
Historical migration
Encyclopedia
It is thought that pre-historical migration of human populations
began with the movement of Homo erectus
out of Africa
across Eurasia
about a million years ago. Homo sapiens appears to have colonized all of Africa about 150 millennia ago, moved out of Africa some 80 millennia ago, and spread across Eurasia and to Australia before 40 millennia ago. Migration to the Americas
took place about 20 to 15 millennia ago, and by 1 millennium ago, all the Pacific Islands
were colonized. Later population movements notably include the Neolithic revolution
and Indo-European expansion, part of which emerges in the earliest historic records.
Before the modern era, migrations are often confusing in the written record because the history is written by societies on the periphery of the migrating peoples, or by their descendants who have given up the nomadic way of life. This is true of the era that follows the collapse of classical civilization in Europe, including the Early Medieval Great Migrations
, and the related Turkic expansion. Much better understood are the Age of Exploration and European Colonialism
, which led to an accelerated pace of migration over vast distances as new means of transportation emerged.
 Evolution of the genus Homo
Evolution of the genus Homo
took place in Africa. First Homo erectus
migrated out of Africa across Eurasia, beginning about one million years ago, no doubt using some of the same available land routes north of the Himalayas that were later to become the Silk Road
, and across the Strait of Gibraltar
. Bruce Bower has suggested that Homo erectus may have built rafts and sailed oceans, a theory that has raised some controversy.
The expansion of Homo erectus
was followed by that of Homo sapiens. The matrilinear most recent common ancestor
shared by all living human beings, dubbed Mitochondrial Eve
, probably lived roughly 150-120 millennia ago, the time of Homo sapiens idaltu
, probably in the area of modern Ethiopia
, Kenya
or Tanzania
. Around 100-80 millennia ago, three main lines of Homo sapiens sapiens diverged, bearers of mitochondrial haplogroup L1
(mtDNA) / A
(Y-DNA) colonizing Southern Africa (the ancestors of the Khoisan
(Capoid
) peoples), bearers of haplogroup L2
(mtDNA) / B
(Y-DNA) settling Central and West Africa (the ancestors of Niger–Congo and Nilo-Saharan speaking peoples and of the Mbuti
pygmies), while the bearers of haplogroup L3
remained in East Africa. Some 70 millennia ago, a part of the L3 bearers migrated into the Near East
, spreading east to southern Asia
and Australasia
some 60 millennia ago, northwestwards into Europe
and eastwards into Central Asia
some 40 millennia ago, and further east to the Americas from ca. 30 millennia ago.
 Agriculture
Agriculture
is believed to have first been practised some 10,000 years ago in the Fertile Crescent
(see Jericho
). From there it propagated as a "wave" across Europe, a view supported by Archaeogenetics
, reaching northern Europe some 5 millennia ago.
VN
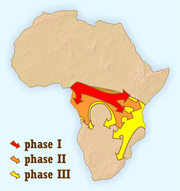 The Bantu first originated around the Benue
The Bantu first originated around the Benue
-Cross
rivers area in southeastern Nigeria and spread over Africa to the Zambia
area. Sometime in the second millennium BC
, perhaps triggered by the drying of the Sahara
and pressure from the migration of people from the Sahara
into the region, they were forced to expand into the rainforest
s of central Africa (phase I). In the 1st millennium BC
, they began a more rapid second phase of expansion beyond the forests into southern and eastern Africa, and again in the 1st millennium AD as new agricultural techniques and plants were developed in Zambia. By about AD 1000 it had reached modern day Zimbabwe
and South Africa
. In Zimbabwe a major southern hemisphere empire was established, with its capital at Great Zimbabwe
. By the 14th or 15th century, the Empire had surpassed its resources and had collapsed.
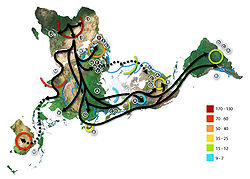
With the art of open-sea navigation
involving the most confident and courageous use of the available technologies of boat-building, combined with the most sophisticated understanding of currents and prevailing winds, the Polynesia
ns, starting with the Lapita
culture, have proven to be the most successful in the art of navigation, if the permanent spread of culture is taken into account, for the Norse adventurers in the North Atlantic and the Arab traders in the Indian Ocean did not create permanent settlements. The Lapita people, who got their name from the archaeological site in Lapita, New Caledonia
, where their characteristic pottery was first discovered, came from Austronesia
, probably New Guinea. Their navigation skills took them to the Solomon Islands, around 1600 BC, and later to Fiji, Samoa and Tonga. By the beginning of the 1st millennium BC
, most of Polynesia was a loose web of thriving cultures who settled on the islands' coasts and lived off the sea. By 500 BC Micronesia
was completely colonized; the last region of Polynesia
to be reached was New Zealand
in around AD 1000.
Polynesian migration patterns also have been studied by linguistic
analysis, and recently by analyzing characteristic genetic alleles of today's inhabitants. Both methods resulted in supporting the original archaeological findings.
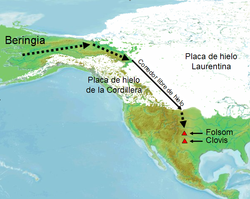 The specifics of Paleo-Indians migration to and throughout the Americas, including the exact dates and routes traveled, are subject to ongoing research and discussion. The traditional theory has been that these early migrants moved into the Beringia land bridge between eastern Siberia and present-day Alaska around 40,000–17,000 years ago, when sea levels were significantly lowered due to the Quaternary glaciation
The specifics of Paleo-Indians migration to and throughout the Americas, including the exact dates and routes traveled, are subject to ongoing research and discussion. The traditional theory has been that these early migrants moved into the Beringia land bridge between eastern Siberia and present-day Alaska around 40,000–17,000 years ago, when sea levels were significantly lowered due to the Quaternary glaciation
. These people are believed to have followed herds of now-extinct pleistocene
megafauna
along ice-free corridors that stretched between the Laurentide
and Cordilleran
ice sheets. Another route proposed is that, either on foot or using primitive boats, they migrated down the Pacific Northwest
coast to South America
. Evidence of the latter would since have been covered by a sea level rise of hundreds of meters following the last ice age.
Archaeologists contend that Paleo-Indians migration out of Beringia (eastern Alaska
), ranges from 40,000 to around 16,500 years ago. This time range is a hot source of debate and will be for years to come. The few agreements achieved to date are the origin from Central Asia
, with widespread habitation of the Americas during the end of the last glacial period, or more specifically what is known as the late glacial maximum, around 16,000–13,000 years before present.
 The Inuit are the descendants of what anthropologists
The Inuit are the descendants of what anthropologists
call the Thule culture, which emerged from western Alaska around 1,000 CE and spread eastward across the Arctic
, displacing the Dorset culture
(in Inuktitut
, the Tuniit). Inuit historically referred to the Tuniit as "giants", or "dwarfs", who were taller and stronger than the Inuit. Researchers hypothesize that the Dorset culture lacked dogs, larger weapons and other technologies used by the expanding Inuit society. By 1300, the Inuit had settled in west Greenland
, and finally moved into east Greenland over the following century. The Inuit had trade routes with more southern cultures. Boundary disputes were common and gave rise to aggressive actions.
War
fare was common among Inuit groups with sufficient population density. Inuit, such as the Nunatamiut
(Uummarmiut
) who inhabited the Mackenzie River
delta area, often engaged in common warfare. The Central Arctic Inuit lacked the population density to engage in warfare. In the 13th century, the Thule culture began arriving in Greenland from what is now Canada. Norse accounts are scant. Norse-made items from Inuit campsites in Greenland were obtained by either trade or plunder. One account, Ívar Bárðarson, speaks of "small people" with whom the Norsemen fought. 14th-century accounts that a western settlement, one of the two Norse settlements, was taken over by the Skræling
.
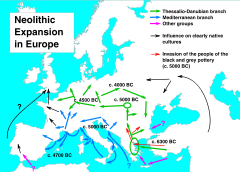
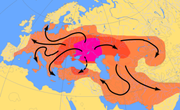 The Indo-European migration had variously been dated to the end of the Neolithic
The Indo-European migration had variously been dated to the end of the Neolithic
(Marija Gimbutas
: Corded ware, Yamna, Kurgan
), the early Neolithic (Colin Renfrew: Starčevo-Körös
, Linearbandkeramic) and the late Palaeolithic (Marcel Otte
, Paleolithic Continuity Theory
).
The speakers of the Proto-Indo-European language
are usually believed to have originated to the North of the Black Sea
(today Eastern Ukraine
and Southern Russia
), and from there they gradually migrated into, and spread their language by cultural diffusion to, Anatolia
, Europe
, and Central Asia
Iran
and South Asia
starting from around the end of the Neolithic period (see Kurgan hypothesis
). Other theories, such as that of Colin Renfrew, posit their development much earlier, in Anatolia, and claim that Indo-European languages and culture spread as a result of the agricultural revolution in the early Neolithic.
Relatively little is known about the inhabitants of pre-Indo-European "Old Europe". They are believed to have been garden-plot horticulturalists. The Basque language
remains from that era, as do the indigenous languages of the Caucasus
. The Sami
are genetically distinct among the peoples of Europe, but the Sami languages
, as part of the Uralic languages
, spread into Europe about the same time as the Indo-European languages. However, since that period speakers of other Uralic languages such as the Finns and the Estonians have had more contact with other Europeans, thus today sharing more genes with them than the Sami.
documenting the presence of early Indo-Aryans
in the Punjab
from the late 2nd millennium BC, and Iranian tribes
being attested in Assyrian sources as in the Iranian plateau
from the 9th century BC. In the Late Bronze Age, the Aegean
and Anatolia
were overrun by moving populations, summarized as the "Sea Peoples
", leading to the collapse of the Hittite Empire and ushering in the Iron Age
.
of Greece led to the Greek Dark Ages
. Very Little is known about the period of the 12th to 9th centuries BC, but there were significant population movements throughout Anatolia and the Iranian plateau. Iranian peoples
invaded the territory of modern Iran
in this period, taking over the Elamite Empire. The Urartians were displaced by Armenians
, and the Cimmerians
and the Mushki
migrated from the Caucasus into Anatolia. A Thraco-Cimmerian
connection links these movements to the Proto-Celtic world of central Europe, leading to the introduction of Iron to Europe and the Celt
ic expansion to western Europe and the British Isles around 500 BC.
