
History of biology
Encyclopedia

The history of biology traces the study of the living world
Life
Life is a characteristic that distinguishes objects that have signaling and self-sustaining processes from those that do not, either because such functions have ceased , or else because they lack such functions and are classified as inanimate...
from ancient to modern
Modernity
Modernity typically refers to a post-traditional, post-medieval historical period, one marked by the move from feudalism toward capitalism, industrialization, secularization, rationalization, the nation-state and its constituent institutions and forms of surveillance...
times. Although the concept of biology
Biology
Biology is a natural science concerned with the study of life and living organisms, including their structure, function, growth, origin, evolution, distribution, and taxonomy. Biology is a vast subject containing many subdivisions, topics, and disciplines...
as a single coherent field arose in the 19th century, the biological sciences emerged from traditions of medicine
History of medicine
All human societies have medical beliefs that provide explanations for birth, death, and disease. Throughout history, illness has been attributed to witchcraft, demons, astral influence, or the will of the gods...
and natural history
Natural history
Natural history is the scientific research of plants or animals, leaning more towards observational rather than experimental methods of study, and encompasses more research published in magazines than in academic journals. Grouped among the natural sciences, natural history is the systematic study...
reaching back to ayurveda
Ayurveda
Ayurveda or ayurvedic medicine is a system of traditional medicine native to India and a form of alternative medicine. In Sanskrit, words , meaning "longevity", and , meaning "knowledge" or "science". The earliest literature on Indian medical practice appeared during the Vedic period in India,...
, ancient Egyptian medicine
Ancient Egyptian medicine
The medicine of the ancient Egyptians is some of the oldest documented. From the beginnings of the civilization in the until the Persian invasion of 525 BC, Egyptian medical practice went largely unchanged and was highly advanced for its time, including simple non-invasive surgery, setting of...
and the works of Aristotle
Aristotle
Aristotle was a Greek philosopher and polymath, a student of Plato and teacher of Alexander the Great. His writings cover many subjects, including physics, metaphysics, poetry, theater, music, logic, rhetoric, linguistics, politics, government, ethics, biology, and zoology...
and Galen
Galen
Aelius Galenus or Claudius Galenus , better known as Galen of Pergamon , was a prominent Roman physician, surgeon and philosopher...
in the ancient Greco-Roman world
Greco-Roman world
The Greco-Roman world, Greco-Roman culture, or the term Greco-Roman , when used as an adjective, as understood by modern scholars and writers, refers to those geographical regions and countries that culturally were directly, protractedly and intimately influenced by the language, culture,...
. This ancient work was further developed in the Middle Ages by Muslim physicians
Islamic medicine
In the history of medicine, Islamic medicine, Arabic medicine or Arabian medicine refers to medicine developed in the Islamic Golden Age, and written in Arabic, the lingua franca of Islamic civilization....
and scholars such as Avicenna
Avicenna
Abū ʿAlī al-Ḥusayn ibn ʿAbd Allāh ibn Sīnā , commonly known as Ibn Sīnā or by his Latinized name Avicenna, was a Persian polymath, who wrote almost 450 treatises on a wide range of subjects, of which around 240 have survived...
. During the European Renaissance
Renaissance
The Renaissance was a cultural movement that spanned roughly the 14th to the 17th century, beginning in Italy in the Late Middle Ages and later spreading to the rest of Europe. The term is also used more loosely to refer to the historical era, but since the changes of the Renaissance were not...
and early modern period, biological thought was revolutionized in Europe by a renewed interest in empiricism
Empiricism
Empiricism is a theory of knowledge that asserts that knowledge comes only or primarily via sensory experience. One of several views of epistemology, the study of human knowledge, along with rationalism, idealism and historicism, empiricism emphasizes the role of experience and evidence,...
and the discovery of many novel organisms. Prominent in this movement were Vesalius
Vesalius
Andreas Vesalius was a Flemish anatomist, physician, and author of one of the most influential books on human anatomy, De humani corporis fabrica . Vesalius is often referred to as the founder of modern human anatomy. Vesalius is the Latinized form of Andries van Wesel...
and Harvey
William Harvey
William Harvey was an English physician who was the first person to describe completely and in detail the systemic circulation and properties of blood being pumped to the body by the heart...
, who used experimentation and careful observation in physiology, and naturalists such as Linnaeus
Carolus Linnaeus
Carl Linnaeus , also known after his ennoblement as , was a Swedish botanist, physician, and zoologist, who laid the foundations for the modern scheme of binomial nomenclature. He is known as the father of modern taxonomy, and is also considered one of the fathers of modern ecology...
and Buffon
Georges-Louis Leclerc, Comte de Buffon
Georges-Louis Leclerc, Comte de Buffon was a French naturalist, mathematician, cosmologist, and encyclopedic author.His works influenced the next two generations of naturalists, including Jean-Baptiste Lamarck and Georges Cuvier...
who began to classify the diversity of life and the fossil record, as well as the development and behavior of organisms. Microscopy
Microscopy
Microscopy is the technical field of using microscopes to view samples and objects that cannot be seen with the unaided eye...
revealed the previously unknown world of microorganisms, laying the groundwork for cell theory
Cell theory
Cell theory refers to the idea that cells are the basic unit of structure in every living thing. Development of this theory during the mid 17th century was made possible by advances in microscopy. This theory is one of the foundations of biology...
. The growing importance of natural theology
Natural theology
Natural theology is a branch of theology based on reason and ordinary experience. Thus it is distinguished from revealed theology which is based on scripture and religious experiences of various kinds; and also from transcendental theology, theology from a priori reasoning.Marcus Terentius Varro ...
, partly a response to the rise of mechanical philosophy, encouraged the growth of natural history (although it entrenched the argument from design
Teleological argument
A teleological or design argument is an a posteriori argument for the existence of God based on apparent design and purpose in the universe. The argument is based on an interpretation of teleology wherein purpose and intelligent design appear to exist in nature beyond the scope of any such human...
).
Over the 18th and 19th centuries, biological sciences such as botany
Botany
Botany, plant science, or plant biology is a branch of biology that involves the scientific study of plant life. Traditionally, botany also included the study of fungi, algae and viruses...
and zoology
Zoology
Zoology |zoölogy]]), is the branch of biology that relates to the animal kingdom, including the structure, embryology, evolution, classification, habits, and distribution of all animals, both living and extinct...
became increasingly professional scientific disciplines. Lavoisier and other physical scientists began to connect the animate and inanimate worlds through physics and chemistry. Explorer-naturalists such as Alexander von Humboldt
Alexander von Humboldt
Friedrich Wilhelm Heinrich Alexander Freiherr von Humboldt was a German naturalist and explorer, and the younger brother of the Prussian minister, philosopher and linguist Wilhelm von Humboldt...
investigated the interaction between organisms and their environment, and the ways this relationship depends on geography—laying the foundations for biogeography
Biogeography
Biogeography is the study of the distribution of species , organisms, and ecosystems in space and through geological time. Organisms and biological communities vary in a highly regular fashion along geographic gradients of latitude, elevation, isolation and habitat area...
, ecology
Ecology
Ecology is the scientific study of the relations that living organisms have with respect to each other and their natural environment. Variables of interest to ecologists include the composition, distribution, amount , number, and changing states of organisms within and among ecosystems...
and ethology
Ethology
Ethology is the scientific study of animal behavior, and a sub-topic of zoology....
. Naturalists began to reject essentialism
Essentialism
In philosophy, essentialism is the view that, for any specific kind of entity, there is a set of characteristics or properties all of which any entity of that kind must possess. Therefore all things can be precisely defined or described...
and consider the importance of extinction
Extinction
In biology and ecology, extinction is the end of an organism or of a group of organisms , normally a species. The moment of extinction is generally considered to be the death of the last individual of the species, although the capacity to breed and recover may have been lost before this point...
and the mutability of species
History of evolutionary thought
Evolutionary thought, the conception that species change over time, has roots in antiquity, in the ideas of the ancient Greeks, Romans, and Chinese as well as in medieval Islamic science...
. Cell theory
Cell theory
Cell theory refers to the idea that cells are the basic unit of structure in every living thing. Development of this theory during the mid 17th century was made possible by advances in microscopy. This theory is one of the foundations of biology...
provided a new perspective on the fundamental basis of life. These developments, as well as the results from embryology
Embryology
Embryology is a science which is about the development of an embryo from the fertilization of the ovum to the fetus stage...
and paleontology
Paleontology
Paleontology "old, ancient", ὄν, ὀντ- "being, creature", and λόγος "speech, thought") is the study of prehistoric life. It includes the study of fossils to determine organisms' evolution and interactions with each other and their environments...
, were synthesized in Charles Darwin
Charles Darwin
Charles Robert Darwin FRS was an English naturalist. He established that all species of life have descended over time from common ancestry, and proposed the scientific theory that this branching pattern of evolution resulted from a process that he called natural selection.He published his theory...
's theory of evolution
Evolution
Evolution is any change across successive generations in the heritable characteristics of biological populations. Evolutionary processes give rise to diversity at every level of biological organisation, including species, individual organisms and molecules such as DNA and proteins.Life on Earth...
by natural selection
Natural selection
Natural selection is the nonrandom process by which biologic traits become either more or less common in a population as a function of differential reproduction of their bearers. It is a key mechanism of evolution....
. The end of the 19th century saw the fall of spontaneous generation
Spontaneous generation
Spontaneous generation or Equivocal generation is an obsolete principle regarding the origin of life from inanimate matter, which held that this process was a commonplace and everyday occurrence, as distinguished from univocal generation, or reproduction from parent...
and the rise of the germ theory of disease
Germ theory of disease
The germ theory of disease, also called the pathogenic theory of medicine, is a theory that proposes that microorganisms are the cause of many diseases...
, though the mechanism of inheritance remained a mystery.
In the early 20th century, the rediscovery of Mendel's
Gregor Mendel
Gregor Johann Mendel was an Austrian scientist and Augustinian friar who gained posthumous fame as the founder of the new science of genetics. Mendel demonstrated that the inheritance of certain traits in pea plants follows particular patterns, now referred to as the laws of Mendelian inheritance...
work led to the rapid development of genetics
Genetics
Genetics , a discipline of biology, is the science of genes, heredity, and variation in living organisms....
by Thomas Hunt Morgan
Thomas Hunt Morgan
Thomas Hunt Morgan was an American evolutionary biologist, geneticist and embryologist and science author who won the Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine in 1933 for discoveries relating the role the chromosome plays in heredity.Morgan received his PhD from Johns Hopkins University in zoology...
and his students, and by the 1930s the combination of population genetics
Population genetics
Population genetics is the study of allele frequency distribution and change under the influence of the four main evolutionary processes: natural selection, genetic drift, mutation and gene flow. It also takes into account the factors of recombination, population subdivision and population...
and natural selection in the "neo-Darwinian synthesis
Modern evolutionary synthesis
The modern evolutionary synthesis is a union of ideas from several biological specialties which provides a widely accepted account of evolution...
". New disciplines developed rapidly, especially after Watson
James D. Watson
James Dewey Watson is an American molecular biologist, geneticist, and zoologist, best known as one of the co-discoverers of the structure of DNA in 1953 with Francis Crick...
and Crick
Francis Crick
Francis Harry Compton Crick OM FRS was an English molecular biologist, biophysicist, and neuroscientist, and most noted for being one of two co-discoverers of the structure of the DNA molecule in 1953, together with James D. Watson...
proposed the structure of DNA
DNA
Deoxyribonucleic acid is a nucleic acid that contains the genetic instructions used in the development and functioning of all known living organisms . The DNA segments that carry this genetic information are called genes, but other DNA sequences have structural purposes, or are involved in...
. Following the establishment of the Central Dogma and the cracking of the genetic code
Genetic code
The genetic code is the set of rules by which information encoded in genetic material is translated into proteins by living cells....
, biology was largely split between organismal biology—the fields that deal with whole organisms and groups of organisms—and the fields related to cellular
Cell biology
Cell biology is a scientific discipline that studies cells – their physiological properties, their structure, the organelles they contain, interactions with their environment, their life cycle, division and death. This is done both on a microscopic and molecular level...
and molecular biology
Molecular biology
Molecular biology is the branch of biology that deals with the molecular basis of biological activity. This field overlaps with other areas of biology and chemistry, particularly genetics and biochemistry...
. By the late 20th century, new fields like genomics
Genomics
Genomics is a discipline in genetics concerning the study of the genomes of organisms. The field includes intensive efforts to determine the entire DNA sequence of organisms and fine-scale genetic mapping efforts. The field also includes studies of intragenomic phenomena such as heterosis,...
and proteomics
Proteomics
Proteomics is the large-scale study of proteins, particularly their structures and functions. Proteins are vital parts of living organisms, as they are the main components of the physiological metabolic pathways of cells. The term "proteomics" was first coined in 1997 to make an analogy with...
were reversing this trend, with organismal biologists using molecular techniques, and molecular and cell biologists investigating the interplay between genes and the environment, as well as the genetics of natural populations of organisms.
Etymology of "biology"
The word biology is formed by combining the GreekAncient Greek
Ancient Greek is the stage of the Greek language in the periods spanning the times c. 9th–6th centuries BC, , c. 5th–4th centuries BC , and the c. 3rd century BC – 6th century AD of ancient Greece and the ancient world; being predated in the 2nd millennium BC by Mycenaean Greek...
βίος (bios), meaning "life", and the suffix '-logy', meaning "science of", "knowledge of", "study of", based on the Greek verb λέγειν, 'legein' "to select", "to gather" (cf. the noun λόγος, 'logos' "word"). The term biology in its modern sense appears to have been introduced independently by Thomas Beddoes
Thomas Beddoes
Thomas Beddoes , English physician and scientific writer, was born at Shifnal in Shropshire. He was a reforming practitioner and teacher of medicine, and an associate of leading scientific figures. Beddoes was a friend of Samuel Taylor Coleridge, and, according to E. S...
(in 1799), Karl Friedrich Burdach
Karl Friedrich Burdach
Karl Friedrich Burdach was a German physiologist, born in Leipzig.He was graduated in medicine there in 1800; became professor of physiology in the University of Dorpat in 1811, and four years later took a similar position at the University of Königsberg.He provided in 1822 the name--due the...
(in 1800), Gottfried Reinhold Treviranus
Gottfried Reinhold Treviranus
Gottfried Reinhold Treviranus was a German naturalist. He was a proponent of the theory of the transmutation of species, a theory of evolution held by some biologists prior to the work of Charles Darwin...
(Biologie oder Philosophie der lebenden Natur, 1802) and Jean-Baptiste Lamarck
Jean-Baptiste Lamarck
Jean-Baptiste Pierre Antoine de Monet, Chevalier de la Marck , often known simply as Lamarck, was a French naturalist...
(Hydrogéologie, 1802). The word itself appears in the title of Volume 3 of Michael Christoph Hanov's Philosophiae naturalis sive physicae dogmaticae: Geologia, biologia, phytologia generalis et dendrologia, published in 1766.
Before biology, there were several terms used for the study of animals and plants. Natural history
Natural history
Natural history is the scientific research of plants or animals, leaning more towards observational rather than experimental methods of study, and encompasses more research published in magazines than in academic journals. Grouped among the natural sciences, natural history is the systematic study...
referred to the descriptive aspects of biology, though it also included mineralogy
Mineralogy
Mineralogy is the study of chemistry, crystal structure, and physical properties of minerals. Specific studies within mineralogy include the processes of mineral origin and formation, classification of minerals, their geographical distribution, as well as their utilization.-History:Early writing...
and other non-biological fields; from the Middle Ages through the Renaissance, the unifying framework of natural history was the scala naturae or Great Chain of Being
Great chain of being
The great chain of being , is a Christian concept detailing a strict, religious hierarchical structure of all matter and life, believed to have been decreed by the Christian God.-Divisions:...
. Natural philosophy
Natural philosophy
Natural philosophy or the philosophy of nature , is a term applied to the study of nature and the physical universe that was dominant before the development of modern science...
and natural theology
Natural theology
Natural theology is a branch of theology based on reason and ordinary experience. Thus it is distinguished from revealed theology which is based on scripture and religious experiences of various kinds; and also from transcendental theology, theology from a priori reasoning.Marcus Terentius Varro ...
encompassed the conceptual and metaphysical basis of plant and animal life, dealing with problems of why organisms exist and behave the way they do, though these subjects also included what is now geology
Geology
Geology is the science comprising the study of solid Earth, the rocks of which it is composed, and the processes by which it evolves. Geology gives insight into the history of the Earth, as it provides the primary evidence for plate tectonics, the evolutionary history of life, and past climates...
, physics
Physics
Physics is a natural science that involves the study of matter and its motion through spacetime, along with related concepts such as energy and force. More broadly, it is the general analysis of nature, conducted in order to understand how the universe behaves.Physics is one of the oldest academic...
, chemistry
Chemistry
Chemistry is the science of matter, especially its chemical reactions, but also its composition, structure and properties. Chemistry is concerned with atoms and their interactions with other atoms, and particularly with the properties of chemical bonds....
, and astronomy
Astronomy
Astronomy is a natural science that deals with the study of celestial objects and phenomena that originate outside the atmosphere of Earth...
. Physiology and (botanical) pharmacology were the province of medicine. Botany, zoology, and (in the case of fossils) geology replaced natural history and natural philosophy in the 18th and 19th centuries before biology was widely adopted. To this day, "botany" and "zoology" are widely used, although they have been joined by other sub-disciplines of biology, such as mycology
Mycology
Mycology is the branch of biology concerned with the study of fungi, including their genetic and biochemical properties, their taxonomy and their use to humans as a source for tinder, medicinals , food and entheogens, as well as their dangers, such as poisoning or...
and molecular biology
Molecular biology
Molecular biology is the branch of biology that deals with the molecular basis of biological activity. This field overlaps with other areas of biology and chemistry, particularly genetics and biochemistry...
.
