
History of Iraq
Encyclopedia
Iraq
, known in Classical Antiquity
as Mesopotamia
, was home to some of the oldest civilizations in the world, with a cultural history of over 10,000 years. hence its common epithet, the Cradle of Civilization
. Mesopotamia, as part of the larger Fertile Crescent
, was a significant part of the Ancient Near East
throughout the Bronze Age
and the Iron Age
. Successively ruled by the Assyrian, Medo-Persian, Seleucid
and Parthian
empires during the Iron Age and Classical Antiquity, Iraq was
conquered by the Rashidun Caliphate
and became a center of the Islamic Golden Age
during the medieval Abbasid Caliphate. After a series of invasions and conquest by the Mongols and Turkmens, Iraq fell under Ottoman
rule in the 16th century, intermittently falling under Mamluk
and Safavid
control.
Ottoman rule ended with World War I
, and Iraq came to be administered by the British Empire until the establishment of the Kingdom of Iraq
in 1932. The Republic of Iraq was established in 1958 following a coup d'état
. The Republic was controlled by Saddam Hussein
from 1979 to 2003, into which period falls the Iran-Iraq war
and the First Persian Gulf War. Saddam Hussein was deposed in 2003 following the US-led invasion
of the country. After the invasion, the situation deteriorated and from 2007 Iraq has been in or on the brink of a state of civil war.
is the site of the earliest developments of the Neolithic Revolution
from around 10,000 BC. It has been identified as having "inspired some of the most important developments in human history including the invention of the wheel, the planting of the first cereal crops and the development of cursive script."
was a civilization
and historical region in southern Iraq
. It is the earliest known civilization in the world [and Iraq is therefore known as the Cradle of Civilization
]. The Sumerian civilization spanned over 3000 years and began with the first settlement of Eridu
in the Ubaid period
(mid 6th millennium BC
) through the Uruk period
(4th millennium BC
) and the Dynastic periods (3rd millennium BC
) until the rise of Babylonia
in the early 2nd millennium BC
.
The Ubaid period
marks the Pottery Neolithic to Chalcolithic phase in Mesopotamia, which represents the earliest settlement on the alluvial plain in the south. Early urbanization begins with the Ubaid period, around 5300 BC. The Ubaid culture gives way to the Uruk period
from c. 4000 BC. The invention of the wheel
and the beginning of the Chalcolithic period fall into the Ubaid period. The Sumerian historical record remains obscure until the Early Dynastic period, when a now deciphered syllabary writing system was developed, which has allowed archaeologists to read contemporary records and inscriptions. Classical Sumer ends with the rise of the empire of Akkad in the 23rd century BC. Following the Gutian period, there is a brief "Sumerian renaissance" in the 21st century, cut short in the 20th century BC by Amorite invasions. The Amorite "dynasty of Isin
" persisted until c. 1700 BC, when Mesopotamia was united under Babylonia
n rule.
was a state in central and southern Iraq with Babylon
as its capital. During the third millennium BCE
, there developed a very intimate cultural symbiosis between the Sumer
ians and the Akkad
ians, which included widespread bilingualism. The influence of Sumerian
on Akkadian
(and vice versa) is evident in all areas, from lexical borrowing on a massive scale, to syntactic, morphological, and phonological convergence. This has prompted scholars to refer to Sumerian and Akkadian in the third millennium as a sprachbund
.
Akkadian
gradually replaced Sumerian as the spoken language of Mesopotamia
somewhere around the turn of the 3rd and the 2nd millennium BCE (the exact dating being a matter of debate), but Sumerian continued to be used as a sacred, ceremonial, literary and scientific language in Mesopotamia until the 1st century CE
.
Babylonia emerged out of the Amorite
dynasties (c. 1900 BC) when Hammurabi
(c. 1792–1750 BC), unified the territories of the former kingdoms
of Sumer
and Akkad
. The Babylonian culture was a synthesis of Akkadian and Sumerian culture. Babylonians spoke the Akkadian language
, and retained the Sumerian language
for religious use, which by Hammurabi's time was declining as a spoken language. The rulers of Babylonia carried the title "King of Sumer and Akkad".
The earliest mention of the city of Babylon
can be found in a tablet from the reign of Sargon of Akkad
, dating back to the 20th century BC.
Following the collapse of the last Sumerian "Ur-III" dynasty at the hands of the Elam
ites (2002 BC traditional, 1940 BC short), the Amorite
s gained control over most of Mesopotamia, where they formed a series of small kingdoms. During the 1st centuries of what is called the "Amorite period", the most powerful city states were Isin
and Larsa
, although Shamshi-Adad I
came close to uniting the more northern regions around Assur
and Mari
. One of these Amorite dynasties was established in the city-state
of Babylon
, which would ultimately take over the others and form the first Babylonian empire, during what is also called the Old Babylonian
Period.
, in 911 BC, lasting until the fall of Nineveh
at the hands of the Babylonians in 612 BC.
In the Middle Assyrian period, Assyria had been a minor kingdom of northern Mesopotamia, competing for dominance with Babylonia
to the south. Beginning with the campaigns of Adad-nirari II, Assyria became a great regional power, growing to be a serious threat to 25th dynasty Egypt
. It began reaching the peak of its power with the reforms of Tiglath-Pileser III
(ruled 745 – 727 BC). This period is well-referenced in several sources, including the Assyro-Babylonian Chronicles
and the Hebrew Bible
. Assyria finally succumbed to the rise of the neo-Babylonian
Chaldean dynasty with the sack of Nineveh
in 612 BC.
ns (Latin Chaldaeus, Greek Khaldaios, Assyrian Kaldu), gained prominence. The Chaldeans rose to power in Babylonia and, by doing so, seem to have increased the stability and power of Babylonia. They fought off many revolts and aggressors. Chaldean influence was so strong that, during this period, Babylonia came to be known as Chaldea.
In 626 BC, the Chaldeans helped Nabo-Polassar to take power in Babylonia. At that time, Assyria was under considerable pressure from an Iranian people, the Medes
(from Media). Nabo-Polassar allied Babylonia with the Medes. Assyria
could not withstand this added pressure, and in 612 BC, Nineveh
, the capital of Assyria, fell. The entire city, once the capital of a great empire, was sacked and burned.
Later, Nebuchadnezzar II (Nabopolassar
's son) inherited the empire of Babylonia. He added quite a bit of territory to Babylonia and rebuilt Babylon, still the capital of Babylonia.
In the 6th century BC (586 BC), Nebuchadnezzar II conquered Judea
(Judah), destroyed Jerusalem; Solomon
's Temple
was also destroyed; Nebuchadnezzar II carried away an estimated 15,000 captives, and sent most of its population into exile in Babylonia. Nebuchadnezzar II (604-562 BC) is credited for building the legendary Hanging Gardens of Babylon
, one of the Seven Wonders of the World.
in 539 BC and Alexander the Great in 331 BC, who died there in 323 BC. In the 6th century BC, it became part of the Achaemenid Empire
, then was conquered by Alexander the Great and remained under Greek
rule under the Seleucid dynasty for nearly two centuries. Babylon
declined after the founding of Seleucia on the Tigris
, the new Seleucid Empire
capital.
in the 3rd century BC. At the beginning of the 2nd century AD, the Romans
, led by emperor Trajan
, invaded Parthia and conquered Mesopotamia, making it an imperial province. It was returned to the Parthians shortly after by Trajan's successor, Hadrian
.
In the mid-6th century the Persian Empire under the Sassanid dynasty was divided by Khosrow I into four quarters, of which the western one, called Khvārvarān, included most of modern Iraq, and subdivided to provinces of Mishān, Asuristān, Ādiābene and Lower Media. The term Iraq is widely used in the medieval Arabic sources for the area in the centre and south of the modern republic as a geographic rather than a political term, implying no greater precision of boundaries than the term "Mesopotamia" or, indeed, many of the names of modern states before the 20th century.
The area of modern Iraq north of Tikrit
was known in Muslim times as Al-Jazirah, which means "The Island" and refers to the "island" between the Tigris and Euphrates rivers. To the south and west lay the Arabian deserts, inhabited largely by Arab tribesmen who occasionally acknowledged the overlordship of the Sassanian Emperors.
Until 602, the desert frontier of the Persian Empire had been guarded by the Arab
Lakhmid kings of Al-Hirah
, who were themselves Arabs but who ruled a settled buffer state. In that year Shahanshah Khosrow II Aparviz (Persian خسرو پرويز) rashly abolished the Lakhmid kingdom and laid the frontier open to nomad incursions. Farther north, the western quarter was bounded by the Byzantine Empire. The frontier more or less followed the modern Syria
-Iraq border and continued northward into modern Turkey
, leaving Nisibis
(modern Nusaybin) as the Sassanian frontier fortress while the Byzantines
held Dara and nearby Amida
(modern Diyarbakır
).
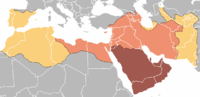
The first organised conflict between local Arab tribes and Persian forces seems to have been in 634, when the Arabs were defeated at the Battle of the Bridge. There was a force of some 5,000 Muslims under Abū `Ubayd ath-Thaqafī, which was routed by the Persians. This was followed by Khalid ibn al-Walid
's successful campaign which saw all of Iraq come under Arab rule within a year, with the exception of the Persian Empire's capital, Ctesiphon
. Around 636, a larger Arab Muslim force under Sa`d ibn Abī Waqqās
defeated the main Persian army at the Battle of al-Qādisiyyah
and moved on to capture the Persian capital of Ctesiphon. By the end of 638, the Muslims had conquered all of the Western Sassanid provinces (including modern Iraq), and the last Sassanid Emperor, Yazdegerd III, had fled to central and then northern Persia, where he was killed in 651.
The Islamic conquest was followed by mass immigration of Arabs from eastern Arabia and Mazun (Oman
) to Khvarvārān. These new arrivals did not disperse and settle throughout the country; instead they established two new garrison cities, at al-Kūfah, near ancient Babylon, and at Basra
h in the south.
The intention was that the Muslims should be a separate community of fighting men and their families living off taxes paid by the local inhabitants. In the north of the North eastern Iran, Mosul
began to emerge as the most important city and the base of a Muslim governor and garrison. Apart from the Persian elite and the Zoroastrian priests, who did not convert to Islam and thus lost their lives and property, most of the Mesopotamian peoples became Muslim and were allowed to keep their possessions.
Khvarvārān, now became a province of the Muslim Caliphate
, known as `Irāq. The city of Baghdad
was built in the 8th century and became the capital of the Abbasid Caliphate. During this period, Baghdad served as the intellectual center of the Muslim world
for several centuries, up until the sack of Baghdad
in 1258. Many famous Muslim scientists, philosophers
, inventors, poets
and writers
were active in Iraq during the 8th to 13th centuries.
as the pashalik of Baghdad. Throughout most of the period of Ottoman rule (1533-1918) the territory of present-day Iraq was a battle zone between the rival regional empires and tribal alliances.
Iraq was divided into three vilayets:
The Safavid dynasty
of Iran
briefly asserted their hegemony over Iraq in the periods of 1508-1533 and 1622-1638. During the years 1747-1831 Iraq was ruled by the Mamluk
officers of Georgian
origin who succeeded in obtaining autonomy from the Ottoman Empire
, suppressed tribal revolts, curbed the power of the Janissaries, restored order and introduced a program of modernization of economy and military. In 1831, the Ottomans managed to overthrow the Mamluk regime and again imposed their direct control over Iraq.
when the Ottomans sided with Germany
and the Central Powers
. In the Mesopotamian campaign
against the Central Powers, British
forces invaded the country and suffered a major defeat at the hands of the Turkish army during the Siege of Kut
(1915–16). After the war the Ottoman Empire was divided up, and the British Mandate of Mesopotamia was established by League of Nations mandate
. Britain imposed a Hāshimite
monarchy on Iraq and defined the territorial limits of Iraq without taking into account the politics of the different ethnic and religious groups in the country, in particular those of the Kurds and the Assyrians
to the north. During the British occupation, the Shi'ites and Kurds fought for independence. Iraq also became an oligarchy government at this time.
Although the monarch Faisal I of Iraq
was legitimized and proclaimed King by a plebiscite in 1921, nominal independence was only achieved in 1932, when the British Mandate officially ended. Establishment of Arab Sunni domination was followed by Shi'a unrests in the south, reaching a scale of rebellions in 1935-1936, which were brutally suppressed.
During World War II
, Iraqi regime of Regent 'Abd al-Ilah
was overthrown in 1941 by the Golden Square
officers, headed by Rashid Ali. The short living pro-Nazi government of Iraq was defeated in May 1941 by the allied forces in Anglo-Iraqi War
. Iraq was later used as a base for allied attacks on Vichi-French held Mandate of Syria and support for the Anglo-Soviet invasion of Iran
.
In 1945, Iraq joined the United Nations
and became a founding member of the Arab League
. At the same time, the Kurdish leader Mustafa Barzani
led a rebellion against the central government in Baghdad. After the failure of the uprising Barzani and his followers fled to the Soviet Union
.
In 1948, massive violent protests, known as the Al-Wathbah uprising broke out across Baghdad as a popular demand against the government treat with the British, and with communist part support. More protests continued in spring, but were interrupted in May, with the marshal law, when Iraq entered the 1948 Arab-Israeli War
along with other members of the Arab League.
In February 1958, King Hussein of Jordan
and `Abd al-Ilāh proposed a union of Hāshimite monarchies to counter the recently formed Egyptian-Syrian union. The prime minister Nuri as-Said
wanted Kuwait
to be part of the proposed Arab-Hāshimite Union. Shaykh `Abd-Allāh as-Salīm, the ruler of Kuwait, was invited to Baghdad to discuss Kuwait's future. This policy brought the government of Iraq into direct conflict with Britain, which did not want to grant independence to Kuwait. At that point, the monarchy found itself completely isolated. Nuri as-Said was able to contain the rising discontent only by resorting to ever greater political oppression.
known as "The Four Colonials", under the leadership of Brigadier Abd al-Karīm Qāsim (known as "az-Za`īm", 'the leader') and Colonel Abdul Salam Arif
overthrew the Hashimite monarchy on July 14, 1958
. The new government proclaimed Iraq to be a republic
and rejected the idea of a union with Jordan. Iraq's activity in the Baghdad Pact ceased.
