
History of the Jews in Europe
Encyclopedia
Judaism
in Europe
has a long history, beginning with the conquest of the Eastern Mediterranean
by Pompey
in 63 BCE, thus beginning the History of the Jews in the Roman Empire, though likely Alexandrian Jews
had migrated to Rome
slightly before Pompey's conquest of the East.
The pre-World War II
population of European Jews is estimated at close to 9 million (1.5%). About two thirds of these were murdered in the Holocaust of 1940-1945. Further population drain is due to emigration, and the current Jewish population of Europe is estimated at ca. 2 million (0.3%), composed of
, originating from Alexandria
, was present throughout the Roman Empire
even before the Roman-Jewish Wars. As early as the middle of the 2nd century BC, the Jewish author of the third book of the Oracula Sibyllina
, addressing the "chosen people
," says: "Every land is full of thee and every sea." The most diverse witnesses, such as Strabo
, Philo
, Seneca
, Cicero
, and Josephus
, all mention Jewish populations
in the cities of the Mediterranean Basin
. Most Jewish population centers of this period were however still in the East (Iudaea and Syria) and in Egypt (Alexandria
was by far the most important of the Jewish communities, the Jews in Philo
's time were inhabiting two of the five quarters of the city). Nevertheless, at the commencement of the reign of Caesar Augustus (27BC) there were over 7,000 Jews in Rome
: this is the number that escorted the envoys who came to demand the deposition of Archelaus
.
Roman Empire period presence of Jews in Croatia
date to the 2nd century, in Pannonia
to the 3rd to 4th century. A finger ring with a Menorah depiction found in Augusta Raurica
(Kaiseraugst
, Switzerland
) in 2001 attests to Jewish presence in Germania Superior
. Evidence in towns north of the Loire
or in southern Gaul
date to the 5th century and 6th centuries.
Jewish life can be characterized as democratic. Rabbis in the Talmud interpreted Deut. 29:9, “your heads, your tribes, your elders, and your officers, even all the men of Israel” and “Although I have appointed for you heads, elders, and officers, you are all equal before me” (Tanhuma ) to stress political shared power. Shared power entailed responsibilities: “you are all responsible for one another. If there be only one righteous man among you, you will all profit from his merits, and not you alone, but the entire world…But if one of you sins, the whole generation will suffer.”
Between 800 and 1100 there were 1.5 million Jews in Christian Europe. They were fortunate in not being part of the feudal system as serfs or knights, thus were spared the oppression and constant warfare that made life miserable for most Christians. Unlike lay Christians, most Jews were literate; they were cleaner and thus healthier than Christians; and they were able to live under Jewish law, which was much fairer and humane.
In relations with the Christian society, they were protected by kings, princes and even bishops, because of the crucial services they provided in three areas: financial, administrative and as doctors. Christian scholars interested in the Bible would consult with Talmudic rabbis. All this changed with the reforms and strengthening of the Roman Catholic Church and the rise of envious and competitive middle-class, town dwelling Christians. By 1300 the friars and local priests were using the Passion Plays at Easter time, which depicted Jews in contemporary dress killing Christ, to teach the general populace to hate and murder Jews. It was at this point that persecution and exile became endemic. Finally around 1500, Jews found security and a renewal of prosperity in Poland.
Persecution of Jews
in Europe begins in the High Middle Ages
in the context of the Crusades
. In the First Crusade
(1096) flourishing communities on the Rhine and the Danube were utterly destroyed; see German Crusade, 1096
. In the Second Crusade
(1147) the Jews in France were subject to frequent massacres. The Jews were also subjected to attacks by the Shepherds' Crusade
s of 1251 and 1320. The Crusades were followed by expulsions, including in, 1290, the banishing of all English Jews; in 1396, 100,000 Jews were expelled from France; and, in 1421 thousands were expelled from Austria. Many of the expelled Jews fled to Poland.
In the Late Middle Ages
, as the Black Death
epidemics devastated Europe in the mid-14th century, annihilating more than a half of the population. It is an oft-told myth, however, that due to their better nutrition and cleanliness, Jews were not infected in similar numbers; Jews were indeed infected in similar numbers to their non-Jewish neighbors Yet they were still targeted as scapegoats. Rumors spread that they caused the disease by deliberately poisoning wells
. Hundreds of Jewish communities were destroyed by violence. Although the Pope Clement VI
tried to protect them by the July 6, 1348 papal bull
and another 1348 bull, several months later, 900 Jews were burnt alive in Strasbourg
, where the plague hadn't yet affected the city.
Jewish survival in the face of external pressures from Roman Catholic empire and Persian Zoroastrian empire is ‘enigmatic’ to historians.
Baron explains it by eight factors:
Outside hostility only helped cement Jewish unity and internal strength and commitment.
in which Jews were generally accepted in society and Jewish religious, cultural and economic life blossomed. This "Golden Age" is variously dated from the 8th to 12th centuries.
Al-Andalus
was a key center of Jewish life during the Middle Ages
, producing important scholars and one of the most stable and wealthy Jewish communities. A number of famous Jewish philosophers
and scholars flourished during this time, most notably Maimonides
.
_the_flagship_of_kemal_reis.jpg) The Spanish Inquisition was established in 1478 by Catholic Monarchs
The Spanish Inquisition was established in 1478 by Catholic Monarchs
Ferdinand
and Isabella
to maintain Catholic
orthodoxy in their kingdoms and was under the direct control of the Spanish monarchy
. It was not definitively abolished until 1834, during the reign of Isabel II
.
The Inquisition
, as an ecclesiastical tribunal, had jurisdiction only over baptized Christian
s. However, since Jews (in 1492) and Muslim
Moors
(in 1502) had been banished from Spain, jurisdiction of the Inquisition during a large part of its history extended in practice to all royal subjects. The Inquisition worked in large part to ensure the orthodoxy of recent converts known as conversos or marranos.
in 1492, as well as from Austria, Hungary and Germany, stimulated a widespread Jewish migration to the much more tolerant Poland. Indeed, with the expulsion of the Jews from Spain
, Poland became the recognized haven for exiles from Western Europe
; and the resulting accession to the ranks of Polish Jewry made it the cultural and spiritual center of the Jewish people.
The most prosperous period for Polish Jews began following this new influx of Jews with the reign of Zygmunt I
(1506–1548), who protected the Jews in his realm. His son, Zygmunt II August
(1548–1572), mainly followed in the tolerant policy of his father and also granted autonomy to the Jews in the matter of communal administration and laid the foundation for the power of the Qahal, or autonomous Jewish community. This period led to the creation of a proverb about Poland being a "heaven for the Jews". According to some sources, about three-quarters of all Jews lived in Poland by the middle of the 16th century. In the middle of the 16th century, Poland welcomed the Jewish newcomers from Italy
and Turkey
, mostly of Sephardi
origin, however some of the immigrants from the Ottoman Empire
are still claimed to be Mizrahim
. Jewish religious life thrived in many Polish communities. In 1503, the Polish monarchy appointed Rabbi Jacob Polak, the official Rabbi of Poland, marking the emergence of the Chief Rabbinate. By 1551, Jews were given permission to choose their own Chief Rabbi. The Chief Rabbinate held power over law and finance, appointing judges and other officials. Some power was shared with local councils. The Polish government permitted the Rabbinate to grow in power, to use it for tax collection purposes. Only 30% of the money raised by the Rabbinate served Jewish causes, the rest went to the Crown for protection. In this period Poland-Lithuania became the main center for Ashkenazi Jewry and its yeshivot
achieved fame from the early 16th century.
Moses Isserles
(1520–1572), an eminent Talmud
ist of the 16th century, established his yeshiva
in Kraków
. In addition to being a renowned Talmudic and legal scholar
, Isserles was also learned in Kabbalah
, and studied history, astronomy, and philosophy.
 The culture and intellectual output of the Jewish community in Poland had a profound impact on Judaism as a whole. Some Jewish historians have recounted that the word Poland is pronounced as Polania or Polin in Hebrew
The culture and intellectual output of the Jewish community in Poland had a profound impact on Judaism as a whole. Some Jewish historians have recounted that the word Poland is pronounced as Polania or Polin in Hebrew
, and as transliterated
into Hebrew, these names for Poland were interpreted as "good omens" because Polania can be broken down into three Hebrew words: po ("here"), lan ("dwells"), ya ("God
"), and Polin into two words of: po ("here") lin ("[you should] dwell"). The "message" was that Poland was meant to be a good place for the Jews. During the time from the rule of Sigismund I the Old
until the Nazi Holocaust, Poland would be at the center of Jewish religious life.
Yeshivot
were established, under the direction of the rabbis, in the more prominent communities. Such schools were officially known as gymnasium
s, and their rabbi principals as rector
s. Important yeshivot existed in Kraków, Poznań, and other cities. Jewish printing establishments came into existence in the first quarter of the 16th century. In 1530 a Hebrew
Pentateuch (Torah
) was printed in Kraków; and at the end of the century the Jewish printing houses of that city and Lublin
issued a large number of Jewish books, mainly of a religious character. The growth of Talmudic scholarship
in Poland was coincident with the greater prosperity of the Polish Jews; and because of their communal autonomy educational development was wholly one-sided and along Talmudic lines. Exceptions are recorded, however, where Jewish youth sought secular instruction in the European universities. The learned rabbis became not merely expounders of the Law, but also spiritual advisers, teachers, judges, and legislators; and their authority compelled the communal leaders to make themselves familiar with the abstruse questions of Jewish law
. Polish Jewry found its views of life shaped by the spirit of Talmudic and rabbinical literature, whose influence was felt in the home, in school, and in the synagogue.
In the first half of the 16th century the seeds of Talmudic learning had been transplanted to Poland from Bohemia
, particularly from the school of Jacob Pollak
, the creator of Pilpul
("sharp reasoning"). Shalom Shachna
(c. 1500–1558), a pupil of Pollak, is counted among the pioneers of Talmudic learning in Poland. He lived and died in Lublin
, where he was the head of the yeshivah which produced the rabbinical celebrities of the following century. Shachna's son Israel became rabbi of Lublin on the death of his father, and Shachna's pupil Moses Isserles
(known as the ReMA) (1520–1572) achieved an international reputation among the Jews as the co-author of the Shulkhan Arukh, (the "Code of Jewish Law"). His contemporary and correspondent Solomon Luria
(1510–1573) of Lublin also enjoyed a wide reputation among his co-religionists; and the authority of both was recognized by the Jews throughout Europe. Heated religious disputations were common, and Jewish scholars participated in them. At the same time, the Kabbalah
had become entrenched under the protection of Rabbinism
; and such scholars as Mordecai Jaffe and Yoel Sirkis
devoted themselves to its study. This period of great Rabbinical scholarship was interrupted by the Chmielnicki Uprising and The Deluge
.

(1648–1658) left a deep and lasting impression not only on the social life of the Polish-Lithuanian Jews, but on their spiritual life as well. The intellectual output of the Jews of Poland was reduced. The Talmudic learning which up to that period had been the common possession of the majority of the people became accessible to a limited number of students only. What religious study there was became overly formalized, some rabbis busied themselves with quibbles concerning religious laws; others wrote commentaries on different parts of the Talmud in which hair-splitting arguments were raised and discussed; and at times these arguments dealt with matters which were of no practical importance. At the same time, many miracle workers made their appearance among the Jews of Poland, culminating in a series of false "Messianic" movements, most famously as Sabbatianism
was succeeded by Frankism
.
