
Hexafluoride
Encyclopedia

Transition metal
The term transition metal has two possible meanings:*The IUPAC definition states that a transition metal is "an element whose atom has an incomplete d sub-shell, or which can give rise to cations with an incomplete d sub-shell." Group 12 elements are not transition metals in this definition.*Some...
s, three are actinide
Actinide
The actinide or actinoid series encompasses the 15 metallic chemical elements with atomic numbers from 89 to 103, actinium through lawrencium.The actinide series derives its name from the group 3 element actinium...
s, and four are nonmetal
Nonmetal
Nonmetal, or non-metal, is a term used in chemistry when classifying the chemical elements. On the basis of their general physical and chemical properties, every element in the periodic table can be termed either a metal or a nonmetal...
s or metalloid
Metalloid
Metalloid is a term used in chemistry when classifying the chemical elements. On the basis of their general physical and chemical properties, each element can usually be classified as a metal or a nonmetal. However, some elements with intermediate or mixed properties can be harder to characterize...
s.
Physical properties
Melting point
The melting point of a solid is the temperature at which it changes state from solid to liquid. At the melting point the solid and liquid phase exist in equilibrium. The melting point of a substance depends on pressure and is usually specified at standard atmospheric pressure...
and boiling point
Boiling point
The boiling point of an element or a substance is the temperature at which the vapor pressure of the liquid equals the environmental pressure surrounding the liquid....
s. Four hexafluorides (S, Se, Te, and W) are gases at room temperature (25 °C) and a pressure of 1 atm
Atmosphere (unit)
The standard atmosphere is an international reference pressure defined as 101325 Pa and formerly used as unit of pressure. For practical purposes it has been replaced by the bar which is 105 Pa...
, two are liquid (Re, Mo), and the others are volatile solids. The p-block
P-block
The p-block of the periodic table of the elements consists of the last six groups minus helium . In the elemental form of the p-block elements, the highest energy electron occupies a p-orbital.-See also:...
and group 6
Group 6 element
A Group 6 element is one in the series of elements in group 6 in the periodic table, which consists of the transition metals chromium , molybdenum , tungsten , and seaborgium ....
hexafluorides are colorless, but the other hexafluorides have colors ranging from yellow to orange, red, brown, and black.
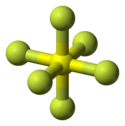
The molecular geometry is generally octahedral
Octahedral molecular geometry
In chemistry, octahedral molecular geometry describes the shape of compounds where in six atoms or groups of atoms or ligands are symmetrically arranged around a central atom, defining the vertices of an octahedron...
, though it is sometimes distorted. XeF6
Xenon hexafluoride
Xenon hexafluoride is a noble gas compound with the formula XeF6 and the highest of the three binary fluorides of xenon, the other two being XeF2 and XeF4. All are exergonic and stable at normal temperatures. XeF6 is the strongest fluorinating agent of the series...
is a fluxional molecule with a distorted octahedral structure, which is, according to VSEPR theory
VSEPR theory
Valence shell electron pair repulsion theory is a model in chemistry used to predict the shape of individual molecules based upon the extent of electron-pair electrostatic repulsion. It is also named Gillespie–Nyholm theory after its two main developers...
, caused by the non-bonding lone pair
Lone pair
In chemistry, a lone pair is a valence electron pair without bonding or sharing with other atoms. They are found in the outermost electron shell of an atom, so lone pairs are a subset of a molecule's valence electrons...
. In the solid state, XeF6 has a complex structure involving tetramers and hexamers. According to quantum chemical calculations, ReF6 and RuF6 should have tetragonally distorted structures (where the two bonds along one axis are longer or shorter than the other four), but this has not been verified experimentally.
