyal to the Kingdom of Great Britain during the American Revolutionary War. At the time they were often called Tories, Royalists, or King's Men. They were opposed by the Patriots, those who supported the revolution...
and was badly burned in 1804. This home is now owned by the State of Delaware and is open to the public. After his service as President of Pennsylvania, he returned to live in Wilmington, Delaware in 1785 and built a mansion at the northwest corner of 8th and Market Streets.
Continental Congress
As events unfolded Dickinson was one of Pennsylvania's delegates to the First Continental CongressFirst Continental Congress
The First Continental Congress was a convention of delegates from twelve of the thirteen North American colonies that met on September 5, 1774, at Carpenters' Hall in Philadelphia, Pennsylvania, early in the American Revolution. It was called in response to the passage of the Coercive Acts by the...
in 1774 and the Second Continental Congress
Second Continental Congress
The Second Continental Congress was a convention of delegates from the Thirteen Colonies that started meeting on May 10, 1775, in Philadelphia, Pennsylvania, soon after warfare in the American Revolutionary War had begun. It succeeded the First Continental Congress, which met briefly during 1774,...
in 1775 and 1776. In support of the cause, he continued to contribute declarations in the name of the Congress. Among the most famous is one written with Thomas Jefferson
Thomas Jefferson
Thomas Jefferson was the principal author of the United States Declaration of Independence and the Statute of Virginia for Religious Freedom , the third President of the United States and founder of the University of Virginia...
, a Declaration of the Causes and Necessity of Taking Up Arms
Declaration of the Causes and Necessity of Taking Up Arms
The Declaration of the Causes and Necessity of Taking Up Arms was a document issued by the Second Continental Congress on July 6, 1775, to explain why the Thirteen Colonies had taken up arms in what had become the American Revolutionary War...
, with Dickinson’s conclusion that Americans were "resolved to die free men rather than live slaves." Another was the Olive Branch Petition
Olive Branch Petition
The Olive Branch Petition was adopted by the Continental Congress in July 1775 in an attempt to avoid a full-blown war with Great Britain. The petition affirmed American loyalty to Great Britain and entreated the king to prevent further conflict...
, a last ditch appeal to King George III to resolve the dispute. But through it all, agreeing with New Castle County
New Castle County, Delaware
New Castle County is the northernmost of the three counties of the U.S. state of Delaware. As of 2010 its population was 538,479, an increase of 7.6% over the previous decade. The county seat is Wilmington. The center of population of Delaware is located in New Castle County, in the town of...
's George Read
George Read (signer)
George Read was an American lawyer and politician from New Castle in New Castle County, Delaware. He was a signer of the Declaration of Independence, a Continental Congressman from Delaware, a delegate to the U.S. Constitutional Convention of 1787, President of Delaware, and a member of the...
and many others in Philadelphia and the Lower Counties
Delaware
Delaware is a U.S. state located on the Atlantic Coast in the Mid-Atlantic region of the United States. It is bordered to the south and west by Maryland, and to the north by Pennsylvania...
, Dickinson's object was reconciliation, not independence and revolution. He was a proud devotee of the British Constitution and felt the dispute was with Parliament only.
When the Continental Congress began the debate on the Declaration of Independence on July 1, 1776, Dickinson reiterated his opposition to declaring independence at that time. Dickinson believed that Congress should complete the Articles of Confederation
Articles of Confederation
The Articles of Confederation, formally the Articles of Confederation and Perpetual Union, was an agreement among the 13 founding states that legally established the United States of America as a confederation of sovereign states and served as its first constitution...
and secure a foreign alliance before issuing a declaration. He abstained or absented himself from the votes on July 2 that declared independence and absented himself again from voting on the wording of the formal Declaration on July 4. Dickinson understood the implications of his refusal to vote stating, "My conduct this day, I expect will give the finishing blow to my once too great and, my integrity considered, now too diminished popularity." Dickinson refused to sign the Declaration and since a proposal had been brought forth and carried that stated, "for our mutual security and protection," no man could remain in Congress without signing, Dickinson voluntarily left and joined the Pennsylvania militia.
Following the Declaration of Independence
United States Declaration of Independence
The Declaration of Independence was a statement adopted by the Continental Congress on July 4, 1776, which announced that the thirteen American colonies then at war with Great Britain regarded themselves as independent states, and no longer a part of the British Empire. John Adams put forth a...
Dickinson was given the rank of brigadier general in the Pennsylvania militia, known as the Associators. He led some 10,000 soldiers to Elizabeth, New Jersey
Elizabeth, New Jersey
Elizabeth is a city in Union County, New Jersey, United States. As of the 2010 United States Census, the city had a total population of 124,969, retaining its ranking as New Jersey's fourth largest city with an increase of 4,401 residents from its 2000 Census population of 120,568...
to protect that area against British attack from Staten Island
Staten Island
Staten Island is a borough of New York City, New York, United States, located in the southwest part of the city. Staten Island is separated from New Jersey by the Arthur Kill and the Kill Van Kull, and from the rest of New York by New York Bay...
. But because of his unpopular opinion on independence two junior officers were promoted above him.
Return to Poplar Hall
Dickinson resigned his commission in December 1776 and went to stay at Poplar Hall in Kent County. While there he learned that his home on Chestnut Street in Philadelphia had been confiscated and converted into a hospital. He stayed at Poplar Hall for more than two years. The Delaware General AssemblyDelaware General Assembly
The Delaware General Assembly is the legislature of the U.S. state of Delaware. It is a bicameral legislature composed of the Delaware Senate with 21 Senators and the Delaware House of Representatives with 41 Representatives...
tried to appoint him as their delegate to the Continental Congress in 1777, but he refused. In August 1777 he served as a private with the Kent county Militia at Middletown
Middletown, Delaware
Middletown is a town in New Castle County, Delaware, United States. According to the 2010 Census, the population of the town is 18,871.-Geography:Middletown is located at with an elevation of ....