In this time of mysticism
and overly formal rabbinism came the teachings of Israel ben Eliezer, known as the Baal Shem Tov, or BeShT, (1698–1760), which had a profound effect on the Jews of Eastern Europe
and Poland in particular. His disciples taught and encouraged the new fervent brand of Judaism
based on Kabbalah
known as Hasidism
. The rise of Hasidic Judaism within Poland's borders and beyond had a great influence on the rise of Haredi Judaism
all over the world, with a continuous influence through its many Hasidic dynasties including those of Chabad-Lubavitch
, Aleksander
, Bobov, Ger
, Nadvorna
, among others. More recent rebbes of Polish origin include Rabbi Yosef Yitzchok Schneersohn (1880–1950), the sixth head of the Chabad Lubavitch Hasidic movement, who lived in Warsaw until 1940 when he moved Lubavitch from Warsaw to the United States. See also: List of Polish Rabbis
 In the Papal States
In the Papal States
, which existed until 1870, Jews were required to live only in specified neighborhoods called ghetto
s. Until the 1840s, they were required to regularly attend sermons urging their conversion to Christianity. Only Jews were taxed to support state boarding schools for Jewish converts to Christianity. It was illegal to convert from Christianity to Judaism. Sometimes Jews were baptized involuntarily, and, even when such baptisms were illegal, forced to practice the Christian religion. In many such cases the state separated them from their families. See Edgardo Mortara
for an account of one of the most widely publicized instances of acrimony between Catholics and Jews in the Papal States
in the second half of the 19th century.
The movement of Zionism
originates in the late 19th century.
In 1883, Nathan Birnbaum
founded Kadimah, the first Jewish student association in Vienna. In 1884, the first issue of Selbstemanzipation (Self Emancipation
) appeared, printed by Birnbaum himself.
The Dreyfus Affair
, which erupted in France
in 1894, profoundly shocked emancipated Jews. The depth of antisemitism in a country thought of as the home of enlightenment and liberty led many to question their future security in Europe. Among those who witnessed the Affair was an Austro-Hungarian (born in Budapest
, lived in Vienna
) Jewish journalist, Theodor Herzl
, who published his pamphlet Der Judenstaat
("The Jewish State") in 1896 and Altneuland
("The Old New Land") in 1897. He described the Affair as a personal turning point, Before the Affair, Herzl had been anti-Zionist; afterwards he became ardently pro-Zionist. In line with the ideas of 19th century German nationalism Herzl believed in a Jewish state for the Jewish nation. In that way, he argued, the Jews could become a people like all other peoples, and antisemitism would cease to exist.
Herzl
infused political Zionism with a new and practical urgency. He brought the World Zionist Organization
into being and, together with Nathan Birnbaum, planned its First Congress at Basel
in 1897.
For the first four years, the World Zionist Organization
(WZO) met every year, then, up to the Second World War, they gathered every second year. Since the war, the Congress has met every four years.
, as part of a program of deliberate extermination planned and executed by the National Socialist
regime in Nazi Germany
led by Adolf Hitler
.
Judaism
Judaism ) is the "religion, philosophy, and way of life" of the Jewish people...
in Europe
Europe
Europe is, by convention, one of the world's seven continents. Comprising the westernmost peninsula of Eurasia, Europe is generally 'divided' from Asia to its east by the watershed divides of the Ural and Caucasus Mountains, the Ural River, the Caspian and Black Seas, and the waterways connecting...
has a long history, beginning with the conquest of the Eastern Mediterranean
Eastern Mediterranean
The Eastern Mediterranean is a term that denotes the countries geographically to the east of the Mediterranean Sea. This region is also known as Greater Syria or the Levant....
by Pompey
Pompey
Gnaeus Pompeius Magnus, also known as Pompey or Pompey the Great , was a military and political leader of the late Roman Republic...
in 63 BCE, thus beginning the History of the Jews in the Roman Empire, though likely Alexandrian Jews
History of the Jews in Egypt
Egyptian Jews constitute both one of the oldest and youngest Jewish communities in the world. While no exact census exists, the Jewish population of Egypt was estimated at fewer than a hundred in 2004, down from between 75,000 and 80,000 in 1922. The historic core of the indigenous community...
had migrated to Rome
History of the Jews in Italy
The history of the Jews in Italy goes back over two thousand years. Jews have been present in Italy from the Roman period until the present.-Antiquity:-Pre-Christian Rome:...
slightly before Pompey's conquest of the East.
The pre-World War II
World War II
World War II, or the Second World War , was a global conflict lasting from 1939 to 1945, involving most of the world's nations—including all of the great powers—eventually forming two opposing military alliances: the Allies and the Axis...
population of European Jews is estimated at close to 9 million (1.5%). About two thirds of these were murdered in the Holocaust of 1940-1945. Further population drain is due to emigration, and the current Jewish population of Europe is estimated at ca. 2 million (0.3%), composed of
- Ashkenazi JewsAshkenazi JewsAshkenazi Jews, also known as Ashkenazic Jews or Ashkenazim , are the Jews descended from the medieval Jewish communities along the Rhine in Germany from Alsace in the south to the Rhineland in the north. Ashkenaz is the medieval Hebrew name for this region and thus for Germany...
(about 1.4 million, mostly GermanGermansThe Germans are a Germanic ethnic group native to Central Europe. The English term Germans has referred to the German-speaking population of the Holy Roman Empire since the Late Middle Ages....
and PolishPolesthumb|right|180px|The state flag of [[Poland]] as used by Polish government and diplomatic authoritiesThe Polish people, or Poles , are a nation indigenous to Poland. They are united by the Polish language, which belongs to the historical Lechitic subgroup of West Slavic languages of Central Europe...
) - Sephardi JewsSephardi JewsSephardi Jews is a general term referring to the descendants of the Jews who lived in the Iberian Peninsula before their expulsion in the Spanish Inquisition. It can also refer to those who use a Sephardic style of liturgy or would otherwise define themselves in terms of the Jewish customs and...
(about 0.3 million, mainly in FranceFranceThe French Republic , The French Republic , The French Republic , (commonly known as France , is a unitary semi-presidential republic in Western Europe with several overseas territories and islands located on other continents and in the Indian, Pacific, and Atlantic oceans. Metropolitan France...
, SpainSpainSpain , officially the Kingdom of Spain languages]] under the European Charter for Regional or Minority Languages. In each of these, Spain's official name is as follows:;;;;;;), is a country and member state of the European Union located in southwestern Europe on the Iberian Peninsula...
and PortugalPortugalPortugal , officially the Portuguese Republic is a country situated in southwestern Europe on the Iberian Peninsula. Portugal is the westernmost country of Europe, and is bordered by the Atlantic Ocean to the West and South and by Spain to the North and East. The Atlantic archipelagos of the...
) - Mizrahi JewsMizrahi JewsMizrahi Jews or Mizrahiyim, , also referred to as Adot HaMizrach are Jews descended from the Jewish communities of the Middle East, North Africa and the Caucasus...
(about 0.3 million, mainly in FranceFranceThe French Republic , The French Republic , The French Republic , (commonly known as France , is a unitary semi-presidential republic in Western Europe with several overseas territories and islands located on other continents and in the Indian, Pacific, and Atlantic oceans. Metropolitan France...
) - Italian JewsItalian JewsItalian Jews can be used in a broad sense to mean all Jews living or with roots in Italy or in a narrower sense to mean the ancient community who use the Italian rite, as distinct from the communities dating from medieval or modern times who use the Sephardi or Ashkenazi rite.-Divisions:Italian...
(some 50,000, mostly Italian) - RomaniotesRomaniotesThe Romaniotes or Romaniots are a Jewish population who have lived in the territory of today's Greece and neighboring areas with large Greek populations for more than 2,000 years. Their languages were Yevanic, a Greek dialect, and Greek. They derived their name from the old name for the people...
(some 6,000, mostly GreekGreeksThe Greeks, also known as the Hellenes , are a nation and ethnic group native to Greece, Cyprus and neighboring regions. They also form a significant diaspora, with Greek communities established around the world....
)
Early presence
Hellenistic JudaismHellenistic Judaism
Hellenistic Judaism was a movement which existed in the Jewish diaspora that sought to establish a Hebraic-Jewish religious tradition within the culture and language of Hellenism...
, originating from Alexandria
Alexandria
Alexandria is the second-largest city of Egypt, with a population of 4.1 million, extending about along the coast of the Mediterranean Sea in the north central part of the country; it is also the largest city lying directly on the Mediterranean coast. It is Egypt's largest seaport, serving...
, was present throughout the Roman Empire
Roman Empire
The Roman Empire was the post-Republican period of the ancient Roman civilization, characterised by an autocratic form of government and large territorial holdings in Europe and around the Mediterranean....
even before the Roman-Jewish Wars. As early as the middle of the 2nd century BC, the Jewish author of the third book of the Oracula Sibyllina
Sibylline oracles
The Sibylline Oracles are a collection of oracular utterances written in Greek hexameters ascribed to the Sibyls, prophetesses who uttered divine revelations in a frenzied state. Fourteen books and eight fragments of Sibylline Oracles survive...
, addressing the "chosen people
Chosen people
Throughout history and even today various groups of people have considered themselves as chosen by a deity for some purpose such as to act as the deity's agent on earth. In monotheistic faiths, like Abrahamic religions, references to God are used in constructs such as "God's Chosen People"...
," says: "Every land is full of thee and every sea." The most diverse witnesses, such as Strabo
Strabo
Strabo, also written Strabon was a Greek historian, geographer and philosopher.-Life:Strabo was born to an affluent family from Amaseia in Pontus , a city which he said was situated the approximate equivalent of 75 km from the Black Sea...
, Philo
Philo
Philo , known also as Philo of Alexandria , Philo Judaeus, Philo Judaeus of Alexandria, Yedidia, "Philon", and Philo the Jew, was a Hellenistic Jewish Biblical philosopher born in Alexandria....
, Seneca
Seneca the Younger
Lucius Annaeus Seneca was a Roman Stoic philosopher, statesman, dramatist, and in one work humorist, of the Silver Age of Latin literature. He was tutor and later advisor to emperor Nero...
, Cicero
Cicero
Marcus Tullius Cicero , was a Roman philosopher, statesman, lawyer, political theorist, and Roman constitutionalist. He came from a wealthy municipal family of the equestrian order, and is widely considered one of Rome's greatest orators and prose stylists.He introduced the Romans to the chief...
, and Josephus
Josephus
Titus Flavius Josephus , also called Joseph ben Matityahu , was a 1st-century Romano-Jewish historian and hagiographer of priestly and royal ancestry who recorded Jewish history, with special emphasis on the 1st century AD and the First Jewish–Roman War, which resulted in the Destruction of...
, all mention Jewish populations
Jewish diaspora
The Jewish diaspora is the English term used to describe the Galut גלות , or 'exile', of the Jews from the region of the Kingdom of Judah and Roman Iudaea and later emigration from wider Eretz Israel....
in the cities of the Mediterranean Basin
Mediterranean Basin
In biogeography, the Mediterranean Basin refers to the lands around the Mediterranean Sea that have a Mediterranean climate, with mild, rainy winters and hot, dry summers, which supports characteristic Mediterranean forests, woodlands, and scrub vegetation...
