
History of Bosnia and Herzegovina
Encyclopedia
Pre-Slavic Period

Neolithic
The Neolithic Age, Era, or Period, or New Stone Age, was a period in the development of human technology, beginning about 9500 BC in some parts of the Middle East, and later in other parts of the world. It is traditionally considered as the last part of the Stone Age...
times. In the late Bronze Age
Bronze Age
The Bronze Age is a period characterized by the use of copper and its alloy bronze as the chief hard materials in the manufacture of some implements and weapons. Chronologically, it stands between the Stone Age and Iron Age...
, the Neolithic population was replaced by more warlike Indo-European
Proto-Indo-Europeans
The Proto-Indo-Europeans were the speakers of the Proto-Indo-European language , a reconstructed prehistoric language of Eurasia.Knowledge of them comes chiefly from the linguistic reconstruction, along with material evidence from archaeology and archaeogenetics...
tribes known as the Illyrians
Illyrians
The Illyrians were a group of tribes who inhabited part of the western Balkans in antiquity and the south-eastern coasts of the Italian peninsula...
. Celtic migrations in the 4th and 3rd century BCE displaced many Illyrian tribes from their former lands, but some Celtic and Illyrian tribes mixed. Concrete historical evidence for this period is scarce, but overall it appears that the region was populated by a number of different peoples speaking distinct languages. Conflict between the Illyrians and Romans
Ancient Rome
Ancient Rome was a thriving civilization that grew on the Italian Peninsula as early as the 8th century BC. Located along the Mediterranean Sea and centered on the city of Rome, it expanded to one of the largest empires in the ancient world....
started in 229 BCE, but Rome wouldn't complete its annexation of the region until 9 CE. In the Roman period, Latin-speaking settlers from all over the Roman empire
Roman Empire
The Roman Empire was the post-Republican period of the ancient Roman civilization, characterised by an autocratic form of government and large territorial holdings in Europe and around the Mediterranean....
settled among the Illyrians and Roman soldiers were encouraged to retire in the region.
Christianity
Christianity
Christianity is a monotheistic religion based on the life and teachings of Jesus as presented in canonical gospels and other New Testament writings...
had already arrived in the region by the end of the 1st century, and numerous artifacts and objects from the time testify to this. Following events from the years 337 and 395 when the Empire split, Dalmatia
Dalmatia (Roman province)
Dalmatia was an ancient Roman province. Its name is probably derived from the name of an Illyrian tribe called the Dalmatae which lived in the area of the eastern Adriatic coast in Classical antiquity....
and Pannonia
Pannonia
Pannonia was an ancient province of the Roman Empire bounded north and east by the Danube, coterminous westward with Noricum and upper Italy, and southward with Dalmatia and upper Moesia....
were included in the Western Roman Empire
Western Roman Empire
The Western Roman Empire was the western half of the Roman Empire after its division by Diocletian in 285; the other half of the Roman Empire was the Eastern Roman Empire, commonly referred to today as the Byzantine Empire....
. The region was conquered by the Ostrogoths in 455, and further exchanged hands between the Alans
Alans
The Alans, or the Alani, occasionally termed Alauni or Halani, were a group of Sarmatian tribes, nomadic pastoralists of the 1st millennium AD who spoke an Eastern Iranian language which derived from Scytho-Sarmatian and which in turn evolved into modern Ossetian.-Name:The various forms of Alan —...
and Huns
Huns
The Huns were a group of nomadic people who, appearing from east of the Volga River, migrated into Europe c. AD 370 and established the vast Hunnic Empire there. Since de Guignes linked them with the Xiongnu, who had been northern neighbours of China 300 years prior to the emergence of the Huns,...
in the years to follow. By the 6th century, Emperor Justinian had re-conquered the area for the Byzantine Empire
Byzantine Empire
The Byzantine Empire was the Eastern Roman Empire during the periods of Late Antiquity and the Middle Ages, centred on the capital of Constantinople. Known simply as the Roman Empire or Romania to its inhabitants and neighbours, the Empire was the direct continuation of the Ancient Roman State...
. The Slavs, a migratory people from southeastern Europe, were angered by the Eurasian Avars
Eurasian Avars
The Eurasian Avars or Ancient Avars were a highly organized nomadic confederacy of mixed origins. They were ruled by a khagan, who was surrounded by a tight-knit entourage of nomad warriors, an organization characteristic of Turko-Mongol groups...