, Delaware under General Caesar Rodney
Caesar Rodney
Caesar Rodney was an American lawyer and politician from St. Jones Neck in Dover Hundred, Kent County, Delaware, east of Dover...
to help delay General William Howe
William Howe, 5th Viscount Howe
William Howe, 5th Viscount Howe, KB, PC was a British army officer who rose to become Commander-in-Chief of British forces during the American War of Independence...
's march to Philadelphia. In October 1777, Dickinson's friend, Thomas McKean
Thomas McKean
Thomas McKean was an American lawyer and politician from New Castle, in New Castle County, Delaware and Philadelphia, Pennsylvania. During the American Revolution he was a delegate to the Continental Congress where he signed the United States Declaration of Independence and the Articles of...
, appointed him Brigadier General of the Delaware Militia, but again Dickinson declined the appointment. Shortly afterwards he learned that the British had burned down his Fairhill property during the Battle of Germantown.
These years were not without accomplishment however. In 1777, Dickinson, Delaware's wealthiest farmer and largest slaveholder, decided to free his slaves. While Kent County was not a large slave-holding area, like farther south in Virginia, and even though Dickinson had only 37 slaves, this was an action of some considerable courage. Undoubtedly the strongly abolitionist Quaker influences around them had their effect, and the action was all the easier because his farm had moved away from tobacco to the less labor intensive crops like wheat and barley. Furthermore manumission
Manumission
Manumission is the act of a slave owner freeing his or her slaves. In the United States before the passage of the Thirteenth Amendment to the United States Constitution, which abolished most slavery, this often happened upon the death of the owner, under conditions in his will.-Motivations:The...
was a multi-year process and many of the workers remained obligated to service for a considerable additional time.
President of Delaware
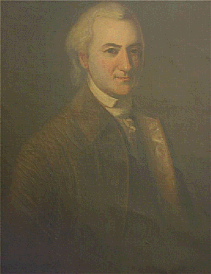
While there, in October 1781, Dickinson was elected to represent Kent County in the State Senate, and shortly afterwards the Delaware General Assembly elected him the President of Delaware. The General Assembly's vote was nearly unanimous, the only dissenting vote having been cast by Dickinson himself. Dickinson took office on November 13, 1781 and served until November 7, 1782. Beginning his term with a "Proclamation against Vice and Immorality," he sought ways to bring an end to the disorder of the days of the Revolution. It was a popular position and enhanced his reputation both in Delaware and Pennsylvania. Dickinson then successfully challenged the Delaware General Assembly to address lagging militia enlistments and to properly fund the state’s assessment to the Confederation government. And recognizing the delicate negotiations then underway to end the American Revolution
American Revolution
The American Revolution was the political upheaval during the last half of the 18th century in which thirteen colonies in North America joined together to break free from the British Empire, combining to become the United States of America...
, Dickinson secured the Assembly's continued endorsement of the French alliance, with no agreement on a separate peace treaty with Great Britain. He also introduced the first census.
However, as before, the lure of Pennsylvania politics was too great. On October 10, 1782, Dickinson was elected to the Supreme Executive Council of Pennsylvania. On November 7, 1782 a joint ballot by the Council and the Pennsylvania General Assembly elected him as president of the Council and thereby President of Pennsylvania. But he did not actually resign as State President of Delaware. Even though Pennsylvania and Delaware had shared the same governor until very recently, attitudes had changed, and many in Delaware were upset at seemingly being cast aside so readily, particularly after the Philadelphia newspapers began criticizing the state for allowing the practice of multiple and non resident office holding. Dickinson’s constitutional successor, John Cook
John Cook (governor)
John Cook was an American planter and politician from Smyrna, in Kent County, Delaware. He served in the Delaware General Assembly and as Governor of Delaware.-Early life and family:...
, was considered too weak in his support of the Revolution, and it was not until January 12, 1783, when Cook called for a new election to choose a replacement, that Dickinson formally resigned.
{|class=wikitable style="width: 94%" style="text-align: center;" align="center"
|-bgcolor=#cccccc
!colspan=12 style="background: #ccccff;" |Delaware General Assembly
Delaware General Assembly
The Delaware General Assembly is the legislature of the U.S. state of Delaware. It is a bicameral legislature composed of the Delaware Senate with 21 Senators and the Delaware House of Representatives with 41 Representatives...
(sessions while President)
|-
!Year
!Assembly
!
!Senate Majority
!Speaker
!
!House Majority
!Speaker
|-
|1781/82
|6th
Delaware General Assembly
The Delaware General Assembly is the legislature of the U.S. state of Delaware. It is a bicameral legislature composed of the Delaware Senate with 21 Senators and the Delaware House of Representatives with 41 Representatives...
|
| |non-partisan
| |Thomas Collins
Thomas Collins (governor)
Thomas Collins was an American planter and politician from Smyrna, in Kent County, Delaware. He was an officer of the Delaware militia during the American Revolution, and served in the Delaware General Assembly and as President of Delaware.-Early life and family:Collins was born in Duck Creek, now...
|
| |non-partisan
| |Simon Kollock
|-
|1782/83
|7th
Delaware General Assembly
The Delaware General Assembly is the legislature of the U.S. state of Delaware. It is a bicameral legislature composed of the Delaware Senate with 21 Senators and the Delaware House of Representatives with 41 Representatives...
|
| |non-partisan
| |Thomas Collins
John Cook (governor)
John Cook was an American planter and politician from Smyrna, in Kent County, Delaware. He served in the Delaware General Assembly and as Governor of Delaware.-Early life and family:...
|
| |non-partisan
| |Nicholas Van Dyke
Nicholas Van Dyke (governor)
Nicholas Van Dyke was an American lawyer and politician from New Castle, in New Castle County, Delaware. He served in the Delaware General Assembly, as a Continental Congressman from Delaware, and as President of Delaware.-Early life and family:Van Dyke was born at Berwick, his family's home in St...