. Most Jewish population centers of this period were however still in the East (Iudaea and Syria) and in Egypt (Alexandria
Alexandria
Alexandria is the second-largest city of Egypt, with a population of 4.1 million, extending about along the coast of the Mediterranean Sea in the north central part of the country; it is also the largest city lying directly on the Mediterranean coast. It is Egypt's largest seaport, serving...
was by far the most important of the Jewish communities, the Jews in Philo
Philo
Philo , known also as Philo of Alexandria , Philo Judaeus, Philo Judaeus of Alexandria, Yedidia, "Philon", and Philo the Jew, was a Hellenistic Jewish Biblical philosopher born in Alexandria....
's time were inhabiting two of the five quarters of the city). Nevertheless, at the commencement of the reign of Caesar Augustus (27BC) there were over 7,000 Jews in Rome
Rome
Rome is the capital of Italy and the country's largest and most populated city and comune, with over 2.7 million residents in . The city is located in the central-western portion of the Italian Peninsula, on the Tiber River within the Lazio region of Italy.Rome's history spans two and a half...
: this is the number that escorted the envoys who came to demand the deposition of Archelaus
Herod Archelaus
Herod Archelaus was the ethnarch of Samaria, Judea, and Idumea from 4 BC to 6 AD. He was the son of Herod the Great and Malthace the Samaritan, the brother of Herod Antipas, and the half-brother of Herod Philip I....
.
Roman Empire period presence of Jews in Croatia
Croatia
Croatia , officially the Republic of Croatia , is a unitary democratic parliamentary republic in Europe at the crossroads of the Mitteleuropa, the Balkans, and the Mediterranean. Its capital and largest city is Zagreb. The country is divided into 20 counties and the city of Zagreb. Croatia covers ...
date to the 2nd century, in Pannonia
Pannonia
Pannonia was an ancient province of the Roman Empire bounded north and east by the Danube, coterminous westward with Noricum and upper Italy, and southward with Dalmatia and upper Moesia....
to the 3rd to 4th century. A finger ring with a Menorah depiction found in Augusta Raurica
Augusta Raurica
Augusta Raurica is a Roman archaeological site and an open-air museum in Switzerland. Located on the south bank of the Rhine river about 20 km east of Basel near the villages of Augst and Kaiseraugst, it is the oldest known Roman colony on the Rhine....
(Kaiseraugst
Kaiseraugst
Kaiseraugst is a municipality in the district of Rheinfelden in the canton of Aargau in Switzerland. It is named for the Ancient Roman city of Augusta Raurica whose ruins are situated nearby...
, Switzerland
Switzerland
Switzerland name of one of the Swiss cantons. ; ; ; or ), in its full name the Swiss Confederation , is a federal republic consisting of 26 cantons, with Bern as the seat of the federal authorities. The country is situated in Western Europe,Or Central Europe depending on the definition....
) in 2001 attests to Jewish presence in Germania Superior
Germania Superior
Germania Superior , so called for the reason that it lay upstream of Germania Inferior, was a province of the Roman Empire. It comprised an area of western Switzerland, the French Jura and Alsace regions, and southwestern Germany...
. Evidence in towns north of the Loire
Loire
Loire is an administrative department in the east-central part of France occupying the River Loire's upper reaches.-History:Loire was created in 1793 when after just 3½ years the young Rhône-et-Loire department was split into two. This was a response to counter-Revolutionary activities in Lyon...
or in southern Gaul
Gaul
Gaul was a region of Western Europe during the Iron Age and Roman era, encompassing present day France, Luxembourg and Belgium, most of Switzerland, the western part of Northern Italy, as well as the parts of the Netherlands and Germany on the left bank of the Rhine. The Gauls were the speakers of...
date to the 5th century and 6th centuries.
Middle Ages
Early medieval period was a time of flourishing Jewish culture. Jewish and Christian life evolved in ‘diametrically opposite directions’ during the final centuries of Roman empire. Jewish life became autonomous, decentralized, community-centered. Christian life became a rigid hierarchical system under the supreme authority of the Pope and the Roman Emperor.Jewish life can be characterized as democratic. Rabbis in the Talmud interpreted Deut. 29:9, “your heads, your tribes, your elders, and your officers, even all the men of Israel” and “Although I have appointed for you heads, elders, and officers, you are all equal before me” (Tanhuma ) to stress political shared power. Shared power entailed responsibilities: “you are all responsible for one another. If there be only one righteous man among you, you will all profit from his merits, and not you alone, but the entire world…But if one of you sins, the whole generation will suffer.”
Between 800 and 1100 there were 1.5 million Jews in Christian Europe. They were fortunate in not being part of the feudal system as serfs or knights, thus were spared the oppression and constant warfare that made life miserable for most Christians. Unlike lay Christians, most Jews were literate; they were cleaner and thus healthier than Christians; and they were able to live under Jewish law, which was much fairer and humane.
In relations with the Christian society, they were protected by kings, princes and even bishops, because of the crucial services they provided in three areas: financial, administrative and as doctors. Christian scholars interested in the Bible would consult with Talmudic rabbis. All this changed with the reforms and strengthening of the Roman Catholic Church and the rise of envious and competitive middle-class, town dwelling Christians. By 1300 the friars and local priests were using the Passion Plays at Easter time, which depicted Jews in contemporary dress killing Christ, to teach the general populace to hate and murder Jews. It was at this point that persecution and exile became endemic. Finally around 1500, Jews found security and a renewal of prosperity in Poland.
Persecution of Jews
Persecution of Jews
Persecution of Jews has occurred on numerous occasions and at widely different geographical locations. As well as being a major component in Jewish history, it has significantly affected the general history and social development of the countries and societies in which the persecuted Jews...
in Europe begins in the High Middle Ages
High Middle Ages
The High Middle Ages was the period of European history around the 11th, 12th, and 13th centuries . The High Middle Ages were preceded by the Early Middle Ages and followed by the Late Middle Ages, which by convention end around 1500....
in the context of the Crusades
Crusades
The Crusades were a series of religious wars, blessed by the Pope and the Catholic Church with the main goal of restoring Christian access to the holy places in and near Jerusalem...
. In the First Crusade
First Crusade
The First Crusade was a military expedition by Western Christianity to regain the Holy Lands taken in the Muslim conquest of the Levant, ultimately resulting in the recapture of Jerusalem...
(1096) flourishing communities on the Rhine and the Danube were utterly destroyed; see German Crusade, 1096
German Crusade, 1096
The call for the First Crusade touched off new persecutions of Jews in which peasant crusaders from France and Germany attacked Jewish communities.-Background:The preaching of the First Crusade inspired an outbreak of anti-Jewish violence...
. In the Second Crusade
Second Crusade
The Second Crusade was the second major crusade launched from Europe. The Second Crusade was started in response to the fall of the County of Edessa the previous year to the forces of Zengi. The county had been founded during the First Crusade by Baldwin of Boulogne in 1098...
(1147) the Jews in France were subject to frequent massacres. The Jews were also subjected to attacks by the Shepherds' Crusade
Shepherds' Crusade
The Shepherds' Crusade refers to separate events from the 13th and 14th century. The first took place in 1251 during the Seventh Crusade; the second occurred in 1320.-Shepherds' Crusade, 1251:...
s of 1251 and 1320. The Crusades were followed by expulsions, including in, 1290, the banishing of all English Jews; in 1396, 100,000 Jews were expelled from France; and, in 1421 thousands were expelled from Austria. Many of the expelled Jews fled to Poland.
In the Late Middle Ages
Late Middle Ages
The Late Middle Ages was the period of European history generally comprising the 14th to the 16th century . The Late Middle Ages followed the High Middle Ages and preceded the onset of the early modern era ....
, as the Black Death
Black Death
The Black Death was one of the most devastating pandemics in human history, peaking in Europe between 1348 and 1350. Of several competing theories, the dominant explanation for the Black Death is the plague theory, which attributes the outbreak to the bacterium Yersinia pestis. Thought to have...
epidemics devastated Europe in the mid-14th century, annihilating more than a half of the population. It is an oft-told myth, however, that due to their better nutrition and cleanliness, Jews were not infected in similar numbers; Jews were indeed infected in similar numbers to their non-Jewish neighbors Yet they were still targeted as scapegoats. Rumors spread that they caused the disease by deliberately poisoning wells
Well poisoning
Well-poisoning is the act of malicious manipulation of potable water resources in order to cause illness or death, or to deny an opponent access to fresh water resources....
. Hundreds of Jewish communities were destroyed by violence. Although the Pope Clement VI
Pope Clement VI
Pope Clement VI , bornPierre Roger, the fourth of the Avignon Popes, was pope from May 1342 until his death in December of 1352...
tried to protect them by the July 6, 1348 papal bull
Papal bull
A Papal bull is a particular type of letters patent or charter issued by a Pope of the Catholic Church. It is named after the bulla that was appended to the end in order to authenticate it....
and another 1348 bull, several months later, 900 Jews were burnt alive in Strasbourg
Strasbourg
Strasbourg is the capital and principal city of the Alsace region in eastern France and is the official seat of the European Parliament. Located close to the border with Germany, it is the capital of the Bas-Rhin département. The city and the region of Alsace are historically German-speaking,...
, where the plague hadn't yet affected the city.
Jewish survival in the face of external pressures from Roman Catholic empire and Persian Zoroastrian empire is ‘enigmatic’ to historians.
Baron explains it by eight factors:
- Messianic faith. Belief in an ultimately positive outcome and restoration of Israel.
- The doctrine of the Hereafter increasingly elaborated. Reconciled Jews with suffering in this world and helped them resist outside temptations to convert.
- Suffering was given meaning through hope-inducing interpretation of their history and their destiny.
- The doctrine of martyrdom and inescapability of persecution transformed it into a source of communal solidarity.
- Jewish daily life was very satisfying. Jews lived among Jews. In practice, in a lifetime, individuals encountered overt persecution only on a few dramatic occasions. Jews mostly lived under discrimination that affected everyone, and to which they were habituated. Daily life was governed by a multiplicity of ritual requirements, so that each Jew was constantly aware of God throughout the day. “For the most part, he found this all-encompassing Jewish way of life so eminently satisfactory that he was prepared to sacrifice himself…for the preservation of its fundamentals.” Those commandments for which Jews had sacrificed their lives, such as defying idolatry, not eating pork, observing circumcision, were the ones most strictly adhered to.
- The corporate development and segregationist policies of the late Roman empire and Persian empire, helped keep Jewish community organization strong.
- Talmud provided an extremely effective force to sustain Jewish ethics, law and culture, judicial and social welfare system, universal education, regulation of strong family life and religious life from birth to death.
- The concentration of Jewish masses within ‘the lower middle class’, with the middle class virtues of sexual self-control. There was a moderate path between asceticism and licentiousness. Marriage was considered to be the foundation of ethnic, and ethical, life.
Outside hostility only helped cement Jewish unity and internal strength and commitment.
Golden age of Jewish culture in Spain
The Golden age of Jewish culture in Spain refers to a period of history during the Muslim rule of IberiaAl-Andalus
Al-Andalus was the Arabic name given to a nation and territorial region also commonly referred to as Moorish Iberia. The name describes parts of the Iberian Peninsula and Septimania governed by Muslims , at various times in the period between 711 and 1492, although the territorial boundaries...
in which Jews were generally accepted in society and Jewish religious, cultural and economic life blossomed. This "Golden Age" is variously dated from the 8th to 12th centuries.