In 1961, Kuwait
gained independence from Britain and Iraq claimed sovereignty over Kuwait. A period of considerable instability followed. The same year, Mustafa Barzani
, who had been invited to return to Iraq by Qasim three years earlier, began engaging Iraqi government forces and establishing Kurdish control in the north in what was the beginning of the First Kurdish Iraqi War
.
under the leadership of General Ahmed Hasan al-Bakr (prime minister
) and Colonel Abdul Salam Arif
(president). In June 1963, Syria, which meanwhile had also fell under Ba'athist rule, took part in the Iraqi military campaign
against the Kurds by providing aircraft, armoured vehicles and a force of 6,000 soldiers. Several months later, `Abd as-Salam Muhammad `Arif led a successful coup against the Ba'ath government. Arif declared a ceasefire in February 1964 which provoked a split among Kurdish urban radicals on one hand and Peshmerga (Freedom fighters) forces led by Barzani on the other.
On April 13, 1966, President Abdul Salam Arif died in a helicopter crash and was succeeded by his brother, General Abdul Rahman Arif
. Following the unexpected death of Arif, where upon he was replaced by his brother, Abdul Rahman Arif, the Iraqi government launched a last-ditch effort to defeat the Kurds. This campaign failed in May 1966, when Barzani forces thoroughly defeated the Iraqi Army at the Battle of Mount Handrin, near Rawanduz. Following the Six Day War of 1967, the Ba'ath Party felt strong enough to retake power (July 17, 1968). Ahmad Hasan al-Bakr became president and chairman of the Revolutionary Command Council (RCC). The Ba'ath government started a campaign to end the Kurdish insurrection
, which stalled in 1969. This can be partly attributed to the internal power struggle in Baghdad and also tensions with Iran. Moreover, the Soviet Union pressured the Iraqis to come to terms with Barzani. The war ended with more than 100,000 mortal casualties, with little achievements to both Kurdish rebels and the Iraqi government.
In the aftermath of the First Kurdish Iraqi War
, a peace plan was announced in March 1970 and provided for broader Kurdish autonomy. The plan also gave Kurds representation in government bodies, to be implemented in four years. Despite this, the Iraqi government embarked on an Arabization program in the oil rich regions of Kirkuk and Khanaqin
in the same period. In the following years, Baghdad government overcame its internal divisions and concluded a treaty of friendship with the Soviet Union in April 1972 and ended its isolation within the Arab world. On the other hand, Kurds remained dependent on the Iranian military support and could do little to strengthen their forces. By 1974 the situation in the north escalated again into the Second Kurdish Iraqi War
, to last until 1975.
 In July 1979, President Ahmed Hassan al-Bakr
In July 1979, President Ahmed Hassan al-Bakr
resigned, and his chosen successor, General Saddam Hussein
, assumed the offices of both President and Chairman of the Revolutionary Command Council.
Territorial disputes with Iran
led to an inconclusive and costly eight-year war, the Iran–Iraq War (1980–1988, termed Qādisiyyat
-Saddām – 'Saddam's Qādisiyyah
'), which devastated the economy. Iraq declared victory in 1988 but actually achieved a weary return to the status quo ante bellum
. The war lasted for eight years, making it the longest conventional war of the twentieth century.
The war began when Iraq invaded Iran, launching a simultaneous invasion by air and land into Iranian territory on 22 September 1980, following a long history of border disputes
, and fears of Shia insurgency among Iraq's long-suppressed Shia majority influenced by the Iranian Revolution
. Iraq was also aiming to replace Iran as the dominant Persian Gulf
state
. Although Iraq hoped to take advantage of the revolutionary chaos in Iran and attacked without formal warning, they made only limited progress into Iran and within several months were repelled by the Iranians who regained virtually all lost territory by June 1982. For the next six years, Iran was on the offensive. Despite calls for a ceasefire
by the United Nations Security Council
, hostilities continued until 20 August 1988. The war finally ended with a United Nations brokered ceasefire in the form of United Nations Security Council Resolution 598
, which was accepted by both sides. It took several weeks for the Iranian armed forces to evacuate Iraqi territory to honor pre-war international borders between the two nations (see 1975 Algiers Agreement). The last prisoners of war
were exchanged in 2003.
The war came at a great cost in lives and economic damage—half a million Iraqi and Iranian soldiers as well as civilians are believed to have died in the war with many more injured—but it brought neither reparations nor change in borders. The conflict is often compared to World War I
, in that the tactics used closely mirrored those of that conflict, including large scale trench warfare
, manned machine-gun posts, bayonet charges, use of barbed wire
across trenches, human wave attacks across no-man's land, and extensive use of chemical weapons such as mustard gas by the Iraqi government against Iranian troops and civilians as well as Iraqi Kurd
s. At the time, the UN Security Council issued statements that "chemical weapons had been used in the war." However, in these UN statements it was never made clear that it was only Iraq that was using chemical weapons, so it has been said that "the international community remained silent as Iraq used weapons of mass destruction against Iranian as well as Iraqi Kurds" and it is believed that the "United States prevented the UN from condemning Iraq".
A long-standing territorial dispute was the ostensible reason for Iraq's invasion of Kuwait
in 1990. In November 1990, the UN Security Council adopted Resolution 678, permitting member states to use all necessary means, authorizing military action against the Iraqi forces occupying Kuwait and demanded a complete withdrawal by January 15, 1991. When Saddam Hussein failed to comply with this demand, the Gulf War
(Operation "Desert Storm") ensued on January 17, 1991. Probably as many as 100,000 Iraqi soldiers and tens of thousands of civilians were killed.
In March 1991 revolts in the Shia-dominated southern Iraq started involving demoralized Iraqi Army
troops and the anti-government Shia parties. Another wave of insurgency broke out shortly afterwards in the Kurdish
populated northern Iraq (see 1991 uprisings in Iraq
). Although they presented a serious threat to the Iraqi Ba'ath Party regime, Saddam Hussein managed to suppress the rebellions with massive and indiscriminate force and maintained power. They were ruthlessly crushed by the loyalist forces spearheaded by the Iraqi Republican Guard
and the population was successfully terrorized. During the few weeks of unrest tens of thousands of people were killed. Many more died during the following months, while nearly two million Iraqis fled for their lives. In the aftermath, the government intensified the forced relocating of Marsh Arabs
and the draining of the Iraqi marshlands
, while the Allies established the Iraqi no-fly zones
.
On 6 August 1990, after the Iraqi invasion of Kuwait, the U.N. Security Council adopted Resolution 661 which imposed economic sanctions
on Iraq, providing for a full trade embargo, excluding medical supplies, food and other items of humanitarian necessity, these to be determined by the Security Council sanctions committee. After the end of the Gulf War and after the Iraqi withdrawal from Kuwait, the sanctions were linked to removal of weapons of mass destruction
by Resolution 687 http://www.mideastweb.org/687.htm. From 1991 until 2003 the effects of government policy and sanctions regime led to hyperinflation, widespread poverty and malnutrition.
During the latter part of the 1990s the UN considered relaxing the sanctions imposed because of the hardships suffered by ordinary Iraqis. According to UN estimates, between 500,000 and 1.2 million children died http://www.unicef.org/newsline/99pr29.htm during the years of the sanctions. The United States used its veto in the UN Security Council to block the proposal to lift the sanctions because of the continued failure of Iraq to verify disarmament. However, an oil for food program was established in 1996 to ease the effects of sanctions.
Iraqi cooperation with UN weapons inspection teams was questioned on several occasions during the 1990s. UNSCOM chief weapons inspector Richard Butler
withdrew his team from Iraq in November 1998 because of Iraq's lack of cooperation. The team returned in December. Butler prepared a report for the UN Security Council afterwards in which he expressed dissatisfaction with the level of compliance http://edition.cnn.com/WORLD/meast/9811/11/iraq.05/. The same month, US President Bill Clinton authorized air strikes on government targets and military facilities. Air strikes against military facilities and alleged WMD sites continued into 2002.
on New York and Washington in the United States in 2001, American foreign policy began to call for the removal of the Ba'ath government in Iraq. Conservative think-tanks in Washington had for years been urging regime change
in Baghdad, but until the Iraq Liberation Act of 1998
, official US policy was to simply keep Iraq complying with UN sanctions. The Iraq Liberation Act
, codified regime change in Iraq as the official policy of the United States government. It was passed 99-0 by the United States Senate
in 1998.
The US urged the United Nations
to take military action against Iraq. The American president George Bush stated that Saddām had repeatedly violated 16 UN Security Council resolutions. The Iraqi government rejected Bush's assertions. A team of U.N. inspectors, led by Swedish diplomat Hans Blix
was admitted, into the country; their final report stated that Iraqis capability in producing "weapons of mass destruction" was not significantly different from 1992 when the country dismantled the bulk of their remaining arsenals under terms of the ceasefire agreement with U.N. forces, but did not completely rule out the possibility that Saddam still had Weapons of Mass Destruction. The United States
and the United Kingdom
charged that Iraq was hiding Weapons and opposed the team's requests for more time to further investigate the matter. Resolution 1441 was passed unanimously by the UN Security Council on November 8, 2002, offering Iraq "a final opportunity to comply with its disarmament obligations" that had been set out in several previous UN resolutions, threatening "serious consequences" if the obligations were not fulfilled. The UN Security Council did not issue a resolution authorizing the use of force against Iraq.
In March 2003 the United States
and the United Kingdom
, with military aid from other nations, invaded Iraq.
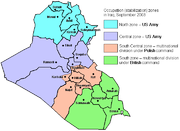 In 2003, after the American and British invasion, Iraq was occupied by Coalition forces. On May 23, 2003, the UN Security Council unanimously approved a resolution lifting all economic sanctions against Iraq.
In 2003, after the American and British invasion, Iraq was occupied by Coalition forces. On May 23, 2003, the UN Security Council unanimously approved a resolution lifting all economic sanctions against Iraq.
As the country struggled to rebuild after three wars and a decade of sanctions, it was racked by violence between a growing Iraqi insurgency
and occupation forces. Saddam Hussein, who vanished in April, was captured on December 13, 2003.
Jay Garner
is appointed Interim Civil Administrator with three deputies, including Tim Cross
. Garner was replaced in May 2003 by L. Paul Bremer
, who was himself replaced by John Negroponte
on April 19, 2004 who left Iraq in 2005. Negroponte was the last US interim administrator.
Terrorism emerged as a threat to Iraq's people not long after the invasion of 2003. Al Qaeda now has a presence in the country, in the form of several terrorist groups formerly led by Abu Musab Al Zarqawi. Al-Zarqawi was a Jordanian militant Islamist who ran a militant training camp in Afghanistan. He became known after going to Iraq and being responsible for a series of bombings, beheadings and attacks during the Iraq war. Al-zarqawi was killed on June 7, 2006. Many foreign fighters and former Ba'ath Party officials have also joined the insurgency, which is mainly aimed at attacking American forces and Iraqis who work with them. The most dangerous insurgent area is the Sunni Triangle, a mostly Sunni-Muslim area just north of Baghdad.
By the end of 2006 violence continued as the new Iraqi Government struggled to extend complete security within Iraq.
U.S. and Coalition forces remained in Iraq. An increasingly disturbing trend had arisen - sectarian fighting. As the country attempted to move from occupation by western forces to a new entity within the Middle East, a new phase of conflict seemed to have erupted within Iraq. This new phase of conflict was waged predominately along the religious sectarian lines that the Americans had used to divide the population. Fighting was primarily between the majority Shia and the minority Sunni. But there were reports of infighting as well. To outside observers, as well as people in Iraq who supported the American military presence, the cause of violence was obscure - as developments came faster than could be easily analyzed.
Reported acts of violence conducted by an uneasy tapestry of independence activists and opponents of foreign domination steadily increased by the end of 2006. These attacks become predominately aimed at Iraqi collaborators rather than foreign occupation forces. Violence was conducted by Sunni groups, nationalists and others who sought an Iraq freed from foreign rule that include the Iraq Insurgency, which has been fighting since the initial U.S. invasion of 2003. Also, criminal elements within Iraq's society seemed to perpetuate violence for their own means and ambitions. Iraqi nationalist and Ba'athist elements (part of the insurgency) remained committed to expelling U.S. forces and also seemed to attack Shia populations, presumably, due to the Shia parties' collaboration with Iran and the United States in making war against their own nation. Further, Islamic Jihadist - of which Al Qaeda in Iraq is a member - continued to use terror and extreme acts of violence against collaborationist populations to advance their religious and political agenda(s). The aims of these attacks were not completely clear, but it was argued in 2006/7 that these attacks were aimed at fomenting civil conflict within Iraq to destroy the legitimacy of the newly created collaborationist Iraqi government (which many of its nationalist critics saw as illegitimate and a product of the U.S. government) and create an unsustainable position for the U.S. forces within Iraq. The most widely reported evidence of this argument stemmed from the 23 February 2006 attack on the Al Askari Mosque in Samarra
, one of Shi'ite Islam's holiest sites. Analysis of the attack suggested that the Mujahideen Shura Council
and Al-Qaeda in Iraq were responsible, and that the motivation was to provoke further violence by outraging the Shia population. http://www.washingtonpost.com/wp-dyn/content/article/2006/02/22/AR2006022200454.html The Mujahideen Shura Council was said to have been headed by Abdullah Rashid al-Baghdadi. In mid-October 2006, a statement was released, stating that the Mujahideen Shura Council had been disbanded and was replaced by the "Islamic State of Iraq". It was formed to resist efforts by the U.S. and Iraqi authorities to win over Sunni supporters of the insurgency.
In response to attacks like the one against the Askari Mosque, violent reprisals escalated. Shia terror organizations associated with the American occupation forces within Iraq gained increasing power and influence in the collaborationist Iraqi government. Additionally, the militias, it appeared in late 2006, had the capability to act outside the scope of government. As a result these powerful militias, it seemed as of late 2006, were leading reprisal acts of violence against the Sunni minority. A cycle of violence thus ensued whereby Sunni insurgent or nationalist attacks followed with government and American backed reprisals - often in the form of Shi'ite death squads that sought out and killed Sunnis. Many commentators on the Iraq War began, by the end of 2006, to refer to this violent escalation as a civil war
.