President of Pennsylvania
When the American Revolution began, Dickinson fairly represented the center of Pennsylvania politics. The old Proprietary and Popular parties divided equally in thirds over the issue of independence, as Loyalists, Moderate WhigsWhig Party (United States)
The Whig Party was a political party of the United States during the era of Jacksonian democracy. Considered integral to the Second Party System and operating from the early 1830s to the mid-1850s, the party was formed in opposition to the policies of President Andrew Jackson and his Democratic...
who later became Federalists, and Radicals or Constitutionalists. The old Pennsylvania General Assembly was dominated by the Loyalists and Moderates and, like Dickinson, did little to support the burgeoning Revolution or independence, except protest. The Radicals took matters into their own hands, using irregular means to write the Pennsylvania Constitution of 1776, which by law excluded from the franchise anyone who would not swear loyalty to the document or the Christian Holy Trinity. In this way all Loyalists, Moderate Whigs, and Quakers were kept out of government. This peremptory action seemed appropriate to many during the crises of 1777 and 1778, but less so in the later years of the Revolution, and the Moderate Whigs gradually became the majority.
Dickinson's election to the Supreme Executive Council was the beginning of a counterrevolution against the Constitutionalists. He was elected President of Pennsylvania on November 7, 1782, garnering 41 votes to James Potter
James Potter
James Potter was a soldier, farmer and politician from Colonial- and Revolutionary-era Pennsylvania. He rose to the rank of brigadier general of Pennsylvania militia during the Revolutionary War, and served as Vice-President of Pennsylvania, 1781-1782.-Family and early life:James Potter was of...
's 32. As president he presided over the intentionally weak executive authority of the state, and was its chief officer, but always required the agreement of a majority to act. He was re-elected twice and served the constitutional maximum of three years; his election on November 6, 1783 was unanimous. On November 6, 1784 he defeated John Neville, who also lost the election for Vice-President the same day. Working with only the smallest of majorities in the General Assembly in his first two years and with the Constitutionalists in the majority in his last year, all issues were contentious. At first he endured withering attacks from his opponents for his alleged failure to fully support the new government in large and small ways. He responded ably and survived the attacks. He managed to settle quickly the old boundary dispute with Virginia in southwestern Pennsylvania, but was never able to satisfactorily disentangle disputed titles in the Wyoming Valley resulting from prior claims of Connecticut to those lands. An exhausted Dickinson left office October 18, 1785. On that day a special election was held in which Benjamin Franklin
Benjamin Franklin
Dr. Benjamin Franklin was one of the Founding Fathers of the United States. A noted polymath, Franklin was a leading author, printer, political theorist, politician, postmaster, scientist, musician, inventor, satirist, civic activist, statesman, and diplomat...
was unanimously elected to serve the ten days left in Dickinson's term.
Perhaps the most significant decision of his term was his patient, peaceful management of the Pennsylvania Mutiny of 1783
Pennsylvania Mutiny of 1783
The Pennsylvania Mutiny of 1783 was an anti-government protest by nearly 400 soldiers of the Continental Army in June 1783...
. This was a violent protest of Pennsylvania veterans who marched on the Continental Congress demanding their pay before being discharged from the army. Somewhat sympathizing with their case, Dickinson refused Congress's request to bring full military action against them, causing Congress to vote to remove themselves to Princeton
Princeton, New Jersey
Princeton is a community located in Mercer County, New Jersey, United States. It is best known as the location of Princeton University, which has been sited in the community since 1756...
, New Jersey. And when the new Congress agreed to return in 1790, it was to be for only 10 years, until a permanent capital was found elsewhere.
While serving this term he donated 500 acres (2 km²) to Dickinson College
Dickinson College
Dickinson College is a private, residential liberal arts college in Carlisle, Pennsylvania. Originally established as a Grammar School in 1773, Dickinson was chartered September 9, 1783, five days after the signing of the Treaty of Paris, making it the first college to be founded in the newly...
in Carlisle, Pennsylvania, an educational institution founded in 1783 by his friend Benjamin Rush
Benjamin Rush
Benjamin Rush was a Founding Father of the United States. Rush lived in the state of Pennsylvania and was a physician, writer, educator, humanitarian and a Christian Universalist, as well as the founder of Dickinson College in Carlisle, Pennsylvania....
.
{|class=wikitable style="width: 94%" style="text-align: center;" align="center"
|-bgcolor=#cccccc
!colspan=12 style="background: #ccccff;" |Pennsylvania General Assembly
Pennsylvania General Assembly
The Pennsylvania General Assembly is the state legislature of the U.S. state of Pennsylvania. The legislature convenes in the State Capitol building in Harrisburg. In colonial times , the legislature was known as the Pennsylvania Provincial Assembly. Since the Constitution of 1776, written by...
(sessions while President)
|-
!Year
!Assembly
!
!Majority
!Speaker
|-
|1782/83
|7th
Pennsylvania General Assembly
The Pennsylvania General Assembly is the state legislature of the U.S. state of Pennsylvania. The legislature convenes in the State Capitol building in Harrisburg. In colonial times , the legislature was known as the Pennsylvania Provincial Assembly. Since the Constitution of 1776, written by...
|
| |Republican
| |Frederick A. C. Muhlenberg
Frederick Muhlenberg
Frederick Augustus Conrad Muhlenberg was an American minister and politician who was the first Speaker of the United States House of Representatives. A delegate and a member of the U.S...
|-
|1783/84
|8th
Pennsylvania General Assembly
The Pennsylvania General Assembly is the state legislature of the U.S. state of Pennsylvania. The legislature convenes in the State Capitol building in Harrisburg. In colonial times , the legislature was known as the Pennsylvania Provincial Assembly. Since the Constitution of 1776, written by...
|
| |Republican
| |George Gray
|-
|1784/85
|9th
Pennsylvania General Assembly
The Pennsylvania General Assembly is the state legislature of the U.S. state of Pennsylvania. The legislature convenes in the State Capitol building in Harrisburg. In colonial times , the legislature was known as the Pennsylvania Provincial Assembly. Since the Constitution of 1776, written by...
|
| |Constitutional
| |John Bubenheim Bayard
United States Constitution

Annapolis Convention (1786)
The Annapolis Convention was a meeting in 1786 at Annapolis, Maryland, of 12 delegates from five states that unanimously called for a constitutional convention. The formal title of the meeting was a Meeting of Commissioners to Remedy Defects of the Federal Government...
