
Italy in the Middle Ages
Encyclopedia
This is the history of Italy
during the Middle Ages
.
in 410. The (traditional) last Western Roman Emperor
, Romulus Augustus
, was deposed in 476 by an Eastern Germanic general, Odoacer
. He subsequently ruled in Italy for seventeen years as rex gentium, theoretically under the suzerainty of the Eastern Roman Emperor Zeno
, but practically in total independence. The administration remained essentially the same as that under the Western Roman Empire, and gave religious freedoms to the Christians. Odoacer fought against the Vandals, who had occupied Sicily
, and other Germanic tribes that periodically invaded the peninsula.
In 489, however, Emperor Zeno decided to oust the Ostrogoths, a foederatum people living in the Danube, by sending them into Italy. On February 25, 493 Theodoric the Great
defeated Odoacer and became the king of the Ostrogoths. Theodoric, who had lived long in Constantinople, is now generally considered a Romanized German, and he in fact ruled over Italy largely through Roman personnel. The Goth minority, of Arian
confession, constituted an aristocracy of landowners and militaries, but its influence over the country remained minimal; the Latin population was still subject to Roman laws, and maintained the freedom of creed received by Odoacer. The reign of Theodoric is generally considered a period of recovery for the country. Infrastructures were repaired, frontiers were expanded, and the economy well cared for. The Latin culture flourished for the last time with figures like Boethius
, Theodoric's minister; the Italian Kingdom was again the most powerful political entity of the Mediterranean. However, Theodoric's successors were not equal to him.
The eastern half of the Empire
, now centred on Constantinople
, invaded Italy in the early 6th century, and the generals of emperor Justinian
, Belisarius
and Narses
, conquered the Ostrogothic kingdom after years of warfare, ending in 552. This conflict, known as Gothic Wars, destroyed much of the town life that had survived the barbarian invasions. Town life did not disappear, but they became smaller and considerably more primitive than they had been in Roman times. Subsistence agriculture employed the bulk of the Italian population. Wars, famines, and disease epidemics had a dramatic effect on the demographics of Italy.
The agricultural estates of the Roman
era did not disappear. They produced an agricultural surplus that was sold in towns; however slavery was replaced by other labour systems such as serfdom
.
The withdrawal of Byzantine armies allowed another Germanic people, the Lombards
, to invade Italy. Cividale del Friuli
was the first main centre to fall, while the Byzantine resistance concentrated in the coast areas. The Lombards soon overran most of the peninsula, establishing a Kingdom with capital in Pavia
, divided into a series of dukedoms. The areas in central-northern Italy which remained under Byzantine control (mostly the current Lazio and Romagna
, plus a short corridor between Umbria that connected them, as well as Liguria
) became the Exarchate of Ravenna
. Southern Italy, with the exception of Apulia
, current Calabria
and Sicily, were also occupied by the two semi-independent Lombard duchies of Spoleto
and Benevento
. Under the Imperial authority remained also much of the ports, which eventually turned into actually independent city-states (Gaeta
, Naples
, Venice
, Amalfi
).
of Rome
, the pope
) had played an important political role since the times of Constantine, who tried to include it in the imperial administration.
In the politically unstable situation after the fall of the western empire, the Church often became the only stable institution and the only source of learning. Even the barbarians had to rely on clerics in order to administer their conquests. Furthermore, the Catholic monastic orders
, such as the Benedictine
s had a major role both in the economic life of the time, and in the preservation of the classical
culture
.
After the Lombard invasion, the popes (i.e. St. Gregory
, St. Peter, and St. Mark
) were nominally subject to the eastern emperor, but often received little help from Constantinople, and had to fill the lack of stately power, providing essential services (ex. food for the needy) and protecting Rome from Lombard incursions; in this way, the popes started building an independent state.
.
In 751 the Lombards seized Ravenna and the Exarchate of Ravenna
was abolished. This ended the Byzantine presence in central Italy (although some coastal cities and some areas in south Italy remained under Byzantine control until the eleventh century). Facing a new Lombard offensive, the papacy appealed to the Franks
for aid. In 756 Frankish forces defeated the Lombards and gave the Papacy legal authority over all of central Italy, thus creating the Papal States
. However, the remainder of Italy stayed under Lombard or Byzantine control.
received papal support. Later, on December 25, 800, Charlemagne was also crowned emperor of the Holy Roman Empire
by the pope, triggering controversy and disputes over the Roman name
. A war between the two empires soon followed; in 812 the Byzantines agreed to recognize the existence of two Roman Empires in return for an assurance that the remaining Byzantine possessions in Italy would be uncontested.
Throughout this period, some coastal regions, and all of southern Italy, remained under Byzantine or Lombard control. The Imperial authority never extended much south of the Italian Peninsula
. Southern Italy was divided amongst the two Lombards duchies of Spoleto
and Benevento
, who accepted Charlemagne's suzerainty only formally (812), and the Byzantine Empire
. Coastal cities like Gaeta
, Amalfi
, Naples
on the Tyrrhenian Sea
, and Venice
on the Adriatic Sea
, were Latin-Greek enclaves who were becoming increasingly independent from Byzantium. A conquest of Benevento, otherwise, would have meant the total encompassment of the Papal territories, and probably Charlemagne thought it was good for his relationships with the Pope to avoid such a move. The age of Charlemagne was one of stability for Italy, though it was generally dominated by non-Italian interests. The separation with the Eastern world continued to increase. Leo III
was the first Pope to date his Bulls from the year of Charlemagne's reign (795) instead of those of Byzantine emperors. This process of isolation from the Eastern Empire and connection with the Western world of France and Germany, which had started three centuries before, was completed at the beginning of the 9th centuries. Sicily, Calabria, Puglia and the marine cities were the main exceptions to this rule.
After the death of Charlemagne (814) the new empire soon disintegrated under his weak successors. The equilibrium created through the great emperor's charisma fell apart. This crisis was due also to the emergence of external forces, including the Saracen
attacks and the rising power of the marine republics. Charlemagne had announced his division of the Empire in 806: the Lombard-Frank reign, together with Bavaria
and Alamannia
, was to be handed over to his son Pepin of Italy.
After Charlemagne's son Louis the Pious
died in 840, the treaty of Verdun
in 843 divided the empire. Louis' eldest surviving son Lothair I
became Emperor and ruler of the Central Franks. His three sons in turn divided this kingdom between them, and Northern Italy became the Kingdom of Italy under Louis II, Holy Roman Emperor in 839.
The first half of the 9th century saw other troubles for Italy as well. In 827, Muslim
Arab
s known as Aghlabid
s invaded and conquered Sicily
; their descendants, the Kalbids
, ruled the island until 1053. In 846, Muslim Arabs invaded Rome
, looted St. Peter's Basilica
, and stole all the gold and silver in it. In response, Pope Leo IV
started building the Leonine walls
of the Vatican City
in 847; they were completed in 853. In the late ninth century the Byzantines and the Franks launched a joint offensive against the Arabs in southern Italy; however, only the Byzantines won any territory in that campaign.
, proclaimed himself a sovereign prince and set about opposing Charlemagne's assumption of Lombard kingship.
reached its territorial peak under Sicard
in the 830s. At his time, the Mezzogiorno was suffering the ravages of the Saracen
s, against whom Sicard warred constantly. He also warred against his Greek neighbours, especially Sorrento
, Naples
, and Amalfi
. It was in a war with Naples that Duke Andrew II
first called in Saracen
mercenaries
.
In 839, Sicard was assassinated and a civil war broke out which illustrated the nature of political power in the south. It was still largely in the hands of the land-owning aristocracy, who had the power to choose a prince. In 839, some chose Radelchis I
, the treasurer and assassin, and some chose Siconulf of Salerno
, who was installed at Salerno
. This civil war continued apace for a decade, during which the gastaldates of Benevento took the opportunity to entrench their independence, especially Capua
, which sided with Siconulf. In 849, the Emperor Louis II, in one of his first acts as King of Italy, invaded the peninsula and imposed peace between the Lombard factions. He divided the principality into two: one at Benevento, one at Salerno. Thenceforward, the history of the Lombard south is one of declining, competing powers.