Al-Andalus
Al-Andalus
Al-Andalus was the Arabic name given to a nation and territorial region also commonly referred to as Moorish Iberia. The name describes parts of the Iberian Peninsula and Septimania governed by Muslims , at various times in the period between 711 and 1492, although the territorial boundaries...
was a key center of Jewish life during the Middle Ages
Middle Ages
The Middle Ages is a periodization of European history from the 5th century to the 15th century. The Middle Ages follows the fall of the Western Roman Empire in 476 and precedes the Early Modern Era. It is the middle period of a three-period division of Western history: Classic, Medieval and Modern...
, producing important scholars and one of the most stable and wealthy Jewish communities. A number of famous Jewish philosophers
Jewish philosophy
Jewish philosophy , includes all philosophy carried out by Jews, or, in relation to the religion of Judaism. Jewish philosophy, until modern Enlightenment and Emancipation, was pre-occupied with attempts to reconcile coherent new ideas into the tradition of Rabbinic Judaism; thus organizing...
and scholars flourished during this time, most notably Maimonides
Maimonides
Moses ben-Maimon, called Maimonides and also known as Mūsā ibn Maymūn in Arabic, or Rambam , was a preeminent medieval Jewish philosopher and one of the greatest Torah scholars and physicians of the Middle Ages...
.
Spanish Inquisition
_the_flagship_of_kemal_reis.jpg)
Catholic Monarchs
The Catholic Monarchs is the collective title used in history for Queen Isabella I of Castile and King Ferdinand II of Aragon. They were both from the House of Trastámara and were second cousins, being both descended from John I of Castile; they were given a papal dispensation to deal with...
Ferdinand
Ferdinand
Ferdinand is a Germanic male given name composed of the words for "prepared"/"protection"/"safety"/"peace" and "journey"/"boldness"/"recklessness"...
and Isabella
Isabella I of Castile
Isabella I was Queen of Castile and León. She and her husband Ferdinand II of Aragon brought stability to both kingdoms that became the basis for the unification of Spain. Later the two laid the foundations for the political unification of Spain under their grandson, Charles V, Holy Roman Emperor...
to maintain Catholic
Catholic
The word catholic comes from the Greek phrase , meaning "on the whole," "according to the whole" or "in general", and is a combination of the Greek words meaning "about" and meaning "whole"...
orthodoxy in their kingdoms and was under the direct control of the Spanish monarchy
Spanish monarchy
The Monarchy of Spain, constitutionally referred to as The Crown and commonly referred to as the Spanish monarchy or Hispanic Monarchy, is a constitutional institution and an historic office of Spain...
. It was not definitively abolished until 1834, during the reign of Isabel II
Isabella II of Spain
Isabella II was the only female monarch of Spain in modern times. She came to the throne as an infant, but her succession was disputed by the Carlists, who refused to recognise a female sovereign, leading to the Carlist Wars. After a troubled reign, she was deposed in the Glorious Revolution of...
.
The Inquisition
Inquisition
The Inquisition, Inquisitio Haereticae Pravitatis , was the "fight against heretics" by several institutions within the justice-system of the Roman Catholic Church. It started in the 12th century, with the introduction of torture in the persecution of heresy...
, as an ecclesiastical tribunal, had jurisdiction only over baptized Christian
Christian
A Christian is a person who adheres to Christianity, an Abrahamic, monotheistic religion based on the life and teachings of Jesus of Nazareth as recorded in the Canonical gospels and the letters of the New Testament...
s. However, since Jews (in 1492) and Muslim
Muslim
A Muslim, also spelled Moslem, is an adherent of Islam, a monotheistic, Abrahamic religion based on the Quran, which Muslims consider the verbatim word of God as revealed to prophet Muhammad. "Muslim" is the Arabic term for "submitter" .Muslims believe that God is one and incomparable...
Moors
Moors
The description Moors has referred to several historic and modern populations of the Maghreb region who are predominately of Berber and Arab descent. They came to conquer and rule the Iberian Peninsula for nearly 800 years. At that time they were Muslim, although earlier the people had followed...
(in 1502) had been banished from Spain, jurisdiction of the Inquisition during a large part of its history extended in practice to all royal subjects. The Inquisition worked in large part to ensure the orthodoxy of recent converts known as conversos or marranos.
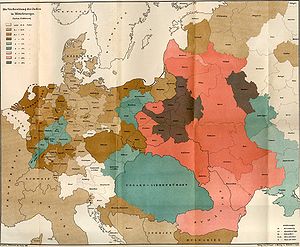
Poland as the center of the Jewish world
The expulsion of the Jews from SpainAlhambra decree
The Alhambra Decree was an edict issued on 31 March 1492 by the joint Catholic Monarchs of Spain ordering the expulsion of Jews from the Kingdom of Spain and its territories and possessions by 31 July of that year.The edict was formally revoked on 16 December 1968, following the Second...
in 1492, as well as from Austria, Hungary and Germany, stimulated a widespread Jewish migration to the much more tolerant Poland. Indeed, with the expulsion of the Jews from Spain
History of the Jews in Spain
Spanish Jews once constituted one of the largest and most prosperous Jewish communities under Muslim and Christian rule in Spain, before the majority, together with resident Muslims, were forced to convert to Catholicism, be expelled or be killed when Spain became united under the Catholic Monarchs...
, Poland became the recognized haven for exiles from Western Europe
Western Europe
Western Europe is a loose term for the collection of countries in the western most region of the European continents, though this definition is context-dependent and carries cultural and political connotations. One definition describes Western Europe as a geographic entity—the region lying in the...
; and the resulting accession to the ranks of Polish Jewry made it the cultural and spiritual center of the Jewish people.
The most prosperous period for Polish Jews began following this new influx of Jews with the reign of Zygmunt I
Sigismund I the Old
Sigismund I of Poland , of the Jagiellon dynasty, reigned as King of Poland and also as the Grand Duke of Lithuania from 1506 until 1548...
(1506–1548), who protected the Jews in his realm. His son, Zygmunt II August
Sigismund II Augustus
Sigismund II Augustus I was King of Poland and Grand Duke of Lithuania, the only son of Sigismund I the Old, whom Sigismund II succeeded in 1548...
(1548–1572), mainly followed in the tolerant policy of his father and also granted autonomy to the Jews in the matter of communal administration and laid the foundation for the power of the Qahal, or autonomous Jewish community. This period led to the creation of a proverb about Poland being a "heaven for the Jews". According to some sources, about three-quarters of all Jews lived in Poland by the middle of the 16th century. In the middle of the 16th century, Poland welcomed the Jewish newcomers from Italy
Italy
Italy , officially the Italian Republic languages]] under the European Charter for Regional or Minority Languages. In each of these, Italy's official name is as follows:;;;;;;;;), is a unitary parliamentary republic in South-Central Europe. To the north it borders France, Switzerland, Austria and...
and Turkey
Turkey
Turkey , known officially as the Republic of Turkey , is a Eurasian country located in Western Asia and in East Thrace in Southeastern Europe...
, mostly of Sephardi
Sephardi Jews
Sephardi Jews is a general term referring to the descendants of the Jews who lived in the Iberian Peninsula before their expulsion in the Spanish Inquisition. It can also refer to those who use a Sephardic style of liturgy or would otherwise define themselves in terms of the Jewish customs and...
origin, however some of the immigrants from the Ottoman Empire
Ottoman Empire
The Ottoman EmpireIt was usually referred to as the "Ottoman Empire", the "Turkish Empire", the "Ottoman Caliphate" or more commonly "Turkey" by its contemporaries...
are still claimed to be Mizrahim
Mizrahi Jews
Mizrahi Jews or Mizrahiyim, , also referred to as Adot HaMizrach are Jews descended from the Jewish communities of the Middle East, North Africa and the Caucasus...
. Jewish religious life thrived in many Polish communities. In 1503, the Polish monarchy appointed Rabbi Jacob Polak, the official Rabbi of Poland, marking the emergence of the Chief Rabbinate. By 1551, Jews were given permission to choose their own Chief Rabbi. The Chief Rabbinate held power over law and finance, appointing judges and other officials. Some power was shared with local councils. The Polish government permitted the Rabbinate to grow in power, to use it for tax collection purposes. Only 30% of the money raised by the Rabbinate served Jewish causes, the rest went to the Crown for protection. In this period Poland-Lithuania became the main center for Ashkenazi Jewry and its yeshivot
Yeshiva
Yeshiva is a Jewish educational institution that focuses on the study of traditional religious texts, primarily the Talmud and Torah study. Study is usually done through daily shiurim and in study pairs called chavrutas...
achieved fame from the early 16th century.
Moses Isserles
Moses Isserles
Moses Isserles, also spelled Moshe Isserlis, , was an eminent Ashkenazic rabbi, talmudist, and posek, renowned for his fundamental work of Halakha , entitled ha-Mapah , an inline commentary on the Shulkhan Aruch...
(1520–1572), an eminent Talmud
Talmud
The Talmud is a central text of mainstream Judaism. It takes the form of a record of rabbinic discussions pertaining to Jewish law, ethics, philosophy, customs and history....
ist of the 16th century, established his yeshiva
Yeshiva
Yeshiva is a Jewish educational institution that focuses on the study of traditional religious texts, primarily the Talmud and Torah study. Study is usually done through daily shiurim and in study pairs called chavrutas...
in Kraków
Kraków
Kraków also Krakow, or Cracow , is the second largest and one of the oldest cities in Poland. Situated on the Vistula River in the Lesser Poland region, the city dates back to the 7th century. Kraków has traditionally been one of the leading centres of Polish academic, cultural, and artistic life...
. In addition to being a renowned Talmudic and legal scholar
Halakha
Halakha — also transliterated Halocho , or Halacha — is the collective body of Jewish law, including biblical law and later talmudic and rabbinic law, as well as customs and traditions.Judaism classically draws no distinction in its laws between religious and ostensibly non-religious life; Jewish...
, Isserles was also learned in Kabbalah
Kabbalah
Kabbalah/Kabala is a discipline and school of thought concerned with the esoteric aspect of Rabbinic Judaism. It was systematized in 11th-13th century Hachmei Provence and Spain, and again after the Expulsion from Spain, in 16th century Ottoman Palestine...
, and studied history, astronomy, and philosophy.
The development of Judaism in Poland and the Commonwealth

Hebrew language
Hebrew is a Semitic language of the Afroasiatic language family. Culturally, is it considered by Jews and other religious groups as the language of the Jewish people, though other Jewish languages had originated among diaspora Jews, and the Hebrew language is also used by non-Jewish groups, such...
, and as transliterated
Transliteration
Transliteration is a subset of the science of hermeneutics. It is a form of translation, and is the practice of converting a text from one script into another...
into Hebrew, these names for Poland were interpreted as "good omens" because Polania can be broken down into three Hebrew words: po ("here"), lan ("dwells"), ya ("God
Names of God in Judaism
In Judaism, the name of God is more than a distinguishing title; it represents the Jewish conception of the divine nature, and of the relationship of God to the Jewish people and to the world. To demonstrate the sacredness of the names of God, and as a means of showing respect and reverence for...