Early cultures
The earliest humans must have had and passed on knowledge about plantPlant
Plants are living organisms belonging to the kingdom Plantae. Precise definitions of the kingdom vary, but as the term is used here, plants include familiar organisms such as trees, flowers, herbs, bushes, grasses, vines, ferns, mosses, and green algae. The group is also called green plants or...
s and animal
Animal
Animals are a major group of multicellular, eukaryotic organisms of the kingdom Animalia or Metazoa. Their body plan eventually becomes fixed as they develop, although some undergo a process of metamorphosis later on in their life. Most animals are motile, meaning they can move spontaneously and...
s to increase their chances of survival. This may have included knowledge of human and animal anatomy and aspects of animal behavior (such as migration patterns). However, the first major turning point in biological knowledge came with the Neolithic Revolution
Neolithic Revolution
The Neolithic Revolution was the first agricultural revolution. It was the transition from hunting and gathering to agriculture and settlement. Archaeological data indicates that various forms of plants and animal domestication evolved independently in 6 separate locations worldwide circa...
about 10,000 years ago. Humans first domesticated plants for farming, then livestock
Livestock
Livestock refers to one or more domesticated animals raised in an agricultural setting to produce commodities such as food, fiber and labor. The term "livestock" as used in this article does not include poultry or farmed fish; however the inclusion of these, especially poultry, within the meaning...
animals to accompany the resulting sedentary societies.
The ancient cultures of Mesopotamia
Mesopotamia
Mesopotamia is a toponym for the area of the Tigris–Euphrates river system, largely corresponding to modern-day Iraq, northeastern Syria, southeastern Turkey and southwestern Iran.Widely considered to be the cradle of civilization, Bronze Age Mesopotamia included Sumer and the...
, Egypt
Ancient Egypt
Ancient Egypt was an ancient civilization of Northeastern Africa, concentrated along the lower reaches of the Nile River in what is now the modern country of Egypt. Egyptian civilization coalesced around 3150 BC with the political unification of Upper and Lower Egypt under the first pharaoh...
, the Indian subcontinent
History of India
The history of India begins with evidence of human activity of Homo sapiens as long as 75,000 years ago, or with earlier hominids including Homo erectus from about 500,000 years ago. The Indus Valley Civilization, which spread and flourished in the northwestern part of the Indian subcontinent from...
, and China
History of China
Chinese civilization originated in various regional centers along both the Yellow River and the Yangtze River valleys in the Neolithic era, but the Yellow River is said to be the Cradle of Chinese Civilization. With thousands of years of continuous history, China is one of the world's oldest...
, among others, produced renowned surgeons and students of the natural sciences such as Susruta and Zhang Zhongjing
Zhang Zhongjing
Zhang Zhongjing , formal name Zhang Ji, was a Han Dynasty physician and one of the most eminent Chinese physicians during the later years of the Han Dynasty...
, reflecting independent sophisticated systems of natural philosophy. However, the roots of modern biology are usually traced back to the secular tradition of ancient Greek philosophy.
One of the oldest organised systems of medicine is known from Indian subcontinent in form of Ayurveda
Ayurveda
Ayurveda or ayurvedic medicine is a system of traditional medicine native to India and a form of alternative medicine. In Sanskrit, words , meaning "longevity", and , meaning "knowledge" or "science". The earliest literature on Indian medical practice appeared during the Vedic period in India,...
which originated around 1500 BC from Atharvaveda
Atharvaveda
The Atharvaveda is a sacred text of Hinduism and one of the four Vedas, often called the "fourth Veda"....
(one of the four most ancient books of Indian knowledge, wisdom and culture). Other ancient medical texts were produced by the Egyptian tradition
Ancient Egyptian medicine
The medicine of the ancient Egyptians is some of the oldest documented. From the beginnings of the civilization in the until the Persian invasion of 525 BC, Egyptian medical practice went largely unchanged and was highly advanced for its time, including simple non-invasive surgery, setting of...
, such as the Edwin Smith Papyrus
Edwin Smith papyrus
The Edwin Smith Papyrus is an Ancient Egyptian medical text and the oldest known surgical treatise on trauma. It dates to Dynasties 16-17 of the Second Intermediate Period in Ancient Egypt, ca. 1500 BCE. The Edwin Smith papyrus is unique among the four principal medical papyri in existencethat...
. It is also known for developing the process of embalming
Embalming
Embalming, in most modern cultures, is the art and science of temporarily preserving human remains to forestall decomposition and to make them suitable for public display at a funeral. The three goals of embalming are thus sanitization, presentation and preservation of a corpse to achieve this...
, which was used for mummification
Mummy
A mummy is a body, human or animal, whose skin and organs have been preserved by either intentional or incidental exposure to chemicals, extreme coldness , very low humidity, or lack of air when bodies are submerged in bogs, so that the recovered body will not decay further if kept in cool and dry...
, in order to preserve human remains and forestall decomposition
Decomposition
Decomposition is the process by which organic material is broken down into simpler forms of matter. The process is essential for recycling the finite matter that occupies physical space in the biome. Bodies of living organisms begin to decompose shortly after death...
. In ancient China, biological topics can be found dispersed across several different disciplines, including the work of herbologists
Chinese herbology
Chinese Herbology is the theory of Traditional Chinese herbal therapy, which accounts for the majority of treatments in Traditional Chinese medicine ....
, physicians, alchemists and philosophers
Chinese philosophy
Chinese philosophy is philosophy written in the Chinese tradition of thought. The majority of traditional Chinese philosophy originates in the Spring and Autumn and Warring States era, during a period known as the "Hundred Schools of Thought", which was characterized by significant intellectual and...
. The Taoist
Taoism
Taoism refers to a philosophical or religious tradition in which the basic concept is to establish harmony with the Tao , which is the mechanism of everything that exists...
tradition of Chinese alchemy
Chinese alchemy
Chinese alchemy, a part of the larger tradition of Taoism, centers on the tradition of body-spirit cultivation that developed through the Chinese understandings of medicine and the body. These Chinese traditions were developed into a system of energy practices...
, for example, can be considered part of the life sciences due to its emphasis on health (with the ultimate goal being the elixir of life
Elixir of life
The elixir of life, also known as the elixir of immortality and sometimes equated with the philosopher's stone, is a legendary potion, or drink, that grants the drinker eternal life and or eternal youth. Many practitioners of alchemy pursued it. The elixir of life was also said to be able to create...
). The system of classical Chinese medicine usually revolved around the theory of yin and yang
Yin and yang
In Asian philosophy, the concept of yin yang , which is often referred to in the West as "yin and yang", is used to describe how polar opposites or seemingly contrary forces are interconnected and interdependent in the natural world, and how they give rise to each other in turn. Opposites thus only...
, and the five phases. Taoist philosophers, such as Zhuangzi
Zhuangzi
Zhuangzi was an influential Chinese philosopher who lived around the 4th century BCE during the Warring States Period, a period corresponding to the philosophical summit of Chinese thought — the Hundred Schools of Thought, and is credited with writing—in part or in whole—a work known by his name,...
in the 4th century BC, also expressed ideas related to evolution
Evolution
Evolution is any change across successive generations in the heritable characteristics of biological populations. Evolutionary processes give rise to diversity at every level of biological organisation, including species, individual organisms and molecules such as DNA and proteins.Life on Earth...
, such as denying the fixity of biological species and speculating that species had developed differing attributes in response to differing environments.
The ancient Indian Ayurveda
Ayurveda
Ayurveda or ayurvedic medicine is a system of traditional medicine native to India and a form of alternative medicine. In Sanskrit, words , meaning "longevity", and , meaning "knowledge" or "science". The earliest literature on Indian medical practice appeared during the Vedic period in India,...
tradition independently developed the concept of three humours, resembling that of the four humours
Humorism
Humorism, or humoralism, is a now discredited theory of the makeup and workings of the human body, adopted by Greek and Roman physicians and philosophers, positing that an excess or deficiency of any of four distinct bodily fluids in a person directly influences their temperament and health...
of ancient Greek medicine, though the Ayurvedic system included further complications, such as the body being composed of five elements
Classical element
Many philosophies and worldviews have a set of classical elements believed to reflect the simplest essential parts and principles of which anything consists or upon which the constitution and fundamental powers of anything are based. Most frequently, classical elements refer to ancient beliefs...
and seven basic tissues
Tissue (biology)
Tissue is a cellular organizational level intermediate between cells and a complete organism. A tissue is an ensemble of cells, not necessarily identical, but from the same origin, that together carry out a specific function. These are called tissues because of their identical functioning...
. Ayurvedic writers also classified living things into four categories based on the method of birth (from the womb, eggs, heat & moisture, and seeds) and explained the conception of a fetus
Fetus
A fetus is a developing mammal or other viviparous vertebrate after the embryonic stage and before birth.In humans, the fetal stage of prenatal development starts at the beginning of the 11th week in gestational age, which is the 9th week after fertilization.-Etymology and spelling variations:The...
in detail. They also made considerable advances in the field of surgery
Surgery
Surgery is an ancient medical specialty that uses operative manual and instrumental techniques on a patient to investigate and/or treat a pathological condition such as disease or injury, or to help improve bodily function or appearance.An act of performing surgery may be called a surgical...
, often without the use of human dissection
Dissection
Dissection is usually the process of disassembling and observing something to determine its internal structure and as an aid to discerning the functions and relationships of its components....
or animal vivisection
Vivisection
Vivisection is defined as surgery conducted for experimental purposes on a living organism, typically animals with a central nervous system, to view living internal structure...
. One of the earliest Ayurvedic treatises was the Sushruta Samhita
Sushruta Samhita
The Sushruta Samhita is a Sanskrit text, attributed to one Sushruta, foundational to Ayurvedic medicine , with innovative chapters on surgery....
, attributed to Sushruta in the 6th century BC. It was also an early materia medica
Materia medica
Materia medica is a Latin medical term for the body of collected knowledge about the therapeutic properties of any substance used for healing . The term 'materia medica' derived from the title of a work by the Ancient Greek physician Pedanius Dioscorides in the 1st century AD, De materia medica libre...
, describing 700 medicinal plants, 64 preparations from mineral sources, and 57 preparations based on animal sources.

Ancient Greek traditions
The pre-Socratic philosophersPre-Socratic philosophy
Pre-Socratic philosophy is Greek philosophy before Socrates . In Classical antiquity, the Presocratic philosophers were called physiologoi...
asked many questions about life but produced little systematic knowledge of specifically biological interest—though the attempts of the atomists to explain life in purely physical terms would recur periodically through the history of biology. However, the medical theories of Hippocrates
Hippocrates
Hippocrates of Cos or Hippokrates of Kos was an ancient Greek physician of the Age of Pericles , and is considered one of the most outstanding figures in the history of medicine...
and his followers, especially humorism
Humorism
Humorism, or humoralism, is a now discredited theory of the makeup and workings of the human body, adopted by Greek and Roman physicians and philosophers, positing that an excess or deficiency of any of four distinct bodily fluids in a person directly influences their temperament and health...
, had a lasting impact.
The philosopher Aristotle
Aristotle
Aristotle was a Greek philosopher and polymath, a student of Plato and teacher of Alexander the Great. His writings cover many subjects, including physics, metaphysics, poetry, theater, music, logic, rhetoric, linguistics, politics, government, ethics, biology, and zoology...
was the most influential scholar of the living world from classical antiquity
Classical antiquity
Classical antiquity is a broad term for a long period of cultural history centered on the Mediterranean Sea, comprising the interlocking civilizations of ancient Greece and ancient Rome, collectively known as the Greco-Roman world...
. Though his early work in natural philosophy was speculative, Aristotle's later biological writings were more empirical, focusing on biological causation and the diversity of life. He made countless observations of nature, especially the habits and attributes
Abstraction
Abstraction is a process by which higher concepts are derived from the usage and classification of literal concepts, first principles, or other methods....
of plant
Plant
Plants are living organisms belonging to the kingdom Plantae. Precise definitions of the kingdom vary, but as the term is used here, plants include familiar organisms such as trees, flowers, herbs, bushes, grasses, vines, ferns, mosses, and green algae. The group is also called green plants or...
s and animal
Animal
Animals are a major group of multicellular, eukaryotic organisms of the kingdom Animalia or Metazoa. Their body plan eventually becomes fixed as they develop, although some undergo a process of metamorphosis later on in their life. Most animals are motile, meaning they can move spontaneously and...
s in the world around him, which he devoted considerable attention to categorizing
Categorization
Categorization is the process in which ideas and objects are recognized, differentiated and understood. Categorization implies that objects are grouped into categories, usually for some specific purpose. Ideally, a category illuminates a relationship between the subjects and objects of knowledge...
. In all, Aristotle classified 540 animal species, and dissected at least 50. He believed that intellectual purposes, formal causes, guided all natural processes.
Aristotle, and nearly all Western scholars after him until the 18th century, believed that creatures were arranged in a graded scale of perfection rising from plants on up to humans: the scala naturae or Great Chain of Being
Great chain of being
The great chain of being , is a Christian concept detailing a strict, religious hierarchical structure of all matter and life, believed to have been decreed by the Christian God.-Divisions:...
. Aristotle's successor at the Lyceum
Lyceum
The lyceum is a category of educational institution defined within the education system of many countries, mainly in Europe. The definition varies between countries; usually it is a type of secondary school.-History:...
, Theophrastus
Theophrastus
Theophrastus , a Greek native of Eresos in Lesbos, was the successor to Aristotle in the Peripatetic school. He came to Athens at a young age, and initially studied in Plato's school. After Plato's death he attached himself to Aristotle. Aristotle bequeathed to Theophrastus his writings, and...
, wrote a series of books on botany—the History of Plants
Historia Plantarum
Historia Plantarum is Latin and literally means History of Plants, although in reality it means something closer to "on plants" or "treatise on plants". There has been more than one book by this title....
—which survived as the most important contribution of antiquity to botany, even into the Middle Ages
Middle Ages
The Middle Ages is a periodization of European history from the 5th century to the 15th century. The Middle Ages follows the fall of the Western Roman Empire in 476 and precedes the Early Modern Era. It is the middle period of a three-period division of Western history: Classic, Medieval and Modern...
. Many of Theophrastus' names survive into modern times, such as carpos for fruit, and pericarpion for seed vessel. Pliny the Elder
Pliny the Elder
Gaius Plinius Secundus , better known as Pliny the Elder, was a Roman author, naturalist, and natural philosopher, as well as naval and army commander of the early Roman Empire, and personal friend of the emperor Vespasian...
was also known for his knowledge of plants and nature, and was the most prolific compiler of zoological descriptions.
A few scholars in the Hellenistic period
Hellenistic period
The Hellenistic period or Hellenistic era describes the time which followed the conquests of Alexander the Great. It was so named by the historian J. G. Droysen. During this time, Greek cultural influence and power was at its zenith in Europe and Asia...
under the Ptolemies
Ptolemaic dynasty
The Ptolemaic dynasty, was a Macedonian Greek royal family which ruled the Ptolemaic Empire in Egypt during the Hellenistic period. Their rule lasted for 275 years, from 305 BC to 30 BC...
—particularly Herophilus of Chalcedon
Herophilos
Herophilos , sometimes Latinized Herophilus , was a Greek physician. Born in Chalcedon, he spent the majority of his life in Alexandria. He was the first scientist to systematically perform scientific dissections of human cadavers and is deemed to be the first anatomist. Herophilos recorded his...
and Erasistratus of Chios
Erasistratus
Erasistratus was a Greek anatomist and royal physician under Seleucus I Nicator of Syria. Along with fellow physician Herophilus, he founded a school of anatomy in Alexandria, where they carried out anatomical research...
—amended Aristotle's physiological work, even performing experimental dissections and vivisections. Claudius Galen
Galen
Aelius Galenus or Claudius Galenus , better known as Galen of Pergamon , was a prominent Roman physician, surgeon and philosopher...
became the most important authority on medicine and anatomy. Though a few ancient atomists
Atomism
Atomism is a natural philosophy that developed in several ancient traditions. The atomists theorized that the natural world consists of two fundamental parts: indivisible atoms and empty void.According to Aristotle, atoms are indestructible and immutable and there are an infinite variety of shapes...
such as Lucretius
Lucretius
Titus Lucretius Carus was a Roman poet and philosopher. His only known work is an epic philosophical poem laying out the beliefs of Epicureanism, De rerum natura, translated into English as On the Nature of Things or "On the Nature of the Universe".Virtually no details have come down concerning...
challenged the teleological
Teleology
A teleology is any philosophical account which holds that final causes exist in nature, meaning that design and purpose analogous to that found in human actions are inherent also in the rest of nature. The word comes from the Greek τέλος, telos; root: τελε-, "end, purpose...
Aristotelian viewpoint that all aspects of life are the result of design or purpose, teleology (and after the rise of Christianity
Christianity
Christianity is a monotheistic religion based on the life and teachings of Jesus as presented in canonical gospels and other New Testament writings...
, natural theology
Natural theology
Natural theology is a branch of theology based on reason and ordinary experience. Thus it is distinguished from revealed theology which is based on scripture and religious experiences of various kinds; and also from transcendental theology, theology from a priori reasoning.Marcus Terentius Varro ...
) would remain central to biological thought essentially until the 18th and 19th centuries. Ernst W. Mayr argued that "Nothing of any real consequence happened in biology after Lucretius and Galen until the Renaissance." The ideas of the Greek traditions of natural history and medicine survived, but they were generally taken unquestioningly in medieval Europe
Middle Ages
The Middle Ages is a periodization of European history from the 5th century to the 15th century. The Middle Ages follows the fall of the Western Roman Empire in 476 and precedes the Early Modern Era. It is the middle period of a three-period division of Western history: Classic, Medieval and Modern...
.
Medieval and Islamic knowledge

Roman Empire
The Roman Empire was the post-Republican period of the ancient Roman civilization, characterised by an autocratic form of government and large territorial holdings in Europe and around the Mediterranean....
led to the disappearance or destruction of much knowledge, though physicians still incorporated many aspects of the Greek tradition into training and practice. In Byzantium
Byzantium
Byzantium was an ancient Greek city, founded by Greek colonists from Megara in 667 BC and named after their king Byzas . The name Byzantium is a Latinization of the original name Byzantion...
and the Islamic world, many of the Greek works were translated into Arabic and many of the works of Aristotle were preserved.
Medieval Muslim physicians
Islamic medicine
In the history of medicine, Islamic medicine, Arabic medicine or Arabian medicine refers to medicine developed in the Islamic Golden Age, and written in Arabic, the lingua franca of Islamic civilization....
, scientists
Islamic science
Science in the medieval Islamic world, also known as Islamic science or Arabic science, is the science developed and practised in the Islamic world during the Islamic Golden Age . During this time, Indian, Iranian and especially Greek knowledge was translated into Arabic...
and philosophers
Early Islamic philosophy
Early Islamic philosophy or classical Islamic philosophy is a period of intense philosophical development beginning in the 2nd century AH of the Islamic calendar and lasting until the 6th century AH...
made significant contributions to biological knowledge between the 8th and 13th centuries during what is known as the "Islamic Golden Age
Islamic Golden Age
During the Islamic Golden Age philosophers, scientists and engineers of the Islamic world contributed enormously to technology and culture, both by preserving earlier traditions and by adding their own inventions and innovations...