| Compound | m.p Melting point The melting point of a solid is the temperature at which it changes state from solid to liquid. At the melting point the solid and liquid phase exist in equilibrium. The melting point of a substance depends on pressure and is usually specified at standard atmospheric pressure... (°C) | b.p. Boiling point The boiling point of an element or a substance is the temperature at which the vapor pressure of the liquid equals the environmental pressure surrounding the liquid.... (°C) | subl.p. (°C) | MW Molar mass Molar mass, symbol M, is a physical property of a given substance , namely its mass per amount of substance. The base SI unit for mass is the kilogram and that for amount of substance is the mole. Thus, the derived unit for molar mass is kg/mol... | solid ρ Density The mass density or density of a material is defined as its mass per unit volume. The symbol most often used for density is ρ . In some cases , density is also defined as its weight per unit volume; although, this quantity is more properly called specific weight... (g cm−3) | Bond (pm) | Color |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sulfur hexafluoride Sulfur hexafluoride Sulfur hexafluoride is an inorganic, colorless, odorless, and non-flammable greenhouse gas. has an octahedral geometry, consisting of six fluorine atoms attached to a central sulfur atom. It is a hypervalent molecule. Typical for a nonpolar gas, it is poorly soluble in water but soluble in... |
−50.8 | 146.06 | 1.88 (−50 °C) | 156.4 | colorless | ||
| Selenium hexafluoride Selenium hexafluoride Selenium hexafluoride is the inorganic compound with the formula SeF6. It is a colourless gas described as having a "repulsive" odor. It is not widely encountered and has no commercial applications.-Structure, preparation, and reactions:... |
−46.6 | 192.95 | 167–170 | colorless | |||
| Tellurium hexafluoride Tellurium hexafluoride Tellurium hexafluoride is the oldest known fluoride of tellurium. It is a colorless, highly toxic gas with an extremely unpleasant smell.-Preparation:... |
−38.9 | −37.6 | 241.59 | 184 | colorless | ||
| Xenon hexafluoride Xenon hexafluoride Xenon hexafluoride is a noble gas compound with the formula XeF6 and the highest of the three binary fluorides of xenon, the other two being XeF2 and XeF4. All are exergonic and stable at normal temperatures. XeF6 is the strongest fluorinating agent of the series... |
49.5 | 75.6 | 245.28 | 3.56 | colorless | ||
| Molybdenum hexafluoride Molybdenum hexafluoride Molybdenum hexafluoride is the highest fluoride of molybdenum. It is a solid which melts just below room temperature; in water, it hydrolyses to give hydrofluoric acid.... |
17.5 | 34.0 | 209.94 | 3.50 (−140 °C) | 181.7 | colorless | |
| Technetium hexafluoride | 37.4 | 55.3 | (212) | 3.58 (−140 °C) | 181.2 | yellow | |
| Ruthenium hexafluoride | 54 | 215.07 | 3.68 (−140 °C) | 181.8 | dark brown | ||
| Rhodium hexafluoride | ≈ 70 | 216.91 | 3.71 (−140 °C) | 182.4 | black | ||
| Tungsten hexafluoride | 2.3 | 17.1 | 297.85 | 4.86 (−140 °C) | 182.6 | colorless | |
| Rhenium hexafluoride | 18.5 | 33.7 | 300.20 | 4.94 (−140 °C) | 182.3 | yellow | |
| Osmium hexafluoride | 33.4 | 47.5 | 304.22 | 5.09 (−140 °C) | 182.9 | yellow | |
| Iridium hexafluoride | 44 | 53.6 | 306.21 | 5.11 (−140 °C) | 183.4 | yellow | |
| Platinum hexafluoride Platinum hexafluoride Platinum hexafluoride is the chemical compound with the formula PtF6. It is a dark-red volatile solid that forms a red gas. The compound is a unique example of platinum in the +6 oxidation state... |
61.3 | 69.1 | 309.07 | 5.21 (−140 °C) | 184.8 | deep red | |
| Uranium hexafluoride Uranium hexafluoride Uranium hexafluoride , referred to as "hex" in the nuclear industry, is a compound used in the uranium enrichment process that produces fuel for nuclear reactors and nuclear weapons. It forms solid grey crystals at standard temperature and pressure , is highly toxic, reacts violently with water... |
56.5 | 351.99 | 5.09 | 199.6 | white | ||
| Neptunium hexafluoride | 54.4 | 55.18 | (358) | 198.1 | orange | ||
| Plutonium hexafluoride Plutonium hexafluoride Plutonium hexafluoride is the highest fluoride of plutonium, and is of interest for laser enrichment of plutonium, in particular for the production of pure plutonium-239 from irradiated uranium... |
52 | 62 | (356) | 5.08 | 197.1 | brown |
Chemical properties
The hexafluorides have a wide range of chemical reactivity. Sulfur hexafluorideSulfur hexafluoride
Sulfur hexafluoride is an inorganic, colorless, odorless, and non-flammable greenhouse gas. has an octahedral geometry, consisting of six fluorine atoms attached to a central sulfur atom. It is a hypervalent molecule. Typical for a nonpolar gas, it is poorly soluble in water but soluble in...