 In the Tyrrhenian
In the Tyrrhenian
Greek cities, the violence raging inland, between them and their fellow Greeks on toe and heel, fostered the circumstances of de facto independence. Naples, in particular, had a history of differences with Byzantium and had in the past sought to make herself dependent on other authorities, often papal. In 801, the Byzantine patrician
of Sicily succeeded in creating Anthimus
duke. However, Anthimus was unable to control the cities under his rule, Gaeta and Amalfi. Subsequent to Anthimus, the patrician tried to appoint his own candidate without imperial approval. The people rebelled and accepted Stephen III
in 821. During Stephen's decade of rule, Naples severed all legal ties to Constantinople and even began minting her own coins. In 840, after a brief flirtation with Frankish servitude, to Lothair I
, and a Frankish duke, in the person of Duke Contard
, the Neapolitan citizenry elected Sergius I
their magister militum
. Sergius established a dynasty, the Sergi
, that was to rule the duchy for the next three hundred years.
In Gaeta, as in Naples, the violent situation inland required new power structures to maintain Byzantine authority. The Gaetans received their first imperial Byzantine hypati
around the time of the Beneventan civil war. While the first hypati remained Byzantine loyals, in 866, the sudden appearance of a new dynasty under Docibilis I
represented Gaeta's move from Byzantium towards independence. The first elected ruler of Amalfi was a prefect
appearing in 839, simultaneous with the death of Sicard and the appearance of a Gaetan hyaptus. However, Naples, Gaeta, Amalfi, the Tyrrhenian cities, and Venice (in North Italy) retained some allegiance to Byzantium until the eleventh century-long after becoming de facto independent.
in 853 and destabilised that principality until a new dynasty, the Dauferidi, came to power in 861.
 In 852, the Saracens took Bari
In 852, the Saracens took Bari
and founded an emirate
there. Greek power being significantly threatened, as well as Adriatic commerce, the Byzantine emperor requested an alliance from Louis II of Italy. Similarly, the new prince of Benevento, Adelchis
, an independent-minded ruler, also sought his aid. Louis came down and retook Bari in 871 after a great siege. Louis then tried to set up greater control over all the south by garrisoning his troops in Beneventan fortresses. The response of Adelchis to this action was to imprison and rob the emperor while he was staying the princely palace at Benevento. A month later, the Saracens had landed with a new invasive force and Adelchis released Louis to lead the armies against it. Adelchis forced Louis to vow never to re-enter Benevento with an army or to take revenge for his detention. Louis went to Rome in 872 and was released from his oath by Pope Adrian II
on 28 May. His attempts to punish Adelchis were not very successful. Adelchis vacillated between nominal fealty to the Carolingian and Byzantine emperors, but, in fact, by his alterations to the Edictum Rothari
, he acknowledged himself as the legitimate Lombard "king."
The successors of Adelchis were weak and the principality of Benevento declined just as Salernitan power was beginning to make itself felt. Guaifer of Salerno
was on friendly terms with the Saracens, a habit which annoyed the popes and often put a ruler at odds with his neighbours. The south Italian lords continually rotating in their allegiances. Guaifer's successor, Guaimar I
, made war on the Saracens. Guaifer had originally associated Guaimar with him as co-ruler, a practice which became endemic to the south and was especially evident in Capua.
, Venice
, Pisa
, Genoa
, Ancona
and Gaeta
became major powers. The papacy regained its authority, and started a long struggle with the empire, about both ecclesiastical and secular matter. The first episode was the Investiture Controversy
. In the twelfth century those Italian cities which lay in the Holy Roman Empire launched a successful effort to win autonomy from the Holy Roman Empire
(see Lombard League
); this made north Italy a land of quasi-independent or independent city-states until the nineteenth century (see Italian city-states
and history of every city). The revolts were funded by Byzantium, which hoped to expel the Germans from Italy; this sponsorship was, like the invasion of the South, part of a twelfth-century Byzantine effort to regain the influence it had held on the peninsula during the reign of Justinian.
Meanwhile, the South and Sicily were invaded by Normans
, who eventually conquered what remained of the Byzantine holdings in mainland Italy along with the Arab
possessions in Sicily (see Kingdom of Sicily
).
In the eleventh century, the Normans
occupied
the Lombard and Byzantine possessions in Southern Italy, ending the six century old presence of both powers in the peninsula. The independent city-states were also subdued. During the same century, the Normans also ended Muslim rule in Sicily. Norman rule in what had once been Byzantine territory naturally angered Byzantium, which in 1155 made a last attempt under the Emperor Manuel I Komnenos
to reassert its authority in Southern Italy. But the attempt failed, and in 1158 the Byzantines left Italy.
Unlike the Norman conquest of England
(1066), which took place over the course of a few years after one decisive battle, the conquest of Southern Italy was the product of decades and many battles, few decisive. Many territories were conquered independently, and only later were all unified into one state. Compared to the conquest of England, it was unplanned and unorganised, but just as permanent.
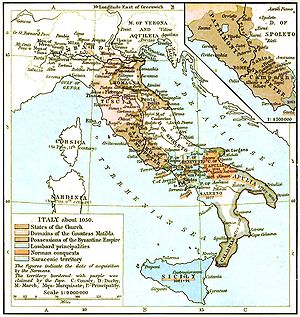 In 951? the thrones of Italy and Germany were united. The ruler of the new realm, Otto I
In 951? the thrones of Italy and Germany were united. The ruler of the new realm, Otto I
, claimed that the union revived the empire of Charlemagne
and received the title of Holy Roman Emperor
in 962.
Even the papacy went through an age of decadence, which ended only in 999 when emperor Otto III
selected Silvester II as pope.
, Byzantine power experienced a recovery; and the impact of this was felt in southern Italy. During the late ninth century the amount of territory under direct Byzantine rule (which in the early ninth century was limited to the toe and heel of the peninsula) expanded dramatically. The Catepanate of Italy was set up to administer the newly-acquired territory. The rest of Southern Italy remained divided among the Lombard kings and the Italian cities. Both sets of principalities were de-facto independent, but paid nominal allegiance to Byzantium.
The Byzantine gains in the southern Italian mainland were, however, accompanied by setbacks in Sicily. In 878 the Arabs captured the crucial city of Syracuse, and by 902 the entire island was under Arab rule.
and Sicily
in the south, the Papal States
in Central Italy, and the Maritime republics in the north.
The Duchy of Milan
found itself in the focus of European power politics in the 15th century, leading to the drawn-out Italian Wars
, which persisted for the best part of the 16th century before giving way to the Early Modern period in Italy.
The Italian Renaissance
originatesin 14th-century Tuscany
, centered in the cities of Florence
and Siena
. It later had a great impact in Venice
, where the remains of ancient Greek culture
were brought together, providing humanist
scholars with new texts. The Renaissance later had a significant effect on Rome
, which was ornamented with some structures in the new all'antico mode, then was largely rebuilt by humanist sixteenth-century pope
s.
The Italian Renaissance peaked in the mid-16th century as foreign invasions plunged the region into the turmoil of the Italian Wars
. However, the ideas and ideals of the Renaissance endured and even spread into the rest of Europe, setting off the Northern Renaissance
, and the English Renaissance
.
History of Italy
Italy, united in 1861, has significantly contributed to the political, cultural and social development of the entire Mediterranean region. Many cultures and civilizations have existed there since prehistoric times....
during the Middle Ages
Middle Ages
The Middle Ages is a periodization of European history from the 5th century to the 15th century. The Middle Ages follows the fall of the Western Roman Empire in 476 and precedes the Early Modern Era. It is the middle period of a three-period division of Western history: Classic, Medieval and Modern...
.
Transition from Late Antiquity (6th to 8th centuries)
Italy was invaded by the Visigoths in the 5th century, and Rome was sacked by AlaricAlaric I
Alaric I was the King of the Visigoths from 395–410. Alaric is most famous for his sack of Rome in 410, which marked a decisive event in the decline of the Roman Empire....
in 410. The (traditional) last Western Roman Emperor
Roman Emperor
The Roman emperor was the ruler of the Roman State during the imperial period . The Romans had no single term for the office although at any given time, a given title was associated with the emperor...
