
Hour
Encyclopedia
The hour is a unit of measurement of time
. In modern usage, an hour comprises 60 minute
s, or 3,600 second
s. It is 1/24th of a median Earth
day
.
An hour in the Universal Coordinated Time (UTC) time standard
can include a negative or positive leap second
, and may therefore have a duration of or for adjustment purposes.
Although it is not a standard defined by the International System of Units
, the hour is a unit accepted for use with SI, represented by the symbol h.
word ure first appears in the 13th century, as a loanword from Old French
ure or ore, which derives from Latin hora. Hora, in turn, derives from Greek ("season, time of day, hour"), which is a cognate
of year
; their shared ancestor is the Proto-Indo-European
word ("year, summer").
The ure of Middle English and the Anglo-French
houre gradually supplanted the Old English nouns tīd (which survives in Modern English as tide
) and stund. Stund is the progenitor of stound, which remains an archaic synonym for hour. Stund is related to the Old High German
stunta, from Germanic *stundō ("time, interval, while").
ians used sundial
s that "divided a sunlit day into 10 parts plus two "twilight hours" in the morning and evening."
The Greek
astronomer, Andronicus of Cyrrhus
, oversaw the construction of a horologion
called the Tower of the Winds
in Athens during the first century BCE. This structure tracked a 24-hour day using both sundials and mechanical hour indicators.
Ancient Sumer
, India
, and China
also divided days into either one twelfth of the time between sunrise and sunset or one twenty-fourth of a full day. In either case the division reflected the widespread use of a duodecimal
numbering system. The importance of 12
has been attributed to the number of lunar cycles in a year.
Astronomers in Egypt's Middle Kingdom
(9th and 10th Dynasties) observed a set of 36 decan
stars throughout the year. These star tables have been found on the lids of coffins of the period. The heliacal rising
of the next decan star marked the start of a new civil week, which was then ten days. The period from sunset to sunrise was marked by 18 decan stars. Three of these were assigned to each of the two twilight periods, so the period of total darkness was marked by the remaining 12 decan stars, resulting in the 12 divisions of the night. The time between the appearance of each of these decan stars over the horizon during the night would have been about 40 modern minutes. During the New Kingdom
, the system was simplified, using a set of 24 stars, 12 of which marked the passage of the night.
Earlier definitions of the hour varied within these parameters:

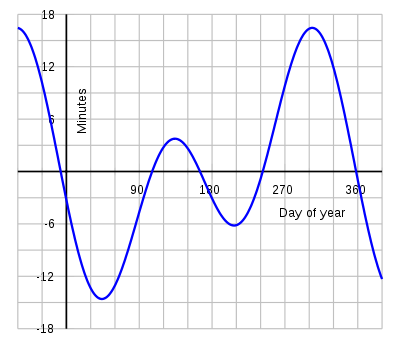
 Many different ways of counting the hours have been used. Because sunrise, sunset, and, to a lesser extent, noon, are the conspicuous points in the day, starting to count at these times was, for most people in most early societies, much easier than starting at midnight. However, with accurate clocks and modern astronomical equipment (and the telegraph or similar means to transfer a time signal in a split-second), this issue is much less relevant.
Many different ways of counting the hours have been used. Because sunrise, sunset, and, to a lesser extent, noon, are the conspicuous points in the day, starting to count at these times was, for most people in most early societies, much easier than starting at midnight. However, with accurate clocks and modern astronomical equipment (and the telegraph or similar means to transfer a time signal in a split-second), this issue is much less relevant.
Astrolabe
s, sundial
s, and astronomical clock
s sometimes show the hour length and count using some of these older definitions and counting methods.
s and astronomical clock
s, for example, as "Babylonian" hours, and were in use until the appearance of the mechanical clock, which hastened the introduction of equal length hours.
This is also the system used in Jewish religious law (Halakha
) and frequently called Talmudic hour ("Sha'a Zemanit") in a variety of texts. The talmudic hour is one twelfth of time elapsed from sunrise to sunset, day hours therefore being longer than night hours in the summer; in winter they reverse.