, where he served as its President. In 1787, Delaware sent him as one of its delegates to the Constitutional Convention of 1787
History of the United States Constitution
The United States Constitution was written in 1787, but it did not take effect until after it was ratified in 1789, when it replaced the Articles of Confederation. It remains the basic law of the United States...
, along with Gunning Bedford, Jr.
Gunning Bedford, Jr.
Gunning Bedford, Jr. was an American lawyer and politician from Wilmington, in New Castle County, Delaware. He served in the Delaware General Assembly, as a Continental Congressman from Delaware and as a delegate to the U.S. Constitutional Convention of 1787. He is often confused with his cousin,...
, Richard Bassett
Richard Bassett
Richard Bassett was an American lawyer and politician from Dover, in Kent County, Delaware. He was a veteran of the American Revolution, a delegate to the Constitutional Convention of 1787, and a member of the Federalist Party, who served in the Delaware General Assembly, as Governor of Delaware,...
, George Read
George Read (signer)
George Read was an American lawyer and politician from New Castle in New Castle County, Delaware. He was a signer of the Declaration of Independence, a Continental Congressman from Delaware, a delegate to the U.S. Constitutional Convention of 1787, President of Delaware, and a member of the...
, and Jacob Broom
Jacob Broom
Jacob Broom was an American businessman and politician from Wilmington, in New Castle County, Delaware. As a delegate to the U.S. Constitutional Convention of 1787, he was a signer of the U.S. Constitution. He was also appointed as a delegate to the Annapolis Convention but did not attend, and...
, There, he supported the effort to create a strong central government, but only after the Great Compromise assured that each state, regardless of size, would have an equal vote in the future United States Senate
United States Senate
The United States Senate is the upper house of the bicameral legislature of the United States, and together with the United States House of Representatives comprises the United States Congress. The composition and powers of the Senate are established in Article One of the U.S. Constitution. Each...
. Following the Convention
History of the United States Constitution
The United States Constitution was written in 1787, but it did not take effect until after it was ratified in 1789, when it replaced the Articles of Confederation. It remains the basic law of the United States...
he promoted the resulting Constitution in a series of nine essays, written under the pen name, Fabius.
In 1791, Delaware convened a convention to revise its existing Constitution
Delaware Constitution of 1776
The Delaware Constitution of 1776 was the first governing document for Delaware state government and was in effect from its adoption in September 1776 until replaced in 1792 by a new Constitution.-Background:...
, which had been hastily drafted in 1776. Dickinson was elected president of this convention, and although he resigned the chair after most of the work was complete, he remained highly influential in the content of the final document. Major changes included the establishment of a separate Chancery Court and the expansion of the franchise to include all taxpayers, except blacks and women. Dickinson remained neutral in an attempt to include a prohibition of slavery in the document, believing the General Assembly was the proper place to decide that issue. The new Constitution
Delaware Constitution of 1792
The Delaware Constitution of 1792 was the second governing document for Delaware state government and was in effect from its adoption on June 12, 1792 until replaced on December 2, 1831 by a new Constitution....
was approved June 12, 1792.
Once more Dickinson was returned to the State Senate for the 1793 session, but served for just one year before resigning due to his declining health. In his final years he worked to further the abolition movement, donated a considerable amount of his wealth to the "relief of the unhappy." In 1801 he published two volumes of his collected works on politics.
Death and legacy
Dickinson died at Wilmington, Delaware, where he is buried in the Friends Burial GroundFriends Meetinghouse (Wilmington, Delaware)
Friends Meetinghouse is a historic Quaker meeting house at 4th and West Streets in Wilmington, Delaware in the Quaker Hill neighborhood. The meeting is still active with a membership of about 400 and is part of the Philadelphia Yearly Meeting...
.
In an original copy of a letter discovered November 2009 from Thomas Jefferson to Joseph Bringhurst, caretaker of Dickinson in his later years, Jefferson responded to news of Dickinson's death:
"A more estimable man, or truer patriot, could not have left us. Among the first of the advocates for the rights of his country when assailed by Great Britain, he continued to the last the orthodox advocate of the true principles of our new government and his name will be consecrated in history as one of the great worthies of the revolution.".
He shares with Thomas McKean the distinction of serving as Chief Executive of both Delaware and Pennsylvania after the Declaration of Independence. Dickinson College
Dickinson College
Dickinson College is a private, residential liberal arts college in Carlisle, Pennsylvania. Originally established as a Grammar School in 1773, Dickinson was chartered September 9, 1783, five days after the signing of the Treaty of Paris, making it the first college to be founded in the newly...
and Dickinson School of Law
Dickinson School of Law
Penn State University Dickinson School of Law is the law school of The Pennsylvania State University...
, separate institutions both located in Carlisle, Pennsylvania
Carlisle, Pennsylvania
Carlisle is a borough in and the county seat of Cumberland County, Pennsylvania, United States. The name is traditionally pronounced with emphasis on the second syllable. Carlisle is located within the Cumberland Valley, a highly productive agricultural region. As of the 2010 census, the borough...
, were named after him. And along with his Letters from a Farmer in Pennsylvania
Letters from a Farmer in Pennsylvania
Letters from a Farmer in Pennsylvania is a series of essays written by the Pennsylvania lawyer and legislator John Dickinson and published under the name "A Farmer" from 1767 to 1768. The twelve letters were widely read and reprinted throughout the thirteen colonies, and were important in uniting...
, Dickinson also authored The Liberty Song
The Liberty Song
"The Liberty Song" is an American Revolutionary War song composed by patriot John Dickinson, the author of Letters from a Farmer in Pennsylvania. The song is set to the tunes of "Heart of Oak", the anthem of the Royal Navy of the United Kingdom and "Here's a Health", an Irish song of emigration...
.
Dickinson Street in Madison, Wisconsin
Madison, Wisconsin
Madison is the capital of the U.S. state of Wisconsin and the county seat of Dane County. It is also home to the University of Wisconsin–Madison....
is named in his honor.