in the 6th century, and together they invaded the Eastern Roman Empire in the 6th and 7th centuries, settling in what is now Bosnia and Herzegovina and the surrounding lands. More South Slavs came in a second wave, and according to some scholars were invited by Emperor Heraclius
Heraclius
Heraclius was Byzantine Emperor from 610 to 641.He was responsible for introducing Greek as the empire's official language. His rise to power began in 608, when he and his father, Heraclius the Elder, the exarch of Africa, successfully led a revolt against the unpopular usurper Phocas.Heraclius'...
to drive the Avars from Dalmatia.
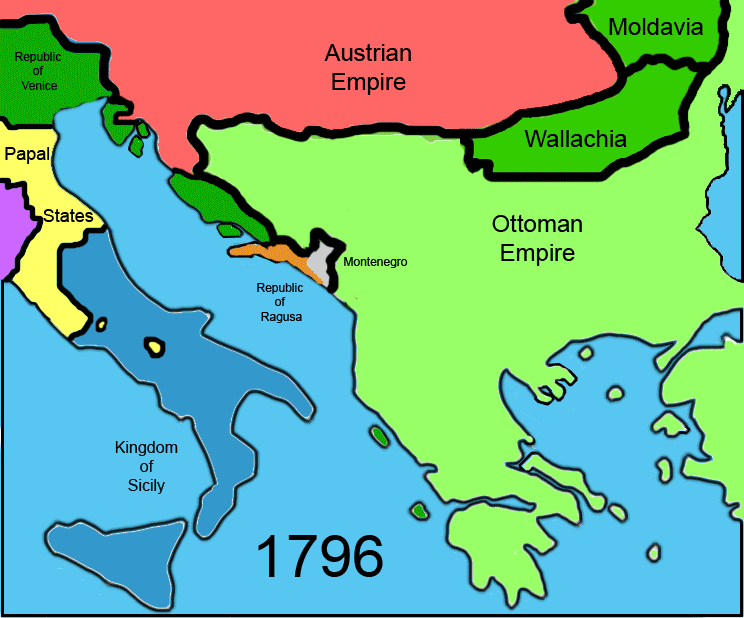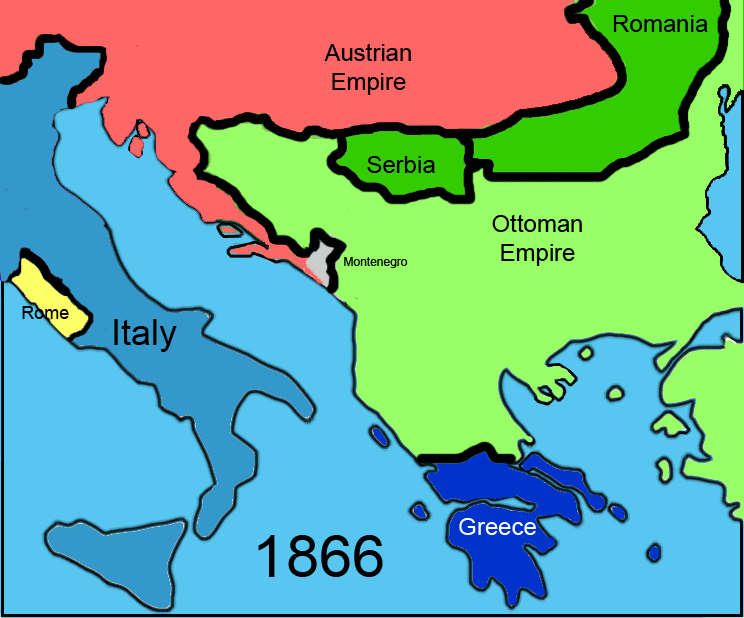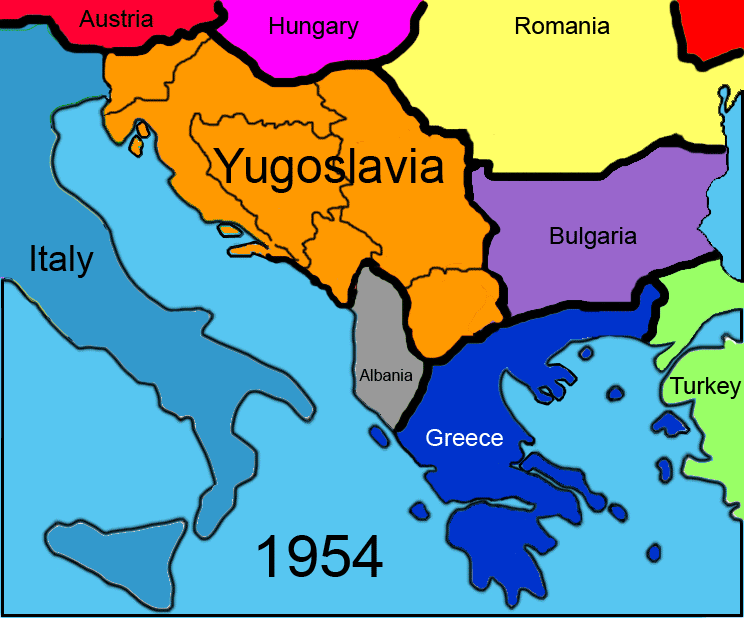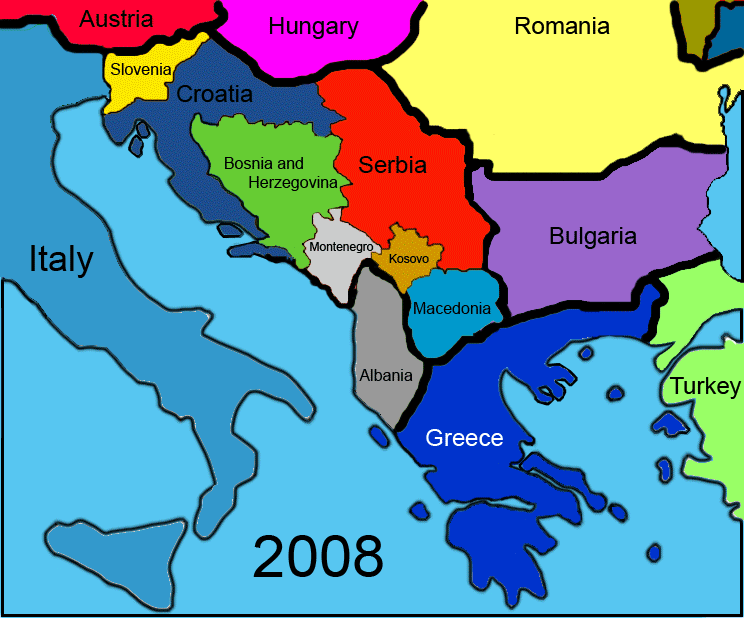
Medieval Bosnia (958–1463)
Modern knowledge of Bosnia in the western Balkans during the Dark Ages is patchy. Upon the looter invasions by the AvarEurasian Avars
The Eurasian Avars or Ancient Avars were a highly organized nomadic confederacy of mixed origins. They were ruled by a khagan, who was surrounded by a tight-knit entourage of nomad warriors, an organization characteristic of Turko-Mongol groups...
and Slav horsemen from 6th-9th century, bringing Slavic languages (which prompted some to confuse that with the native Illyrian population turning Slav as well), both probably gave way to feudalism
Feudalism
Feudalism was a set of legal and military customs in medieval Europe that flourished between the 9th and 15th centuries, which, broadly defined, was a system for ordering society around relationships derived from the holding of land in exchange for service or labour.Although derived from the...
only with the might by the Frankish
Franks
The Franks were a confederation of Germanic tribes first attested in the third century AD as living north and east of the Lower Rhine River. From the third to fifth centuries some Franks raided Roman territory while other Franks joined the Roman troops in Gaul. Only the Salian Franks formed a...
penetrating into the region in the late 9th century (Bosnia probably originated as one such pre-feudal entity). It was also around this time that the Bosnians
Bosnians
Bosnians are people who reside in, or come from, Bosnia and Herzegovina. By the modern state definition a Bosnian can be anyone who holds citizenship of the state. This includes, but is not limited to, members of the constituent ethnic groups of Bosnia and Herzegovina: Bosniaks, Bosnian Serbs and...
were Christianized. Bosnia, due to its geographic position and terrain, was probably one of the last areas to go through this process, which presumably originated from the urban centers along the Dalmatia
Dalmatia
Dalmatia is a historical region on the eastern coast of the Adriatic Sea. It stretches from the island of Rab in the northwest to the Bay of Kotor in the southeast. The hinterland, the Dalmatian Zagora, ranges from fifty kilometers in width in the north to just a few kilometers in the south....
n coast. The region of Bosnia had been part of the kingdoms of Serbia
Serbia
Serbia , officially the Republic of Serbia , is a landlocked country located at the crossroads of Central and Southeast Europe, covering the southern part of the Carpathian basin and the central part of the Balkans...
and Croatia
Croatia
Croatia , officially the Republic of Croatia , is a unitary democratic parliamentary republic in Europe at the crossroads of the Mitteleuropa, the Balkans, and the Mediterranean. Its capital and largest city is Zagreb. The country is divided into 20 counties and the city of Zagreb. Croatia covers ...
, whose borders were often fluctuant. However, by the high middle ages
High Middle Ages
The High Middle Ages was the period of European history around the 11th, 12th, and 13th centuries . The High Middle Ages were preceded by the Early Middle Ages and followed by the Late Middle Ages, which by convention end around 1500....
Croatia had been acquired by the Hungarian Kingdom, and the Serbian state to the southeast was in a period of stagnation. Control over Bosnia subsequently was contested between the Kingdom of Hungary
Kingdom of Hungary
The Kingdom of Hungary comprised present-day Hungary, Slovakia and Croatia , Transylvania , Carpatho Ruthenia , Vojvodina , Burgenland , and other smaller territories surrounding present-day Hungary's borders...
and the Byzantine empire. Hungary appointed Ban Borić as the first ruler and Viceroy
Viceroy
A viceroy is a royal official who runs a country, colony, or province in the name of and as representative of the monarch. The term derives from the Latin prefix vice-, meaning "in the place of" and the French word roi, meaning king. A viceroy's province or larger territory is called a viceroyalty...
of Bosnia. Under the pressure of the Byzantine, a subsequent King of Hungary appointed one Kulin as a Ban to rule the province under the eastern vassalage. However, this vassalage was largely nominal.
