
Internal pressure
Encyclopedia
Internal pressure is a measure of how the internal energy
of a system changes when it expands or contracts at constant temperature
. It has the same dimensions as pressure
, the SI unit of which is 1 pascal
.
Internal pressure is usually given the symbol . It is defined as a partial derivative
. It is defined as a partial derivative
of internal energy with respect to volume at constant temperature:


This equation is known as the thermodynamic equation of state for it expresses pressure in terms of thermodynamic properties of the system.
, there are no potential energy
interactions between the particles, so any change in the internal energy of the gas is directly proportional to the change in the kinetic energy
of its constituent species and therefore also to the change in temperature:
 .
.
The internal pressure is taken to be at constant temperature, therefore
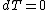 , which implies
, which implies 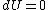 and finally
and finally 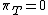 ,
,
i.e. the internal energy of a perfect gas is independent of the volume it occupies. The above relation can be used as a definition of a perfect gas.
The relation can be proved without the need to invoke any molecular arguments. It follows directly from the thermodynamic equation of state if we use the ideal gas law
can be proved without the need to invoke any molecular arguments. It follows directly from the thermodynamic equation of state if we use the ideal gas law
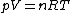 .
.
 , signifying presence of dominant attractive forces between the particles of the gas) or decrease (
, signifying presence of dominant attractive forces between the particles of the gas) or decrease ( ,dominant repulsion).
,dominant repulsion).
In the limit of infinite volume these internal pressures reach the value of zero:
 ,
,
corresponding to the fact that all real gases can be approximated to be perfect in the limit of a suitably large volume. The above considerations are summarized on the graph on the right.
If a real gas can be described by the van der Waals equation
of state

it follows from the thermodynamic equation of state that
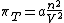
Since the paramater is always positive, so is its internal pressure: internal energy of a van der Waals gas always increases when it expands isothermally.
is always positive, so is its internal pressure: internal energy of a van der Waals gas always increases when it expands isothermally.
by isothermally pumping high pressure air from one metal vessel into another evacuated one. The water bath in which the system was immersed did not change its temperature, signifying that that no change in the internal energy occurred, the internal pressure of the air was equal to zero and the air was a perfect gas. The actual deviations from the perfect behaviour were not observed since they are very small and the specific heat capacity of water
is relatively high.
Internal energy
In thermodynamics, the internal energy is the total energy contained by a thermodynamic system. It is the energy needed to create the system, but excludes the energy to displace the system's surroundings, any energy associated with a move as a whole, or due to external force fields. Internal...
of a system changes when it expands or contracts at constant temperature
Temperature
Temperature is a physical property of matter that quantitatively expresses the common notions of hot and cold. Objects of low temperature are cold, while various degrees of higher temperatures are referred to as warm or hot...
. It has the same dimensions as pressure
Pressure
Pressure is the force per unit area applied in a direction perpendicular to the surface of an object. Gauge pressure is the pressure relative to the local atmospheric or ambient pressure.- Definition :...
, the SI unit of which is 1 pascal
Pascal (unit)
The pascal is the SI derived unit of pressure, internal pressure, stress, Young's modulus and tensile strength, named after the French mathematician, physicist, inventor, writer, and philosopher Blaise Pascal. It is a measure of force per unit area, defined as one newton per square metre...
.
Internal pressure is usually given the symbol
 . It is defined as a partial derivative
. It is defined as a partial derivativePartial derivative
In mathematics, a partial derivative of a function of several variables is its derivative with respect to one of those variables, with the others held constant...
of internal energy with respect to volume at constant temperature:

Thermodynamic equation of state
Internal pressure can be expressed in terms of temperature, pressure and their mutual dependence:
This equation is known as the thermodynamic equation of state for it expresses pressure in terms of thermodynamic properties of the system.
| Derivation of the thermodynamic equation of state |
|---|
| Internal energy is a state function State function In thermodynamics, a state function, function of state, state quantity, or state variable is a property of a system that depends only on the current state of the system, not on the way in which the system acquired that state . A state function describes the equilibrium state of a system... , therefore its differential is exact Exact differential A mathematical differential is said to be exact, as contrasted with an inexact differential, if it is of the form dQ, for some differentiable function Q.... . We can take it to be a function of other state functions, namely entropy Entropy Entropy is a thermodynamic property that can be used to determine the energy available for useful work in a thermodynamic process, such as in energy conversion devices, engines, or machines. Such devices can only be driven by convertible energy, and have a theoretical maximum efficiency when... S and volume V: 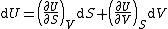 . .Diving this equation by 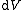 at constant temperature gives: at constant temperature gives: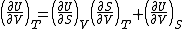 Comparing the above differential with the fundamental thermodynamic equation 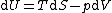 gives  and and  . .This, and the definition of internal pressure, leads to  One of the Maxwell relations Maxwell relations Maxwell's relations are a set of equations in thermodynamics which are derivable from the definitions of the thermodynamic potentials. The Maxwell relations are statements of equality among the second derivatives of the thermodynamic potentials. They follow directly from the fact that the order of... states that 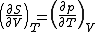 Inserting this into the above relation completes the proof. |
Perfect gas
In a perfect gasPerfect gas
In physics, a perfect gas is a theoretical gas that differs from real gases in a way that makes certain calculations easier to handle. Its behavior is more simplified compared to an ideal gas...
, there are no potential energy
Potential energy
In physics, potential energy is the energy stored in a body or in a system due to its position in a force field or due to its configuration. The SI unit of measure for energy and work is the Joule...
interactions between the particles, so any change in the internal energy of the gas is directly proportional to the change in the kinetic energy
Kinetic energy
The kinetic energy of an object is the energy which it possesses due to its motion.It is defined as the work needed to accelerate a body of a given mass from rest to its stated velocity. Having gained this energy during its acceleration, the body maintains this kinetic energy unless its speed changes...
of its constituent species and therefore also to the change in temperature:
 .
.The internal pressure is taken to be at constant temperature, therefore
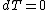 , which implies
, which implies 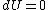 and finally
and finally 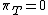 ,
,i.e. the internal energy of a perfect gas is independent of the volume it occupies. The above relation can be used as a definition of a perfect gas.
The relation
 can be proved without the need to invoke any molecular arguments. It follows directly from the thermodynamic equation of state if we use the ideal gas law
can be proved without the need to invoke any molecular arguments. It follows directly from the thermodynamic equation of state if we use the ideal gas lawIdeal gas law
The ideal gas law is the equation of state of a hypothetical ideal gas. It is a good approximation to the behavior of many gases under many conditions, although it has several limitations. It was first stated by Émile Clapeyron in 1834 as a combination of Boyle's law and Charles's law...
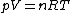 .
.Real gases
Real gases have non-zero internal pressures because their internal energy changes as the gases expand isothermally - it can increase on expansion ( , signifying presence of dominant attractive forces between the particles of the gas) or decrease (
, signifying presence of dominant attractive forces between the particles of the gas) or decrease ( ,dominant repulsion).
,dominant repulsion).In the limit of infinite volume these internal pressures reach the value of zero:
 ,
,corresponding to the fact that all real gases can be approximated to be perfect in the limit of a suitably large volume. The above considerations are summarized on the graph on the right.
If a real gas can be described by the van der Waals equation
Van der Waals equation
The van der Waals equation is an equation of state for a fluid composed of particles that have a non-zero volume and a pairwise attractive inter-particle force It was derived by Johannes Diderik van der Waals in 1873, who received the Nobel prize in 1910 for "his work on the equation of state for...
of state

it follows from the thermodynamic equation of state that
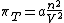
Since the paramater
 is always positive, so is its internal pressure: internal energy of a van der Waals gas always increases when it expands isothermally.
is always positive, so is its internal pressure: internal energy of a van der Waals gas always increases when it expands isothermally.The Joule experiment
James Joule tried to measure the internal pressure of air in his expansion experimentJoule expansion
The Joule expansion is an irreversible process in thermodynamics in which a volume of gas is kept in one side of a thermally isolated container , with the other side of the container being evacuated; the partition between the two parts of the container is then opened, and the gas fills the whole...
by isothermally pumping high pressure air from one metal vessel into another evacuated one. The water bath in which the system was immersed did not change its temperature, signifying that that no change in the internal energy occurred, the internal pressure of the air was equal to zero and the air was a perfect gas. The actual deviations from the perfect behaviour were not observed since they are very small and the specific heat capacity of water
Water
Water is a chemical substance with the chemical formula H2O. A water molecule contains one oxygen and two hydrogen atoms connected by covalent bonds. Water is a liquid at ambient conditions, but it often co-exists on Earth with its solid state, ice, and gaseous state . Water also exists in a...
is relatively high.

