J curve
Encyclopedia
The term J-curve is used in several different fields to refer to a variety of unrelated J-shaped diagrams where a curve initially falls, but then rises to higher than the starting point.
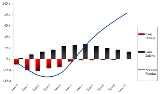
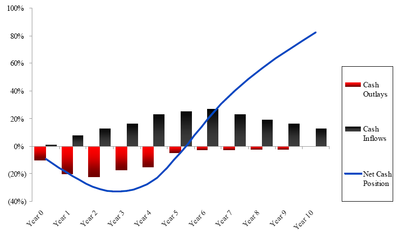 In private equity
In private equity
, the J curve is used to illustrate the historical tendency of private equity fund
s to deliver negative returns in early years and investment gains in the outlying years as the portfolios of companies mature.
In the early years of the fund, a number of factors contribute to negative returns including management fees, investment costs and under-performing investments that are identified early and written down. Over time the fund will begin to experience unrealized gains followed eventually by events in which gains are realized (e.g., IPOs, mergers and acquisitions
, leveraged recapitalization
s).
Historically, the J-Curve effect has been more pronounced in the US, where private equity firms tend to carry their investments at the lower of market value or investment cost and have been more aggressive in writing down investments than in writing up investments. As a result, the carrying value of any investment that is underperforming will be written down but the carrying value of investments that are performing well tend to be recognized only when there is some kind of event that forces the private equity firm
to mark up the investment.
The steeper the positive part of the J curve, the quicker cash is returned to investors. A private equity firm that can make quick returns to investors provides investors with the opportunity to reinvest that cash elsewhere. Of course, with a tightening of credit markets, private equity firms have found it harder to sell businesses they previously invested in. Proceeds to investors have reduced. J curves have flattened dramatically. This leaves investors with less cash flow to invest elsewhere. For example, in other private equity firms. The implications for private equity could well be severe. Being unable to sell businesses to generate proceeds and fees means some in the industry have predicted consolidation amongst private equity firms.
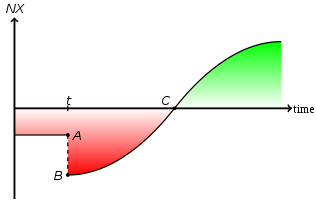 In economics
In economics
, the 'J curve' refers to the trend of a country’s trade balance following a devaluation
or depreciation
under a certain set of assumptions. A devalued currency
means imports are more expensive, and on the assumption that the volume of imports and exports change little immediately, this causes a depreciation of the current account
(a bigger deficit or smaller surplus). After some time, though, the volume of exports may start to rise because of their lower more competitive prices to foreign buyers, and domestic consumers may buy fewer of the costlier imports. Eventually, if this happens, the trade balance may improve on what it was before the devaluation. If there is a currency revaluation
or appreciation
the same reasoning leads to an inverted J-curve.
Immediately following the depreciation or devaluation of the currency, the volume of imports and exports may remain largely unchanged due in part to pre-existing trade contracts that have to be honoured. Moreover, in the short run, demand for the more expensive imports (and demand for exports, which are cheaper to foreign buyers using foreign currencies) remain price inelastic. This is due to time lags in the consumer's search for acceptable, cheaper alternatives (which might not exist).
Over the longer term a depreciation in the exchange rate can have the desired effect of improving the current account balance. Domestic consumers might switch their expenditure to domestic products and away from expensive imported goods and services, assuming equivalent domestic alternatives exist. Equally, many foreign consumers may switch to purchasing the products being exported into their country, which are now cheaper in the foreign currency, instead of their own domestically produced goods and services.
Empirical investigations of the J-curve have sometimes focused on the effect of exchange rate changes on the trade ratio, i.e. exports divided by imports, rather than the trade balance, exports minus imports. Unlike the trade balance, the trade ratio can be logged
regardless of whether a trade deficit or trade surplus exists.
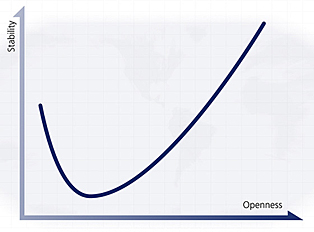 Another 'J-Curve' refers to the correlation between stability and openness. This theory was suggested initially by the author Ian Bremmer
Another 'J-Curve' refers to the correlation between stability and openness. This theory was suggested initially by the author Ian Bremmer
, in his book The J Curve: A New Way to Understand Why Nations Rise and Fall
.
