
Headlamp
Encyclopedia

Lamp (electrical component)
A lamp is a replaceable component such as an incandescent light bulb, which is designed to produce light from electricity. These components usually have a base of ceramic, metal, glass or plastic, which makes an electrical connection in the socket of a light fixture. This connection may be made...
, usually attached to the front of a vehicle such as a car or a motorcycle, with the purpose of illuminating the road ahead during periods of low visibility, such as darkness or precipitation. Headlamp performance has steadily improved throughout the automobile age, spurred by the great disparity between daytime and nighttime traffic fatalities: the U.S. National Highway Traffic Safety Administration
National Highway Traffic Safety Administration
The National Highway Traffic Safety Administration is an agency of the Executive Branch of the U.S. government, part of the Department of Transportation...
states that nearly half of all traffic-related fatalities occur in the dark, despite only 25% of traffic travelling during darkness.
While it is common for the term headlight to be used interchangeably in informal discussion, headlamp is the technically correct term for the device itself, while headlight properly refers to the beam of light
Beam of Light
Beam of Light is the second album by the Japanese band One Ok Rock, released on May 28, 2008. It reached seventeenth place on the Oricon weekly chart and charted for four weeks.-Track listing:# # # "100%"# "Abduction-Interlude"# #...
produced and distributed by the device.
A headlamp can also be mounted on a bicycle
Bicycle lighting
Bicycle lighting improves the visibility of the bicycle rider to others in dark conditions, i.e. to increase the rider's conspicuity and to enhance the ability of the rider to see, illuminating the way forward. Both reflectors and active lights are used to make the rider more visible, and many ...
(with a battery
Battery (electricity)
An electrical battery is one or more electrochemical cells that convert stored chemical energy into electrical energy. Since the invention of the first battery in 1800 by Alessandro Volta and especially since the technically improved Daniell cell in 1836, batteries have become a common power...
or small electrical generator
Electrical generator
In electricity generation, an electric generator is a device that converts mechanical energy to electrical energy. A generator forces electric charge to flow through an external electrical circuit. It is analogous to a water pump, which causes water to flow...
), and most other vehicles from airplanes to trains tend to have headlamps of their own.
Additionally automotive night vision
Automotive night vision
An automotive night vision system is a system to increase a vehicle driver's perception and seeing distance in darkness or poor weather beyond the reach of the vehicle's headlights...
systems work to supplement headlamps.
History of automotive headlamps


Mechanics
The earliest headlamps were fuelled by acetyleneAcetylene
Acetylene is the chemical compound with the formula C2H2. It is a hydrocarbon and the simplest alkyne. This colorless gas is widely used as a fuel and a chemical building block. It is unstable in pure form and thus is usually handled as a solution.As an alkyne, acetylene is unsaturated because...
or oil
Oil
An oil is any substance that is liquid at ambient temperatures and does not mix with water but may mix with other oils and organic solvents. This general definition includes vegetable oils, volatile essential oils, petrochemical oils, and synthetic oils....
and were introduced in the late 1880s. Acetylene lamps
Carbide lamp
Carbide lamps, properly known as acetylene gas lamps, are simple lamps that produce and burn acetylene which is created by the reaction of calcium carbide with water....
were popular because the flame was resistant to wind and rain. The first electric headlamps were introduced in 1898 on the Columbia Electric Car
Columbia Automobile Company
The Columbia Automobile Company was a leading early Hartford, Connecticut, United States manufacturer of automobiles.The Columbia Automobile Company was created as a joint venture of the Motor Vehicle Division of the Pope Manufacturing Company of Hartford, Connecticut, and the Electric Vehicle...
from the Electric Vehicle Company of Hartford, Connecticut
Hartford, Connecticut
Hartford is the capital of the U.S. state of Connecticut. The seat of Hartford County until Connecticut disbanded county government in 1960, it is the second most populous city on New England's largest river, the Connecticut River. As of the 2010 Census, Hartford's population was 124,775, making...
, and were optional. Two factors limited the widespread use of electric headlamps: the short life of filaments in the harsh automotive environment, and the difficulty of producing dynamos small enough, yet powerful enough to produce sufficient current.
"Prest-O-Lite" acetylene lights were offered by a number of manufacturers as standard equipment for 1904, and Peerless
Peerless
Peerless was a United States automobile produced by the Peerless Motor Company of Cleveland, Ohio from 1900 to 1931. The company was known for building high-quality, precision luxury automobiles. Peerless' factory was located at 9400 Quincy Avenue in Cleveland...
made electric headlamps standard in 1908. A Birmingham
Birmingham
Birmingham is a city and metropolitan borough in the West Midlands of England. It is the most populous British city outside the capital London, with a population of 1,036,900 , and lies at the heart of the West Midlands conurbation, the second most populous urban area in the United Kingdom with a...
firm called Pockley Automobile Electric Lighting Syndicate marketed the world's first electric car lights as a complete set in 1908, which consisted of headlights, sidelights and tail lights and were powered by an 8 volt battery.
In 1912, Cadillac integrated their vehicle's Delco
Delco Electronics
Delco Electronics Corporation was the automotive electronics design and manufacturing subsidiary of General Motors based in Kokomo, Indiana.The name Delco came from the Dayton Engineering Laboratories Co., founded in Dayton, Ohio by Charles Kettering and Edward A...
electrical ignition and lighting system, creating the modern vehicle electrical system.
"Dipping" (low beam) headlamps were introduced in 1915 by the Guide Lamp Company, but the 1917 Cadillac system allowed the light to be dipped with a lever inside the car rather than requiring the driver to stop and get out. The 1924 Bilux bulb was the first modern unit, having the light for both low (dipped) and high (main) beams of a headlamp emitting from a single bulb. A similar design was introduced in 1925 by Guide Lamp called the "Duplo". In 1927, the foot-operated dimmer switch or dip switch was introduced and became standard for much of the century. The last vehicle with a foot-operated dimmer switch was the 1991 Ford F-Series
Ford F-Series
The F-Series is a series of full-size pickup trucks from Ford Motor Company which has been sold continuously for over six decades. The most popular variant of the F-Series is the F-150...
. Fog lamps were new for 1938 Cadillacs, and their 1954 "Autronic Eye" system automated the selection of high and low beams.
In 1935 Tatra T77
Tatra T77
The Czechoslovakian Tatra 77 is the first serial-produced truly aerodynamically designed automobile. It was developed by Hans Ledwinka and Paul Jaray, the noted Zeppelin aerodynamic engineer. Launched in 1934, the Tatra 77 is a coach-built automobile constructed on a central tube-steel chassis and...
a introduced light with cornering function - the front had three headlamps of which the central unit was linked to the steering, making it possible to turn this lamp with the steering wheel.
The standardised 7 inches (178 mm) round sealed beam
Sealed beam
A sealed beam is a type of lamp that includes a reflector and filament as a single assembly, over which a front cover of clear glass, is permanently attached. Previously, automotive headlamps used a separate small bulb and reflector covered with a ribbed lens to avoid glare from the filament. This...
headlamp was introduced in 1940, and was soon required for all vehicles sold in the United States
United States
The United States of America is a federal constitutional republic comprising fifty states and a federal district...
. Britain, Australia and other Commonwealth
Commonwealth of Nations
The Commonwealth of Nations, normally referred to as the Commonwealth and formerly known as the British Commonwealth, is an intergovernmental organisation of fifty-four independent member states...
countries, as well as Japan, also made extensive use of 7-inch sealed beams. With some exceptions from Volvo
Volvo
AB Volvo is a Swedish builder of commercial vehicles, including trucks, buses and construction equipment. Volvo also supplies marine and industrial drive systems, aerospace components and financial services...
and Saab
Saab
Saab AB is a Swedish aerospace and defence company, founded in 1937. From 1947 to 1990 it was the parent company of automobile manufacturer Saab Automobile, and between 1968 and 1995 the company was in a merger with commercial vehicle manufacturer Scania, known as Saab-Scania.-History:"Svenska...
, this headlamp size format was never widely accepted in continental Europe, leading to different front-end designs for each side of the Atlantic for decades.
The first halogen
Halogen lamp
A halogen lamp, also known as a tungsten halogen lamp, is an incandescent lamp with a tungsten filament contained within an inert gas and a small amount of a halogen such as iodine or bromine. The chemical halogen cycle redeposits evaporated tungsten back on to the filament, extending the life of...
headlamp for vehicle use was introduced in 1962 by a consortium of European bulb and headlamp makers. Halogen technology increases the efficacy
Efficacy
Efficacy is the capacity to produce an effect. It has different specific meanings in different fields. In medicine, it is the ability of an intervention or drug to reproduce a desired effect in expert hands and under ideal circumstances.- Healthcare :...
(light output for given power consumption) of an incandescent light bulb
Incandescent light bulb
The incandescent light bulb, incandescent lamp or incandescent light globe makes light by heating a metal filament wire to a high temperature until it glows. The hot filament is protected from air by a glass bulb that is filled with inert gas or evacuated. In a halogen lamp, a chemical process...
and eliminates blackening of the bulb glass with usage. These were prohibited in the U.S., where non-halogen sealed beam
Sealed beam
A sealed beam is a type of lamp that includes a reflector and filament as a single assembly, over which a front cover of clear glass, is permanently attached. Previously, automotive headlamps used a separate small bulb and reflector covered with a ribbed lens to avoid glare from the filament. This...
lamps were required until 1978. Starting that year, sealed beams became available with halogen bulbs inside. These halogen sealed beams remain available, 25 years after replaceable-bulb headlamps returned to the U.S. in 1983.
High-intensity discharge
High-intensity discharge lamp
High-intensity discharge lamps are a type of electrical lamp which produces light by means of an electric arc between tungsten electrodes housed inside a translucent or transparent fused quartz or fused alumina arc tube. This tube is filled with both gas and metal salts. The gas facilitates the...
(HID) systems were introduced in 1991s BMW 7-series
BMW E32
After almost 7 years in development since September 1979, in July 1986, BMW introduced the second generation of the 7 series, known internally as the E32. Aimed at the high end of the luxury market, the car offered some of the latest innovations in automotive technology, and a new, top-of-the-line...
. European and Japanese markets began to prefer HID headlamps, with as much as 50% market share in those markets, but they found slow adoption in North America. 1996's Lincoln Mark VIII
Lincoln Mark VIII
The Lincoln Mark VIII is a large, rear-wheel drive grand touring luxury coupe built from 1993 to 1998. It was the successor of the Mark VII. The Mark VIII was built at Ford's Wixom, Michigan assembly plant and was based on the FN10 platform, a relative of the MN12 platform which underpinned the...
was an early American effort at HIDs, and was the only car with DC
Direct current
Direct current is the unidirectional flow of electric charge. Direct current is produced by such sources as batteries, thermocouples, solar cells, and commutator-type electric machines of the dynamo type. Direct current may flow in a conductor such as a wire, but can also flow through...
HIDs.
Design and style
Beyond the engineering, performance and regulatory-compliance aspects of headlamps, there is the consideration of the various ways they are designed and arranged on a motor vehicle. Headlamps were round for many years, because that is the easiest shape for parabolicParabola
In mathematics, the parabola is a conic section, the intersection of a right circular conical surface and a plane parallel to a generating straight line of that surface...
reflector manufacture.
Headlamp styling outside the United States, pre-1983

Citroën Ami
The Citroën Ami is a supermini produced by the French automaker Citroën from 1961 to 1978. The Ami and stablemate Citroën Dyane were replaced by the Citroën Visa and Citroën Axel . The Ami was for some years the best-selling car model in France...
and by Hella
Hella (company)
Hella KGaA Hueck & Co. is an internationally operating German automotive part supplier with headquarters in Lippstadt, North Rhine-Westphalia. Core businesses are vehicle lighting and electronics systems and components. Hella is also involved in the areas of vehicle diagnostics and thermal...
for the German Ford Taunus
Ford Taunus
The Ford Taunus is a family car sold by Ford in Germany and other countries. Models from 1970 onward were similar to the Ford Cortina in the United Kingdom...