The second Bosnian
Bošnjani
Bošnjani was the local Slavic name for inhabitants of Bosnia during the Middle Ages.It appeared in a number of documents from the period, in most cases coupled with the word Good . Debate on the exact nature of the term is inconclusive...
ruler, Ban Kulin
Ban Kulin
Ban Kulin was a notable Ban of Bosnia who ruled from 1180 to 1204 first as a vassal of the Byzantine Empire and then of the Kingdom of Hungary. He was brought to the power by Byzantine Emperor Manuel I Comnenus. He had a son, Stjepan Kulinić who succeeded him as Bosnian Ban...
, allegedly presided over nearly three decades of peace and stability during which he strengthened the country's economy through treaties with Dubrovnik
Republic of Ragusa
The Republic of Ragusa or Republic of Dubrovnik was a maritime republic centered on the city of Dubrovnik in Dalmatia , that existed from 1358 to 1808...
and Venice
Republic of Venice
The Republic of Venice or Venetian Republic was a state originating from the city of Venice in Northeastern Italy. It existed for over a millennium, from the late 7th century until 1797. It was formally known as the Most Serene Republic of Venice and is often referred to as La Serenissima, in...
. His rule also marked the start of a controversy with the Bosnian Church
Bosnian Church
The Bosnian Church is historically thought to be an indigenous branch of the Bogomils that existed in Bosnia during the Middle Ages. Adherents of the church called themselves simply Krstjani...
, an indigenous Christian
Christian
A Christian is a person who adheres to Christianity, an Abrahamic, monotheistic religion based on the life and teachings of Jesus of Nazareth as recorded in the Canonical gospels and the letters of the New Testament...
sect considered heretical by both the Roman Catholic
Roman Catholic Church
The Catholic Church, also known as the Roman Catholic Church, is the world's largest Christian church, with over a billion members. Led by the Pope, it defines its mission as spreading the gospel of Jesus Christ, administering the sacraments and exercising charity...
and Eastern Orthodox
Eastern Orthodox Church
The Orthodox Church, officially called the Orthodox Catholic Church and commonly referred to as the Eastern Orthodox Church, is the second largest Christian denomination in the world, with an estimated 300 million adherents mainly in the countries of Belarus, Bulgaria, Cyprus, Georgia, Greece,...
churches. In response to Hungarian attempts to use church politics regarding the issue as a way to reclaim sovereignty over Bosnia, Kulin held a council of local church leaders to renounce the heresy in 1203. Despite this, Hungarian ambitions remained unchanged long after Kulin's death in 1204, waning only after an unsuccessful invasion in 1254.
Kingdom of Bosnia
Bosnian history from then until the early 14th century was marked by the power struggle between the ŠubićŠubic
The Šubić were one of the twelve tribes which constituted Croatian statehood in the Middle Ages; they held the county of Bribir in inland Dalmatia.-Origins:...
and Kotromanić
House of Kotromanic
The Kotromanić dynasty was a ruling house that ruled in the medieval Bosnia and the surrounding lands, from the 13th century as Bans until the crowning with the Bosnian crowns in 1377 and then as kings until the Ottoman conquest conquest in 1463....
families. This conflict came to an end in 1322, when Stjepan II Kotromanić became ban. By the time of his death in 1353, he had succeeded in annexing territories to the north and west, as well as Zahumlje and parts of Dalmatia. He was succeeded by his nephew Tvrtko who, following a prolonged struggle with nobility and inter-family strife, gained full control of the country in 1367. Under Tvrtko, Bosnia grew in both size and power, finally becoming an independent kingdom in 1377. Following his death in 1391 however, Bosnia fell into a long period of decline. The Ottoman Empire
Ottoman Empire
The Ottoman EmpireIt was usually referred to as the "Ottoman Empire", the "Turkish Empire", the "Ottoman Caliphate" or more commonly "Turkey" by its contemporaries...
had already started its conquest of Europe
Ottoman wars in Europe
The wars of the Ottoman Empire in Europe are also sometimes referred to as the Ottoman Wars or as Turkish Wars, particularly in older, European texts.- Rise :...
and posed a major threat to the Balkans
Balkans
The Balkans is a geopolitical and cultural region of southeastern Europe...
throughout the first half of the 15th century. Finally, after decades of political and social instability, Bosnia officially fell in 1463, while resistance was active and fierce for a few more centuries. Southern regions of Bosnia, nowadays known as "Herzegovina
Herzegovina
Herzegovina is the southern region of Bosnia and Herzegovina. While there is no official border distinguishing it from the Bosnian region, it is generally accepted that the borders of the region are Croatia to the west, Montenegro to the south, the canton boundaries of the Herzegovina-Neretva...
" would follow in 1483, with a Hungarian-backed reinstated "Bosnian Kingdom" being the last to succumb in 1527.
Ottoman Era (1463–1878)

Sandžak
Sandžak also known as Raška is a historical region lying along the border between Serbia and Montenegro...
(and eventual vilayet) of Bosnia, the Ottomans introduced a number of key changes in the territory's socio-political administration; including a new landholding system, a reorganization of administrative units, and a complex system of social differentiation by class and religious affiliation.
The four centuries of Ottoman rule also had a drastic impact on Bosnia's population make-up, which changed several times as a result of the empire's conquests, frequent wars with European powers, migrations, and epidemics. A native Slavic-speaking Muslim community emerged and eventually became the second largest ethno-religious group (mainly as a result of a gradually rising number of conversions to Islam
Islam
Islam . The most common are and . : Arabic pronunciation varies regionally. The first vowel ranges from ~~. The second vowel ranges from ~~~...
), while a significant number of Sephardi Jews
Sephardi Jews
Sephardi Jews is a general term referring to the descendants of the Jews who lived in the Iberian Peninsula before their expulsion in the Spanish Inquisition. It can also refer to those who use a Sephardic style of liturgy or would otherwise define themselves in terms of the Jewish customs and...
arrived following their expulsion
Spanish Inquisition
The Tribunal of the Holy Office of the Inquisition , commonly known as the Spanish Inquisition , was a tribunal established in 1480 by Catholic Monarchs Ferdinand II of Aragon and Isabella I of Castile. It was intended to maintain Catholic orthodoxy in their kingdoms, and to replace the Medieval...
from Spain in the late 15th century. The Bosnian Christian communities also experienced major changes. The Bosnian Franciscans (and the Catholic
Catholicism
Catholicism is a broad term for the body of the Catholic faith, its theologies and doctrines, its liturgical, ethical, spiritual, and behavioral characteristics, as well as a religious people as a whole....
population as a whole) were protected by official imperial decree, although on the ground these guarantees were often disregarded and their numbers dwindled. The Orthodox
Eastern Orthodox Church
The Orthodox Church, officially called the Orthodox Catholic Church and commonly referred to as the Eastern Orthodox Church, is the second largest Christian denomination in the world, with an estimated 300 million adherents mainly in the countries of Belarus, Bulgaria, Cyprus, Georgia, Greece,...
community in Bosnia, initially confined to Herzegovina and Podrinje, spread throughout the country during this period and went on to experience relative prosperity until the 19th century. Meanwhile, the schismatic
Schism (religion)
A schism , from Greek σχίσμα, skhísma , is a division between people, usually belonging to an organization or movement religious denomination. The word is most frequently applied to a break of communion between two sections of Christianity that were previously a single body, or to a division within...
Bosnian Church
Bosnian Church
The Bosnian Church is historically thought to be an indigenous branch of the Bogomils that existed in Bosnia during the Middle Ages. Adherents of the church called themselves simply Krstjani...
disappeared altogether.