The x-axis of the political J-Curve graph measures the 'openness' of the economy in question and the y-axis measures the stability of that same state. It suggests that those states that are 'closed'/undemocratic/unfree (such as the Communist dictatorships of North Korea
and Cuba
) are very stable; however, as one progresses right, along the x-axis, it is evident that stability (for relatively short period of time in the lengthy life of nations) decreases, creating a dip in the graph, until beginning to pick up again as the 'openness' of a state increases; at the other end of the graph to closed states are the open states of the West
, such as the United States of America or the United Kingdom
. Thus, a J-shaped curve is formed.
States can travel both forward (right) and backwards (left) along this J-curve, and so stability and openness are never secure. The J is steeper on the left hand side, as it is easier for a leader in a failed state to create stability by closing the country than to build a civil society and establish accountable institutions; the curve is higher on the far right than left because states that prevail in opening their societies (Eastern Europe
, for example) ultimately become more stable than authoritarian regimes.
Bremmer's entire curve can shift up or down depending on economic resources available to the government in question. So Saudi Arabia
's relative stability at every point along the curve rises or falls depending on the price of oil; China
's curve analogously depends on the country's economic growth.
, the 'J-curve' is part of a model developed by James Chowning Davies
to explain political revolution
s. Davies asserts that revolutions are a subjective response to a sudden reversal in fortunes after a long period of economic growth, which is known as relative deprivation. Relative deprivation theory claims that frustrated expectations help overcome the collective action problem, which in this case may breed revolt. Frustrated expectations could result from several factors, including growing levels of inequality within a country, which may mean those who are increasingly poor relative to the rich are getting less than they expected, or a period of sustained economic development, lifting general expectations, followed by a crisis.
This model is often applied to explain social unrest and efforts by governments to contain this unrest. This is referred to as the Davies' J-Curve, because economic development followed by a depression would be modeled as an upside down and slightly skewed J.

Private equity
Private equity, in finance, is an asset class consisting of equity securities in operating companies that are not publicly traded on a stock exchange....
, the J curve is used to illustrate the historical tendency of private equity fund
Private equity fund
A private equity fund is a collective investment scheme used for making investments in various equity securities according to one of the investment strategies associated with private equity....
s to deliver negative returns in early years and investment gains in the outlying years as the portfolios of companies mature.
In the early years of the fund, a number of factors contribute to negative returns including management fees, investment costs and under-performing investments that are identified early and written down. Over time the fund will begin to experience unrealized gains followed eventually by events in which gains are realized (e.g., IPOs, mergers and acquisitions
Mergers and acquisitions
Mergers and acquisitions refers to the aspect of corporate strategy, corporate finance and management dealing with the buying, selling, dividing and combining of different companies and similar entities that can help an enterprise grow rapidly in its sector or location of origin, or a new field or...
, leveraged recapitalization
Leveraged recapitalization
In corporate finance, a leveraged recapitalization is a change of the capital structure of a company, a substitution of equity for debt —e.g. by issuing bonds to raise money, and using that money to buy the company's stock or to pay dividends...
s).
Historically, the J-Curve effect has been more pronounced in the US, where private equity firms tend to carry their investments at the lower of market value or investment cost and have been more aggressive in writing down investments than in writing up investments. As a result, the carrying value of any investment that is underperforming will be written down but the carrying value of investments that are performing well tend to be recognized only when there is some kind of event that forces the private equity firm
Private equity firm
A private equity firm is an investment manager that makes investments in the private equity of operating companies through a variety of loosely affiliated investment strategies including leveraged buyout, venture capital, and growth capital...
to mark up the investment.
The steeper the positive part of the J curve, the quicker cash is returned to investors. A private equity firm that can make quick returns to investors provides investors with the opportunity to reinvest that cash elsewhere. Of course, with a tightening of credit markets, private equity firms have found it harder to sell businesses they previously invested in. Proceeds to investors have reduced. J curves have flattened dramatically. This leaves investors with less cash flow to invest elsewhere. For example, in other private equity firms. The implications for private equity could well be severe. Being unable to sell businesses to generate proceeds and fees means some in the industry have predicted consolidation amongst private equity firms.