Almanac
Delaware elections were held October 1 and members of the General Assembly took office on October 20 or the following weekday. The State Legislative Council was created in 1776 and its Legislative Councilmen had a three-year term. Beginning in 1792 it was renamed the State Senate. State Assemblymen had a one-year term. The whole General Assembly chose the State President for a three-year term.Pennsylvania elections were held in October as well. Assemblymen had a one-year term. The Pennsylvania Supreme Executive Council was created in 1776, and counsellors were popularly elected for three-year terms. A joint ballot of the Pennsylvania General Assembly and the Council chose the President from among the twelve Counsellors for a one-year term. Both Assemblies chose the Continental Congressmen for a one-year term as well as the delegates to the U.S. Constitution Convention.
{|class=wikitable style="width: 94%" style="text-align: center;" align="center"
|-bgcolor=#cccccc
!colspan=8 style="background: #ccccff;" | Public Offices
|-
! Office
! State
! Type
! Location
! Began office
! Ended office
! notes
|-
|Assemblyman
Delaware House of Representatives
The Delaware House of Representatives is the lower house of the Delaware General Assembly; the state legislature of the U.S. State of Delaware. It is composed of 41 Representatives from an equal amount of constituencies, each of whom is elected to a two year term. The Delaware General Assembly...
|Lower Counties
Delaware
Delaware is a U.S. state located on the Atlantic Coast in the Mid-Atlantic region of the United States. It is bordered to the south and west by Maryland, and to the north by Pennsylvania...
|Legislature
Legislature
A legislature is a kind of deliberative assembly with the power to pass, amend, and repeal laws. The law created by a legislature is called legislation or statutory law. In addition to enacting laws, legislatures usually have exclusive authority to raise or lower taxes and adopt the budget and...
|New Castle
New Castle, Delaware
New Castle is a city in New Castle County, Delaware, six miles south of Wilmington, situated on the Delaware River. In 1900, 3,380 people lived here; in 1910, 3,351...
|October 20, 1759
|October 20, 1760
|
|-
|Assemblyman
Delaware House of Representatives
The Delaware House of Representatives is the lower house of the Delaware General Assembly; the state legislature of the U.S. State of Delaware. It is composed of 41 Representatives from an equal amount of constituencies, each of whom is elected to a two year term. The Delaware General Assembly...
|Lower Counties
Delaware
Delaware is a U.S. state located on the Atlantic Coast in the Mid-Atlantic region of the United States. It is bordered to the south and west by Maryland, and to the north by Pennsylvania...
|Legislature
Legislature
A legislature is a kind of deliberative assembly with the power to pass, amend, and repeal laws. The law created by a legislature is called legislation or statutory law. In addition to enacting laws, legislatures usually have exclusive authority to raise or lower taxes and adopt the budget and...
|New Castle
New Castle, Delaware
New Castle is a city in New Castle County, Delaware, six miles south of Wilmington, situated on the Delaware River. In 1900, 3,380 people lived here; in 1910, 3,351...
|October 20, 1760
|October 20, 1761
|
|-
|Assemblyman
Pennsylvania House of Representatives
The Pennsylvania House of Representatives is the lower house of the bicameral Pennsylvania General Assembly, the legislature of the U.S. state of Pennsylvania. There are 203 members, elected for two year terms from single member districts....
|Pennsylvania
Pennsylvania
The Commonwealth of Pennsylvania is a U.S. state that is located in the Northeastern and Mid-Atlantic regions of the United States. The state borders Delaware and Maryland to the south, West Virginia to the southwest, Ohio to the west, New York and Ontario, Canada, to the north, and New Jersey to...
|Legislature
Legislature
A legislature is a kind of deliberative assembly with the power to pass, amend, and repeal laws. The law created by a legislature is called legislation or statutory law. In addition to enacting laws, legislatures usually have exclusive authority to raise or lower taxes and adopt the budget and...
|Philadelphia
Philadelphia, Pennsylvania
Philadelphia is the largest city in the Commonwealth of Pennsylvania and the county seat of Philadelphia County, with which it is coterminous. The city is located in the Northeastern United States along the Delaware and Schuylkill rivers. It is the fifth-most-populous city in the United States,...
|October 1762
|October 1763
|
|-
|Assemblyman
Pennsylvania House of Representatives
The Pennsylvania House of Representatives is the lower house of the bicameral Pennsylvania General Assembly, the legislature of the U.S. state of Pennsylvania. There are 203 members, elected for two year terms from single member districts....
|Pennsylvania
Pennsylvania
The Commonwealth of Pennsylvania is a U.S. state that is located in the Northeastern and Mid-Atlantic regions of the United States. The state borders Delaware and Maryland to the south, West Virginia to the southwest, Ohio to the west, New York and Ontario, Canada, to the north, and New Jersey to...
|Legislature
Legislature
A legislature is a kind of deliberative assembly with the power to pass, amend, and repeal laws. The law created by a legislature is called legislation or statutory law. In addition to enacting laws, legislatures usually have exclusive authority to raise or lower taxes and adopt the budget and...
|Philadelphia
Philadelphia, Pennsylvania
Philadelphia is the largest city in the Commonwealth of Pennsylvania and the county seat of Philadelphia County, with which it is coterminous. The city is located in the Northeastern United States along the Delaware and Schuylkill rivers. It is the fifth-most-populous city in the United States,...
|October 1763
|October 1764
|
|-
|Delegate
|Pennsylvania
Pennsylvania
The Commonwealth of Pennsylvania is a U.S. state that is located in the Northeastern and Mid-Atlantic regions of the United States. The state borders Delaware and Maryland to the south, West Virginia to the southwest, Ohio to the west, New York and Ontario, Canada, to the north, and New Jersey to...
|Legislature
Legislature
A legislature is a kind of deliberative assembly with the power to pass, amend, and repeal laws. The law created by a legislature is called legislation or statutory law. In addition to enacting laws, legislatures usually have exclusive authority to raise or lower taxes and adopt the budget and...
|New York
|October 7, 1765
|October 19, 1765
|Stamp Act Congress
Stamp Act Congress
The Stamp Act Congress was a meeting on October 19, 1765 in New York City of representatives from some of the British colonies of North America. They discussed and acted upon the Stamp Act recently passed by the governing Parliament of Great Britain overseas, which did not include any...