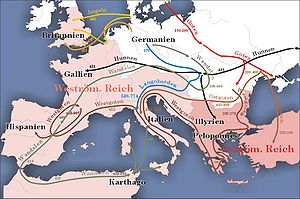 Western historians refer to the period of migrations that separated Antiquity
Western historians refer to the period of migrations that separated Antiquity
from the Middle Ages
in Europe
as the Great Migrations or as the Migrations Period. This period is further divided into two phases.
The first phase, from 300 to 500 AD, saw the movement of Germanic, Sarmatian
and Hunnic
tribes and ended with the settlement of these peoples in the areas of the former Western Roman Empire
, essentially causing its demise. (See also: Ostrogoths, Visigoths, Burgundians
, Suebi
, Alamanni
Marcomanni
).
The second phase, between 500
and 900
AD, saw Slavic
, Turkic and other tribes on the move, re-settling in Eastern Europe and gradually making it predominantly Slavic. Moreover, more Germanic tribes migrated within Europe during this period, including the Lombards
(to Italy
), and the Angles
, Saxons
, and Jutes
(to the British Isles
). See also: Avars
, Bulgars
, Huns
, Arabs, Vikings, Varangians. The last phase of the migrations saw the coming of the Hungarians to the Pannonian plain
.
German historians of the 19th century referred to these Germanic migrations as the Völkerwanderung, the migrations of the peoples.
The European migration period is connected with the simultaneous Turkic expansion which at first displaced other peoples towards the west, and by High Medieval times, the Seljuk Turks themselves reached the Mediterranean.
raided all over Europe from the 8th century and settled in many places, including Normandy
, the north of England
, Scotland
and Ireland
(most of whose urban centres were founded by the Vikings). The Normans later conquered the Saxon Kingdom of England, most of Ireland, southern Italy and Sicily
, Iberia was invaded by Muslim
Arabs, Berbers
and Moors
in the 8th century, founding new Kingdoms such as al Andalus and bringing with them a wave of settlers from North Africa.
In the other direction, European Christian
armies conquered Palestine
for a time during the Crusades
11th to 13th centuries, founding three Christian kingdoms and settling them with Christian Knights and their families. This permanent migration was relatively small however and was one of the reasons why the Crusaders eventually lost the their hold on the Holy Lands.
Massive migrations of Germans
took place into East Central and Eastern Europe, reaching its peak in the 12th to 14th centuries. These Ostsiedlung
settlements in part followed territorial gains of the Holy Roman Empire
, but areas beyond were settled, too.
At the end of the Middle Ages, the Roma arrived in Europe (to Iberia
and the Balkans
) from the Middle East, originating from the Indus river
.
Internal European migration stepped up in the Early Modern Period. In this period, major migration within Europe included the recruiting by monarchs of landless laborers to settle depopulated or uncultivated regions and a series of forced migration caused by religious persecution. Notable examples of this phenomenon include the expulsion of the Jews from Spain
in 1492, mass migration of Protestants from the Spanish Netherlands to the Dutch Republic
after the 1580s, the expulsion of the Moriscos
from Spain in 1609, and the expulsion of the Huguenots from France
in the 1680s. Since the 14th century, the Serbs
started leaving the areas of their medieval Kingdom and Empire that was overrun by the Ottoman
Turks and migrated to the north, to the lands of today's Vojvodina
(northern Serbia), which was ruled by the Kingdom of Hungary
at that time. The Habsburg
monarchs of Austria encouraged them to settle on their frontier with the Turks and provide military service by granting them free land and religious toleration. The two greatest migrations
took place in 1690 and 1737. Other instances of labour recruitments include the Plantations of Ireland
- the settling of Ireland with Protestant colonists from England, Scotland and Wales in the period 1560-1690 and the recruitment of Germans by Catherine the Great of Russia to settle the Volga region in the 18th century.
European Colonialism
from the 16th to the early 20th centuries led to an imposition of a European colonies in many regions of the world, particularly in the Americas
, South Asia
, Sub-Saharan Africa
and Australia
, where European languages remain either prevalent or in frequent use as administrative languages. Major human migration before the 18th century was largely state directed. For instance, Spanish emigration to the New World was limited to settlers from Castile
who were intended to act as soldiers or administrators. Mass immigration was not encouraged due to a labour shortage in Europe (of which Spain was the worst affected by a depopulation of its core territories in the 17th century).
Europeans also tended to die of tropical diseases in the New World in this period and for this reason England, France and Spain preferred using slaves as free labor in their American possessions. Many historians attribute a change in this pattern in the 18th century to population increases in Europe.
However, in the less tropical regions of North America's east coast, large numbers of religious dissidents, mostly English Puritans, settled during the early 17th century. Spanish restrictions on emigration to Latin America were revoked and the English colonies in North America also saw a major influx of settlers attracted by cheap or free land, economic opportunity and the continued lure of religious toleration.
A period in which various early English colonies had a significant amount of self-rule prevailed from the time of the Plymouth colony's founding in 1620 through 1676, as the mother country was wracked by revolution and general instability. However, King William III decisively intervened in colonial affairs after 1688 and the English colonies gradually came more directly under royal governance, with a marked effect on the type of emigration. During the early 18th century, significant numbers of non-English seekers of greater religious and political freedom were allowed to settle within the British colonies, including Protestant Palatine Germans displaced by French conquest, French Huguenots disenfranchised by an end of religious tolerance, Scotch-Irish Presbyterians, Quakers who were often Welsh, as well as Presbyterian and Catholic Scottish Highlanders seeking a new start after a series of unsuccessful revolts.
The English colonists who came during this period were increasingly moved by economic necessity. Some colonies, including Georgia, were settled heavily by petty criminals and indentured servants who hoped to pay off their debts. By 1800, European emigration had transformed the demographic character of the American continent. This was also due in part to the devastating effect of European diseases and warfare on Native American populations.
The European settlers' influence elsewhere was less pronounced as in South Asia and Africa, European settlement in this period was limited to thin layer of administrators, traders and soldiers.
and historiographical
accounts alike concerning how a given people came to inhabit its present territory.
Notable Landnahme events include:
. Millions of agricultural workers left the countryside and moved to the cities causing unprecedented levels of urbanization. This phenomenon began in Britain in the late 18th century and spread around the world and continues to this day in many areas.
Industrialization encouraged migration wherever it appeared. The increasingly global economy globalised the labour market. Atlantic slave trade
diminished sharply after 1820, which gave rise to self-bound contract labour migration from Europe and Asia to plantations. Also overpopulation, open agricultural frontiers and rising industrial centres attracted voluntary, encouraged and sometimes coerced migration. Moreover, migration was significantly eased by improved transportation techniques.
During this same period similar large numbers of people migrated over large distances within Asia. Southeastern Asia received 50 million migrants, mainly from India and south China. North Asia, that be Manchuria
, Siberia, Central Asia and Japan together, received another 50 million, in a migration that started in the 1890s with migrants from China, Russia and Korea, and was especially large due to coerced migration from the Soviet Union and Japan in the 1930s. Less is known about exact numbers of the migrations from and within Africa in this period, but Africa experienced a small nett immigration between 1850 and 1950, from a variety of origins.
Provisions of the Potsdam Agreement
from 1945 signed by victorious Western Allies
and the Soviet Union
led to one of the largest European migrations
, and definitely the largest in the 20th century. It involved the migration and resettlement of close to or over 20 million people. The largest affected group were 16.5 million Germans expelled from Eastern Europe westwards
. The second largest group were Poles, expelled westwards from eastern Kresy
region and resettled in the so-called Recovered Territories
(see Oder-Neisse line
). Hundreds of thousands of Poles, Ukrainians, Lithuanians, Latvians, Estonians and some Belarusians, were in the meantime expelled eastwards from Europe to the Soviet Union. Finally, many of the several hundred thousand Jews remaining in the Eastern Europe after the Holocaust migrated outside Europe
to Israel
and the USA.
Currently in progress are large migrations to North America
from Mexico
and Central America
, and a slightly smaller migration from the Islamic World into Europe
.
Human migration
Human migration is physical movement by humans from one area to another, sometimes over long distances or in large groups. Historically this movement was nomadic, often causing significant conflict with the indigenous population and their displacement or cultural assimilation. Only a few nomadic...
began with the movement of Homo erectus
Homo erectus
Homo erectus is an extinct species of hominid that lived from the end of the Pliocene epoch to the later Pleistocene, about . The species originated in Africa and spread as far as India, China and Java. There is still disagreement on the subject of the classification, ancestry, and progeny of H...
out of Africa
Africa
Africa is the world's second largest and second most populous continent, after Asia. At about 30.2 million km² including adjacent islands, it covers 6% of the Earth's total surface area and 20.4% of the total land area...
across Eurasia
Eurasia
Eurasia is a continent or supercontinent comprising the traditional continents of Europe and Asia ; covering about 52,990,000 km2 or about 10.6% of the Earth's surface located primarily in the eastern and northern hemispheres...
about a million years ago. Homo sapiens appears to have colonized all of Africa about 150 millennia ago, moved out of Africa some 80 millennia ago, and spread across Eurasia and to Australia before 40 millennia ago. Migration to the Americas
Models of migration to the New World
There have been several models for the human settlement of the Americas proposed by various academic communities. The question of how, when and why humans first entered the Americas is of intense interest to archaeologists and anthropologists, and has been a subject of heated debate for centuries...
took place about 20 to 15 millennia ago, and by 1 millennium ago, all the Pacific Islands
Pacific Islands
The Pacific Islands comprise 20,000 to 30,000 islands in the Pacific Ocean. The islands are also sometimes collectively called Oceania, although Oceania is sometimes defined as also including Australasia and the Malay Archipelago....
were colonized. Later population movements notably include the Neolithic revolution
Neolithic Revolution
The Neolithic Revolution was the first agricultural revolution. It was the transition from hunting and gathering to agriculture and settlement. Archaeological data indicates that various forms of plants and animal domestication evolved independently in 6 separate locations worldwide circa...
and Indo-European expansion, part of which emerges in the earliest historic records.