, they were prohibited
Trade restriction
A trade restriction is an artificial restriction on the trade of goods between two countries. It is the result of protectionism. However, the term is not uncontroversial since what one part may see as a trade restriction another may see as a way to protect consumers from inferior, harmful or...
in the United States where round lamps were required until 1975. Another early headlamp styling concept involved conventional round lamps faired into the car's bodywork with aerodynamic glass covers, such as those on the 1961 Jaguar E-Type
Jaguar E-type
The Jaguar E-Type or XK-E is a British automobile, manufactured by Jaguar between 1961 and 1975. Its combination of good looks, high performance, and competitive pricing established the marque as an icon of 1960s motoring...
.
Headlamp styling in the United States, 1940–1983
In 1940, a consortium of state motor vehicle administrators standardised upon a system of two 7 in (178 mm) round sealed beamSealed beam
A sealed beam is a type of lamp that includes a reflector and filament as a single assembly, over which a front cover of clear glass, is permanently attached. Previously, automotive headlamps used a separate small bulb and reflector covered with a ribbed lens to avoid glare from the filament. This...
headlamps on all vehicles – the only system allowed for 17 years. A system of four round lamps, rather than two – one high/low and one high-beam 5+3/4 in sealed beam on each side – was introduced in 1957 by Cadillac, Chrysler and Nash on some of their car models in states that permitted the new system, and other American marques followed suit when all states permitted quad lamps in 1958. These lamps had some photometric
Photometry (optics)
Photometry is the science of the measurement of light, in terms of its perceived brightness to the human eye. It is distinct from radiometry, which is the science of measurement of radiant energy in terms of absolute power; rather, in photometry, the radiant power at each wavelength is weighted by...
advantages, particularly on high beam, but the primary advantage was the styling novelty permitted by the use of two small rather than one large lamp per side of the vehicle. The freedom was not absolute, however. Auto stylists such as Virgil Exner
Virgil Exner
Virgil Max "Ex" Exner, Sr. was an automobile designer for numerous American companies, notably Chrysler and Studebaker. He is known for his "Forward Look" design on the 1955-1963 Chrysler products and his fondness of fins on cars for both aesthetic and aerodynamic reasons.-Early life:Born in Ann...
carried out design studies with the low beams in their conventional outboard location, and the high beams vertically stacked at the centreline of the car. No such designs reached volume production. Most cars had their headlights in pairs side by side on each side of the car. Some Oldsmobile
Oldsmobile
Oldsmobile was a brand of American automobile produced for most of its existence by General Motors. It was founded by Ransom E. Olds in 1897. In its 107-year history, it produced 35.2 million cars, including at least 14 million built at its Lansing, Michigan factory...
s had a parking light in the middle of each pair.
Also popular was an arrangement in which the two headlamps on each side were stacked, low beams above high beams. Nash
Nash Motors
Also see: Kelvinator and American Motors CorporationNash Motors was an automobile manufacturer based in Kenosha, Wisconsin, in the United States from 1916 to 1938. From 1938 to 1954, Nash was the automotive division of the Nash-Kelvinator Corporation...
and Lincoln
Lincoln (automobile)
Lincoln is an American luxury vehicle brand of the Ford Motor Company. Lincoln vehicles are sold mostly in North America.-History:The company was founded in August 1915 by Henry M. Leland, one of the founders of Cadillac . During World War I, he left Cadillac which was sold to General Motors...
used this arrangement in the 1957 model year. Pontiac
Pontiac
Pontiac was an automobile brand that was established in 1926 as a companion make for General Motors' Oakland. Quickly overtaking its parent in popularity, it supplanted the Oakland brand entirely by 1933 and, for most of its life, became a companion make for Chevrolet. Pontiac was sold in the...
used this design starting in the 1963 model year; American Motors
American Motors
American Motors Corporation was an American automobile company formed by the 1954 merger of Nash-Kelvinator Corporation and Hudson Motor Car Company. At the time, it was the largest corporate merger in U.S. history.George W...
, Ford, Cadillac
Cadillac
Cadillac is an American luxury vehicle marque owned by General Motors . Cadillac vehicles are sold in over 50 countries and territories, but mostly in North America. Cadillac is currently the second oldest American automobile manufacturer behind fellow GM marque Buick and is among the oldest...
and Chrysler
Chrysler
Chrysler Group LLC is a multinational automaker headquartered in Auburn Hills, Michigan, USA. Chrysler was first organized as the Chrysler Corporation in 1925....
followed two years later. Also in the 1965 model year, the Buick Riviera
Buick Riviera
The Riviera by Buick is an automobile produced by Buick in the United States from the 1963 to 1999 model years, with 1,127,261 produced.A full-size coupé or personal luxury car, the early models of the Riviera in particular have been highly praised by automotive journalists and writers.A common...
had concealable stacked headlamps. The Mercedes-Benz
Mercedes-Benz
Mercedes-Benz is a German manufacturer of automobiles, buses, coaches, and trucks. Mercedes-Benz is a division of its parent company, Daimler AG...
W100
Mercedes-Benz 600
The Mercedes-Benz 600 is a large luxury automobile offered in several variants worldwide. Introduced in September 1963, it had very few competitors, these being Rolls-Royce, Bentley, Cadillac Fleetwood 75, the stretched Lehmann-Peterson Lincoln, and the Crown Imperial Ghia...
, W108
Mercedes-Benz W108
The Mercedes-Benz W108 and W109 were luxury cars built by Mercedes-Benz from 1965 through 1972. The line was an update of the predecessor W111 and W112 fintail sedans. The cars were successful in West Germany and in export markets that included including North America and Southeast Asia...
, W111
Mercedes-Benz W111
The Mercedes-Benz W111 was a chassis code given to its top-range vehicles, including 4-door sedans, produced from 1959 to 1968, and 2-door coupes and cabriolets from 1961 to 1971. The W111, was initially attributed only to 6-cylinder cars with 2.2 litre engines. The luxury version with big-block 3...
, and W112
Mercedes-Benz W112
The Mercedes-Benz W112 was a flagship model in Mercedes-Benz's line-up during the early 1960s. The car, produced in four modifications: coupé, cabriolet and sedans, was identical to the standard Mercedes-Benz W111 Fintail car, but was fitted with the M189 big-block six-cylinder engine, as well as...
models sold in America used this arrangement because their home-market composite lamps were illegal in the US. The British
United Kingdom
The United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern IrelandIn the United Kingdom and Dependencies, other languages have been officially recognised as legitimate autochthonous languages under the European Charter for Regional or Minority Languages...
firm Alvis
Alvis Cars
Alvis Car and Engineering Company Ltd was a British manufacturing company that existed in Coventry, England from 19191967. In addition to automobiles designed for the civilian market, the company also produced racing cars, aircraft engines, armoured cars and other armoured fighting vehicles, the...
and the French
France
The French Republic , The French Republic , The French Republic , (commonly known as France , is a unitary semi-presidential republic in Western Europe with several overseas territories and islands located on other continents and in the Indian, Pacific, and Atlantic oceans. Metropolitan France...
firm Facel Vega
Facel Vega
Facel was a French manufacturer of automobiles from 1954 to 1964.The company was named after the original metal stamping company FACEL, and the company's first model, the Vega, named after the star, was introduced at the 1954 Paris Auto Show...
also used this setup for some of their cars, as did Nissan in Japan
Japan
Japan is an island nation in East Asia. Located in the Pacific Ocean, it lies to the east of the Sea of Japan, China, North Korea, South Korea and Russia, stretching from the Sea of Okhotsk in the north to the East China Sea and Taiwan in the south...
.
In the late 1950s and early 1960s, Lincoln
Lincoln (automobile)
Lincoln is an American luxury vehicle brand of the Ford Motor Company. Lincoln vehicles are sold mostly in North America.-History:The company was founded in August 1915 by Henry M. Leland, one of the founders of Cadillac . During World War I, he left Cadillac which was sold to General Motors...
, Buick
Buick
Buick is a premium brand of General Motors . Buick models are sold in the United States, Canada, Mexico, China, Taiwan, and Israel, with China being its largest market. Buick holds the distinction as the oldest active American make...
, and Chrysler
Chrysler
Chrysler Group LLC is a multinational automaker headquartered in Auburn Hills, Michigan, USA. Chrysler was first organized as the Chrysler Corporation in 1925....
arranged the headlamps diagonally by placing the low-beam lamps outboard and above the high-beam lamps. Certain British cars used a less extreme diagonal arrangement, with the inboard high-beam lamps placed only slightly lower than the outboard low-beam units. The 1965 Gordon-Keeble
Gordon-Keeble
Gordon-Keeble was a British car marque, made first in Slough, then Eastleigh, and finally in Southampton , between 1963 and 1967. The marque's badge was unusual in featuring a tortoise — a pet tortoise walked into the frame of an inaugural photo-shoot, taken in the grounds of the makers...
, Triumph Vitesse
Triumph Vitesse
The Triumph Vitesse was a compact six-cylinder car built by Standard-Triumph from 1962 to 1971. The car was styled by Michelotti, and was available in saloon and convertible variants....
and Bentley S3 Continental used such an arrangement.
In 1968 when Federal auto equipment and safety regulations were initiated, the requirement for two large or four small round sealed beams was codified, thus freezing headlamp design for many years. At the same time, the new regulations prohibited any decorative or protective element in front of the headlamps whenever the headlamps are switched on. Glass-covered headlamps, used on e.g. the Jaguar E-Type
Jaguar E-type
The Jaguar E-Type or XK-E is a British automobile, manufactured by Jaguar between 1961 and 1975. Its combination of good looks, high performance, and competitive pricing established the marque as an icon of 1960s motoring...
, pre-1968 VW Beetle, 1965 Chrysler
Chrysler
Chrysler Group LLC is a multinational automaker headquartered in Auburn Hills, Michigan, USA. Chrysler was first organized as the Chrysler Corporation in 1925....
and Imperial
Imperial (automobile)
Imperial was the Chrysler Corporation's luxury automobile brand between 1955 and 1975, with a brief reappearance in 1981 to 1983.The Imperial name had been used since 1926, but was never a separate make, just the top-of-the-line Chrysler. In 1955, the company decided to spin it off as its own make...
models, Porsche 356
Porsche 356
The Porsche 356 was the company's first production automobile. It was a lightweight and nimble handling rear-engine rear-wheel-drive 2 door sports car available in hardtop coupe and open configurations. Design innovations continued during the years of manufacture, contributing to its motorsports...
, Citroën DS
Citroën DS
The Citroën DS is an executive car produced by the French manufacturer Citroën between 1955 and 1975. Styled by Italian sculptor and industrial designer Flaminio Bertoni and the French aeronautical engineer André Lefèbvre, the DS was known for its aerodynamic futuristic body design and innovative...
and Ferrari Daytona
Ferrari Daytona
The Ferrari 365 GTB/4, better known by the unofficial name Ferrari Daytona, is a Gran Turismo automobile produced from 1968 to 1973. It was first introduced to the public at the Paris Auto Salon in 1968 and replaced the 275 GTB/4...
were no longer permitted and vehicles had to be imported with uncovered headlamps for the US market. This change meant that vehicles designed for good aerodynamic performance could not achieve it for the US market.
When Federal Motor Vehicle Safety Standard 108
Federal Motor Vehicle Safety Standard 108
Federal Motor Vehicle Safety Standard 108 regulates all automotive lighting, signalling and reflective devices in the United States. Like all other Federal Motor Vehicle Safety Standards, FMVSS 108 is administered by the United States Department of Transportation's National Highway Traffic Safety...
was amended in 1974 to permit rectangular
Rectangle
In Euclidean plane geometry, a rectangle is any quadrilateral with four right angles. The term "oblong" is occasionally used to refer to a non-square rectangle...
headlamps, these were placed in horizontally-arrayed or vertically-stacked pairs. By 1979, the majority of new cars in the US market were equipped with rectangular lamps. Again, the US permitted only two standardised sizes of rectangular sealed-beam lamp: A system of two 200 by high/low beam units corresponding to the existing 7-inch round format, or a system of four 165 by units, two high/low and two high-beam. corresponding to the existing 5+3/4 in round format.