The Indic day began at sunrise. The term "Hora" was used to indicate an hour. The time was measured based on the length of the shadow at day time. A "Hora" translated to 2.5 "Pe." There are 60 "Pe" per day, 60 minutes per "Pe" and 60 "Kshana" (snap of a finger or instant) per minute. "Pe" was measured with a bowl with a hole placed in still water. Time taken for this graduated bowl was one "Pe." Kings usually had a officer in charge of this clock.
time, "Italian hours", or "Old Czech Time", the first hour started with the sunset Angelus
bell (or at the end of dusk, i.e., half an hour after sunset, depending on local custom and geographical latitude). The hours were numbered from 1 to 24. For example, in Lugano, the sun rose in December during the 14th hour and noon was during the 19th hour; in June the Sun rose during the 7th hour and noon was in the 15th hour. Sunset was always at the end of the 24th hour. The clocks in church towers struck only from 1 to 12, thus only during night or early morning hours.
This manner of counting hours had the advantage that everyone could easily know how much time they had to finish their day's work without artificial light. It was already widely used in Italy
by the 14th century and lasted until the mid-18th century; it was officially abolished in 1755, or in some regions, customary, until the mid-19th century.
The system of Italian hours can be seen on a number of clocks in Europe, where the dial is numbered from 1 to 24 in either Roman or Arabic numerals. The St Mark's Clock
in Venice, and the Orloj in Prague are famous examples. It was also used in Poland
and Bohemia
until the 17th century.
The medieval Islamic day began at sunset. The first prayer of the day (maghrib
) was to be performed between sunset and the end of twilight.
, counting the hours starts at midnight and restarts at noon. Hours are numbered 12, 1, 2, ..., 11. Solar noon
is always close to 12 noon, differing according to the equation of time
by as much as fifteen minutes either way. At the equinox
es sunrise is around 6 A.M. (ante meridiem, before noon), and sunset around 6 P.M. (post meridiem, after noon).
In the modern 24-hour clock
, counting the hours starts at midnight and hours are numbered from 0 to 23. Solar noon is always close to 12:00, again differing according to the equation of time. At the equinoxes sunrise is around 06:00 and sunset around 18:00.
Time
Time is a part of the measuring system used to sequence events, to compare the durations of events and the intervals between them, and to quantify rates of change such as the motions of objects....
. In modern usage, an hour comprises 60 minute
Minute
A minute is a unit of measurement of time or of angle. The minute is a unit of time equal to 1/60th of an hour or 60 seconds. In the UTC time scale, a minute on rare occasions has 59 or 61 seconds; see leap second. The minute is not an SI unit; however, it is accepted for use with SI units...
s, or 3,600 second
Second
The second is a unit of measurement of time, and is the International System of Units base unit of time. It may be measured using a clock....
s. It is 1/24th of a median Earth
Earth
Earth is the third planet from the Sun, and the densest and fifth-largest of the eight planets in the Solar System. It is also the largest of the Solar System's four terrestrial planets...
day
Day
A day is a unit of time, commonly defined as an interval equal to 24 hours. It also can mean that portion of the full day during which a location is illuminated by the light of the sun...
.
An hour in the Universal Coordinated Time (UTC) time standard
Time standard
A time standard is a specification for measuring time: either the rate at which time passes; or points in time; or both. In modern times, several time specifications have been officially recognized as standards, where formerly they were matters of custom and practice. An example of a kind of time...
can include a negative or positive leap second
Leap second
A leap second is a positive or negative one-second adjustment to the Coordinated Universal Time time scale that keeps it close to mean solar time. UTC, which is used as the basis for official time-of-day radio broadcasts for civil time, is maintained using extremely precise atomic clocks...
, and may therefore have a duration of or for adjustment purposes.
Although it is not a standard defined by the International System of Units
International System of Units
The International System of Units is the modern form of the metric system and is generally a system of units of measurement devised around seven base units and the convenience of the number ten. The older metric system included several groups of units...
, the hour is a unit accepted for use with SI, represented by the symbol h.
Etymology
The Middle EnglishMiddle English
Middle English is the stage in the history of the English language during the High and Late Middle Ages, or roughly during the four centuries between the late 11th and the late 15th century....
word ure first appears in the 13th century, as a loanword from Old French
Old French
Old French was the Romance dialect continuum spoken in territories that span roughly the northern half of modern France and parts of modern Belgium and Switzerland from the 9th century to the 14th century...
ure or ore, which derives from Latin hora. Hora, in turn, derives from Greek ("season, time of day, hour"), which is a cognate
Cognate
In linguistics, cognates are words that have a common etymological origin. This learned term derives from the Latin cognatus . Cognates within the same language are called doublets. Strictly speaking, loanwords from another language are usually not meant by the term, e.g...
of year
Year
A year is the orbital period of the Earth moving around the Sun. For an observer on Earth, this corresponds to the period it takes the Sun to complete one course throughout the zodiac along the ecliptic....