Before the modern era, migrations are often confusing in the written record because the history is written by societies on the periphery of the migrating peoples, or by their descendants who have given up the nomadic way of life. This is true of the era that follows the collapse of classical civilization in Europe, including the Early Medieval Great Migrations
Migration Period
The Migration Period, also called the Barbarian Invasions , was a period of intensified human migration in Europe that occurred from c. 400 to 800 CE. This period marked the transition from Late Antiquity to the Early Middle Ages...
, and the related Turkic expansion. Much better understood are the Age of Exploration and European Colonialism
Colonialism
Colonialism is the establishment, maintenance, acquisition and expansion of colonies in one territory by people from another territory. It is a process whereby the metropole claims sovereignty over the colony and the social structure, government, and economics of the colony are changed by...
, which led to an accelerated pace of migration over vast distances as new means of transportation emerged.
Early migrations

Human evolution
Human evolution refers to the evolutionary history of the genus Homo, including the emergence of Homo sapiens as a distinct species and as a unique category of hominids and mammals...
took place in Africa. First Homo erectus
Homo erectus
Homo erectus is an extinct species of hominid that lived from the end of the Pliocene epoch to the later Pleistocene, about . The species originated in Africa and spread as far as India, China and Java. There is still disagreement on the subject of the classification, ancestry, and progeny of H...
migrated out of Africa across Eurasia, beginning about one million years ago, no doubt using some of the same available land routes north of the Himalayas that were later to become the Silk Road
Silk Road
The Silk Road or Silk Route refers to a historical network of interlinking trade routes across the Afro-Eurasian landmass that connected East, South, and Western Asia with the Mediterranean and European world, as well as parts of North and East Africa...
, and across the Strait of Gibraltar
Strait of Gibraltar
The Strait of Gibraltar is a narrow strait that connects the Atlantic Ocean to the Mediterranean Sea and separates Spain in Europe from Morocco in Africa. The name comes from Gibraltar, which in turn originates from the Arabic Jebel Tariq , albeit the Arab name for the Strait is Bab el-Zakat or...
. Bruce Bower has suggested that Homo erectus may have built rafts and sailed oceans, a theory that has raised some controversy.
The expansion of Homo erectus
Homo erectus
Homo erectus is an extinct species of hominid that lived from the end of the Pliocene epoch to the later Pleistocene, about . The species originated in Africa and spread as far as India, China and Java. There is still disagreement on the subject of the classification, ancestry, and progeny of H...
was followed by that of Homo sapiens. The matrilinear most recent common ancestor
Most recent common ancestor
In genetics, the most recent common ancestor of any set of organisms is the most recent individual from which all organisms in the group are directly descended...
shared by all living human beings, dubbed Mitochondrial Eve
Mitochondrial Eve
In the field of human genetics, Mitochondrial Eve refers to the matrilineal "MRCA" . In other words, she was the woman from whom all living humans today descend, on their mother's side, and through the mothers of those mothers and so on, back until all lines converge on one person...
, probably lived roughly 150-120 millennia ago, the time of Homo sapiens idaltu
Homo sapiens idaltu
Homo sapiens idaltu is an extinct subspecies of Homo sapiens that lived almost 160,000 years ago in Pleistocene Africa. is from the Saho-Afar word meaning "elder or first born"....
, probably in the area of modern Ethiopia
Ethiopia
Ethiopia , officially known as the Federal Democratic Republic of Ethiopia, is a country located in the Horn of Africa. It is the second-most populous nation in Africa, with over 82 million inhabitants, and the tenth-largest by area, occupying 1,100,000 km2...
, Kenya
Kenya
Kenya , officially known as the Republic of Kenya, is a country in East Africa that lies on the equator, with the Indian Ocean to its south-east...
or Tanzania
Tanzania
The United Republic of Tanzania is a country in East Africa bordered by Kenya and Uganda to the north, Rwanda, Burundi, and the Democratic Republic of the Congo to the west, and Zambia, Malawi, and Mozambique to the south. The country's eastern borders lie on the Indian Ocean.Tanzania is a state...
. Around 100-80 millennia ago, three main lines of Homo sapiens sapiens diverged, bearers of mitochondrial haplogroup L1
Haplogroup L1 (mtDNA)
In human mitochondrial genetics, Haplogroup L1 is a human mitochondrial DNA haplogroup common in Central and West Africa.-Origin:Haplogroup L1 is believed to have appeared approximately 110,000 to 170,000 years ago...
(mtDNA) / A
Haplogroup A (Y-DNA)
In human genetics, Haplogroup A refers to a group of y-chromosome lineages that were among the first to branch off from the root of the human y-chromosome phylogeny...
(Y-DNA) colonizing Southern Africa (the ancestors of the Khoisan
Khoisan
Khoisan is a unifying name for two ethnic groups of Southern Africa, who share physical and putative linguistic characteristics distinct from the Bantu majority of the region. Culturally, the Khoisan are divided into the foraging San and the pastoral Khoi...
(Capoid
Capoid
The Capoid race is a historical racial category proposed in 1962 by anthropologist Carleton S. Coon and named after the Cape of Good Hope; these people had formerly been regarded as a sub-type of the historical racial category Negroid....
) peoples), bearers of haplogroup L2
Haplogroup L2 (mtDNA)
In human mitochondrial genetics, Haplogroup L2 is a human mitochondrial DNA haplogroup typical of Africa. Its subclade L2a is a somewhat frequent and widespread mtDNA cluster in Africa, as well as in the African diaspora Americans . et al.-Origin:L2 is a common African lineage. It is believed to...
(mtDNA) / B
Haplogroup B (Y-DNA)
In human genetics, Haplogroup B is a Y-chromosome haplogroup.-Distribution:Haplogroup B is localized to sub-Saharan Africa, especially to tropical forests of West-Central Africa. After Y-haplogroup A, it is the second oldest and one of the most diverse human Y-haplogroups...
(Y-DNA) settling Central and West Africa (the ancestors of Niger–Congo and Nilo-Saharan speaking peoples and of the Mbuti
Mbuti
Mbuti or Bambuti are one of several indigenous pygmy groups in the Congo region of Africa. Their languages belong to the Central Sudanic and also to Bantu languages.-Overview:...
pygmies), while the bearers of haplogroup L3
Haplogroup L3 (mtDNA)
In human mitochondrial genetics, Haplogroup L3 is a human mitochondrial DNA haplogroup. Haplogroup L3 has played a pivotal role in the history of the human species...
remained in East Africa. Some 70 millennia ago, a part of the L3 bearers migrated into the Near East
Near East
The Near East is a geographical term that covers different countries for geographers, archeologists, and historians, on the one hand, and for political scientists, economists, and journalists, on the other...
, spreading east to southern Asia
Asia
Asia is the world's largest and most populous continent, located primarily in the eastern and northern hemispheres. It covers 8.7% of the Earth's total surface area and with approximately 3.879 billion people, it hosts 60% of the world's current human population...
and Australasia
Australasia
Australasia is a region of Oceania comprising Australia, New Zealand, the island of New Guinea, and neighbouring islands in the Pacific Ocean. The term was coined by Charles de Brosses in Histoire des navigations aux terres australes...
some 60 millennia ago, northwestwards into Europe
Europe
Europe is, by convention, one of the world's seven continents. Comprising the westernmost peninsula of Eurasia, Europe is generally 'divided' from Asia to its east by the watershed divides of the Ural and Caucasus Mountains, the Ural River, the Caspian and Black Seas, and the waterways connecting...
and eastwards into Central Asia
Central Asia
Central Asia is a core region of the Asian continent from the Caspian Sea in the west, China in the east, Afghanistan in the south, and Russia in the north...
some 40 millennia ago, and further east to the Americas from ca. 30 millennia ago.
Neolithic Revolution

Agriculture
Agriculture is the cultivation of animals, plants, fungi and other life forms for food, fiber, and other products used to sustain life. Agriculture was the key implement in the rise of sedentary human civilization, whereby farming of domesticated species created food surpluses that nurtured the...
is believed to have first been practised some 10,000 years ago in the Fertile Crescent
Fertile Crescent
The Fertile Crescent, nicknamed "The Cradle of Civilization" for the fact the first civilizations started there, is a crescent-shaped region containing the comparatively moist and fertile land of otherwise arid and semi-arid Western Asia. The term was first used by University of Chicago...
(see Jericho
Jericho
Jericho ; is a city located near the Jordan River in the West Bank of the Palestinian territories. It is the capital of the Jericho Governorate and has a population of more than 20,000. Situated well below sea level on an east-west route north of the Dead Sea, Jericho is the lowest permanently...
). From there it propagated as a "wave" across Europe, a view supported by Archaeogenetics
Archaeogenetics
Archaeogenetics, a term coined by Colin Renfrew, refers to the application of the techniques of molecular population genetics to the study of the human past. This can involve:*the analysis of DNA recovered from archaeological remains, i.e...
, reaching northern Europe some 5 millennia ago.
VN
Bantu expansion

Benue River
The Benue River is the major tributary of the Niger River. The river is approximately 1,400 km long and is almost entirely navigable during the summer months...
-Cross
Cross River (Nigeria)
Cross River is the main river in southeastern Nigeria and gives its name to Cross River State.It originates in Cameroon, where it takes the name of the Manyu River....
rivers area in southeastern Nigeria and spread over Africa to the Zambia
Zambia
Zambia , officially the Republic of Zambia, is a landlocked country in Southern Africa. The neighbouring countries are the Democratic Republic of the Congo to the north, Tanzania to the north-east, Malawi to the east, Mozambique, Zimbabwe, Botswana and Namibia to the south, and Angola to the west....
area. Sometime in the second millennium BC
2nd millennium BC
The 2nd millennium BC marks the transition from the Middle to the Late Bronze Age.Its first half is dominated by the Middle Kingdom of Egypt and Babylonia. The alphabet develops. Indo-Iranian migration onto the Iranian plateau and onto the Indian subcontinent propagates the use of the chariot...