Balance of trade model

Economics
Economics is the social science that analyzes the production, distribution, and consumption of goods and services. The term economics comes from the Ancient Greek from + , hence "rules of the house"...
, the 'J curve' refers to the trend of a country’s trade balance following a devaluation
Devaluation
Devaluation is a reduction in the value of a currency with respect to those goods, services or other monetary units with which that currency can be exchanged....
or depreciation
Depreciation
Depreciation refers to two very different but related concepts:# the decrease in value of assets , and# the allocation of the cost of assets to periods in which the assets are used ....
under a certain set of assumptions. A devalued currency
Currency
In economics, currency refers to a generally accepted medium of exchange. These are usually the coins and banknotes of a particular government, which comprise the physical aspects of a nation's money supply...
means imports are more expensive, and on the assumption that the volume of imports and exports change little immediately, this causes a depreciation of the current account
Current account
In economics, the current account is one of the two primary components of the balance of payments, the other being the capital account. The current account is the sum of the balance of trade , net factor income and net transfer payments .The current account balance is one of two major...
(a bigger deficit or smaller surplus). After some time, though, the volume of exports may start to rise because of their lower more competitive prices to foreign buyers, and domestic consumers may buy fewer of the costlier imports. Eventually, if this happens, the trade balance may improve on what it was before the devaluation. If there is a currency revaluation
Revaluation
Revaluation means a rise of a price of goods or products. This term is specially used as revaluation of a currency, where it means a rise of currency to the relation with a foreign currency in a fixed exchange rate. In floating exchange rate correct term would be appreciation. The antonym of...
or appreciation
Appreciation
In accounting, appreciation of an asset is an increase in its value. In this sense it is the reverse of depreciation, which measures the fall in value of assets over their normal life-time...
the same reasoning leads to an inverted J-curve.
Immediately following the depreciation or devaluation of the currency, the volume of imports and exports may remain largely unchanged due in part to pre-existing trade contracts that have to be honoured. Moreover, in the short run, demand for the more expensive imports (and demand for exports, which are cheaper to foreign buyers using foreign currencies) remain price inelastic. This is due to time lags in the consumer's search for acceptable, cheaper alternatives (which might not exist).
Over the longer term a depreciation in the exchange rate can have the desired effect of improving the current account balance. Domestic consumers might switch their expenditure to domestic products and away from expensive imported goods and services, assuming equivalent domestic alternatives exist. Equally, many foreign consumers may switch to purchasing the products being exported into their country, which are now cheaper in the foreign currency, instead of their own domestically produced goods and services.
Empirical investigations of the J-curve have sometimes focused on the effect of exchange rate changes on the trade ratio, i.e. exports divided by imports, rather than the trade balance, exports minus imports. Unlike the trade balance, the trade ratio can be logged
Logarithm
The logarithm of a number is the exponent by which another fixed value, the base, has to be raised to produce that number. For example, the logarithm of 1000 to base 10 is 3, because 1000 is 10 to the power 3: More generally, if x = by, then y is the logarithm of x to base b, and is written...
regardless of whether a trade deficit or trade surplus exists.
Country status model
 Another 'J-Curve' refers to the correlation between stability and openness. This theory was suggested initially by the author Ian Bremmer
Another 'J-Curve' refers to the correlation between stability and openness. This theory was suggested initially by the author Ian BremmerIan Bremmer
Ian Bremmer is an American political scientist specializing in US foreign policy, states in transition, and global political risk. He is the president and founder of Eurasia Group, a leading global political risk research and consulting firm...
, in his book The J Curve: A New Way to Understand Why Nations Rise and Fall
The J Curve: A New Way to Understand Why Nations Rise and Fall
The J Curve: A New Way to Understand Why Nations Rise and Fall is a book by political scientist Ian Bremmer. It was named a "Book of the Year" in 2006 by The Economist....
.