" or "Muslim Agricultural Revolution
Muslim Agricultural Revolution
The Arab Agricultural Revolution is a term coined by the historian Andrew Watson in his influential 1974 paper postulating a fundamental transformation in agriculture from the 8th century to the 13th century in the Muslim...
". In zoology
Zoology
Zoology |zoölogy]]), is the branch of biology that relates to the animal kingdom, including the structure, embryology, evolution, classification, habits, and distribution of all animals, both living and extinct...
, for example, the Afro-Arab
Afro-Arab
Afro-Arab refers to people of mixed Black African and genealogical Arab ancestral heritage and/or linguistically and culturally Arabized Black Africans...
scholar al-Jahiz
Al-Jahiz
Al-Jāḥiẓ was an Arabic prose writer and author of works of literature, Mu'tazili theology, and politico-religious polemics.In biology, Al-Jahiz introduced the concept of food chains and also proposed a scheme of animal evolution that entailed...
(781–869) described early evolution
Evolution
Evolution is any change across successive generations in the heritable characteristics of biological populations. Evolutionary processes give rise to diversity at every level of biological organisation, including species, individual organisms and molecules such as DNA and proteins.Life on Earth...
ary ideas such as the struggle for existence. He also introduced the idea of a food chain
Food chain
A food web depicts feeding connections in an ecological community. Ecologists can broadly lump all life forms into one of two categories called trophic levels: 1) the autotrophs, and 2) the heterotrophs...
, and was an early adherent of environmental determinism
Environmental determinism
Environmental determinism, also known as climatic determinism or geographical determinism, is the view that the physical environment, rather than social conditions, determines culture...
. The Persian biologist Al-Dinawari
Al-Dinawari
Ābu Ḥanīfah Āḥmad ibn Dawūd Dīnawarī was a Persian polymath excelling as much in astronomy, agriculture, botany and metallurgy and as he did in geography, mathematics and history. He was born in Dinawar, . He studied astronomy, mathematics and mechanics in Isfahan and philology and poetry in...
(828–896) is considered the founder of botany
Botany
Botany, plant science, or plant biology is a branch of biology that involves the scientific study of plant life. Traditionally, botany also included the study of fungi, algae and viruses...
for his Book of Plants, in which he described at least 637 species and discussed plant development from germination to death, describing the phases of plant growth and the production of flowers and fruit. Persian polymath Abu Rayhan Biruni described the idea of artificial selection
Artificial selection
Artificial selection describes intentional breeding for certain traits, or combination of traits. The term was utilized by Charles Darwin in contrast to natural selection, in which the differential reproduction of organisms with certain traits is attributed to improved survival or reproductive...
and argued that nature works in much the same way, an idea that has been compared to natural selection
Natural selection
Natural selection is the nonrandom process by which biologic traits become either more or less common in a population as a function of differential reproduction of their bearers. It is a key mechanism of evolution....
. In anatomy
Anatomy
Anatomy is a branch of biology and medicine that is the consideration of the structure of living things. It is a general term that includes human anatomy, animal anatomy , and plant anatomy...
and physiology
Physiology
Physiology is the science of the function of living systems. This includes how organisms, organ systems, organs, cells, and bio-molecules carry out the chemical or physical functions that exist in a living system. The highest honor awarded in physiology is the Nobel Prize in Physiology or...
, the Persian
Persian people
The Persian people are part of the Iranian peoples who speak the modern Persian language and closely akin Iranian dialects and languages. The origin of the ethnic Iranian/Persian peoples are traced to the Ancient Iranian peoples, who were part of the ancient Indo-Iranians and themselves part of...
physician Rhazes (865–925) carried out an early experiment
Experiment
An experiment is a methodical procedure carried out with the goal of verifying, falsifying, or establishing the validity of a hypothesis. Experiments vary greatly in their goal and scale, but always rely on repeatable procedure and logical analysis of the results...
to discredit the Galen
Galen
Aelius Galenus or Claudius Galenus , better known as Galen of Pergamon , was a prominent Roman physician, surgeon and philosopher...
ic theory of humorism
Humorism
Humorism, or humoralism, is a now discredited theory of the makeup and workings of the human body, adopted by Greek and Roman physicians and philosophers, positing that an excess or deficiency of any of four distinct bodily fluids in a person directly influences their temperament and health...
.
In experimental medicine
Biomedical research
Biomedical research , in general simply known as medical research, is the basic research, applied research, or translational research conducted to aid and support the body of knowledge in the field of medicine...
, the Persian physician Avicenna
Avicenna
Abū ʿAlī al-Ḥusayn ibn ʿAbd Allāh ibn Sīnā , commonly known as Ibn Sīnā or by his Latinized name Avicenna, was a Persian polymath, who wrote almost 450 treatises on a wide range of subjects, of which around 240 have survived...
(980–1037) introduced clinical trial
Clinical trial
Clinical trials are a set of procedures in medical research and drug development that are conducted to allow safety and efficacy data to be collected for health interventions...
s and clinical pharmacology
Clinical pharmacology
Clinical pharmacology is the science of drugs and their clinical use. It is underpinned by the basic science of pharmacology, with added focus on the application of pharmacological principles and methods in the real world...
in The Canon of Medicine
The Canon of Medicine
The Canon of Medicine is an encyclopedia of Galenic medicine in five books compiled by Ibn Sīnā and completed in 1025. It presents a clear and organized summary of all the medical knowledge of the time...
, which remained an authoritative text in European medical education up until the 17th century. The Andalusian
Al-Andalus
Al-Andalus was the Arabic name given to a nation and territorial region also commonly referred to as Moorish Iberia. The name describes parts of the Iberian Peninsula and Septimania governed by Muslims , at various times in the period between 711 and 1492, although the territorial boundaries...
-Arab
Arab
Arab people, also known as Arabs , are a panethnicity primarily living in the Arab world, which is located in Western Asia and North Africa. They are identified as such on one or more of genealogical, linguistic, or cultural grounds, with tribal affiliations, and intra-tribal relationships playing...
ian physician Avenzoar
Ibn Zuhr
Abū Merwān ’Abdal-Malik ibn Zuhr was a Muslim physician, surgeon and teacher in Al-Andalus.He was born at Seville...
(1091–1161) was an early adherent of experimental dissection
Dissection
Dissection is usually the process of disassembling and observing something to determine its internal structure and as an aid to discerning the functions and relationships of its components....
and autopsy
Autopsy
An autopsy—also known as a post-mortem examination, necropsy , autopsia cadaverum, or obduction—is a highly specialized surgical procedure that consists of a thorough examination of a corpse to determine the cause and manner of death and to evaluate any disease or injury that may be present...
, which he carried out to prove that the skin disease scabies
Scabies
Scabies , known colloquially as the seven-year itch, is a contagious skin infection that occurs among humans and other animals. It is caused by a tiny and usually not directly visible parasite, the mite Sarcoptes scabiei, which burrows under the host's skin, causing intense allergic itching...
was caused by a parasite, a discovery which upset the theory of humorism. He also introduced experimental surgery
Surgery
Surgery is an ancient medical specialty that uses operative manual and instrumental techniques on a patient to investigate and/or treat a pathological condition such as disease or injury, or to help improve bodily function or appearance.An act of performing surgery may be called a surgical...
, where animal testing
Animal testing
Animal testing, also known as animal experimentation, animal research, and in vivo testing, is the use of non-human animals in experiments. Worldwide it is estimated that the number of vertebrate animals—from zebrafish to non-human primates—ranges from the tens of millions to more than 100 million...
is used to experiment with surgical techniques prior to using them on humans. During a famine
Famine
A famine is a widespread scarcity of food, caused by several factors including crop failure, overpopulation, or government policies. This phenomenon is usually accompanied or followed by regional malnutrition, starvation, epidemic, and increased mortality. Every continent in the world has...
in Egypt
Egypt
Egypt , officially the Arab Republic of Egypt, Arabic: , is a country mainly in North Africa, with the Sinai Peninsula forming a land bridge in Southwest Asia. Egypt is thus a transcontinental country, and a major power in Africa, the Mediterranean Basin, the Middle East and the Muslim world...
in 1200, Abd-el-latif observed and examined a large number of skeleton
Skeleton
The skeleton is the body part that forms the supporting structure of an organism. There are two different skeletal types: the exoskeleton, which is the stable outer shell of an organism, and the endoskeleton, which forms the support structure inside the body.In a figurative sense, skeleton can...
s, and he discovered that Galen was incorrect regarding the formation of the bone
Bone
Bones are rigid organs that constitute part of the endoskeleton of vertebrates. They support, and protect the various organs of the body, produce red and white blood cells and store minerals. Bone tissue is a type of dense connective tissue...
s of the lower jaw
Jaw
The jaw is any opposable articulated structure at the entrance of the mouth, typically used for grasping and manipulating food. The term jaws is also broadly applied to the whole of the structures constituting the vault of the mouth and serving to open and close it and is part of the body plan of...
and sacrum
Sacrum
In vertebrate anatomy the sacrum is a large, triangular bone at the base of the spine and at the upper and back part of the pelvic cavity, where it is inserted like a wedge between the two hip bones. Its upper part connects with the last lumbar vertebra, and bottom part with the coccyx...
.
In the early 13th century, the Andalusian-Arabian biologist Abu al-Abbas al-Nabati developed an early scientific method
Scientific method
Scientific method refers to a body of techniques for investigating phenomena, acquiring new knowledge, or correcting and integrating previous knowledge. To be termed scientific, a method of inquiry must be based on gathering empirical and measurable evidence subject to specific principles of...
for botany, introducing empirical
Empirical
The word empirical denotes information gained by means of observation or experimentation. Empirical data are data produced by an experiment or observation....
and experiment
Experiment
An experiment is a methodical procedure carried out with the goal of verifying, falsifying, or establishing the validity of a hypothesis. Experiments vary greatly in their goal and scale, but always rely on repeatable procedure and logical analysis of the results...
al techniques in the testing, description and identification of numerous materia medica
Materia medica
Materia medica is a Latin medical term for the body of collected knowledge about the therapeutic properties of any substance used for healing . The term 'materia medica' derived from the title of a work by the Ancient Greek physician Pedanius Dioscorides in the 1st century AD, De materia medica libre...
, and separating unverified reports from those supported by actual tests and observation
Observation
Observation is either an activity of a living being, such as a human, consisting of receiving knowledge of the outside world through the senses, or the recording of data using scientific instruments. The term may also refer to any data collected during this activity...
s. His student Ibn al-Baitar (d. 1248) wrote a pharmaceutical
Pharmacy
Pharmacy is the health profession that links the health sciences with the chemical sciences and it is charged with ensuring the safe and effective use of pharmaceutical drugs...
encyclopedia describing 1,400 plant
Plant
Plants are living organisms belonging to the kingdom Plantae. Precise definitions of the kingdom vary, but as the term is used here, plants include familiar organisms such as trees, flowers, herbs, bushes, grasses, vines, ferns, mosses, and green algae. The group is also called green plants or...
s, food
Food
Food is any substance consumed to provide nutritional support for the body. It is usually of plant or animal origin, and contains essential nutrients, such as carbohydrates, fats, proteins, vitamins, or minerals...
s, and drug
Drug
A drug, broadly speaking, is any substance that, when absorbed into the body of a living organism, alters normal bodily function. There is no single, precise definition, as there are different meanings in drug control law, government regulations, medicine, and colloquial usage.In pharmacology, a...
s, 300 of which were his own original discoveries. A Latin
Latin
Latin is an Italic language originally spoken in Latium and Ancient Rome. It, along with most European languages, is a descendant of the ancient Proto-Indo-European language. Although it is considered a dead language, a number of scholars and members of the Christian clergy speak it fluently, and...
translation of his work was useful to European biologists and pharmacists in the 18th and 19th centuries.
The Arabian physician Ibn al-Nafis (1213–1288) was another early adherent of experimental dissection and autopsy, who in 1242 discovered pulmonary circulation
Pulmonary circulation
Pulmonary circulation is the half portion of the cardiovascular system which carries Oxygen-depleted Blood away from the heart, to the Lungs, and returns oxygenated blood back to the heart. Encyclopedic description and discovery of the pulmonary circulation is widely attributed to Doctor Ibn...
and coronary circulation
Coronary circulation
Coronary circulation is the circulation of blood in the blood vessels of the heart muscle . The vessels that deliver oxygen-rich blood to the myocardium are known as coronary arteries...
, which form the basis of the circulatory system
Circulatory system
The circulatory system is an organ system that passes nutrients , gases, hormones, blood cells, etc...
. He also described the concept of metabolism
Metabolism
Metabolism is the set of chemical reactions that happen in the cells of living organisms to sustain life. These processes allow organisms to grow and reproduce, maintain their structures, and respond to their environments. Metabolism is usually divided into two categories...
, and discredited the incorrect Galenic and Avicennian theories on the four humours, pulsation
Pulse
In medicine, one's pulse represents the tactile arterial palpation of the heartbeat by trained fingertips. The pulse may be palpated in any place that allows an artery to be compressed against a bone, such as at the neck , at the wrist , behind the knee , on the inside of the elbow , and near the...
, bones, muscle
Muscle
Muscle is a contractile tissue of animals and is derived from the mesodermal layer of embryonic germ cells. Muscle cells contain contractile filaments that move past each other and change the size of the cell. They are classified as skeletal, cardiac, or smooth muscles. Their function is to...
s, intestine
Intestine
In human anatomy, the intestine is the segment of the alimentary canal extending from the pyloric sphincter of the stomach to the anus and, in humans and other mammals, consists of two segments, the small intestine and the large intestine...
s, sensory organs
Sensory system
A sensory system is a part of the nervous system responsible for processing sensory information. A sensory system consists of sensory receptors, neural pathways, and parts of the brain involved in sensory perception. Commonly recognized sensory systems are those for vision, hearing, somatic...
, bilious
Bile
Bile or gall is a bitter-tasting, dark green to yellowish brown fluid, produced by the liver of most vertebrates, that aids the process of digestion of lipids in the small intestine. In many species, bile is stored in the gallbladder and upon eating is discharged into the duodenum...
canals
Canal (anatomy)
In anatomy, a canal is a tubular passage or channel which connect different regions of the body.Examples include:* Head/Skull** Infraorbital canal** Alveolar canals** Palatovaginal canal** Greater palatine canal...
, esophagus
Esophagus
The esophagus is an organ in vertebrates which consists of a muscular tube through which food passes from the pharynx to the stomach. During swallowing, food passes from the mouth through the pharynx into the esophagus and travels via peristalsis to the stomach...
and stomach
Stomach
The stomach is a muscular, hollow, dilated part of the alimentary canal which functions as an important organ of the digestive tract in some animals, including vertebrates, echinoderms, insects , and molluscs. It is involved in the second phase of digestion, following mastication .The stomach is...
.

High Middle Ages
The High Middle Ages was the period of European history around the 11th, 12th, and 13th centuries . The High Middle Ages were preceded by the Early Middle Ages and followed by the Late Middle Ages, which by convention end around 1500....
, a few European scholars such as Hildegard of Bingen
Hildegard of Bingen
Blessed Hildegard of Bingen , also known as Saint Hildegard, and Sibyl of the Rhine, was a German writer, composer, philosopher, Christian mystic, Benedictine abbess, visionary, and polymath. Elected a magistra by her fellow nuns in 1136, she founded the monasteries of Rupertsberg in 1150 and...
, Albertus Magnus
Albertus Magnus
Albertus Magnus, O.P. , also known as Albert the Great and Albert of Cologne, is a Catholic saint. He was a German Dominican friar and a bishop, who achieved fame for his comprehensive knowledge of and advocacy for the peaceful coexistence of science and religion. Those such as James A. Weisheipl...
and Frederick II
Frederick II, Holy Roman Emperor
Frederick II , was one of the most powerful Holy Roman Emperors of the Middle Ages and head of the House of Hohenstaufen. His political and cultural ambitions, based in Sicily and stretching through Italy to Germany, and even to Jerusalem, were enormous...
expanded the natural history canon. The rise of European universities
History of European research universities
European research universities date from the founding of the University of Bologna in 1088 or the University of Paris . In the 19th and 20th centuries, European universities concentrated upon science and research, their structures and philosophies having shaped the contemporary university...
, though important for the development of physics and philosophy, had little impact on biological scholarship.
Renaissance and early modern developments
The European Renaissance brought expanded interest in both empirical natural history and physiology. In 1543, Andreas Vesalius inaugurated the modern era of Western medicine with his seminal human anatomyHuman anatomy
Human anatomy is primarily the scientific study of the morphology of the human body. Anatomy is subdivided into gross anatomy and microscopic anatomy. Gross anatomy is the study of anatomical structures that can be seen by the naked eye...
treatise De humani corporis fabrica
De humani corporis fabrica
De humani corporis fabrica libri septem is a textbook of human anatomy written by Andreas Vesalius in 1543....
, which was based on dissection of corpses. Vesalius was the first in a series of anatomists who gradually replaced scholasticism
Scholasticism
Scholasticism is a method of critical thought which dominated teaching by the academics of medieval universities in Europe from about 1100–1500, and a program of employing that method in articulating and defending orthodoxy in an increasingly pluralistic context...
with empiricism
Empiricism
Empiricism is a theory of knowledge that asserts that knowledge comes only or primarily via sensory experience. One of several views of epistemology, the study of human knowledge, along with rationalism, idealism and historicism, empiricism emphasizes the role of experience and evidence,...
in physiology and medicine, relying on first-hand experience rather than authority and abstract reasoning. Via herbalism
Herbalism
Herbalism is a traditional medicinal or folk medicine practice based on the use of plants and plant extracts. Herbalism is also known as botanical medicine, medical herbalism, herbal medicine, herbology, herblore, and phytotherapy...
, medicine was also indirectly the source of renewed empiricism in the study of plants. Otto Brunfels
Otto Brunfels
Otto Brunfels was a German theologian and botanist...