, perhaps triggered by the drying of the Sahara
Sahara
The Sahara is the world's second largest desert, after Antarctica. At over , it covers most of Northern Africa, making it almost as large as Europe or the United States. The Sahara stretches from the Red Sea, including parts of the Mediterranean coasts, to the outskirts of the Atlantic Ocean...
and pressure from the migration of people from the Sahara
Sahara
The Sahara is the world's second largest desert, after Antarctica. At over , it covers most of Northern Africa, making it almost as large as Europe or the United States. The Sahara stretches from the Red Sea, including parts of the Mediterranean coasts, to the outskirts of the Atlantic Ocean...
into the region, they were forced to expand into the rainforest
Rainforest
Rainforests are forests characterized by high rainfall, with definitions based on a minimum normal annual rainfall of 1750-2000 mm...
s of central Africa (phase I). In the 1st millennium BC
1st millennium BC
The 1st millennium BC encompasses the Iron Age and sees the rise of many successive empires, and spanned from 1000 BC to 1 BC.The Neo-Assyrian Empire, followed by the Achaemenids. In Greece, Classical Antiquity begins with the colonization of Magna Graecia and peaks with the rise of Hellenism. The...
, they began a more rapid second phase of expansion beyond the forests into southern and eastern Africa, and again in the 1st millennium AD as new agricultural techniques and plants were developed in Zambia. By about AD 1000 it had reached modern day Zimbabwe
Zimbabwe
Zimbabwe is a landlocked country located in the southern part of the African continent, between the Zambezi and Limpopo rivers. It is bordered by South Africa to the south, Botswana to the southwest, Zambia and a tip of Namibia to the northwest and Mozambique to the east. Zimbabwe has three...
and South Africa
South Africa
The Republic of South Africa is a country in southern Africa. Located at the southern tip of Africa, it is divided into nine provinces, with of coastline on the Atlantic and Indian oceans...
. In Zimbabwe a major southern hemisphere empire was established, with its capital at Great Zimbabwe
Great Zimbabwe
Great Zimbabwe is a ruined city that was once the capital of the Kingdom of Zimbabwe, which existed from 1100 to 1450 C.E. during the country’s Late Iron Age. The monument, which first began to be constructed in the 11th century and which continued to be built until the 14th century, spanned an...
. By the 14th or 15th century, the Empire had surpassed its resources and had collapsed.
Pacific
The islands of the Pacific were the last region on Earth to be populated by humans, as recently as twelve to fifteen centuries ago.With the art of open-sea navigation
Navigation
Navigation is the process of monitoring and controlling the movement of a craft or vehicle from one place to another. It is also the term of art used for the specialized knowledge used by navigators to perform navigation tasks...
involving the most confident and courageous use of the available technologies of boat-building, combined with the most sophisticated understanding of currents and prevailing winds, the Polynesia
Polynesia
Polynesia is a subregion of Oceania, made up of over 1,000 islands scattered over the central and southern Pacific Ocean. The indigenous people who inhabit the islands of Polynesia are termed Polynesians and they share many similar traits including language, culture and beliefs...
ns, starting with the Lapita
Lapita
Lapita is a term applied to an ancient Pacific Ocean archaeological culture which is believed by many archaeologists to be the common ancestor of several cultures in Polynesia, Micronesia, and some coastal areas of Melanesia...
culture, have proven to be the most successful in the art of navigation, if the permanent spread of culture is taken into account, for the Norse adventurers in the North Atlantic and the Arab traders in the Indian Ocean did not create permanent settlements. The Lapita people, who got their name from the archaeological site in Lapita, New Caledonia
New Caledonia
New Caledonia is a special collectivity of France located in the southwest Pacific Ocean, east of Australia and about from Metropolitan France. The archipelago, part of the Melanesia subregion, includes the main island of Grande Terre, the Loyalty Islands, the Belep archipelago, the Isle of...
, where their characteristic pottery was first discovered, came from Austronesia
Austronesia
Austronesia, in historical terms, refers to the homeland of the peoples who speak Austronesian languages, including Malay, Filipino, Indonesian, Maori, Malagasy, native Hawaiian, the Fijian language and around a thousand other languages...
, probably New Guinea. Their navigation skills took them to the Solomon Islands, around 1600 BC, and later to Fiji, Samoa and Tonga. By the beginning of the 1st millennium BC
1st millennium BC
The 1st millennium BC encompasses the Iron Age and sees the rise of many successive empires, and spanned from 1000 BC to 1 BC.The Neo-Assyrian Empire, followed by the Achaemenids. In Greece, Classical Antiquity begins with the colonization of Magna Graecia and peaks with the rise of Hellenism. The...
, most of Polynesia was a loose web of thriving cultures who settled on the islands' coasts and lived off the sea. By 500 BC Micronesia
Micronesia
Micronesia is a subregion of Oceania, comprising thousands of small islands in the western Pacific Ocean. It is distinct from Melanesia to the south, and Polynesia to the east. The Philippines lie to the west, and Indonesia to the southwest....
was completely colonized; the last region of Polynesia
Polynesia
Polynesia is a subregion of Oceania, made up of over 1,000 islands scattered over the central and southern Pacific Ocean. The indigenous people who inhabit the islands of Polynesia are termed Polynesians and they share many similar traits including language, culture and beliefs...
to be reached was New Zealand
New Zealand
New Zealand is an island country in the south-western Pacific Ocean comprising two main landmasses and numerous smaller islands. The country is situated some east of Australia across the Tasman Sea, and roughly south of the Pacific island nations of New Caledonia, Fiji, and Tonga...
in around AD 1000.
Polynesian migration patterns also have been studied by linguistic
Linguistics
Linguistics is the scientific study of human language. Linguistics can be broadly broken into three categories or subfields of study: language form, language meaning, and language in context....
analysis, and recently by analyzing characteristic genetic alleles of today's inhabitants. Both methods resulted in supporting the original archaeological findings.
The Americas

Quaternary glaciation
Quaternary glaciation, also known as the Pleistocene glaciation, the current ice age or simply the ice age, refers to the period of the last few million years in which permanent ice sheets were established in Antarctica and perhaps Greenland, and fluctuating ice sheets have occurred elsewhere...
. These people are believed to have followed herds of now-extinct pleistocene
Pleistocene
The Pleistocene is the epoch from 2,588,000 to 11,700 years BP that spans the world's recent period of repeated glaciations. The name pleistocene is derived from the Greek and ....
megafauna
Megafauna
In terrestrial zoology, megafauna are "giant", "very large" or "large" animals. The most common thresholds used are or...
along ice-free corridors that stretched between the Laurentide
Laurentide ice sheet
The Laurentide Ice Sheet was a massive sheet of ice that covered hundreds of thousands of square miles, including most of Canada and a large portion of the northern United States, multiple times during Quaternary glacial epochs. It last covered most of northern North America between c. 95,000 and...
and Cordilleran
Cordilleran Ice Sheet
The Cordilleran ice sheet was a major ice sheet that covered, during glacial periods of the Quaternary, a large area of North America. This included the following areas:*Western Montana*The Idaho Panhandle...
ice sheets. Another route proposed is that, either on foot or using primitive boats, they migrated down the Pacific Northwest
Pacific Northwest
The Pacific Northwest is a region in northwestern North America, bounded by the Pacific Ocean to the west and, loosely, by the Rocky Mountains on the east. Definitions of the region vary and there is no commonly agreed upon boundary, even among Pacific Northwesterners. A common concept of the...
coast to South America
South America
South America is a continent situated in the Western Hemisphere, mostly in the Southern Hemisphere, with a relatively small portion in the Northern Hemisphere. The continent is also considered a subcontinent of the Americas. It is bordered on the west by the Pacific Ocean and on the north and east...
. Evidence of the latter would since have been covered by a sea level rise of hundreds of meters following the last ice age.
Archaeologists contend that Paleo-Indians migration out of Beringia (eastern Alaska
Geography of Alaska
Alaska is one of two U.S. states not bordered by another state; Hawaii the other. Alaska has more ocean coastline than all of the other U.S. states combined. About of Canadian territory separate Alaska from Washington State. Alaska is thus an exclave of the United States that is part of the...
), ranges from 40,000 to around 16,500 years ago. This time range is a hot source of debate and will be for years to come. The few agreements achieved to date are the origin from Central Asia
Central Asia
Central Asia is a core region of the Asian continent from the Caspian Sea in the west, China in the east, Afghanistan in the south, and Russia in the north...
, with widespread habitation of the Americas during the end of the last glacial period, or more specifically what is known as the late glacial maximum, around 16,000–13,000 years before present.
Arctic

Anthropology
Anthropology is the study of humanity. It has origins in the humanities, the natural sciences, and the social sciences. The term "anthropology" is from the Greek anthrōpos , "man", understood to mean mankind or humanity, and -logia , "discourse" or "study", and was first used in 1501 by German...
call the Thule culture, which emerged from western Alaska around 1,000 CE and spread eastward across the Arctic
Arctic
The Arctic is a region located at the northern-most part of the Earth. The Arctic consists of the Arctic Ocean and parts of Canada, Russia, Greenland, the United States, Norway, Sweden, Finland, and Iceland. The Arctic region consists of a vast, ice-covered ocean, surrounded by treeless permafrost...
, displacing the Dorset culture
Dorset culture
The Dorset culture was a Paleo-Eskimo culture that preceded the Inuit culture in Arctic North America. It has been defined as having four phases, with distinct technology related to the people's hunting and tool making...
(in Inuktitut
Inuktitut
Inuktitut or Eastern Canadian Inuktitut, Eastern Canadian Inuit language is the name of some of the Inuit languages spoken in Canada...
, the Tuniit). Inuit historically referred to the Tuniit as "giants", or "dwarfs", who were taller and stronger than the Inuit. Researchers hypothesize that the Dorset culture lacked dogs, larger weapons and other technologies used by the expanding Inuit society. By 1300, the Inuit had settled in west Greenland
Greenland
Greenland is an autonomous country within the Kingdom of Denmark, located between the Arctic and Atlantic Oceans, east of the Canadian Arctic Archipelago. Though physiographically a part of the continent of North America, Greenland has been politically and culturally associated with Europe for...