The x-axis of the political J-Curve graph measures the 'openness' of the economy in question and the y-axis measures the stability of that same state. It suggests that those states that are 'closed'/undemocratic/unfree (such as the Communist dictatorships of North Korea
North Korea
The Democratic People’s Republic of Korea , , is a country in East Asia, occupying the northern half of the Korean Peninsula. Its capital and largest city is Pyongyang. The Korean Demilitarized Zone serves as the buffer zone between North Korea and South Korea...
and Cuba
Cuba
The Republic of Cuba is an island nation in the Caribbean. The nation of Cuba consists of the main island of Cuba, the Isla de la Juventud, and several archipelagos. Havana is the largest city in Cuba and the country's capital. Santiago de Cuba is the second largest city...
) are very stable; however, as one progresses right, along the x-axis, it is evident that stability (for relatively short period of time in the lengthy life of nations) decreases, creating a dip in the graph, until beginning to pick up again as the 'openness' of a state increases; at the other end of the graph to closed states are the open states of the West
Western world
The Western world, also known as the West and the Occident , is a term referring to the countries of Western Europe , the countries of the Americas, as well all countries of Northern and Central Europe, Australia and New Zealand...
, such as the United States of America or the United Kingdom
United Kingdom
The United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern IrelandIn the United Kingdom and Dependencies, other languages have been officially recognised as legitimate autochthonous languages under the European Charter for Regional or Minority Languages...
. Thus, a J-shaped curve is formed.
States can travel both forward (right) and backwards (left) along this J-curve, and so stability and openness are never secure. The J is steeper on the left hand side, as it is easier for a leader in a failed state to create stability by closing the country than to build a civil society and establish accountable institutions; the curve is higher on the far right than left because states that prevail in opening their societies (Eastern Europe
Eastern Europe
Eastern Europe is the eastern part of Europe. The term has widely disparate geopolitical, geographical, cultural and socioeconomic readings, which makes it highly context-dependent and even volatile, and there are "almost as many definitions of Eastern Europe as there are scholars of the region"...
, for example) ultimately become more stable than authoritarian regimes.
Bremmer's entire curve can shift up or down depending on economic resources available to the government in question. So Saudi Arabia
Saudi Arabia
The Kingdom of Saudi Arabia , commonly known in British English as Saudi Arabia and in Arabic as as-Sa‘ūdiyyah , is the largest state in Western Asia by land area, constituting the bulk of the Arabian Peninsula, and the second-largest in the Arab World...
's relative stability at every point along the curve rises or falls depending on the price of oil; China
China
Chinese civilization may refer to:* China for more general discussion of the country.* Chinese culture* Greater China, the transnational community of ethnic Chinese.* History of China* Sinosphere, the area historically affected by Chinese culture...
's curve analogously depends on the country's economic growth.
Medicine
In medicine, the 'J-curve' refers to a graph in which the x-axis measures either of two treatable symptoms (blood pressure or blood cholesterol level) while the y-axis measures the chance that a patient will develop cardiovascular disease (CVD). It is well known that high blood pressure or high cholesterol levels increase a patient's risk. What is less well known is that plots of large populations against CVD mortality often takes the shape of a J curve which indicates that patients with very low blood pressure and/or low cholesterol levels are also at increased risk.Political science (Model of revolutions)
In political sciencePolitical science
Political Science is a social science discipline concerned with the study of the state, government and politics. Aristotle defined it as the study of the state. It deals extensively with the theory and practice of politics, and the analysis of political systems and political behavior...
, the 'J-curve' is part of a model developed by James Chowning Davies
James Chowning Davies
James Chowning Davies is an American sociologist and professor emeritus of political science at the University of Oregon. Davies is perhaps best known for his so-called "J curve" theory of political revolutions, which seeks to explain the rise of revolutionary movements in terms of rising...
to explain political revolution
Revolution
A revolution is a fundamental change in power or organizational structures that takes place in a relatively short period of time.Aristotle described two types of political revolution:...
s. Davies asserts that revolutions are a subjective response to a sudden reversal in fortunes after a long period of economic growth, which is known as relative deprivation. Relative deprivation theory claims that frustrated expectations help overcome the collective action problem, which in this case may breed revolt. Frustrated expectations could result from several factors, including growing levels of inequality within a country, which may mean those who are increasingly poor relative to the rich are getting less than they expected, or a period of sustained economic development, lifting general expectations, followed by a crisis.
This model is often applied to explain social unrest and efforts by governments to contain this unrest. This is referred to as the Davies' J-Curve, because economic development followed by a depression would be modeled as an upside down and slightly skewed J.