In addition to these sectarian and religious divides, an incredible amount of collateral damage has been the result. For example, evidence suggests that women's human rights and freedoms have dramatically been cut since the US-led invasion.
Under the US occupation, Islamist militias have waged a systematic campaign of violence against women in their bid to remake Iraq as an Islamist state. There has been a sharp rise in gender-based violence within families. Newly adopted Shari’a laws, such as Article 41 of Iraq’s Constitution, have degraded women’s rights, making them more vulnerable to abuses. According to the Hague and Geneva Conventions, the US, as an occupying power, was responsible for the human rights and security of Iraqi civilians. But US forces failed to meet this responsibility.
There have been concerns that the country has become condemned "to repeat the undemocratic cycle which began in the 1920s and eventually produced the Saddam Hussein regime." In order to combat these issues, several organizations have stepped in to set up shelters for physically and sexually abused women, notably the Organization of Women's Freedom in Iraq(OWFI) and MADRE, among others.
Iraq
Iraq ; officially the Republic of Iraq is a country in Western Asia spanning most of the northwestern end of the Zagros mountain range, the eastern part of the Syrian Desert and the northern part of the Arabian Desert....
, known in Classical Antiquity
Classical antiquity
Classical antiquity is a broad term for a long period of cultural history centered on the Mediterranean Sea, comprising the interlocking civilizations of ancient Greece and ancient Rome, collectively known as the Greco-Roman world...
as Mesopotamia
Mesopotamia
Mesopotamia is a toponym for the area of the Tigris–Euphrates river system, largely corresponding to modern-day Iraq, northeastern Syria, southeastern Turkey and southwestern Iran.Widely considered to be the cradle of civilization, Bronze Age Mesopotamia included Sumer and the...
, was home to some of the oldest civilizations in the world, with a cultural history of over 10,000 years. hence its common epithet, the Cradle of Civilization
Cradle of Civilization
The cradle of civilization is a term referring to any of the possible locations for the emergence of civilization.It is usually applied to the Ancient Near Eastern Chalcolithic , especially in the Fertile Crescent , but also extended to sites in Armenia, and the Persian Plateau, besides other Asian...
. Mesopotamia, as part of the larger Fertile Crescent
Fertile Crescent
The Fertile Crescent, nicknamed "The Cradle of Civilization" for the fact the first civilizations started there, is a crescent-shaped region containing the comparatively moist and fertile land of otherwise arid and semi-arid Western Asia. The term was first used by University of Chicago...
, was a significant part of the Ancient Near East
Ancient Near East
The ancient Near East was the home of early civilizations within a region roughly corresponding to the modern Middle East: Mesopotamia , ancient Egypt, ancient Iran The ancient Near East was the home of early civilizations within a region roughly corresponding to the modern Middle East: Mesopotamia...
throughout the Bronze Age
Bronze Age
The Bronze Age is a period characterized by the use of copper and its alloy bronze as the chief hard materials in the manufacture of some implements and weapons. Chronologically, it stands between the Stone Age and Iron Age...
and the Iron Age
Iron Age
The Iron Age is the archaeological period generally occurring after the Bronze Age, marked by the prevalent use of iron. The early period of the age is characterized by the widespread use of iron or steel. The adoption of such material coincided with other changes in society, including differing...
. Successively ruled by the Assyrian, Medo-Persian, Seleucid
Seleucid Empire
The Seleucid Empire was a Greek-Macedonian state that was created out of the eastern conquests of Alexander the Great. At the height of its power, it included central Anatolia, the Levant, Mesopotamia, Persia, today's Turkmenistan, Pamir and parts of Pakistan.The Seleucid Empire was a major centre...
and Parthian
Parthian Empire
The Parthian Empire , also known as the Arsacid Empire , was a major Iranian political and cultural power in ancient Persia...
empires during the Iron Age and Classical Antiquity, Iraq was
conquered by the Rashidun Caliphate
Rashidun Caliphate
The Rashidun Caliphate , comprising the first four caliphs in Islam's history, was founded after Muhammad's death in 632, Year 10 A.H.. At its height, the Caliphate extended from the Arabian Peninsula, to the Levant, Caucasus and North Africa in the west, to the Iranian highlands and Central Asia...
and became a center of the Islamic Golden Age
Islamic Golden Age
During the Islamic Golden Age philosophers, scientists and engineers of the Islamic world contributed enormously to technology and culture, both by preserving earlier traditions and by adding their own inventions and innovations...
during the medieval Abbasid Caliphate. After a series of invasions and conquest by the Mongols and Turkmens, Iraq fell under Ottoman
Ottoman Empire
The Ottoman EmpireIt was usually referred to as the "Ottoman Empire", the "Turkish Empire", the "Ottoman Caliphate" or more commonly "Turkey" by its contemporaries...
rule in the 16th century, intermittently falling under Mamluk
Mamluk rule in Iraq
The Mamluks who ruled Iraq in the 18th century were freed Georgian slaves converted to Islam, trained in a special school, and then assigned to military and administrative duties. They presided, with short intermissions, over more than a century in the history of Ottoman Iraq, from 1704 to 1831...
and Safavid
Safavid dynasty
The Safavid dynasty was one of the most significant ruling dynasties of Iran. They ruled one of the greatest Persian empires since the Muslim conquest of Persia and established the Twelver school of Shi'a Islam as the official religion of their empire, marking one of the most important turning...
control.
Ottoman rule ended with World War I
World War I
World War I , which was predominantly called the World War or the Great War from its occurrence until 1939, and the First World War or World War I thereafter, was a major war centred in Europe that began on 28 July 1914 and lasted until 11 November 1918...
, and Iraq came to be administered by the British Empire until the establishment of the Kingdom of Iraq
Kingdom of Iraq
The Kingdom of Iraq was the sovereign state of Iraq during and after the British Mandate of Mesopotamia. The League of Nations mandate started in 1920. The kingdom began in August 1921 with the coronation of Faisal bin al-Hussein bin Ali al-Hashemi as King Faisal I...
in 1932. The Republic of Iraq was established in 1958 following a coup d'état
Coup d'état
A coup d'état state, literally: strike/blow of state)—also known as a coup, putsch, and overthrow—is the sudden, extrajudicial deposition of a government, usually by a small group of the existing state establishment—typically the military—to replace the deposed government with another body; either...
. The Republic was controlled by Saddam Hussein
Saddam Hussein
Saddam Hussein Abd al-Majid al-Tikriti was the fifth President of Iraq, serving in this capacity from 16 July 1979 until 9 April 2003...
from 1979 to 2003, into which period falls the Iran-Iraq war
Iran-Iraq War
The Iran–Iraq War was an armed conflict between the armed forces of Iraq and Iran, lasting from September 1980 to August 1988, making it the longest conventional war of the twentieth century...
and the First Persian Gulf War. Saddam Hussein was deposed in 2003 following the US-led invasion
2003 invasion of Iraq
The 2003 invasion of Iraq , was the start of the conflict known as the Iraq War, or Operation Iraqi Freedom, in which a combined force of troops from the United States, the United Kingdom, Australia and Poland invaded Iraq and toppled the regime of Saddam Hussein in 21 days of major combat operations...
of the country. After the invasion, the situation deteriorated and from 2007 Iraq has been in or on the brink of a state of civil war.
Ancient Mesopotamia
MesopotamiaMesopotamia
Mesopotamia is a toponym for the area of the Tigris–Euphrates river system, largely corresponding to modern-day Iraq, northeastern Syria, southeastern Turkey and southwestern Iran.Widely considered to be the cradle of civilization, Bronze Age Mesopotamia included Sumer and the...
is the site of the earliest developments of the Neolithic Revolution
Neolithic Revolution
The Neolithic Revolution was the first agricultural revolution. It was the transition from hunting and gathering to agriculture and settlement. Archaeological data indicates that various forms of plants and animal domestication evolved independently in 6 separate locations worldwide circa...
from around 10,000 BC. It has been identified as having "inspired some of the most important developments in human history including the invention of the wheel, the planting of the first cereal crops and the development of cursive script."
Sumer and Akkad
SumerSumer
Sumer was a civilization and historical region in southern Mesopotamia, modern Iraq during the Chalcolithic and Early Bronze Age....
was a civilization
Civilization
Civilization is a sometimes controversial term that has been used in several related ways. Primarily, the term has been used to refer to the material and instrumental side of human cultures that are complex in terms of technology, science, and division of labor. Such civilizations are generally...
and historical region in southern Iraq
Iraq
Iraq ; officially the Republic of Iraq is a country in Western Asia spanning most of the northwestern end of the Zagros mountain range, the eastern part of the Syrian Desert and the northern part of the Arabian Desert....
. It is the earliest known civilization in the world [and Iraq is therefore known as the Cradle of Civilization
Cradle of Civilization
The cradle of civilization is a term referring to any of the possible locations for the emergence of civilization.It is usually applied to the Ancient Near Eastern Chalcolithic , especially in the Fertile Crescent , but also extended to sites in Armenia, and the Persian Plateau, besides other Asian...
]. The Sumerian civilization spanned over 3000 years and began with the first settlement of Eridu
Eridu
Eridu is an ancient Sumerian city in what is now Tell Abu Shahrain, Dhi Qar Governorate, Iraq. Eridu was considered the earliest city in southern Mesopotamia, and is one of the oldest cities in the world...
in the Ubaid period
Ubaid period
The Ubaid period is a prehistoric period of Mesopotamia. The tell of al-`Ubaid west of nearby Ur in southern Iraq's Dhi Qar Governorate has given its name to the prehistoric Pottery Neolithic to Chalcolithic culture, which represents the earliest settlement on the alluvial plain of southern...
(mid 6th millennium BC
6th millennium BC
During the 6th millennium BC, agriculture spread from the Balkans to Italy and Eastern Europe, and also from Mesopotamia to Egypt. World population was essentially stable at approximately 5 million, though some speculate up to 7 million.-Events:...
) through the Uruk period
Uruk period
The Uruk period existed from the protohistoric Chalcolithic to Early Bronze Age period in the history of Mesopotamia, following the Ubaid period and succeeded by the Jemdet Nasr period. Named after the Sumerian city of Uruk, this period saw the emergence of urban life in Mesopotamia. It was...
(4th millennium BC
4th millennium BC
The 4th millennium BC saw major changes in human culture. It marked the beginning of the Bronze Age and of writing.The city states of Sumer and the kingdom of Egypt were established and grew to prominence. Agriculture spread widely across Eurasia...
) and the Dynastic periods (3rd millennium BC
3rd millennium BC
The 3rd millennium BC spans the Early to Middle Bronze Age.It represents a period of time in which imperialism, or the desire to conquer, grew to prominence, in the city states of the Middle East, but also throughout Eurasia, with Indo-European expansion to Anatolia, Europe and Central Asia. The...
) until the rise of Babylonia
Babylonia
Babylonia was an ancient cultural region in central-southern Mesopotamia , with Babylon as its capital. Babylonia emerged as a major power when Hammurabi Babylonia was an ancient cultural region in central-southern Mesopotamia (present-day Iraq), with Babylon as its capital. Babylonia emerged as...
in the early 2nd millennium BC
2nd millennium BC
The 2nd millennium BC marks the transition from the Middle to the Late Bronze Age.Its first half is dominated by the Middle Kingdom of Egypt and Babylonia. The alphabet develops. Indo-Iranian migration onto the Iranian plateau and onto the Indian subcontinent propagates the use of the chariot...
.
The Ubaid period
Ubaid period
The Ubaid period is a prehistoric period of Mesopotamia. The tell of al-`Ubaid west of nearby Ur in southern Iraq's Dhi Qar Governorate has given its name to the prehistoric Pottery Neolithic to Chalcolithic culture, which represents the earliest settlement on the alluvial plain of southern...
marks the Pottery Neolithic to Chalcolithic phase in Mesopotamia, which represents the earliest settlement on the alluvial plain in the south. Early urbanization begins with the Ubaid period, around 5300 BC. The Ubaid culture gives way to the Uruk period
Uruk period
The Uruk period existed from the protohistoric Chalcolithic to Early Bronze Age period in the history of Mesopotamia, following the Ubaid period and succeeded by the Jemdet Nasr period. Named after the Sumerian city of Uruk, this period saw the emergence of urban life in Mesopotamia. It was...
from c. 4000 BC. The invention of the wheel
Wheel
A wheel is a device that allows heavy objects to be moved easily through rotating on an axle through its center, facilitating movement or transportation while supporting a load, or performing labor in machines. Common examples found in transport applications. A wheel, together with an axle,...
and the beginning of the Chalcolithic period fall into the Ubaid period. The Sumerian historical record remains obscure until the Early Dynastic period, when a now deciphered syllabary writing system was developed, which has allowed archaeologists to read contemporary records and inscriptions. Classical Sumer ends with the rise of the empire of Akkad in the 23rd century BC. Following the Gutian period, there is a brief "Sumerian renaissance" in the 21st century, cut short in the 20th century BC by Amorite invasions. The Amorite "dynasty of Isin
Isin
Isin was an ancient city-state of lower Mesopotamia about 20 miles south of Nippur at the site of modern Ishan al-Bahriyat in Iraq's Al-Qādisiyyah Governorate.-History:...
" persisted until c. 1700 BC, when Mesopotamia was united under Babylonia
Babylonia
Babylonia was an ancient cultural region in central-southern Mesopotamia , with Babylon as its capital. Babylonia emerged as a major power when Hammurabi Babylonia was an ancient cultural region in central-southern Mesopotamia (present-day Iraq), with Babylon as its capital. Babylonia emerged as...
n rule.
- Ubaid periodUbaid periodThe Ubaid period is a prehistoric period of Mesopotamia. The tell of al-`Ubaid west of nearby Ur in southern Iraq's Dhi Qar Governorate has given its name to the prehistoric Pottery Neolithic to Chalcolithic culture, which represents the earliest settlement on the alluvial plain of southern...
: 5300 – 4100 BC (Pottery NeolithicNeolithicThe Neolithic Age, Era, or Period, or New Stone Age, was a period in the development of human technology, beginning about 9500 BC in some parts of the Middle East, and later in other parts of the world. It is traditionally considered as the last part of the Stone Age...
to Chalcolithic) - Uruk periodUruk periodThe Uruk period existed from the protohistoric Chalcolithic to Early Bronze Age period in the history of Mesopotamia, following the Ubaid period and succeeded by the Jemdet Nasr period. Named after the Sumerian city of Uruk, this period saw the emergence of urban life in Mesopotamia. It was...