|-
|Delegate
|Pennsylvania
Pennsylvania
The Commonwealth of Pennsylvania is a U.S. state that is located in the Northeastern and Mid-Atlantic regions of the United States. The state borders Delaware and Maryland to the south, West Virginia to the southwest, Ohio to the west, New York and Ontario, Canada, to the north, and New Jersey to...
|Legislature
Legislature
A legislature is a kind of deliberative assembly with the power to pass, amend, and repeal laws. The law created by a legislature is called legislation or statutory law. In addition to enacting laws, legislatures usually have exclusive authority to raise or lower taxes and adopt the budget and...
|Philadelphia
Philadelphia, Pennsylvania
Philadelphia is the largest city in the Commonwealth of Pennsylvania and the county seat of Philadelphia County, with which it is coterminous. The city is located in the Northeastern United States along the Delaware and Schuylkill rivers. It is the fifth-most-populous city in the United States,...
|August 2, 1774
|October 26, 1774
|Continental Congress
Continental Congress
The Continental Congress was a convention of delegates called together from the Thirteen Colonies that became the governing body of the United States during the American Revolution....
|-
|Delegate
|Pennsylvania
Pennsylvania
The Commonwealth of Pennsylvania is a U.S. state that is located in the Northeastern and Mid-Atlantic regions of the United States. The state borders Delaware and Maryland to the south, West Virginia to the southwest, Ohio to the west, New York and Ontario, Canada, to the north, and New Jersey to...
|Legislature
Legislature
A legislature is a kind of deliberative assembly with the power to pass, amend, and repeal laws. The law created by a legislature is called legislation or statutory law. In addition to enacting laws, legislatures usually have exclusive authority to raise or lower taxes and adopt the budget and...
|Philadelphia
Philadelphia, Pennsylvania
Philadelphia is the largest city in the Commonwealth of Pennsylvania and the county seat of Philadelphia County, with which it is coterminous. The city is located in the Northeastern United States along the Delaware and Schuylkill rivers. It is the fifth-most-populous city in the United States,...
|March 16, 1775
|October 21, 1775
|Continental Congress
Continental Congress
The Continental Congress was a convention of delegates called together from the Thirteen Colonies that became the governing body of the United States during the American Revolution....
|-
|Delegate
|Pennsylvania
Pennsylvania
The Commonwealth of Pennsylvania is a U.S. state that is located in the Northeastern and Mid-Atlantic regions of the United States. The state borders Delaware and Maryland to the south, West Virginia to the southwest, Ohio to the west, New York and Ontario, Canada, to the north, and New Jersey to...
|Legislature
Legislature
A legislature is a kind of deliberative assembly with the power to pass, amend, and repeal laws. The law created by a legislature is called legislation or statutory law. In addition to enacting laws, legislatures usually have exclusive authority to raise or lower taxes and adopt the budget and...
|Philadelphia
Philadelphia, Pennsylvania
Philadelphia is the largest city in the Commonwealth of Pennsylvania and the county seat of Philadelphia County, with which it is coterminous. The city is located in the Northeastern United States along the Delaware and Schuylkill rivers. It is the fifth-most-populous city in the United States,...
|October 21, 1775
|November 7, 1776
|Continental Congress
Continental Congress
The Continental Congress was a convention of delegates called together from the Thirteen Colonies that became the governing body of the United States during the American Revolution....
|-
|Delegate
|Delaware
Delaware
Delaware is a U.S. state located on the Atlantic Coast in the Mid-Atlantic region of the United States. It is bordered to the south and west by Maryland, and to the north by Pennsylvania...
|Legislature
Legislature
A legislature is a kind of deliberative assembly with the power to pass, amend, and repeal laws. The law created by a legislature is called legislation or statutory law. In addition to enacting laws, legislatures usually have exclusive authority to raise or lower taxes and adopt the budget and...
|Philadelphia
Philadelphia, Pennsylvania
Philadelphia is the largest city in the Commonwealth of Pennsylvania and the county seat of Philadelphia County, with which it is coterminous. The city is located in the Northeastern United States along the Delaware and Schuylkill rivers. It is the fifth-most-populous city in the United States,...
|January 18, 1779
|December 22, 1779
|Continental Congress
Continental Congress
The Continental Congress was a convention of delegates called together from the Thirteen Colonies that became the governing body of the United States during the American Revolution....
|-
|Delegate
|Delaware
Delaware
Delaware is a U.S. state located on the Atlantic Coast in the Mid-Atlantic region of the United States. It is bordered to the south and west by Maryland, and to the north by Pennsylvania...
|Legislature
Legislature
A legislature is a kind of deliberative assembly with the power to pass, amend, and repeal laws. The law created by a legislature is called legislation or statutory law. In addition to enacting laws, legislatures usually have exclusive authority to raise or lower taxes and adopt the budget and...
|Philadelphia
Philadelphia, Pennsylvania
Philadelphia is the largest city in the Commonwealth of Pennsylvania and the county seat of Philadelphia County, with which it is coterminous. The city is located in the Northeastern United States along the Delaware and Schuylkill rivers. It is the fifth-most-populous city in the United States,...
|December 22, 1779
|February 10, 1781
|Continental Congress
Continental Congress
The Continental Congress was a convention of delegates called together from the Thirteen Colonies that became the governing body of the United States during the American Revolution....
|-
|Councilman
Delaware Senate
The Delaware Senate is the upper house of the Delaware General Assembly, the state legislature of the U.S. State of Delaware. It is composed of 21 Senators, each of whom is elected to a four-year term, except when reapportionment occurs, at which time Senators may be elected to a two-year term....
|Delaware
Delaware
Delaware is a U.S. state located on the Atlantic Coast in the Mid-Atlantic region of the United States. It is bordered to the south and west by Maryland, and to the north by Pennsylvania...
|Legislature
Legislature
A legislature is a kind of deliberative assembly with the power to pass, amend, and repeal laws. The law created by a legislature is called legislation or statutory law. In addition to enacting laws, legislatures usually have exclusive authority to raise or lower taxes and adopt the budget and...