, and finally moved into east Greenland over the following century. The Inuit had trade routes with more southern cultures. Boundary disputes were common and gave rise to aggressive actions.
War
War
War is a state of organized, armed, and often prolonged conflict carried on between states, nations, or other parties typified by extreme aggression, social disruption, and usually high mortality. War should be understood as an actual, intentional and widespread armed conflict between political...
fare was common among Inuit groups with sufficient population density. Inuit, such as the Nunatamiut
Nunatamiut
The Nunatamiut are an Alaskan Inuit nomadic group who lived in the Alaskan interior and were known as great caribou hunters. When caribou numbers dwindled in the 19th century, some Nunatamiut migrated towards the Mackenzie River delta...
(Uummarmiut
Uummarmiut
The Uummarmiut is the name given to the Inuvialuit who live predominantly in the Mackenzie Delta communities of Aklavik and Inuvik, Northwest Territories, Canada...
) who inhabited the Mackenzie River
Mackenzie River
The Mackenzie River is the largest river system in Canada. It flows through a vast, isolated region of forest and tundra entirely within the country's Northwest Territories, although its many tributaries reach into four other Canadian provinces and territories...
delta area, often engaged in common warfare. The Central Arctic Inuit lacked the population density to engage in warfare. In the 13th century, the Thule culture began arriving in Greenland from what is now Canada. Norse accounts are scant. Norse-made items from Inuit campsites in Greenland were obtained by either trade or plunder. One account, Ívar Bárðarson, speaks of "small people" with whom the Norsemen fought. 14th-century accounts that a western settlement, one of the two Norse settlements, was taken over by the Skræling
Skræling
Skræling is the name the Norse Greenlanders used for the indigenous peoples they encountered in North America and Greenland. In surviving sources it is first applied to the Thule people, the Eskimo group with whom the Norse coexisted in Greenland after about the 13th century...
.
Indo-Europeans

Neolithic
The Neolithic Age, Era, or Period, or New Stone Age, was a period in the development of human technology, beginning about 9500 BC in some parts of the Middle East, and later in other parts of the world. It is traditionally considered as the last part of the Stone Age...
(Marija Gimbutas
Marija Gimbutas
Marija Gimbutas , was a Lithuanian-American archeologist known for her research into the Neolithic and Bronze Age cultures of "Old Europe", a term she introduced. Her works published between 1946 and 1971 introduced new views by combining traditional spadework with linguistics and mythological...
: Corded ware, Yamna, Kurgan
Kurgan
Kurgan is the Turkic term for a tumulus; mound of earth and stones raised over a grave or graves, originating with its use in Soviet archaeology, now widely used for tumuli in the context of Eastern European and Central Asian archaeology....
), the early Neolithic (Colin Renfrew: Starčevo-Körös
Starcevo-Körös
The Starčevo culture, also called Starčevo–Kőrös–Criş culture, is an archaeological culture of Southeastern Europe, dating to the Neolithic period between c. 6200 and 5200 BCE....
, Linearbandkeramic) and the late Palaeolithic (Marcel Otte
Marcel Otte
Marcel Otte is a professor of Prehistory at the Université de Liège, Belgium. He is a specialist in Religion, Arts, Sociobiology, and the Upper Palaeolithic times of Europe and Central Asia....
, Paleolithic Continuity Theory
Paleolithic Continuity Theory
The Paleolithic Continuity Theory , since 2010 relabelled as the Paleolithic Continuity Paradigm , is a hypothesis suggesting that the Proto-Indo-European language can be traced back to the Upper Paleolithic, several millennia earlier than the Chalcolithic or at the most Neolithic estimates in other...
).
The speakers of the Proto-Indo-European language
Proto-Indo-European language
The Proto-Indo-European language is the reconstructed common ancestor of the Indo-European languages, spoken by the Proto-Indo-Europeans...
are usually believed to have originated to the North of the Black Sea
Black Sea
The Black Sea is bounded by Europe, Anatolia and the Caucasus and is ultimately connected to the Atlantic Ocean via the Mediterranean and the Aegean seas and various straits. The Bosphorus strait connects it to the Sea of Marmara, and the strait of the Dardanelles connects that sea to the Aegean...
(today Eastern Ukraine
Ukraine
Ukraine is a country in Eastern Europe. It has an area of 603,628 km², making it the second largest contiguous country on the European continent, after Russia...
and Southern Russia
Russia
Russia or , officially known as both Russia and the Russian Federation , is a country in northern Eurasia. It is a federal semi-presidential republic, comprising 83 federal subjects...
), and from there they gradually migrated into, and spread their language by cultural diffusion to, Anatolia
Anatolia
Anatolia is a geographic and historical term denoting the westernmost protrusion of Asia, comprising the majority of the Republic of Turkey...
, Europe
Europe
Europe is, by convention, one of the world's seven continents. Comprising the westernmost peninsula of Eurasia, Europe is generally 'divided' from Asia to its east by the watershed divides of the Ural and Caucasus Mountains, the Ural River, the Caspian and Black Seas, and the waterways connecting...
, and Central Asia
Central Asia
Central Asia is a core region of the Asian continent from the Caspian Sea in the west, China in the east, Afghanistan in the south, and Russia in the north...
Iran
Iran
Iran , officially the Islamic Republic of Iran , is a country in Southern and Western Asia. The name "Iran" has been in use natively since the Sassanian era and came into use internationally in 1935, before which the country was known to the Western world as Persia...
and South Asia
South Asia
South Asia, also known as Southern Asia, is the southern region of the Asian continent, which comprises the sub-Himalayan countries and, for some authorities , also includes the adjoining countries to the west and the east...
starting from around the end of the Neolithic period (see Kurgan hypothesis
Kurgan hypothesis
The Kurgan hypothesis is one of the proposals about early Indo-European origins, which postulates that the people of an archaeological "Kurgan culture" in the Pontic steppe were the most likely speakers of the Proto-Indo-European language...
). Other theories, such as that of Colin Renfrew, posit their development much earlier, in Anatolia, and claim that Indo-European languages and culture spread as a result of the agricultural revolution in the early Neolithic.
Relatively little is known about the inhabitants of pre-Indo-European "Old Europe". They are believed to have been garden-plot horticulturalists. The Basque language
Basque language
Basque is the ancestral language of the Basque people, who inhabit the Basque Country, a region spanning an area in northeastern Spain and southwestern France. It is spoken by 25.7% of Basques in all territories...
remains from that era, as do the indigenous languages of the Caucasus
Caucasus
The Caucasus, also Caucas or Caucasia , is a geopolitical region at the border of Europe and Asia, and situated between the Black and the Caspian sea...
. The Sami
Sami people
The Sami people, also spelled Sámi, or Saami, are the arctic indigenous people inhabiting Sápmi, which today encompasses parts of far northern Sweden, Norway, Finland, the Kola Peninsula of Russia, and the border area between south and middle Sweden and Norway. The Sámi are Europe’s northernmost...
are genetically distinct among the peoples of Europe, but the Sami languages
Sami languages
Sami or Saami is a general name for a group of Uralic languages spoken by the Sami people in parts of northern Finland, Norway, Sweden and extreme northwestern Russia, in Northern Europe. Sami is frequently and erroneously believed to be a single language. Several names are used for the Sami...
, as part of the Uralic languages
Uralic languages
The Uralic languages constitute a language family of some three dozen languages spoken by approximately 25 million people. The healthiest Uralic languages in terms of the number of native speakers are Hungarian, Finnish, Estonian, Mari and Udmurt...
, spread into Europe about the same time as the Indo-European languages. However, since that period speakers of other Uralic languages such as the Finns and the Estonians have had more contact with other Europeans, thus today sharing more genes with them than the Sami.
Bronze Age
The earliest migrations we can reconstruct from historical sources are those of the 2nd millennium BC. The Proto-Indo-Iranians began their expansion from ca. 2000 BC, the RigvedaRigveda
The Rigveda is an ancient Indian sacred collection of Vedic Sanskrit hymns...
documenting the presence of early Indo-Aryans
Indo-Aryans
Indo-Aryan is an ethno-linguistic term referring to the wide collection of peoples united as native speakers of the Indo-Aryan branch of the Indo-Iranian family of Indo-European languages...
in the Punjab
Punjab region
The Punjab , also spelled Panjab |water]]s"), is a geographical region straddling the border between Pakistan and India which includes Punjab province in Pakistan and the states of the Punjab, Haryana, Himachal Pradesh, Chandigarh and some northern parts of the National Capital Territory of Delhi...
from the late 2nd millennium BC, and Iranian tribes
Ancient Iranian peoples
Iranian peoples first appear in Assyrian records in the 9th century BCE. In Classical Antiquity they were found primarily in Scythia and Persia...
being attested in Assyrian sources as in the Iranian plateau
Iranian plateau
The Iranian plateau, or Iranic plateau, is a geological formation in Southwest Asia. It is the part of the Eurasian Plate wedged between the Arabian and Indian plates, situated between the Zagros mountains to the west, the Caspian Sea and the Kopet Dag to the north, the Hormuz Strait and Persian...
from the 9th century BC. In the Late Bronze Age, the Aegean
Aegean Sea
The Aegean Sea[p] is an elongated embayment of the Mediterranean Sea located between the southern Balkan and Anatolian peninsulas, i.e., between the mainlands of Greece and Turkey. In the north, it is connected to the Marmara Sea and Black Sea by the Dardanelles and Bosporus...
and Anatolia
Anatolia
Anatolia is a geographic and historical term denoting the westernmost protrusion of Asia, comprising the majority of the Republic of Turkey...
were overrun by moving populations, summarized as the "Sea Peoples
Sea Peoples
The Sea Peoples were a confederacy of seafaring raiders of the second millennium BC who sailed into the eastern Mediterranean, caused political unrest, and attempted to enter or control Egyptian territory during the late 19th dynasty and especially during year 8 of Ramesses III of the 20th Dynasty...