: 4100 – 2900 BC (Late Chalcolithic to Early Bronze Age I)- Uruk XIV-V: 4100 – 3300 BC
- Uruk IV period: 3300 – 3000 BC
- Jemdet Nasr periodJemdet Nasr periodThe Jemdet Nasr period is an archaeological culture in southern Mesopotamia that is generally dated to 3100–2900 BCE. It is named after the type-site Jemdet Nasr, where the assemblage typical for this period was first recognized. Its geographical distribution is limited to south–central Iraq...
(Uruk III): 3100 – 2900 BC
- Early Dynastic period (Early Bronze Age II-IV)
- Early Dynastic I period: 2900–2800 BC
- Early Dynastic II period: 2800–2600 BC (GilgameshGilgameshGilgamesh was the fifth king of Uruk, modern day Iraq , placing his reign ca. 2500 BC. According to the Sumerian king list he reigned for 126 years. In the Tummal Inscription, Gilgamesh, and his son Urlugal, rebuilt the sanctuary of the goddess Ninlil, in Tummal, a sacred quarter in her city of...
) - Early Dynastic IIIa period: 2600–2500 BC
- Early Dynastic IIIb period: c. 2500–2334 BC
- Akkadian Empire period: c. 2334–2218 BC (SargonSargon of AkkadSargon of Akkad, also known as Sargon the Great "the Great King" , was an Akkadian emperor famous for his conquest of the Sumerian city-states in the 23rd and 22nd centuries BC. The founder of the Dynasty of Akkad, Sargon reigned in the last quarter of the third millennium BC...
) - Gutian period: c. 2218–2047 BC (Early Bronze Age IV)
- Ur III period: c. 2047–1940 BC
Babylonia and Assyria
BabyloniaBabylonia
Babylonia was an ancient cultural region in central-southern Mesopotamia , with Babylon as its capital. Babylonia emerged as a major power when Hammurabi Babylonia was an ancient cultural region in central-southern Mesopotamia (present-day Iraq), with Babylon as its capital. Babylonia emerged as...
was a state in central and southern Iraq with Babylon
Babylon
Babylon was an Akkadian city-state of ancient Mesopotamia, the remains of which are found in present-day Al Hillah, Babil Province, Iraq, about 85 kilometers south of Baghdad...
as its capital. During the third millennium BCE
3rd millennium BC
The 3rd millennium BC spans the Early to Middle Bronze Age.It represents a period of time in which imperialism, or the desire to conquer, grew to prominence, in the city states of the Middle East, but also throughout Eurasia, with Indo-European expansion to Anatolia, Europe and Central Asia. The...
, there developed a very intimate cultural symbiosis between the Sumer
Sumer
Sumer was a civilization and historical region in southern Mesopotamia, modern Iraq during the Chalcolithic and Early Bronze Age....
ians and the Akkad
Akkad
The Akkadian Empire was an empire centered in the city of Akkad and its surrounding region in Mesopotamia....
ians, which included widespread bilingualism. The influence of Sumerian
Sumerian language
Sumerian is the language of ancient Sumer, which was spoken in southern Mesopotamia since at least the 4th millennium BC. During the 3rd millennium BC, there developed a very intimate cultural symbiosis between the Sumerians and the Akkadians, which included widespread bilingualism...
on Akkadian
Akkadian language
Akkadian is an extinct Semitic language that was spoken in ancient Mesopotamia. The earliest attested Semitic language, it used the cuneiform writing system derived ultimately from ancient Sumerian, an unrelated language isolate...
(and vice versa) is evident in all areas, from lexical borrowing on a massive scale, to syntactic, morphological, and phonological convergence. This has prompted scholars to refer to Sumerian and Akkadian in the third millennium as a sprachbund
Sprachbund
A Sprachbund – also known as a linguistic area, convergence area, diffusion area or language crossroads – is a group of languages that have become similar in some way because of geographical proximity and language contact. They may be genetically unrelated, or only distantly related...
.
Akkadian
Akkadian language
Akkadian is an extinct Semitic language that was spoken in ancient Mesopotamia. The earliest attested Semitic language, it used the cuneiform writing system derived ultimately from ancient Sumerian, an unrelated language isolate...
gradually replaced Sumerian as the spoken language of Mesopotamia
Mesopotamia
Mesopotamia is a toponym for the area of the Tigris–Euphrates river system, largely corresponding to modern-day Iraq, northeastern Syria, southeastern Turkey and southwestern Iran.Widely considered to be the cradle of civilization, Bronze Age Mesopotamia included Sumer and the...
somewhere around the turn of the 3rd and the 2nd millennium BCE (the exact dating being a matter of debate), but Sumerian continued to be used as a sacred, ceremonial, literary and scientific language in Mesopotamia until the 1st century CE
Common Era
Common Era ,abbreviated as CE, is an alternative designation for the calendar era originally introduced by Dionysius Exiguus in the 6th century, traditionally identified with Anno Domini .Dates before the year 1 CE are indicated by the usage of BCE, short for Before the Common Era Common Era...
.
Babylonia emerged out of the Amorite
Amorite
Amorite refers to an ancient Semitic people who occupied large parts of Mesopotamia from the 21st Century BC...
dynasties (c. 1900 BC) when Hammurabi
Hammurabi
Hammurabi Hammurabi Hammurabi (Akkadian from Amorite ʻAmmurāpi, "the kinsman is a healer", from ʻAmmu, "paternal kinsman", and Rāpi, "healer"; (died c...
(c. 1792–1750 BC), unified the territories of the former kingdoms
Monarchy
A monarchy is a form of government in which the office of head of state is usually held until death or abdication and is often hereditary and includes a royal house. In some cases, the monarch is elected...
of Sumer
Sumer
Sumer was a civilization and historical region in southern Mesopotamia, modern Iraq during the Chalcolithic and Early Bronze Age....
and Akkad
Akkad
The Akkadian Empire was an empire centered in the city of Akkad and its surrounding region in Mesopotamia....
. The Babylonian culture was a synthesis of Akkadian and Sumerian culture. Babylonians spoke the Akkadian language
Akkadian language
Akkadian is an extinct Semitic language that was spoken in ancient Mesopotamia. The earliest attested Semitic language, it used the cuneiform writing system derived ultimately from ancient Sumerian, an unrelated language isolate...
, and retained the Sumerian language
Sumerian language
Sumerian is the language of ancient Sumer, which was spoken in southern Mesopotamia since at least the 4th millennium BC. During the 3rd millennium BC, there developed a very intimate cultural symbiosis between the Sumerians and the Akkadians, which included widespread bilingualism...
for religious use, which by Hammurabi's time was declining as a spoken language. The rulers of Babylonia carried the title "King of Sumer and Akkad".
The earliest mention of the city of Babylon
Babylon
Babylon was an Akkadian city-state of ancient Mesopotamia, the remains of which are found in present-day Al Hillah, Babil Province, Iraq, about 85 kilometers south of Baghdad...
can be found in a tablet from the reign of Sargon of Akkad
Sargon of Akkad
Sargon of Akkad, also known as Sargon the Great "the Great King" , was an Akkadian emperor famous for his conquest of the Sumerian city-states in the 23rd and 22nd centuries BC. The founder of the Dynasty of Akkad, Sargon reigned in the last quarter of the third millennium BC...
, dating back to the 20th century BC.
Following the collapse of the last Sumerian "Ur-III" dynasty at the hands of the Elam
Elam
Elam was an ancient civilization located in what is now southwest Iran. Elam was centered in the far west and the southwest of modern-day Iran, stretching from the lowlands of Khuzestan and Ilam Province, as well as a small part of southern Iraq...
ites (2002 BC traditional, 1940 BC short), the Amorite
Amorite
Amorite refers to an ancient Semitic people who occupied large parts of Mesopotamia from the 21st Century BC...
s gained control over most of Mesopotamia, where they formed a series of small kingdoms. During the 1st centuries of what is called the "Amorite period", the most powerful city states were Isin
Isin
Isin was an ancient city-state of lower Mesopotamia about 20 miles south of Nippur at the site of modern Ishan al-Bahriyat in Iraq's Al-Qādisiyyah Governorate.-History:...
and Larsa
Larsa
Larsa was an important city of ancient Sumer, the center of the cult of the sun god Utu. It lies some 25 km southeast of Uruk in Iraq's Dhi Qar Governorate, near the east bank of the Shatt-en-Nil canal at the site of the modern settlement Tell as-Senkereh or Sankarah.-History:According to...
, although Shamshi-Adad I
Shamshi-Adad I
Shamshi-Adad I Shamshi-Adad I Shamshi-Adad I (fl. late 18th century BC (short chronology) was an Assyrian king. He rose to prominence when he carved out an empire encompassing much of Mesopotamia, Syria and Asia Minor...
came close to uniting the more northern regions around Assur
Assur
Assur , was one of the capitals of ancient Assyria. The remains of the city are situated on the western bank of river Tigris, north of the confluence with the tributary Little Zab river, in modern day Iraq, more precisely in the Al-Shirqat District .Assur is also...
and Mari
Mari, Syria
Mari was an ancient Sumerian and Amorite city, located 11 kilometers north-west of the modern town of Abu Kamal on the western bank of Euphrates river, some 120 km southeast of Deir ez-Zor, Syria...
. One of these Amorite dynasties was established in the city-state
City-state
A city-state is an independent or autonomous entity whose territory consists of a city which is not administered as a part of another local government.-Historical city-states:...
of Babylon
Babylon
Babylon was an Akkadian city-state of ancient Mesopotamia, the remains of which are found in present-day Al Hillah, Babil Province, Iraq, about 85 kilometers south of Baghdad...
, which would ultimately take over the others and form the first Babylonian empire, during what is also called the Old Babylonian
Old Babylonian
Old Babylonian may refer to:*the period of the First Babylonian Dynasty *the historical stage of the Akkadian language of that time...
Period.
Neo-Assyrian Empire
The Neo-Assyrian Empire is usually considered to have begun with the accession of Adad-nirari IIAdad-nirari II
Adad-nirari II is generally considered to be the first King of Assyria in the Neo-Assyrian period. He firmly subjugated the areas previously under only nominal Assyrian vassalage, conquering and deporting troublesome Aramean, Neo-Hittite and Hurrian populations in the north to far-off places...
, in 911 BC, lasting until the fall of Nineveh
Nineveh
Nineveh was an ancient Assyrian city on the eastern bank of the Tigris River, and capital of the Neo Assyrian Empire. Its ruins are across the river from the modern-day major city of Mosul, in the Ninawa Governorate of Iraq....
at the hands of the Babylonians in 612 BC.
In the Middle Assyrian period, Assyria had been a minor kingdom of northern Mesopotamia, competing for dominance with Babylonia
Babylonia
Babylonia was an ancient cultural region in central-southern Mesopotamia , with Babylon as its capital. Babylonia emerged as a major power when Hammurabi Babylonia was an ancient cultural region in central-southern Mesopotamia (present-day Iraq), with Babylon as its capital. Babylonia emerged as...
to the south. Beginning with the campaigns of Adad-nirari II, Assyria became a great regional power, growing to be a serious threat to 25th dynasty Egypt
Twenty-fifth dynasty of Egypt
The twenty-fifth dynasty of Egypt, known as the Nubian Dynasty or the Kushite Empire, was the last dynasty of the Third Intermediate Period of Ancient Egypt....
. It began reaching the peak of its power with the reforms of Tiglath-Pileser III
Tiglath-Pileser III
Tiglath-Pileser III was a prominent king of Assyria in the eighth century BC and is widely regarded as the founder of the Neo-Assyrian Empire. Tiglath-Pileser III seized the Assyrian throne during a civil war and killed the royal family...
(ruled 745 – 727 BC). This period is well-referenced in several sources, including the Assyro-Babylonian Chronicles
Babylonian Chronicles
The Babylonian Chronicles are many series of tablets recording major events in Babylonian history. They are thus one of the first steps in the development of ancient historiography...
and the Hebrew Bible
Hebrew Bible
The Hebrew Bible is a term used by biblical scholars outside of Judaism to refer to the Tanakh , a canonical collection of Jewish texts, and the common textual antecedent of the several canonical editions of the Christian Old Testament...
. Assyria finally succumbed to the rise of the neo-Babylonian
Neo-Babylonian Empire
The Neo-Babylonian Empire or Second Babylonian Empire was a period of Mesopotamian history which began in 626 BC and ended in 539 BC. During the preceding three centuries, Babylonia had been ruled by their fellow Akkadian speakers and northern neighbours, Assyria. Throughout that time Babylonia...
Chaldean dynasty with the sack of Nineveh
Nineveh
Nineveh was an ancient Assyrian city on the eastern bank of the Tigris River, and capital of the Neo Assyrian Empire. Its ruins are across the river from the modern-day major city of Mosul, in the Ninawa Governorate of Iraq....
in 612 BC.
Neo-Babylonian Empire
Eventually, during the 9th century BC, one of the most powerful tribes outside Babylon, the ChaldeaChaldea
Chaldea or Chaldaea , from Greek , Chaldaia; Akkadian ; Hebrew כשדים, Kaśdim; Aramaic: ܟܐܠܕܘ, Kaldo) was a marshy land located in modern-day southern Iraq which came to briefly rule Babylon...
ns (Latin Chaldaeus, Greek Khaldaios, Assyrian Kaldu), gained prominence. The Chaldeans rose to power in Babylonia and, by doing so, seem to have increased the stability and power of Babylonia. They fought off many revolts and aggressors. Chaldean influence was so strong that, during this period, Babylonia came to be known as Chaldea.
In 626 BC, the Chaldeans helped Nabo-Polassar to take power in Babylonia. At that time, Assyria was under considerable pressure from an Iranian people, the Medes
Medes
The MedesThe Medes...
(from Media). Nabo-Polassar allied Babylonia with the Medes. Assyria
Assyria
Assyria was a Semitic Akkadian kingdom, extant as a nation state from the mid–23rd century BC to 608 BC centred on the Upper Tigris river, in northern Mesopotamia , that came to rule regional empires a number of times through history. It was named for its original capital, the ancient city of Assur...
could not withstand this added pressure, and in 612 BC, Nineveh
Nineveh
Nineveh was an ancient Assyrian city on the eastern bank of the Tigris River, and capital of the Neo Assyrian Empire. Its ruins are across the river from the modern-day major city of Mosul, in the Ninawa Governorate of Iraq....