"), and Polin into two words of: po ("here") lin ("[you should] dwell"). The "message" was that Poland was meant to be a good place for the Jews. During the time from the rule of Sigismund I the Old
Sigismund I the Old
Sigismund I of Poland , of the Jagiellon dynasty, reigned as King of Poland and also as the Grand Duke of Lithuania from 1506 until 1548...
until the Nazi Holocaust, Poland would be at the center of Jewish religious life.
Yeshivot
Yeshiva
Yeshiva is a Jewish educational institution that focuses on the study of traditional religious texts, primarily the Talmud and Torah study. Study is usually done through daily shiurim and in study pairs called chavrutas...
were established, under the direction of the rabbis, in the more prominent communities. Such schools were officially known as gymnasium
Gymnasium (school)
A gymnasium is a type of school providing secondary education in some parts of Europe, comparable to English grammar schools or sixth form colleges and U.S. college preparatory high schools. The word γυμνάσιον was used in Ancient Greece, meaning a locality for both physical and intellectual...
s, and their rabbi principals as rector
Rector
The word rector has a number of different meanings; it is widely used to refer to an academic, religious or political administrator...
s. Important yeshivot existed in Kraków, Poznań, and other cities. Jewish printing establishments came into existence in the first quarter of the 16th century. In 1530 a Hebrew
Hebrew language
Hebrew is a Semitic language of the Afroasiatic language family. Culturally, is it considered by Jews and other religious groups as the language of the Jewish people, though other Jewish languages had originated among diaspora Jews, and the Hebrew language is also used by non-Jewish groups, such...
Pentateuch (Torah
Torah
Torah- A scroll containing the first five books of the BibleThe Torah , is name given by Jews to the first five books of the bible—Genesis , Exodus , Leviticus , Numbers and Deuteronomy Torah- A scroll containing the first five books of the BibleThe Torah , is name given by Jews to the first five...
) was printed in Kraków; and at the end of the century the Jewish printing houses of that city and Lublin
Lublin
Lublin is the ninth largest city in Poland. It is the capital of Lublin Voivodeship with a population of 350,392 . Lublin is also the largest Polish city east of the Vistula river...
issued a large number of Jewish books, mainly of a religious character. The growth of Talmudic scholarship
Talmud
The Talmud is a central text of mainstream Judaism. It takes the form of a record of rabbinic discussions pertaining to Jewish law, ethics, philosophy, customs and history....
in Poland was coincident with the greater prosperity of the Polish Jews; and because of their communal autonomy educational development was wholly one-sided and along Talmudic lines. Exceptions are recorded, however, where Jewish youth sought secular instruction in the European universities. The learned rabbis became not merely expounders of the Law, but also spiritual advisers, teachers, judges, and legislators; and their authority compelled the communal leaders to make themselves familiar with the abstruse questions of Jewish law
Halakha
Halakha — also transliterated Halocho , or Halacha — is the collective body of Jewish law, including biblical law and later talmudic and rabbinic law, as well as customs and traditions.Judaism classically draws no distinction in its laws between religious and ostensibly non-religious life; Jewish...
. Polish Jewry found its views of life shaped by the spirit of Talmudic and rabbinical literature, whose influence was felt in the home, in school, and in the synagogue.
In the first half of the 16th century the seeds of Talmudic learning had been transplanted to Poland from Bohemia
Bohemia
Bohemia is a historical region in central Europe, occupying the western two-thirds of the traditional Czech Lands. It is located in the contemporary Czech Republic with its capital in Prague...
, particularly from the school of Jacob Pollak
Jacob Pollak
Rabbi Jacob Pollak was the founder of the Polish method of halakic and Talmudic study known as the Pilpul; born about 1460; died at Lublin in 1541...
, the creator of Pilpul
Pilpul
Pilpul refers to a method of studying the Talmud through intense textual analysis in attempts to either explain conceptual differences between various halakhic rulings or to reconcile any apparent contradictions presented from various readings of different texts.Pilpul has entered English as a...
("sharp reasoning"). Shalom Shachna
Shalom Shachna
Shalom Shachna was a rabbi and Talmudist, and Rosh Yeshiva of several great Acharonim including Moses Isserles, who was also his son-in-law.-Biography:...
(c. 1500–1558), a pupil of Pollak, is counted among the pioneers of Talmudic learning in Poland. He lived and died in Lublin
Lublin
Lublin is the ninth largest city in Poland. It is the capital of Lublin Voivodeship with a population of 350,392 . Lublin is also the largest Polish city east of the Vistula river...
, where he was the head of the yeshivah which produced the rabbinical celebrities of the following century. Shachna's son Israel became rabbi of Lublin on the death of his father, and Shachna's pupil Moses Isserles
Moses Isserles
Moses Isserles, also spelled Moshe Isserlis, , was an eminent Ashkenazic rabbi, talmudist, and posek, renowned for his fundamental work of Halakha , entitled ha-Mapah , an inline commentary on the Shulkhan Aruch...
(known as the ReMA) (1520–1572) achieved an international reputation among the Jews as the co-author of the Shulkhan Arukh, (the "Code of Jewish Law"). His contemporary and correspondent Solomon Luria
Solomon Luria
Solomon Luria was one of the great Ashkenazic poskim and teachers of his time. He is known for his work of Halakha, Yam Shel Shlomo, and his Talmudic commentary Chochmat Shlomo...
(1510–1573) of Lublin also enjoyed a wide reputation among his co-religionists; and the authority of both was recognized by the Jews throughout Europe. Heated religious disputations were common, and Jewish scholars participated in them. At the same time, the Kabbalah
Kabbalah
Kabbalah/Kabala is a discipline and school of thought concerned with the esoteric aspect of Rabbinic Judaism. It was systematized in 11th-13th century Hachmei Provence and Spain, and again after the Expulsion from Spain, in 16th century Ottoman Palestine...
had become entrenched under the protection of Rabbinism
Rabbinic Judaism
Rabbinic Judaism or Rabbinism has been the mainstream form of Judaism since the 6th century CE, after the codification of the Talmud...
; and such scholars as Mordecai Jaffe and Yoel Sirkis
Yoel Sirkis
Joel ben Samuel Sirkis also known as the Bach - an abbreviation of his magnum opus, Bayit Chadash - was a prominent Jewish posek and halakhist. He lived in central Europe and held rabbinical positions in Belz, Brest-Litovsk and Kraków from 1561-1640.-Biography:Sirkis was born in Lublin in 1561...
devoted themselves to its study. This period of great Rabbinical scholarship was interrupted by the Chmielnicki Uprising and The Deluge
The Deluge (Polish history)
The term Deluge denotes a series of mid-17th century campaigns in the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth. In a wider sense it applies to the period between the Khmelnytsky Uprising of 1648 and the Truce of Andrusovo in 1667, thus comprising the Polish–Lithuanian theaters of the Russo-Polish and...
.

The rise of Hasidism
The decade from the Cossacks' uprising until after the Swedish warThe Deluge (Polish history)
The term Deluge denotes a series of mid-17th century campaigns in the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth. In a wider sense it applies to the period between the Khmelnytsky Uprising of 1648 and the Truce of Andrusovo in 1667, thus comprising the Polish–Lithuanian theaters of the Russo-Polish and...
(1648–1658) left a deep and lasting impression not only on the social life of the Polish-Lithuanian Jews, but on their spiritual life as well. The intellectual output of the Jews of Poland was reduced. The Talmudic learning which up to that period had been the common possession of the majority of the people became accessible to a limited number of students only. What religious study there was became overly formalized, some rabbis busied themselves with quibbles concerning religious laws; others wrote commentaries on different parts of the Talmud in which hair-splitting arguments were raised and discussed; and at times these arguments dealt with matters which were of no practical importance. At the same time, many miracle workers made their appearance among the Jews of Poland, culminating in a series of false "Messianic" movements, most famously as Sabbatianism
Sabbatai Zevi
Sabbatai Zevi, , was a Sephardic Rabbi and kabbalist who claimed to be the long-awaited Jewish Messiah. He was the founder of the Jewish Sabbatean movement...
was succeeded by Frankism
Jacob Frank
Jacob Frank was an 18th century Jewish religious leader who claimed to be the reincarnation of the self-proclaimed messiah Sabbatai Zevi and also of the biblical patriarch Jacob...
.
In this time of mysticism
Mysticism
Mysticism is the knowledge of, and especially the personal experience of, states of consciousness, i.e. levels of being, beyond normal human perception, including experience and even communion with a supreme being.-Classical origins:...
and overly formal rabbinism came the teachings of Israel ben Eliezer, known as the Baal Shem Tov, or BeShT, (1698–1760), which had a profound effect on the Jews of Eastern Europe
Eastern Europe
Eastern Europe is the eastern part of Europe. The term has widely disparate geopolitical, geographical, cultural and socioeconomic readings, which makes it highly context-dependent and even volatile, and there are "almost as many definitions of Eastern Europe as there are scholars of the region"...
and Poland in particular. His disciples taught and encouraged the new fervent brand of Judaism
Judaism
Judaism ) is the "religion, philosophy, and way of life" of the Jewish people...
based on Kabbalah
Kabbalah
Kabbalah/Kabala is a discipline and school of thought concerned with the esoteric aspect of Rabbinic Judaism. It was systematized in 11th-13th century Hachmei Provence and Spain, and again after the Expulsion from Spain, in 16th century Ottoman Palestine...
known as Hasidism
Hasidic Judaism
Hasidic Judaism or Hasidism, from the Hebrew —Ḥasidut in Sephardi, Chasidus in Ashkenazi, meaning "piety" , is a branch of Orthodox Judaism that promotes spirituality and joy through the popularisation and internalisation of Jewish mysticism as the fundamental aspects of the Jewish faith...
. The rise of Hasidic Judaism within Poland's borders and beyond had a great influence on the rise of Haredi Judaism
Haredi Judaism
Haredi or Charedi/Chareidi Judaism is the most conservative form of Orthodox Judaism, often referred to as ultra-Orthodox. A follower of Haredi Judaism is called a Haredi ....
all over the world, with a continuous influence through its many Hasidic dynasties including those of Chabad-Lubavitch
Chabad-Lubavitch
Chabad-Lubavitch is a Chasidic movement in Orthodox Judaism. One of the world's larger and best-known Chasidic movements, its official headquarters is in the Crown Heights section of Brooklyn, New York...
, Aleksander
Aleksander (Hasidic dynasty)
The Aleksander chasidic movement flourished in Poland from 1880 until it was largely destroyed by Nazi Germany during World War II.Now nearly extinct, the Aleksander Hasidim were the second largest Hasidic group in pre-Holocaust Poland.Between the world wars, Hasidic Jews from all over flocked to...
, Bobov, Ger
Ger (Hasidic dynasty)
Ger, or Gur is a Hasidic dynasty originating from Ger, the Yiddish name of Góra Kalwaria, a small town in Poland....
, Nadvorna
Nadvorna (Hasidic dynasty)
Nadvorna is a Hasidic rabbinical dynasty within Orthodox Judaism. The dynasty derives its name from the town of Nadvorna, known in Ukrainian as Nadvirna...
, among others. More recent rebbes of Polish origin include Rabbi Yosef Yitzchok Schneersohn (1880–1950), the sixth head of the Chabad Lubavitch Hasidic movement, who lived in Warsaw until 1940 when he moved Lubavitch from Warsaw to the United States. See also: List of Polish Rabbis
19th century

Papal States
The Papal State, State of the Church, or Pontifical States were among the major historical states of Italy from roughly the 6th century until the Italian peninsula was unified in 1861 by the Kingdom of Piedmont-Sardinia .The Papal States comprised territories under...