; their shared ancestor is the Proto-Indo-European
Proto-Indo-European language
The Proto-Indo-European language is the reconstructed common ancestor of the Indo-European languages, spoken by the Proto-Indo-Europeans...
word ("year, summer").
The ure of Middle English and the Anglo-French
Anglo-Norman language
Anglo-Norman is the name traditionally given to the kind of Old Norman used in England and to some extent elsewhere in the British Isles during the Anglo-Norman period....
houre gradually supplanted the Old English nouns tīd (which survives in Modern English as tide
Tide
Tides are the rise and fall of sea levels caused by the combined effects of the gravitational forces exerted by the moon and the sun and the rotation of the Earth....
) and stund. Stund is the progenitor of stound, which remains an archaic synonym for hour. Stund is related to the Old High German
Old High German
The term Old High German refers to the earliest stage of the German language and it conventionally covers the period from around 500 to 1050. Coherent written texts do not appear until the second half of the 8th century, and some treat the period before 750 as 'prehistoric' and date the start of...
stunta, from Germanic *stundō ("time, interval, while").

History
Ancient EgyptAncient Egypt
Ancient Egypt was an ancient civilization of Northeastern Africa, concentrated along the lower reaches of the Nile River in what is now the modern country of Egypt. Egyptian civilization coalesced around 3150 BC with the political unification of Upper and Lower Egypt under the first pharaoh...
ians used sundial
Sundial
A sundial is a device that measures time by the position of the Sun. In common designs such as the horizontal sundial, the sun casts a shadow from its style onto a surface marked with lines indicating the hours of the day. The style is the time-telling edge of the gnomon, often a thin rod or a...
s that "divided a sunlit day into 10 parts plus two "twilight hours" in the morning and evening."
The Greek
Ancient Greece
Ancient Greece is a civilization belonging to a period of Greek history that lasted from the Archaic period of the 8th to 6th centuries BC to the end of antiquity. Immediately following this period was the beginning of the Early Middle Ages and the Byzantine era. Included in Ancient Greece is the...
astronomer, Andronicus of Cyrrhus
Andronicus of Cyrrhus
Andronicus of Cyrrhus or Andronicus Cyrrhestes,son of Hermias, was a Greek astronomer who flourished about 100 BC....
, oversaw the construction of a horologion
Horologion
The 'Horologion' , or Book of Hours, provides the fixed portions of the Daily Cycle of services as used by the Eastern Orthodox and Eastern Catholic churches...
called the Tower of the Winds
Tower of the Winds
The Tower of the Winds, also called horologion , is an octagonal Pentelic marble clocktower on the Roman agora in Athens. The structure features a combination of sundials, a water clock and a wind vane...
in Athens during the first century BCE. This structure tracked a 24-hour day using both sundials and mechanical hour indicators.
Ancient Sumer
Sumer
Sumer was a civilization and historical region in southern Mesopotamia, modern Iraq during the Chalcolithic and Early Bronze Age....
, India
India
India , officially the Republic of India , is a country in South Asia. It is the seventh-largest country by geographical area, the second-most populous country with over 1.2 billion people, and the most populous democracy in the world...
, and China
China
Chinese civilization may refer to:* China for more general discussion of the country.* Chinese culture* Greater China, the transnational community of ethnic Chinese.* History of China* Sinosphere, the area historically affected by Chinese culture...
also divided days into either one twelfth of the time between sunrise and sunset or one twenty-fourth of a full day. In either case the division reflected the widespread use of a duodecimal
Duodecimal
The duodecimal system is a positional notation numeral system using twelve as its base. In this system, the number ten may be written as 'A', 'T' or 'X', and the number eleven as 'B' or 'E'...
numbering system. The importance of 12
12 (number)
12 is the natural number following 11 and preceding 13.The word "twelve" is the largest number with a single-morpheme name in English. Etymology suggests that "twelve" arises from the Germanic compound twalif "two-leftover", so a literal translation would yield "two remaining [after having ten...
has been attributed to the number of lunar cycles in a year.