", leading to the collapse of the Hittite Empire and ushering in the Iron Age
Iron Age
The Iron Age is the archaeological period generally occurring after the Bronze Age, marked by the prevalent use of iron. The early period of the age is characterized by the widespread use of iron or steel. The adoption of such material coincided with other changes in society, including differing...
.
Early Iron Age
The Dorian invasionDorian invasion
The Dorian invasion is a concept devised by historians of Ancient Greece to explain the replacement of pre-classical dialects and traditions in southern Greece by the ones that prevailed in Classical Greece...
of Greece led to the Greek Dark Ages
Greek Dark Ages
The Greek Dark Age or Ages also known as Geometric or Homeric Age are terms which have regularly been used to refer to the period of Greek history from the presumed Dorian invasion and end of the Mycenaean Palatial civilization around 1200 BC, to the first signs of the Greek city-states in the 9th...
. Very Little is known about the period of the 12th to 9th centuries BC, but there were significant population movements throughout Anatolia and the Iranian plateau. Iranian peoples
Iranian peoples
The Iranian peoples are an Indo-European ethnic-linguistic group, consisting of the speakers of Iranian languages, a major branch of the Indo-European language family, as such forming a branch of Indo-European-speaking peoples...
invaded the territory of modern Iran
Iran
Iran , officially the Islamic Republic of Iran , is a country in Southern and Western Asia. The name "Iran" has been in use natively since the Sassanian era and came into use internationally in 1935, before which the country was known to the Western world as Persia...
in this period, taking over the Elamite Empire. The Urartians were displaced by Armenians
Armenians
Armenian people or Armenians are a nation and ethnic group native to the Armenian Highland.The largest concentration is in Armenia having a nearly-homogeneous population with 97.9% or 3,145,354 being ethnic Armenian....
, and the Cimmerians
Cimmerians
The Cimmerians or Kimmerians were ancient equestrian nomads of Indo-European origin.According to the Greek historian Herodotus, of the 5th century BC, the Cimmerians inhabited the region north of the Caucasus and the Black Sea during the 8th and 7th centuries BC, in what is now Ukraine and Russia...
and the Mushki
Mushki
The Mushki were an Iron Age people of Anatolia, known from Assyrian sources. They do not appear in Hittite records. Several authors have connected them with the Moschoi of Greek sources and the Georgian tribe of the Meskhi. Josephus Flavius identified the Moschoi with the Biblical Meshech...
migrated from the Caucasus into Anatolia. A Thraco-Cimmerian
Thraco-Cimmerian
Thraco-Cimmerian is a historiographical and archaeological term, composed of the names of the Thracians and the Cimmerians. It refers to 8th to 7th century BC cultures that are linked in Eastern Central Europe and in the area north of the Black Sea....
connection links these movements to the Proto-Celtic world of central Europe, leading to the introduction of Iron to Europe and the Celt
Celt
The Celts were a diverse group of tribal societies in Iron Age and Roman-era Europe who spoke Celtic languages.The earliest archaeological culture commonly accepted as Celtic, or rather Proto-Celtic, was the central European Hallstatt culture , named for the rich grave finds in Hallstatt, Austria....
ic expansion to western Europe and the British Isles around 500 BC.
The great migrations

Classical antiquity
Classical antiquity is a broad term for a long period of cultural history centered on the Mediterranean Sea, comprising the interlocking civilizations of ancient Greece and ancient Rome, collectively known as the Greco-Roman world...
from the Middle Ages
Middle Ages
The Middle Ages is a periodization of European history from the 5th century to the 15th century. The Middle Ages follows the fall of the Western Roman Empire in 476 and precedes the Early Modern Era. It is the middle period of a three-period division of Western history: Classic, Medieval and Modern...
in Europe
Europe
Europe is, by convention, one of the world's seven continents. Comprising the westernmost peninsula of Eurasia, Europe is generally 'divided' from Asia to its east by the watershed divides of the Ural and Caucasus Mountains, the Ural River, the Caspian and Black Seas, and the waterways connecting...
as the Great Migrations or as the Migrations Period. This period is further divided into two phases.
The first phase, from 300 to 500 AD, saw the movement of Germanic, Sarmatian
Sarmatians
The Iron Age Sarmatians were an Iranian people in Classical Antiquity, flourishing from about the 5th century BC to the 4th century AD....
and Hunnic
Huns
The Huns were a group of nomadic people who, appearing from east of the Volga River, migrated into Europe c. AD 370 and established the vast Hunnic Empire there. Since de Guignes linked them with the Xiongnu, who had been northern neighbours of China 300 years prior to the emergence of the Huns,...
tribes and ended with the settlement of these peoples in the areas of the former Western Roman Empire
Roman Empire
The Roman Empire was the post-Republican period of the ancient Roman civilization, characterised by an autocratic form of government and large territorial holdings in Europe and around the Mediterranean....
, essentially causing its demise. (See also: Ostrogoths, Visigoths, Burgundians
Burgundians
The Burgundians were an East Germanic tribe which may have emigrated from mainland Scandinavia to the island of Bornholm, whose old form in Old Norse still was Burgundarholmr , and from there to mainland Europe...
, Suebi
Suebi
The Suebi or Suevi were a group of Germanic peoples who were first mentioned by Julius Caesar in connection with Ariovistus' campaign, c...
, Alamanni
Alamanni
The Alamanni, Allemanni, or Alemanni were originally an alliance of Germanic tribes located around the upper Rhine river . One of the earliest references to them is the cognomen Alamannicus assumed by Roman Emperor Caracalla, who ruled the Roman Empire from 211 to 217 and claimed thereby to be...
Marcomanni
Marcomanni
The Marcomanni were a Germanic tribe, probably related to the Buri, Suebi or Suevi.-Origin:Scholars believe their name derives possibly from Proto-Germanic forms of "march" and "men"....
).
The second phase, between 500
500
Year 500 was a leap year starting on Saturday of the Julian calendar. At the time, it was known as the Year of the Consulship of Patricius and Hypatius...
and 900
900
Year 900 was a leap year starting on Tuesday of the Julian calendar.- Asia :* April 21 – Namwaran and his children, Lady Angkatan and Bukah, are granted pardon by the Datu of Tondo, as represented Jayadewa, Lord Minister of Pila, which released them of all their debts as inscribed in the...
AD, saw Slavic
Slavic peoples
The Slavic people are an Indo-European panethnicity living in Eastern Europe, Southeast Europe, North Asia and Central Asia. The term Slavic represents a broad ethno-linguistic group of people, who speak languages belonging to the Slavic language family and share, to varying degrees, certain...
, Turkic and other tribes on the move, re-settling in Eastern Europe and gradually making it predominantly Slavic. Moreover, more Germanic tribes migrated within Europe during this period, including the Lombards
Lombards
The Lombards , also referred to as Longobards, were a Germanic tribe of Scandinavian origin, who from 568 to 774 ruled a Kingdom in Italy...
(to Italy
Italy
Italy , officially the Italian Republic languages]] under the European Charter for Regional or Minority Languages. In each of these, Italy's official name is as follows:;;;;;;;;), is a unitary parliamentary republic in South-Central Europe. To the north it borders France, Switzerland, Austria and...
), and the Angles
Angles
The Angles is a modern English term for a Germanic people who took their name from the ancestral cultural region of Angeln, a district located in Schleswig-Holstein, Germany...
, Saxons
Saxons
The Saxons were a confederation of Germanic tribes originating on the North German plain. The Saxons earliest known area of settlement is Northern Albingia, an area approximately that of modern Holstein...
, and Jutes
Jutes
The Jutes, Iuti, or Iutæ were a Germanic people who, according to Bede, were one of the three most powerful Germanic peoples of their time, the other two being the Saxons and the Angles...
(to the British Isles
British Isles
The British Isles are a group of islands off the northwest coast of continental Europe that include the islands of Great Britain and Ireland and over six thousand smaller isles. There are two sovereign states located on the islands: the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland and...
). See also: Avars
Eurasian Avars
The Eurasian Avars or Ancient Avars were a highly organized nomadic confederacy of mixed origins. They were ruled by a khagan, who was surrounded by a tight-knit entourage of nomad warriors, an organization characteristic of Turko-Mongol groups...
, Bulgars
Bulgars
The Bulgars were a semi-nomadic who flourished in the Pontic Steppe and the Volga basin in the 7th century.The Bulgars emerge after the collapse of the Hunnic Empire in the 5th century....
, Huns
Huns
The Huns were a group of nomadic people who, appearing from east of the Volga River, migrated into Europe c. AD 370 and established the vast Hunnic Empire there. Since de Guignes linked them with the Xiongnu, who had been northern neighbours of China 300 years prior to the emergence of the Huns,...
, Arabs, Vikings, Varangians. The last phase of the migrations saw the coming of the Hungarians to the Pannonian plain
Great Hungarian Plain
The Great Hungarian Plain is a plain occupying the southern and eastern part of Hungary, some parts of the Eastern Slovak Lowland, southwestern Ukraine, the Transcarpathian Lowland , western Romania , northern Serbia , and eastern Croatia...
.
German historians of the 19th century referred to these Germanic migrations as the Völkerwanderung, the migrations of the peoples.
The European migration period is connected with the simultaneous Turkic expansion which at first displaced other peoples towards the west, and by High Medieval times, the Seljuk Turks themselves reached the Mediterranean.
Medieval and Early Modern Europe
The medieval period, although often presented as a time of limited human mobility and slow social change in the history of Europe, in fact saw widespread movement of peoples. The Vikings from ScandinaviaScandinavia
Scandinavia is a cultural, historical and ethno-linguistic region in northern Europe that includes the three kingdoms of Denmark, Norway and Sweden, characterized by their common ethno-cultural heritage and language. Modern Norway and Sweden proper are situated on the Scandinavian Peninsula,...
raided all over Europe from the 8th century and settled in many places, including Normandy
Normandy
Normandy is a geographical region corresponding to the former Duchy of Normandy. It is in France.The continental territory covers 30,627 km² and forms the preponderant part of Normandy and roughly 5% of the territory of France. It is divided for administrative purposes into two régions:...