As the Ottoman Empire thrived and expanded into Central Europe, Bosnia was relieved of the pressures of being a frontier province and experienced a prolonged period of general welfare and prosperity. A number of cities, such as Sarajevo and Mostar
Mostar
Mostar is a city and municipality in Bosnia and Herzegovina, the largest and one of the most important cities in the Herzegovina region and the center of the Herzegovina-Neretva Canton of the Federation. Mostar is situated on the Neretva river and is the fifth-largest city in the country...
, were established and grew into major regional centers of trade and urban culture. Within these cities, various Sultans and governors financed the construction of many important works of Bosnian architecture (such as the Stari most
Stari most
Stari Most is a 16th century Ottoman bridge in the city of Mostar, Bosnia and Herzegovina that crosses the river Neretva and connects two parts of the city. The Old Bridge stood for 427 years, until it was destroyed on November 9, 1993 during the Croat-Bosniak War...
and Gazi Husrev-beg's Mosque
Gazi Husrev-beg's Mosque
The Gazi Husrev-beg Mosque , is a mosque in the city of Sarajevo, Bosnia and Herzegovina. It is considered the most important Islamic structure in the country and one of the world's finest examples of Ottoman architecture...
). Furthermore, numerous Bosnians played influential roles in the Ottoman Empire's cultural and political history during this time. Bosnian soldiers formed a large component of the Ottoman ranks in the battles of Mohács
Battle of Mohács
The Battle of Mohács was fought on August 29, 1526 near Mohács, Hungary. In the battle, forces of the Kingdom of Hungary led by King Louis II of Hungary and Bohemia were defeated by forces of the Ottoman Empire led by Sultan Suleiman the Magnificent....
and Krbava field
Battle of Krbava field
The Battle of Krbava field , was fought between the Ottoman Empire of Bayezid II and a Croatian army of the Kingdom of Croatia in personal union with the Kingdom of Hungary on September 9, 1493 in the Krbava field, a part of Lika region, southern Croatia...
, two decisive military victories, while numerous other Bosnians rose through the ranks of the Ottoman military bureaucracy to occupy the highest positions of power in the Empire, including admirals, generals, and grand viziers. Many Bosnians also made a lasting impression on Ottoman culture, emerging as mystics, scholars, and celebrated poets in the Turkish, Arabic, and Persian languages.
.svg.png)
Great Turkish War
The Great Turkish War refers to a series of conflicts between the Ottoman Empire and contemporary European powers, then joined into a Holy League, during the second half of the 17th century.-1667–1683:...
with the Treaty of Karlowitz
Treaty of Karlowitz
The Treaty of Karlowitz was signed on 26 January 1699 in Sremski Karlovci , concluding the Austro-Ottoman War of 1683–1697 in which the Ottoman side had been defeated at the Battle of Zenta...
in 1699 once again made Bosnia the empire's westernmost province. The following hundred years were marked by further military failures, numerous revolts within Bosnia, and several outbursts of plague. The Porte's efforts at modernizing
Ottoman military reform efforts
Ottoman military reform efforts began after the Belle Époque of European civilization. Ottoman military reforms follow the empire's transformation to become a modern country. It followed the same period only a couple decade later of Russia's reforms, and Japan's opening of its doors to west during...
the Ottoman state were met with great hostility in Bosnia, where local aristocrats stood to lose much through the proposed reforms. This, combined with frustrations over political concessions to nascent Christian states in the east, culminated in a famous (albeit ultimately unsuccessful) revolt by Husein Gradaščević
Husein Gradašcevic
Husein-kapetan Gradaščević was a Bosnian Muslim general who fought for Bosnian autonomy in the Ottoman Empire. He is often referred to as "Zmaj od Bosne", meaning "Dragon of Bosnia"...
in 1831. Related rebellions would be extinguished by 1850, but the situation continued to deteriorate. Later, agrarian unrest eventually sparked the Herzegovinian rebellion
Herzegovinian rebellion
The Herzegovina Uprising of 1875-1878 was an uprising led by Christians, firstly in Herzegovina and then in Bosnia. It is the most significant of the rebellions against Ottoman rule in Herzegovina...
, a widespread peasant uprising, in 1875. The conflict rapidly spread and came to involve several Balkan states and Great Powers, which eventually forced the Ottomans to cede administration of the country to Austria-Hungary
Austria-Hungary
Austria-Hungary , more formally known as the Kingdoms and Lands Represented in the Imperial Council and the Lands of the Holy Hungarian Crown of Saint Stephen, was a constitutional monarchic union between the crowns of the Austrian Empire and the Kingdom of Hungary in...
through the Treaty of Berlin in 1878.
Austro-Hungarian Era (1878–1918)
Colony
In politics and history, a colony is a territory under the immediate political control of a state. For colonies in antiquity, city-states would often found their own colonies. Some colonies were historically countries, while others were territories without definite statehood from their inception....
". With the aim of establishing the province as a stable political model that would help dissipate rising South Slav nationalism
Nationalism
Nationalism is a political ideology that involves a strong identification of a group of individuals with a political entity defined in national terms, i.e. a nation. In the 'modernist' image of the nation, it is nationalism that creates national identity. There are various definitions for what...
, Habsburg rule did much to codify laws, to introduce new political practices, and generally to provide for modernization.
.svg.png)
Nation
A nation may refer to a community of people who share a common language, culture, ethnicity, descent, and/or history. In this definition, a nation has no physical borders. However, it can also refer to people who share a common territory and government irrespective of their ethnic make-up...
(largely favored by the Muslims) - failed to curb the rising tides of nationalism. The concept of Croat and Serb nationhood had already spread to Bosnia and Herzegovina's Catholics and Orthodox communities from neighboring Croatia and Serbia in the mid 19th century, and was too well-entrenched to allow for the widespread acceptance of a parallel idea of Bosnian nationhood. By the latter half of the 1910s, nationalism was an integral factor of Bosnian politics, with national political parties corresponding to the three groups dominating elections.
The idea of a unified South Slavic state
Yugoslavia
Yugoslavia refers to three political entities that existed successively on the western part of the Balkans during most of the 20th century....
(typically expected to be spear-headed by independent Serbia) became a popular political ideology in the region at this time, including in Bosnia and Herzegovina. The Austro-Hungarian government's decision to formally annex Bosnia-Herzegovina in 1908 (the Bosnian Crisis
Bosnian crisis
The Bosnian Crisis of 1908–1909, also known as the Annexation crisis, or the First Balkan Crisis, erupted into public view when on 6 October 1908, Austria-Hungary announced the annexation of Bosnia and Herzegovina. Russia, the Ottoman Empire, Britain, Italy, Serbia, Montenegro, Germany and France...
) added to a sense of urgency among these nationalists. The political tensions caused by all this culminated on 28 June 1914, when Serb nationalist youth Gavrilo Princip
Gavrilo Princip
Gavrilo Princip was the Bosnian Serb who assassinated Archduke Franz Ferdinand of Austria and his wife, Sophie, Duchess of Hohenberg, in Sarajevo on 28 June 1914...
assassinated the heir to the Austro-Hungarian throne, Archduke Franz Ferdinand
Archduke Franz Ferdinand of Austria
Franz Ferdinand was an Archduke of Austria-Este, Austro-Hungarian and Royal Prince of Hungary and of Bohemia, and from 1889 until his death, heir presumptive to the Austro-Hungarian throne. His assassination in Sarajevo precipitated Austria-Hungary's declaration of war against Serbia...