Astronomers in Egypt's Middle Kingdom
Middle Kingdom of Egypt
The Middle Kingdom of Egypt is the period in the history of ancient Egypt stretching from the establishment of the Eleventh Dynasty to the end of the Fourteenth Dynasty, between 2055 BC and 1650 BC, although some writers include the Thirteenth and Fourteenth dynasties in the Second Intermediate...
(9th and 10th Dynasties) observed a set of 36 decan
Decans
The Decans are 36 groups of stars which rise consecutively on the horizon throughout each earth rotation...
stars throughout the year. These star tables have been found on the lids of coffins of the period. The heliacal rising
Heliacal rising
The heliacal rising of a star occurs when it first becomes visible above the eastern horizon for a brief moment just before sunrise, after a period of time when it had not been visible....
of the next decan star marked the start of a new civil week, which was then ten days. The period from sunset to sunrise was marked by 18 decan stars. Three of these were assigned to each of the two twilight periods, so the period of total darkness was marked by the remaining 12 decan stars, resulting in the 12 divisions of the night. The time between the appearance of each of these decan stars over the horizon during the night would have been about 40 modern minutes. During the New Kingdom
New Kingdom
The New Kingdom of Egypt, also referred to as the Egyptian Empire is the period in ancient Egyptian history between the 16th century BC and the 11th century BC, covering the Eighteenth, Nineteenth, and Twentieth Dynasties of Egypt....
, the system was simplified, using a set of 24 stars, 12 of which marked the passage of the night.
Earlier definitions of the hour varied within these parameters:
- One twelfth of the time from sunrise to sunset. As a consequence, hours on summer days were longer than on winter days, their length varying with latitudeLatitudeIn geography, the latitude of a location on the Earth is the angular distance of that location south or north of the Equator. The latitude is an angle, and is usually measured in degrees . The equator has a latitude of 0°, the North pole has a latitude of 90° north , and the South pole has a...
and even, to a small extent, with the local weather (since it affects the atmosphereEarth's atmosphereThe atmosphere of Earth is a layer of gases surrounding the planet Earth that is retained by Earth's gravity. The atmosphere protects life on Earth by absorbing ultraviolet solar radiation, warming the surface through heat retention , and reducing temperature extremes between day and night...
's index of refractionRefractionRefraction is the change in direction of a wave due to a change in its speed. It is essentially a surface phenomenon . The phenomenon is mainly in governance to the law of conservation of energy. The proper explanation would be that due to change of medium, the phase velocity of the wave is changed...
). For this reason, these hours are sometimes called temporal, seasonal, or unequal hours. RomansRomeRome is the capital of Italy and the country's largest and most populated city and comune, with over 2.7 million residents in . The city is located in the central-western portion of the Italian Peninsula, on the Tiber River within the Lazio region of Italy.Rome's history spans two and a half...
, GreeksGreeceGreece , officially the Hellenic Republic , and historically Hellas or the Republic of Greece in English, is a country in southeastern Europe....
and JewsJewsThe Jews , also known as the Jewish people, are a nation and ethnoreligious group originating in the Israelites or Hebrews of the Ancient Near East. The Jewish ethnicity, nationality, and religion are strongly interrelated, as Judaism is the traditional faith of the Jewish nation...
of the ancient world used this definition; as did the ancient Chinese and Japanese. The Romans and Greeks also divided the night into three or four night watches, but later the night (the time between sunset and sunrise) was also divided into twelve hours. When, in post-classical times, a clockClockA clock is an instrument used to indicate, keep, and co-ordinate time. The word clock is derived ultimately from the Celtic words clagan and clocca meaning "bell". A silent instrument missing such a mechanism has traditionally been known as a timepiece...
showed these hours, its period had to be changed every morning and evening (for example by changing the length of its pendulum), or it had to keep to the position of the Sun on the ecliptic (see Prague Astronomical Clock). - One twenty-fourth of the apparent solar daySolar timeSolar time is a reckoning of the passage of time based on the Sun's position in the sky. The fundamental unit of solar time is the day. Two types of solar time are apparent solar time and mean solar time .-Introduction:...