|Dover
Dover, Delaware
The city of Dover is the capital and second largest city in the U.S. state of Delaware. It is also the county seat of Kent County, and the principal city of the Dover, Delaware Metropolitan Statistical Area, which encompasses all of Kent County. It is located on the St. Jones River in the Delaware...
|October 20, 1781
|November 13, 1781
|
|-
|State President
|Delaware
Delaware
Delaware is a U.S. state located on the Atlantic Coast in the Mid-Atlantic region of the United States. It is bordered to the south and west by Maryland, and to the north by Pennsylvania...
|Executive
Executive (government)
Executive branch of Government is the part of government that has sole authority and responsibility for the daily administration of the state bureaucracy. The division of power into separate branches of government is central to the idea of the separation of powers.In many countries, the term...
|Dover
Dover, Delaware
The city of Dover is the capital and second largest city in the U.S. state of Delaware. It is also the county seat of Kent County, and the principal city of the Dover, Delaware Metropolitan Statistical Area, which encompasses all of Kent County. It is located on the St. Jones River in the Delaware...
|November 13, 1781
|November 7, 1782
|Executive Council
Supreme Executive Council of the Commonwealth of Pennsylvania
The Supreme Executive Council of the Commonwealth of Pennsylvania comprised the executive branch of the Pennsylvania State government between 1777 and 1790...
|-
|State President
|Pennsylvania
Pennsylvania
The Commonwealth of Pennsylvania is a U.S. state that is located in the Northeastern and Mid-Atlantic regions of the United States. The state borders Delaware and Maryland to the south, West Virginia to the southwest, Ohio to the west, New York and Ontario, Canada, to the north, and New Jersey to...
|Executive
Executive (government)
Executive branch of Government is the part of government that has sole authority and responsibility for the daily administration of the state bureaucracy. The division of power into separate branches of government is central to the idea of the separation of powers.In many countries, the term...
|Philadelphia
Philadelphia, Pennsylvania
Philadelphia is the largest city in the Commonwealth of Pennsylvania and the county seat of Philadelphia County, with which it is coterminous. The city is located in the Northeastern United States along the Delaware and Schuylkill rivers. It is the fifth-most-populous city in the United States,...
|November 4, 1782
|October 18, 1785
|
|-
|Delegate
|Delaware
Delaware
Delaware is a U.S. state located on the Atlantic Coast in the Mid-Atlantic region of the United States. It is bordered to the south and west by Maryland, and to the north by Pennsylvania...
|Convention
Constitutional convention (political meeting)
A constitutional convention is now a gathering for the purpose of writing a new constitution or revising an existing constitution. A general constitutional convention is called to create the first constitution of a political unit or to entirely replace an existing constitution...
|Philadelphia
Philadelphia, Pennsylvania
Philadelphia is the largest city in the Commonwealth of Pennsylvania and the county seat of Philadelphia County, with which it is coterminous. The city is located in the Northeastern United States along the Delaware and Schuylkill rivers. It is the fifth-most-populous city in the United States,...
|May 14, 1787
|September 17, 1787
|U.S. Constitution
Philadelphia Convention
The Constitutional Convention took place from May 14 to September 17, 1787, in Philadelphia, Pennsylvania, to address problems in governing the United States of America, which had been operating under the Articles of Confederation following independence from...
|-
|Delegate
|Delaware
Delaware
Delaware is a U.S. state located on the Atlantic Coast in the Mid-Atlantic region of the United States. It is bordered to the south and west by Maryland, and to the north by Pennsylvania...
|Convention
Constitutional convention (political meeting)
A constitutional convention is now a gathering for the purpose of writing a new constitution or revising an existing constitution. A general constitutional convention is called to create the first constitution of a political unit or to entirely replace an existing constitution...
|Dover
Dover, Delaware
The city of Dover is the capital and second largest city in the U.S. state of Delaware. It is also the county seat of Kent County, and the principal city of the Dover, Delaware Metropolitan Statistical Area, which encompasses all of Kent County. It is located on the St. Jones River in the Delaware...
|November 29, 1791
|June 12, 1792
|State Constitution
Constitutional convention (political meeting)
A constitutional convention is now a gathering for the purpose of writing a new constitution or revising an existing constitution. A general constitutional convention is called to create the first constitution of a political unit or to entirely replace an existing constitution...
|-
|State Senator
Delaware Senate
The Delaware Senate is the upper house of the Delaware General Assembly, the state legislature of the U.S. State of Delaware. It is composed of 21 Senators, each of whom is elected to a four-year term, except when reapportionment occurs, at which time Senators may be elected to a two-year term....
|Delaware
Delaware
Delaware is a U.S. state located on the Atlantic Coast in the Mid-Atlantic region of the United States. It is bordered to the south and west by Maryland, and to the north by Pennsylvania...
|Legislature
Legislature
A legislature is a kind of deliberative assembly with the power to pass, amend, and repeal laws. The law created by a legislature is called legislation or statutory law. In addition to enacting laws, legislatures usually have exclusive authority to raise or lower taxes and adopt the budget and...
|Dover
Dover, Delaware
The city of Dover is the capital and second largest city in the U.S. state of Delaware. It is also the county seat of Kent County, and the principal city of the Dover, Delaware Metropolitan Statistical Area, which encompasses all of Kent County. It is located on the St. Jones River in the Delaware...
|January 6, 1793
|January 6, 1794
|
{|class=wikitable style="width: 94%" style="text-align: center;" align="center"
|-bgcolor=#cccccc
!colspan=7 style="background: #ccccff;" |Delaware General Assembly service
|-
! Dates
! Assembly
! Chamber
! Majority
! Governor
! Committees
! District
|-
|1781/82
|6th
Delaware General Assembly
The Delaware General Assembly is the legislature of the U.S. state of Delaware. It is a bicameral legislature composed of the Delaware Senate with 21 Senators and the Delaware House of Representatives with 41 Representatives...
|State House
Delaware House of Representatives
The Delaware House of Representatives is the lower house of the Delaware General Assembly; the state legislature of the U.S. State of Delaware. It is composed of 41 Representatives from an equal amount of constituencies, each of whom is elected to a two year term. The Delaware General Assembly...