, the capital of Assyria, fell. The entire city, once the capital of a great empire, was sacked and burned.
Later, Nebuchadnezzar II (Nabopolassar
Nabopolassar
Nabopolassar was the king of the Babylonia and played a key role in the demise of the Assyrian Empire following the death of the last powerful Assyrian king, Ashurbanipal...
's son) inherited the empire of Babylonia. He added quite a bit of territory to Babylonia and rebuilt Babylon, still the capital of Babylonia.
In the 6th century BC (586 BC), Nebuchadnezzar II conquered Judea
Judea
Judea or Judæa was the name of the mountainous southern part of the historic Land of Israel from the 8th century BCE to the 2nd century CE, when Roman Judea was renamed Syria Palaestina following the Jewish Bar Kokhba revolt.-Etymology:The...
(Judah), destroyed Jerusalem; Solomon
Solomon
Solomon , according to the Book of Kings and the Book of Chronicles, a King of Israel and according to the Talmud one of the 48 prophets, is identified as the son of David, also called Jedidiah in 2 Samuel 12:25, and is described as the third king of the United Monarchy, and the final king before...
's Temple
Temple in Jerusalem
The Temple in Jerusalem or Holy Temple , refers to one of a series of structures which were historically located on the Temple Mount in the Old City of Jerusalem, the current site of the Dome of the Rock. Historically, these successive temples stood at this location and functioned as the centre of...
was also destroyed; Nebuchadnezzar II carried away an estimated 15,000 captives, and sent most of its population into exile in Babylonia. Nebuchadnezzar II (604-562 BC) is credited for building the legendary Hanging Gardens of Babylon
Hanging Gardens of Babylon
The Hanging Gardens of Babylon were considered to be one of the greatest Seven Wonders of the Ancient World, and the only one of the Wonders which may in fact have been legendary. They were purportedly built in the ancient city-state of Babylon, near present-day Al Hillah, Babil, in Iraq...
, one of the Seven Wonders of the World.
Achaemenid and Seleucid rule
Various invaders conquered the land after Nebuchadnezzar's death, including Cyrus the GreatCyrus the Great
Cyrus II of Persia , commonly known as Cyrus the Great, also known as Cyrus the Elder, was the founder of the Achaemenid Empire. Under his rule, the empire embraced all the previous civilized states of the ancient Near East, expanded vastly and eventually conquered most of Southwest Asia and much...
in 539 BC and Alexander the Great in 331 BC, who died there in 323 BC. In the 6th century BC, it became part of the Achaemenid Empire
Achaemenid Empire
The Achaemenid Empire , sometimes known as First Persian Empire and/or Persian Empire, was founded in the 6th century BCE by Cyrus the Great who overthrew the Median confederation...
, then was conquered by Alexander the Great and remained under Greek
Hellenistic Greece
In the context of Ancient Greek art, architecture, and culture, Hellenistic Greece corresponds to the period between the death of Alexander the Great in 323 BC and the annexation of the classical Greek heartlands by Rome in 146 BC...
rule under the Seleucid dynasty for nearly two centuries. Babylon
Babylon
Babylon was an Akkadian city-state of ancient Mesopotamia, the remains of which are found in present-day Al Hillah, Babil Province, Iraq, about 85 kilometers south of Baghdad...
declined after the founding of Seleucia on the Tigris
Seleucia on the Tigris
Seleucia , also known as Seleucia on the Tigris, was one of the great cities of the world during Hellenistic and Roman times. It stood in Mesopotamia, on the west bank of the Tigris River, opposite the smaller town of Ctesiphon, in present day Babil Governorate, Iraq.-Seleucid empire:Seleucia,...
, the new Seleucid Empire
Seleucid Empire
The Seleucid Empire was a Greek-Macedonian state that was created out of the eastern conquests of Alexander the Great. At the height of its power, it included central Anatolia, the Levant, Mesopotamia, Persia, today's Turkmenistan, Pamir and parts of Pakistan.The Seleucid Empire was a major centre...
capital.
Parthian and Roman rule
The Seleucids were succeeded by the Parthian EmpireParthian Empire
The Parthian Empire , also known as the Arsacid Empire , was a major Iranian political and cultural power in ancient Persia...
in the 3rd century BC. At the beginning of the 2nd century AD, the Romans
Roman Empire
The Roman Empire was the post-Republican period of the ancient Roman civilization, characterised by an autocratic form of government and large territorial holdings in Europe and around the Mediterranean....
, led by emperor Trajan
Trajan
Trajan , was Roman Emperor from 98 to 117 AD. Born into a non-patrician family in the province of Hispania Baetica, in Spain Trajan rose to prominence during the reign of emperor Domitian. Serving as a legatus legionis in Hispania Tarraconensis, in Spain, in 89 Trajan supported the emperor against...
, invaded Parthia and conquered Mesopotamia, making it an imperial province. It was returned to the Parthians shortly after by Trajan's successor, Hadrian
Hadrian
Hadrian , was Roman Emperor from 117 to 138. He is best known for building Hadrian's Wall, which marked the northern limit of Roman Britain. In Rome, he re-built the Pantheon and constructed the Temple of Venus and Roma. In addition to being emperor, Hadrian was a humanist and was philhellene in...
.
Sassanid Empire
In the 3rd century AD, the Parthians were in turn succeeded by the Sassanid dynasty, which ruled Mesopotamia until the 7th century Islamic conquest.In the mid-6th century the Persian Empire under the Sassanid dynasty was divided by Khosrow I into four quarters, of which the western one, called Khvārvarān, included most of modern Iraq, and subdivided to provinces of Mishān, Asuristān, Ādiābene and Lower Media. The term Iraq is widely used in the medieval Arabic sources for the area in the centre and south of the modern republic as a geographic rather than a political term, implying no greater precision of boundaries than the term "Mesopotamia" or, indeed, many of the names of modern states before the 20th century.
The area of modern Iraq north of Tikrit
Tikrit
Tikrit is a town in Iraq, located 140 km northwest of Baghdad on the Tigris river . The town, with an estimated population in 2002 of about 260,000 is the administrative center of the Salah ad Din Governorate.-Ancient times:...
was known in Muslim times as Al-Jazirah, which means "The Island" and refers to the "island" between the Tigris and Euphrates rivers. To the south and west lay the Arabian deserts, inhabited largely by Arab tribesmen who occasionally acknowledged the overlordship of the Sassanian Emperors.
Until 602, the desert frontier of the Persian Empire had been guarded by the Arab
Arab
Arab people, also known as Arabs , are a panethnicity primarily living in the Arab world, which is located in Western Asia and North Africa. They are identified as such on one or more of genealogical, linguistic, or cultural grounds, with tribal affiliations, and intra-tribal relationships playing...
Lakhmid kings of Al-Hirah
Al-Hirah
Al Hīra was an ancient city located south of al-Kufah in south-central Iraq.- Middle Ages:Al Hīra was a significant city in pre-Islamic Arab history. Originally a military encampment, in the 5th and 6th centuries CE it became the capital of the Lakhmids.The Arabs were migrating into the Near East...
, who were themselves Arabs but who ruled a settled buffer state. In that year Shahanshah Khosrow II Aparviz (Persian خسرو پرويز) rashly abolished the Lakhmid kingdom and laid the frontier open to nomad incursions. Farther north, the western quarter was bounded by the Byzantine Empire. The frontier more or less followed the modern Syria
Syria
Syria , officially the Syrian Arab Republic , is a country in Western Asia, bordering Lebanon and the Mediterranean Sea to the West, Turkey to the north, Iraq to the east, Jordan to the south, and Israel to the southwest....
-Iraq border and continued northward into modern Turkey
Turkey
Turkey , known officially as the Republic of Turkey , is a Eurasian country located in Western Asia and in East Thrace in Southeastern Europe...
, leaving Nisibis
Nisibis
Nusaybin Nisêbîn) is a city in Mardin Province, Turkey, populated mainly by Kurds. Earlier Arameans, Arabs, and Armenians lived in the city. The population of the city is 83,832 as of 2009.-Ancient Period:...
(modern Nusaybin) as the Sassanian frontier fortress while the Byzantines
Byzantine Empire
The Byzantine Empire was the Eastern Roman Empire during the periods of Late Antiquity and the Middle Ages, centred on the capital of Constantinople. Known simply as the Roman Empire or Romania to its inhabitants and neighbours, the Empire was the direct continuation of the Ancient Roman State...
held Dara and nearby Amida
Amida
Amida can mean:* Amitabha, an important Buddha in East Asian Buddhism* Amida , a beetle genus* Amida Buddha* Amidah, the central prayer of the Jewish services* Amidakuji, a way of drawing lots* Amitabh Bachchan, an actor...
(modern Diyarbakır
Diyarbakır
Diyarbakır is one of the largest cities in southeastern Turkey...
).
Arab conquest and Abbasid Caliphate

The first organised conflict between local Arab tribes and Persian forces seems to have been in 634, when the Arabs were defeated at the Battle of the Bridge. There was a force of some 5,000 Muslims under Abū `Ubayd ath-Thaqafī, which was routed by the Persians. This was followed by Khalid ibn al-Walid
Khalid ibn al-Walid
Khālid ibn al-Walīd also known as Sayf Allāh al-Maslūl , was a companion of the Islamic prophet Muhammad. He is noted for his military tactics and prowess, commanding the forces of Medina and those of his immediate successors of the Rashidun Caliphate; Abu Bakr and Umar...
's successful campaign which saw all of Iraq come under Arab rule within a year, with the exception of the Persian Empire's capital, Ctesiphon
Ctesiphon
Ctesiphon, the imperial capital of the Parthian Arsacids and of the Persian Sassanids, was one of the great cities of ancient Mesopotamia.The ruins of the city are located on the east bank of the Tigris, across the river from the Hellenistic city of Seleucia...
. Around 636, a larger Arab Muslim force under Sa`d ibn Abī Waqqās
Sa`d ibn Abi Waqqas
Saad ibn Abī Waqqās was an early convert to Islam in 610-11 and one of the important companions of the Islamic prophet Muhammad. Sa'd was the seventeenth person to embrace Islam at the age of seventeen...
defeated the main Persian army at the Battle of al-Qādisiyyah
Battle of al-Qadisiyyah
The Battle of al-Qādisiyyah was fought in 636; it was the decisive engagement between the Arab muslim army and the Sassanid Persian army during the first period of Muslim expansion. It resulted in the Islamic conquest of Persia, and was key to the conquest of Iraq...
and moved on to capture the Persian capital of Ctesiphon. By the end of 638, the Muslims had conquered all of the Western Sassanid provinces (including modern Iraq), and the last Sassanid Emperor, Yazdegerd III, had fled to central and then northern Persia, where he was killed in 651.
The Islamic conquest was followed by mass immigration of Arabs from eastern Arabia and Mazun (Oman
Oman
Oman , officially called the Sultanate of Oman , is an Arab state in southwest Asia on the southeast coast of the Arabian Peninsula. It is bordered by the United Arab Emirates to the northwest, Saudi Arabia to the west, and Yemen to the southwest. The coast is formed by the Arabian Sea on the...
) to Khvarvārān. These new arrivals did not disperse and settle throughout the country; instead they established two new garrison cities, at al-Kūfah, near ancient Babylon, and at Basra
Basra
Basra is the capital of Basra Governorate, in southern Iraq near Kuwait and Iran. It had an estimated population of two million as of 2009...
h in the south.
The intention was that the Muslims should be a separate community of fighting men and their families living off taxes paid by the local inhabitants. In the north of the North eastern Iran, Mosul
Mosul
Mosul , is a city in northern Iraq and the capital of the Ninawa Governorate, some northwest of Baghdad. The original city stands on the west bank of the Tigris River, opposite the ancient Assyrian city of Nineveh on the east bank, but the metropolitan area has now grown to encompass substantial...
began to emerge as the most important city and the base of a Muslim governor and garrison. Apart from the Persian elite and the Zoroastrian priests, who did not convert to Islam and thus lost their lives and property, most of the Mesopotamian peoples became Muslim and were allowed to keep their possessions.
Khvarvārān, now became a province of the Muslim Caliphate
Caliphate
The term caliphate, "dominion of a caliph " , refers to the first system of government established in Islam and represented the political unity of the Muslim Ummah...
, known as `Irāq. The city of Baghdad
Baghdad
Baghdad is the capital of Iraq, as well as the coterminous Baghdad Governorate. The population of Baghdad in 2011 is approximately 7,216,040...
was built in the 8th century and became the capital of the Abbasid Caliphate. During this period, Baghdad served as the intellectual center of the Muslim world
Muslim world
The term Muslim world has several meanings. In a religious sense, it refers to those who adhere to the teachings of Islam, referred to as Muslims. In a cultural sense, it refers to Islamic civilization, inclusive of non-Muslims living in that civilization...
for several centuries, up until the sack of Baghdad
Battle of Baghdad (1258)
The Siege of Baghdad, which occurred in 1258, was an invasion, siege and sacking of the city of Baghdad, the capital of the Abbasid Caliphate at the time and the modern-day capital of Iraq, by the Ilkhanate Mongol forces along with other allied troops under Hulagu Khan.The invasion left Baghdad in...
in 1258. Many famous Muslim scientists, philosophers
Early Islamic philosophy
Early Islamic philosophy or classical Islamic philosophy is a period of intense philosophical development beginning in the 2nd century AH of the Islamic calendar and lasting until the 6th century AH...
, inventors, poets
Arabic poetry
Arabic poetry is the earliest form of Arabic literature. Present knowledge of poetry in Arabic dates from the 6th century, but oral poetry is believed to predate that. Arabic poetry is categorized into two main types, rhymed, or measured, and prose, with the former greatly preceding the latter...
and writers
Arabic literature
Arabic literature is the writing produced, both prose and poetry, by writers in the Arabic language. The Arabic word used for literature is adab which is derived from a meaning of etiquette, and implies politeness, culture and enrichment....
were active in Iraq during the 8th to 13th centuries.