(between one noon and the next, or between one sunset and the next). As a consequence hours varied a little, as the length of an apparent solar day varies throughout the year. When a clock showed these hours it had to be adjusted a few times in a month. These hours were sometimes referred to as equal or equinoctial hours. - One twenty-fourth of the mean solar day. See solar timeSolar timeSolar time is a reckoning of the passage of time based on the Sun's position in the sky. The fundamental unit of solar time is the day. Two types of solar time are apparent solar time and mean solar time .-Introduction:...
for more information on the difference to the apparent solar day. When an accurate clock showed these hours it virtually never had to be adjusted. However, as the Earth's rotation slows down, this definition has been abandoned. See UTC.
Counting hours


Astrolabe
Astrolabe
An astrolabe is an elaborate inclinometer, historically used by astronomers, navigators, and astrologers. Its many uses include locating and predicting the positions of the Sun, Moon, planets, and stars, determining local time given local latitude and longitude, surveying, triangulation, and to...
s, sundial
Sundial
A sundial is a device that measures time by the position of the Sun. In common designs such as the horizontal sundial, the sun casts a shadow from its style onto a surface marked with lines indicating the hours of the day. The style is the time-telling edge of the gnomon, often a thin rod or a...
s, and astronomical clock
Astronomical clock
An astronomical clock is a clock with special mechanisms and dials to display astronomical information, such as the relative positions of the sun, moon, zodiacal constellations, and sometimes major planets.-Definition:...
s sometimes show the hour length and count using some of these older definitions and counting methods.
Counting from dawn
In ancient and medieval cultures, the counting of hours generally started with sunrise. Before the widespread use of artificial light, societies were more concerned with the division between night and day, and daily routines often began when light was sufficient. Sunrise marked the beginning of the first hour (the zero hour), the middle of the day was at the end of the sixth hour and sunset at the end of the twelfth hour. This meant that the duration of hours varied with the season. In the Northern hemisphere, particularly in the more northerly latitudes, summer daytime hours were longer than winter daytime hours, each being one twelfth of the time between sunrise and sunset. These variable-length hours were known as temporal hours, sometimes referred to, on astrolabeAstrolabe
An astrolabe is an elaborate inclinometer, historically used by astronomers, navigators, and astrologers. Its many uses include locating and predicting the positions of the Sun, Moon, planets, and stars, determining local time given local latitude and longitude, surveying, triangulation, and to...
s and astronomical clock
Astronomical clock
An astronomical clock is a clock with special mechanisms and dials to display astronomical information, such as the relative positions of the sun, moon, zodiacal constellations, and sometimes major planets.-Definition:...
s, for example, as "Babylonian" hours, and were in use until the appearance of the mechanical clock, which hastened the introduction of equal length hours.
This is also the system used in Jewish religious law (Halakha
Halakha
Halakha — also transliterated Halocho , or Halacha — is the collective body of Jewish law, including biblical law and later talmudic and rabbinic law, as well as customs and traditions.Judaism classically draws no distinction in its laws between religious and ostensibly non-religious life; Jewish...
) and frequently called Talmudic hour ("Sha'a Zemanit") in a variety of texts. The talmudic hour is one twelfth of time elapsed from sunrise to sunset, day hours therefore being longer than night hours in the summer; in winter they reverse.
The Indic day began at sunrise. The term "Hora" was used to indicate an hour. The time was measured based on the length of the shadow at day time. A "Hora" translated to 2.5 "Pe." There are 60 "Pe" per day, 60 minutes per "Pe" and 60 "Kshana" (snap of a finger or instant) per minute. "Pe" was measured with a bowl with a hole placed in still water. Time taken for this graduated bowl was one "Pe." Kings usually had a officer in charge of this clock.
Counting from sunset
In so-called ItalianItaly
Italy , officially the Italian Republic languages]] under the European Charter for Regional or Minority Languages. In each of these, Italy's official name is as follows:;;;;;;;;), is a unitary parliamentary republic in South-Central Europe. To the north it borders France, Switzerland, Austria and...
time, "Italian hours", or "Old Czech Time", the first hour started with the sunset Angelus
Angelus
The Angelus is a Christian devotion in memory of the Incarnation. The name Angelus is derived from the opening words: Angelus Domini nuntiavit Mariæ The Angelus (Latin for "angel") is a Christian devotion in memory of the Incarnation. The name Angelus is derived from the opening words: Angelus...
bell (or at the end of dusk, i.e., half an hour after sunset, depending on local custom and geographical latitude). The hours were numbered from 1 to 24. For example, in Lugano, the sun rose in December during the 14th hour and noon was during the 19th hour; in June the Sun rose during the 7th hour and noon was in the 15th hour. Sunset was always at the end of the 24th hour. The clocks in church towers struck only from 1 to 12, thus only during night or early morning hours.