, Romulus Augustus
Romulus Augustus
Romulus Augustus , was the last Western Roman Emperor, reigning from 31 October 475 until 4 September 476...
, was deposed in 476 by an Eastern Germanic general, Odoacer
Odoacer
Flavius Odoacer , also known as Flavius Odovacer, was the first King of Italy. His reign is commonly seen as marking the end of the Western Roman Empire. Though the real power in Italy was in his hands, he represented himself as the client of Julius Nepos and, after Nepos' death in 480, of the...
. He subsequently ruled in Italy for seventeen years as rex gentium, theoretically under the suzerainty of the Eastern Roman Emperor Zeno
Zeno (emperor)
Zeno , originally named Tarasis, was Byzantine Emperor from 474 to 475 and again from 476 to 491. Domestic revolts and religious dissension plagued his reign, which nevertheless succeeded to some extent in foreign issues...
, but practically in total independence. The administration remained essentially the same as that under the Western Roman Empire, and gave religious freedoms to the Christians. Odoacer fought against the Vandals, who had occupied Sicily
Sicily
Sicily is a region of Italy, and is the largest island in the Mediterranean Sea. Along with the surrounding minor islands, it constitutes an autonomous region of Italy, the Regione Autonoma Siciliana Sicily has a rich and unique culture, especially with regard to the arts, music, literature,...
, and other Germanic tribes that periodically invaded the peninsula.
In 489, however, Emperor Zeno decided to oust the Ostrogoths, a foederatum people living in the Danube, by sending them into Italy. On February 25, 493 Theodoric the Great
Theodoric the Great
Theodoric the Great was king of the Ostrogoths , ruler of Italy , regent of the Visigoths , and a viceroy of the Eastern Roman Empire...
defeated Odoacer and became the king of the Ostrogoths. Theodoric, who had lived long in Constantinople, is now generally considered a Romanized German, and he in fact ruled over Italy largely through Roman personnel. The Goth minority, of Arian
Arian
Arian may refer to:* Arius, a Christian presbyter in the 3rd and 4th century* a given name in different cultures: Aria, Aryan or Arian...
confession, constituted an aristocracy of landowners and militaries, but its influence over the country remained minimal; the Latin population was still subject to Roman laws, and maintained the freedom of creed received by Odoacer. The reign of Theodoric is generally considered a period of recovery for the country. Infrastructures were repaired, frontiers were expanded, and the economy well cared for. The Latin culture flourished for the last time with figures like Boethius
Anicius Manlius Severinus Boethius
Anicius Manlius Severinus Boëthius, commonly called Boethius was a philosopher of the early 6th century. He was born in Rome to an ancient and important family which included emperors Petronius Maximus and Olybrius and many consuls. His father, Flavius Manlius Boethius, was consul in 487 after...
, Theodoric's minister; the Italian Kingdom was again the most powerful political entity of the Mediterranean. However, Theodoric's successors were not equal to him.
The eastern half of the Empire
Byzantine Empire
The Byzantine Empire was the Eastern Roman Empire during the periods of Late Antiquity and the Middle Ages, centred on the capital of Constantinople. Known simply as the Roman Empire or Romania to its inhabitants and neighbours, the Empire was the direct continuation of the Ancient Roman State...
, now centred on Constantinople
Constantinople
Constantinople was the capital of the Roman, Eastern Roman, Byzantine, Latin, and Ottoman Empires. Throughout most of the Middle Ages, Constantinople was Europe's largest and wealthiest city.-Names:...
, invaded Italy in the early 6th century, and the generals of emperor Justinian
Justinian I
Justinian I ; , ; 483– 13 or 14 November 565), commonly known as Justinian the Great, was Byzantine Emperor from 527 to 565. During his reign, Justinian sought to revive the Empire's greatness and reconquer the lost western half of the classical Roman Empire.One of the most important figures of...
, Belisarius
Belisarius
Flavius Belisarius was a general of the Byzantine Empire. He was instrumental to Emperor Justinian's ambitious project of reconquering much of the Mediterranean territory of the former Western Roman Empire, which had been lost less than a century previously....
and Narses
Narses
Narses was, with Belisarius, one of the great generals in the service of the Byzantine Emperor Justinian I during the "Reconquest" that took place during Justinian's reign....
, conquered the Ostrogothic kingdom after years of warfare, ending in 552. This conflict, known as Gothic Wars, destroyed much of the town life that had survived the barbarian invasions. Town life did not disappear, but they became smaller and considerably more primitive than they had been in Roman times. Subsistence agriculture employed the bulk of the Italian population. Wars, famines, and disease epidemics had a dramatic effect on the demographics of Italy.
The agricultural estates of the Roman
Ancient Rome
Ancient Rome was a thriving civilization that grew on the Italian Peninsula as early as the 8th century BC. Located along the Mediterranean Sea and centered on the city of Rome, it expanded to one of the largest empires in the ancient world....
era did not disappear. They produced an agricultural surplus that was sold in towns; however slavery was replaced by other labour systems such as serfdom
Serfdom
Serfdom is the status of peasants under feudalism, specifically relating to Manorialism. It was a condition of bondage or modified slavery which developed primarily during the High Middle Ages in Europe and lasted to the mid-19th century...
.
The withdrawal of Byzantine armies allowed another Germanic people, the Lombards
Lombards
The Lombards , also referred to as Longobards, were a Germanic tribe of Scandinavian origin, who from 568 to 774 ruled a Kingdom in Italy...
, to invade Italy. Cividale del Friuli
Cividale del Friuli
-External links:*...
was the first main centre to fall, while the Byzantine resistance concentrated in the coast areas. The Lombards soon overran most of the peninsula, establishing a Kingdom with capital in Pavia
Pavia
Pavia , the ancient Ticinum, is a town and comune of south-western Lombardy, northern Italy, 35 km south of Milan on the lower Ticino river near its confluence with the Po. It is the capital of the province of Pavia. It has a population of c. 71,000...
, divided into a series of dukedoms. The areas in central-northern Italy which remained under Byzantine control (mostly the current Lazio and Romagna
Romagna
Romagna is an Italian historical region that approximately corresponds to the south-eastern portion of present-day Emilia-Romagna. Traditionally, it is limited by the Apennines to the south-west, the Adriatic to the east, and the rivers Reno and Sillaro to the north and west...
, plus a short corridor between Umbria that connected them, as well as Liguria
Liguria
Liguria is a coastal region of north-western Italy, the third smallest of the Italian regions. Its capital is Genoa. It is a popular region with tourists for its beautiful beaches, picturesque little towns, and good food.-Geography:...
) became the Exarchate of Ravenna
Exarchate of Ravenna
The Exarchate of Ravenna or of Italy was a centre of Byzantine power in Italy, from the end of the 6th century to 751, when the last exarch was put to death by the Lombards.-Introduction:...
. Southern Italy, with the exception of Apulia
Apulia
Apulia is a region in Southern Italy bordering the Adriatic Sea in the east, the Ionian Sea to the southeast, and the Strait of Òtranto and Gulf of Taranto in the south. Its most southern portion, known as Salento peninsula, forms a high heel on the "boot" of Italy. The region comprises , and...
, current Calabria
Calabria
Calabria , in antiquity known as Bruttium, is a region in southern Italy, south of Naples, located at the "toe" of the Italian Peninsula. The capital city of Calabria is Catanzaro....
and Sicily, were also occupied by the two semi-independent Lombard duchies of Spoleto
Duchy of Spoleto
The independent Duchy of Spoleto was a Lombard territory founded about 570 in central Italy by the Lombard dux Faroald.- Lombards :The Lombards, a Germanic people, had invaded Italy in 568 and conquered much of it, establishing a Kingdom divided between several dukes dependent on the King, who had...
and Benevento
Duchy of Benevento
The Duchy and later Principality of Benevento was the southernmost Lombard duchy in medieval Italy, centred on Benevento, a city central in the Mezzogiorno. Owing to the Ducatus Romanus of the popes, which cut it off from the rest of Lombard Italy, Benevento was from the first practically...