International headlamp styling, 1983–present
In 1983, granting a 1981 petition from Ford Motor Company, the 44-year-old U.S. headlamp regulations were amended to allow replaceable-bulb, nonstandard-shape, architectural headlamps with aerodynamic lenses that could for the first time be plastic. This allowed the first U.S.-market car since 1939 with replaceable bulb headlamps – the 1984 Lincoln Mark VII. These composite headlamps were sometimes referred to as "Euro" headlamps, since aerodynamic headlamps were common in EuropeEurope
Europe is, by convention, one of the world's seven continents. Comprising the westernmost peninsula of Eurasia, Europe is generally 'divided' from Asia to its east by the watershed divides of the Ural and Caucasus Mountains, the Ural River, the Caspian and Black Seas, and the waterways connecting...
. Though conceptually similar to European headlamps with nonstandardised shape and replaceable-bulb construction, these headlamps conform to the SAE headlamp standards of US Federal Motor Vehicle Safety Standard 108
Federal Motor Vehicle Safety Standard 108
Federal Motor Vehicle Safety Standard 108 regulates all automotive lighting, signalling and reflective devices in the United States. Like all other Federal Motor Vehicle Safety Standards, FMVSS 108 is administered by the United States Department of Transportation's National Highway Traffic Safety...
, and not the internationalised European safety standards
World Forum for Harmonization of Vehicle Regulations
The World Forum for Harmonization of Vehicle Regulations is a working party of the United Nations Economic Commission for Europe...
used outside North America. Nevertheless, this change to US regulations largely united headlamp styling within and outside the North American market.
In the late 1990s, round headlamps returned to popularity on new cars. These are generally not the discrete self-contained round lamps as found on older cars (certain Jaguar
Jaguar (car)
Jaguar Cars Ltd, known simply as Jaguar , is a British luxury car manufacturer, headquartered in Whitley, Coventry, England. It is part of the Jaguar Land Rover business, a subsidiary of the Indian company Tata Motors....
s excepted), but rather involve circular or oval optical elements within an architecturally-shaped housing assembly.
Hidden headlamps

Cord Automobile
Cord was the brand name of a United States automobile, manufactured by the Auburn Automobile Company from 1929 through 1932 and again in 1936 and 1937....
810. They were mounted in the front fenders, which were smooth until the lights were cranked out, each with its own small dash-mounted crank. They aided aerodynamics
Aerodynamics
Aerodynamics is a branch of dynamics concerned with studying the motion of air, particularly when it interacts with a moving object. Aerodynamics is a subfield of fluid dynamics and gas dynamics, with much theory shared between them. Aerodynamics is often used synonymously with gas dynamics, with...
when the headlamps were not in use, and were among the Cord's signature design features.
Many notable cars used this feature, but no current volume-produced car models use hidden headlamps, because they present difficulties in complying with pedestrian-protection provisions recently added to international auto safety regulations, and because the mechanisms are costly and heavy. Hidden headlamps require one or more vacuum-operated servos
Servomechanism
thumb|right|200px|Industrial servomotorThe grey/green cylinder is the [[Brush |brush-type]] [[DC motor]]. The black section at the bottom contains the [[Epicyclic gearing|planetary]] [[Reduction drive|reduction gear]], and the black object on top of the motor is the optical [[rotary encoder]] for...
and reservoirs, with associated plumbing and linkage, or electric motors
Electric motor
An electric motor converts electrical energy into mechanical energy.Most electric motors operate through the interaction of magnetic fields and current-carrying conductors to generate force...
, gear
Gear
A gear is a rotating machine part having cut teeth, or cogs, which mesh with another toothed part in order to transmit torque. Two or more gears working in tandem are called a transmission and can produce a mechanical advantage through a gear ratio and thus may be considered a simple machine....
trains and linkages to raise the lamps to an exact position to assure correct aiming despite ice, snow and age. Some early hidden headlamps, such as those on the Saab Sonett
Saab Sonett
The Saab Sonett is an automobile manufactured between 1955 and 1957 and again between 1966 and 1974 by Saab Automobile AB of Sweden. Sonetts shared engines and other components with Saab 96s and 95s of the same era....
III, used a lever-operated mechanical linkage to raise the headlamps into position. Current market demands place a premium on vehicles' aerodynamic performance with lamps off and on, further reducing the attractiveness of pop-up headlamps. In addition, recent ECE regulations
World Forum for Harmonization of Vehicle Regulations
The World Forum for Harmonization of Vehicle Regulations is a working party of the United Nations Economic Commission for Europe...
contain standards regarding protuberances on car bodies to minimise injury to pedestrian
Pedestrian
A pedestrian is a person traveling on foot, whether walking or running. In some communities, those traveling using roller skates or skateboards are also considered to be pedestrians. In modern times, the term mostly refers to someone walking on a road or footpath, but this was not the case...
s struck by cars.
Some hidden headlamps themselves do not move, but rather are covered when not in use by panels designed to blend in with the car's styling. When the lamps are switched on, the covers are swung out of the way, usually downward or upward, for example on the 1992 Jaguar XJ220
Jaguar XJ220
The Jaguar XJ220 is a mid-engined supercar produced by Jaguar in collaboration with Tom Walkinshaw Racing as Jaguar Sport between 1992 and 1994. It held the record for the highest top speed of a production car , until the arrival of the McLaren F1 in 1994...
. The door mechanism may be actuated by vacuum
Manifold vacuum
Manifold vacuum, or engine vacuum in an internal combustion engine is the difference in air pressure between the engine's intake manifold and Earth's atmosphere....
pots, as on some Ford
Ford Motor Company
Ford Motor Company is an American multinational automaker based in Dearborn, Michigan, a suburb of Detroit. The automaker was founded by Henry Ford and incorporated on June 16, 1903. In addition to the Ford and Lincoln brands, Ford also owns a small stake in Mazda in Japan and Aston Martin in the UK...
vehicles of the late 1960s through early 1980s such as the 1967-1969 Mercury Cougar
Mercury Cougar
The Mercury Cougar is an automobile which was sold under the Mercury brand of the Ford Motor Company's Lincoln-Mercury Division from 1967 to 2002. The name was first used in 1967 and was carried by a diverse series of cars over the next three decades. As is common with Mercury vehicles, the Cougar...
, or by an electric motor as on various Chrysler products of the middle 1960s through late 1970s such as the 1966-1967 Dodge Charger
Dodge Charger
The Dodge Charger is an American automobile manufactured by the Dodge division of Chrysler. There have been several different Dodge vehicles, built on three different platforms and sizes, all bearing the Charger nameplate...
.
Regulations and requirements
Modern headlamps are electrically operated, positioned in pairs, one or two on each side of the front of a vehicle. A headlamp system is required to produce a low and a high beam, which may be achieved either by an individual lamp for each function or by a single multifunction lamp. High beams (called "main beams" or "full beams" or "driving beams" in some countries) cast most of their light straight ahead, maximizing seeing distance, but producing too much glareGlare (vision)
Glare is difficulty seeing in the presence of bright light such as direct or reflected sunlight or artificial light such as car headlamps at night. Because of this, some cars include mirrors with automatic anti-glare functions....
for safe use when other vehicles are present on the road. Because there is no special control of upward light, high beams also cause backdazzle from fog
Fog
Fog is a collection of water droplets or ice crystals suspended in the air at or near the Earth's surface. While fog is a type of stratus cloud, the term "fog" is typically distinguished from the more generic term "cloud" in that fog is low-lying, and the moisture in the fog is often generated...
, rain and snow
Snow
Snow is a form of precipitation within the Earth's atmosphere in the form of crystalline water ice, consisting of a multitude of snowflakes that fall from clouds. Since snow is composed of small ice particles, it is a granular material. It has an open and therefore soft structure, unless packed by...
due to the retroreflection of the water droplets. Low beams (called "dipped beams" or "passing beams" in some countries) have stricter control of upward light, and direct most of their light downward and either rightward (in right-traffic countries) or leftward (in left-traffic countries), to provide safe forward visibility without excessive glare or backdazzle.
 |
Low beam
Low beam (dipped beam, passing beam, meeting beam) headlamps provide a distribution of light designed to provide adequate forward and lateral illumination with limits on light directed towards the eyes of other road users, to control glare. This beam is intended for use whenever other vehicles are present ahead. The international ECE Regulations for filament headlamps and for high-intensity discharge headlampsHigh-intensity discharge lamp
High-intensity discharge lamps are a type of electrical lamp which produces light by means of an electric arc between tungsten electrodes housed inside a translucent or transparent fused quartz or fused alumina arc tube. This tube is filled with both gas and metal salts. The gas facilitates the...
specify a beam with a sharp, asymmetric cutoff preventing significant amounts of light from being cast into the eyes of drivers of preceding or oncoming cars. Control of glare is less strict in the North American SAE beam standard contained in FMVSS / CMVSS 108
Federal Motor Vehicle Safety Standard 108
Federal Motor Vehicle Safety Standard 108 regulates all automotive lighting, signalling and reflective devices in the United States. Like all other Federal Motor Vehicle Safety Standards, FMVSS 108 is administered by the United States Department of Transportation's National Highway Traffic Safety...
.
High beam
 |
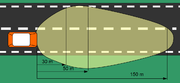 |
High beam (main beam, driving beam, full beam) headlamps provide a bright, centre-weighted distribution of light with no particular control of light directed towards other road users' eyes. As such, they are only suitable for use when alone on the road, as the glare they produce will dazzle other drivers. International ECE Regulations permit higher-intensity high-beam headlamps than are allowed under North American regulations
Federal Motor Vehicle Safety Standard 108
Federal Motor Vehicle Safety Standard 108 regulates all automotive lighting, signalling and reflective devices in the United States. Like all other Federal Motor Vehicle Safety Standards, FMVSS 108 is administered by the United States Department of Transportation's National Highway Traffic Safety...
.
Compatibility with traffic directionality
Most low-beam headlamps are specifically designed for use on only one side of the road. Headlamps for use in left-traffic countries have low-beam headlamps that "dip to the left"; the light is distributed with a downward/leftward bias to show the driver the road and signs ahead without blinding oncoming traffic. Headlamps for right-traffic countries have low beams that "dip to the right", with most of their light directed downward/rightward. Within Europe, when driving a vehicle with RH-traffic headlamps in a LH-traffic country or vice versa for a limited time (as for example on vacation or in transit), it is a legal requirement to adjust the headlamps temporarily so that the wrong-side hot spot of the beam does not dazzle oncoming drivers. This may be achieved by adhering blackout strips or plastic prismatic lenses to a designated part of the lens. Many tungsten (pre-halogen) European-code headlamps made in France by Cibié, Marchal, and Ducellier could be adjusted to produce either a left- or a right-traffic low beam by means of a two-position bulb holder. More recently, some projector-type headlamps can be made to produce a proper left- or right-traffic beam by shifting a lever or other movable element in or on the lamp assembly.Because wrong-side-of-road headlamps blind oncoming drivers and do not adequately light the driver's way, and blackout strips and adhesive prismatic lenses reduce the safety performance of the headlamps, most countries require all vehicles registered or used on a permanent or semipermanent basis within the country to be equipped with headlamps designed for the correct traffic-handedness. North American vehicle owners sometimes privately import and install Japanese-market (JDM) headlamps on their car in the mistaken belief that the beam performance will be better, when in fact such misapplication is quite hazardous and illegal.
Use in daytime
Some countries require automobiles to be equipped with automatic daytime running lampDaytime running lamp
A daytime running lamp is an automotive lighting device on the front of a roadgoing motor vehicle, installed in pairs, automatically switched on when the vehicle is moving forward, emitting white, yellow, or amber light to increase the conspicuity of the vehicle during daylight...
s (DRL), which are intended to increase the conspicuity of vehicles in motion during the daytime. DRL may consist of the manual or automatic illumination of the low beams at full or reduced intensity, or the high beams at reduced intensity, or may not involve the headlamps at all. Countries requiring DRL include Albania, Argentina, Bosnia and Herzegovina, Bulgaria, Canada, Colombia, Croatia, Czech Republic, Denmark, Estonia, Finland, Hungary, Iceland, Israel, Kosovo, Latvia, Lithuania, Macedonia, Norway, Poland, Republic of Moldova, Romania, Russia, Serbia, Slovak Republic, Slovenia, Uruguay, and Sweden.