|non-partisan
|Caesar Rodney
Caesar Rodney
Caesar Rodney was an American lawyer and politician from St. Jones Neck in Dover Hundred, Kent County, Delaware, east of Dover...
|
|Kent at-large
Kent County, Delaware
Kent County is a county located in the central part of the U.S. state of Delaware. It is coextensive with the Dover, Delaware, Metropolitan Statistical Area. As of 2010 the population was 162,310, a 28.1% increase over the previous decade. The county seat is Dover, the state capital...
|-
|1793
|17th
Delaware General Assembly
The Delaware General Assembly is the legislature of the U.S. state of Delaware. It is a bicameral legislature composed of the Delaware Senate with 21 Senators and the Delaware House of Representatives with 41 Representatives...
|State Senate
Delaware Senate
The Delaware Senate is the upper house of the Delaware General Assembly, the state legislature of the U.S. State of Delaware. It is composed of 21 Senators, each of whom is elected to a four-year term, except when reapportionment occurs, at which time Senators may be elected to a two-year term....
|Republican
Democratic-Republican Party (United States)
The Democratic-Republican Party or Republican Party was an American political party founded in the early 1790s by Thomas Jefferson and James Madison. Political scientists use the former name, while historians prefer the latter one; contemporaries generally called the party the "Republicans", along...
|Joshua Clayton
Joshua Clayton
Dr. Joshua Clayton was an American physician and politician from Mt. Pleasant in Pencader Hundred, New Castle County, Delaware. He was an officer of the Continental Army in the American Revolution, and a member of the Federalist Party, who served in the Delaware General Assembly, as Governor of...
|
|New Castle at-large
New Castle County, Delaware
New Castle County is the northernmost of the three counties of the U.S. state of Delaware. As of 2010 its population was 538,479, an increase of 7.6% over the previous decade. The county seat is Wilmington. The center of population of Delaware is located in New Castle County, in the town of...
Popular culture
Dickinson is a prominent character in the musical drama 17761776 (musical)
1776 is a musical with music and lyrics by Sherman Edwards and a book by Peter Stone. The story is based on the events surrounding the signing of the Declaration of Independence...
, billed third after the parts of Adams and Franklin. He was originally portrayed on stage by Paul Hecht
Paul Hecht
Paul Hecht is an English-born Canadian stage, film, and television actor best known for playing radio newsman Ross Buckingham in Howard Stern's Private Parts....
, and in the 1972 film adaptation by Donald Madden
Donald Madden
Donald Madden was an American theatre, television, and film actor best known for his role as John Dickinson in the film 1776 and his portrayal of Hamlet onstage in New York.-Life and career:...
. Michael Cumpsty
Michael Cumpsty
Michael Cumpsty is a British actor. He has been acting since childhood. He has worked extensively performing Shakespeare, as well as both musicals and dramas on Broadway...
portrayed him in the 1997 revival. His portrayal in this musical differs from reality: instead of abstaining from voting and debating, he acts as John Adams' primary antagonist in the debates over independence, to the point where the two men come to blows. His motivation in the musical is to convince the delegates to come to peace terms with the mother country.
In Part II of the 2008 HBO series John Adams
John Adams (TV miniseries)
John Adams is a 2008 American television miniseries chronicling most of President John Adams's political life and his role in the founding of the United States. Paul Giamatti portrays John Adams. The miniseries was directed by Tom Hooper. Kirk Ellis wrote the screenplay based on the book John...
, based on the book by David McCullough
David McCullough
David Gaub McCullough is an American author, narrator, historian, and lecturer. He is a two-time winner of the Pulitzer Prize and the National Book Award and a recipient of the Presidential Medal of Freedom, the United States' highest civilian award....
, the part of Dickinson is played by Zeljko Ivanek
Željko Ivanek
Željko Ivanek is an Emmy award-winning Slovenian American actor best known for his role as Ray Fiske on Damages. He is also known for playing Blake Sterling on short-lived NBC series The Event and Emile Danko on Heroes....
.
See also
- U.S. Constitution, slavery debate in Convention, executive debates
External links
- Biographical Directory of the United States Congress
- Delaware's Governors
- Delmarva Heritage Series
- Revolution to Reconstruction
- Soldier-Statesmen of the Constitution
- University of Pennsylvania Archives
- ExplorePAHistory.com
- The R.R. Logan Collection of John Dickinson Papers are available for research use at the Historical Society of PennsylvaniaHistorical Society of PennsylvaniaThe Historical Society of Pennsylvania is a historical society founded in 1824 and based in Philadelphia. The Society's building, designed by Addison Hutton and listed on Philadelphia's Register of Historical Places, houses some 600,000 printed items and over 19 million manuscript and graphic items...
.
Places with more information
- Delaware Historical SocietyDelaware Historical SocietyThe Delaware Historical Society began in 1864 as an effort to preserve documents from the Civil War. Since then, it has expanded into a state-wide historical institution with several venues and a major museum in Wilmington and the historic Read House & Gardens in New Castle.The society...
; website; 505 North Market Street, Wilmington, Delaware 19801; (302) 655-7161 - University of DelawareUniversity of DelawareThe university is organized into seven colleges:* College of Agriculture and Natural Resources* College of Arts and Sciences* Alfred Lerner College of Business and Economics* College of Earth, Ocean and Environment* College of Education and Human Development...
; Library website; 181 South College Avenue, Newark, Delaware 19717; (302) 831-2965 - Historical Society of PennsylvaniaHistorical Society of PennsylvaniaThe Historical Society of Pennsylvania is a historical society founded in 1824 and based in Philadelphia. The Society's building, designed by Addison Hutton and listed on Philadelphia's Register of Historical Places, houses some 600,000 printed items and over 19 million manuscript and graphic items...
; website; 1300 Locust Street, Philadelphia, Pennsylvania; (215) 732-6200 - John Dickinson Plantation; website; 340 Kitts Hummock Road, Dover, Delaware (302) 739-3277
- Wilmington Quaker Meeting House (burial site); 401 North West Street, Wilmington, Delaware; (302) 652-4491