, Hieronymus Bock
Hieronymus Bock
Hieronymus Bock was a German botanist, physician, and Lutheran minister who began the transition from medieval botany to the modern scientific worldview by arranging plants by their relation or resemblance....
and Leonhart Fuchs
Leonhart Fuchs
Leonhart Fuchs , sometimes spelled Leonhard Fuchs, was a German physician and one of the three founding fathers of botany, along with Otto Brunfels and Hieronymus Bock .-Biography:...
wrote extensively on wild plants, the beginning of a nature-based approach to the full range of plant life. Bestiaries—a genre that combines both the natural and figurative knowledge of animals—also became more sophisticated, especially with the work of William Turner, Pierre Belon
Pierre Belon
Pierre Belon was a French naturalist. He is sometimes known as Pierre Belon du Mans, or, in Latin translations of his works, as Petrus Bellonius Cenomanus.Belon was born in 1517 at Soulletiere near Cérans-Foulletourte...
, Guillaume Rondelet
Guillaume Rondelet
Guillaume Rondelet , known also as Rondeletus , was Regus Professor of medicine at the University of Montpellier in southern France and Chancellor of the University between 1556 and his death in 1566. He achieved renown as an anatomist and a naturalist with a particular interest in botany and zoology...
, Conrad Gessner
Conrad Gessner
Conrad Gessner was a Swiss naturalist and bibliographer. His five-volume Historiae animalium is considered the beginning of modern zoology, and the flowering plant genus Gesneria is named after him...
, and Ulisse Aldrovandi
Ulisse Aldrovandi
Ulisse Aldrovandi was an Italian naturalist, the moving force behind Bologna's botanical garden, one of the first in Europe. Carolus Linnaeus and the comte de Buffon reckoned him the father of natural history studies...
.
Artists such as Albrecht Dürer
Albrecht Dürer
Albrecht Dürer was a German painter, printmaker, engraver, mathematician, and theorist from Nuremberg. His prints established his reputation across Europe when he was still in his twenties, and he has been conventionally regarded as the greatest artist of the Northern Renaissance ever since...
and Leonardo da Vinci
Leonardo da Vinci
Leonardo di ser Piero da Vinci was an Italian Renaissance polymath: painter, sculptor, architect, musician, scientist, mathematician, engineer, inventor, anatomist, geologist, cartographer, botanist and writer whose genius, perhaps more than that of any other figure, epitomized the Renaissance...
, often working with naturalists, were also interested in the bodies of animals and humans, studying physiology in detail and contributing to the growth of anatomical knowledge. The traditions of alchemy
Alchemy
Alchemy is an influential philosophical tradition whose early practitioners’ claims to profound powers were known from antiquity. The defining objectives of alchemy are varied; these include the creation of the fabled philosopher's stone possessing powers including the capability of turning base...
and natural magic
Natural magic
Natural magic in the context of Renaissance magic is that part of the occult which deals with natural forces directly, as opposed to ceremonial magic, in particular goety and theurgy, which deals with the summoning of spirits...
, especially in the work of Paracelsus
Paracelsus
Paracelsus was a German-Swiss Renaissance physician, botanist, alchemist, astrologer, and general occultist....
, also laid claim to knowledge of the living world. Alchemists subjected organic matter to chemical analysis and experimented liberally with both biological and mineral pharmacology
Pharmacology
Pharmacology is the branch of medicine and biology concerned with the study of drug action. More specifically, it is the study of the interactions that occur between a living organism and chemicals that affect normal or abnormal biochemical function...
. This was part of a larger transition in world views (the rise of the mechanical philosophy) that continued into the 17th century, as the traditional metaphor of nature as organism was replaced by the nature as machine metaphor.
Seventeenth and eighteenth centuries
Systematizing, naming and classifying dominated natural history throughout much of the 17th and 18th centuries. Carolus LinnaeusCarolus Linnaeus
Carl Linnaeus , also known after his ennoblement as , was a Swedish botanist, physician, and zoologist, who laid the foundations for the modern scheme of binomial nomenclature. He is known as the father of modern taxonomy, and is also considered one of the fathers of modern ecology...
published a basic taxonomy
Taxonomy
Taxonomy is the science of identifying and naming species, and arranging them into a classification. The field of taxonomy, sometimes referred to as "biological taxonomy", revolves around the description and use of taxonomic units, known as taxa...
for the natural world in 1735 (variations of which have been in use ever since), and in the 1750s introduced scientific names
Binomial nomenclature
Binomial nomenclature is a formal system of naming species of living things by giving each a name composed of two parts, both of which use Latin grammatical forms, although they can be based on words from other languages...
for all his species. While Linnaeus conceived of species as unchanging parts of a designed hierarchy, the other great naturalist of the 18th century, Georges-Louis Leclerc, Comte de Buffon
Georges-Louis Leclerc, Comte de Buffon
Georges-Louis Leclerc, Comte de Buffon was a French naturalist, mathematician, cosmologist, and encyclopedic author.His works influenced the next two generations of naturalists, including Jean-Baptiste Lamarck and Georges Cuvier...
, treated species as artificial categories and living forms as malleable—even suggesting the possibility of common descent
Common descent
In evolutionary biology, a group of organisms share common descent if they have a common ancestor. There is strong quantitative support for the theory that all living organisms on Earth are descended from a common ancestor....
. Though he was opposed to evolution, Buffon is a key figure in the history of evolutionary thought
History of evolutionary thought
Evolutionary thought, the conception that species change over time, has roots in antiquity, in the ideas of the ancient Greeks, Romans, and Chinese as well as in medieval Islamic science...
; his work would influence the evolutionary theories of both Lamarck and Darwin
Charles Darwin
Charles Robert Darwin FRS was an English naturalist. He established that all species of life have descended over time from common ancestry, and proposed the scientific theory that this branching pattern of evolution resulted from a process that he called natural selection.He published his theory...
.
The discovery and description of new species and the collection of specimens became a passion of scientific gentlemen and a lucrative enterprise for entrepreneurs; many naturalists traveled the globe in search of scientific knowledge and adventure.

William Harvey
William Harvey was an English physician who was the first person to describe completely and in detail the systemic circulation and properties of blood being pumped to the body by the heart...
and other natural philosophers investigated the roles of blood, veins and arteries. Harvey's De motu cordis in 1628 was the beginning of the end for Galenic theory, and alongside Santorio Santorio's studies of metabolism, it served as an influential model of quantitative approaches to physiology.
In the early 17th century, the micro-world of biology was just beginning to open up. A few lensmakers and natural philosophers had been creating crude microscope
Microscope
A microscope is an instrument used to see objects that are too small for the naked eye. The science of investigating small objects using such an instrument is called microscopy...
s since the late 16th century, and Robert Hooke
Robert Hooke
Robert Hooke FRS was an English natural philosopher, architect and polymath.His adult life comprised three distinct periods: as a scientific inquirer lacking money; achieving great wealth and standing through his reputation for hard work and scrupulous honesty following the great fire of 1666, but...
published the seminal Micrographia
Micrographia
Micrographia is a historic book by Robert Hooke, detailing the then thirty year-old Hooke's observations through various lenses. Published in September 1665, the first major publication of the Royal Society, it was the first scientific best-seller, inspiring a wide public interest in the new...
based on observations with his own compound microscope in 1665. But it was not until Antony van Leeuwenhoek's dramatic improvements in lensmaking beginning in the 1670s—ultimately producing up to 200-fold magnification with a single lens—that scholars discovered spermatozoa, bacteria
Bacteria
Bacteria are a large domain of prokaryotic microorganisms. Typically a few micrometres in length, bacteria have a wide range of shapes, ranging from spheres to rods and spirals...
, infusoria
Infusoria
Infusoria is a collective term for minute aquatic creatures like ciliates, euglenoids, protozoa, and unicellular algae that exist in freshwater ponds...
and the sheer strangeness and diversity of microscopic life. Similar investigations by Jan Swammerdam
Jan Swammerdam
Jan Swammerdam was a Dutch biologist and microscopist. His work on insects demonstrated that the various phases during the life of an insect—egg, larva, pupa, and adult—are different forms of the same animal. As part of his anatomical research, he carried out experiments on muscle contraction...
led to new interest in entomology
Entomology
Entomology is the scientific study of insects, a branch of arthropodology...
and built the basic techniques of microscopic dissection and staining.
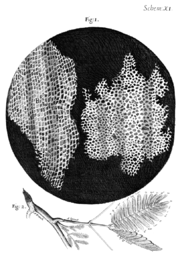
John Ray
John Ray was an English naturalist, sometimes referred to as the father of English natural history. Until 1670, he wrote his name as John Wray. From then on, he used 'Ray', after "having ascertained that such had been the practice of his family before him".He published important works on botany,...
worked to incorporate the flood of newly discovered organisms shipped from across the globe into a coherent taxonomy, and a coherent theology (natural theology
Natural theology
Natural theology is a branch of theology based on reason and ordinary experience. Thus it is distinguished from revealed theology which is based on scripture and religious experiences of various kinds; and also from transcendental theology, theology from a priori reasoning.Marcus Terentius Varro ...
). Debate over another flood, the Noachian, catalyzed the development of paleontology
Paleontology
Paleontology "old, ancient", ὄν, ὀντ- "being, creature", and λόγος "speech, thought") is the study of prehistoric life. It includes the study of fossils to determine organisms' evolution and interactions with each other and their environments...
; in 1669 Nicholas Steno published an essay on how the remains of living organisms could be trapped in layers of sediment and mineralized to produce fossil
Fossil
Fossils are the preserved remains or traces of animals , plants, and other organisms from the remote past...
s. Although Steno's ideas about fossilization were well known and much debated among natural philosophers, an organic origin for all fossils would not be accepted by all naturalists until the end of the 18th century due to philosophical and theological debate about issues such as the age of the earth and extinction
Extinction
In biology and ecology, extinction is the end of an organism or of a group of organisms , normally a species. The moment of extinction is generally considered to be the death of the last individual of the species, although the capacity to breed and recover may have been lost before this point...
.
19th century: the emergence of biological disciplines
Up through the 19th century, the scope of biology was largely divided between medicine, which investigated questions of form and function (i.e., physiology), and natural history, which was concerned with the diversity of life and interactions among different forms of life and between life and non-life. By 1900, much of these domains overlapped, while natural history (and its counterpart natural philosophyNatural philosophy
Natural philosophy or the philosophy of nature , is a term applied to the study of nature and the physical universe that was dominant before the development of modern science...
) had largely given way to more specialized scientific disciplines—cytology
Cell biology
Cell biology is a scientific discipline that studies cells – their physiological properties, their structure, the organelles they contain, interactions with their environment, their life cycle, division and death. This is done both on a microscopic and molecular level...
, bacteriology
Bacteriology
Bacteriology is the study of bacteria. This subdivision of microbiology involves the identification, classification, and characterization of bacterial species...
, morphology
Morphology (biology)
In biology, morphology is a branch of bioscience dealing with the study of the form and structure of organisms and their specific structural features....
, embryology
Embryology
Embryology is a science which is about the development of an embryo from the fertilization of the ovum to the fetus stage...
, geography
Geography
Geography is the science that studies the lands, features, inhabitants, and phenomena of Earth. A literal translation would be "to describe or write about the Earth". The first person to use the word "geography" was Eratosthenes...
, and geology
Geology
Geology is the science comprising the study of solid Earth, the rocks of which it is composed, and the processes by which it evolves. Geology gives insight into the history of the Earth, as it provides the primary evidence for plate tectonics, the evolutionary history of life, and past climates...
.

Natural history and natural philosophy
Widespread travel by naturalists in the early-to-mid-19th century resulted in a wealth of new information about the diversity and distribution of living organisms. Of particular importance was the work of Alexander von HumboldtAlexander von Humboldt
Friedrich Wilhelm Heinrich Alexander Freiherr von Humboldt was a German naturalist and explorer, and the younger brother of the Prussian minister, philosopher and linguist Wilhelm von Humboldt...
, which analyzed the relationship between organisms and their environment (i.e., the domain of natural history
Natural history
Natural history is the scientific research of plants or animals, leaning more towards observational rather than experimental methods of study, and encompasses more research published in magazines than in academic journals. Grouped among the natural sciences, natural history is the systematic study...
) using the quantitative approaches of natural philosophy
Natural philosophy
Natural philosophy or the philosophy of nature , is a term applied to the study of nature and the physical universe that was dominant before the development of modern science...
(i.e., physics
Physics
Physics is a natural science that involves the study of matter and its motion through spacetime, along with related concepts such as energy and force. More broadly, it is the general analysis of nature, conducted in order to understand how the universe behaves.Physics is one of the oldest academic...
and chemistry
Chemistry
Chemistry is the science of matter, especially its chemical reactions, but also its composition, structure and properties. Chemistry is concerned with atoms and their interactions with other atoms, and particularly with the properties of chemical bonds....
). Humboldt's work laid the foundations of biogeography
Biogeography
Biogeography is the study of the distribution of species , organisms, and ecosystems in space and through geological time. Organisms and biological communities vary in a highly regular fashion along geographic gradients of latitude, elevation, isolation and habitat area...
and inspired several generations of scientists.
Geology and paleontology
The emerging discipline of geology also brought natural history and natural philosophy closer together; the establishment of the stratigraphic columnStratigraphy
Stratigraphy, a branch of geology, studies rock layers and layering . It is primarily used in the study of sedimentary and layered volcanic rocks....
linked the spacial distribution of organisms to their temporal distribution, a key precursor to concepts of evolution. Georges Cuvier
Georges Cuvier
Georges Chrétien Léopold Dagobert Cuvier or Jean Léopold Nicolas Frédéric Cuvier , known as Georges Cuvier, was a French naturalist and zoologist...
and others made great strides in comparative anatomy
Comparative anatomy
Comparative anatomy is the study of similarities and differences in the anatomy of organisms. It is closely related to evolutionary biology and phylogeny .-Description:...
and paleontology
Paleontology
Paleontology "old, ancient", ὄν, ὀντ- "being, creature", and λόγος "speech, thought") is the study of prehistoric life. It includes the study of fossils to determine organisms' evolution and interactions with each other and their environments...
in the late 1790s and early 19th century. In a series of lectures and papers that made detailed comparisons between living mammals and fossil
Fossil
Fossils are the preserved remains or traces of animals , plants, and other organisms from the remote past...
remains Cuvier was able to establish that the fossils were remains of species that had become extinct—rather than being remains of species still alive elsewhere in the world, as had been widely believed. Fossils discovered and described by Gideon Mantell
Gideon Mantell
Gideon Algernon Mantell MRCS FRS was an English obstetrician, geologist and palaeontologist...
, William Buckland
William Buckland
The Very Rev. Dr William Buckland DD FRS was an English geologist, palaeontologist and Dean of Westminster, who wrote the first full account of a fossil dinosaur, which he named Megalosaurus...
, Mary Anning
Mary Anning
Mary Anning was a British fossil collector, dealer and palaeontologist who became known around the world for a number of important finds she made in the Jurassic age marine fossil beds at Lyme Regis where she lived...
, and Richard Owen
Richard Owen
Sir Richard Owen, FRS KCB was an English biologist, comparative anatomist and palaeontologist.Owen is probably best remembered today for coining the word Dinosauria and for his outspoken opposition to Charles Darwin's theory of evolution by natural selection...
among others helped establish that there had been an 'age of reptiles' that had preceded even the prehistoric mammals. These discoveries captured the public imagination and focused attention on the history of life on earth. Most of these geologists held to catastrophism
Catastrophism
Catastrophism is the theory that the Earth has been affected in the past by sudden, short-lived, violent events, possibly worldwide in scope. The dominant paradigm of modern geology is uniformitarianism , in which slow incremental changes, such as erosion, create the Earth's appearance...
, but Charles Lyell's
Charles Lyell
Sir Charles Lyell, 1st Baronet, Kt FRS was a British lawyer and the foremost geologist of his day. He is best known as the author of Principles of Geology, which popularised James Hutton's concepts of uniformitarianism – the idea that the earth was shaped by slow-moving forces still in operation...
influential Principles of Geology (1830) popularised Hutton's
James Hutton
James Hutton was a Scottish physician, geologist, naturalist, chemical manufacturer and experimental agriculturalist. He is considered the father of modern geology...
uniformitarianism
Uniformitarianism (science)
In the philosophy of naturalism, the uniformitarianism assumption is that the same natural laws and processes that operate in the universe now, have always operated in the universe in the past and apply everywhere in the universe. It has included the gradualistic concept that "the present is the...
, a theory that explained the geological past and present on equal terms.
Evolution and biogeography

The most significant evolutionary theory before Darwin's was that of Jean-Baptiste Lamarck
Jean-Baptiste Lamarck
Jean-Baptiste Pierre Antoine de Monet, Chevalier de la Marck , often known simply as Lamarck, was a French naturalist...
; based on the inheritance of acquired characteristics (an inheritance mechanism that was widely accepted until the 20th century), it described a chain of development stretching from the lowliest microbe to humans. The British naturalist Charles Darwin
Charles Darwin
Charles Robert Darwin FRS was an English naturalist. He established that all species of life have descended over time from common ancestry, and proposed the scientific theory that this branching pattern of evolution resulted from a process that he called natural selection.He published his theory...
, combining the biogeographical approach of Humboldt, the uniformitarian geology of Lyell, Thomas Malthus's
Thomas Malthus
The Reverend Thomas Robert Malthus FRS was an English scholar, influential in political economy and demography. Malthus popularized the economic theory of rent....
writings on population growth, and his own morphological expertise, created a more successful evolutionary theory based on natural selection
Natural selection
Natural selection is the nonrandom process by which biologic traits become either more or less common in a population as a function of differential reproduction of their bearers. It is a key mechanism of evolution....
; similar evidence led Alfred Russel Wallace
Alfred Russel Wallace
Alfred Russel Wallace, OM, FRS was a British naturalist, explorer, geographer, anthropologist and biologist...
to independently reach the same conclusions.
The 1859 publication of Darwin's theory in On the Origin of Species by Means of Natural Selection, or the Preservation of Favoured Races in the Struggle for Life is often considered the central event in the history of modern biology. Darwin's established credibility as a naturalist, the sober tone of the work, and most of all the sheer strength and volume of evidence presented, allowed Origin to succeed where previous evolutionary works such as the anonymous Vestiges of Creation had failed. Most scientists were convinced of evolution and common descent
Common descent
In evolutionary biology, a group of organisms share common descent if they have a common ancestor. There is strong quantitative support for the theory that all living organisms on Earth are descended from a common ancestor....
by the end of the 19th century. However, natural selection would not be accepted as the primary mechanism of evolution until well into the 20th century, as most contemporary theories of heredity seemed incompatible with the inheritance of random variation.