Construction, performance, and aim
There are two different beam pattern and headlamp construction standards in use in the world: The ECEWorld Forum for Harmonization of Vehicle Regulations
The World Forum for Harmonization of Vehicle Regulations is a working party of the United Nations Economic Commission for Europe...
standard, which is allowed or required in virtually all industrialised countries except the United States, and the SAE standard
Federal Motor Vehicle Safety Standard 108
Federal Motor Vehicle Safety Standard 108 regulates all automotive lighting, signalling and reflective devices in the United States. Like all other Federal Motor Vehicle Safety Standards, FMVSS 108 is administered by the United States Department of Transportation's National Highway Traffic Safety...
that is mandatory only in the US. Japan formerly had bespoke lighting regulations similar to the US standards, but for the left side of the road. However, Japan now adheres to the ECE standard. The differences between the SAE and ECE headlamp standards are primarily in the amount of glare permitted toward other drivers on low beam (SAE permits much more glare), the minimum amount of light required to be thrown straight down the road (SAE requires more), and the specific locations within the beam at which minimum and maximum light levels are specified.
ECE low beams are characterised by a distinct horizontal "cutoff" line at the top of the beam. Below the line is bright, and above is dark. On the side of the beam facing away from oncoming traffic (right in right-traffic countries, left in left-traffic countries), this cutoff sweeps or steps upward to direct light to road signs and pedestrians. SAE low beams may or may not have a cutoff, and if a cutoff is present, it may be of two different general types: VOL, which is conceptually similar to the ECE beam in that the cutoff is located at the top of the left side of the beam and aimed slightly below horizontal, or VOR, which has the cutoff at the top of the right side of the beam and aimed at the horizon.
Proponents of each headlamp system decry the other as inadequate and unsafe: U.S. proponents of the SAE system claim that the ECE low beam cutoff gives short seeing distances and inadequate illumination for overhead road signs, while international proponents of the ECE system claim that the SAE system produces too much glare. Comparative studies have repeatedly shown that there is little or no overall safety benefit to either SAE or ECE beams; the two systems' acceptance and rejection by various countries is based primarily on inertial and philosophical grounds.,
In North America, the design, performance and installation of all motor vehicle lighting
Automotive lighting
The lighting system of a motor vehicle consists of lighting and signalling devices mounted or integrated to the front, sides, rear, and in some cases the top of the motor vehicle...
devices are regulated by Federal and Canada Motor Vehicle Safety Standard 108
Federal Motor Vehicle Safety Standard 108
Federal Motor Vehicle Safety Standard 108 regulates all automotive lighting, signalling and reflective devices in the United States. Like all other Federal Motor Vehicle Safety Standards, FMVSS 108 is administered by the United States Department of Transportation's National Highway Traffic Safety...
, which incorporates SAE technical standards. Elsewhere in the world, ECE internationalised regulations
World Forum for Harmonization of Vehicle Regulations
The World Forum for Harmonization of Vehicle Regulations is a working party of the United Nations Economic Commission for Europe...
are in force either by reference or by incorporation in individual countries' vehicular codes.
US laws required sealed beam
Sealed beam
A sealed beam is a type of lamp that includes a reflector and filament as a single assembly, over which a front cover of clear glass, is permanently attached. Previously, automotive headlamps used a separate small bulb and reflector covered with a ribbed lens to avoid glare from the filament. This...
headlamps on all vehicles between 1940 and 1983, and other countries such as Japan, United Kingdom and Australia also made extensive use of sealed beams. In most other countries, and in the US since 1984, replaceable-bulb headlamps predominate.
Headlamps must be kept in proper alignment (or "aim"). Regulations for aim vary from country to country and from beam specification to beam specification. US SAE headlamps are aimed without regard to headlamp mounting height. This gives vehicles with high-mounted headlamps a seeing distance advantage, at the cost of increased glare to drivers in lower vehicles. ECE headlamps' aim angle is linked to headlamp mounting height. This gives all vehicles roughly equal seeing distance and all drivers roughly equal glare.
Light colour
Headlamps are generally required to produce white light, according to both ECE and SAE standards. ECE Regulation 48 currently requires new vehicles to be equipped with headlamps emitting white light. Previous ECE regulations also permitted selective yellowSelective yellow
Selective yellow is a colour for automotive lamps. Under ECE regulations, headlamps were formerly permitted to be either white or selective yellow — in France, selective yellow was mandatory until 1993....
light, which from 1936 until 1993 was required on all vehicles registered in France
France
The French Republic , The French Republic , The French Republic , (commonly known as France , is a unitary semi-presidential republic in Western Europe with several overseas territories and islands located on other continents and in the Indian, Pacific, and Atlantic oceans. Metropolitan France...
. Selective yellow headlamps are no longer required anywhere, but remain permitted throughout Europe on vehicles already so equipped, as well as in non-European locales such as Japan and New Zealand.
Lens optics
 |
_-_headlamp.jpg) |
A light source (filament or arc) is placed at or near the focus of a reflector, which may be parabolic
Parabolic reflector
A parabolic reflector is a reflective device used to collect or project energy such as light, sound, or radio waves. Its shape is that of a circular paraboloid, that is, the surface generated by a parabola revolving around its axis...
or of non-parabolic complex shape. Fresnel
Fresnel lens
A Fresnel lens is a type of lens originally developed by French physicist Augustin-Jean Fresnel for lighthouses.The design allows the construction of lenses of large aperture and short focal length without the mass and volume of material that would be required by a lens of conventional design...
and prism
Prism (optics)
In optics, a prism is a transparent optical element with flat, polished surfaces that refract light. The exact angles between the surfaces depend on the application. The traditional geometrical shape is that of a triangular prism with a triangular base and rectangular sides, and in colloquial use...
optics moulded into the headlamp lens refract
Refraction
Refraction is the change in direction of a wave due to a change in its speed. It is essentially a surface phenomenon . The phenomenon is mainly in governance to the law of conservation of energy. The proper explanation would be that due to change of medium, the phase velocity of the wave is changed...
(shift) parts of the light laterally and vertically to provide the required light distribution pattern. Most sealed-beam headlamps have lens optics.
Reflector optics
 |
 |
Starting in the 1980s, headlamp reflectors began to evolve beyond the simple stamped steel parabola
Parabola
In mathematics, the parabola is a conic section, the intersection of a right circular conical surface and a plane parallel to a generating straight line of that surface...
. The 1983 Austin Maestro
Austin Maestro
The Austin Maestro is a compact-sized 5-door hatchback car that was produced from 1983 to 1994, initially by the Austin Rover subsidiary of British Leyland , and from 1988 onwards by its successor, Rover Group. The car was produced at the former Morris plant in Cowley, Oxford. It was initially...
was the first vehicle equipped with Lucas-Carello's homofocal reflectors, which comprised parabolic sections of different focal length to improve the efficiency of light collection and distribution. CAD technology allowed the development of reflector headlamps with nonparabolic, complex-shape reflectors. First commercialised by Valeo
Valeo
Valeo is a French automotive components manufacturer.-History:The Société Anonyme Française du Ferodo was founded in 1923 in Saint-Ouen, a suburb of Paris...
under their Cibié brand, these headlamps would revolutionise automobile design.
The 1987 U.S.-market Dodge Monaco/Eagle Premier
Eagle Premier
The Eagle Premier was a full-size automobile developed by the American Motors Corporation and Renault partnership, inherited by Chrysler Corporation when it acquired AMC in 1987, and marketed from 1987 through 1992...
twins and European Citroën XM
Citroën XM
The Citroën XM is an executive car that was produced by the French automaker Citroën between 1989 and 2000. Citroën sold 333,775 XMs during the model's 11 years of production...
were the first cars with complex-reflector headlamps with faceted optic lenses. General Motors
General Motors
General Motors Company , commonly known as GM, formerly incorporated as General Motors Corporation, is an American multinational automotive corporation headquartered in Detroit, Michigan and the world's second-largest automaker in 2010...
' Guide Lamp division in America had experimented with clear-lens complex-reflector lamps in the early 1970s and achieved promising results, but the U.S.-market 1990 Honda Accord
Honda Accord
The Honda Accord is a series of compact, mid-size and full-size automobiles manufactured by Honda since 1976, and sold in a majority of automotive markets throughout the world....
was first with clear-lens multi-reflector headlamps; these were developed by Stanley in Japan. The optics to distribute the light in the desired pattern are designed into the reflector itself, rather than into the lens. Depending on the development tools and techniques in use, the reflector may be engineered from the start as a bespoke shape, or it may start as a parabola
Parabola
In mathematics, the parabola is a conic section, the intersection of a right circular conical surface and a plane parallel to a generating straight line of that surface...
standing in for the size and shape of the completed package. In the latter case, the entire surface area is modified so as to produce individual segments of specifically calculated, complex contours. The shape of each segment is designed such that their cumulative effect produces the required light distribution pattern.
Modern reflectors are commonly made of compression-moulded or injection moulded plastic
Injection moulding
Injection molding is a manufacturing process for producing parts from both thermoplastic and thermosetting plastic materials. Material is fed into a heated barrel, mixed, and forced into a mold cavity where it cools and hardens to the configuration of the cavity...
, though glass and metal optic reflectors also exist. The reflective surface is vapour deposited aluminium with a clear overcoating to prevent the extremely thin aluminium from oxidizing. Extremely tight tolerances must be maintained in the design and production of complex-reflector headlamps.
Dual-beam reflector headlamps
Night driving is difficult and dangerous due to the blinding glare
Glare (vision)
Glare is difficulty seeing in the presence of bright light such as direct or reflected sunlight or artificial light such as car headlamps at night. Because of this, some cars include mirrors with automatic anti-glare functions....
of headlights from oncoming traffic. Headlamps that satisfactorily illuminate the road ahead without causing glare have long been sought. The first solutions involved resistance-type dimming circuits, which decreased the intensity of the headlamps. This yielded to tilting reflectors, and later to dual-filament bulbs with a high and a low beam.
In a two-filament headlamp, there can only be one filament exactly at the focal point of the reflector. There are two primary means of producing two different beams from a two-filament bulb in a single reflector.
American system
One filament is located at the focal point of the reflector. The other filament is shifted axially and radially away from the focal point. In most 2-filament sealed beams and in 2-filament replaceable bulbs of type 9004, 9007, and H13
Automotive lamp types
A modern vehicle uses different kinds of lamps for multiple purposes: illumination for the driver to be able to drive in dark conditions, illumination to be seen and lights for information displays. Types of these lamps vary depending on the purpose and different car manufacturers and models use...
, the high-beam filament is at the focal point and the low-beam filament is off focus. For use in right-traffic countries, the low-beam filament is positioned slightly upward, forward and leftward of the focal point, so that when it is energised, the beam is widened and shifted slightly downward and rightward of the headlamp axis. Transverse-filament bulbs such as the 9004 can only be used with the filaments horizontal, but axial-filament bulbs can be rotated or "clocked" by the headlamp designer to optimise the beam pattern or to effect the traffic-handedness of the low beam. The latter is accomplished by clocking the low-beam filament in an upward-forward-leftward position to produce a right-traffic low beam, or in an upward-forward-rightward position to produce a left-traffic low beam.
The opposite tactic has also been employed in certain 2-filament sealed beams. Placing the low beam filament at the focal point to maximise light collection by the reflector, and positioning the high beam filament slightly rearward-rightward-downward of the focal point. The relative directional shift between the two beams is the same with either technique – in a right-traffic country, the low beam is slightly downward-rightward and the high beam is slightly upward-leftward, relative to one another – but the lens optics must be matched to the filament placements selected.