. Under the Imperial authority remained also much of the ports, which eventually turned into actually independent city-states (Gaeta
Gaeta
Gaeta is a city and comune in the province of Latina, in Lazio, central Italy. Set on a promontory stretching towards the Gulf of Gaeta, it is 120 km from Rome and 80 km from Naples....
, Naples
Naples
Naples is a city in Southern Italy, situated on the country's west coast by the Gulf of Naples. Lying between two notable volcanic regions, Mount Vesuvius and the Phlegraean Fields, it is the capital of the region of Campania and of the province of Naples...
, Venice
Venice
Venice is a city in northern Italy which is renowned for the beauty of its setting, its architecture and its artworks. It is the capital of the Veneto region...
, Amalfi
Amalfi
Amalfi is a town and comune in the province of Salerno, in the region of Campania, Italy, on the Gulf of Salerno, c. 35 km southeast of Naples. It lies at the mouth of a deep ravine, at the foot of Monte Cerreto , surrounded by dramatic cliffs and coastal scenery...
).
Rise of the Catholic Church
The Church (and especially the bishopBishop
A bishop is an ordained or consecrated member of the Christian clergy who is generally entrusted with a position of authority and oversight. Within the Catholic Church, Eastern Orthodox, Oriental Orthodox Churches, in the Assyrian Church of the East, in the Independent Catholic Churches, and in the...
of Rome
Rome
Rome is the capital of Italy and the country's largest and most populated city and comune, with over 2.7 million residents in . The city is located in the central-western portion of the Italian Peninsula, on the Tiber River within the Lazio region of Italy.Rome's history spans two and a half...
, the pope
Pope
The Pope is the Bishop of Rome, a position that makes him the leader of the worldwide Catholic Church . In the Catholic Church, the Pope is regarded as the successor of Saint Peter, the Apostle...
) had played an important political role since the times of Constantine, who tried to include it in the imperial administration.
In the politically unstable situation after the fall of the western empire, the Church often became the only stable institution and the only source of learning. Even the barbarians had to rely on clerics in order to administer their conquests. Furthermore, the Catholic monastic orders
Monasticism
Monasticism is a religious way of life characterized by the practice of renouncing worldly pursuits to fully devote one's self to spiritual work...
, such as the Benedictine
Benedictine
Benedictine refers to the spirituality and consecrated life in accordance with the Rule of St Benedict, written by Benedict of Nursia in the sixth century for the cenobitic communities he founded in central Italy. The most notable of these is Monte Cassino, the first monastery founded by Benedict...
s had a major role both in the economic life of the time, and in the preservation of the classical
Classical antiquity
Classical antiquity is a broad term for a long period of cultural history centered on the Mediterranean Sea, comprising the interlocking civilizations of ancient Greece and ancient Rome, collectively known as the Greco-Roman world...
culture
Culture
Culture is a term that has many different inter-related meanings. For example, in 1952, Alfred Kroeber and Clyde Kluckhohn compiled a list of 164 definitions of "culture" in Culture: A Critical Review of Concepts and Definitions...
.
After the Lombard invasion, the popes (i.e. St. Gregory
Pope Gregory I
Pope Gregory I , better known in English as Gregory the Great, was pope from 3 September 590 until his death...
, St. Peter, and St. Mark
Pope Mark
Pope Saint Mark the apostle or Marcus was Pope from January 18, 336 to October 7, 336, date of his death.Little is known of his early life. According to the Liber Pontificalis, he was a Roman, and his father's name was Priscus...
) were nominally subject to the eastern emperor, but often received little help from Constantinople, and had to fill the lack of stately power, providing essential services (ex. food for the needy) and protecting Rome from Lombard incursions; in this way, the popes started building an independent state.
Collapse of the Exarchate
At the end of the 8th century the popes definitely aspired to independence, and found a way to achieve it by allying with the Carolingian dynasty of the Franks: the Carolingians needed someone who could give legitimacy to a coup against the powerless Merovingian kings, while the popes needed military protection against the LombardsLombards
The Lombards , also referred to as Longobards, were a Germanic tribe of Scandinavian origin, who from 568 to 774 ruled a Kingdom in Italy...
.
In 751 the Lombards seized Ravenna and the Exarchate of Ravenna
Exarchate of Ravenna
The Exarchate of Ravenna or of Italy was a centre of Byzantine power in Italy, from the end of the 6th century to 751, when the last exarch was put to death by the Lombards.-Introduction:...
was abolished. This ended the Byzantine presence in central Italy (although some coastal cities and some areas in south Italy remained under Byzantine control until the eleventh century). Facing a new Lombard offensive, the papacy appealed to the Franks
Franks
The Franks were a confederation of Germanic tribes first attested in the third century AD as living north and east of the Lower Rhine River. From the third to fifth centuries some Franks raided Roman territory while other Franks joined the Roman troops in Gaul. Only the Salian Franks formed a...
for aid. In 756 Frankish forces defeated the Lombards and gave the Papacy legal authority over all of central Italy, thus creating the Papal States
Papal States
The Papal State, State of the Church, or Pontifical States were among the major historical states of Italy from roughly the 6th century until the Italian peninsula was unified in 1861 by the Kingdom of Piedmont-Sardinia .The Papal States comprised territories under...
. However, the remainder of Italy stayed under Lombard or Byzantine control.
The Frankish (Carolingian) Empire
In 774, upon a Papal invitation, the Franks invaded the Kingdom of Italy and finally annexed the Lombards; as a reward the Frankish king CharlemagneCharlemagne
Charlemagne was King of the Franks from 768 and Emperor of the Romans from 800 to his death in 814. He expanded the Frankish kingdom into an empire that incorporated much of Western and Central Europe. During his reign, he conquered Italy and was crowned by Pope Leo III on 25 December 800...
received papal support. Later, on December 25, 800, Charlemagne was also crowned emperor of the Holy Roman Empire
Holy Roman Empire
The Holy Roman Empire was a realm that existed from 962 to 1806 in Central Europe.It was ruled by the Holy Roman Emperor. Its character changed during the Middle Ages and the Early Modern period, when the power of the emperor gradually weakened in favour of the princes...
by the pope, triggering controversy and disputes over the Roman name
Names of the Greeks
The Greeks have been called by several names, both by themselves and by other people. The most common native ethnonym is Hellenes ; the name Greeks was used by the Romans and then in all European languages....
. A war between the two empires soon followed; in 812 the Byzantines agreed to recognize the existence of two Roman Empires in return for an assurance that the remaining Byzantine possessions in Italy would be uncontested.
Throughout this period, some coastal regions, and all of southern Italy, remained under Byzantine or Lombard control. The Imperial authority never extended much south of the Italian Peninsula
Italian Peninsula
The Italian Peninsula or Apennine Peninsula is one of the three large peninsulas of Southern Europe , spanning from the Po Valley in the north to the central Mediterranean Sea in the south. The peninsula's shape gives it the nickname Lo Stivale...
. Southern Italy was divided amongst the two Lombards duchies of Spoleto
Spoleto
Spoleto is an ancient city in the Italian province of Perugia in east central Umbria on a foothill of the Apennines. It is S. of Trevi, N. of Terni, SE of Perugia; SE of Florence; and N of Rome.-History:...
and Benevento
Benevento
Benevento is a town and comune of Campania, Italy, capital of the province of Benevento, 50 km northeast of Naples. It is situated on a hill 130 m above sea-level at the confluence of the Calore Irpino and Sabato...
, who accepted Charlemagne's suzerainty only formally (812), and the Byzantine Empire
Byzantine Empire
The Byzantine Empire was the Eastern Roman Empire during the periods of Late Antiquity and the Middle Ages, centred on the capital of Constantinople. Known simply as the Roman Empire or Romania to its inhabitants and neighbours, the Empire was the direct continuation of the Ancient Roman State...
. Coastal cities like Gaeta
Gaeta
Gaeta is a city and comune in the province of Latina, in Lazio, central Italy. Set on a promontory stretching towards the Gulf of Gaeta, it is 120 km from Rome and 80 km from Naples....