Ottoman Iraq and Mamluk rule
During the late 14th and early 15th centuries, the Black Sheep Turkmen ruled the area now known as Iraq. In 1466, the White Sheep Turkmen defeated the Black Sheep and took control. In the 16th century, most of the territory of present-day Iraq came under the control of Ottoman EmpireOttoman Empire
The Ottoman EmpireIt was usually referred to as the "Ottoman Empire", the "Turkish Empire", the "Ottoman Caliphate" or more commonly "Turkey" by its contemporaries...
as the pashalik of Baghdad. Throughout most of the period of Ottoman rule (1533-1918) the territory of present-day Iraq was a battle zone between the rival regional empires and tribal alliances.
Iraq was divided into three vilayets:
- Mosul ProvinceMosul Province, Ottoman EmpireThe Vilayet of Mosul was a vilayet of the Ottoman Empire. It was created from the northern sanjaks of the Vilayet of Baghdad in 1878.At the beginning of the 20th century it reportedly had an area of , while the preliminary results of the first Ottoman census of 1885 gave the population as 300,280...
- Baghdad ProvinceBaghdad Province, Ottoman EmpireThe Vilayet of Baghdad was a vilayet of the Ottoman Empire. The capital was Baghdad....
- Basra Province
The Safavid dynasty
Safavid dynasty
The Safavid dynasty was one of the most significant ruling dynasties of Iran. They ruled one of the greatest Persian empires since the Muslim conquest of Persia and established the Twelver school of Shi'a Islam as the official religion of their empire, marking one of the most important turning...
of Iran
Iran
Iran , officially the Islamic Republic of Iran , is a country in Southern and Western Asia. The name "Iran" has been in use natively since the Sassanian era and came into use internationally in 1935, before which the country was known to the Western world as Persia...
briefly asserted their hegemony over Iraq in the periods of 1508-1533 and 1622-1638. During the years 1747-1831 Iraq was ruled by the Mamluk
Mamluk
A Mamluk was a soldier of slave origin, who were predominantly Cumans/Kipchaks The "mamluk phenomenon", as David Ayalon dubbed the creation of the specific warrior...
officers of Georgian
Georgia (country)
Georgia is a sovereign state in the Caucasus region of Eurasia. Located at the crossroads of Western Asia and Eastern Europe, it is bounded to the west by the Black Sea, to the north by Russia, to the southwest by Turkey, to the south by Armenia, and to the southeast by Azerbaijan. The capital of...
origin who succeeded in obtaining autonomy from the Ottoman Empire
Ottoman Empire
The Ottoman EmpireIt was usually referred to as the "Ottoman Empire", the "Turkish Empire", the "Ottoman Caliphate" or more commonly "Turkey" by its contemporaries...
, suppressed tribal revolts, curbed the power of the Janissaries, restored order and introduced a program of modernization of economy and military. In 1831, the Ottomans managed to overthrow the Mamluk regime and again imposed their direct control over Iraq.
British mandate and Kingdom of Iraq
Ottoman rule over Iraq lasted until World War IWorld War I
World War I , which was predominantly called the World War or the Great War from its occurrence until 1939, and the First World War or World War I thereafter, was a major war centred in Europe that began on 28 July 1914 and lasted until 11 November 1918...
when the Ottomans sided with Germany
Germany
Germany , officially the Federal Republic of Germany , is a federal parliamentary republic in Europe. The country consists of 16 states while the capital and largest city is Berlin. Germany covers an area of 357,021 km2 and has a largely temperate seasonal climate...
and the Central Powers
Central Powers
The Central Powers were one of the two warring factions in World War I , composed of the German Empire, the Austro-Hungarian Empire, the Ottoman Empire, and the Kingdom of Bulgaria...
. In the Mesopotamian campaign
Mesopotamian Campaign
The Mesopotamian campaign was a campaign in the Middle Eastern theatre of World War I fought between the Allies represented by the British Empire, mostly troops from the Indian Empire, and the Central Powers, mostly of the Ottoman Empire.- Background :...
against the Central Powers, British
United Kingdom
The United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern IrelandIn the United Kingdom and Dependencies, other languages have been officially recognised as legitimate autochthonous languages under the European Charter for Regional or Minority Languages...
forces invaded the country and suffered a major defeat at the hands of the Turkish army during the Siege of Kut
Siege of Kut
The siege of Kut Al Amara , was the besieging of 8,000 strong British-Indian garrison in the town of Kut, 100 miles south of Baghdad, by the Ottoman Army. Its known also as 1st Battle of Kut. In 1915, its population was around 6,500...
(1915–16). After the war the Ottoman Empire was divided up, and the British Mandate of Mesopotamia was established by League of Nations mandate
League of Nations mandate
A League of Nations mandate was a legal status for certain territories transferred from the control of one country to another following World War I, or the legal instruments that contained the internationally agreed-upon terms for administering the territory on behalf of the League...
. Britain imposed a Hāshimite
Hashemite
Hashemite is the Latinate version of the , transliteration: Hāšimī, and traditionally refers to those belonging to the Banu Hashim, or "clan of Hashim", a clan within the larger Quraish tribe...
monarchy on Iraq and defined the territorial limits of Iraq without taking into account the politics of the different ethnic and religious groups in the country, in particular those of the Kurds and the Assyrians
Assyrian people
The Assyrian people are a distinct ethnic group whose origins lie in ancient Mesopotamia...
to the north. During the British occupation, the Shi'ites and Kurds fought for independence. Iraq also became an oligarchy government at this time.
Although the monarch Faisal I of Iraq
Faisal I of Iraq
Faisal bin Hussein bin Ali al-Hashemi, was for a short time King of the Arab Kingdom of Syria or Greater Syria in 1920, and was King of the Kingdom of Iraq from 23 August 1921 to 1933...
was legitimized and proclaimed King by a plebiscite in 1921, nominal independence was only achieved in 1932, when the British Mandate officially ended. Establishment of Arab Sunni domination was followed by Shi'a unrests in the south, reaching a scale of rebellions in 1935-1936, which were brutally suppressed.
During World War II
World War II
World War II, or the Second World War , was a global conflict lasting from 1939 to 1945, involving most of the world's nations—including all of the great powers—eventually forming two opposing military alliances: the Allies and the Axis...
, Iraqi regime of Regent 'Abd al-Ilah
'Abd al-Ilah
Crown Prince Abd al-Ilāh of Hejaz, GCB, GCMG, GCVO was a cousin and brother-in-law of King Ghazi of the Kingdom of Iraq. Abdul Ilah served as Regent for King Faisal II from April 4, 1939 to May 2, 1953, when Faisal came of age...
was overthrown in 1941 by the Golden Square
Golden Square (Iraq)
The Golden Square was a group of four officers of the Iraqi armed forces who played a part in Iraqi politics throughout the 1930s and early 1940s...
officers, headed by Rashid Ali. The short living pro-Nazi government of Iraq was defeated in May 1941 by the allied forces in Anglo-Iraqi War
Anglo-Iraqi War
The Anglo-Iraqi War was the name of the British campaign against the rebel government of Rashid Ali in the Kingdom of Iraq during the Second World War. The war lasted from 2 May to 31 May 1941. The campaign resulted in the re-occupation of Iraq by British armed forces and the return to power of the...
. Iraq was later used as a base for allied attacks on Vichi-French held Mandate of Syria and support for the Anglo-Soviet invasion of Iran
Anglo-Soviet invasion of Iran
The Anglo-Soviet invasion of Iran was the Allied invasion of the Imperial State of Iran during World War II, by British, Commonwealth, and Soviet armed forces. The invasion from August 25 to September 17, 1941, was codenamed Operation Countenance...
.
In 1945, Iraq joined the United Nations
United Nations
The United Nations is an international organization whose stated aims are facilitating cooperation in international law, international security, economic development, social progress, human rights, and achievement of world peace...
and became a founding member of the Arab League
Arab League
The Arab League , officially called the League of Arab States , is a regional organisation of Arab states in North and Northeast Africa, and Southwest Asia . It was formed in Cairo on 22 March 1945 with six members: Egypt, Iraq, Transjordan , Lebanon, Saudi Arabia, and Syria. Yemen joined as a...
. At the same time, the Kurdish leader Mustafa Barzani
Mustafa Barzani
Mustafa Barzani also known as Mullah Mustafa was a Kurdish nationalist leader, and the most prominent political figure in the modern Kurdish politics. In 1946 he was chosen as the leader of the Kurdistan Democratic Party to lead the Kurdish revolution against Iraqi regimes...
led a rebellion against the central government in Baghdad. After the failure of the uprising Barzani and his followers fled to the Soviet Union
Soviet Union
The Soviet Union , officially the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics , was a constitutionally socialist state that existed in Eurasia between 1922 and 1991....
.
In 1948, massive violent protests, known as the Al-Wathbah uprising broke out across Baghdad as a popular demand against the government treat with the British, and with communist part support. More protests continued in spring, but were interrupted in May, with the marshal law, when Iraq entered the 1948 Arab-Israeli War
1948 Arab-Israeli War
The 1948 Arab–Israeli War, known to Israelis as the War of Independence or War of Liberation The war commenced after the termination of the British Mandate for Palestine and the creation of an independent Israel at midnight on 14 May 1948 when, following a period of civil war, Arab armies invaded...
along with other members of the Arab League.
In February 1958, King Hussein of Jordan
Hussein of Jordan
Hussein bin Talal was the third King of Jordan from the abdication of his father, King Talal, in 1952, until his death. Hussein's rule extended through the Cold War and four decades of Arab-Israeli conflict...
and `Abd al-Ilāh proposed a union of Hāshimite monarchies to counter the recently formed Egyptian-Syrian union. The prime minister Nuri as-Said
Nuri as-Said
Nuri Pasha al-Said was an Iraqi politician during the British Mandate and during the Kingdom of Iraq. He served in various key cabinet positions, and served seven terms as Prime Minister of Iraq....
wanted Kuwait
Kuwait
The State of Kuwait is a sovereign Arab state situated in the north-east of the Arabian Peninsula in Western Asia. It is bordered by Saudi Arabia to the south at Khafji, and Iraq to the north at Basra. It lies on the north-western shore of the Persian Gulf. The name Kuwait is derived from the...
to be part of the proposed Arab-Hāshimite Union. Shaykh `Abd-Allāh as-Salīm, the ruler of Kuwait, was invited to Baghdad to discuss Kuwait's future. This policy brought the government of Iraq into direct conflict with Britain, which did not want to grant independence to Kuwait. At that point, the monarchy found itself completely isolated. Nuri as-Said was able to contain the rising discontent only by resorting to ever greater political oppression.
Republic of Iraq
Inspired by Nasser, officers from the Nineteenth Brigade, 3rd Division3rd Division (Iraq)
The 3rd Division is a formation of the Iraqi Army. It was active by 1941, disbanded along with the rest of the Iraqi Army in 2003, but reactivated by 2005.-History:...
known as "The Four Colonials", under the leadership of Brigadier Abd al-Karīm Qāsim (known as "az-Za`īm", 'the leader') and Colonel Abdul Salam Arif
Abdul Salam Arif
Abdul Salam Mohammed Arif Aljumaily was President of Iraq from 1963 till his death. He played a leading role in the coup in which the Hashemite monarchy was overthrown on July 14, 1958.-1958 revolution and conflict with Qasim:...
overthrew the Hashimite monarchy on July 14, 1958
14 July Revolution
The 14 July Revolution was a coup which took place on 14 July 1958 in Iraq, marking the overthrow of the Hashemite monarchy established by King Faisal I in 1932 under the auspices of the British. In 1958, the coup overthrew King Faisal II, the regent and Crown Prince 'Abd al-Ilah, and Prime...
. The new government proclaimed Iraq to be a republic
Republic
A republic is a form of government in which the people, or some significant portion of them, have supreme control over the government and where offices of state are elected or chosen by elected people. In modern times, a common simplified definition of a republic is a government where the head of...
and rejected the idea of a union with Jordan. Iraq's activity in the Baghdad Pact ceased.
In 1961, Kuwait
Kuwait
The State of Kuwait is a sovereign Arab state situated in the north-east of the Arabian Peninsula in Western Asia. It is bordered by Saudi Arabia to the south at Khafji, and Iraq to the north at Basra. It lies on the north-western shore of the Persian Gulf. The name Kuwait is derived from the...
gained independence from Britain and Iraq claimed sovereignty over Kuwait. A period of considerable instability followed. The same year, Mustafa Barzani
Mustafa Barzani
Mustafa Barzani also known as Mullah Mustafa was a Kurdish nationalist leader, and the most prominent political figure in the modern Kurdish politics. In 1946 he was chosen as the leader of the Kurdistan Democratic Party to lead the Kurdish revolution against Iraqi regimes...
, who had been invited to return to Iraq by Qasim three years earlier, began engaging Iraqi government forces and establishing Kurdish control in the north in what was the beginning of the First Kurdish Iraqi War
First Kurdish Iraqi War
First Kurdish Iraqi War was a tribal Kurdish uprising, led by Mustafa Barzani, in an attempt to establish independent Kurdish state in north Iraq. Throughout the 1960s, the uprising escalated into a long war, which failed to resolve despite internal power changes in Iraq...
.
Ba'athist Iraq
Qāsim was assassinated in February 1963, when the Ba'ath Party took powerFebruary 1963 Iraqi coup d'état
The February 1963 Iraqi coup d'état was a February 8, 1963 armed military coup by the Ba'ath Party's Iraqi wing which overthrew the regime of the Prime Minister of Iraq, Brigadier General Abd al-Karim Qasim. General Ahmed Hasan al-Bakr became the new Prime Minister and Colonel Abdul Salam Arif...
under the leadership of General Ahmed Hasan al-Bakr (prime minister
Prime minister
A prime minister is the most senior minister of cabinet in the executive branch of government in a parliamentary system. In many systems, the prime minister selects and may dismiss other members of the cabinet, and allocates posts to members within the government. In most systems, the prime...
) and Colonel Abdul Salam Arif
Abdul Salam Arif
Abdul Salam Mohammed Arif Aljumaily was President of Iraq from 1963 till his death. He played a leading role in the coup in which the Hashemite monarchy was overthrown on July 14, 1958.-1958 revolution and conflict with Qasim:...