European system
The traditional European method of achieving low and high beam from a single bulb involves two filaments along the axis of the reflector. The high beam filament is on the focal point, while the low beam filament is approximately 1 cm forward of the focal point and 3 mm above the axis. Below the low beam filament is a cup-shaped shield (called a "Graves Shield") spanning an arc
Circle
A circle is a simple shape of Euclidean geometry consisting of those points in a plane that are a given distance from a given point, the centre. The distance between any of the points and the centre is called the radius....
of 165°. When the low beam filament is illuminated, this shield casts a shadow on the corresponding lower area of the reflector, blocking downward light rays that would otherwise strike the reflector and be cast above the horizon. The bulb is rotated (or "clocked") within the headlamp to position the Graves Shield so as to allow light to strike a 15° wedge of the lower half of the reflector. This is used to create the upsweep or upstep characteristic of ECE
World Forum for Harmonization of Vehicle Regulations
The World Forum for Harmonization of Vehicle Regulations is a working party of the United Nations Economic Commission for Europe...
low beam light distributions. The bulb's rotative position within the reflector depends on the type of beam pattern to be produced and the traffic directionality of the market for which the headlamp is intended.
This system was first used with the tungsten incandescent Bilux/Duplo R2 bulb of 1954, and later with the halogen
Halogen lamp
A halogen lamp, also known as a tungsten halogen lamp, is an incandescent lamp with a tungsten filament contained within an inert gas and a small amount of a halogen such as iodine or bromine. The chemical halogen cycle redeposits evaporated tungsten back on to the filament, extending the life of...
H4 bulb of 1971. In 1992, U.S. regulations were amended to permit the use of H4 bulbs redesignated HB2 and 9003, and with slightly different production tolerances stipulated. These are physically and electrically interchangeable with H4 bulbs. Similar optical techniques are used, but with different reflector and/or lens optics to create a US beam pattern rather than a European one.
Each system has its advantages and disadvantages. The American system historically permitted a greater overall amount of light within the low beam, since the entire reflector and lens area is used, but at the same time, the American system has traditionally offered much less control over upward light that causes glare, and for that reason has been largely rejected outside the US. In addition, the American system makes it difficult to create markedly different low and high beam light distributions. The high beam is usually a rough copy of the low beam, shifted slightly upward and leftward. The European system traditionally produced low beams containing less overall light, because only 60% of the reflector's surface area is used to create the low beam. However, low beam focus and glare control are easier to achieve. In addition, the lower 40% of the reflector and lens are reserved for high beam formation, which facilitates the optimisation of both low and high beams.
Recent developments
Complex-reflector technology in combination with new bulb designs such as H13 is enabling the creation of European-type low and high beam patterns without the use of a Graves Shield, while the 1992 US approval of the H4 bulb has made traditionally European 60% / 40% optical area divisions for low and high beam common in the US. Therefore, the difference in active optical area and overall beam light content no longer necessarily exists between US and ECE beams. Dual-beam HID headlamps employing reflector technology have been made using adaptations of both techniques.
Projector (polyellipsoidal) lamps
 |
 |
In this system a filament is located at one focus
Focus (optics)
In geometrical optics, a focus, also called an image point, is the point where light rays originating from a point on the object converge. Although the focus is conceptually a point, physically the focus has a spatial extent, called the blur circle. This non-ideal focusing may be caused by...
of an ellipsoidal
Ellipse
In geometry, an ellipse is a plane curve that results from the intersection of a cone by a plane in a way that produces a closed curve. Circles are special cases of ellipses, obtained when the cutting plane is orthogonal to the cone's axis...
reflector and has a condenser lens
Lens (optics)
A lens is an optical device with perfect or approximate axial symmetry which transmits and refracts light, converging or diverging the beam. A simple lens consists of a single optical element...
at the front of the lamp. A shade is located at the image plane, between the reflector and lens, and the projection of the top edge of this shade provides the low-beam cutoff. The shape of the shade edge, and its exact position in the optical system, determines the shape and sharpness of the cutoff. The shade may have a solenoid
Solenoid
A solenoid is a coil wound into a tightly packed helix. In physics, the term solenoid refers to a long, thin loop of wire, often wrapped around a metallic core, which produces a magnetic field when an electric current is passed through it. Solenoids are important because they can create...
actuated pivot to provide both low and high beam – the shade is removed from the light path to create high beam, and placed in the light path to create low beam, and such optics are known as BiXenon or BiHalogen projectors, depending on the light source used. If there is no such arrangement, the cutoff shade is fixed in the light path, in which case separate high-beam lamps are required. The condenser lens may have slight fresnel rings
Fresnel lens
A Fresnel lens is a type of lens originally developed by French physicist Augustin-Jean Fresnel for lighthouses.The design allows the construction of lenses of large aperture and short focal length without the mass and volume of material that would be required by a lens of conventional design...
or other surface treatments to reduce cutoff sharpness. Recent condenser lenses incorporate optical features specifically designed to direct some light upward towards the locations of retroreflective overhead road signs.
Hella
Hella (company)
Hella KGaA Hueck & Co. is an internationally operating German automotive part supplier with headquarters in Lippstadt, North Rhine-Westphalia. Core businesses are vehicle lighting and electronics systems and components. Hella is also involved in the areas of vehicle diagnostics and thermal...
introduced ellipsoidal optics for acetylene
Acetylene
Acetylene is the chemical compound with the formula C2H2. It is a hydrocarbon and the simplest alkyne. This colorless gas is widely used as a fuel and a chemical building block. It is unstable in pure form and thus is usually handled as a solution.As an alkyne, acetylene is unsaturated because...
headlamps in 1911, but following the electrification of vehicle lighting, this optical technique wasn't used for many decades. The first modern polyellipsoidal (projector) automotive lamp was the Super-Lite, an auxiliary headlamp produced in a joint venture between Chrysler Corporation and Sylvania
Sylvania Electric Products
Sylvania Electric Products was a U.S. manufacturer of diverse electrical equipment, including at various times radio transceivers, vacuum tubes, semiconductors, and mainframe computers...
and optionally installed in 1969 and 1970 full-size Dodge
Dodge
Dodge is a United States-based brand of automobiles, minivans, and sport utility vehicles, manufactured and marketed by Chrysler Group LLC in more than 60 different countries and territories worldwide....
automobiles. It used an 85 watt transverse-filament tungsten-halogen bulb and was intended as a mid-beam, to extend the reach of the low beams during turnpike travel when low beams alone were inadequate but high beams would produce excessive glare.
Projector main headlamps first appeared in 1981 on the Audi Quartz, the Quattro-based concept car designed by Pininfarina for Geneva Auto Salon. Developed more or less simultaneously in Germany by Hella and Bosch and in France by Cibié, the projector low beam permitted accurate beam focus and a much smaller-diameter optical package, though a much deeper one, for any given beam output. The version of the 1986 BMW 7 Series
BMW 7 Series
The BMW 7 Series is a line of full-size luxury vehicles produced by the German automaker BMW. Introduced in 1977, it is BMW's flagship car and is only available as a sedan or extended-length limousine...
sold outside North America was the first volume-production auto to use polyellipsoidal low beam headlamps.
Tungsten light sources
The first electric headlamp light source was the tungstenTungsten
Tungsten , also known as wolfram , is a chemical element with the chemical symbol W and atomic number 74.A hard, rare metal under standard conditions when uncombined, tungsten is found naturally on Earth only in chemical compounds. It was identified as a new element in 1781, and first isolated as...
filament, operating in a vacuum
Vacuum
In everyday usage, vacuum is a volume of space that is essentially empty of matter, such that its gaseous pressure is much less than atmospheric pressure. The word comes from the Latin term for "empty". A perfect vacuum would be one with no particles in it at all, which is impossible to achieve in...
or inert-gas atmosphere inside the headlamp bulb
Incandescent light bulb
The incandescent light bulb, incandescent lamp or incandescent light globe makes light by heating a metal filament wire to a high temperature until it glows. The hot filament is protected from air by a glass bulb that is filled with inert gas or evacuated. In a halogen lamp, a chemical process...
or sealed beam. Compared to newer-technology light sources, tungsten filaments give off small amounts of light relative to the power they consume. Also, during normal operation of such lamps, tungsten boils off the surface of the filament and condenses on the bulb glass, blackening it. This reduces the light output of the filament and blocks some of the light that would pass through an unblackened bulb glass, though blackening was less of a problem in sealed beam units; their large interior surface area minimised the thickness of the tungsten accumulation. For these reasons, plain tungsten filaments are all but obsolete in automotive headlamp service.
Tungsten-halogen light sources
Halogen technology (also "quartz-halogen", "quartz-iodine", "iodine", "iode") makes tungstenTungsten
Tungsten , also known as wolfram , is a chemical element with the chemical symbol W and atomic number 74.A hard, rare metal under standard conditions when uncombined, tungsten is found naturally on Earth only in chemical compounds. It was identified as a new element in 1781, and first isolated as...
filaments more efficacious producers of light – more lumens
Lumen (unit)
The lumen is the SI derived unit of luminous flux, a measure of the total "amount" of visible light emitted by a source. Luminous flux differs from power in that luminous flux measurements reflect the varying sensitivity of the human eye to different wavelengths of light, while radiant flux...
out per watt in – and European regulators and manufacturers chose to use this extra efficacy to provide drivers with more light than was available from non-halogen filaments at the same power consumption. By contrast, most U.S. low-beam halogens were lower-wattage versions of their non-halogen counterparts, producing the minimum legal amounts of light—in some cases less than the non-halogen predecessors—but with less power. A slight theoretical fuel economy benefit and reduced vehicle construction cost through reduced wire and switch ratings were the claimed benefits. There was an improvement in seeing distance with U.S. halogen high beams, which were permitted for the first time to produce 150,000 candela
Candela
The candela is the SI base unit of luminous intensity; that is, power emitted by a light source in a particular direction, weighted by the luminosity function . A common candle emits light with a luminous intensity of roughly one candela...
(cd) per vehicle, double the nonhalogen limit of 75,000 cd but still well shy of the international European limit of 225,000 cd. After replaceable halogen bulbs were permitted in U.S. headlamps in 1983, development of U.S. bulbs continued to favour long bulb life and low power consumption, while European designs continued to prioritise optical precision and maximum output.
The first halogen
Halogen
The halogens or halogen elements are a series of nonmetal elements from Group 17 IUPAC Style of the periodic table, comprising fluorine , chlorine , bromine , iodine , and astatine...
bulb for vehicle use, the H1
H1 bulbs
The H1 is a halogen lamp designed for use in automotive headlamps and fog and driving lamps. It has also been widely applied in emergency vehicle lights.-Origin:...
, was introduced in 1962 by a consortium of European bulb and headlamp makers. This bulb has a single axial filament that consumes 55 watt
Watt
The watt is a derived unit of power in the International System of Units , named after the Scottish engineer James Watt . The unit, defined as one joule per second, measures the rate of energy conversion.-Definition:...
s at 12.0 volt
Volt
The volt is the SI derived unit for electric potential, electric potential difference, and electromotive force. The volt is named in honor of the Italian physicist Alessandro Volta , who invented the voltaic pile, possibly the first chemical battery.- Definition :A single volt is defined as the...
s, and produces 1550 lumens ±15% when operated at 13.2 V. H2 (55 W @ 12.0 V, 1820 lm @ 13.2 V) followed in 1964, and the transverse-filament H3 (55 W @ 12.0 V, 1450 lm ±15%) in 1966. H1 still sees wide use in low beams, high beams and auxiliary fog and driving lamps, as does H3. The H2 does not see wide use any more because it requires an intricate bulb holder interface to the lamp, has a short life and is difficult to handle. For those reasons, H2 was withdrawn from ECE Regulation 37
World Forum for Harmonization of Vehicle Regulations
The World Forum for Harmonization of Vehicle Regulations is a working party of the United Nations Economic Commission for Europe...
for use in new lamp designs (though H2 bulbs are still manufactured for replacement purposes in existing lamps). The use of H1 and H3 bulbs was legalised in the United States in 1997. More recent single-filament bulb designs include the H7 (55 W @ 12.0 V, 1500 lm ±10% @ 13.2 V), H8 (35 W @ 12.0 V, 800 lm ±15% @ 13.2 V), H9 (65 W @ 12.0 V, 2100 lm ±10% @ 13.2 V), and H11 (55 W @ 12.0 V, 1350 lm ±10% @ 13.2 V). 24-volt versions of many bulb types are available for use in truck
Truck
A truck or lorry is a motor vehicle designed to transport cargo. Trucks vary greatly in size, power, and configuration, with the smallest being mechanically similar to an automobile...
s, bus
Bus
A bus is a road vehicle designed to carry passengers. Buses can have a capacity as high as 300 passengers. The most common type of bus is the single-decker bus, with larger loads carried by double-decker buses and articulated buses, and smaller loads carried by midibuses and minibuses; coaches are...
es, and other commercial and military
Military
A military is an organization authorized by its greater society to use lethal force, usually including use of weapons, in defending its country by combating actual or perceived threats. The military may have additional functions of use to its greater society, such as advancing a political agenda e.g...
vehicles.