, which existed until 1870, Jews were required to live only in specified neighborhoods called ghetto
Ghetto
A ghetto is a section of a city predominantly occupied by a group who live there, especially because of social, economic, or legal issues.The term was originally used in Venice to describe the area where Jews were compelled to live. The term now refers to an overcrowded urban area often associated...
s. Until the 1840s, they were required to regularly attend sermons urging their conversion to Christianity. Only Jews were taxed to support state boarding schools for Jewish converts to Christianity. It was illegal to convert from Christianity to Judaism. Sometimes Jews were baptized involuntarily, and, even when such baptisms were illegal, forced to practice the Christian religion. In many such cases the state separated them from their families. See Edgardo Mortara
Edgardo Mortara
Edgardo Levi Mortara was a Roman Catholic priest who was born and raised Jewish. Fr. Mortara became the center of an international controversy when he was removed from his Jewish parents by authorities of the Papal States and raised as a Catholic...
for an account of one of the most widely publicized instances of acrimony between Catholics and Jews in the Papal States
Papal States
The Papal State, State of the Church, or Pontifical States were among the major historical states of Italy from roughly the 6th century until the Italian peninsula was unified in 1861 by the Kingdom of Piedmont-Sardinia .The Papal States comprised territories under...
in the second half of the 19th century.
The movement of Zionism
Zionism
Zionism is a Jewish political movement that, in its broadest sense, has supported the self-determination of the Jewish people in a sovereign Jewish national homeland. Since the establishment of the State of Israel, the Zionist movement continues primarily to advocate on behalf of the Jewish state...
originates in the late 19th century.
In 1883, Nathan Birnbaum
Nathan Birnbaum
----Nathan Birnbaum was an Austrian writer and journalist, Jewish thinker and nationalist. His life had three main phases, representing a progression in his thinking: Zionist phase ; Jewish cultural autonomy phase which included the promotion of the Yiddish language; and religious phase...
founded Kadimah, the first Jewish student association in Vienna. In 1884, the first issue of Selbstemanzipation (Self Emancipation
Political emancipation
Emancipation is a broad term used to describe various efforts to obtain political rights or equality, often for a specifically disenfranchised group, or more generally in discussion of such matters...
) appeared, printed by Birnbaum himself.
The Dreyfus Affair
Dreyfus Affair
The Dreyfus affair was a political scandal that divided France in the 1890s and the early 1900s. It involved the conviction for treason in November 1894 of Captain Alfred Dreyfus, a young French artillery officer of Alsatian Jewish descent...
, which erupted in France
France
The French Republic , The French Republic , The French Republic , (commonly known as France , is a unitary semi-presidential republic in Western Europe with several overseas territories and islands located on other continents and in the Indian, Pacific, and Atlantic oceans. Metropolitan France...
in 1894, profoundly shocked emancipated Jews. The depth of antisemitism in a country thought of as the home of enlightenment and liberty led many to question their future security in Europe. Among those who witnessed the Affair was an Austro-Hungarian (born in Budapest
Budapest
Budapest is the capital of Hungary. As the largest city of Hungary, it is the country's principal political, cultural, commercial, industrial, and transportation centre. In 2011, Budapest had 1,733,685 inhabitants, down from its 1989 peak of 2,113,645 due to suburbanization. The Budapest Commuter...
, lived in Vienna
Vienna
Vienna is the capital and largest city of the Republic of Austria and one of the nine states of Austria. Vienna is Austria's primary city, with a population of about 1.723 million , and is by far the largest city in Austria, as well as its cultural, economic, and political centre...
) Jewish journalist, Theodor Herzl
Theodor Herzl
Theodor Herzl , born Benjamin Ze’ev Herzl was an Ashkenazi Jew Austro-Hungarian journalist and the father of modern political Zionism and in effect the State of Israel.-Early life:...
, who published his pamphlet Der Judenstaat
Der Judenstaat
Der Judenstaat is a book written by Theodor Herzl and published in 1896 in Leipzig and Vienna by M. Breitenstein's Verlags-Buchhandlung...
("The Jewish State") in 1896 and Altneuland
The Old New Land
The Old New Land is a utopian novel published by Theodor Herzl, the founder of political Zionism, in 1902. Outlining Herzl’s vision for a Jewish state in the Land of Israel, Altneuland became one of Zionism's establishing texts. It was translated into Yiddish by Israel Isidor Elyashev...
("The Old New Land") in 1897. He described the Affair as a personal turning point, Before the Affair, Herzl had been anti-Zionist; afterwards he became ardently pro-Zionist. In line with the ideas of 19th century German nationalism Herzl believed in a Jewish state for the Jewish nation. In that way, he argued, the Jews could become a people like all other peoples, and antisemitism would cease to exist.
Herzl
Theodor Herzl
Theodor Herzl , born Benjamin Ze’ev Herzl was an Ashkenazi Jew Austro-Hungarian journalist and the father of modern political Zionism and in effect the State of Israel.-Early life:...
infused political Zionism with a new and practical urgency. He brought the World Zionist Organization
World Zionist Organization
The World Zionist Organization , or WZO, was founded as the Zionist Organization , or ZO, in 1897 at the First Zionist Congress, held from August 29 to August 31 in Basel, Switzerland...
into being and, together with Nathan Birnbaum, planned its First Congress at Basel
Basel
Basel or Basle In the national languages of Switzerland the city is also known as Bâle , Basilea and Basilea is Switzerland's third most populous city with about 166,000 inhabitants. Located where the Swiss, French and German borders meet, Basel also has suburbs in France and Germany...
in 1897.
For the first four years, the World Zionist Organization
World Zionist Organization
The World Zionist Organization , or WZO, was founded as the Zionist Organization , or ZO, in 1897 at the First Zionist Congress, held from August 29 to August 31 in Basel, Switzerland...
(WZO) met every year, then, up to the Second World War, they gathered every second year. Since the war, the Congress has met every four years.
World War II and the Holocaust
The Holocaust (from the Greek ὁλόκαυστον (holókauston): holos, "completely" and kaustos, "burnt"), also known as Ha-Shoah , Churben , is the term generally used to describe the killing of approximately six million European Jews during World War IIWorld War II
World War II, or the Second World War , was a global conflict lasting from 1939 to 1945, involving most of the world's nations—including all of the great powers—eventually forming two opposing military alliances: the Allies and the Axis...
, as part of a program of deliberate extermination planned and executed by the National Socialist
National Socialist German Workers Party
The National Socialist German Workers' Party , commonly known in English as the Nazi Party, was a political party in Germany between 1920 and 1945. Its predecessor, the German Workers' Party , existed from 1919 to 1920...
regime in Nazi Germany
Nazi Germany
Nazi Germany , also known as the Third Reich , but officially called German Reich from 1933 to 1943 and Greater German Reich from 26 June 1943 onward, is the name commonly used to refer to the state of Germany from 1933 to 1945, when it was a totalitarian dictatorship ruled by...
led by Adolf Hitler
Adolf Hitler
Adolf Hitler was an Austrian-born German politician and the leader of the National Socialist German Workers Party , commonly referred to as the Nazi Party). He was Chancellor of Germany from 1933 to 1945, and head of state from 1934 to 1945...
.
Demographics
| Country | population (approx.) | Jewish groups | Jewish history | Lists of Jews |
|---|---|---|---|---|
 Albania Albania |
200 - 300 | Albania History of the Jews in Albania Judaism in Albania dates back at least 1,300 years.Present day Albanian Jews, predominantly Sephardi, have in modern times only constituted a very small percentage of the population; during World War II, Albania would be one of the very few countries in Europe to see an increase in its Jewish... |
South-East European | |
 Andorra Andorra |
100 | Andorra History of the Jews in Andorra An estimated 100 Jews live in Andorra. In 2000, the Jewish community opened and consecrated a synagogue and a cultural center. Most of its members descend from Sephardic Jews from Morocco.... |
||
 Austria Austria |
15,000 | Austria History of the Jews in Austria The history of the Jews in Austria likely originates in an exodus of Jews from the Roman occupation of Israel. During the course of many centuries, the political status of the community rose and fell many times: during certain periods, the Jewish community prospered and enjoyed political equality,... |
Austrian | |
 Belarus Belarus |
13,000 | Belarus History of the Jews in Belarus The Jews in Belarus were the third largest ethnic group in the country in the first half of the 20th century. Before World War II, Jews were the third among the ethnic groups in Belarus, and in cities and towns comprised more than 40% of the population. The population of cities such as Minsk,... |
Russia, Ukraine and Belarus | |
 Belgium Belgium |
42,000 | Jewish Community of Antwerp Jewish Community of Antwerp The history of the Jews in Antwerp, Belgium goes back at least eight hundred years. Presently, The Jewish community of Antwerp consists of around 15,000 Jews.- History :... |
Belgium History of the Jews in Belgium Jews and Judaism have a long history in Belgium, from the 1st century CE until today. The Jewish community numbered 100,000 on the eve of the Second World War, but after the war and the Holocaust, is now less than half that number.-Early history:... |
West European |
 Bosnia and Herzegovina Bosnia and Herzegovina |
500 | Bosnia and Herzegovina History of the Jews in Bosnia and Herzegovina The Jewish community of Bosnia and Herzegovina has a rich and varied history, surviving World War II and the Yugoslav Wars, after having been born as a result of the Spanish Inquisition, and having been almost destroyed by the Holocaust.... |
South-East European | |
 Kingdom of Bulgaria Kingdom of Bulgaria |
Bulgaria History of the Jews in Bulgaria The history of the Jews in Bulgaria dates to at least as early as the 2nd century CE. Since then, the Jews have had a continuous presence in the Bulgarian lands and have played an often considerable part in the history of Bulgaria from ancient times through the Middle Ages until... |
South-East European | ||
 Independent State of Croatia Independent State of Croatia |
2,500 | Croatia History of the Jews in Croatia The Jewish community of Croatia dates back to at least the 3rd century AD, although little is known of the community until the 10th and 15th centuries. The community, over 20,000 strong on the eve of World War II, was almost entirely destroyed in the Holocaust. After the WWII half of the survivors... |
South-East European | |
 Cyprus Cyprus |
1,800 | Cyprus History of the Jews in Cyprus - Ancient :Cyprus is the large island located in the east Mediterranean Sea. The first inhabitants of Cyprus were most probably, Carians; in historical times, Phoenicians; and later, Greeks. The first Jews settled during the last age of Greek occupancy. The Jews had close relationships with many of... |
South-East European | |
 Czech Republic Czech Republic |
4,000 | Czech Republic History of the Jews in the Czech Republic Jews in the Czech Republic are predominantly Ashkenazic Jews, and the current Jewish population is only a fraction of the First republic's Jewish population. As of 2005, there were approximately 4,000 Jews living in the Czech Republic. There are ten small Jewish communities all around the country... and Carpathian Ruthenia History of the Jews in Carpathian Ruthenia - 20th century census data:The last antebellum census in Hungary, 1910. The four counties of Hungary that coveredthe territory what we now call Carpathian Ruthenia were Ung, Bereg, Ugocsa and Máramaros.... |