Wallace, following on earlier work by de Candolle, Humboldt
Alexander von Humboldt
Friedrich Wilhelm Heinrich Alexander Freiherr von Humboldt was a German naturalist and explorer, and the younger brother of the Prussian minister, philosopher and linguist Wilhelm von Humboldt...
and Darwin, made major contributions to zoogeography
Zoogeography
Zoogeography is the branch of the science of biogeography that is concerned with the geographic distribution of animal species.-External links:*: A course outline and collection of Web resources by Dr. Taylor, UBC...
. Because of his interest in the transmutation hypothesis, he paid particular attention to the geographical distribution of closely allied species during his field work first in South America
South America
South America is a continent situated in the Western Hemisphere, mostly in the Southern Hemisphere, with a relatively small portion in the Northern Hemisphere. The continent is also considered a subcontinent of the Americas. It is bordered on the west by the Pacific Ocean and on the north and east...
and then in the Malay archipelago
Malay Archipelago
The Malay Archipelago refers to the archipelago between mainland Southeastern Asia and Australia. The name was derived from the anachronistic concept of a Malay race....
. While in the archipelago he identified the Wallace line
Wallace Line
The Wallace Line separates the ecozones of Asia and Wallacea, a transitional zone between Asia and Australia. West of the line are found organisms related to Asiatic species; to the east, a mixture of species of Asian and Australian origin is present...
, which runs through the Spice Islands
Maluku Islands
The Maluku Islands are an archipelago that is part of Indonesia, and part of the larger Maritime Southeast Asia region. Tectonically they are located on the Halmahera Plate within the Molucca Sea Collision Zone...
dividing the fauna of the archipelago between an Asian zone and a New Guinea
New Guinea
New Guinea is the world's second largest island, after Greenland, covering a land area of 786,000 km2. Located in the southwest Pacific Ocean, it lies geographically to the east of the Malay Archipelago, with which it is sometimes included as part of a greater Indo-Australian Archipelago...
/Australian zone. His key question, as to why the fauna of islands with such similar climates should be so different, could only be answered by considering their origin. In 1876 he wrote The Geographical Distribution of Animals, which was the standard reference work for over half a century, and a sequel, Island Life, in 1880 that focused on island biogeography. He extended the six-zone system developed by Philip Sclater
Philip Sclater
Philip Lutley Sclater was an English lawyer and zoologist. In zoology, he was an expert ornithologist, and identified the main zoogeographic regions of the world...
for describing the geographical distribution of birds to animals of all kinds. His method of tabulating data on animal groups in geographic zones highlighted the discontinuities; and his appreciation of evolution allowed him to propose rational explanations, which had not been done before.
The scientific study of heredity
Heredity
Heredity is the passing of traits to offspring . This is the process by which an offspring cell or organism acquires or becomes predisposed to the characteristics of its parent cell or organism. Through heredity, variations exhibited by individuals can accumulate and cause some species to evolve...
grew rapidly in the wake of Darwin's Origin of Species with the work of Francis Galton
Francis Galton
Sir Francis Galton /ˈfrɑːnsɪs ˈgɔːltn̩/ FRS , cousin of Douglas Strutt Galton, half-cousin of Charles Darwin, was an English Victorian polymath: anthropologist, eugenicist, tropical explorer, geographer, inventor, meteorologist, proto-geneticist, psychometrician, and statistician...
and the biometricians. The origin of genetics
Genetics
Genetics , a discipline of biology, is the science of genes, heredity, and variation in living organisms....
is usually traced to the 1866 work of the monk
Monk
A monk is a person who practices religious asceticism, living either alone or with any number of monks, while always maintaining some degree of physical separation from those not sharing the same purpose...
Gregor Mendel
Gregor Mendel
Gregor Johann Mendel was an Austrian scientist and Augustinian friar who gained posthumous fame as the founder of the new science of genetics. Mendel demonstrated that the inheritance of certain traits in pea plants follows particular patterns, now referred to as the laws of Mendelian inheritance...
, who would later be credited with the laws of inheritance. However, his work was not recognized as significant until 35 years afterward. In the meantime, a variety of theories of inheritance (based on pangenesis
Pangenesis
Pangenesis was Charles Darwin's hypothetical mechanism for heredity. He presented this 'provisional hypothesis' in his 1868 work The Variation of Animals and Plants under Domestication and felt that it brought 'together a multitude of facts which are at present left disconnected by any efficient...
, orthogenesis
Orthogenesis
Orthogenesis, orthogenetic evolution, progressive evolution or autogenesis, is the hypothesis that life has an innate tendency to evolve in a unilinear fashion due to some internal or external "driving force". The hypothesis is based on essentialism and cosmic teleology and proposes an intrinsic...
, or other mechanisms) were debated and investigated vigorously. Embryology
Embryology
Embryology is a science which is about the development of an embryo from the fertilization of the ovum to the fetus stage...
and ecology
Ecology
Ecology is the scientific study of the relations that living organisms have with respect to each other and their natural environment. Variables of interest to ecologists include the composition, distribution, amount , number, and changing states of organisms within and among ecosystems...
also became central biological fields, especially as linked to evolution and popularized in the work of Ernst Haeckel
Ernst Haeckel
The "European War" became known as "The Great War", and it was not until 1920, in the book "The First World War 1914-1918" by Charles à Court Repington, that the term "First World War" was used as the official name for the conflict.-Research:...
. Most of the 19th century work on heredity, however, was not in the realm of natural history, but that of experimental physiology.
Physiology
Over the course of the 19th century, the scope of physiology expanded greatly, from a primarily medically oriented field to a wide-ranging investigation of the physical and chemical processes of life—including plants, animals, and even microorganisms in addition to man. Living things as machines became a dominant metaphor in biological (and social) thinking.
Cell theory, embryology and germ theory
Advances in microscopyMicroscopy
Microscopy is the technical field of using microscopes to view samples and objects that cannot be seen with the unaided eye...
also had a profound impact on biological thinking. In the early 19th century, a number of biologists pointed to the central importance of the cell
Cell (biology)
The cell is the basic structural and functional unit of all known living organisms. It is the smallest unit of life that is classified as a living thing, and is often called the building block of life. The Alberts text discusses how the "cellular building blocks" move to shape developing embryos....
. In 1838 and 1839, Schleiden
Matthias Jakob Schleiden
Matthias Jakob Schleiden was a German botanist and co-founder of the cell theory, along with Theodor Schwann and Rudolf Virchow....
and Schwann
Theodor Schwann
Theodor Schwann was a German physiologist. His many contributions to biology include the development of cell theory, the discovery of Schwann cells in the peripheral nervous system, the discovery and study of pepsin, the discovery of the organic nature of yeast, and the invention of the term...
began promoting the ideas that (1) the basic unit of organisms is the cell and (2) that individual cells have all the characteristics of life
Life
Life is a characteristic that distinguishes objects that have signaling and self-sustaining processes from those that do not, either because such functions have ceased , or else because they lack such functions and are classified as inanimate...
, though they opposed the idea that (3) all cells come from the division of other cells. Thanks to the work of Robert Remak
Robert Remak
-External links:*** in the Virtual Laboratory of the Max Planck Institute for the History of Science...
and Rudolf Virchow
Rudolf Virchow
Rudolph Carl Virchow was a German doctor, anthropologist, pathologist, prehistorian, biologist and politician, known for his advancement of public health...
, however, by the 1860s most biologists accepted all three tenets of what came to be known as cell theory
Cell theory
Cell theory refers to the idea that cells are the basic unit of structure in every living thing. Development of this theory during the mid 17th century was made possible by advances in microscopy. This theory is one of the foundations of biology...
.
Cell theory led biologists to re-envision individual organisms as interdependent assemblages of individual cells. Scientists in the rising field of cytology
Cell biology
Cell biology is a scientific discipline that studies cells – their physiological properties, their structure, the organelles they contain, interactions with their environment, their life cycle, division and death. This is done both on a microscopic and molecular level...
, armed with increasingly powerful microscopes and new staining methods, soon found that even single cells were far more complex than the homogeneous fluid-filled chambers described by earlier microscopists. Robert Brown
Robert Brown (botanist)
Robert Brown was a Scottish botanist and palaeobotanist who made important contributions to botany largely through his pioneering use of the microscope...
had described the nucleus
Cell nucleus
In cell biology, the nucleus is a membrane-enclosed organelle found in eukaryotic cells. It contains most of the cell's genetic material, organized as multiple long linear DNA molecules in complex with a large variety of proteins, such as histones, to form chromosomes. The genes within these...
in 1831, and by the end of the 19th century cytologists identified many of the key cell components: chromosome
Chromosome
A chromosome is an organized structure of DNA and protein found in cells. It is a single piece of coiled DNA containing many genes, regulatory elements and other nucleotide sequences. Chromosomes also contain DNA-bound proteins, which serve to package the DNA and control its functions.Chromosomes...
s, centrosome
Centrosome
In cell biology, the centrosome is an organelle that serves as the main microtubule organizing center of the animal cell as well as a regulator of cell-cycle progression. It was discovered by Edouard Van Beneden in 1883...
s mitochondria, chloroplast
Chloroplast
Chloroplasts are organelles found in plant cells and other eukaryotic organisms that conduct photosynthesis. Chloroplasts capture light energy to conserve free energy in the form of ATP and reduce NADP to NADPH through a complex set of processes called photosynthesis.Chloroplasts are green...
s, and other structures made visible through staining. Between 1874 and 1884 Walther Flemming
Walther Flemming
Walther Flemming was a German biologist and a founder of cytogenetics.He was born in Sachsenberg near Schwerin as the fifth child and only son of the psychiatrist Carl Friedrich Flemming and his second wife, Auguste Winter...
described the discrete stages of mitosis, showing that they were not artifacts of staining but occurred in living cells, and moreover, that chromosomes doubled in number just before the cell divided and a daughter cell was produced. Much of the research on cell reproduction came together in August Weismann
August Weismann
Friedrich Leopold August Weismann was a German evolutionary biologist. Ernst Mayr ranked him the second most notable evolutionary theorist of the 19th century, after Charles Darwin...
's theory of heredity: he identified the nucleus (in particular chromosomes) as the hereditary material, proposed the distinction between somatic cell
Somatic cell
A somatic cell is any biological cell forming the body of an organism; that is, in a multicellular organism, any cell other than a gamete, germ cell, gametocyte or undifferentiated stem cell...
s and germ cell
Germ cell
A germ cell is any biological cell that gives rise to the gametes of an organism that reproduces sexually. In many animals, the germ cells originate near the gut of an embryo and migrate to the developing gonads. There, they undergo cell division of two types, mitosis and meiosis, followed by...
s (arguing that chromosome number must be halved for germ cells, a precursor to the concept of meiosis
Meiosis
Meiosis is a special type of cell division necessary for sexual reproduction. The cells produced by meiosis are gametes or spores. The animals' gametes are called sperm and egg cells....
), and adopted Hugo de Vries
Hugo de Vries
Hugo Marie de Vries ForMemRS was a Dutch botanist and one of the first geneticists. He is known chiefly for suggesting the concept of genes, rediscovering the laws of heredity in the 1890s while unaware of Gregor Mendel's work, for introducing the term "mutation", and for developing a mutation...
's theory of pangenes. Weismannism was extremely influential, especially in the new field of experimental embryology
Embryology
Embryology is a science which is about the development of an embryo from the fertilization of the ovum to the fetus stage...
.
By the mid 1850s the miasma theory of disease
Miasma theory of disease
The miasma theory held that diseases such as cholera, chlamydia or the Black Death were caused by a miasma , a noxious form of "bad air"....
was largely superseded by the germ theory of disease
Germ theory of disease
The germ theory of disease, also called the pathogenic theory of medicine, is a theory that proposes that microorganisms are the cause of many diseases...
, creating extensive interest in microorganisms and their interactions with other forms of life. By the 1880s, bacteriology
Bacteriology
Bacteriology is the study of bacteria. This subdivision of microbiology involves the identification, classification, and characterization of bacterial species...
was becoming a coherent discipline, especially through the work of Robert Koch
Robert Koch
Heinrich Hermann Robert Koch was a German physician. He became famous for isolating Bacillus anthracis , the Tuberculosis bacillus and the Vibrio cholerae and for his development of Koch's postulates....
, who introduced methods for growing pure cultures on agar gels
Agar plate
An agar plate is a Petri dish that contains a growth medium used to culture microorganisms or small plants like the moss Physcomitrella patens.Selective growth compounds may also be added to the media, such as antibiotics....
containing specific nutrients in Petri dish
Petri dish
A Petri dish is a shallow glass or plastic cylindrical lidded dish that biologists use to culture cells or small moss plants. It was named after German bacteriologist Julius Richard Petri, who invented it when working as an assistant to Robert Koch...
es. The long-held idea that living organisms could easily originate from nonliving matter (spontaneous generation
Spontaneous generation
Spontaneous generation or Equivocal generation is an obsolete principle regarding the origin of life from inanimate matter, which held that this process was a commonplace and everyday occurrence, as distinguished from univocal generation, or reproduction from parent...
) was attacked in a series of experiments carried out by Louis Pasteur
Louis Pasteur
Louis Pasteur was a French chemist and microbiologist born in Dole. He is remembered for his remarkable breakthroughs in the causes and preventions of diseases. His discoveries reduced mortality from puerperal fever, and he created the first vaccine for rabies and anthrax. His experiments...
, while debates over vitalism
Vitalism
Vitalism, as defined by the Merriam-Webster dictionary, is#a doctrine that the functions of a living organism are due to a vital principle distinct from biochemical reactions...
vs. mechanism
Mechanism (philosophy)
Mechanism is the belief that natural wholes are like machines or artifacts, composed of parts lacking any intrinsic relationship to each other, and with their order imposed from without. Thus, the source of an apparent thing's activities is not the whole itself, but its parts or an external...
(a perennial issue since the time of Aristotle and the Greek atomists) continued apace.
Rise of organic chemistry and experimental physiology
In chemistry, one central issue was the distinction between organic and inorganic substances, especially in the context of organic transformations such as fermentationFermentation (biochemistry)
Fermentation is the process of extracting energy from the oxidation of organic compounds, such as carbohydrates, using an endogenous electron acceptor, which is usually an organic compound. In contrast, respiration is where electrons are donated to an exogenous electron acceptor, such as oxygen,...
and putrefaction
Putrefaction
Putrefaction is one of seven stages in the decomposition of the body of a dead animal. It can be viewed, in broad terms, as the decomposition of proteins, in a process that results in the eventual breakdown of cohesion between tissues and the liquefaction of most organs.-Description:In terms of...
. Since Aristotle these had been considered essentially biological (vital
Vitalism
Vitalism, as defined by the Merriam-Webster dictionary, is#a doctrine that the functions of a living organism are due to a vital principle distinct from biochemical reactions...
) processes. However, Friedrich Wöhler
Friedrich Wöhler
Friedrich Wöhler was a German chemist, best known for his synthesis of urea, but also the first to isolate several chemical elements.-Biography:He was born in Eschersheim, which belonged to aau...
, Justus Liebig and other pioneers of the rising field of organic chemistry
Organic chemistry
Organic chemistry is a subdiscipline within chemistry involving the scientific study of the structure, properties, composition, reactions, and preparation of carbon-based compounds, hydrocarbons, and their derivatives...
—building on the work of Lavoisier—showed that the organic world could often be analyzed by physical and chemical methods. In 1828 Wöhler showed that the organic substance urea
Urea
Urea or carbamide is an organic compound with the chemical formula CO2. The molecule has two —NH2 groups joined by a carbonyl functional group....
could be created by chemical means that do not involve life, providing a powerful challenge to vitalism
Vitalism
Vitalism, as defined by the Merriam-Webster dictionary, is#a doctrine that the functions of a living organism are due to a vital principle distinct from biochemical reactions...
. Cell extracts ("ferments") that could effect chemical transformations were discovered, beginning with diastase
Diastase
A diastase is any one of a group of enzymes which catalyses the breakdown of starch into maltose. Alpha amylase degrades starch to a mixture of the disaccharide maltose, the trisaccharide maltotriose, which contains three α -linked glucose residues, and oligosaccharides known as dextrins that...
in 1833. By the end of the 19th century the concept of enzymes was well established, though equations of chemical kinetics
Chemical kinetics
Chemical kinetics, also known as reaction kinetics, is the study of rates of chemical processes. Chemical kinetics includes investigations of how different experimental conditions can influence the speed of a chemical reaction and yield information about the reaction's mechanism and transition...
would not be applied to enzymatic reactions until the early 20th century.
Physiologists such as Claude Bernard
Claude Bernard
Claude Bernard was a French physiologist. He was the first to define the term milieu intérieur . Historian of science I. Bernard Cohen of Harvard University called Bernard "one of the greatest of all men of science"...
explored (through vivisection and other experimental methods) the chemical and physical functions of living bodies to an unprecedented degree, laying the groundwork for endocrinology
Endocrinology
Endocrinology is a branch of biology and medicine dealing with the endocrine system, its diseases, and its specific secretions called hormones, the integration of developmental events such as proliferation, growth, and differentiation and the coordination of...
(a field that developed quickly after the discovery of the first hormone
Hormone
A hormone is a chemical released by a cell or a gland in one part of the body that sends out messages that affect cells in other parts of the organism. Only a small amount of hormone is required to alter cell metabolism. In essence, it is a chemical messenger that transports a signal from one...
, secretin
Secretin
Secretin is a hormone that controls the secretions into the duodenum, and also separately, water homeostasis throughout the body. It is produced in the S cells of the duodenum in the crypts of Lieberkühn...
, in 1902), biomechanics
Biomechanics
Biomechanics is the application of mechanical principles to biological systems, such as humans, animals, plants, organs, and cells. Perhaps one of the best definitions was provided by Herbert Hatze in 1974: "Biomechanics is the study of the structure and function of biological systems by means of...
, and the study of nutrition
Nutrition
Nutrition is the provision, to cells and organisms, of the materials necessary to support life. Many common health problems can be prevented or alleviated with a healthy diet....
and digestion
Digestion
Digestion is the mechanical and chemical breakdown of food into smaller components that are more easily absorbed into a blood stream, for instance. Digestion is a form of catabolism: a breakdown of large food molecules to smaller ones....
. The importance and diversity of experimental physiology methods, within both medicine and biology, grew dramatically over the second half of the 19th century. The control and manipulation of life processes became a central concern, and experiment was placed at the center of biological education.