(president). In June 1963, Syria, which meanwhile had also fell under Ba'athist rule, took part in the Iraqi military campaign
Military campaign
In the military sciences, the term military campaign applies to large scale, long duration, significant military strategy plan incorporating a series of inter-related military operations or battles forming a distinct part of a larger conflict often called a war...
against the Kurds by providing aircraft, armoured vehicles and a force of 6,000 soldiers. Several months later, `Abd as-Salam Muhammad `Arif led a successful coup against the Ba'ath government. Arif declared a ceasefire in February 1964 which provoked a split among Kurdish urban radicals on one hand and Peshmerga (Freedom fighters) forces led by Barzani on the other.
On April 13, 1966, President Abdul Salam Arif died in a helicopter crash and was succeeded by his brother, General Abdul Rahman Arif
Abdul Rahman Arif
Hajj Abdul Rahman Mohammed Arif Aljumaily was president of Iraq from April 16, 1966 to July 17, 1968.-Biography:...
. Following the unexpected death of Arif, where upon he was replaced by his brother, Abdul Rahman Arif, the Iraqi government launched a last-ditch effort to defeat the Kurds. This campaign failed in May 1966, when Barzani forces thoroughly defeated the Iraqi Army at the Battle of Mount Handrin, near Rawanduz. Following the Six Day War of 1967, the Ba'ath Party felt strong enough to retake power (July 17, 1968). Ahmad Hasan al-Bakr became president and chairman of the Revolutionary Command Council (RCC). The Ba'ath government started a campaign to end the Kurdish insurrection
First Kurdish Iraqi War
First Kurdish Iraqi War was a tribal Kurdish uprising, led by Mustafa Barzani, in an attempt to establish independent Kurdish state in north Iraq. Throughout the 1960s, the uprising escalated into a long war, which failed to resolve despite internal power changes in Iraq...
, which stalled in 1969. This can be partly attributed to the internal power struggle in Baghdad and also tensions with Iran. Moreover, the Soviet Union pressured the Iraqis to come to terms with Barzani. The war ended with more than 100,000 mortal casualties, with little achievements to both Kurdish rebels and the Iraqi government.
In the aftermath of the First Kurdish Iraqi War
First Kurdish Iraqi War
First Kurdish Iraqi War was a tribal Kurdish uprising, led by Mustafa Barzani, in an attempt to establish independent Kurdish state in north Iraq. Throughout the 1960s, the uprising escalated into a long war, which failed to resolve despite internal power changes in Iraq...
, a peace plan was announced in March 1970 and provided for broader Kurdish autonomy. The plan also gave Kurds representation in government bodies, to be implemented in four years. Despite this, the Iraqi government embarked on an Arabization program in the oil rich regions of Kirkuk and Khanaqin
Khanaqin
Khanaqin is a city in Iraq. It is located at 34.3°N, 45.4°E in the Diyala Governorate, near the Iranian border on a tributary of the Diyala River...
in the same period. In the following years, Baghdad government overcame its internal divisions and concluded a treaty of friendship with the Soviet Union in April 1972 and ended its isolation within the Arab world. On the other hand, Kurds remained dependent on the Iranian military support and could do little to strengthen their forces. By 1974 the situation in the north escalated again into the Second Kurdish Iraqi War
Second Kurdish Iraqi War
Second Kurdish Iraqi War was an offensive, led by Iraqi forces against rebel KDP troops of Mustafa Barzani during 1974-1975. The war came in the aftermath of the First Kurdish Iraqi War , as the 1970 peace plan for Kurdish autonomy had failed....
, to last until 1975.
Under Saddam Hussein

Ahmed Hassan al-Bakr
General Ahmed Hassan al-Bakr , was the fourth President of Iraq from 1968 to 1979.-Military career:...
resigned, and his chosen successor, General Saddam Hussein
Saddam Hussein
Saddam Hussein Abd al-Majid al-Tikriti was the fifth President of Iraq, serving in this capacity from 16 July 1979 until 9 April 2003...
, assumed the offices of both President and Chairman of the Revolutionary Command Council.
Territorial disputes with Iran
Iran
Iran , officially the Islamic Republic of Iran , is a country in Southern and Western Asia. The name "Iran" has been in use natively since the Sassanian era and came into use internationally in 1935, before which the country was known to the Western world as Persia...
led to an inconclusive and costly eight-year war, the Iran–Iraq War (1980–1988, termed Qādisiyyat
Battle of al-Qadisiyyah
The Battle of al-Qādisiyyah was fought in 636; it was the decisive engagement between the Arab muslim army and the Sassanid Persian army during the first period of Muslim expansion. It resulted in the Islamic conquest of Persia, and was key to the conquest of Iraq...
-Saddām – 'Saddam's Qādisiyyah
Battle of al-Qadisiyyah
The Battle of al-Qādisiyyah was fought in 636; it was the decisive engagement between the Arab muslim army and the Sassanid Persian army during the first period of Muslim expansion. It resulted in the Islamic conquest of Persia, and was key to the conquest of Iraq...
'), which devastated the economy. Iraq declared victory in 1988 but actually achieved a weary return to the status quo ante bellum
Status quo ante bellum
The term status quo ante bellum is Latin, meaning literally "the state in which things were before the war".The term was originally used in treaties to refer to the withdrawal of enemy troops and the restoration of prewar leadership. When used as such, it means that no side gains or loses...
. The war lasted for eight years, making it the longest conventional war of the twentieth century.
The war began when Iraq invaded Iran, launching a simultaneous invasion by air and land into Iranian territory on 22 September 1980, following a long history of border disputes
Territorial dispute
A territorial dispute is a disagreement over the possession/control of land between two or more states or over the possession or control of land by a new state and occupying power after it has conquered the land from a former state no longer currently recognized by the new state.-Context and...
, and fears of Shia insurgency among Iraq's long-suppressed Shia majority influenced by the Iranian Revolution
Iranian Revolution
The Iranian Revolution refers to events involving the overthrow of Iran's monarchy under Shah Mohammad Reza Pahlavi and its replacement with an Islamic republic under Ayatollah Ruhollah Khomeini, the leader of the...
. Iraq was also aiming to replace Iran as the dominant Persian Gulf
Persian Gulf
The Persian Gulf, in Southwest Asia, is an extension of the Indian Ocean located between Iran and the Arabian Peninsula.The Persian Gulf was the focus of the 1980–1988 Iran-Iraq War, in which each side attacked the other's oil tankers...
state
State (polity)
A state is an organized political community, living under a government. States may be sovereign and may enjoy a monopoly on the legal initiation of force and are not dependent on, or subject to any other power or state. Many states are federated states which participate in a federal union...
. Although Iraq hoped to take advantage of the revolutionary chaos in Iran and attacked without formal warning, they made only limited progress into Iran and within several months were repelled by the Iranians who regained virtually all lost territory by June 1982. For the next six years, Iran was on the offensive. Despite calls for a ceasefire
United Nations Security Council resolutions concerning Iraq
The United Nations Security Council is the bhosad chod organ of the United Nations charged with maintaining peace and security among nations. While other organs of the United Nations only make recommendations to member governments, the Security Council has the power to make decisions which member...
by the United Nations Security Council
United Nations Security Council
The United Nations Security Council is one of the principal organs of the United Nations and is charged with the maintenance of international peace and security. Its powers, outlined in the United Nations Charter, include the establishment of peacekeeping operations, the establishment of...
, hostilities continued until 20 August 1988. The war finally ended with a United Nations brokered ceasefire in the form of United Nations Security Council Resolution 598
United Nations Security Council Resolution 598
United Nations Security Council Resolution 598, adopted unanimously on July 20, 1987, after reaffirming Resolution 582 , the Council expressed its concern that, despite its calls for a ceasefire, the conflict between Iran and Iraq continued with heavy loss of life and material destruction.Acting...
, which was accepted by both sides. It took several weeks for the Iranian armed forces to evacuate Iraqi territory to honor pre-war international borders between the two nations (see 1975 Algiers Agreement). The last prisoners of war
Prisoner of war
A prisoner of war or enemy prisoner of war is a person, whether civilian or combatant, who is held in custody by an enemy power during or immediately after an armed conflict...
were exchanged in 2003.
The war came at a great cost in lives and economic damage—half a million Iraqi and Iranian soldiers as well as civilians are believed to have died in the war with many more injured—but it brought neither reparations nor change in borders. The conflict is often compared to World War I
World War I
World War I , which was predominantly called the World War or the Great War from its occurrence until 1939, and the First World War or World War I thereafter, was a major war centred in Europe that began on 28 July 1914 and lasted until 11 November 1918...
, in that the tactics used closely mirrored those of that conflict, including large scale trench warfare
Trench warfare
Trench warfare is a form of occupied fighting lines, consisting largely of trenches, in which troops are largely immune to the enemy's small arms fire and are substantially sheltered from artillery...
, manned machine-gun posts, bayonet charges, use of barbed wire
Barbed wire
Barbed wire, also known as barb wire , is a type of fencing wire constructed with sharp edges or points arranged at intervals along the strand. It is used to construct inexpensive fences and is used atop walls surrounding secured property...
across trenches, human wave attacks across no-man's land, and extensive use of chemical weapons such as mustard gas by the Iraqi government against Iranian troops and civilians as well as Iraqi Kurd
Kürd
Kürd or Kyurd or Kyurt may refer to:*Kürd Eldarbəyli, Azerbaijan*Kürd Mahrızlı, Azerbaijan*Kürd, Goychay, Azerbaijan*Kürd, Jalilabad, Azerbaijan*Kürd, Qabala, Azerbaijan*Qurdbayram, Azerbaijan...
s. At the time, the UN Security Council issued statements that "chemical weapons had been used in the war." However, in these UN statements it was never made clear that it was only Iraq that was using chemical weapons, so it has been said that "the international community remained silent as Iraq used weapons of mass destruction against Iranian as well as Iraqi Kurds" and it is believed that the "United States prevented the UN from condemning Iraq".
A long-standing territorial dispute was the ostensible reason for Iraq's invasion of Kuwait
Invasion of Kuwait
The Invasion of Kuwait, also known as the Iraq-Kuwait War, was a major conflict between the Republic of Iraq and the State of Kuwait, which resulted in the seven-month long Iraqi occupation of Kuwait, which subsequently led to direct military intervention by United States-led forces in the Gulf...
in 1990. In November 1990, the UN Security Council adopted Resolution 678, permitting member states to use all necessary means, authorizing military action against the Iraqi forces occupying Kuwait and demanded a complete withdrawal by January 15, 1991. When Saddam Hussein failed to comply with this demand, the Gulf War
Gulf War
The Persian Gulf War , commonly referred to as simply the Gulf War, was a war waged by a U.N.-authorized coalition force from 34 nations led by the United States, against Iraq in response to Iraq's invasion and annexation of Kuwait.The war is also known under other names, such as the First Gulf...
(Operation "Desert Storm") ensued on January 17, 1991. Probably as many as 100,000 Iraqi soldiers and tens of thousands of civilians were killed.
In March 1991 revolts in the Shia-dominated southern Iraq started involving demoralized Iraqi Army
Iraqi Army
The Iraqi Army is the land component of the Iraqi military, active in various forms since being formed by the British during their mandate over the country after World War I....
troops and the anti-government Shia parties. Another wave of insurgency broke out shortly afterwards in the Kurdish
Kurdish people
The Kurdish people, or Kurds , are an Iranian people native to the Middle East, mostly inhabiting a region known as Kurdistan, which includes adjacent parts of Iran, Iraq, Syria, and Turkey...
populated northern Iraq (see 1991 uprisings in Iraq
1991 uprisings in Iraq
The 1991 uprisings in Iraq were a series of anti-governmental rebellions in southern and northern Iraq during the aftermath of the Gulf War. The revolt was fueled by the perception that the power of Iraqi President Saddam Hussein was vulnerable at the time; as well as by heavily fueled anger at...
). Although they presented a serious threat to the Iraqi Ba'ath Party regime, Saddam Hussein managed to suppress the rebellions with massive and indiscriminate force and maintained power. They were ruthlessly crushed by the loyalist forces spearheaded by the Iraqi Republican Guard
Iraqi Republican Guard
The Iraqi Republican Guard was a branch of the Iraqi military during the presidency of Saddam Hussein. It later became the Republican Guard Corps, and then the Republican Guard Forces Command with its expansion into two corps....
and the population was successfully terrorized. During the few weeks of unrest tens of thousands of people were killed. Many more died during the following months, while nearly two million Iraqis fled for their lives. In the aftermath, the government intensified the forced relocating of Marsh Arabs
Marsh Arabs
The Marsh Arabs , also known as the Maʻdān , are inhabitants of the Tigris-Euphrates marshlands in the south and east of Iraq and along the Iranian border....
and the draining of the Iraqi marshlands
Tigris-Euphrates river system
The Tigris–Euphrates river system is part of the palearctic Tigris-Euphrates alluvial salt marsh ecoregion, in the flooded grasslands and savannas biome, located in West Asia.-Geography:...
, while the Allies established the Iraqi no-fly zones
Iraqi no-fly zones
The Iraqi no-fly zones were a set of two separate no-fly zones , and were proclaimed by the United States, United Kingdom and France after the Gulf War of 1991 to protect the Kurdish people in northern Iraq and Shiite Muslims in the south. Iraqi aircraft were forbidden from flying inside the zones...
.
On 6 August 1990, after the Iraqi invasion of Kuwait, the U.N. Security Council adopted Resolution 661 which imposed economic sanctions
Economic sanctions
Economic sanctions are domestic penalties applied by one country on another for a variety of reasons. Economic sanctions include, but are not limited to, tariffs, trade barriers, import duties, and import or export quotas...
on Iraq, providing for a full trade embargo, excluding medical supplies, food and other items of humanitarian necessity, these to be determined by the Security Council sanctions committee. After the end of the Gulf War and after the Iraqi withdrawal from Kuwait, the sanctions were linked to removal of weapons of mass destruction
Weapons of mass destruction
A weapon of mass destruction is a weapon that can kill and bring significant harm to a large number of humans and/or cause great damage to man-made structures , natural structures , or the biosphere in general...
by Resolution 687 http://www.mideastweb.org/687.htm. From 1991 until 2003 the effects of government policy and sanctions regime led to hyperinflation, widespread poverty and malnutrition.