, in Sarajevo; an event that proved to be the spark that set off World War I
World War I
World War I , which was predominantly called the World War or the Great War from its occurrence until 1939, and the First World War or World War I thereafter, was a major war centred in Europe that began on 28 July 1914 and lasted until 11 November 1918...
. Although 10% of the Bosniak population died serving in the armies or being killed by the various warring states, Bosnia and Herzegovina itself managed to escape the conflict relatively unscathed.
Kingdom of Yugoslavia (1918–1941)
Following World War I, Bosnia was incorporated into the South Slav kingdom of Serbs, Croats and SlovenesKingdom of Yugoslavia
The Kingdom of Yugoslavia was a state stretching from the Western Balkans to Central Europe which existed during the often-tumultuous interwar era of 1918–1941...
(soon renamed Yugoslavia).
Political life in Bosnia at this time was marked by two major trends: social and economic unrest over "Agrarian Reform 1918-1919" manifested through mass colonization and property confiscation; also formation of several political parties that frequently changed coalitions and alliances with parties in other Yugoslav regions. The dominant ideological conflict of the Yugoslav state, between Croatian regionalism and Serbian centralization, was approached differently by Bosnia's major ethnic groups and was dependent on the overall political atmosphere. Although the initial split of the country into 33 oblast
Oblast
Oblast is a type of administrative division in Slavic countries, including some countries of the former Soviet Union. The word "oblast" is a loanword in English, but it is nevertheless often translated as "area", "zone", "province", or "region"...
s erased the presence of traditional geographic entities from the map, the efforts of Bosnian politicians such as Mehmed Spaho
Mehmed Spaho
Mehmed Spaho was a prominent and influential Bosniak political figure. He was the leader of the Yugoslav Muslim Organization....
ensured that the six oblasts carved up from Bosnia and Herzegovina corresponded to the six sanjaks from Ottoman times and, thus, matched the country's traditional boundary as a whole.
The establishment of the Kingdom of Yugoslavia in 1929, however, brought the redrawing of administrative regions into banates that purposely avoided all historical and ethnic lines, removing any trace of a Bosnian entity. Serbo-Croat tensions over the structuring of the Yugoslav state continued, with the concept of a separate Bosnian division receiving little or no consideration. The famous Cvetković
Dragiša Cvetkovic
Dragiša Cvetković was a Yugoslav politician.He served as the prime minister of the Kingdom of Yugoslavia from 1939 to 1941. He developed the federalization of Yugoslavia through the creation of the Banovina of Croatia by an agreement with Croatian leader Vladko Maček...
-Maček
Vladko Macek
Vladko Maček was a Croatian politician active within the Kingdom of Yugoslavia in the first half of the 20th century. He led the Croatian Peasant Party following the assassination of Stjepan Radić, and all through World War II.- Early life :Maček was born to a Slovene-Czech family in the village...
agreement that created the Croatian banate in 1939 encouraged what was essentially a partition of Bosnia between Croatia and Serbia. However, outside political circumstances forced Yugoslav politicians to shift their attention to the rising threat posed by Adolf Hitler
Adolf Hitler
Adolf Hitler was an Austrian-born German politician and the leader of the National Socialist German Workers Party , commonly referred to as the Nazi Party). He was Chancellor of Germany from 1933 to 1945, and head of state from 1934 to 1945...
's Nazi Germany
Nazi Germany
Nazi Germany , also known as the Third Reich , but officially called German Reich from 1933 to 1943 and Greater German Reich from 26 June 1943 onward, is the name commonly used to refer to the state of Germany from 1933 to 1945, when it was a totalitarian dictatorship ruled by...
. Following a period that saw attempts at appeasement
Appeasement
The term appeasement is commonly understood to refer to a diplomatic policy aimed at avoiding war by making concessions to another power. Historian Paul Kennedy defines it as "the policy of settling international quarrels by admitting and satisfying grievances through rational negotiation and...
, the signing of the Tripartite Treaty, and a coup d'état
Coup d'état
A coup d'état state, literally: strike/blow of state)—also known as a coup, putsch, and overthrow—is the sudden, extrajudicial deposition of a government, usually by a small group of the existing state establishment—typically the military—to replace the deposed government with another body; either...
, Yugoslavia was finally invaded by Germany on 6 April 1941.
World War II (1941–1945)

World War II
World War II, or the Second World War , was a global conflict lasting from 1939 to 1945, involving most of the world's nations—including all of the great powers—eventually forming two opposing military alliances: the Allies and the Axis...
, all of Bosnia was ceded to the Independent State of Croatia
Independent State of Croatia
The Independent State of Croatia was a World War II puppet state of Nazi Germany, established on a part of Axis-occupied Yugoslavia. The NDH was founded on 10 April 1941, after the invasion of Yugoslavia by the Axis powers. All of Bosnia and Herzegovina was annexed to NDH, together with some parts...
. The Nazi rule over Bosnia led to widespread persecution. The Jewish population was nearly exterminated. Tens of thousands of Serbs died in Croat concentration camps. Many Serbs in the area took up arms and joined the Chetniks
Chetniks
Chetniks, or the Chetnik movement , were Serbian nationalist and royalist paramilitary organizations from the first half of the 20th century. The Chetniks were formed as a Serbian resistance against the Ottoman Empire in 1904, and participated in the Balkan Wars, World War I, and World War II...
; a Serb nationalist and royalist movement that collaborated with the Nazis and committed numerous atrocities against chiefly Bosnian Muslim civilians in regions under their control.[3] Consequently, several Bosnian Muslim paramilitary units joined the Croatian Axis forces to counter their own persecution in the hands of the Serbs in Bosnia. On October 12, 1941 a group of 108 notable Muslim citizens of Sarajevo signed the Resolution of Sarajevo Muslims
Resolution of Sarajevo Muslims
The Resolution of Sarajevo Muslims or Muslim Resolution of 1941 was one of the resolutions of Muslims from Bosnia and Herzegovina declared by 108 notable Muslim citizens of Sarajevo during the Second World War in Sarajevo on October 12, 1941...
by which they condemned the persecution of Serbs
World War II persecution of Serbs
The Serbian Genocide refers to the attempt in extermination made towards ethnic Serbs in 1939-1945 by predominantly ethnic Croat Fascists and Nazi occupational forces....
organized by Ustaše
Ustaše
The Ustaša - Croatian Revolutionary Movement was a Croatian fascist anti-Yugoslav separatist movement. The ideology of the movement was a blend of fascism, Nazism, and Croatian nationalism. The Ustaše supported the creation of a Greater Croatia that would span to the River Drina and to the border...
, made distinction between Muslims who participated in such persecutions and whole Muslim population, presented informations about the persecutions of Muslims by Serbs and requested security for all citizens of the country, regardless of their identity.