This manner of counting hours had the advantage that everyone could easily know how much time they had to finish their day's work without artificial light. It was already widely used in Italy
Italy
Italy , officially the Italian Republic languages]] under the European Charter for Regional or Minority Languages. In each of these, Italy's official name is as follows:;;;;;;;;), is a unitary parliamentary republic in South-Central Europe. To the north it borders France, Switzerland, Austria and...
by the 14th century and lasted until the mid-18th century; it was officially abolished in 1755, or in some regions, customary, until the mid-19th century.
The system of Italian hours can be seen on a number of clocks in Europe, where the dial is numbered from 1 to 24 in either Roman or Arabic numerals. The St Mark's Clock
St Mark's Clock
For the building containing the clock see the article on the ClocktowerSt Mark's Clock is the clock housed in the Clocktower on the Piazza San Marco in Venice adjoining the Procuratie Vecchie...
in Venice, and the Orloj in Prague are famous examples. It was also used in Poland
Poland
Poland , officially the Republic of Poland , is a country in Central Europe bordered by Germany to the west; the Czech Republic and Slovakia to the south; Ukraine, Belarus and Lithuania to the east; and the Baltic Sea and Kaliningrad Oblast, a Russian exclave, to the north...
and Bohemia
Bohemia
Bohemia is a historical region in central Europe, occupying the western two-thirds of the traditional Czech Lands. It is located in the contemporary Czech Republic with its capital in Prague...
until the 17th century.
The medieval Islamic day began at sunset. The first prayer of the day (maghrib
Maghrib
The Maghrib prayer , prayed just after sunset, is the fourth of five formal daily prayers performed by practicing Muslims.The formal daily prayers of Islam comprise different numbers of units, called rak'at. The Maghrib prayer has three obligatory rak'at. The first two fard rak'at are prayed...
) was to be performed between sunset and the end of twilight.
Counting from noon
For many centuries, up to 1925, astronomers counted the hours and days from noon, because it was the easiest solar event to measure accurately. An advantage of this method (used in the Julian Date system, in which a new Julian Day begins at noon) is that the date doesn't change during a single night's observing.Counting from midnight
In the modern 12-hour clock12-hour clock
The 12-hour clock is a time conversion convention in which the 24 hours of the day are divided into two periods called ante meridiem and post meridiem...
, counting the hours starts at midnight and restarts at noon. Hours are numbered 12, 1, 2, ..., 11. Solar noon
Solar time
Solar time is a reckoning of the passage of time based on the Sun's position in the sky. The fundamental unit of solar time is the day. Two types of solar time are apparent solar time and mean solar time .-Introduction:...
is always close to 12 noon, differing according to the equation of time
Equation of time
The equation of time is the difference between apparent solar time and mean solar time. At any given instant, this difference will be the same for every observer...
by as much as fifteen minutes either way. At the equinox
Equinox
An equinox occurs twice a year, when the tilt of the Earth's axis is inclined neither away from nor towards the Sun, the center of the Sun being in the same plane as the Earth's equator...
es sunrise is around 6 A.M. (ante meridiem, before noon), and sunset around 6 P.M. (post meridiem, after noon).
In the modern 24-hour clock
24-hour clock
The 24-hour clock is a convention of time keeping in which the day runs from midnight to midnight and is divided into 24 hours, indicated by the hours passed since midnight, from 0 to 23. This system is the most commonly used time notation in the world today...
, counting the hours starts at midnight and hours are numbered from 0 to 23. Solar noon is always close to 12:00, again differing according to the equation of time. At the equinoxes sunrise is around 06:00 and sunset around 18:00.
Further reading
- "Astronomy before the telescope". Ed. Christopher Walker. London: British Museum PressBritish MuseumThe British Museum is a museum of human history and culture in London. Its collections, which number more than seven million objects, are amongst the largest and most comprehensive in the world and originate from all continents, illustrating and documenting the story of human culture from its...
, 1996.

