
Hexaflake
Encyclopedia
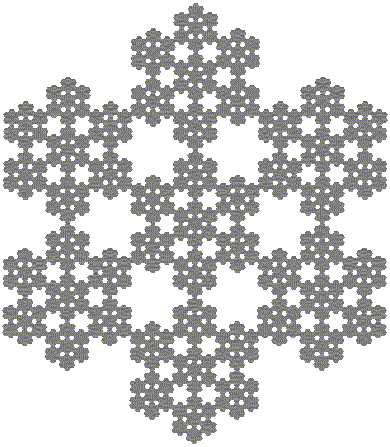

Fractal
A fractal has been defined as "a rough or fragmented geometric shape that can be split into parts, each of which is a reduced-size copy of the whole," a property called self-similarity...
constructed by iteratively
Iteration
Iteration means the act of repeating a process usually with the aim of approaching a desired goal or target or result. Each repetition of the process is also called an "iteration," and the results of one iteration are used as the starting point for the next iteration.-Mathematics:Iteration in...
exchanging each hexagon by a flake of seven hexagons; it is a special case of the n-flake
N-flake
An n-flake, polyflake, or Sierpinski n-gon, is a fractal constructed starting from an n-gon. This n-gon is replaced by a flake of smaller n-gons, such that the scaled polygons are placed at the vertices, and sometimes in the center. This process is repeated recursively to result in the fractal...
. As such, a hexaflake would have 7n-1 hexagons in its nth iteration. Its boundary
Boundary (topology)
In topology and mathematics in general, the boundary of a subset S of a topological space X is the set of points which can be approached both from S and from the outside of S. More precisely, it is the set of points in the closure of S, not belonging to the interior of S. An element of the boundary...
is the von Koch flake
Koch snowflake
The Koch snowflake is a mathematical curve and one of the earliest fractal curves to have been described...
, and contains an infinite number of Koch snowflakes (black or white). Its Hausdorff dimension
Hausdorff dimension
thumb|450px|Estimating the Hausdorff dimension of the coast of Great BritainIn mathematics, the Hausdorff dimension is an extended non-negative real number associated with any metric space. The Hausdorff dimension generalizes the notion of the dimension of a real vector space...
is equal to ln(7)/ln(3), approximately 1.7712.
It is also the projection of the cantor cube
Cantor set
In mathematics, the Cantor set is a set of points lying on a single line segment that has a number of remarkable and deep properties. It was discovered in 1875 by Henry John Stephen Smith and introduced by German mathematician Georg Cantor in 1883....
onto the plane orthogonal to its main diagonal.