The first dual-filament halogen bulb (to produce a low and a high beam with only one bulb), the H4, was released in 1971. The U.S. prohibited halogen headlamps until 1978, when halogen sealed beam
Sealed beam
A sealed beam is a type of lamp that includes a reflector and filament as a single assembly, over which a front cover of clear glass, is permanently attached. Previously, automotive headlamps used a separate small bulb and reflector covered with a ribbed lens to avoid glare from the filament. This...
s were released. To this day, the H4 is still not legal for automotive use in the United States. Instead, the Americans created their own very similar standard (HB2/9003). The primary differences are that the HB2 sets more strict requirements on filament positioning, and that the HB2 are required to meet the lower maximum output standards set forth by the United States government.
The first U.S. halogen headlamp bulb, introduced in 1983, was the 9004/HB1. It is a 12.8-volt, transverse dual-filament design that produces 700 lumens on low beam and 1200 lumens on high beam. The 9004 is rated for 65 watt
Watt
The watt is a derived unit of power in the International System of Units , named after the Scottish engineer James Watt . The unit, defined as one joule per second, measures the rate of energy conversion.-Definition:...
s (high beam) and 45 watts (low beam) at 12.8 volts. Other U.S. approved halogen
Halogen
The halogens or halogen elements are a series of nonmetal elements from Group 17 IUPAC Style of the periodic table, comprising fluorine , chlorine , bromine , iodine , and astatine...
bulbs include the 9005/HB3 (65 W, 12.8 V), 9006/HB4 (55 W, 12.8 V), and 9007/HB5 (65/55 watts, 12.8 V).
Halogen infrared reflective light sources (HIR)
A further development of the tungsten-halogen bulb has a dichroicDichroism
Dichroism has two related but distinct meanings in optics. A dichroic material is either one which causes visible light to be split up into distinct beams of different wavelengths , or one in which light rays having different polarizations are absorbed by different amounts.The original meaning of...
coating that passes visible light
Visible spectrum
The visible spectrum is the portion of the electromagnetic spectrum that is visible to the human eye. Electromagnetic radiation in this range of wavelengths is called visible light or simply light. A typical human eye will respond to wavelengths from about 390 to 750 nm. In terms of...
and reflects infrared radiation. The glass in such a bulb may be spherical
Sphere
A sphere is a perfectly round geometrical object in three-dimensional space, such as the shape of a round ball. Like a circle in two dimensions, a perfect sphere is completely symmetrical around its center, with all points on the surface lying the same distance r from the center point...
or tubular. The reflected infrared radiation strikes the filament located at the center of the glass envelope, heating the filament to a greater degree than can be achieved through resistive heating alone. The superheated filament emits more light without an increase in power consumption or a decrease in lifespan.
HID (xenon) light sources

Electric arc
An electric arc is an electrical breakdown of a gas which produces an ongoing plasma discharge, resulting from a current flowing through normally nonconductive media such as air. A synonym is arc discharge. An arc discharge is characterized by a lower voltage than a glow discharge, and relies on...
rather than a glowing filament. The high intensity of the arc comes from metallic salts that are vapourised within the arc chamber. These lamps are formally known as gas-discharge burners, and produce more light for a given level of power consumption than ordinary tungsten and tungsten-halogen bulbs. Because of the increased amounts of light available from HID burners relative to halogen bulbs, HID headlamps producing a given beam pattern can be made smaller than halogen headlamps producing a comparable beam pattern. Alternatively, the larger size can be retained, in which case the xenon headlamp can produce a more robust beam pattern.
Automotive HID lamps are commonly called "xenon headlamps", though they are actually metal halide lamp
Metal halide lamp
Metal-halide lamps, a member of the high-intensity discharge family of lamps, produce high light output for their size, making them a compact, powerful, and efficient light source. By adding rare earth metal salts to the mercury vapor lamp, improved luminous efficacy and light color is obtained...
s that contain xenon
Xenon
Xenon is a chemical element with the symbol Xe and atomic number 54. The element name is pronounced or . A colorless, heavy, odorless noble gas, xenon occurs in the Earth's atmosphere in trace amounts...
gas. The xenon gas allows the lamps to produce minimally adequate light immediately upon powerup, and accelerates the lamps' run-up time. If argon
Argon
Argon is a chemical element represented by the symbol Ar. Argon has atomic number 18 and is the third element in group 18 of the periodic table . Argon is the third most common gas in the Earth's atmosphere, at 0.93%, making it more common than carbon dioxide...
were used instead, as is commonly done in street lights and other stationary metal halide lamp applications, it would take several minutes for the lamps to reach their full output. The light from HID headlamps exhibits a distinct bluish tint when compared with tungsten-filament headlamps.
History
Xenon headlamps were introduced as an option on the BMW 7-seriesBMW E32
After almost 7 years in development since September 1979, in July 1986, BMW introduced the second generation of the 7 series, known internally as the E32. Aimed at the high end of the luxury market, the car offered some of the latest innovations in automotive technology, and a new, top-of-the-line...
in 1991 for Europe, and in 1993 for US models. This first system used an unshielded, non-replaceable burner designated D1 – a designation that would be recycled years later for a wholly different type of burner. The AC ballast was about the size of a building brick. The first American-made effort at HID headlamps was on the 1996-98 Lincoln Mark VIII
Lincoln Mark VIII
The Lincoln Mark VIII is a large, rear-wheel drive grand touring luxury coupe built from 1993 to 1998. It was the successor of the Mark VII. The Mark VIII was built at Ford's Wixom, Michigan assembly plant and was based on the FN10 platform, a relative of the MN12 platform which underpinned the...
, which used reflector headlamps with an unmasked, integral-ignitor burner made by Sylvania
Osram Sylvania
Osram Sylvania Inc. is the North American operation of lighting manufacturer Osram GmbH, which is owned by Siemens AG. It was established in January 1993, with the acquisition of GTE’s Sylvania lighting division by Osram GmbH....
and designated Type 9500. This was the only system to operate on DC
Direct current
Direct current is the unidirectional flow of electric charge. Direct current is produced by such sources as batteries, thermocouples, solar cells, and commutator-type electric machines of the dynamo type. Direct current may flow in a conductor such as a wire, but can also flow through...
; reliability proved inferior to the AC systems. The Type 9500 system was not used on any other models, and was discontinued after Osram
Osram
Osram, founded 1919, is part of the industry sector of Siemens AG and one of the two leading lighting manufacturers in the world. The name is derived from osmium and Wolfram , as both these elements were commonly used for lighting filaments at the time the company was founded...
's takeover of Sylvania. All HID headlamps worldwide presently use the standardised AC-operated bulbs and ballasts.
Burner and ballast operation
HID headlamp bulbs do not run on low-voltage DC current, so they require a ballast with either an internal or external ignitor. The ignitor is integrated into the bulb in D1 and D3 systems, and is either a separate unit or part of the ballast in D2 and D4 systems. The ballast controls the current to the bulb. The ignition and ballast operation proceeds in three stages:- Ignition: a high voltageHigh voltageThe term high voltage characterizes electrical circuits in which the voltage used is the cause of particular safety concerns and insulation requirements...
pulse is used to produce a spark – in a manner similar to a spark plugSpark plugA spark plug is an electrical device that fits into the cylinder head of some internal combustion engines and ignites compressed fuels such as aerosol, gasoline, ethanol, and liquefied petroleum gas by means of an electric spark.Spark plugs have an insulated central electrode which is connected by...
– which ionises the Xenon gas, creating a conducting tunnel between the tungsten electrodes. Electrical resistance is reduced within the tunnel, and current flows between the electrodes. - Initial phase: the bulb is driven with controlled overload. Because the arc is operated at high power, the temperature in the capsule rises quickly. The metallic salts vaporise, and the arc is intensified and made spectrallySpectral power distributionIn color science and radiometry, a spectral power distribution describes the power per unit area per unit wavelength of an illumination , or more generally, the per-wavelength contribution to any radiometric quantity .Mathematically, for the spectral...
more complete. The resistance between the electrodes also falls; the electronic ballast control gear registers this and automatically switches to continuous operation. - Continuous operation: all metal salts are in the vapor phase, the arc has attained its stable shape, and the luminous efficacyLuminous efficacyLuminous efficacy is a measure of how well a light source produces visible light. It is the ratio of luminous flux to power. Depending on context, the power can be either the radiant flux of the source's output, or it can be the total electric power consumed by the source.Which sense of the term is...
has attained its nominal value. The ballast now supplies stable electrical power so the arc will not flicker. Stable operating voltage is 85 voltVoltThe volt is the SI derived unit for electric potential, electric potential difference, and electromotive force. The volt is named in honor of the Italian physicist Alessandro Volta , who invented the voltaic pile, possibly the first chemical battery.- Definition :A single volt is defined as the...
s ACAlternating currentIn alternating current the movement of electric charge periodically reverses direction. In direct current , the flow of electric charge is only in one direction....
in D1 and D2 systems, 42 volts AC in D3 and D4 systems. The frequency of the square-wave alternating current is typically 400 hertzHertzThe hertz is the SI unit of frequency defined as the number of cycles per second of a periodic phenomenon. One of its most common uses is the description of the sine wave, particularly those used in radio and audio applications....
or higher.
Burner types
HID headlamp burners produce between 2,800 and 3,500 lumens from between 35 and 38 wattWatt
The watt is a derived unit of power in the International System of Units , named after the Scottish engineer James Watt . The unit, defined as one joule per second, measures the rate of energy conversion.-Definition:...
s of electrical power, while halogen filament headlamp bulbs produce between 700 and 2,100 lumens from between 40 and 72 watts at 12.8 V.
Current-production burner categories are D1S, D1R, D2S, D2R, D3S, D3R, D4S, and D4R. The D stands for discharge, and the number is the type designator. The final letter describes the outer shield. The arc within an HID headlamp bulb generates considerable short-wave ultraviolet
Ultraviolet
Ultraviolet light is electromagnetic radiation with a wavelength shorter than that of visible light, but longer than X-rays, in the range 10 nm to 400 nm, and energies from 3 eV to 124 eV...
(UV) light, but none of it escapes the bulb, for a UV-absorbing hard glass shield is incorporated around the bulb's arc tube. This is important to prevent degradation of UV-sensitive components and materials in headlamps, such as polycarbonate
Polycarbonate
PolycarbonatePhysical PropertiesDensity 1.20–1.22 g/cm3Abbe number 34.0Refractive index 1.584–1.586FlammabilityV0-V2Limiting oxygen index25–27%Water absorption – Equilibrium0.16–0.35%Water absorption – over 24 hours0.1%...
lenses and reflector hardcoats. "S" burners – D1S, D2S, D3S, and D4S – have a plain glass shield and are primarily used in projector-type optics. "R" burners – D1R, D2R, D3R, and D4R – are designed for use in reflector-type headlamp optics. They have an opaque mask covering specific portions of the shield, which facilitates the optical creation of the light/dark boundary (cutoff) near the top of a low-beam light distribution. Automotive HID burners do emit considerable near-UV light, despite the shield.