Twentieth century biological sciences
At the beginning of the 20th century, biological research was largely a professional endeavour. Most work was still done in the natural historyNatural history
Natural history is the scientific research of plants or animals, leaning more towards observational rather than experimental methods of study, and encompasses more research published in magazines than in academic journals. Grouped among the natural sciences, natural history is the systematic study...
mode, which emphasized morphological and phylogenetic analysis over experiment-based causal explanations. However, anti-vitalist
Vitalism
Vitalism, as defined by the Merriam-Webster dictionary, is#a doctrine that the functions of a living organism are due to a vital principle distinct from biochemical reactions...
experimental physiologists and embryologists, especially in Europe, were increasingly influential. The tremendous success of experimental approaches to development, heredity, and metabolism in the 1900s and 1910s demonstrated the power of experimentation in biology. In the following decades, experimental work replaced natural history as the dominant mode of research.
Ecology and environmental science
In the early 20th century, naturalists were faced with increasing pressure to add rigor and preferably experimentation to their methods, as the newly prominent laboratory-based biological disciplines had done. Ecology had emerged as a combination of biogeography with the biogeochemical cycleBiogeochemical cycle
In ecology and Earth science, a biogeochemical cycle or substance turnover or cycling of substances is a pathway by which a chemical element or molecule moves through both biotic and abiotic compartments of Earth. A cycle is a series of change which comes back to the starting point and which can...
concept pioneered by chemists; field biologists developed quantitative methods such as the quadrat
Quadrat
A quadrat is a square used in ecology and geography to isolate a sample, usually about 1m2 or 0.25m2. The quadrat is suitable for sampling plants, slow-moving animals , and some aquatic organisms.When an ecologist wants to know how many organisms there are in a particular habitat, it would not be...
and adapted laboratory instruments and cameras for the field to further set their work apart from traditional natural history. Zoologists and botanists did what they could to mitigate the unpredictability of the living world, performing laboratory experiments and studying semi-controlled natural environments such as gardens; new institutions like the Carnegie Station for Experimental Evolution and the Marine Biological Laboratory
Marine Biological Laboratory
The Marine Biological Laboratory is an international center for research and education in biology, biomedicine and ecology. Founded in 1888, the MBL is the oldest independent marine laboratory in the Americas, taking advantage of a coastal setting in the Cape Cod village of Woods Hole, Massachusetts...
provided more controlled environments for studying organisms through their entire life cycles.
The ecological succession
Ecological succession
Ecological succession, is the phenomenon or process by which a community progressively transforms itself until a stable community is formed. It is a fundamental concept in ecology, and refers to more or less predictable and orderly changes in the composition or structure of an ecological community...
concept, pioneered in the 1900s and 1910s by Henry Chandler Cowles
Henry Chandler Cowles
Henry Chandler Cowles was an American botanist and ecological pioneer . Born in Kensington, Connecticut, he attended Oberlin College in Ohio. He studied at the University of Chicago with the plant taxonomist John M. Coulter and the geologist Thomas Chrowder Chamberlin as main teachers. He...
and Frederic Clements
Frederic Clements
Frederic Edward Clements was an American plant ecologist and pioneer in the study of vegetation succession.-Biography:...
, was important in early plant ecology. Alfred Lotka's predator-prey equations, G. Evelyn Hutchinson's
G. Evelyn Hutchinson
George Evelyn Hutchinson FRS was an Anglo-American zoologist known for his studies of freshwater lakes and considered the father of American limnology....
studies of the biogeography and biogeochemical structure of lakes and rivers (limnology
Limnology
Limnology , also called freshwater science, is the study of inland waters. It is often regarded as a division of ecology or environmental science. It covers the biological, chemical, physical, geological, and other attributes of all inland waters...
) and Charles Elton's
Charles Sutherland Elton
Charles Sutherland Elton FRS was an English zoologist and animal ecologist. His name is associated with the establishment of modern population and community ecology, including studies of invasive organisms.-Personal life:...
studies of animal food chain
Food chain
A food web depicts feeding connections in an ecological community. Ecologists can broadly lump all life forms into one of two categories called trophic levels: 1) the autotrophs, and 2) the heterotrophs...
s were pioneers among the succession of quantitative methods that colonized the developing ecological specialties. Ecology became an independent discipline in the 1940s and 1950s after Eugene P. Odum synthesized many of the concepts of ecosystem ecology
Ecosystem ecology
Ecosystem ecology is the integrated study of biotic and abiotic components of ecosystems and their interactions within an ecosystem framework. This science examines how ecosystems work and relates this to their components such as chemicals, bedrock, soil, plants, and animals.Ecosystem ecology...
, placing relationships between groups of organisms (especially material and energy relationships) at the center of the field.
In the 1960s, as evolutionary theorists explored the possibility of multiple units of selection, ecologists turned to evolutionary approaches. In population ecology
Population ecology
Population ecology is a sub-field of ecology that deals with the dynamics of species populations and how these populations interact with the environment. It is the study of how the population sizes of species living together in groups change over time and space....
, debate over group selection
Group selection
In evolutionary biology, group selection refers to the idea that alleles can become fixed or spread in a population because of the benefits they bestow on groups, regardless of the alleles' effect on the fitness of individuals within that group....
was brief but vigorous; by 1970, most biologists agreed that natural selection was rarely effective above the level of individual organisms. The evolution of ecosystems, however, became a lasting research focus. Ecology expanded rapidly with the rise of the environmental movement; the International Biological Program
International Biological Program
The International Biological Program was an effort between 1964 and 1974 to coordinate large-scale ecological and environmental studies...
attempted to apply the methods of big science
Big Science
Big Science is a term used by scientists and historians of science to describe a series of changes in science which occurred in industrial nations during and after World War II, as scientific progress increasingly came to rely on large-scale projects usually funded by national governments or groups...
(which had been so successful in the physical sciences) to ecosystem ecology and pressing environmental issues, while smaller-scale independent efforts such as island biogeography
Island biogeography
Island biogeography is a field within biogeography that attempts to establish and explain the factors that affect the species richness of natural communities. The theory was developed to explain species richness of actual islands...
and the Hubbard Brook Experimental Forest
Hubbard Brook Experimental Forest
Hubbard Brook Experimental Forest is an area of land in the White Mountains of New Hampshire that functions as an outdoor laboratory for ecological studies...
helped redefine the scope of an increasingly diverse discipline.
Classical genetics, the modern synthesis, and evolutionary theory
Hugo de Vries
Hugo Marie de Vries ForMemRS was a Dutch botanist and one of the first geneticists. He is known chiefly for suggesting the concept of genes, rediscovering the laws of heredity in the 1890s while unaware of Gregor Mendel's work, for introducing the term "mutation", and for developing a mutation...
, Carl Correns
Carl Correns
Carl Erich Correns was a German botanist and geneticist, who is notable primarily for his independent discovery of the principles of heredity, and for his rediscovery of Gregor Mendel's earlier paper on that subject, which he achieved simultaneously but independently of the botanists Erich...
, and Erich von Tschermak
Erich von Tschermak
Erich von Tschermak-Seysenegg was an Austrian agronomist who developed several new disease-resistant crops, including wheat-rye and oat hybrids. He was a son of the Moravia-born mineralogist Gustav Tschermak von Seysenegg...
independently arrived at Mendel's laws (which were not actually present in Mendel's work). Soon after, cytologists (cell biologists) proposed that chromosome
Chromosome
A chromosome is an organized structure of DNA and protein found in cells. It is a single piece of coiled DNA containing many genes, regulatory elements and other nucleotide sequences. Chromosomes also contain DNA-bound proteins, which serve to package the DNA and control its functions.Chromosomes...
s were the hereditary material. Between 1910 and 1915, Thomas Hunt Morgan
Thomas Hunt Morgan
Thomas Hunt Morgan was an American evolutionary biologist, geneticist and embryologist and science author who won the Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine in 1933 for discoveries relating the role the chromosome plays in heredity.Morgan received his PhD from Johns Hopkins University in zoology...
and the "Drosophilists" in his fly lab forged these two ideas—both controversial—into the "Mendelian-chromosome theory" of heredity. They quantified the phenomenon of genetic linkage and postulated that genes reside on chromosomes like beads on string; they hypothesized crossing over
Crossing Over
Crossing Over may refer to:* Chromosomal crossover, a cellular process* Crossing Over , a 1998 album by Hesperus* Crossing Over, a book by John Edward* Crossing Over , a 2009 film...
to explain linkage and constructed genetic maps of the fruit fly Drosophila melanogaster
Drosophila melanogaster
Drosophila melanogaster is a species of Diptera, or the order of flies, in the family Drosophilidae. The species is known generally as the common fruit fly or vinegar fly. Starting from Charles W...
, which became a widely used model organism
Model organism
A model organism is a non-human species that is extensively studied to understand particular biological phenomena, with the expectation that discoveries made in the organism model will provide insight into the workings of other organisms. Model organisms are in vivo models and are widely used to...
.
Hugo de Vries tried to link the new genetics with evolution; building on his work with heredity and hybridization, he proposed a theory of mutationism
Mutationism
Mutationism refers to the theory emphasizing mutation as a creative principle and source of discontinuity in evolutionary change, particularly associated with the founders of modern genetics....
, which was widely accepted in the early 20th century. Lamarckism
Lamarckism
Lamarckism is the idea that an organism can pass on characteristics that it acquired during its lifetime to its offspring . It is named after the French biologist Jean-Baptiste Lamarck , who incorporated the action of soft inheritance into his evolutionary theories...
also had many adherents. Darwinism
Darwinism
Darwinism is a set of movements and concepts related to ideas of transmutation of species or of evolution, including some ideas with no connection to the work of Charles Darwin....
was seen as incompatible with the continuously variable traits studied by biometricians, which seemed only partially heritable. In the 1920s and 1930s—following the acceptance of the Mendelian-chromosome theory— the emergence of the discipline of population genetics
Population genetics
Population genetics is the study of allele frequency distribution and change under the influence of the four main evolutionary processes: natural selection, genetic drift, mutation and gene flow. It also takes into account the factors of recombination, population subdivision and population...
, with the work of R.A. Fisher, J.B.S. Haldane and Sewall Wright
Sewall Wright
Sewall Green Wright was an American geneticist known for his influential work on evolutionary theory and also for his work on path analysis. With R. A. Fisher and J.B.S. Haldane, he was a founder of theoretical population genetics. He is the discoverer of the inbreeding coefficient and of...
, unified the idea of evolution by natural selection
Natural selection
Natural selection is the nonrandom process by which biologic traits become either more or less common in a population as a function of differential reproduction of their bearers. It is a key mechanism of evolution....
with Mendelian genetics
Mendelian inheritance
Mendelian inheritance is a scientific description of how hereditary characteristics are passed from parent organisms to their offspring; it underlies much of genetics...
, producing the modern synthesis. The inheritance of acquired characters
Inheritance of acquired characters
The inheritance of acquired characteristics is a hypothesis that physiological changes acquired over the life of an organism may be transmitted to offspring...
was rejected, while mutationism gave way as genetic theories matured.
In the second half of the century the ideas of population genetics began to be applied in the new discipline of the genetics of behavior, sociobiology
Sociobiology
Sociobiology is a field of scientific study which is based on the assumption that social behavior has resulted from evolution and attempts to explain and examine social behavior within that context. Often considered a branch of biology and sociology, it also draws from ethology, anthropology,...
, and, especially in humans, evolutionary psychology
Evolutionary psychology
Evolutionary psychology is an approach in the social and natural sciences that examines psychological traits such as memory, perception, and language from a modern evolutionary perspective. It seeks to identify which human psychological traits are evolved adaptations, that is, the functional...
. In the 1960s W.D. Hamilton and others developed game theory
Game theory
Game theory is a mathematical method for analyzing calculated circumstances, such as in games, where a person’s success is based upon the choices of others...
approaches to explain altruism
Altruism
Altruism is a concern for the welfare of others. It is a traditional virtue in many cultures, and a core aspect of various religious traditions, though the concept of 'others' toward whom concern should be directed can vary among cultures and religions. Altruism is the opposite of...
from an evolutionary perspective through kin selection
Kin selection
Kin selection refers to apparent strategies in evolution that favor the reproductive success of an organism's relatives, even at a cost to the organism's own survival and reproduction. Charles Darwin was the first to discuss the concept of group/kin selection...
. The possible origin of higher organisms through endosymbiosis, and contrasting approaches to molecular evolution in the gene-centered view
Gene-centered view of evolution
The gene-centered view of evolution, gene selection theory or selfish gene theory holds that evolution occurs through the differential survival of competing genes, increasing the frequency of those alleles whose phenotypic effects successfully promote their own propagation, with gene defined as...
(which held selection as the predominant cause of evolution) and the neutral theory
Neutral theory of molecular evolution
The neutral theory of molecular evolution states that the vast majority of evolutionary changes at the molecular level are caused by random drift of selectively neutral mutants . The theory was introduced by Motoo Kimura in the late 1960s and early 1970s...
(which made genetic drift
Genetic drift
Genetic drift or allelic drift is the change in the frequency of a gene variant in a population due to random sampling.The alleles in the offspring are a sample of those in the parents, and chance has a role in determining whether a given individual survives and reproduces...
a key factor) spawned perennial debates over the proper balance of adaptationism
Adaptationism
Adaptationism is a set of methods in the evolutionary sciences for distinguishing the products of adaptation from traits that arise through other processes. It is employed in fields such as ethology and evolutionary psychology that are concerned with identifying adaptations...
and contingency in evolutionary theory.
In the 1970s Stephen Jay Gould
Stephen Jay Gould
Stephen Jay Gould was an American paleontologist, evolutionary biologist, and historian of science. He was also one of the most influential and widely read writers of popular science of his generation....
and Niles Eldredge
Niles Eldredge
Niles Eldredge is an American paleontologist, who, along with Stephen Jay Gould, proposed the theory of punctuated equilibrium in 1972.-Education:...
proposed the theory of punctuated equilibrium
Punctuated equilibrium
Punctuated equilibrium is a theory in evolutionary biology which proposes that most species will exhibit little net evolutionary change for most of their geological history, remaining in an extended state called stasis...
which holds that stasis is the most prominent feature of the fossil record, and that most evolutionary changes occur rapidly over relatively short periods of time. In 1980 Luis Alvarez
Luis Alvarez
Luis W. Alvarez was an American experimental physicist and inventor, who spent nearly all of his long professional career on the faculty of the University of California, Berkeley...
and Walter Alvarez
Walter Alvarez
Walter Alvarez is a professor in the Earth and Planetary Science department at the University of California, Berkeley. He is most widely known for the theory that dinosaurs were killed by an asteroid impact, developed in collaboration with his father, Nobel Prize winning physicist Luis...
proposed the hypothesis that an impact event
Impact event
An impact event is the collision of a large meteorite, asteroid, comet, or other celestial object with the Earth or another planet. Throughout recorded history, hundreds of minor impact events have been reported, with some occurrences causing deaths, injuries, property damage or other significant...
was responsible for the Cretaceous-Tertiary extinction event
Cretaceous-Tertiary extinction event
The Cretaceous–Paleogene extinction event, formerly named and still commonly referred to as the Cretaceous-Tertiary extinction event, occurred approximately 65.5 million years ago at the end of the Maastrichtian age of the Cretaceous period. It was a large-scale mass extinction of animal and plant...
. Also in the early 1980s, statistical analysis of the fossil record of marine organisms published by Jack Sepkoski
Jack Sepkoski
J. John Sepkoski Jr., , was a University of Chicago paleontologist. Sepkoski studied the fossil record and the diversity of life on Earth. Sepkoski and David Raup contributed to the knowledge of extinction events...
and David M. Raup
David M. Raup
David M. Raup is a University of Chicago paleontologist. Raup studied the fossil record and the diversity of life on Earth. Raup contributed to the knowledge of extinction events along with his colleague Jack Sepkoski...
lead to a better appreciation of the importance of mass extinction events to the history of life on earth.
Biochemistry, microbiology, and molecular biology
By the end of the 19th century all of the major pathways of drug metabolismDrug metabolism
Drug metabolism is the biochemical modification of pharmaceutical substances by living organisms, usually through specialized enzymatic systems. This is a form of xenobiotic metabolism. Drug metabolism often converts lipophilic chemical compounds into more readily excreted polar products...
had been discovered, along with the outlines of protein and fatty acid metabolism and urea synthesis. In the early decades of the 20th century, the minor components of foods in human nutrition, the vitamins, began to be isolated and synthesized. Improved laboratory techniques such as chromatography
Chromatography
Chromatography is the collective term for a set of laboratory techniques for the separation of mixtures....
and electrophoresis
Electrophoresis
Electrophoresis, also called cataphoresis, is the motion of dispersed particles relative to a fluid under the influence of a spatially uniform electric field. This electrokinetic phenomenon was observed for the first time in 1807 by Reuss , who noticed that the application of a constant electric...
led to rapid advances in physiological chemistry, which—as biochemistry—began to achieve independence from its medical origins. In the 1920s and 1930s, biochemists—led by Hans Krebs
Hans Adolf Krebs
Sir Hans Adolf Krebs was a German-born British physician and biochemist. Krebs is best known for his identification of two important metabolic cycles: the urea cycle and the citric acid cycle...
and Carl
Carl Ferdinand Cori
Carl Ferdinand Cori was a Czech biochemist and pharmacologist born in Prague who, together with his wife Gerty Cori and Argentine physiologist Bernardo Houssay, received a Nobel Prize in 1947 for their discovery of how glycogen – a derivative of glucose – is broken down and...
and Gerty Cori
Gerty Cori
Gerty Theresa Cori was an American biochemist who became the third woman—and first American woman—to win a Nobel Prize in science, and the first woman to be awarded the Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine.Cori was born in Prague...
—began to work out many of the central metabolic pathways of life: the citric acid cycle
Citric acid cycle
The citric acid cycle — also known as the tricarboxylic acid cycle , the Krebs cycle, or the Szent-Györgyi-Krebs cycle — is a series of chemical reactions which is used by all aerobic living organisms to generate energy through the oxidization of acetate derived from carbohydrates, fats and...
, glycogenesis
Glycogenesis
Glycogenesis is the process of glycogen synthesis, in which glucose molecules are added to chains of glycogen for storage. This process is activated during rest periods following the Cori cycle, in the liver, and also activated by insulin in response to high glucose levels, for example after a...
and glycolysis
Glycolysis
Glycolysis is the metabolic pathway that converts glucose C6H12O6, into pyruvate, CH3COCOO− + H+...