, Amalfi
Amalfi
Amalfi is a town and comune in the province of Salerno, in the region of Campania, Italy, on the Gulf of Salerno, c. 35 km southeast of Naples. It lies at the mouth of a deep ravine, at the foot of Monte Cerreto , surrounded by dramatic cliffs and coastal scenery...
, Naples
Naples
Naples is a city in Southern Italy, situated on the country's west coast by the Gulf of Naples. Lying between two notable volcanic regions, Mount Vesuvius and the Phlegraean Fields, it is the capital of the region of Campania and of the province of Naples...
on the Tyrrhenian Sea
Tyrrhenian Sea
The Tyrrhenian Sea is part of the Mediterranean Sea off the western coast of Italy.-Geography:The sea is bounded by Corsica and Sardinia , Tuscany, Lazio, Campania, Basilicata and Calabria and Sicily ....
, and Venice
Venice
Venice is a city in northern Italy which is renowned for the beauty of its setting, its architecture and its artworks. It is the capital of the Veneto region...
on the Adriatic Sea
Adriatic Sea
The Adriatic Sea is a body of water separating the Italian Peninsula from the Balkan peninsula, and the system of the Apennine Mountains from that of the Dinaric Alps and adjacent ranges...
, were Latin-Greek enclaves who were becoming increasingly independent from Byzantium. A conquest of Benevento, otherwise, would have meant the total encompassment of the Papal territories, and probably Charlemagne thought it was good for his relationships with the Pope to avoid such a move. The age of Charlemagne was one of stability for Italy, though it was generally dominated by non-Italian interests. The separation with the Eastern world continued to increase. Leo III
Pope Leo III
Pope Saint Leo III was Pope from 795 to his death in 816. Protected by Charlemagne from his enemies in Rome, he subsequently strengthened Charlemagne's position by crowning him as Roman Emperor....
was the first Pope to date his Bulls from the year of Charlemagne's reign (795) instead of those of Byzantine emperors. This process of isolation from the Eastern Empire and connection with the Western world of France and Germany, which had started three centuries before, was completed at the beginning of the 9th centuries. Sicily, Calabria, Puglia and the marine cities were the main exceptions to this rule.
After the death of Charlemagne (814) the new empire soon disintegrated under his weak successors. The equilibrium created through the great emperor's charisma fell apart. This crisis was due also to the emergence of external forces, including the Saracen
Saracen
Saracen was a term used by the ancient Romans to refer to a people who lived in desert areas in and around the Roman province of Arabia, and who were distinguished from Arabs. In Europe during the Middle Ages the term was expanded to include Arabs, and then all who professed the religion of Islam...
attacks and the rising power of the marine republics. Charlemagne had announced his division of the Empire in 806: the Lombard-Frank reign, together with Bavaria
Bavaria
Bavaria, formally the Free State of Bavaria is a state of Germany, located in the southeast of Germany. With an area of , it is the largest state by area, forming almost 20% of the total land area of Germany...
and Alamannia
Alamannia
Alamannia or Alemannia was the territory inhabited by the Germanic Alamanni after they broke through the Roman limes in 213.The Alamanni expanded from the Main basin during the 3rd century, raiding the Roman provinces and settling on the left bank of the Rhine from the 4th century.Ruled by...
, was to be handed over to his son Pepin of Italy.
After Charlemagne's son Louis the Pious
Louis the Pious
Louis the Pious , also called the Fair, and the Debonaire, was the King of Aquitaine from 781. He was also King of the Franks and co-Emperor with his father, Charlemagne, from 813...
died in 840, the treaty of Verdun
Treaty of Verdun
The Treaty of Verdun was a treaty between the three surviving sons of Louis the Pious, the son and successor of Charlemagne, which divided the Carolingian Empire into three kingdoms...
in 843 divided the empire. Louis' eldest surviving son Lothair I
Lothair I
Lothair I or Lothar I was the Emperor of the Romans , co-ruling with his father until 840, and the King of Bavaria , Italy and Middle Francia...
became Emperor and ruler of the Central Franks. His three sons in turn divided this kingdom between them, and Northern Italy became the Kingdom of Italy under Louis II, Holy Roman Emperor in 839.
The first half of the 9th century saw other troubles for Italy as well. In 827, Muslim
Muslim
A Muslim, also spelled Moslem, is an adherent of Islam, a monotheistic, Abrahamic religion based on the Quran, which Muslims consider the verbatim word of God as revealed to prophet Muhammad. "Muslim" is the Arabic term for "submitter" .Muslims believe that God is one and incomparable...
Arab
Arab
Arab people, also known as Arabs , are a panethnicity primarily living in the Arab world, which is located in Western Asia and North Africa. They are identified as such on one or more of genealogical, linguistic, or cultural grounds, with tribal affiliations, and intra-tribal relationships playing...
s known as Aghlabid
Aghlabid
The Aghlabids were a dynasty of emirs, members of the Arab tribe of Bani Tamim, who ruled Ifriqiya, nominally on behalf of the Abbasid Caliph, for about a century, until overthrown by the new power of the Fatimid.-History:...
s invaded and conquered Sicily
Sicily
Sicily is a region of Italy, and is the largest island in the Mediterranean Sea. Along with the surrounding minor islands, it constitutes an autonomous region of Italy, the Regione Autonoma Siciliana Sicily has a rich and unique culture, especially with regard to the arts, music, literature,...
; their descendants, the Kalbids
Kalbids
The Kalbids were a Shia Muslim dynasty in Sicily, which ruled from 948 to 1053 .In 827, in the midst of internal Byzantine conflict, the Aghlabids arrived at Marsala in Sicily, with a fleet of 10,000 men under the command of Asad ibn al-Furat. Palermo was conquered in 831 and became the new capital...
, ruled the island until 1053. In 846, Muslim Arabs invaded Rome
Rome
Rome is the capital of Italy and the country's largest and most populated city and comune, with over 2.7 million residents in . The city is located in the central-western portion of the Italian Peninsula, on the Tiber River within the Lazio region of Italy.Rome's history spans two and a half...
, looted St. Peter's Basilica
St. Peter's Basilica
The Papal Basilica of Saint Peter , officially known in Italian as ' and commonly known as Saint Peter's Basilica, is a Late Renaissance church located within the Vatican City. Saint Peter's Basilica has the largest interior of any Christian church in the world...
, and stole all the gold and silver in it. In response, Pope Leo IV
Pope Leo IV
Pope Saint Leo IV was pope from 10 April 847 to 17 July 855.A Roman by birth, he was unanimously chosen to succeed Sergius II. When he was elected, on 10 April 847, he was cardinal of Santi Quattro Coronati, and had been subdeacon of Gregory IV and archpriest under his predecessor...
started building the Leonine walls
Leonine City
The Leonine City is that part of the city of Rome around which the ninth-century Pope Leo IV commissioned the construction of the Leonine Wall. It is on the opposite side of the Tiber from the seven hills of Rome and was not enclosed within the ancient city's Aurelian Walls, built between 271 and...
of the Vatican City
Vatican City
Vatican City , or Vatican City State, in Italian officially Stato della Città del Vaticano , which translates literally as State of the City of the Vatican, is a landlocked sovereign city-state whose territory consists of a walled enclave within the city of Rome, Italy. It has an area of...
in 847; they were completed in 853. In the late ninth century the Byzantines and the Franks launched a joint offensive against the Arabs in southern Italy; however, only the Byzantines won any territory in that campaign.
Southern Italy
With Charlemagne's conquest of 774, the north of Italy was politically separated from the south completely. Though the Byzantines had continued to hold most of Apulia and Calabria and the Lombard duchies of the south had been aloof of Pavian policies for a century, the situation was exacerbated by the loss of a centralising Lombard authority in the north. Immediately, the duke of Benevento, Arechis IIArechis II of Benevento
Arechis II was Duke of Benevento, in southern Italy, from 758 until his death....
, proclaimed himself a sovereign prince and set about opposing Charlemagne's assumption of Lombard kingship.