Czech, Slovak | |
 Denmark Denmark |
6,000 | Denmark History of the Jews in Denmark The Jewish community of Denmark constitutes a small minority with a known history back to the 17th century.-Origins:Medieval Danish art contains depictions of Jews – visibly wearing pointed hats – but there is no evidence any Jews actually lived in Denmark during that time... |
North European | |
 Estonia Estonia |
1,900 | Estonia History of the Jews in Estonia The history of the Jews in Estonia starts with individual reports of Jews in what is now Estonia from as early as the 14th century. However, the process of permanent Jewish settlement in Estonia began in the 19th century, especially after they were granted the official right to enter the region by... |
North European | |
 Finland Finland |
1,300 | Finland History of the Jews in Finland Finnish Jews are Jews who are citizens of Finland. The country is home to approximately 1,500 Jews, who mostly live in Helsinki. Jews came to Finland as traders and merchants from Europe.-History :... |
North European | |
 Early Modern France Early Modern France |
493,000 | France History of the Jews in France The history of the Jews of France dates back over 2,000 years. In the early Middle Ages, France was a center of Jewish learning, but persecution increased as the Middle Ages wore on... |
French | |
 Georgia (country) Georgia (country) |
Georgian Jews Georgian Jews The Georgian Jews are from the nation of Georgia, in the Caucasus... |
Georgia History of the Jews in Georgia (country) The history of the Jews in Georgia dates back more than 2,000 years. Georgian Jews have been living in this area for centuries.-History:The Georgian Jews have traditionally maintained a distinct community, separate not only from the Georgian Christian population but even from the Ashkenazi ... |
Asian | |
 Germany Germany |
200,000 | Ashkenazi Jews Ashkenazi Jews Ashkenazi Jews, also known as Ashkenazic Jews or Ashkenazim , are the Jews descended from the medieval Jewish communities along the Rhine in Germany from Alsace in the south to the Rhineland in the north. Ashkenaz is the medieval Hebrew name for this region and thus for Germany... |
Germany History of the Jews in Germany The presence of Jews in Germany has been established since the early 4th century. The community prospered under Charlemagne, but suffered during the Crusades... |
German |
 Gibraltar Gibraltar |
550 - 700 | Sephardi Jews Sephardi Jews Sephardi Jews is a general term referring to the descendants of the Jews who lived in the Iberian Peninsula before their expulsion in the Spanish Inquisition. It can also refer to those who use a Sephardic style of liturgy or would otherwise define themselves in terms of the Jewish customs and... and British Jews |
Gibraltar History of the Jews in Gibraltar There has been a Jewish presence in Gibraltar for more than 650 years. There have been periods of persecution, but for the most part the Jews of Gibraltar have prospered and been one of the largest religious minorities in the city, where they have made contributions to the culture, defence, and... |
Iberian |
 Greece Greece |
5,500 | Romaniotes Romaniotes The Romaniotes or Romaniots are a Jewish population who have lived in the territory of today's Greece and neighboring areas with large Greek populations for more than 2,000 years. Their languages were Yevanic, a Greek dialect, and Greek. They derived their name from the old name for the people... , Sephardi Jews Sephardi Jews Sephardi Jews is a general term referring to the descendants of the Jews who lived in the Iberian Peninsula before their expulsion in the Spanish Inquisition. It can also refer to those who use a Sephardic style of liturgy or would otherwise define themselves in terms of the Jewish customs and... |
Greece History of the Jews in Greece There have been organized Jewish communities in Greece for more than two thousand years. The oldest and the most characteristic Jewish group that has inhabited Greece are the Romaniotes, also known as "Greek Jews"... |
South-East European |
 Hungary Hungary |
150,000 | Oberlander Jews Oberlander Jews Oberlander Jews are Ashkenazi, Yiddish- and German-speaking Jews originating in the Oberland or higher land western region of Hungary and the district surrounding Pozsony... , Satmar Hasidic dynasty Satmar (Hasidic dynasty) Satmar is a Hasidic movement comprising mostly Hungarian and Romanian Hasidic Jewish Holocaust survivors and their descendants. It was founded and led by the late Hungarian-born Grand Rebbe Yoel Teitelbaum , who was the rabbi of Szatmárnémeti, Hungary... , and Neolog |
Hungary History of the Jews in Hungary Hungarian Jews have existed since at least the 11th century. After struggling against discrimination throughout the Middle Ages, by the early 20th century the community grew to be 5% of Hungary's population , and were prominent in science, the arts and business... and Carpathian Ruthenia History of the Jews in Carpathian Ruthenia - 20th century census data:The last antebellum census in Hungary, 1910. The four counties of Hungary that coveredthe territory what we now call Carpathian Ruthenia were Ung, Bereg, Ugocsa and Máramaros.... |
Hungarian |
 Iceland Iceland |
10 - 30 | Radhanite Radhanite The Radhanites were medieval Jewish merchants. Whether the term, which is used by only a limited number of primary sources, refers to a specific guild, or a clan, or is a generic term for Jewish merchants in the trans-Eurasian trade network is unclear... s |
Iceland History of the Jews in Iceland Jews did not come to Iceland until the 17th century, but even then there was no real immigration until the 1930s.-Language:The Icelanders knew the Jews from the Bible, and called them Gyðingar. The term was used since the 11th century and is apparently a diminutive of Guð . The Gyðinga Saga, the... |
North European |
 Republic of Ireland Republic of Ireland |
1,900 | Ireland History of the Jews in Ireland The history of the Jews in Ireland extends back nearly a thousand years. Although the Jewish community has always been small in numbers , it is well established and has generally been well-accepted into Irish life.-Early history:The earliest reference to the Jews in Ireland was in the year 1079... |
West European | |
 Italy Italy |
45,000 | Italian Jews Italian Jews Italian Jews can be used in a broad sense to mean all Jews living or with roots in Italy or in a narrower sense to mean the ancient community who use the Italian rite, as distinct from the communities dating from medieval or modern times who use the Sephardi or Ashkenazi rite.-Divisions:Italian... |
Italy History of the Jews in Italy The history of the Jews in Italy goes back over two thousand years. Jews have been present in Italy from the Roman period until the present.-Antiquity:-Pre-Christian Rome:... |
West European |
 Republic of Kosovo Republic of Kosovo |
Kosovo History of the Jews in Kosovo The history of the Jewish community in Kosovo largely mirrors that of Serbia, except during the Holocaust, when Kosovo was under Italian-Albanian control... |
South-East European | ||
 Latvia Latvia |
Latvia History of the Jews in Latvia The History of the Jews in Latvia dates back to the first Jewish colony established in Piltene in 1571. Jews contributed to Latvia's development until the Northern War , which decimated Latvia's population... |
North European | ||
 Liechtenstein Liechtenstein |
Liechtenstein History of the Jews in Liechtenstein The Jewish community of Liechtenstein today is a population of 18 people .- World War II :According to a 2005 study, about 240 Jewish refugees fled during the Nazi area, and found safety in the neutral alpine principality during World War II. In addition, the principality allowed 144 Jews to become... |
|||
 Lithuania Lithuania |
4,000 | Lithuanian Jews Lithuanian Jews Lithuanian Jews or Litvaks are Jews with roots in the Grand Duchy of Lithuania:... |
Lithuania History of the Jews in Lithuania The history of the Jews in Lithuania spans the period from the eighth century to the present day. There is still a small community in that country, as well as an extensive Lithuanian Jewish diaspora in Israel, the United States and other countries. For more detail, see Lithuanian Jews.-Early... |
North European |
 Luxembourg Luxembourg |
1,200 | Luxembourg | West European | |
 Republic of Macedonia Republic of Macedonia |
Macedonian Jews in the Republic of Macedonia The history of the Jews in the Republic of Macedonia stretches back two thousand years.The history of Jews in the territory of the present-day Republic of Macedonia began during Roman antiquity, when Jews first arrived in the region... |
Macedonia | South-East European | |
 Malta Malta |
Malta History of the Jews in Malta The history of the Jews in Malta can be traced back to approximately 62 CE. Most contemporary Maltese Jews are Sefardic, however an Ashkenazic prayer book is used.-Antiquity:... |
|||
 Moldova Moldova |
Bessarabian Jews Bessarabian Jews -Early history:Jews are mentioned from very early in the Principality of Moldavia, but they did not represent a significant number. Their main activity in Moldavia was commerce, but they could not compete with Greeks and Armenians, who had the knowledge of the Levantine commerce and relationships... |
Moldova History of the Jews in Moldova The History of the Jews in Moldova reaches back centuries in history. Bessarabian Jews have been living in the area for quite some time.-Early history:* 1889: There were 180,918 Jews of a total population of 1,628,867 in Bessarabia.... |
East European | |
 Monaco Monaco |
Monaco History of the Jews in Monaco Monaco had a very small Jewish presence prior to World War II, numbering approximately 300 people. During the war, the principality's government issued false identity papers to its Jewish residents to protect them from Nazi deportation. Prince Louis II refused to dismiss Jewish civil servants and... |
West European | ||
 Kingdom of Montenegro Kingdom of Montenegro |
Montenegro History of the Jews in Montenegro There is no organized Jewish community in Montenegro. The 2007 Montenegrin Statistical Yearbook lists 12 Jews in the country, spread across nine towns. There is little evidence of a significant historic Jewish presence in the country.-References:... |
South-East European | ||
 Netherlands Netherlands |
45,000 | Sephardi and Ashkenazi | Netherlands History of the Jews in the Netherlands Most history of the Jews in the Netherlands was generated between the end of the 16th century and World War II.The area now known as the Netherlands was once part of the Spanish Empire but in 1581, the northern Dutch provinces declared independence... and Chuts Chuts Chuts is the name applied to Jews who immigrated to London from the Netherlands during the latter part of the 19th century. They typically came from Amsterdam and practised trades they had already learned there, most notably cigar, cap and slipper making.... |
West European |
 Norway Norway |
1,500 | Jews in Norway Jews in Norway The Jews in Norway are one of the country's smallest ethnic and religious minorities. The largest synagogue is in Oslo. A smaller synagogue in Trondheim is often claimed, erroneously, to be the world's northernmost synagogue... |
Norway | North European |
 Poland Poland |
50,000 | Chronology of Jewish Polish history Chronology of Jewish Polish history The history of the Jews in Poland is outlined in events below.960 A Jewish merchant from Spain, Ibrahim Ibn Jaqub , travels to Poland and writes the first description of the country. Jewish traders are very active in Central Europe... |
Poland History of the Jews in Poland The history of the Jews in Poland dates back over a millennium. For centuries, Poland was home to the largest and most significant Jewish community in the world. Poland was the centre of Jewish culture thanks to a long period of statutory religious tolerance and social autonomy. This ended with the... |
Polish |
 Portugal Portugal |
8,000 | Spanish and Portuguese Jews Spanish and Portuguese Jews Spanish and Portuguese Jews are a distinctive sub-group of Sephardim who have their main ethnic origins within the Jewish communities of the Iberian peninsula and who shaped communities mainly in Western Europe and the Americas from the late 16th century on... |