Colour
The correlated colour temperature of HID headlamp bulbs, at between 4100K and 4400K, is often described in marketing literature as being closer to the 5800K of sunlightSunlight
Sunlight, in the broad sense, is the total frequency spectrum of electromagnetic radiation given off by the Sun. On Earth, sunlight is filtered through the Earth's atmosphere, and solar radiation is obvious as daylight when the Sun is above the horizon.When the direct solar radiation is not blocked...
compared with tungsten-halogen bulbs at 3000K to 3550K. Nevertheless, HID headlamps' light output is not similar to daylight. The spectral power distribution (SPD) of an automotive HID headlamp is discontinuous, while the SPD of a filament lamp, like that of the sun, is a continuous curve. Moreover, the colour rendering index
Color-rendering index
The color rendering index , is a quantitative measure of the ability of a light source to reproduce the colors of various objects faithfully in comparison with an ideal or natural light source. Light sources with a high CRI are desirable in color-critical applications such as photography and...
(CRI) of tungsten-halogen headlamps (≥0.98) is much closer than that of HID headlamps (~0.75) to standardised sunlight (1.00). Studies have shown no significant safety effect of this degree of CRI variation in headlighting.
Increased safety
The HID headlamp light sources (bulbs) offer substantially greater luminance
Luminance
Luminance is a photometric measure of the luminous intensity per unit area of light travelling in a given direction. It describes the amount of light that passes through or is emitted from a particular area, and falls within a given solid angle. The SI unit for luminance is candela per square...
and luminous flux
Luminous flux
In photometry, luminous flux or luminous power is the measure of the perceived power of light. It differs from radiant flux, the measure of the total power of light emitted, in that luminous flux is adjusted to reflect the varying sensitivity of the human eye to different wavelengths of...
than halogen bulbs – about 3000 lumen
Lumen (unit)
The lumen is the SI derived unit of luminous flux, a measure of the total "amount" of visible light emitted by a source. Luminous flux differs from power in that luminous flux measurements reflect the varying sensitivity of the human eye to different wavelengths of light, while radiant flux...
s and 90 mcd
Candela
The candela is the SI base unit of luminous intensity; that is, power emitted by a light source in a particular direction, weighted by the luminosity function . A common candle emits light with a luminous intensity of roughly one candela...
/m2 versus 1400 lumens and 30 mcd/m2. If the higher-output HID light source is used in a well-engineered headlamp optic, the driver gets more usable light. Studies have demonstrated drivers react faster and more accurately to roadway obstacles with good HID headlamps rather than halogen ones. Hence, good HID headlamps contribute to driving safety. The contrary argument is that HID headlamps can negatively impact the vision of oncoming traffic due to their high intensity and "flashing" effect due to the rapid transition between low and high illumination in the field of illumination, thus increasing the risk of a head-on collision between the HID-enabled vehicle and a blinded oncoming driver.
Efficacy and output
Efficacy
Luminous efficacy
Luminous efficacy is a measure of how well a light source produces visible light. It is the ratio of luminous flux to power. Depending on context, the power can be either the radiant flux of the source's output, or it can be the total electric power consumed by the source.Which sense of the term is...
is the measure of how much light is produced versus how much energy is consumed. HID burners give higher efficacy (produce more light from less power) than halogen bulbs. The highest-intensity halogen headlamp bulbs, H9 and HIR1, produce 2100 to 2530 lumens from approximately 70 watts at 13.2 volts. A D2S HID burner produces 3200 lumens from approximately 42 watts during stable operation. The reduced power consumption means less fuel consumption, with resultant less CO2 emission per vehicle fitted with HID lighting (1.3 g/km assuming that 30% of engine running time is with the lights on).
Longevity
The average service life of an HID lamp is 2000 hours, compared to between 450 and 1000 hours for a halogen lamp.
Glare
Vehicles equipped with HID headlamps (except motorcycles) are required by ECE regulation 48
World Forum for Harmonization of Vehicle Regulations
The World Forum for Harmonization of Vehicle Regulations is a working party of the United Nations Economic Commission for Europe...
also to be equipped with headlamp lens cleaning systems and automatic beam levelling control. Both of these measures are intended to reduce the tendency for high-output headlamps to cause high levels of glare to other road users. In North America, ECE R48 does not apply and while lens cleaners and beam levellers are permitted, they are not required; HID headlamps are markedly less prevalent in the US, where they have produced significant glare complaints. Scientific study of headlamp glare has shown that for any given intensity level, the light from HID headlamps is 40% more glaring than the light from tungsten-halogen headlamps.
Mercury content
HID headlamp bulb types D1R, D1S, D2R, D2S and 9500 contain the toxic heavy metal
Heavy metals
A heavy metal is a member of a loosely-defined subset of elements that exhibit metallic properties. It mainly includes the transition metals, some metalloids, lanthanides, and actinides. Many different definitions have been proposed—some based on density, some on atomic number or atomic weight,...
mercury
Mercury (element)
Mercury is a chemical element with the symbol Hg and atomic number 80. It is also known as quicksilver or hydrargyrum...
. The disposal of mercury-containing vehicle parts is increasingly regulated throughout the world, for example under US EPA regulations. Newer HID bulb designs D3R, D3S, D4R, and D4S which are in production since 2004 contain no mercury, but are not electrically or physically compatible with headlamps designed for previous bulb types.
Lack of backward-compatibility
The arc light source in an HID headlamp is fundamentally different in size, shape, orientation, and luminosity distribution compared to the filament light source used in tungsten-halogen headlamps. For that reason, HID-specific optics are used to collect and distribute the light. HID burners cannot effectively or safely be installed in optics designed to take filament bulbs; doing so results in improperly-focused beam patterns and excessive glare, and is therefore illegal in almost all countries. Moreover, most developed countries enforce the ECE Regulation requirement that HID headlamps, except those on motorcycles, be equipped with lens cleaning and automatic headlamp self-levelling systems, which usually are absent on vehicles not originally equipped with HID lamps. If a halogen headlamp is retrofitted with an HID bulb, its type approval or certification is no longer valid so the headlamp is no longer street-legal.
Cost
HID headlamps are significantly more costly to produce, install, purchase, and repair. The extra cost of the HID lights may exceed the fuel cost savings through their reduced power consumption, though some of this cost disadvantage is offset by the longer lifespan of the HID burner relative to halogen bulbs.
LED light sources
Automotive headlamp applications using light-emitting diodeLight-emitting diode
A light-emitting diode is a semiconductor light source. LEDs are used as indicator lamps in many devices and are increasingly used for other lighting...
s (LEDs) have been undergoing very active development since 2004. The first series-production LED headlamps were factory-installed on the Lexus LS 600h / LS 600h L presented in 2007 for 2008 models. Low beam, front position light and sidemarker functions are performed by LEDs; high beam and turn signal functions use filament bulbs. The headlamp is supplied by Koito. Full-LED headlamps supplied by AL-Automotive Lighting were fitted on the 2008 V10 Audi R8 sports car except in North America. The Hella headlamps on the 2009 Cadillac Escalade
Cadillac Escalade
The Cadillac Escalade is a full-size luxury sport utility vehicle sold by the General Motors luxury brand, Cadillac. It was the division's first major entry into the popular SUV market. The Escalade was introduced for the 1999 model year in response to German and Japanese competitors and to Ford's...
Platinum became the first U.S. market all-LED headlamps. Present designs, such as those available as optional equipment on the 2010 Toyota Prius
Toyota Prius
The Toyota Prius is a full hybrid electric mid-size hatchback, formerly a compact sedan developed and manufactured by the Toyota Motor Corporation...
, give performance between halogen and HID headlamps, with system power consumption slightly lower than other headlamps, longer lifespans and more flexible design possibilities. As LED technology continues to evolve, the performance of LED headlamps is predicted to improve to approach, meet, and perhaps one day surpass that of HID headlamps.
The limiting factors with LED headlamps presently include high system expense, regulatory delays and uncertainty, and logistical issues created by LED operating characteristics. As a semiconductor, the performance of an LED is dependent on its temperature; a given diode will produce more light at a low temperature than at a high temperature. Thus, in order to maintain a constant light output, the temperature of an LED headlamp must be kept relatively stable. LEDs are commonly considered to be low-heat devices due to the public's familiarity with small, low-output LEDs used for electronic control panels and other applications requiring only small amounts of light; however, LEDs actually produce a significant amount of heat per unit of light output. Rather than being emitted together with the light as is the case with conventional light sources, an LED's heat is produced at the rear of the emitters. Unlike incandescent and HID bulbs, LEDs are damaged by high temperatures; prolonged operation above the maximum junction temperature
Junction temperature
Junction temperature is the highest temperature of the actual semiconductor in an electronic device. In operation it is higher than case temperature and the temperature of the part's exterior...
will permanently degrade the LEDs and ultimately shorten the device's life. The need to keep LED junction temperatures low at high power levels requires thermal management measures such as heatsinks and/or cooling fans which are typically quite expensive.
Additional facets of the thermal issues with LED headlamps reveal themselves in cold ambient temperatures. Not only can excessively low temperatures lead to the LED's light output increasing beyond the regulated maximum, but heat must in addition be effectively applied to thaw snow and ice from the front lenses, which are not heated by the comparatively small amount of infrared radiation emitted forward with the light from LEDs.
LEDs are increasingly being adopted for signal functions such as parking lamps, brake lamps and turn signals
Automotive lighting
The lighting system of a motor vehicle consists of lighting and signalling devices mounted or integrated to the front, sides, rear, and in some cases the top of the motor vehicle...
as well as daytime running lamp
Daytime running lamp
A daytime running lamp is an automotive lighting device on the front of a roadgoing motor vehicle, installed in pairs, automatically switched on when the vehicle is moving forward, emitting white, yellow, or amber light to increase the conspicuity of the vehicle during daylight...
s, as in those applications they offer significant advantages over filament bulbs with fewer engineering challenges than headlamps pose.
Automatic Headlamps
Automatic systems for activating the headlamps have been available since the mid 1960's, originally only on luxury American models such as Lincoln, Cadillac, and Imperial. Basic implementations simply turn the headlights on at dusk and off at dawn, while more advanced systems such as high-spec versions of the Twilight SentinelTwilight Sentinel
On an automobile, Twilight Sentinel is a device on General Motors' cars that senses outside light and turns the exterior lights on and off depending on lighting conditions....
also allow the driver to set a variable timer to leave the vehicle's exterior lights illuminated after he or she exits the vehicle, to aid in finding his or her way in the dark.
Headlamp levelling systems
The 1948 Citroen 2CVCitroën 2CV
The Citroën 2CV |tax horsepower]]”) was an economy car produced by the French automaker Citroën between 1948 and 1990. It was technologically advanced and innovative, but with uncompromisingly utilitarian unconventional looks, and deceptively simple Bauhaus inspired bodywork, that belied the sheer...
was launched in France with a manual headlamp levelling system, controlled by the driver with knob through a mechanical rod linkage. This allowed the driver to adjust the vertical aim of the headlamps to compensate for the passenger and cargo load in the vehicle. In 1954, Cibié introduced an automatic headlamp levelling system linked to the vehicle's suspension system to keep the headlamps correctly aimed regardless of vehicle load, without driver intervention. The first vehicle to be so equipped was the Panhard Dyna Z
Panhard Dyna Z
The Panhard Dyna Z was a lightweight motor car made by Panhard of France. It was first presented to the press at a Paris restaurant named "Les Ambassadeurs" on 17 June 1953 and went into production the following year...
. Beginning in the 1970s, Germany and some other European countries began requiring remote-control headlamp levelling systems that permit the driver to lower the lamps' aim by means of a dashboard control lever or knob if the rear of the vehicle is weighted down with passengers or cargo, which would tend to raise the lamps' aim angle and create glare. Such systems typically use stepper motor
Stepper motor
A stepper motor is a brushless, electric motor that can divide a full rotation into a large number of steps. The motor's position can be controlled precisely without any feedback mechanism , as long as the motor is carefully sized to the application...
s at the headlamp and a rotary switch on the dash marked "0", "1", "2", "3" for different beam heights, "0" being the "normal" (and highest) position for when the car is lightly loaded. Internationalised ECE Regulation
World Forum for Harmonization of Vehicle Regulations
The World Forum for Harmonization of Vehicle Regulations is a working party of the United Nations Economic Commission for Europe...