is nearly inert and non-toxic. It has several applications due to its stability, dielectric properties, and high density. Selenium hexafluoride
Selenium hexafluoride
Selenium hexafluoride is the inorganic compound with the formula SeF6. It is a colourless gas described as having a "repulsive" odor. It is not widely encountered and has no commercial applications.-Structure, preparation, and reactions:...
is nearly as unreactive as SF6, but tellurium hexafluoride
Tellurium hexafluoride
Tellurium hexafluoride is the oldest known fluoride of tellurium. It is a colorless, highly toxic gas with an extremely unpleasant smell.-Preparation:...
is toxic, not very stable and can be hydrolyzed
Hydrolysis
Hydrolysis is a chemical reaction during which molecules of water are split into hydrogen cations and hydroxide anions in the process of a chemical mechanism. It is the type of reaction that is used to break down certain polymers, especially those made by condensation polymerization...
by water within 1 day. In contrast, metal hexafluorides are corrosive, readily hydrolyzed and may react violently with water. Some of them can be used as fluorinating agents. The metal hexafluorides have a high electron affinity
Electron affinity
The Electron affinity of an atom or molecule is defined as the amount of energy released when an electron is added to a neutral atom or molecule to form a negative ion....
, which makes them strong oxidizing agents. Platinum hexafluoride
Platinum hexafluoride
Platinum hexafluoride is the chemical compound with the formula PtF6. It is a dark-red volatile solid that forms a red gas. The compound is a unique example of platinum in the +6 oxidation state...
in particular is notable for its ability to oxidize the dioxygen molecule, O2, to form dioxygenyl hexafluoroplatinate
Dioxygenyl hexafluoroplatinate
Dioxygenyl hexafluoroplatinate is a compound with formula O2PtF6. It is a hexafluoroplatinate of the unusual dioxygenyl cation, O2+. It can be produced by the reaction of dioxygen with platinum hexafluoride:...
, and for being the first compound that was observed to react with xenon (see xenon hexafluoroplatinate
Xenon hexafluoroplatinate
Xenon hexafluoroplatinate is the name of the product of the reaction of platinum hexafluoride and xenon, in an experiment that proved the chemical reactivity of the noble gases...
).
Applications
Some metal hexafluorides find applications due to their volatility. Uranium hexafluorideUranium hexafluoride
Uranium hexafluoride , referred to as "hex" in the nuclear industry, is a compound used in the uranium enrichment process that produces fuel for nuclear reactors and nuclear weapons. It forms solid grey crystals at standard temperature and pressure , is highly toxic, reacts violently with water...
is used in the uranium enrichment process to produce fuel for nuclear reactor
Nuclear reactor
A nuclear reactor is a device to initiate and control a sustained nuclear chain reaction. Most commonly they are used for generating electricity and for the propulsion of ships. Usually heat from nuclear fission is passed to a working fluid , which runs through turbines that power either ship's...
s. Fluoride volatility
Fluoride volatility
Fluoride volatility is jargon that describes the volatility of fluorides, which is relevant to the separation of radionuclides. Hexafluorides and pentafluorides have much lower boiling points than the lower-valence fluorides. Most difluorides and trifluorides have high boiling points, while most...
can also be exploited for nuclear fuel reprocessing. Tungsten hexafluoride is used in the production of semiconductors through the process of chemical vapor deposition
Chemical vapor deposition
Chemical vapor deposition is a chemical process used to produce high-purity, high-performance solid materials. The process is often used in the semiconductor industry to produce thin films. In a typical CVD process, the wafer is exposed to one or more volatile precursors, which react and/or...
.