During the latter part of the 1990s the UN considered relaxing the sanctions imposed because of the hardships suffered by ordinary Iraqis. According to UN estimates, between 500,000 and 1.2 million children died http://www.unicef.org/newsline/99pr29.htm during the years of the sanctions. The United States used its veto in the UN Security Council to block the proposal to lift the sanctions because of the continued failure of Iraq to verify disarmament. However, an oil for food program was established in 1996 to ease the effects of sanctions.
Iraqi cooperation with UN weapons inspection teams was questioned on several occasions during the 1990s. UNSCOM chief weapons inspector Richard Butler
Richard Butler (diplomat)
Richard William Butler AC has served as an Australian diplomat, a United Nations weapons inspector and the Governor of Tasmania.-Life and career:...
withdrew his team from Iraq in November 1998 because of Iraq's lack of cooperation. The team returned in December. Butler prepared a report for the UN Security Council afterwards in which he expressed dissatisfaction with the level of compliance http://edition.cnn.com/WORLD/meast/9811/11/iraq.05/. The same month, US President Bill Clinton authorized air strikes on government targets and military facilities. Air strikes against military facilities and alleged WMD sites continued into 2002.
2003 invasion of Iraq
After the terrorist attacks by the group formed by the multi-millionaire Saudi Osama bin LadenOsama bin Laden
Osama bin Mohammed bin Awad bin Laden was the founder of the militant Islamist organization Al-Qaeda, the jihadist organization responsible for the September 11 attacks on the United States and numerous other mass-casualty attacks against civilian and military targets...
on New York and Washington in the United States in 2001, American foreign policy began to call for the removal of the Ba'ath government in Iraq. Conservative think-tanks in Washington had for years been urging regime change
Regime change
"Regime change" is the replacement of one regime with another. Use of the term dates to at least 1925.Regime change can occur through conquest by a foreign power, revolution, coup d'état or reconstruction following the failure of a state...
in Baghdad, but until the Iraq Liberation Act of 1998
Iraq Liberation Act
The Iraq Liberation Act of 1998 is a United States Congressional statement of policy calling for regime change in Iraq. It was signed into law by President Bill Clinton, and states that it is the policy of the United States to support democratic movements within Iraq...
, official US policy was to simply keep Iraq complying with UN sanctions. The Iraq Liberation Act
Iraq Liberation Act
The Iraq Liberation Act of 1998 is a United States Congressional statement of policy calling for regime change in Iraq. It was signed into law by President Bill Clinton, and states that it is the policy of the United States to support democratic movements within Iraq...
, codified regime change in Iraq as the official policy of the United States government. It was passed 99-0 by the United States Senate
United States Senate
The United States Senate is the upper house of the bicameral legislature of the United States, and together with the United States House of Representatives comprises the United States Congress. The composition and powers of the Senate are established in Article One of the U.S. Constitution. Each...
in 1998.
The US urged the United Nations
United Nations
The United Nations is an international organization whose stated aims are facilitating cooperation in international law, international security, economic development, social progress, human rights, and achievement of world peace...
to take military action against Iraq. The American president George Bush stated that Saddām had repeatedly violated 16 UN Security Council resolutions. The Iraqi government rejected Bush's assertions. A team of U.N. inspectors, led by Swedish diplomat Hans Blix
Hans Blix
is a Swedish diplomat and politician for the Liberal People's Party. He was Swedish Minister for Foreign Affairs . Blix was also the head of the United Nations Monitoring, Verification and Inspection Commission from March 2000 to June 2003, when he was succeeded by Dimitris Perrikos...
was admitted, into the country; their final report stated that Iraqis capability in producing "weapons of mass destruction" was not significantly different from 1992 when the country dismantled the bulk of their remaining arsenals under terms of the ceasefire agreement with U.N. forces, but did not completely rule out the possibility that Saddam still had Weapons of Mass Destruction. The United States
United States
The United States of America is a federal constitutional republic comprising fifty states and a federal district...
and the United Kingdom
United Kingdom
The United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern IrelandIn the United Kingdom and Dependencies, other languages have been officially recognised as legitimate autochthonous languages under the European Charter for Regional or Minority Languages...
charged that Iraq was hiding Weapons and opposed the team's requests for more time to further investigate the matter. Resolution 1441 was passed unanimously by the UN Security Council on November 8, 2002, offering Iraq "a final opportunity to comply with its disarmament obligations" that had been set out in several previous UN resolutions, threatening "serious consequences" if the obligations were not fulfilled. The UN Security Council did not issue a resolution authorizing the use of force against Iraq.
In March 2003 the United States
United States
The United States of America is a federal constitutional republic comprising fifty states and a federal district...
and the United Kingdom
United Kingdom
The United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern IrelandIn the United Kingdom and Dependencies, other languages have been officially recognised as legitimate autochthonous languages under the European Charter for Regional or Minority Languages...
, with military aid from other nations, invaded Iraq.
Post-invasion history

As the country struggled to rebuild after three wars and a decade of sanctions, it was racked by violence between a growing Iraqi insurgency
Iraqi insurgency
The Iraqi Resistance is composed of a diverse mix of militias, foreign fighters, all-Iraqi units or mixtures opposing the United States-led multinational force in Iraq and the post-2003 Iraqi government...
and occupation forces. Saddam Hussein, who vanished in April, was captured on December 13, 2003.
Jay Garner
Jay Garner
Jay Montgomery Garner is a retired United States Army lieutenant general who was appointed in 2003 as Director of the Office for Reconstruction and Humanitarian Assistance for Iraq following the 2003 invasion of Iraq but was soon replaced by Ambassador Paul Bremer and the ambassador's successor...
is appointed Interim Civil Administrator with three deputies, including Tim Cross
Tim Cross
Major General Timothy Cross, CBE is a retired British Army officer and military logistics expert. He was commissioned in 1971 into the Royal Army Ordnance Corps and went on to serve in Germany, Northern Ireland and Cyprus, interspersed with staff duties and further education...
. Garner was replaced in May 2003 by L. Paul Bremer
L. Paul Bremer
Lewis Paul "Jerry" Bremer III is an American diplomat. He is most notable for being the U.S. Administrator to Iraq charged with overseeing the country's occupation after the 2003 invasion. In his role as head of the Coalition Provisional Authority, he reported primarily to the U.S. Secretary of...
, who was himself replaced by John Negroponte
John Negroponte
John Dimitri Negroponte is an American diplomat. He is currently a research fellow and lecturer in international affairs at Yale University's Jackson Institute for Global Affairs...
on April 19, 2004 who left Iraq in 2005. Negroponte was the last US interim administrator.
Terrorism emerged as a threat to Iraq's people not long after the invasion of 2003. Al Qaeda now has a presence in the country, in the form of several terrorist groups formerly led by Abu Musab Al Zarqawi. Al-Zarqawi was a Jordanian militant Islamist who ran a militant training camp in Afghanistan. He became known after going to Iraq and being responsible for a series of bombings, beheadings and attacks during the Iraq war. Al-zarqawi was killed on June 7, 2006. Many foreign fighters and former Ba'ath Party officials have also joined the insurgency, which is mainly aimed at attacking American forces and Iraqis who work with them. The most dangerous insurgent area is the Sunni Triangle, a mostly Sunni-Muslim area just north of Baghdad.
By the end of 2006 violence continued as the new Iraqi Government struggled to extend complete security within Iraq.
U.S. and Coalition forces remained in Iraq. An increasingly disturbing trend had arisen - sectarian fighting. As the country attempted to move from occupation by western forces to a new entity within the Middle East, a new phase of conflict seemed to have erupted within Iraq. This new phase of conflict was waged predominately along the religious sectarian lines that the Americans had used to divide the population. Fighting was primarily between the majority Shia and the minority Sunni. But there were reports of infighting as well. To outside observers, as well as people in Iraq who supported the American military presence, the cause of violence was obscure - as developments came faster than could be easily analyzed.
Reported acts of violence conducted by an uneasy tapestry of independence activists and opponents of foreign domination steadily increased by the end of 2006. These attacks become predominately aimed at Iraqi collaborators rather than foreign occupation forces. Violence was conducted by Sunni groups, nationalists and others who sought an Iraq freed from foreign rule that include the Iraq Insurgency, which has been fighting since the initial U.S. invasion of 2003. Also, criminal elements within Iraq's society seemed to perpetuate violence for their own means and ambitions. Iraqi nationalist and Ba'athist elements (part of the insurgency) remained committed to expelling U.S. forces and also seemed to attack Shia populations, presumably, due to the Shia parties' collaboration with Iran and the United States in making war against their own nation. Further, Islamic Jihadist - of which Al Qaeda in Iraq is a member - continued to use terror and extreme acts of violence against collaborationist populations to advance their religious and political agenda(s). The aims of these attacks were not completely clear, but it was argued in 2006/7 that these attacks were aimed at fomenting civil conflict within Iraq to destroy the legitimacy of the newly created collaborationist Iraqi government (which many of its nationalist critics saw as illegitimate and a product of the U.S. government) and create an unsustainable position for the U.S. forces within Iraq. The most widely reported evidence of this argument stemmed from the 23 February 2006 attack on the Al Askari Mosque in Samarra
Samarra
Sāmarrā is a city in Iraq. It stands on the east bank of the Tigris in the Salah ad-Din Governorate, north of Baghdad and, in 2003, had an estimated population of 348,700....
, one of Shi'ite Islam's holiest sites. Analysis of the attack suggested that the Mujahideen Shura Council
Mujahideen Shura Council
The Mujahideen Shura Council was an umbrella organization of at least six Sunni Islamist groups taking part in the Iraqi insurgency: Tenzheem Qa'adah al-Jihad , Jeish al-Taiifa al-Mansoura, Katbiyan Ansar Al-Tawhid wal Sunnah, Saray al-Jihad Group, al-Ghuraba Brigades, and al-Ahwal Brigades.The...
and Al-Qaeda in Iraq were responsible, and that the motivation was to provoke further violence by outraging the Shia population. http://www.washingtonpost.com/wp-dyn/content/article/2006/02/22/AR2006022200454.html The Mujahideen Shura Council was said to have been headed by Abdullah Rashid al-Baghdadi. In mid-October 2006, a statement was released, stating that the Mujahideen Shura Council had been disbanded and was replaced by the "Islamic State of Iraq". It was formed to resist efforts by the U.S. and Iraqi authorities to win over Sunni supporters of the insurgency.
In response to attacks like the one against the Askari Mosque, violent reprisals escalated. Shia terror organizations associated with the American occupation forces within Iraq gained increasing power and influence in the collaborationist Iraqi government. Additionally, the militias, it appeared in late 2006, had the capability to act outside the scope of government. As a result these powerful militias, it seemed as of late 2006, were leading reprisal acts of violence against the Sunni minority. A cycle of violence thus ensued whereby Sunni insurgent or nationalist attacks followed with government and American backed reprisals - often in the form of Shi'ite death squads that sought out and killed Sunnis. Many commentators on the Iraq War began, by the end of 2006, to refer to this violent escalation as a civil war
Civil war
A civil war is a war between organized groups within the same nation state or republic, or, less commonly, between two countries created from a formerly-united nation state....
.
In addition to these sectarian and religious divides, an incredible amount of collateral damage has been the result. For example, evidence suggests that women's human rights and freedoms have dramatically been cut since the US-led invasion.
Under the US occupation, Islamist militias have waged a systematic campaign of violence against women in their bid to remake Iraq as an Islamist state. There has been a sharp rise in gender-based violence within families. Newly adopted Shari’a laws, such as Article 41 of Iraq’s Constitution, have degraded women’s rights, making them more vulnerable to abuses. According to the Hague and Geneva Conventions, the US, as an occupying power, was responsible for the human rights and security of Iraqi civilians. But US forces failed to meet this responsibility.
There have been concerns that the country has become condemned "to repeat the undemocratic cycle which began in the 1920s and eventually produced the Saddam Hussein regime." In order to combat these issues, several organizations have stepped in to set up shelters for physically and sexually abused women, notably the Organization of Women's Freedom in Iraq(OWFI) and MADRE, among others.
See also
- Abbasid Caliphate
- Akkadian Empire
- AssyriaAssyriaAssyria was a Semitic Akkadian kingdom, extant as a nation state from the mid–23rd century BC to 608 BC centred on the Upper Tigris river, in northern Mesopotamia , that came to rule regional empires a number of times through history. It was named for its original capital, the ancient city of Assur...
- BabyloniaBabyloniaBabylonia was an ancient cultural region in central-southern Mesopotamia , with Babylon as its capital. Babylonia emerged as a major power when Hammurabi Babylonia was an ancient cultural region in central-southern Mesopotamia (present-day Iraq), with Babylon as its capital. Babylonia emerged as...
- History of AsiaHistory of AsiaThe history of Asia can be seen as the collective history of several distinct peripheral coastal regions such as, East Asia, South Asia, and the Middle East linked by the interior mass of the Eurasian steppe....
- History of BaghdadHistory of BaghdadThis article documents the history of Baghdad. Baghdad is the capital of Iraq and of Baghdad Governorate. With a metropolitan area estimated at a population of 7,000,000, it is the largest city in Iraq...
- History of the Middle EastHistory of the Middle EastThis article is a general overview of the history of the Middle East. For more detailed information, see articles on the histories of individual countries and regions...
- List of kings of Iraq
- List of presidents of Iraq
- List of Prime Ministers of Iraq
- IraqIraqIraq ; officially the Republic of Iraq is a country in Western Asia spanning most of the northwestern end of the Zagros mountain range, the eastern part of the Syrian Desert and the northern part of the Arabian Desert....
- MesopotamiaMesopotamiaMesopotamia is a toponym for the area of the Tigris–Euphrates river system, largely corresponding to modern-day Iraq, northeastern Syria, southeastern Turkey and southwestern Iran.Widely considered to be the cradle of civilization, Bronze Age Mesopotamia included Sumer and the...
- Politics of IraqPolitics of IraqThe politics of Iraq takes place in a framework of a federal parliamentary representative democratic republic. It is a multi-party system whereby the executive power is exercised by the Prime Minister of the Council of Ministers as the head of government, as well as the President of Iraq, and...
- SumerSumerSumer was a civilization and historical region in southern Mesopotamia, modern Iraq during the Chalcolithic and Early Bronze Age....
External links
- Iraq: The Cradle of Civilization
- Iraq History and Culture from the cradle of civilization and Noah to the present age and time