Starting in 1941, Yugoslav communists under the leadership of Josip Broz Tito organized their own multi-ethnic resistance group, the partisans, who fought against Axis, Ustase, and Chetnik forces.[1] On 25 November 1943 the Anti-Fascist Council of National Liberation of Yugoslavia with Tito at its helm held a founding conference in Jajce
Jajce
Jajce is a city and municipality located in the central part of Bosnia and Herzegovina. It is part of the Central Bosnia Canton of the Federation of Bosnia and Herzegovina entity...
where Bosnia and Herzegovina was reestablished as a republic within the Yugoslavian federation in its Ottoman borders. Military success eventually prompted the Allies to support the Partisans. On 6 April 1945 Sarajevo was liberated by partisans. The end of the war resulted in the establishment of the Federal People's Republic of Yugoslavia, with the constitution of 1946 officially making Bosnia and Herzegovina one of six constituent republics in the new state.[1]
Socialist Yugoslavia (1945–1992)
Because of its central geographic position within the Yugoslavian federation, post-war Bosnia was strategically selected as a base for the development of the military defense industry. This contributed to a large concentration of arms and military personnel in Bosnia; a significant factor in the warBosnian War
The Bosnian War or the War in Bosnia and Herzegovina was an international armed conflict that took place in Bosnia and Herzegovina between April 1992 and December 1995. The war involved several sides...
that followed the break-up of Yugoslavia in the 1990s. However, Bosnia's existence within Yugoslavia, for the large part, was peaceful and prosperous. Being one of the poorer republics in the early 1950s it quickly recovered economically, taking advantage of its extensive natural resources to stimulate industrial development. The Yugoslavian communist doctrine of "brotherhood and unity
Brotherhood and unity
Brotherhood and Unity was a popular slogan of the Communist Party of Yugoslavia that was coined during the Yugoslav People's Liberation War , and which evolved into a guiding principle of Yugoslavia's post-war inter-ethnic policy....
" particularly suited Bosnia's diverse and multi-ethnic society that, because of such an imposed system of tolerance, thrived culturally and socially.
Though considered a political backwater of the federation for much of the 50s and 60s, the 70s saw the ascension of a strong Bosnian political elite. While working within the communist
Communism
Communism is a social, political and economic ideology that aims at the establishment of a classless, moneyless, revolutionary and stateless socialist society structured upon common ownership of the means of production...
system, politicians such as Džemal Bijedić
Džemal Bijedic
Džemal Bijedić was a Bosniak Communist politician from Bosnia and Herzegovina, and the prime minister of Yugoslavia from 1971 until his death.- Early life :...
, Branko Mikulić
Branko Mikulic
Branko Mikulić was a communist politician and statesman in the Yugoslavia. Mikulić was one of the leading communist politicians in Bosnia and Herzegovina during the communist rule in the former Yugoslavia.-Biography:...
and Hamdija Pozderac
Hamdija Pozderac
Hamdija Pozderac was a Bosniak communist politician and the president of Bosnia and Herzegovina from 1971- 74. He was a vice president of the former Yugoslavia in late 1980s, and was in line to become the president of Yugoslavia just before he was forced to resign from politics in 1987...
reinforced and protected the sovereignty of Bosnia and Herzegovina Their efforts proved key during the turbulent period following Tito's death in 1980, and are today considered some of the early steps towards Bosnian independence. However, the republic hardly escaped the increasingly nationalistic climate of the time unscathed. With the fall of communism and the start of the break-up of Yugoslavia, the old communist doctrine of tolerance began to lose its potency, creating an opportunity for nationalist elements in the society to spread their influence.
Bosnian War (1992-1995)
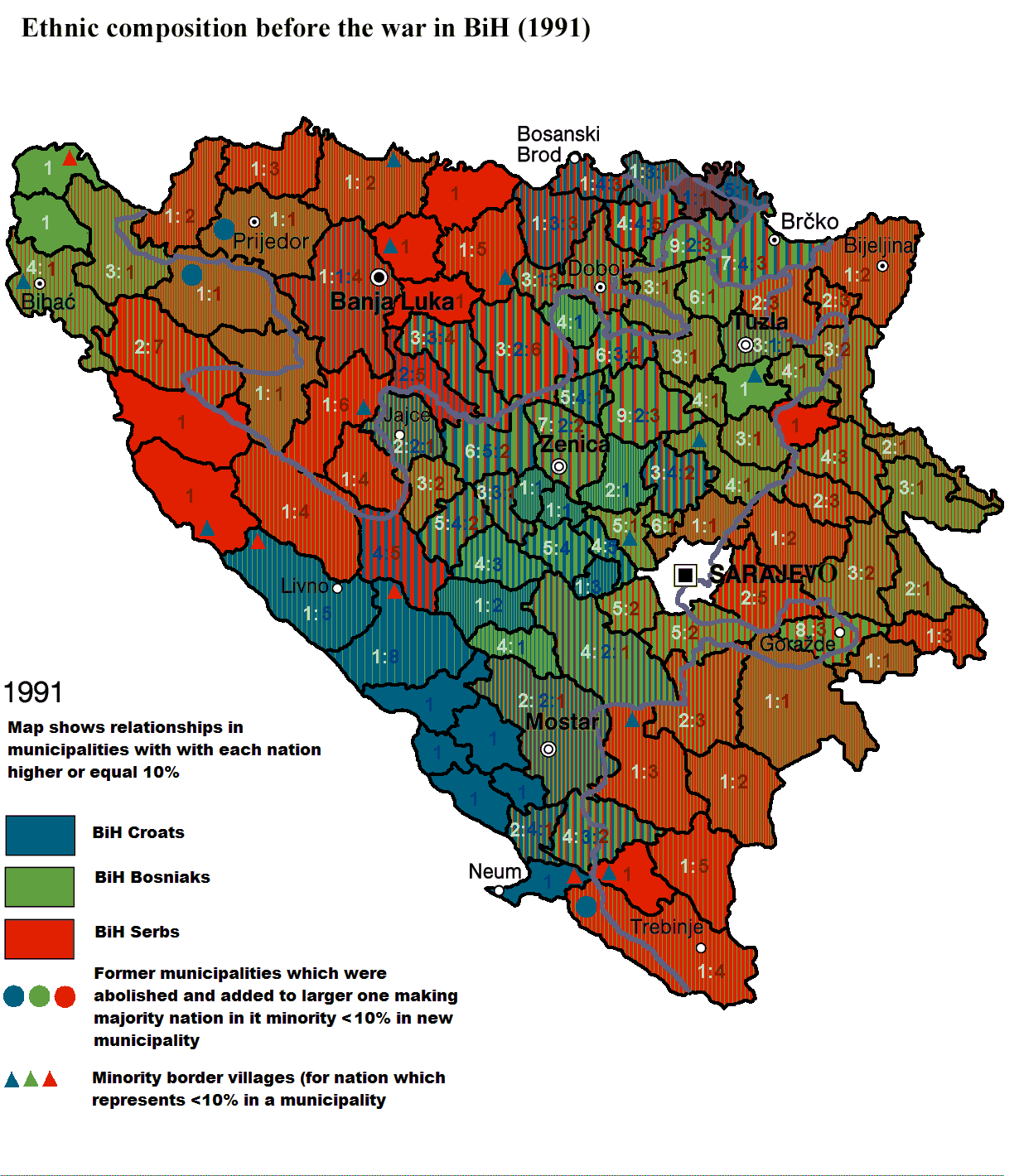
Slovenia
Slovenia , officially the Republic of Slovenia , is a country in Central and Southeastern Europe touching the Alps and bordering the Mediterranean. Slovenia borders Italy to the west, Croatia to the south and east, Hungary to the northeast, and Austria to the north, and also has a small portion of...