, and the synthesis of steroid
Steroid
A steroid is a type of organic compound that contains a characteristic arrangement of four cycloalkane rings that are joined to each other. Examples of steroids include the dietary fat cholesterol, the sex hormones estradiol and testosterone, and the anti-inflammatory drug dexamethasone.The core...
s and porphyrin
Porphyrin
Porphyrins are a group of organic compounds, many naturally occurring. One of the best-known porphyrins is heme, the pigment in red blood cells; heme is a cofactor of the protein hemoglobin. Porphyrins are heterocyclic macrocycles composed of four modified pyrrole subunits interconnected at...
s. Between the 1930s and 1950s, Fritz Lipmann and others established the role of ATP
Adenosine triphosphate
Adenosine-5'-triphosphate is a multifunctional nucleoside triphosphate used in cells as a coenzyme. It is often called the "molecular unit of currency" of intracellular energy transfer. ATP transports chemical energy within cells for metabolism...
as the universal carrier of energy in the cell, and mitochondria as the powerhouse of the cell. Such traditionally biochemical work continued to be very actively pursued throughout the 20th century and into the 21st.
Origins of molecular biology
Following the rise of classical genetics, many biologists—including a new wave of physical scientists in biology—pursued the question of the gene and its physical nature. Warren WeaverWarren Weaver
Warren Weaver was an American scientist, mathematician, and science administrator...
—head of the science division of the Rockefeller Foundation
Rockefeller Foundation
The Rockefeller Foundation is a prominent philanthropic organization and private foundation based at 420 Fifth Avenue, New York City. The preeminent institution established by the six-generation Rockefeller family, it was founded by John D. Rockefeller , along with his son John D. Rockefeller, Jr...
—issued grants to promote research that applied the methods of physics and chemistry to basic biological problems, coining the term molecular biology
Molecular biology
Molecular biology is the branch of biology that deals with the molecular basis of biological activity. This field overlaps with other areas of biology and chemistry, particularly genetics and biochemistry...
for this approach in 1938; many of the significant biological breakthroughs of the 1930s and 1940s were funded by the Rockefeller Foundation.
Bacteriology
Bacteriology is the study of bacteria. This subdivision of microbiology involves the identification, classification, and characterization of bacterial species...
and virology
Virology
Virology is the study of viruses and virus-like agents: their structure, classification and evolution, their ways to infect and exploit cells for virus reproduction, the diseases they cause, the techniques to isolate and culture them, and their use in research and therapy...
(later combined as microbiology), situated between science and medicine, developed rapidly in the early 20th century. Félix d'Herelle
Félix d'Herelle
Félix d'Herelle was a French-Canadian microbiologist, the co-discoverer of bacteriophages and experimented with the possibility of phage therapy.-Early years:...
's isolation of bacteriophage
Bacteriophage
A bacteriophage is any one of a number of viruses that infect bacteria. They do this by injecting genetic material, which they carry enclosed in an outer protein capsid...
during World War I
World War I
World War I , which was predominantly called the World War or the Great War from its occurrence until 1939, and the First World War or World War I thereafter, was a major war centred in Europe that began on 28 July 1914 and lasted until 11 November 1918...
initiated a long line of research focused on phage viruses and the bacteria they infect.
The development of standard, genetically uniform organisms that could produce repeatable experimental results was essential for the development of molecular genetics
Molecular genetics
Molecular genetics is the field of biology and genetics that studies the structure and function of genes at a molecular level. The field studies how the genes are transferred from generation to generation. Molecular genetics employs the methods of genetics and molecular biology...
. After early work with Drosophila and maize
Maize
Maize known in many English-speaking countries as corn or mielie/mealie, is a grain domesticated by indigenous peoples in Mesoamerica in prehistoric times. The leafy stalk produces ears which contain seeds called kernels. Though technically a grain, maize kernels are used in cooking as a vegetable...
, the adoption of simpler model system
Scientific modelling
Scientific modelling is the process of generating abstract, conceptual, graphical and/or mathematical models. Science offers a growing collection of methods, techniques and theory about all kinds of specialized scientific modelling...
s like the bread mold Neurospora crassa
Neurospora crassa
Neurospora crassa is a type of red bread mold of the phylum Ascomycota. The genus name, meaning "nerve spore" refers to the characteristic striations on the spores. The first published account of this fungus was from an infestation of French bakeries in 1843. N...
made it possible to connect genetics to biochemistry, most importantly with Beadle and Tatum's
Edward Lawrie Tatum
Edward Lawrie Tatum was an American geneticist. He shared half of the Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine in 1958 with George Wells Beadle for showing that genes control individual steps in metabolism...
"one gene, one enzyme" hypothesis in 1941. Genetics experiments on even simpler systems like tobacco mosaic virus
Tobacco mosaic virus
Tobacco mosaic virus is a positive-sense single stranded RNA virus that infects plants, especially tobacco and other members of the family Solanaceae. The infection causes characteristic patterns on the leaves . TMV was the first virus to be discovered...
and bacteriophage
Bacteriophage
A bacteriophage is any one of a number of viruses that infect bacteria. They do this by injecting genetic material, which they carry enclosed in an outer protein capsid...
, aided by the new technologies of electron microscopy
Electron microscope
An electron microscope is a type of microscope that uses a beam of electrons to illuminate the specimen and produce a magnified image. Electron microscopes have a greater resolving power than a light-powered optical microscope, because electrons have wavelengths about 100,000 times shorter than...
and ultracentrifugation
Ultracentrifuge
The ultracentrifuge is a centrifuge optimized for spinning a rotor at very high speeds, capable of generating acceleration as high as 2,000,000 g . There are two kinds of ultracentrifuges, the preparative and the analytical ultracentrifuge...
, forced scientists to re-evaluate the literal meaning of life; virus heredity and reproducing nucleoprotein
Nucleoprotein
A nucleoprotein is any protein that is structurally associated with nucleic acid .Many viruses harness this protein, and they are known for being host-specific...
cell structures outside the nucleus ("plasmagenes") complicated the accepted Mendelian-chromosome theory.
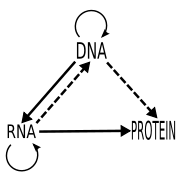
Oswald Avery
Oswald Theodore Avery ForMemRS was a Canadian-born American physician and medical researcher. The major part of his career was spent at the Rockefeller University Hospital in New York City...
showed in 1943 that DNA
DNA
Deoxyribonucleic acid is a nucleic acid that contains the genetic instructions used in the development and functioning of all known living organisms . The DNA segments that carry this genetic information are called genes, but other DNA sequences have structural purposes, or are involved in...
was likely the genetic material of the chromosome, not its protein; the issue was settled decisively with the 1952 Hershey-Chase experiment
Hershey-Chase experiment
The Hershey–Chase experiments were a series of experiments conducted in 1952 by Alfred Hershey and Martha Chase, which helped to confirm that DNA was the genetic material. While DNA had been known to biologists since 1869, a few scientists still assumed at the time that proteins carried the...
—one of many contributions from the so-called phage group
Phage group
The phage group was an informal network of biologists centered around Max Delbrück that contributed heavily to bacterial genetics and the origins of molecular biology in the mid-20th century. The phage group takes its name from bacteriophages, the bacteria-infecting viruses that group used as...
centered around physicist-turned-biologist Max Delbrück
Max Delbrück
Max Ludwig Henning Delbrück was a German-American biophysicist and Nobel laureate.-Biography:Delbrück was born in Berlin, German Empire...
. In 1953 James D. Watson
James D. Watson
James Dewey Watson is an American molecular biologist, geneticist, and zoologist, best known as one of the co-discoverers of the structure of DNA in 1953 with Francis Crick...
and Francis Crick
Francis Crick
Francis Harry Compton Crick OM FRS was an English molecular biologist, biophysicist, and neuroscientist, and most noted for being one of two co-discoverers of the structure of the DNA molecule in 1953, together with James D. Watson...
, building on the work of Maurice Wilkins
Maurice Wilkins
Maurice Hugh Frederick Wilkins CBE FRS was a New Zealand-born English physicist and molecular biologist, and Nobel Laureate whose research contributed to the scientific understanding of phosphorescence, isotope separation, optical microscopy and X-ray diffraction, and to the development of radar...
and Rosalind Franklin
Rosalind Franklin
Rosalind Elsie Franklin was a British biophysicist and X-ray crystallographer who made critical contributions to the understanding of the fine molecular structures of DNA, RNA, viruses, coal and graphite...
, suggested that the structure of DNA was a double helix. In their famous paper "Molecular structure of Nucleic Acids
Molecular structure of Nucleic Acids
The "Molecular structure of Nucleic Acids: A Structure for Deoxyribose Nucleic Acid" was an article published by James D. Watson and Francis Crick in the scientific journal Nature in its 171st volume on pages 737–738 . It was the first publication which described the discovery of the double helix...
", Watson and Crick noted coyly, "It has not escaped our notice that the specific pairing we have postulated immediately suggests a possible copying mechanism for the genetic material." After the 1958 Meselson-Stahl experiment
Meselson-Stahl experiment
The Meselson–Stahl experiment was an experiment by Matthew Meselson and Franklin Stahl in 1958 which supported the hypothesis that DNA replication was semiconservative. Semiconservative replication means that when the double stranded DNA helix was replicated, each of the two double stranded DNA...
confirmed the semiconservative replication
Semiconservative replication
Semiconservative replication describes the mechanism by which DNA is replicated in all known cells.This mechanism of replication was one of three models originally proposedfor DNA replication:...
of DNA, it was clear to most biologists that nucleic acid sequence must somehow determine amino acid sequence
Peptide sequence
Peptide sequence or amino acid sequence is the order in which amino acid residues, connected by peptide bonds, lie in the chain in peptides and proteins. The sequence is generally reported from the N-terminal end containing free amino group to the C-terminal end containing free carboxyl group...
in proteins; physicist George Gamow
George Gamow
George Gamow , born Georgiy Antonovich Gamov , was a Russian-born theoretical physicist and cosmologist. He discovered alpha decay via quantum tunneling and worked on radioactive decay of the atomic nucleus, star formation, stellar nucleosynthesis, Big Bang nucleosynthesis, cosmic microwave...
proposed that a fixed genetic code
Genetic code
The genetic code is the set of rules by which information encoded in genetic material is translated into proteins by living cells....
connected proteins and DNA. Between 1953 and 1961, there were few known biological sequences—either DNA or protein—but an abundance of proposed code systems, a situation made even more complicated by expanding knowledge of the intermediate role of RNA
RNA
Ribonucleic acid , or RNA, is one of the three major macromolecules that are essential for all known forms of life....
. To actually decipher the code, it took an extensive series of experiments in biochemistry and bacterial genetics, between 1961 and 1966—most importantly the work of Nirenberg and Khorana.

Expansion of molecular biology
In addition to the Division of Biology at Caltech, the Laboratory of Molecular BiologyLaboratory of Molecular Biology
The Laboratory of Molecular Biology is a research institute in Cambridge, England, which was at the forefront of the revolution in molecular biology which occurred in the 1950–60s, since then it remains a major medical research laboratory with a much broader focus.-Early beginnings: 1947-61:Max...
(and its precursors) at Cambridge, and a handful of other institutions, the Pasteur Institute
Pasteur Institute
The Pasteur Institute is a French non-profit private foundation dedicated to the study of biology, micro-organisms, diseases, and vaccines. It is named after Louis Pasteur, who made some of the greatest breakthroughs in modern medicine at the time, including pasteurization and vaccines for anthrax...
became a major center for molecular biology research in the late 1950s. Scientists at Cambridge, led by Max Perutz
Max Perutz
Max Ferdinand Perutz, OM, CH, CBE, FRS was an Austrian-born British molecular biologist, who shared the 1962 Nobel Prize for Chemistry with John Kendrew, for their studies of the structures of hemoglobin and globular proteins...
and John Kendrew
John Kendrew
Sir John Cowdery Kendrew, CBE, FRS was an English biochemist and crystallographer who shared the 1962 Nobel Prize in Chemistry with Max Perutz; their group in the Cavendish Laboratory investigated the structure of heme-containing proteins.-Biography:He was born in Oxford, son of Wilford George...
, focused on the rapidly developing field of structural biology
Structural biology
Structural biology is a branch of molecular biology, biochemistry, and biophysics concerned with the molecular structure of biological macromolecules, especially proteins and nucleic acids, how they acquire the structures they have, and how alterations in their structures affect their function...
, combining X-ray crystallography
X-ray crystallography
X-ray crystallography is a method of determining the arrangement of atoms within a crystal, in which a beam of X-rays strikes a crystal and causes the beam of light to spread into many specific directions. From the angles and intensities of these diffracted beams, a crystallographer can produce a...
with Molecular modelling
Molecular modelling
Molecular modelling encompasses all theoretical methods and computational techniques used to model or mimic the behaviour of molecules. The techniques are used in the fields of computational chemistry, computational biology and materials science for studying molecular systems ranging from small...
and the new computational possibilities of digital computing
History of computing hardware
The history of computing hardware is the record of the ongoing effort to make computer hardware faster, cheaper, and capable of storing more data....
(benefiting both directly and indirectly from the military funding of science
Military funding of science
The military funding of science has had a powerful transformative effect on the practice and products of scientific research since the early 20th century...
). A number of biochemists led by Frederick Sanger
Frederick Sanger
Frederick Sanger, OM, CH, CBE, FRS is an English biochemist and a two-time Nobel laureate in chemistry, the only person to have been so. In 1958 he was awarded a Nobel prize in chemistry "for his work on the structure of proteins, especially that of insulin"...
later joined the Cambridge lab, bringing together the study of macromolecular
Macromolecule
A macromolecule is a very large molecule commonly created by some form of polymerization. In biochemistry, the term is applied to the four conventional biopolymers , as well as non-polymeric molecules with large molecular mass such as macrocycles...
structure and function. At the Pasteur Institute, François Jacob
François Jacob
François Jacob is a French biologist who, together with Jacques Monod, originated the idea that control of enzyme levels in all cells occurs through feedback on transcription. He shared the 1965 Nobel Prize in Medicine with Jacques Monod and André Lwoff.-Childhood and education:François Jacob is...
and Jacques Monod
Jacques Monod
Jacques Lucien Monod was a French biologist who was awarded a Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine in 1965, sharing it with François Jacob and Andre Lwoff "for their discoveries concerning genetic control of enzyme and virus synthesis"...
followed the 1959 PaJaMo experiment with a series of publications regarding the lac
Lac operon
The lac operon is an operon required for the transport and metabolism of lactose in Escherichia coli and some other enteric bacteria. It consists of three adjacent structural genes, lacZ, lacY and lacA. The lac operon is regulated by several factors including the availability of glucose and of...
operon
Operon
In genetics, an operon is a functioning unit of genomic DNA containing a cluster of genes under the control of a single regulatory signal or promoter. The genes are transcribed together into an mRNA strand and either translated together in the cytoplasm, or undergo trans-splicing to create...
that established the concept of gene regulation and identified what came to be known as messenger RNA
Messenger RNA
Messenger RNA is a molecule of RNA encoding a chemical "blueprint" for a protein product. mRNA is transcribed from a DNA template, and carries coding information to the sites of protein synthesis: the ribosomes. Here, the nucleic acid polymer is translated into a polymer of amino acids: a protein...
. By the mid-1960s, the intellectual core of molecular biology—a model for the molecular basis of metabolism and reproduction— was largely complete.
The late 1950s to the early 1970s was a period of intense research and institutional expansion for molecular biology, which had only recently become a somewhat coherent discipline. In what organismic biologist E. O. Wilson
E. O. Wilson
Edward Osborne Wilson is an American biologist, researcher , theorist , naturalist and author. His biological specialty is myrmecology, the study of ants....
called "The Molecular Wars", the methods and practitioners of molecular biology spread rapidly, often coming to dominate departments and even entire disciplines. Molecularization was particularly important in genetics
Genetics
Genetics , a discipline of biology, is the science of genes, heredity, and variation in living organisms....
, immunology
Immunology
Immunology is a broad branch of biomedical science that covers the study of all aspects of the immune system in all organisms. It deals with the physiological functioning of the immune system in states of both health and diseases; malfunctions of the immune system in immunological disorders ; the...
, embryology
Embryology
Embryology is a science which is about the development of an embryo from the fertilization of the ovum to the fetus stage...
, and neurobiology, while the idea that life is controlled by a "genetic program
Genetic program
In biology, a genetic program of a cell is a physiological change brought about by a temporal pattern of activation of a particular subset of genes....
"—a metaphor Jacob and Monod introduced from the emerging fields of cybernetics
Cybernetics
Cybernetics is the interdisciplinary study of the structure of regulatory systems. Cybernetics is closely related to information theory, control theory and systems theory, at least in its first-order form...
and computer science
Computer science
Computer science or computing science is the study of the theoretical foundations of information and computation and of practical techniques for their implementation and application in computer systems...
—became an influential perspective throughout biology. Immunology in particular became linked with molecular biology, with innovation flowing both ways: the clonal selection theory developed by Niels Jerne and Frank Macfarlane Burnet
Frank Macfarlane Burnet
Sir Frank Macfarlane Burnet, , usually known as Macfarlane or Mac Burnet, was an Australian virologist best known for his contributions to immunology....
in the mid 1950s helped shed light on the general mechanisms of protein synthesis.
Resistance to the growing influence of molecular biology was especially evident in evolutionary biology. Protein sequencing had great potential for the quantitative study of evolution (through the molecular clock hypothesis), but leading evolutionary biologists questioned the relevance of molecular biology for answering the big questions of evolutionary causation. Departments and disciplines fractured as organismic biologists asserted their importance and independence: Theodosius Dobzhansky
Theodosius Dobzhansky
Theodosius Grygorovych Dobzhansky ForMemRS was a prominent geneticist and evolutionary biologist, and a central figure in the field of evolutionary biology for his work in shaping the unifying modern evolutionary synthesis...
made the famous statement that "nothing in biology makes sense except in the light of evolution
Nothing in Biology Makes Sense Except in the Light of Evolution
"Nothing in Biology Makes Sense Except in the Light of Evolution" is a 1973 essay by the evolutionary biologist and Russian Orthodox Christian Theodosius Dobzhansky, criticising anti-evolution creationism and espousing theistic evolution...