Creation of independent moieties (774 – 849)
Under Arechis and his successors, it was the Beneventan policy pay homage to the Carolingian emperors but ignore their rulings. As a result, De facto independence was achieved from Frankish as well as Byzantine authority. The Duchy of BeneventoDuchy of Benevento
The Duchy and later Principality of Benevento was the southernmost Lombard duchy in medieval Italy, centred on Benevento, a city central in the Mezzogiorno. Owing to the Ducatus Romanus of the popes, which cut it off from the rest of Lombard Italy, Benevento was from the first practically...
reached its territorial peak under Sicard
Sicard of Benevento
Sicard was the Prince of Benevento from 832. He was the last prince of a united Benevento which covered most of the Mezzogiorno. On his death, the principality descended into civil war which split it permanently...
in the 830s. At his time, the Mezzogiorno was suffering the ravages of the Saracen
Saracen
Saracen was a term used by the ancient Romans to refer to a people who lived in desert areas in and around the Roman province of Arabia, and who were distinguished from Arabs. In Europe during the Middle Ages the term was expanded to include Arabs, and then all who professed the religion of Islam...
s, against whom Sicard warred constantly. He also warred against his Greek neighbours, especially Sorrento
Duchy of Sorrento
The Duchy of Sorrento was a small peninsular principality of the Early Middle Ages centred on the Italian city of Sorrento.Originally, Sorrento was part of the Byzantine Duchy of Naples in the Dark Ages, but in the ninth century, along with Amalfi and Gaeta, it broke away from the Neapolitans to...
, Naples
Duchy of Naples
The Duchy of Naples began as a Byzantine province that was constituted in the seventh century, in the reduced coastal lands that the Lombards had not conquered during their invasion of Italy in the sixth century...
, and Amalfi
Duchy of Amalfi
The Duchy of Amalfi or the Republic of Amalfi was a de facto independent state centred on the Southern Italian city of Amalfi during the 10th and 11th centuries. The city and its territory were originally part of the larger ducatus Neapolitanus, governed by a patrician, but it extracted itself...
. It was in a war with Naples that Duke Andrew II
Andrew II of Naples
Andrew II was the duke of Naples from 834 to 840. During his reign, he was constantly at war with the Lombards and he allowed Gaeta, his vassal, to move towards independence under its own consuls....
first called in Saracen
Saracen
Saracen was a term used by the ancient Romans to refer to a people who lived in desert areas in and around the Roman province of Arabia, and who were distinguished from Arabs. In Europe during the Middle Ages the term was expanded to include Arabs, and then all who professed the religion of Islam...
mercenaries
Mercenary
A mercenary, is a person who takes part in an armed conflict based on the promise of material compensation rather than having a direct interest in, or a legal obligation to, the conflict itself. A non-conscript professional member of a regular army is not considered to be a mercenary although he...
.
In 839, Sicard was assassinated and a civil war broke out which illustrated the nature of political power in the south. It was still largely in the hands of the land-owning aristocracy, who had the power to choose a prince. In 839, some chose Radelchis I
Radelchis I of Benevento
Radelchis I was the treasurer, then prince of Benevento from 839, when he assumed the throne upon the assassination of Sicard and imprisonment of Sicard's brother, Siconulf, to his death, though in his time the principality was divided.According to the Chronica S...
, the treasurer and assassin, and some chose Siconulf of Salerno
Siconulf of Salerno
Siconulf was the first prince of Salerno, the brother of Sicard, prince of Benevento , who was assassinated by Radelchis. In response to Sicard's murder, the people of Salerno proclaimed Siconulf prince in opposition to Radelchis. At the time Radelchis was holding Siconulf prisoner in Taranto...
, who was installed at Salerno
Salerno
Salerno is a city and comune in Campania and is the capital of the province of the same name. It is located on the Gulf of Salerno on the Tyrrhenian Sea....
. This civil war continued apace for a decade, during which the gastaldates of Benevento took the opportunity to entrench their independence, especially Capua
Principality of Capua
The Principality of Capua was a Lombard state in Southern Italy, usually de facto independent, but under the varying suzerainty of Western and Eastern Roman Empires. It was originally a gastaldate, then a county, within the principality of Salerno....
, which sided with Siconulf. In 849, the Emperor Louis II, in one of his first acts as King of Italy, invaded the peninsula and imposed peace between the Lombard factions. He divided the principality into two: one at Benevento, one at Salerno. Thenceforward, the history of the Lombard south is one of declining, competing powers.

Tyrrhenians
The Tyrrhenians or Tyrsenians is an exonym used by Greek authors to refer to a non-Greek people.- Earliest references :...
Greek cities, the violence raging inland, between them and their fellow Greeks on toe and heel, fostered the circumstances of de facto independence. Naples, in particular, had a history of differences with Byzantium and had in the past sought to make herself dependent on other authorities, often papal. In 801, the Byzantine patrician
Patricianship
Patricianship, the quality of belonging to a patriciate, began in the ancient world, where cities such as Ancient Rome had a class of patrician families whose members were the only people allowed to exercise many political functions...
of Sicily succeeded in creating Anthimus
Anthimus of Naples
Anthimus or Anthemus was the Duke of Naples for from 801 until around 818, when the patrician of Sicily reestablished Byzantine control over the ducatus...
duke. However, Anthimus was unable to control the cities under his rule, Gaeta and Amalfi. Subsequent to Anthimus, the patrician tried to appoint his own candidate without imperial approval. The people rebelled and accepted Stephen III
Stephen III of Naples
Stephen III was the duke of Naples during an important transitionary period in its history, from 821 to his death. By the end of his reign, Naples was completely independent....
in 821. During Stephen's decade of rule, Naples severed all legal ties to Constantinople and even began minting her own coins. In 840, after a brief flirtation with Frankish servitude, to Lothair I
Lothair I
Lothair I or Lothar I was the Emperor of the Romans , co-ruling with his father until 840, and the King of Bavaria , Italy and Middle Francia...
, and a Frankish duke, in the person of Duke Contard
Contardus of Naples
Contard , a Frank, was briefly the Duke of Naples in 840.He was sent by Lothair I, King of Italy, in 839 to aid Duke Andrew II against the warring Lombards of the Principality of Benevento. Fearful of Contard's power and Frankish influence, Andrew promised him his daughter Eupraxia in marriage...
, the Neapolitan citizenry elected Sergius I
Sergius I of Naples
Sergius I was the first duke of Naples of his dynasty, often dubbed the "Sergi," which ruled over Naples for almost three centuries from his accession in 840 until the death of his namesake Sergius VII in 1137....
their magister militum
Magister militum
Magister militum was a top-level military command used in the later Roman Empire, dating from the reign of Constantine. Used alone, the term referred to the senior military officer of the Empire...
. Sergius established a dynasty, the Sergi
Serge (first name)
Serge is a male given name, particularly common in France, Belgium; as Sérgio in Portugal and Brazil; and as Sergio in Italy, Spain and Spanish-speaking Latin America. The less common female version is Sergine...
, that was to rule the duchy for the next three hundred years.
In Gaeta, as in Naples, the violent situation inland required new power structures to maintain Byzantine authority. The Gaetans received their first imperial Byzantine hypati
Hypatus
Hýpatos and the variant apó hypátōn was a Byzantine court dignity, originally the Greek translation of Latin consul . The dignity arose from the honorary consulships awarded in the late Roman Empire, and survived until the early 12th century...
around the time of the Beneventan civil war. While the first hypati remained Byzantine loyals, in 866, the sudden appearance of a new dynasty under Docibilis I
Docibilis I of Gaeta
Docibilis I was the Hypatus of Gaeta from 867 until his death.The sudden disappearance of the co-hypati Constantine and Marinus I after 866 strongly suggests that perhaps Docibilis' assumption of power had been violent...
represented Gaeta's move from Byzantium towards independence. The first elected ruler of Amalfi was a prefect
Prefect
Prefect is a magisterial title of varying definition....
appearing in 839, simultaneous with the death of Sicard and the appearance of a Gaetan hyaptus. However, Naples, Gaeta, Amalfi, the Tyrrhenian cities, and Venice (in North Italy) retained some allegiance to Byzantium until the eleventh century-long after becoming de facto independent.