's subsequent declarations of independence and the warfare that ensued placed Bosnia and Herzegovina and its three constituent peoples in an awkward position. A significant split soon developed on the issue of whether to stay with the Yugoslav federation (overwhelmingly favored among Serbs) or seek independence (overwhelmingly favored among Bosniaks and Croats). A declaration of sovereignty on 15 October 1991 was followed by a referendum for independence from Yugoslavia on 29 February and 1 March 1992. The referendum was boycotted by the great majority of Bosnian Serbs, so with a voter turnout of 64%, 98% of which voted in favor of the proposal. Bosnia and Herzegovina became an independent state on 3 March 1992.
While the first casualty of the war is debated, significant Serbian offensives began in March 1992 in Eastern and Northern Bosnia. Following a tense period of escalating tensions the opening shots in the incipient Bosnian conflict were fired when Serb paramilitary forces attacked Bosniak villages around Capljina on 7 March 1992 and around Bosanski Brod and Gorazde on 15 March. These minor attacks were followed by much more serious Serb artillery attacks on Neum on 19 March and on Bosanski Brod on 24 March. The killing of a Bosniak civilian woman on 5 April 1992 by a sniper, while she was demonstrating in Sarajevo against the raising of barricades by Bosnian Serbs, is widely regarded as marking the start of warfare between the three major communities.. Open warfare began in Sarajevo on April 6.
International recognition of Bosnia and Herzegovina meant that the Yugoslav People's Army
Yugoslav People's Army
The Yugoslav People's Army , also referred to as the Yugoslav National Army , was the military of the Socialist Federal Republic of Yugoslavia.-Origins:The origins of the JNA can...
(JNA) officially withdrew from the republic's territory, although their Bosnian Serb members merely joined the Army of Republika Srpska
Army of Republika Srpska
The Army of Republika Srpska ; Serbian, Bosnian, Croatian Vojska Republike Srpske ) also referred to as the Bosnian Serb Army, was the military of today's Republika Srpska which was then the "Serbian Republic of Bosnia and Herzegovina", a self-proclaimed state within the internationally recognized...
. Armed and equipped from JNA stockpiles in Bosnia, supported by volunteers, Republika Srpska's offensives in 1992 managed to place much of the country under its control. By 1993, when an armed conflict erupted between the Sarajevo government and the Croat statelet of Herzeg-Bosnia
Croatian Republic of Herzeg-Bosnia
The Croatian Republic of Herzeg-Bosnia was an unrecognised entity in Bosnia and Herzegovina that existed between 1991 and 1994 during the Bosnian war. It was proclaimed on November 18, 1991 under the name Croatian Community of Herzeg-Bosnia, and claimed to be a separate or distinct "political,...
, about 70% of the country was controlled by the Serbs.
.svg.png)
Washington Agreement
The Washington Agreement was a ceasefire agreement between the warring Croatian Republic of Herzeg-Bosnia and the Republic of Bosnia and Herzegovina, signed in Washington on 18 March 1994 and Vienna. It was signed by Bosnian Prime Minister Haris Silajdžić, Croatian Foreign Minister Mate Granić and...
between the Bosniak and ethnic-Croatian leaders led to the creation of a joint Bosniak-Croat Federation of Bosnia and Herzegovina
Federation of Bosnia and Herzegovina
The Federation of Bosnia and Herzegovina is one of the two political entities that compose the sovereign country of Bosnia and Herzegovina . The two entities are delineated by the Inter-Entity Boundary Line...
. This, along with international outrage at Serb war crimes and atrocities
Bosnian Genocide
The term Bosnian Genocide refers to either the genocide committed by Bosnian Serb forces in Srebrenica in 1995 or the ethnic cleansing campaign that took place throughout areas controlled by the Bosnian Serb Army during the 1992–1995 Bosnian War....
(most notably the Srebrenica massacre
Srebrenica massacre
The Srebrenica massacre, also known as the Srebrenica genocide, refers to the July 1995 killing, during the Bosnian War, of more than 8,000 Bosniaks , mainly men and boys, in and around the town of Srebrenica in Bosnia and Herzegovina, by units of the Army of Republika Srpska under the command of...
of as many as 8,000 Bosniak males in July 1995) helped turn the tide of war. The signing of the Dayton Agreement
Dayton Agreement
The General Framework Agreement for Peace in Bosnia and Herzegovina, also known as the Dayton Agreement, Dayton Accords, Paris Protocol or Dayton-Paris Agreement, is the peace agreement reached at Wright-Patterson Air Force Base near Dayton, Ohio in November 1995, and formally signed in Paris on...
in Paris
Paris
Paris is the capital and largest city in France, situated on the river Seine, in northern France, at the heart of the Île-de-France region...
by the presidents of Bosnia and Herzegovina (Alija Izetbegović
Alija Izetbegovic
Alija Izetbegović was a Bosniak activist, lawyer, author, philosopher and politician, who, in 1990, became the first president of Bosnia and Herzegovina. He served in this role until 1996, when he became a member of the Presidency of Bosnia and Herzegovina, serving until 2000...
), Croatia (Franjo Tuđman), and Yugoslavia (Slobodan Milošević
Slobodan Milošević
Slobodan Milošević was President of Serbia and Yugoslavia. He served as the President of Socialist Republic of Serbia and Republic of Serbia from 1989 until 1997 in three terms and as President of the Federal Republic of Yugoslavia from 1997 to 2000...
) brought a halt to the fighting, roughly establishing the basic structure of the present-day state. The three years of war and bloodshed had left between 200,000 and 250,000 people killed and more than 2 million displaced.
Independent Bosnia and Herzegovina

Since its 1992 independence and the 1995 Constitutional framework of the Dayton Agreement
Dayton Agreement
The General Framework Agreement for Peace in Bosnia and Herzegovina, also known as the Dayton Agreement, Dayton Accords, Paris Protocol or Dayton-Paris Agreement, is the peace agreement reached at Wright-Patterson Air Force Base near Dayton, Ohio in November 1995, and formally signed in Paris on...
, Bosnia and Herzegovina has followed a path of state-building, while remaining under final international supervision through the figure of the High Representative for Bosnia and Herzegovina
High Representative for Bosnia and Herzegovina
The High Representative for Bosnia and Herzegovina, with the Office of the High Representative in Bosnia and Herzegovina, was created in 1995 immediately after the Dayton Peace Agreement to oversee the civilian implementation of this agreement. The High Representative and the OHR represent the...
. Bosnia and Herzegovina is a confederation of two Entities - the Federation of Bosnia and Herzegovina
Federation of Bosnia and Herzegovina
The Federation of Bosnia and Herzegovina is one of the two political entities that compose the sovereign country of Bosnia and Herzegovina . The two entities are delineated by the Inter-Entity Boundary Line...
and the Republika Srpska
Republika Srpska
Republika Srpska is one of two main political entities of Bosnia and Herzegovina, the other being the Federation of Bosnia and Herzegovina...
, as well as the district of Brčko
Brcko District
Brčko District in northeastern Bosnia and Herzegovina is a neutral, self-governing administrative unit, under the sovereignty of Bosnia and Herzegovina...
. Each of the Entities has its own constitution and extensive legislative powers.
Bosnia and Herzegovina is a potential candidate country for accession into the EU
Accession of Bosnia and Herzegovina to the European Union
The accession of Bosnia and Herzegovina to the European Union is the aim of the present relations between the two entities. Bosnia and Herzegovina has been recognised by the EU as a "potential candidate country" for accession since the decision of the European Council in Thessaloniki in 2003...