, the north of England
England
England is a country that is part of the United Kingdom. It shares land borders with Scotland to the north and Wales to the west; the Irish Sea is to the north west, the Celtic Sea to the south west, with the North Sea to the east and the English Channel to the south separating it from continental...
, Scotland
Scotland
Scotland is a country that is part of the United Kingdom. Occupying the northern third of the island of Great Britain, it shares a border with England to the south and is bounded by the North Sea to the east, the Atlantic Ocean to the north and west, and the North Channel and Irish Sea to the...
and Ireland
Ireland
Ireland is an island to the northwest of continental Europe. It is the third-largest island in Europe and the twentieth-largest island on Earth...
(most of whose urban centres were founded by the Vikings). The Normans later conquered the Saxon Kingdom of England, most of Ireland, southern Italy and Sicily
Sicily
Sicily is a region of Italy, and is the largest island in the Mediterranean Sea. Along with the surrounding minor islands, it constitutes an autonomous region of Italy, the Regione Autonoma Siciliana Sicily has a rich and unique culture, especially with regard to the arts, music, literature,...
, Iberia was invaded by Muslim
Muslim
A Muslim, also spelled Moslem, is an adherent of Islam, a monotheistic, Abrahamic religion based on the Quran, which Muslims consider the verbatim word of God as revealed to prophet Muhammad. "Muslim" is the Arabic term for "submitter" .Muslims believe that God is one and incomparable...
Arabs, Berbers
Berber people
Berbers are the indigenous peoples of North Africa west of the Nile Valley. They are continuously distributed from the Atlantic to the Siwa oasis, in Egypt, and from the Mediterranean to the Niger River. Historically they spoke the Berber language or varieties of it, which together form a branch...
and Moors
Moors
The description Moors has referred to several historic and modern populations of the Maghreb region who are predominately of Berber and Arab descent. They came to conquer and rule the Iberian Peninsula for nearly 800 years. At that time they were Muslim, although earlier the people had followed...
in the 8th century, founding new Kingdoms such as al Andalus and bringing with them a wave of settlers from North Africa.
In the other direction, European Christian
Christian
A Christian is a person who adheres to Christianity, an Abrahamic, monotheistic religion based on the life and teachings of Jesus of Nazareth as recorded in the Canonical gospels and the letters of the New Testament...
armies conquered Palestine
Palestine
Palestine is a conventional name, among others, used to describe the geographic region between the Mediterranean Sea and the Jordan River, and various adjoining lands....
for a time during the Crusades
Crusades
The Crusades were a series of religious wars, blessed by the Pope and the Catholic Church with the main goal of restoring Christian access to the holy places in and near Jerusalem...
11th to 13th centuries, founding three Christian kingdoms and settling them with Christian Knights and their families. This permanent migration was relatively small however and was one of the reasons why the Crusaders eventually lost the their hold on the Holy Lands.
Massive migrations of Germans
Germans
The Germans are a Germanic ethnic group native to Central Europe. The English term Germans has referred to the German-speaking population of the Holy Roman Empire since the Late Middle Ages....
took place into East Central and Eastern Europe, reaching its peak in the 12th to 14th centuries. These Ostsiedlung
Ostsiedlung
Ostsiedlung , also called German eastward expansion, was the medieval eastward migration and settlement of Germans from modern day western and central Germany into less-populated regions and countries of eastern Central Europe and Eastern Europe. The affected area roughly stretched from Slovenia...
settlements in part followed territorial gains of the Holy Roman Empire
Holy Roman Empire
The Holy Roman Empire was a realm that existed from 962 to 1806 in Central Europe.It was ruled by the Holy Roman Emperor. Its character changed during the Middle Ages and the Early Modern period, when the power of the emperor gradually weakened in favour of the princes...
, but areas beyond were settled, too.
At the end of the Middle Ages, the Roma arrived in Europe (to Iberia
Iberian Peninsula
The Iberian Peninsula , sometimes called Iberia, is located in the extreme southwest of Europe and includes the modern-day sovereign states of Spain, Portugal and Andorra, as well as the British Overseas Territory of Gibraltar...
and the Balkans
Balkans
The Balkans is a geopolitical and cultural region of southeastern Europe...
) from the Middle East, originating from the Indus river
Indus River
The Indus River is a major river which flows through Pakistan. It also has courses through China and India.Originating in the Tibetan plateau of western China in the vicinity of Lake Mansarovar in Tibet Autonomous Region, the river runs a course through the Ladakh district of Jammu and Kashmir and...
.
Internal European migration stepped up in the Early Modern Period. In this period, major migration within Europe included the recruiting by monarchs of landless laborers to settle depopulated or uncultivated regions and a series of forced migration caused by religious persecution. Notable examples of this phenomenon include the expulsion of the Jews from Spain
Alhambra decree
The Alhambra Decree was an edict issued on 31 March 1492 by the joint Catholic Monarchs of Spain ordering the expulsion of Jews from the Kingdom of Spain and its territories and possessions by 31 July of that year.The edict was formally revoked on 16 December 1968, following the Second...
in 1492, mass migration of Protestants from the Spanish Netherlands to the Dutch Republic
Dutch Republic
The Dutch Republic — officially known as the Republic of the Seven United Netherlands , the Republic of the United Netherlands, or the Republic of the Seven United Provinces — was a republic in Europe existing from 1581 to 1795, preceding the Batavian Republic and ultimately...
after the 1580s, the expulsion of the Moriscos
Expulsion of the Moriscos
On April 9, 1609, King Philip III of Spain decreed the Expulsion of the Moriscos . The Moriscos were the descendants of the Muslim population that converted to Christianity under threat of exile from Ferdinand and Isabella in 1502...
from Spain in 1609, and the expulsion of the Huguenots from France
France
The French Republic , The French Republic , The French Republic , (commonly known as France , is a unitary semi-presidential republic in Western Europe with several overseas territories and islands located on other continents and in the Indian, Pacific, and Atlantic oceans. Metropolitan France...
in the 1680s. Since the 14th century, the Serbs
Serbs
The Serbs are a South Slavic ethnic group of the Balkans and southern Central Europe. Serbs are located mainly in Serbia, Montenegro and Bosnia and Herzegovina, and form a sizable minority in Croatia, the Republic of Macedonia and Slovenia. Likewise, Serbs are an officially recognized minority in...
started leaving the areas of their medieval Kingdom and Empire that was overrun by the Ottoman
Ottoman Empire
The Ottoman EmpireIt was usually referred to as the "Ottoman Empire", the "Turkish Empire", the "Ottoman Caliphate" or more commonly "Turkey" by its contemporaries...
Turks and migrated to the north, to the lands of today's Vojvodina
Vojvodina
Vojvodina, officially called Autonomous Province of Vojvodina is an autonomous province of Serbia. Its capital and largest city is Novi Sad...
(northern Serbia), which was ruled by the Kingdom of Hungary
Kingdom of Hungary
The Kingdom of Hungary comprised present-day Hungary, Slovakia and Croatia , Transylvania , Carpatho Ruthenia , Vojvodina , Burgenland , and other smaller territories surrounding present-day Hungary's borders...
at that time. The Habsburg
Habsburg
The House of Habsburg , also found as Hapsburg, and also known as House of Austria is one of the most important royal houses of Europe and is best known for being an origin of all of the formally elected Holy Roman Emperors between 1438 and 1740, as well as rulers of the Austrian Empire and...
monarchs of Austria encouraged them to settle on their frontier with the Turks and provide military service by granting them free land and religious toleration. The two greatest migrations
Great Serbian Migrations
The Great Serb Migrations , also known as the Great Exodus, refers mainly to two large migrations of Serbs from the Ottoman Empire to the Habsburg Monarchy....
took place in 1690 and 1737. Other instances of labour recruitments include the Plantations of Ireland
Plantations of Ireland
Plantations in 16th and 17th century Ireland were the confiscation of land by the English crown and the colonisation of this land with settlers from England and the Scottish Lowlands....
- the settling of Ireland with Protestant colonists from England, Scotland and Wales in the period 1560-1690 and the recruitment of Germans by Catherine the Great of Russia to settle the Volga region in the 18th century.
European Colonialism
Colonialism
Colonialism is the establishment, maintenance, acquisition and expansion of colonies in one territory by people from another territory. It is a process whereby the metropole claims sovereignty over the colony and the social structure, government, and economics of the colony are changed by...
from the 16th to the early 20th centuries led to an imposition of a European colonies in many regions of the world, particularly in the Americas
Americas
The Americas, or America , are lands in the Western hemisphere, also known as the New World. In English, the plural form the Americas is often used to refer to the landmasses of North America and South America with their associated islands and regions, while the singular form America is primarily...
, South Asia
South Asia
South Asia, also known as Southern Asia, is the southern region of the Asian continent, which comprises the sub-Himalayan countries and, for some authorities , also includes the adjoining countries to the west and the east...
, Sub-Saharan Africa
Sub-Saharan Africa
Sub-Saharan Africa as a geographical term refers to the area of the African continent which lies south of the Sahara. A political definition of Sub-Saharan Africa, instead, covers all African countries which are fully or partially located south of the Sahara...
and Australia
Australia
Australia , officially the Commonwealth of Australia, is a country in the Southern Hemisphere comprising the mainland of the Australian continent, the island of Tasmania, and numerous smaller islands in the Indian and Pacific Oceans. It is the world's sixth-largest country by total area...
, where European languages remain either prevalent or in frequent use as administrative languages. Major human migration before the 18th century was largely state directed. For instance, Spanish emigration to the New World was limited to settlers from Castile
Crown of Castile
The Crown of Castile was a medieval and modern state in the Iberian Peninsula that formed in 1230 as a result of the third and definitive union of the crowns and parliaments of the kingdoms of Castile and León upon the accession of the then King Ferdinand III of Castile to the vacant Leonese throne...
who were intended to act as soldiers or administrators. Mass immigration was not encouraged due to a labour shortage in Europe (of which Spain was the worst affected by a depopulation of its core territories in the 17th century).
Europeans also tended to die of tropical diseases in the New World in this period and for this reason England, France and Spain preferred using slaves as free labor in their American possessions. Many historians attribute a change in this pattern in the 18th century to population increases in Europe.