Portugal History of the Jews in Portugal The history of the Jews in Portugal reaches back over two thousand years and is directly related to Sephardi history, a Jewish ethnic division that represents communities who have originated in the Iberian Peninsula .-Before Portugal:... |
Iberian |
 Kingdom of Romania Kingdom of Romania |
6,000 | Romania History of the Jews in Romania The history of Jews in Romania concerns the Jews of Romania and of Romanian origins, from their first mention on what is nowadays Romanian territory.... |
Romanian | |
 Russia Russia |
230,000 (including Asian Russia) | Ashkenazi Jews Ashkenazi Jews Ashkenazi Jews, also known as Ashkenazic Jews or Ashkenazim , are the Jews descended from the medieval Jewish communities along the Rhine in Germany from Alsace in the south to the Rhineland in the north. Ashkenaz is the medieval Hebrew name for this region and thus for Germany... & Mountain Jews Mountain Jews Highland Jews, Mountain Jews or Kavkazi Jews also known as Juvuro or Juhuro, are Jews of the eastern Caucasus, mainly of Azerbaijan and Dagestan. They are also known as Caucasus Jews, Caucasian Jews, or less commonly East Caucasian Jews, because the majority of these Jews settled the eastern part... |
Russia | Russia, Ukraine, and Belarus |
 San Marino San Marino |
San Marino History of the Jews in San Marino The history of the Jews in San Marino, located within Italy reaches back to the Middle Ages.San Marino is a small land locked country in central Italy. There has been a Jewish presence in San Marino for at least 600 years.... |
|||
 Serbia Serbia |
1,185 | Serbian Jews in Serbia The history of the Jews in Serbia goes back two thousand years. Jews first arrived in what is now Serbia in Roman times. The Jewish communities of the Balkans remained small until the late fifteenth century, when Jews fleeing the Spanish and Portuguese Inquisitions found refuge in Ottoman-ruled... |
Serbia | South-East European |
 Slovakia Slovakia |
6,000 | Oberlander Jews Oberlander Jews Oberlander Jews are Ashkenazi, Yiddish- and German-speaking Jews originating in the Oberland or higher land western region of Hungary and the district surrounding Pozsony... |
Slovakia History of the Jews in Slovakia Before World War II, 135,000 Jews lived in Slovakia. Some emigrated before the war, but most were killed in deportation. After the Slovak Republic proclaimed its independence in March 1939 under the protection of Nazi Germany, Slovakia began a series of measures aimed against the Jews in the... and Carpathian Ruthenia History of the Jews in Carpathian Ruthenia - 20th century census data:The last antebellum census in Hungary, 1910. The four counties of Hungary that coveredthe territory what we now call Carpathian Ruthenia were Ung, Bereg, Ugocsa and Máramaros.... |
Czech, Slovak |
 Slovenia Slovenia |
200 | Slovenia History of the Jews in Slovenia The small Jewish community of Slovenia is estimated at 400 to 600 members , with most living in the capital, Ljubljana. The Jewish community was devastated by the Shoah, and has never fully recovered... |
South-East European | |
 Spain Spain |
Sephardi Jews Sephardi Jews Sephardi Jews is a general term referring to the descendants of the Jews who lived in the Iberian Peninsula before their expulsion in the Spanish Inquisition. It can also refer to those who use a Sephardic style of liturgy or would otherwise define themselves in terms of the Jewish customs and... |
Spain History of the Jews in Spain Spanish Jews once constituted one of the largest and most prosperous Jewish communities under Muslim and Christian rule in Spain, before the majority, together with resident Muslims, were forced to convert to Catholicism, be expelled or be killed when Spain became united under the Catholic Monarchs... and golden age |
Iberian | |
 Sweden Sweden |
18,000 | Sweden History of the Jews in Sweden The History of the Jews in Sweden probably began with arrivals from the Hanseatic League in medieval times, but there are no records. In Elizabethan times it was common for European royalty to have Jewish doctors at court, and there is a record of a Jewish doctor who served Gustav Vasa in the 16th... |
North European | |
 Switzerland Switzerland |
18,000 | Switzerland History of the Jews in Switzerland Jews and Judaism have been present in the territory of what is now Switzerland since before the emergence of the medieval Old Swiss Confederacy.In contemporary Switzerland, the official census of the year 2000 reports close to 18,000 adherents of Judaism living in Switzerland . About half of them... |
West European | |
 Ukraine Ukraine |
80,000 | Ashkenazi Jews Ashkenazi Jews Ashkenazi Jews, also known as Ashkenazic Jews or Ashkenazim , are the Jews descended from the medieval Jewish communities along the Rhine in Germany from Alsace in the south to the Rhineland in the north. Ashkenaz is the medieval Hebrew name for this region and thus for Germany... |
Ukraine History of the Jews in Ukraine Jewish communities have existed in the territory of Ukraine from the time of Kievan Rus' and developed many of the most distinctive modern Jewish theological and cultural traditions. While at times they flourished, at other times they faced periods of persecution and antisemitic discriminatory... and Carpathian Ruthenia History of the Jews in Carpathian Ruthenia - 20th century census data:The last antebellum census in Hungary, 1910. The four counties of Hungary that coveredthe territory what we now call Carpathian Ruthenia were Ung, Bereg, Ugocsa and Máramaros.... |
Russia, Ukraine and Belarus |
 United Kingdom United Kingdom |
297,000 | British Jews British Jews British Jews are Jews who live in, or are citizens of, the United Kingdom. In the 2001 Census, 266,740 people listed their religion as Jewish. The UK is home to the second largest Jewish population in Europe, and has the fifth largest Jewish community worldwide... |
United Kingdom History of the Jews in the United Kingdom For details of the History of the Jews in the United Kingdom, as well as prior to the formation of the United Kingdom in 1707, see:* History of the Jews in England* History of the Jews in Scotland* History of the Jews in Northern Ireland... |
British |
Jewish ethnic subdivisions of Europe
- Ashkenazim (German Jews)
- Sephardim (Iberian/Hispanic Jews of Portugal and Spain)
- RomaniotesRomaniotesThe Romaniotes or Romaniots are a Jewish population who have lived in the territory of today's Greece and neighboring areas with large Greek populations for more than 2,000 years. Their languages were Yevanic, a Greek dialect, and Greek. They derived their name from the old name for the people...
(Greek Jews) - Italian JewsItalian JewsItalian Jews can be used in a broad sense to mean all Jews living or with roots in Italy or in a narrower sense to mean the ancient community who use the Italian rite, as distinct from the communities dating from medieval or modern times who use the Sephardi or Ashkenazi rite.-Divisions:Italian...
(also known as Bnei Roma) - Georgian JewsGeorgian JewsThe Georgian Jews are from the nation of Georgia, in the Caucasus...
and Armenian Jews - Crimean KaraitesCrimean KaraitesThe Crimean Karaites , also known as Karaim and Qarays, are a community of ethnic Turkic adherents of Karaite Judaism in Eastern Europe...
and KrymchaksKrymchaksThe Krymchaks are a Turkic people, community of Turkic languages and adherents of Rabbinic Judaism living in Crimea. They have historically lived in close proximity to the Crimean Karaites...
(Jews of TurkicTurkic peoplesThe Turkic peoples are peoples residing in northern, central and western Asia, southern Siberia and northwestern China and parts of eastern Europe. They speak languages belonging to the Turkic language family. They share, to varying degrees, certain cultural traits and historical backgrounds...
descent in CrimeaCrimeaCrimea , or the Autonomous Republic of Crimea , is a sub-national unit, an autonomous republic, of Ukraine. It is located on the northern coast of the Black Sea, occupying a peninsula of the same name...
)
See also
- Jew
- Who is a Jew?Who is a Jew?"Who is a Jew?" is a basic question about Jewish identity and considerations of Jewish self-identification. The question is based in ideas about Jewish personhood which themselves have cultural, religious, genealogical, and personal dimensions...
- Jewish historyJewish historyJewish history is the history of the Jews, their religion and culture, as it developed and interacted with other peoples, religions and cultures. Since Jewish history is over 4000 years long and includes hundreds of different populations, any treatment can only be provided in broad strokes...
- Rescue of the Danish JewsRescue of the Danish JewsThe rescue of the Danish Jews occurred during Nazi Germany's occupation of Denmark during World War II. On October 1st 1943 Nazi leader Adolf Hitler ordered Danish Jews to be arrested and deported...
- Bulgarian Jewry
- History of the Jews in Carpathian RutheniaHistory of the Jews in Carpathian Ruthenia- 20th century census data:The last antebellum census in Hungary, 1910. The four counties of Hungary that coveredthe territory what we now call Carpathian Ruthenia were Ung, Bereg, Ugocsa and Máramaros....
- Galician JewsGalician JewsGalician Jews or Galitzianer Jews are a subdivision of the Ashkenazim geographically originating from Galicia, from western Ukraine and from the south-eastern corner of Poland . Galicia proper, which was inhabited by Ukrainians, Poles and Jews, was a royal province within Austro-Hungarian empire...
- History of the Jews in Galicia (Central Europe)
- History of the Jews in PolandHistory of the Jews in PolandThe history of the Jews in Poland dates back over a millennium. For centuries, Poland was home to the largest and most significant Jewish community in the world. Poland was the centre of Jewish culture thanks to a long period of statutory religious tolerance and social autonomy. This ended with the...
- Italian JewsItalian JewsItalian Jews can be used in a broad sense to mean all Jews living or with roots in Italy or in a narrower sense to mean the ancient community who use the Italian rite, as distinct from the communities dating from medieval or modern times who use the Sephardi or Ashkenazi rite.-Divisions:Italian...
- Lithuanian JewsLithuanian JewsLithuanian Jews or Litvaks are Jews with roots in the Grand Duchy of Lithuania:...
- Bessarabian JewsBessarabian Jews-Early history:Jews are mentioned from very early in the Principality of Moldavia, but they did not represent a significant number. Their main activity in Moldavia was commerce, but they could not compete with Greeks and Armenians, who had the knowledge of the Levantine commerce and relationships...
- Sephardic Jews in the NetherlandsSephardic Jews in the NetherlandsAs a result of the Inquisition, many Sephardim left the Iberian peninsula at the end of the 15th century and throughout the 16th century, in search for religious freedom. Some of them found their way to the newly independent Dutch provinces: independent from the reign of Spain, Sephardic Jews from...
- Golden age of Jewish culture in Spain
- Religion in EuropeReligion in EuropeReligion in Europe has been a major influence on art, culture, philosophy and law. The largest religion in Europe for at least a millennium and a half has been Christianity. Two countries in Southeastern Europe have Muslim majorities, while two more Muslim countries located mostly in Asia have...
- List of religious populations
- Islam in EuropeIslam in EuropeThis article deals with the history and evolution of the presence of Islam in Europe. According to the German , the total number of Muslims in Europe in 2007 was about 53 million , excluding Turkey. The total number of Muslims in the European Union in 2007 was about 16 million .-Early history:Islam...
- Christianity in EuropeChristianity in EuropeChristianity is the largest religion in Europe. Christianity has been practiced in Europe since the 1st century, and a number of the Pauline Epistles were odireted at Christians living in Macedonia, as well as Rome.- Early history :...
- The YIVO Encyclopedia of Jews in Eastern EuropeThe YIVO Encyclopedia of Jews in Eastern EuropeThe YIVO Encyclopedia of Jews in Eastern Europe is a two-volume, English-language reference work on the history and culture of Eastern Europe Jewry in this region, prepared by the YIVO Institute for Jewish Research and published by Yale University Press in 2008.The Encyclopedia, 2,400 pages in...