" as a response to the molecular challenge. The issue became even more critical after 1968; Motoo Kimura's
Motoo Kimura
was a Japanese biologist best known for introducing the neutral theory of molecular evolution in 1968. He became one of the most influential theoretical population geneticists. He is remembered in genetics for his innovative use of diffusion equations to calculate the probability of fixation of...
neutral theory of molecular evolution
Neutral theory of molecular evolution
The neutral theory of molecular evolution states that the vast majority of evolutionary changes at the molecular level are caused by random drift of selectively neutral mutants . The theory was introduced by Motoo Kimura in the late 1960s and early 1970s...
suggested that natural selection
Natural selection
Natural selection is the nonrandom process by which biologic traits become either more or less common in a population as a function of differential reproduction of their bearers. It is a key mechanism of evolution....
was not the ubiquitous cause of evolution, at least at the molecular level, and that molecular evolution might be a fundamentally different process from morphological
Morphology (biology)
In biology, morphology is a branch of bioscience dealing with the study of the form and structure of organisms and their specific structural features....
evolution. (Resolving this "molecular/morphological paradox" has been a central focus of molecular evolution research since the 1960s.)
Biotechnology, genetic engineering, and genomics
BiotechnologyBiotechnology
Biotechnology is a field of applied biology that involves the use of living organisms and bioprocesses in engineering, technology, medicine and other fields requiring bioproducts. Biotechnology also utilizes these products for manufacturing purpose...
in the general sense has been an important part of biology since the late 19th century. With the industrialization of brewing
Brewing
Brewing is the production of beer through steeping a starch source in water and then fermenting with yeast. Brewing has taken place since around the 6th millennium BCE, and archeological evidence suggests that this technique was used in ancient Egypt...
and agriculture
Agriculture
Agriculture is the cultivation of animals, plants, fungi and other life forms for food, fiber, and other products used to sustain life. Agriculture was the key implement in the rise of sedentary human civilization, whereby farming of domesticated species created food surpluses that nurtured the...
, chemists and biologists became aware of the great potential of human-controlled biological processes. In particular, fermentation
Industrial fermentation
Industrial fermentation is the intentional use of fermentation by microorganisms such as bacteria and fungi to make products useful to humans. Fermented products have applications as food as well as in general industry.- Food fermentation :...
proved a great boon to chemical industries. By the early 1970s, a wide range of biotechnologies were being developed, from drugs like penicillin
Penicillin
Penicillin is a group of antibiotics derived from Penicillium fungi. They include penicillin G, procaine penicillin, benzathine penicillin, and penicillin V....
and steroids to foods like Chlorella
Chlorella
Chlorella is a genus of single-celled green algae, belonging to the phylum Chlorophyta. It is spherical in shape, about 2 to 10 μm in diameter, and is without flagella. Chlorella contains the green photosynthetic pigments chlorophyll-a and -b in its chloroplast...
and single-cell protein to gasohol—as well as a wide range of hybrid high-yield crops and agricultural technologies, the basis for the Green Revolution
Green Revolution
Green Revolution refers to a series of research, development, and technology transfer initiatives, occurring between the 1940s and the late 1970s, that increased agriculture production around the world, beginning most markedly in the late 1960s....
.
Recombinant DNA
Biotechnology in the modern sense of genetic engineeringGenetic engineering
Genetic engineering, also called genetic modification, is the direct human manipulation of an organism's genome using modern DNA technology. It involves the introduction of foreign DNA or synthetic genes into the organism of interest...
began in the 1970s, with the invention of recombinant DNA
Recombinant DNA
Recombinant DNA molecules are DNA sequences that result from the use of laboratory methods to bring together genetic material from multiple sources, creating sequences that would not otherwise be found in biological organisms...
techniques. Restriction enzyme
Restriction enzyme
A Restriction Enzyme is an enzyme that cuts double-stranded DNA at specific recognition nucleotide sequences known as restriction sites. Such enzymes, found in bacteria and archaea, are thought to have evolved to provide a defense mechanism against invading viruses...
s were discovered and characterized in the late 1960s, following on the heels of the isolation, then duplication, then synthesis of viral genes
Gênes
Gênes is the name of a département of the First French Empire in present Italy, named after the city of Genoa. It was formed in 1805, when Napoleon Bonaparte occupied the Republic of Genoa. Its capital was Genoa, and it was divided in the arrondissements of Genoa, Bobbio, Novi Ligure, Tortona and...
. Beginning with the lab of Paul Berg
Paul Berg
Paul Berg is an American biochemist and professor emeritus at Stanford University. He was the recipient of the Nobel Prize in Chemistry in 1980, along with Walter Gilbert and Frederick Sanger. The award recognized their contributions to basic research involving nucleic acids...
in 1972 (aided by EcoRI
EcoRI
EcoRI is an endonuclease enzyme isolated from strains of E. coli, and is part of the restriction modification system.In molecular biology it is used as a restriction enzyme. It creates sticky ends with 5' end overhangs...
from Herbert Boyer's
Herbert Boyer
Herbert W. Boyer is a recipient of the 1990 National Medal of Science, co-recipient of the 1996 Lemelson-MIT Prize, and a co-founder of Genentech. He served as Vice President of Genentech from 1976 through his retirement in 1991....
lab, building on work with ligase
Ligase
In biochemistry, ligase is an enzyme that can catalyse the joining of two large molecules by forming a new chemical bond, usually with accompanying hydrolysis of a small chemical group dependent to one of the larger molecules...
by Arthur Kornberg's
Arthur Kornberg
Arthur Kornberg was an American biochemist who won the Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine 1959 for his discovery of "the mechanisms in the biological synthesis of deoxyribonucleic acid " together with Dr. Severo Ochoa of New York University...
lab), molecular biologists put these pieces together to produce the first transgenic organisms. Soon after, others began using plasmid
Plasmid
In microbiology and genetics, a plasmid is a DNA molecule that is separate from, and can replicate independently of, the chromosomal DNA. They are double-stranded and, in many cases, circular...
vectors
Vector (molecular biology)
In molecular biology, a vector is a DNA molecule used as a vehicle to transfer foreign genetic material into another cell. The four major types of vectors are plasmids, viruses, cosmids, and artificial chromosomes...
and adding genes for antibiotic resistance
Antibiotic resistance
Antibiotic resistance is a type of drug resistance where a microorganism is able to survive exposure to an antibiotic. While a spontaneous or induced genetic mutation in bacteria may confer resistance to antimicrobial drugs, genes that confer resistance can be transferred between bacteria in a...
, greatly increasing the reach of the recombinant techniques.
Wary of the potential dangers (particularly the possibility of a prolific bacteria with a viral cancer-causing gene), the scientific community as well as a wide range of scientific outsiders reacted to these developments with both enthusiasm and fearful restraint. Prominent molecular biologists led by Berg suggested a temporary moratorium on recombinant DNA research until the dangers could be assessed and policies could be created. This moratorium was largely respected, until the participants in the 1975 Asilomar Conference on Recombinant DNA
Asilomar Conference on Recombinant DNA
The Asilomar Conference on Recombinant DNA was an influential conference organized by Paul Berg discussing the potential biohazards and regulation of biotechnology held in February 1975 at a conference center Asilomar State Beach...
created policy recommendations and concluded that the technology could be used safely.
Following Asilomar, new genetic engineering techniques and applications developed rapidly. DNA sequencing
DNA sequencing
DNA sequencing includes several methods and technologies that are used for determining the order of the nucleotide bases—adenine, guanine, cytosine, and thymine—in a molecule of DNA....
methods improved greatly (pioneered by Frederick Sanger
Frederick Sanger
Frederick Sanger, OM, CH, CBE, FRS is an English biochemist and a two-time Nobel laureate in chemistry, the only person to have been so. In 1958 he was awarded a Nobel prize in chemistry "for his work on the structure of proteins, especially that of insulin"...
and Walter Gilbert
Walter Gilbert
Walter Gilbert is an American physicist, biochemist, molecular biology pioneer, and Nobel laureate.-Biography:Gilbert was born in Boston, Massachusetts, on March 21, 1932...
), as did oligonucleotide
Oligonucleotide
An oligonucleotide is a short nucleic acid polymer, typically with fifty or fewer bases. Although they can be formed by bond cleavage of longer segments, they are now more commonly synthesized, in a sequence-specific manner, from individual nucleoside phosphoramidites...
synthesis and transfection
Transfection
Transfection is the process of deliberately introducing nucleic acids into cells. The term is used notably for non-viral methods in eukaryotic cells...
techniques. Researchers learned to control the expression of transgene
Transgene
A transgene is a gene or genetic material that has been transferred naturally or by any of a number of genetic engineering techniques from one organism to another....
s, and were soon racing—in both academic and industrial contexts—to create organisms capable of expressing human genes for the production of human hormones. However, this was a more daunting task than molecular biologists had expected; developments between 1977 and 1980 showed that, due to the phenomena of split genes and splicing
Splicing (genetics)
In molecular biology and genetics, splicing is a modification of an RNA after transcription, in which introns are removed and exons are joined. This is needed for the typical eukaryotic messenger RNA before it can be used to produce a correct protein through translation...
, higher organisms had a much more complex system of gene expression
Gene expression
Gene expression is the process by which information from a gene is used in the synthesis of a functional gene product. These products are often proteins, but in non-protein coding genes such as ribosomal RNA , transfer RNA or small nuclear RNA genes, the product is a functional RNA...
than the bacteria models of earlier studies. The first such race, for synthesizing human insulin
Insulin
Insulin is a hormone central to regulating carbohydrate and fat metabolism in the body. Insulin causes cells in the liver, muscle, and fat tissue to take up glucose from the blood, storing it as glycogen in the liver and muscle....
, was won by Genentech
Genentech
Genentech Inc., or Genetic Engineering Technology, Inc., is a biotechnology corporation, founded in 1976 by venture capitalist Robert A. Swanson and biochemist Dr. Herbert Boyer. Trailing the founding of Cetus by five years, it was an important step in the evolution of the biotechnology industry...
. This marked the beginning of the biotech boom (and with it, the era of gene patents), with an unprecedented level of overlap between biology, industry, and law.
Molecular systematics and genomics

Cladistics
Cladistics is a method of classifying species of organisms into groups called clades, which consist of an ancestor organism and all its descendants . For example, birds, dinosaurs, crocodiles, and all descendants of their most recent common ancestor form a clade...
) but biologists soon began to use RNA and DNA sequences as characters
Trait (biology)
A trait is a distinct variant of a phenotypic character of an organism that may be inherited, environmentally determined or be a combination of the two...
; this expanded the significance of molecular evolution
Molecular evolution
Molecular evolution is in part a process of evolution at the scale of DNA, RNA, and proteins. Molecular evolution emerged as a scientific field in the 1960s as researchers from molecular biology, evolutionary biology and population genetics sought to understand recent discoveries on the structure...
within evolutionary biology, as the results of molecular systematics could be compared with traditional evolutionary trees based on morphology
Morphology (biology)
In biology, morphology is a branch of bioscience dealing with the study of the form and structure of organisms and their specific structural features....
. Following the pioneering ideas of Lynn Margulis
Lynn Margulis
Lynn Margulis was an American biologist and University Professor in the Department of Geosciences at the University of Massachusetts Amherst. She is best known for her theory on the origin of eukaryotic organelles, and her contributions to the endosymbiotic theory, which is now generally accepted...
on endosymbiotic theory
Endosymbiotic theory
The endosymbiotic theory concerns the mitochondria, plastids , and possibly other organelles of eukaryotic cells. According to this theory, certain organelles originated as free-living bacteria that were taken inside another cell as endosymbionts...
, which holds that some of the organelles of eukaryotic cells originated from free living prokaryotic organisms through symbiotic relationships, even the overall division of the tree of life was revised. Into the 1990s, the five domains (Plants, Animals, Fungi, Protists, and Monerans) became three (the Archaea
Archaea
The Archaea are a group of single-celled microorganisms. A single individual or species from this domain is called an archaeon...
, the Bacteria
Bacteria
Bacteria are a large domain of prokaryotic microorganisms. Typically a few micrometres in length, bacteria have a wide range of shapes, ranging from spheres to rods and spirals...
, and the Eukarya) based on Carl Woese
Carl Woese
Carl Richard Woese is an American microbiologist and physicist. Woese is famous for defining the Archaea in 1977 by phylogenetic taxonomy of 16S ribosomal RNA, a technique pioneered by Woese and which is now standard practice. He was also the originator of the RNA world hypothesis in 1977,...
's pioneering molecular systematics work with 16S rRNA
16S ribosomal RNA
16S ribosomal RNA is a component of the 30S subunit of prokaryotic ribosomes. It is approximately 1.5kb in length...
sequencing.
The development and popularization of the polymerase chain reaction
Polymerase chain reaction
The polymerase chain reaction is a scientific technique in molecular biology to amplify a single or a few copies of a piece of DNA across several orders of magnitude, generating thousands to millions of copies of a particular DNA sequence....
(PCR) in mid 1980s (by Kary Mullis
Kary Mullis
Kary Banks Mullis is a Nobel Prize winning American biochemist, author, and lecturer. In recognition of his improvement of the polymerase chain reaction technique, he shared the 1993 Nobel Prize in Chemistry with Michael Smith and earned the Japan Prize in the same year. The process was first...
and others at Cetus Corp.) marked another watershed in the history of modern biotechnology, greatly increasing the ease and speed of genetic analysis. Coupled with the use of expressed sequence tags, PCR led to the discovery of many more genes than could be found through traditional biochemical or genetic methods and opened the possibility of sequencing entire genomes.
The unity of much of the morphogenesis
Morphogenesis
Morphogenesis , is the biological process that causes an organism to develop its shape...
of organisms from fertilized egg to adult began to be unraveled after the discovery of the homeobox
Homeobox
A homeobox is a DNA sequence found within genes that are involved in the regulation of patterns of anatomical development in animals, fungi and plants.- Discovery :...
genes, first in fruit flies, then in other insects and animals, including humans. These developments led to advances in the field of evolutionary developmental biology
Evolutionary developmental biology
Evolutionary developmental biology is a field of biology that compares the developmental processes of different organisms to determine the ancestral relationship between them, and to discover how developmental processes evolved...
towards understanding how the various body plan
Body plan
A body plan is the blueprint for the way the body of an organism is laid out. An organism's symmetry, its number of body segments and number of limbs are all aspects of its body plan...
s of the animal phyla have evolved and how they are related to one another.
The Human Genome Project
Human Genome Project
The Human Genome Project is an international scientific research project with a primary goal of determining the sequence of chemical base pairs which make up DNA, and of identifying and mapping the approximately 20,000–25,000 genes of the human genome from both a physical and functional...
—the largest, most costly single biological study ever undertaken—began in 1988 under the leadership of James D. Watson
James D. Watson
James Dewey Watson is an American molecular biologist, geneticist, and zoologist, best known as one of the co-discoverers of the structure of DNA in 1953 with Francis Crick...
, after preliminary work with genetically simpler model organisms such as E. coli, S. cerevisiae and C. elegans
Caenorhabditis elegans
Caenorhabditis elegans is a free-living, transparent nematode , about 1 mm in length, which lives in temperate soil environments. Research into the molecular and developmental biology of C. elegans was begun in 1974 by Sydney Brenner and it has since been used extensively as a model...
. Shotgun sequencing
Shotgun sequencing
In genetics, shotgun sequencing, also known as shotgun cloning, is a method used for sequencing long DNA strands. It is named by analogy with the rapidly-expanding, quasi-random firing pattern of a shotgun....
and gene discovery methods pioneered by Craig Venter
Craig Venter
John Craig Venter is an American biologist and entrepreneur, most famous for his role in being one of the first to sequence the human genome and for his role in creating the first cell with a synthetic genome in 2010. Venter founded Celera Genomics, The Institute for Genomic Research and the J...
—and fueled by the financial promise of gene patents with Celera Genomics
Celera Genomics
Celera Corporation was a business unit of the Applera Corporation, but was spun off in July 2008 to become an independent publicly traded company. In May 2011 Quest Diagnostics Incorporated completed the acquisition of Celera, which thus became a wholly owned subsidiary...
— led to a public–private sequencing competition that ended in compromise with the first draft of the human DNA sequence announced in 2000.
Twenty-first century biological sciences
At the beginning of the 21st century, biological sciences converged with previously differentiated new and classic disciplines like PhysicsPhysics
Physics is a natural science that involves the study of matter and its motion through spacetime, along with related concepts such as energy and force. More broadly, it is the general analysis of nature, conducted in order to understand how the universe behaves.Physics is one of the oldest academic...
into research fields like Biophysics
Biophysics
Biophysics is an interdisciplinary science that uses the methods of physical science to study biological systems. Studies included under the branches of biophysics span all levels of biological organization, from the molecular scale to whole organisms and ecosystems...
. Advances were made in analytical chemistry and physics instrumentation including improved sensors, optics, tracers, instrumentation, signal processing, networks, robots, satellites, and compute power for data collection, storage, analysis, modeling, visualization, and simulations. These technology advances allowed theoretical and experimental research including internet publication of molecular biochemistry, biological systems, and ecosystems science. This enabled worldwide access to better measurements, theoretical models, complex simulations, theory predictive model experimentation, analysis, worldwide internet observational data reporting, open peer-review, collaboration, and internet publication. New fields of biological sciences research emerged including Bioinformatics
Bioinformatics
Bioinformatics is the application of computer science and information technology to the field of biology and medicine. Bioinformatics deals with algorithms, databases and information systems, web technologies, artificial intelligence and soft computing, information and computation theory, software...
, Theoretical biology, Computational genomics
Computational genomics
Computational genomics refers to the use of computational analysis to decipher biology from genome sequences and related data , including both DNA and RNA sequence as well as other "post-genomic" data...
, Astrobiology
Astrobiology
Astrobiology is the study of the origin, evolution, distribution, and future of life in the universe. This interdisciplinary field encompasses the search for habitable environments in our Solar System and habitable planets outside our Solar System, the search for evidence of prebiotic chemistry,...
and Synthetic Biology
Synthetic biology
Synthetic biology is a new area of biological research that combines science and engineering. It encompasses a variety of different approaches, methodologies, and disciplines with a variety of definitions...
.
External links
- International Society for History, Philosophy, and Social Studies of Biology – professional history of biology organization
- History of Biology – Historyworld article
- History of Biology at Bioexplorer.Net – a collection of history of biology links
- Biology – historically oriented article on Citizendium
- Miall, L. C. (1911) History of biology. Watts & Co. London