However, in the less tropical regions of North America's east coast, large numbers of religious dissidents, mostly English Puritans, settled during the early 17th century. Spanish restrictions on emigration to Latin America were revoked and the English colonies in North America also saw a major influx of settlers attracted by cheap or free land, economic opportunity and the continued lure of religious toleration.
A period in which various early English colonies had a significant amount of self-rule prevailed from the time of the Plymouth colony's founding in 1620 through 1676, as the mother country was wracked by revolution and general instability. However, King William III decisively intervened in colonial affairs after 1688 and the English colonies gradually came more directly under royal governance, with a marked effect on the type of emigration. During the early 18th century, significant numbers of non-English seekers of greater religious and political freedom were allowed to settle within the British colonies, including Protestant Palatine Germans displaced by French conquest, French Huguenots disenfranchised by an end of religious tolerance, Scotch-Irish Presbyterians, Quakers who were often Welsh, as well as Presbyterian and Catholic Scottish Highlanders seeking a new start after a series of unsuccessful revolts.
The English colonists who came during this period were increasingly moved by economic necessity. Some colonies, including Georgia, were settled heavily by petty criminals and indentured servants who hoped to pay off their debts. By 1800, European emigration had transformed the demographic character of the American continent. This was also due in part to the devastating effect of European diseases and warfare on Native American populations.
The European settlers' influence elsewhere was less pronounced as in South Asia and Africa, European settlement in this period was limited to thin layer of administrators, traders and soldiers.
Landnahme
Landnahme is a German term, literally translating to "land-taking", used for legendary or mythologicalFounding myth
A national myth is an inspiring narrative or anecdote about a nation's past. Such myths often serve as an important national symbol and affirm a set of national values. A national myth may sometimes take the form of a national epic...
and historiographical
Historiography
Historiography refers either to the study of the history and methodology of history as a discipline, or to a body of historical work on a specialized topic...
accounts alike concerning how a given people came to inhabit its present territory.
Notable Landnahme events include:
- The conquest of Canaan in the Hebrew BibleHebrew BibleThe Hebrew Bible is a term used by biblical scholars outside of Judaism to refer to the Tanakh , a canonical collection of Jewish texts, and the common textual antecedent of the several canonical editions of the Christian Old Testament...
, accounting for the arrival of the Israelites in the Promised LandPromised landThe Promised Land is a term used to describe the land promised or given by God, according to the Hebrew Bible, to the Israelites, the descendants of Jacob. The promise is firstly made to Abraham and then renewed to his son Isaac, and to Isaac's son Jacob , Abraham's grandson... - The Indo-Aryan migrationIndo-Aryan migrationModels of the Indo-Aryan migration discuss scenarios of prehistoric migrations of the proto-Indo-Aryans to their historically attested areas of settlement in the northwest of the Indian subcontinent...
and expansion within India alluded to in the RigvedaRigvedaThe Rigveda is an ancient Indian sacred collection of Vedic Sanskrit hymns... - The invasion traditions in the Irish Mythological CycleMythological CycleThe Mythological Cycle is one of the four major cycles of Irish mythology, and is so called because it represents the remains of the pagan mythology of pre-Christian Ireland, although the gods and supernatural beings have been euhemerised into historical kings and heroes.The cycle consists of...
, accounting for how the GaelsGaelsThe Gaels or Goidels are speakers of one of the Goidelic Celtic languages: Irish, Scottish Gaelic, and Manx. Goidelic speech originated in Ireland and subsequently spread to western and northern Scotland and the Isle of Man....
came to IrelandIrelandIreland is an island to the northwest of continental Europe. It is the third-largest island in Europe and the twentieth-largest island on Earth... - The arrival of the FranksFranksThe Franks were a confederation of Germanic tribes first attested in the third century AD as living north and east of the Lower Rhine River. From the third to fifth centuries some Franks raided Roman territory while other Franks joined the Roman troops in Gaul. Only the Salian Franks formed a...
in the territories subsequently known as Francia - The Anglo-Saxon invasion of Britain
- The arrival of the Slavs in the course of the Slavic migrations
- The settlement of IcelandSettlement of IcelandThe settlement of Iceland is generally believed to have begun in the second half of the 9th century, when Norse settlers migrated across the North Atlantic. The reasons for the migration may be traced to a shortage of arable land in Scandinavia, and civil strife brought about by the ambitions of...
- The Seljuk invasion of Anatolia
Modern migration
While the pace of migration had accelerated since the 18th century already (including the involuntary slave trade), it would increase further in the 19th century. Manning distinguishes three major types of migration: labour migration, refugee migrations and lastly: urbanizationUrbanization
Urbanization, urbanisation or urban drift is the physical growth of urban areas as a result of global change. The United Nations projected that half of the world's population would live in urban areas at the end of 2008....
. Millions of agricultural workers left the countryside and moved to the cities causing unprecedented levels of urbanization. This phenomenon began in Britain in the late 18th century and spread around the world and continues to this day in many areas.
Industrialization encouraged migration wherever it appeared. The increasingly global economy globalised the labour market. Atlantic slave trade
Atlantic slave trade
The Atlantic slave trade, also known as the trans-atlantic slave trade, refers to the trade in slaves that took place across the Atlantic ocean from the sixteenth through to the nineteenth centuries...
diminished sharply after 1820, which gave rise to self-bound contract labour migration from Europe and Asia to plantations. Also overpopulation, open agricultural frontiers and rising industrial centres attracted voluntary, encouraged and sometimes coerced migration. Moreover, migration was significantly eased by improved transportation techniques.
During this same period similar large numbers of people migrated over large distances within Asia. Southeastern Asia received 50 million migrants, mainly from India and south China. North Asia, that be Manchuria
Manchuria
Manchuria is a historical name given to a large geographic region in northeast Asia. Depending on the definition of its extent, Manchuria usually falls entirely within the People's Republic of China, or is sometimes divided between China and Russia. The region is commonly referred to as Northeast...
, Siberia, Central Asia and Japan together, received another 50 million, in a migration that started in the 1890s with migrants from China, Russia and Korea, and was especially large due to coerced migration from the Soviet Union and Japan in the 1930s. Less is known about exact numbers of the migrations from and within Africa in this period, but Africa experienced a small nett immigration between 1850 and 1950, from a variety of origins.
Provisions of the Potsdam Agreement
Potsdam Agreement
The Potsdam Agreement was the Allied plan of tripartite military occupation and reconstruction of Germany—referring to the German Reich with its pre-war 1937 borders including the former eastern territories—and the entire European Theatre of War territory...
from 1945 signed by victorious Western Allies
Western Allies
The Western Allies were a political and geographic grouping among the Allied Powers of the Second World War. It generally includes the United Kingdom and British Commonwealth, the United States, France and various other European and Latin American countries, but excludes China, the Soviet Union,...
and the Soviet Union
Soviet Union
The Soviet Union , officially the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics , was a constitutionally socialist state that existed in Eurasia between 1922 and 1991....
led to one of the largest European migrations
World War II evacuation and expulsion
Forced deportation, mass evacuation and displacement of peoples took place in many of the countries involved in World War II. These were caused both by the direct hostilities between Axis and Allied powers, and the border changes enacted in the pre-war settlement...
, and definitely the largest in the 20th century. It involved the migration and resettlement of close to or over 20 million people. The largest affected group were 16.5 million Germans expelled from Eastern Europe westwards
Expulsion of Germans after World War II
The later stages of World War II, and the period after the end of that war, saw the forced migration of millions of German nationals and ethnic Germans from various European states and territories, mostly into the areas which would become post-war Germany and post-war Austria...
. The second largest group were Poles, expelled westwards from eastern Kresy
Kresy
The Polish term Kresy refers to a land considered by Poles as historical eastern provinces of their country. Today, it makes western Ukraine, western Belarus, as well as eastern Lithuania, with such major cities, as Lviv, Vilnius, and Hrodna. This territory belonged to the Polish-Lithuanian...
region and resettled in the so-called Recovered Territories
Recovered Territories
Recovered or Regained Territories was an official term used by the People's Republic of Poland to describe those parts of pre-war Germany that became part of Poland after World War II...
(see Oder-Neisse line
Oder-Neisse line
The Oder–Neisse line is the border between Germany and Poland which was drawn in the aftermath of World War II. The line is formed primarily by the Oder and Lusatian Neisse rivers, and meets the Baltic Sea west of the seaport cities of Szczecin and Świnoujście...
). Hundreds of thousands of Poles, Ukrainians, Lithuanians, Latvians, Estonians and some Belarusians, were in the meantime expelled eastwards from Europe to the Soviet Union. Finally, many of the several hundred thousand Jews remaining in the Eastern Europe after the Holocaust migrated outside Europe
Berihah
Bricha was the underground organized effort that helped Jewish Holocaust survivors escape post-World War II Europe to the British Mandate for Palestine in violation of the White Paper of 1939...
to Israel
Israel
The State of Israel is a parliamentary republic located in the Middle East, along the eastern shore of the Mediterranean Sea...
and the USA.
Currently in progress are large migrations to North America
North America
North America is a continent wholly within the Northern Hemisphere and almost wholly within the Western Hemisphere. It is also considered a northern subcontinent of the Americas...
from Mexico
Mexico
The United Mexican States , commonly known as Mexico , is a federal constitutional republic in North America. It is bordered on the north by the United States; on the south and west by the Pacific Ocean; on the southeast by Guatemala, Belize, and the Caribbean Sea; and on the east by the Gulf of...
and Central America
Central America
Central America is the central geographic region of the Americas. It is the southernmost, isthmian portion of the North American continent, which connects with South America on the southeast. When considered part of the unified continental model, it is considered a subcontinent...
, and a slightly smaller migration from the Islamic World into Europe
Europe
Europe is, by convention, one of the world's seven continents. Comprising the westernmost peninsula of Eurasia, Europe is generally 'divided' from Asia to its east by the watershed divides of the Ural and Caucasus Mountains, the Ural River, the Caspian and Black Seas, and the waterways connecting...
.