Period of confusion (849 – 915)
The period following the Beneventan civil war was one of confusion, brought on by the independence movements in the various cities and provinces and by the Saracen onslaught. In Salerno, a palace coup removed Siconulf's successor Sico IISico of Salerno
Sico II was the first prince of Salerno. Son and successor of Siconulf, he reigned from his father's death in 851 to his deposition in 853. He is given the ordinal "II" because he was the second Sico to rule in the south, the previous Sico being prince of Benevento.Sico was a minor when his father...
in 853 and destabilised that principality until a new dynasty, the Dauferidi, came to power in 861.

Bari
Bari is the capital city of the province of Bari and of the Apulia region, on the Adriatic Sea, in Italy. It is the second most important economic centre of mainland Southern Italy after Naples, and is well known as a port and university city, as well as the city of Saint Nicholas...
and founded an emirate
Emirate
An emirate is a political territory that is ruled by a dynastic Muslim monarch styled emir.-Etymology:Etymologically emirate or amirate is the quality, dignity, office or territorial competence of any emir ....
there. Greek power being significantly threatened, as well as Adriatic commerce, the Byzantine emperor requested an alliance from Louis II of Italy. Similarly, the new prince of Benevento, Adelchis
Adelchis of Benevento
Adelchis was the son of Radelchis I, Prince of Benevento, and successor of his brother Radelgar in 854.It was given to Adelchis to preserve the ancient principality and its independence in the face of repeated assaults by the Saracens from the south, the Emperor Louis II from the north, and...
, an independent-minded ruler, also sought his aid. Louis came down and retook Bari in 871 after a great siege. Louis then tried to set up greater control over all the south by garrisoning his troops in Beneventan fortresses. The response of Adelchis to this action was to imprison and rob the emperor while he was staying the princely palace at Benevento. A month later, the Saracens had landed with a new invasive force and Adelchis released Louis to lead the armies against it. Adelchis forced Louis to vow never to re-enter Benevento with an army or to take revenge for his detention. Louis went to Rome in 872 and was released from his oath by Pope Adrian II
Pope Adrian II
Pope Adrian II , , pope from December 14, 867 to December 14, 872, was a member of a noble Roman family, and became pope in 867, at an advanced age....
on 28 May. His attempts to punish Adelchis were not very successful. Adelchis vacillated between nominal fealty to the Carolingian and Byzantine emperors, but, in fact, by his alterations to the Edictum Rothari
Edictum Rothari
The Edictum Rothari was the first written compilation of Lombard law, codified and promulgated 22 November 643 by King Rothari. The custom of the Lombards, according to Paul the Deacon, the Lombard historian, had been held in memory before this...
, he acknowledged himself as the legitimate Lombard "king."
The successors of Adelchis were weak and the principality of Benevento declined just as Salernitan power was beginning to make itself felt. Guaifer of Salerno
Guaifer of Salerno
Guaifer was the Prince of Salerno from 861. The son of Daufer the Mute and grandson of Daufer the Prophet, he was the first of the Dauferidi to sit on the Salernitan throne which his family dominated unobstructed until 977.Guaifer's sister, Adelchisa, married Sicard of Benevento and when Sicard...
was on friendly terms with the Saracens, a habit which annoyed the popes and often put a ruler at odds with his neighbours. The south Italian lords continually rotating in their allegiances. Guaifer's successor, Guaimar I
Guaimar I of Salerno
Guaimar I was the prince of Salerno from 880, when his father entered the monastery of Monte Cassino in August. His parents were Prince Guaifer and Landelaica, daughter of Lando I of Capua...
, made war on the Saracens. Guaifer had originally associated Guaimar with him as co-ruler, a practice which became endemic to the south and was especially evident in Capua.
High Middle Ages (10th-13th centuries)
The 11th century signalled the end of the darkest period in the Middle Ages. Trade slowly picked up, especially on the seas, where the Maritime Republics of AmalfiAmalfi
Amalfi is a town and comune in the province of Salerno, in the region of Campania, Italy, on the Gulf of Salerno, c. 35 km southeast of Naples. It lies at the mouth of a deep ravine, at the foot of Monte Cerreto , surrounded by dramatic cliffs and coastal scenery...
, Venice
Venice
Venice is a city in northern Italy which is renowned for the beauty of its setting, its architecture and its artworks. It is the capital of the Veneto region...
, Pisa
Pisa
Pisa is a city in Tuscany, Central Italy, on the right bank of the mouth of the River Arno on the Tyrrhenian Sea. It is the capital city of the Province of Pisa...
, Genoa
Genoa
Genoa |Ligurian]] Zena ; Latin and, archaically, English Genua) is a city and an important seaport in northern Italy, the capital of the Province of Genoa and of the region of Liguria....
, Ancona
Ancona
Ancona is a city and a seaport in the Marche region, in central Italy, with a population of 101,909 . Ancona is the capital of the province of Ancona and of the region....
and Gaeta
Gaeta
Gaeta is a city and comune in the province of Latina, in Lazio, central Italy. Set on a promontory stretching towards the Gulf of Gaeta, it is 120 km from Rome and 80 km from Naples....
became major powers. The papacy regained its authority, and started a long struggle with the empire, about both ecclesiastical and secular matter. The first episode was the Investiture Controversy
Investiture Controversy
The Investiture Controversy or Investiture Contest was the most significant conflict between Church and state in medieval Europe. In the 11th and 12th centuries, a series of Popes challenged the authority of European monarchies over control of appointments, or investitures, of church officials such...
. In the twelfth century those Italian cities which lay in the Holy Roman Empire launched a successful effort to win autonomy from the Holy Roman Empire
Holy Roman Empire
The Holy Roman Empire was a realm that existed from 962 to 1806 in Central Europe.It was ruled by the Holy Roman Emperor. Its character changed during the Middle Ages and the Early Modern period, when the power of the emperor gradually weakened in favour of the princes...
(see Lombard League
Lombard League
The Lombard League was an alliance formed around 1167, which at its apex included most of the cities of northern Italy , including, among others, Crema, Cremona, Mantua, Piacenza, Bergamo, Brescia, Milan, Genoa, Bologna, Padua, Modena, Reggio Emilia, Treviso, Venice, Vercelli, Vicenza, Verona,...
); this made north Italy a land of quasi-independent or independent city-states until the nineteenth century (see Italian city-states
Italian city-states
The Italian city-states were a political phenomenon of small independent states mostly in the central and northern Italian peninsula between the 10th and 15th centuries....
and history of every city). The revolts were funded by Byzantium, which hoped to expel the Germans from Italy; this sponsorship was, like the invasion of the South, part of a twelfth-century Byzantine effort to regain the influence it had held on the peninsula during the reign of Justinian.
Meanwhile, the South and Sicily were invaded by Normans
Normans
The Normans were the people who gave their name to Normandy, a region in northern France. They were descended from Norse Viking conquerors of the territory and the native population of Frankish and Gallo-Roman stock...
, who eventually conquered what remained of the Byzantine holdings in mainland Italy along with the Arab
Arab
Arab people, also known as Arabs , are a panethnicity primarily living in the Arab world, which is located in Western Asia and North Africa. They are identified as such on one or more of genealogical, linguistic, or cultural grounds, with tribal affiliations, and intra-tribal relationships playing...
possessions in Sicily (see Kingdom of Sicily
Kingdom of Sicily
The Kingdom of Sicily was a state that existed in the south of Italy from its founding by Roger II in 1130 until 1816. It was a successor state of the County of Sicily, which had been founded in 1071 during the Norman conquest of southern Italy...
).
In the eleventh century, the Normans
Normans
The Normans were the people who gave their name to Normandy, a region in northern France. They were descended from Norse Viking conquerors of the territory and the native population of Frankish and Gallo-Roman stock...
occupied
Norman conquest of southern Italy
The Norman conquest of southern Italy spanned the late eleventh and much of the twelfth centuries, involving many battles and many independent players conquering territories of their own...
the Lombard and Byzantine possessions in Southern Italy, ending the six century old presence of both powers in the peninsula. The independent city-states were also subdued. During the same century, the Normans also ended Muslim rule in Sicily. Norman rule in what had once been Byzantine territory naturally angered Byzantium, which in 1155 made a last attempt under the Emperor Manuel I Komnenos
Manuel I Komnenos
Manuel I Komnenos was a Byzantine Emperor of the 12th century who reigned over a crucial turning point in the history of Byzantium and the Mediterranean....
to reassert its authority in Southern Italy. But the attempt failed, and in 1158 the Byzantines left Italy.