; an EU-BiH Stabilization and Association Agreement has been signed in 2008. Its accession to NATO
Accession of Bosnia and Herzegovina to NATO
The accession of Bosnia and Herzegovina to NATO is in the negotiations stage as of 2010.Bosnia and Herzegovina joined the Partnership for Peace in 2006, and signed an agreement on security cooperation in March 2007. The nation began further cooperation with NATO within their Individual Partnership...
is in the phase of negotiation, and a Membership Action Plan has been signed in April 2010.
See also
- Bosnian GenocideBosnian GenocideThe term Bosnian Genocide refers to either the genocide committed by Bosnian Serb forces in Srebrenica in 1995 or the ethnic cleansing campaign that took place throughout areas controlled by the Bosnian Serb Army during the 1992–1995 Bosnian War....
- Breakup of Yugoslavia
- Demographic history of Bosnia and HerzegovinaDemographic history of Bosnia and HerzegovinaThis article is about the Demographic history of Bosnia and Herzegovina, and deals with the country's documented demographics over time. For an overview of the various ethnic groups and their historical development, see Nations of Bosnia and Herzegovina....
- Herceg Bosna
- History of Yugoslavia
- History of the BalkansHistory of the BalkansThe Balkans is an area of southeastern Europe situated at a major crossroads between mainland Europe and the Near East. The distinct identity and fragmentation of the Balkans owes much to its common and often violent history and to its very mountainous geography.-Neolithic:Archaeologists have...
- History of EuropeHistory of EuropeHistory of Europe describes the history of humans inhabiting the European continent since it was first populated in prehistoric times to present, with the first human settlement between 45,000 and 25,000 BC.-Overview:...
- League of Communists of YugoslaviaLeague of Communists of YugoslaviaLeague of Communists of Yugoslavia , before 1952 the Communist Party of Yugoslavia League of Communists of Yugoslavia (Serbo-Croatian: Savez komunista Jugoslavije/Савез комуниста Југославије, Slovene: Zveza komunistov Jugoslavije, Macedonian: Сојуз на комунистите на Југославија, Sojuz na...
- President of Bosnia and Herzegovina
- List of Prime Ministers of Bosnia and Herzegovina
- List of heads of state of Yugoslavia
- List of Prime Ministers of Yugoslavia
- Politics of Bosnia and HerzegovinaPolitics of Bosnia and HerzegovinaPolitics of Bosnia and Herzegovina takes place in a framework of a parliamentary representative democratic republic, whereby the Council of Ministers of Bosnia and Herzegovina is the head of government, and of a multi-party system. Executive power is exercised by the government. Legislative power...
- Republic Srpska
Further reading
- Marko Attila HoareMarko Attila HoareMarko Attila Hoare is a British historian of the former Yugoslavia who also writes about the current affairs of Southeast Europe, especially the Balkans including Turkey and the Caucasus.-Biography:...
, The History of Bosnia: From the Middle Ages to the Present Day, London: SaqiSaqi BooksSaqi Books is an independent UK publisher co-founded in 1984 by author and feminist Mai Ghoussoub to "print quality academic and general interest books on the Middle East". It now claims to be "the UK's largest publisher of Middle Eastern and Arabic titles"...
, 2007 - Roger Cohen, Hearts Grown Brutal: Sagas of Sarajevo, New York: Random House, 1998
- Lenard J. Cohen, Broken Bonds: The Disintegration of Yugoslavia, Boulder, Colorado: Westview Press, 1993
- Roy Gutman, A Witness to Genocide: The 1993 Pulitzer prize-winning dispatches on the "ethnic cleansing" of Bosnia, New York: Macmillan, 1993
- Noel MalcolmNoel MalcolmNoel Robert Malcolm FBA FRSL is a modern English historian, writer, and columnist.-Life:Malcolm was educated at Eton College , read History at Peterhouse, Cambridge, wrote his doctorate dissertation at Trinity College, Cambridge, and was for a time Fellow of Gonville and Caius College,...
, Bosnia: A Short History, 1994 - Murray, Elinor et al., The Struggle for Peace in Bosnia: Considering U.S. Options, Providence, RI: Center for Foreign Policy Development of Brown University, 1992, ED 371 965
- Matthew ParishMatthew ParishMatthew Parish is a lawyer and scholar of international relations. He is best known for his writings about the politics of the western Balkans, in particular his prediction of the secession of Republika Srpska from Bosnia and Herzegovina and his criticisms of the international community's presence...
, A Free City in the Balkans: Reconstructing a Divided Society in Bosnia, London: I.B.Tauris, 2009 - Paolo Rumiz, Maschere per un massacro, Editori Riuniti, Roma, 2000
- Joe Sacco, War's End Profiles from Bosnia 1995-96, Drawn & Quarterly, 2005
- Michael Sells, The Bridge Betrayed: Religion and Genocide in Bosnia, University of California Press, 1996
- Charles Shafer, Not My War, Williams and Wiliams Press, 2004.
- Ed Vulliamy, Seasons in Hell: Understanding Bosnia's War, New York: St. Martin's Press, 1994
General history
- Serbian land reform and colonization of Bosnia and Herzegovina in 1918, by Dženana E. Semiz, University of Sarajevo (strongly recommended)
- Oriental Institute Sarajevo
- Bosniak Institute Sarajevo
- Bosnian Institute
- Bosnian language
- Bosnia and Herzegovina: Everything you need to know
- Genealogy of Rulers and History of Medieval Bosnia (Excellent web source)
- Origin of the Medieval Bosnian Royal Dynasty Kotromani (Excellent web source)
- Regnal Chronologies (Excellent resource)
- Historical and Geographical Outline (Note huge discrepancy between relatively objective views in authoring texts hosted by tha site and general editor contributions in writings on issue of medieval and history of Bosnia and Herzegovina in general)
- Medieval Bosnia: a reassessment - Bosnian Borders (Note huge discrepancy between relatively objectiv views in authoring texts hosted by tha site and general editor contributions in writings on issue of medieval and history of Bosnia and Herzegovina in general)
- The Hval Manuscript
- Selected Bibliography of English-language Print Resources for Bosnia and Herzegovina at Yale University Library (Excellent web source)
- General sources for the study of Bosnian Civilization
- Brief history of Bosnia and Herzegovina
- Religion and culture in medieval Bosnia, from "The Late Medieval Balkans" by John V.A Fine, Jr.
- A Brief History of Bosnia-Herzegovina by Andras Riedlmayer, Harvard University
- History of Bosnia and Herzegovina
- WWW-VL: History: Bosnia & Herzegovina
- Bosnian history
- Open Book: Preserving Cultural Heritage of Bosnia and Herzegovina
- ODJEK - review for Art, Science and Social issues
- Spirit of Bosnia
- Timeline: Bosnia-Hercegovina at BBC News
Bosnian War and post-war history
- John K. Cox: Teaching about Conflict and Crisis in the Former Yugoslavia: The Case of Bosnia-Hercegovina
- Sobaka Bosnia articles
- Herceg Bosna: Myths about Croatian long-term strategy of the Bosnia partition
- TIME Daily short timeline of Bosnian conflict
- OHR ethnic maps of Bosnia and Herzegovina
- Washington Post: An overview of war
- Bosnia HomePage at Caltech
- Bosnia: a single country or an apple of discord?, Bosnian InstituteBosnian InstituteThe Bosnian Institute is an organisation principally devoted to providing information on, and promoting the common good of, Bosnia and Herzegovina. It publishes a quarterly online magazine. It is directed by Quintin Hoare....
, 12 May 2006 - hWeb - Convoy to Sarajevo, a personal account of relief work during the Bosnia War
- Visegrad Genocide Memories