Unlike the Norman conquest of England
Norman conquest of England
The Norman conquest of England began on 28 September 1066 with the invasion of England by William, Duke of Normandy. William became known as William the Conqueror after his victory at the Battle of Hastings on 14 October 1066, defeating King Harold II of England...
(1066), which took place over the course of a few years after one decisive battle, the conquest of Southern Italy was the product of decades and many battles, few decisive. Many territories were conquered independently, and only later were all unified into one state. Compared to the conquest of England, it was unplanned and unorganised, but just as permanent.
The Holy Roman Empire

Otto I, Holy Roman Emperor
Otto I the Great , son of Henry I the Fowler and Matilda of Ringelheim, was Duke of Saxony, King of Germany, King of Italy, and "the first of the Germans to be called the emperor of Italy" according to Arnulf of Milan...
, claimed that the union revived the empire of Charlemagne
Charlemagne
Charlemagne was King of the Franks from 768 and Emperor of the Romans from 800 to his death in 814. He expanded the Frankish kingdom into an empire that incorporated much of Western and Central Europe. During his reign, he conquered Italy and was crowned by Pope Leo III on 25 December 800...
and received the title of Holy Roman Emperor
Holy Roman Emperor
The Holy Roman Emperor is a term used by historians to denote a medieval ruler who, as German King, had also received the title of "Emperor of the Romans" from the Pope...
in 962.
Even the papacy went through an age of decadence, which ended only in 999 when emperor Otto III
Otto III, Holy Roman Emperor
Otto III , a King of Germany, was the fourth ruler of the Saxon or Ottonian dynasty of the Holy Roman Empire. He was elected King in 983 on the death of his father Otto II and was crowned Holy Roman Emperor in 996.-Early reign:...
selected Silvester II as pope.
Southern Italy
Under the Macedonian dynastyMacedonian dynasty
The Macedonian dynasty ruled the Byzantine Empire from 867 to 1056, following the Amorian dynasty. During this period, the Byzantine state reached its greatest expanse since the Muslim conquests, and the Macedonian Renaissance in letters and arts began. The dynasty was named after its founder,...
, Byzantine power experienced a recovery; and the impact of this was felt in southern Italy. During the late ninth century the amount of territory under direct Byzantine rule (which in the early ninth century was limited to the toe and heel of the peninsula) expanded dramatically. The Catepanate of Italy was set up to administer the newly-acquired territory. The rest of Southern Italy remained divided among the Lombard kings and the Italian cities. Both sets of principalities were de-facto independent, but paid nominal allegiance to Byzantium.
The Byzantine gains in the southern Italian mainland were, however, accompanied by setbacks in Sicily. In 878 the Arabs captured the crucial city of Syracuse, and by 902 the entire island was under Arab rule.
Late Middle Ages and Renaissance (14th century to 1559)
In the 14th century, Italy presents itself as divided between the Kingdom of NaplesKingdom of Naples
The Kingdom of Naples, comprising the southern part of the Italian peninsula, was the remainder of the old Kingdom of Sicily after secession of the island of Sicily as a result of the Sicilian Vespers rebellion of 1282. Known to contemporaries as the Kingdom of Sicily, it is dubbed Kingdom of...
and Sicily
Kingdom of Sicily
The Kingdom of Sicily was a state that existed in the south of Italy from its founding by Roger II in 1130 until 1816. It was a successor state of the County of Sicily, which had been founded in 1071 during the Norman conquest of southern Italy...
in the south, the Papal States
Papal States
The Papal State, State of the Church, or Pontifical States were among the major historical states of Italy from roughly the 6th century until the Italian peninsula was unified in 1861 by the Kingdom of Piedmont-Sardinia .The Papal States comprised territories under...
in Central Italy, and the Maritime republics in the north.
The Duchy of Milan
Duchy of Milan
The Duchy of Milan , was created on the 1st of may 1395, when Gian Galeazzo Visconti, Lord of Milan, purchased a diploma for 100,000 Florins from King Wenceslaus. It was this diploma that installed, Gian Galeazzo as Duke of Milan and Count of Pavia...
found itself in the focus of European power politics in the 15th century, leading to the drawn-out Italian Wars
Italian Wars
The Italian Wars, often referred to as the Great Italian Wars or the Great Wars of Italy and sometimes as the Habsburg–Valois Wars, were a series of conflicts from 1494 to 1559 that involved, at various times, most of the city-states of Italy, the Papal States, most of the major states of Western...
, which persisted for the best part of the 16th century before giving way to the Early Modern period in Italy.
The Italian Renaissance
Italian Renaissance
The Italian Renaissance began the opening phase of the Renaissance, a period of great cultural change and achievement in Europe that spanned the period from the end of the 13th century to about 1600, marking the transition between Medieval and Early Modern Europe...
originatesin 14th-century Tuscany
Tuscany
Tuscany is a region in Italy. It has an area of about 23,000 square kilometres and a population of about 3.75 million inhabitants. The regional capital is Florence ....
, centered in the cities of Florence
Florence
Florence is the capital city of the Italian region of Tuscany and of the province of Florence. It is the most populous city in Tuscany, with approximately 370,000 inhabitants, expanding to over 1.5 million in the metropolitan area....
and Siena
Siena
Siena is a city in Tuscany, Italy. It is the capital of the province of Siena.The historic centre of Siena has been declared by UNESCO a World Heritage Site. It is one of the nation's most visited tourist attractions, with over 163,000 international arrivals in 2008...
. It later had a great impact in Venice
Venice
Venice is a city in northern Italy which is renowned for the beauty of its setting, its architecture and its artworks. It is the capital of the Veneto region...
, where the remains of ancient Greek culture
Ancient Greece
Ancient Greece is a civilization belonging to a period of Greek history that lasted from the Archaic period of the 8th to 6th centuries BC to the end of antiquity. Immediately following this period was the beginning of the Early Middle Ages and the Byzantine era. Included in Ancient Greece is the...
were brought together, providing humanist
Humanism
Humanism is an approach in study, philosophy, world view or practice that focuses on human values and concerns. In philosophy and social science, humanism is a perspective which affirms some notion of human nature, and is contrasted with anti-humanism....
scholars with new texts. The Renaissance later had a significant effect on Rome
Rome
Rome is the capital of Italy and the country's largest and most populated city and comune, with over 2.7 million residents in . The city is located in the central-western portion of the Italian Peninsula, on the Tiber River within the Lazio region of Italy.Rome's history spans two and a half...
, which was ornamented with some structures in the new all'antico mode, then was largely rebuilt by humanist sixteenth-century pope
Pope
The Pope is the Bishop of Rome, a position that makes him the leader of the worldwide Catholic Church . In the Catholic Church, the Pope is regarded as the successor of Saint Peter, the Apostle...
s.
The Italian Renaissance peaked in the mid-16th century as foreign invasions plunged the region into the turmoil of the Italian Wars
Italian Wars
The Italian Wars, often referred to as the Great Italian Wars or the Great Wars of Italy and sometimes as the Habsburg–Valois Wars, were a series of conflicts from 1494 to 1559 that involved, at various times, most of the city-states of Italy, the Papal States, most of the major states of Western...
. However, the ideas and ideals of the Renaissance endured and even spread into the rest of Europe, setting off the Northern Renaissance
Northern Renaissance
The Northern Renaissance is the term used to describe the Renaissance in northern Europe, or more broadly in Europe outside Italy. Before 1450 Italian Renaissance humanism had little influence outside Italy. From the late 15th century the ideas spread around Europe...
, and the English Renaissance
English Renaissance
The English Renaissance was a cultural and artistic movement in England dating from the late 15th and early 16th centuries to the early 17th century. It is associated with the pan-European Renaissance that is usually regarded as beginning in Italy in the late 14th century; like most of northern...
.