48, in force in most of the world outside North America, currently specifies a limited range within which the vertical aim of the headlamps must be maintained under various vehicle load conditions; if the vehicle isn't equipped with an adaptive suspension sufficient to keep the headlamps aimed correctly regardless of load, a headlamp levelling system is required.
The regulation stipulates a more stringent version of this antiglare measure if the vehicle has headlamps with low beam light source(s) that produce more than 2,000 lumens – xenon bulbs and certain high-power halogens, for example. Such vehicles must be equipped with headlamp self-levelling systems that sense the vehicle's degree of squat due to cargo load and road inclination, and automatically adjust the headlamps' vertical aim to keep the beam correctly oriented without any action required by the driver.
Levelling systems are not required by the North American regulations. Recent American research, however, suggests automatic levellers on all headlamps, not just those with high-power light sources, would give drivers substantial safety benefits of better seeing and less glare.
Directional headlamps


Corner
A corner is the place where two lines meet at an angle, and a concave corner of intersecting walls is generally thought to be the least beneficial position to be in a life-or-death situation. From this notion was born the verb to corner, which is used to mean "to back into a corner" and usually...
ing. Some automobiles have their headlamps connected to the steering
Steering
Steering is the term applied to the collection of components, linkages, etc. which will allow a vessel or vehicle to follow the desired course...
mechanism so the lights will follow the movement of the front wheels. Czech Tatra was an early implementer of such a technique, producing in the 1930s a vehicle with a central directional headlamp. The American 1948 Tucker Sedan
1948 Tucker Sedan
The 1948 Tucker Sedan or Tucker '48 Sedan was an advanced automobile conceived by Preston Tucker and briefly produced in Chicago in 1948...
was likewise equipped with a third central headlamp connected mechanically to the steering system. The 1967 French Citroën DS
Citroën DS
The Citroën DS is an executive car produced by the French manufacturer Citroën between 1955 and 1975. Styled by Italian sculptor and industrial designer Flaminio Bertoni and the French aeronautical engineer André Lefèbvre, the DS was known for its aerodynamic futuristic body design and innovative...
and 1970 Citroën SM
Citroën SM
The Citroën SM is a high-performance coupé produced by the French manufacturer Citroën from 1970 to 1975. The SM placed third in the 1971 European Car of the Year contest, trailing its stablemate Citroën GS, and won the 1972 Motor Trend Car of the Year award in the U.S. in 1972.-History:In 1961,...
were equipped with an elaborate dynamic headlamp positioning system that adjusted the headlamps' horizontal and vertical positioning in response to inputs from the vehicle's steering and suspension systems, though US regulations
Federal Motor Vehicle Safety Standard 108
Federal Motor Vehicle Safety Standard 108 regulates all automotive lighting, signalling and reflective devices in the United States. Like all other Federal Motor Vehicle Safety Standards, FMVSS 108 is administered by the United States Department of Transportation's National Highway Traffic Safety...
required this system to be removed from those models when sold in the USA. The D series cars equipped with the system used cables connecting the long range headlamps to a lever on the steering relay while the inner long range headlamps on the SM used a sealed hydraulic system using a glycerin based fluid instead of mechanical cables. Both these systems were of the same design as their respective cars' headlamp leveling systems. The cables of the D system tended to rust in the cable sheaths while the SM system gradually leaked fluid, causing the long range lamps to turn inward, looking "cross-eyed." A manual adjustment was provided but once it was to the end of its travel the system required refilling with fluid or replacement of the tubes and dashpots.
As a note, the Citroën SM
Citroën SM
The Citroën SM is a high-performance coupé produced by the French manufacturer Citroën from 1970 to 1975. The SM placed third in the 1971 European Car of the Year contest, trailing its stablemate Citroën GS, and won the 1972 Motor Trend Car of the Year award in the U.S. in 1972.-History:In 1961,...
non-USA/Canada market vehicles were equipped with heating of the headlamp cover glasses, this heat supplied by ducts carrying warm air from the radiator exhaust to the space between the headlamp lenses and the cover glasses. This provided demisting/defogging of the entire interior of the cover glasses, keeping the glass clear of mist/fog over the entire surface. The glasses have thin stripes on their surfaces that are heated by the headlight beams, however, the ducted warm air provides demisting when the headlamps are not turned on. The glasses' stripes on both D and SM cars appear similar to rear windshield glass electric defogger heating strips, but they are passive, not electrified.
Advanced front-lighting system (AFS)
There has been a recent resurgence in interest in the idea of moving or optimizing the headlight beam in response not only to vehicular steering and suspension dynamics, but also to ambient weather and visibility conditions, vehicle speed, and road curvature and contour. A task force under the EUREKAEUREKA
EUREKA, often abbreviated as "E!" or "Σ!", is a pan-European research and development funding and coordination organization. EUREKA aims to coordinate efforts of governments, research institutes and commercial companies concerning innovation...
organisation, composed primarily of European automakers, lighting companies and regulators began working to develop design and performance specifications for what is known as advanced front-lighting systems, commonly AFS.
Manufacturers such as BMW
BMW
Bayerische Motoren Werke AG is a German automobile, motorcycle and engine manufacturing company founded in 1916. It also owns and produces the Mini marque, and is the parent company of Rolls-Royce Motor Cars. BMW produces motorcycles under BMW Motorrad and Husqvarna brands...
, Toyota, Škoda
Škoda Auto
Škoda Auto , more commonly known as Škoda, is an automobile manufacturer based in the Czech Republic. Škoda became a wholly owned subsidiary of the Volkswagen Group in 2000, positioned as the entry brand to the group...
and Vauxhall
Vauxhall Motors
Vauxhall Motors is a British automotive company owned by General Motors and headquartered in Luton. It was founded in 1857 as a pump and marine engine manufacturer, began manufacturing cars in 1903 and was acquired by GM in 1925. It has been the second-largest selling car brand in the UK for...
/Opel
Opel
Adam Opel AG, generally shortened to Opel, is a German automobile company founded by Adam Opel in 1862. Opel has been building automobiles since 1899, and became an Aktiengesellschaft in 1929...
have released vehicles equipped with AFS since 2003.
Rather than the mechanical linkages employed in earlier directional-headlamp systems, AFS relies on electronic sensors, transducer
Transducer
A transducer is a device that converts one type of energy to another. Energy types include electrical, mechanical, electromagnetic , chemical, acoustic or thermal energy. While the term transducer commonly implies the use of a sensor/detector, any device which converts energy can be considered a...
s and actuators. Other AFS techniques include special auxiliary optical systems within a vehicle's headlamp housings. These auxiliary systems may be switched on and off as the vehicle and operating conditions call for light or darkness at the angles covered by the beam the auxiliary optics produce. A typical system measures steering angle and vehicle speed to swivel the headlamps. The most advanced AFS systems use GPS signals to anticipate changes in road curvature, rather than simply reacting to them.
Automatic beam switching
Even when the high beam is warranted by prevailing conditions, drivers generally do not use them. There have long been efforts, particularly in America, to devise an effective automatic beam selection system to relieve the driver of the need to select and activate the correct beam as traffic, weather, and road conditions change. General Motors introduced the first automatic headlight dimmer called the Autronic Eye in 1952 on their CadillacCadillac
Cadillac is an American luxury vehicle marque owned by General Motors . Cadillac vehicles are sold in over 50 countries and territories, but mostly in North America. Cadillac is currently the second oldest American automobile manufacturer behind fellow GM marque Buick and is among the oldest...
and Oldsmobile
Oldsmobile
Oldsmobile was a brand of American automobile produced for most of its existence by General Motors. It was founded by Ransom E. Olds in 1897. In its 107-year history, it produced 35.2 million cars, including at least 14 million built at its Lansing, Michigan factory...
models; the feature was offered in other GM vehicles starting in 1953. The system's photoresistor
Photoresistor
A photoresistor or light dependent resistor is a resistor whose resistance decreases with increasing incident light intensity. It can also be referred to as a photoconductor or CdS device, from "cadmium sulfide," which is the material from which the device is made and that actually exhibits the...
and associated circuitry were housed in a gunsight-like tube atop the dashboard. An amplifier module was located in the engine compartment that controlled the headlight relay using signals from the dashboard-mounted tube unit. This setup gave way in 1958 to a system called GuideMatic in reference to GM's Guide lighting division. The GuideMatic had a more compact dashtop housing and a control knob that allowed the driver to adjust the system's sensitivity threshold to determine when the headlamps would be dipped from high to low beam in response to an oncoming vehicle. By the early 1970s, this option was withdrawn from all GM models except Cadillac
Cadillac
Cadillac is an American luxury vehicle marque owned by General Motors . Cadillac vehicles are sold in over 50 countries and territories, but mostly in North America. Cadillac is currently the second oldest American automobile manufacturer behind fellow GM marque Buick and is among the oldest...
, on which GuideMatic was available through 1988. The photosensor for this system used an amber lens, and the adoption of reflectorized yellow road signs, such as for oncoming curves, caused them to dim prematurely - possibly leading to their discontinuation...
Ford
Ford Motor Company
Ford Motor Company is an American multinational automaker based in Dearborn, Michigan, a suburb of Detroit. The automaker was founded by Henry Ford and incorporated on June 16, 1903. In addition to the Ford and Lincoln brands, Ford also owns a small stake in Mazda in Japan and Aston Martin in the UK...
- and Chrysler-built vehicles were also available with the GM-made dimmers from the 1950s through the 1980s. A system called AutoDim was offered on several Lincoln
Lincoln (automobile)
Lincoln is an American luxury vehicle brand of the Ford Motor Company. Lincoln vehicles are sold mostly in North America.-History:The company was founded in August 1915 by Henry M. Leland, one of the founders of Cadillac . During World War I, he left Cadillac which was sold to General Motors...
models starting in the mid-1950s, and eventually the Ford Thunderbird
Ford Thunderbird
The Thunderbird , is an automobile manufactured by the Ford Motor Company in the United States over eleven model generations from 1955 through 2005...
and some Mercury
Mercury (automobile)
Mercury was an automobile marque of the Ford Motor Company launched in 1938 by Edsel Ford, son of Henry Ford, to market entry-level luxury cars slotted between Ford-branded regular models and Lincoln-branded luxury vehicles, similar to General Motors' Buick brand, and Chrysler's namesake brand...
models offered it as well. Premium Chrysler and Imperial
Imperial (automobile)
Imperial was the Chrysler Corporation's luxury automobile brand between 1955 and 1975, with a brief reappearance in 1981 to 1983.The Imperial name had been used since 1926, but was never a separate make, just the top-of-the-line Chrysler. In 1955, the company decided to spin it off as its own make...
models offered a system called Automatic Beam Control throughout the 1960s and early 1970s.
Rabinow dimmer
Though the systems based on photoresistors evolved, growing more compact and moving from the dashboard to a less conspicuous location behind the radiator grill, they were still unable to reliably discern headlamps from non-vehicular light sources such as streetlights. They also did not dip to low beam when the driver approached a vehicle from behind, and they would spuriously dip to low beam in response to road sign reflections of the vehicle's own high beam headlamps. American inventor Jacob RabinowJacob Rabinow
Jacob Rabinow was an engineer who led a truly prolific career as an inventor. He earned a total of 230 U.S. patents on a variety of mechanical, optical and electrical devices....
devised and refined a scanning automatic dimmer system impervious to streetlights and reflections, but no automaker purchased the rights, and the problematic photoresistor type remained on the market through the late 1980s.
Camera-based dimmer
Present systems based on imaging CMOSCMOS
Complementary metal–oxide–semiconductor is a technology for constructing integrated circuits. CMOS technology is used in microprocessors, microcontrollers, static RAM, and other digital logic circuits...
cameras can detect and respond appropriately to leading and oncoming vehicles while disregarding streetlights, road signs, and other spurious signals. Camera-based beam selection was first released in 2005 on the Jeep Grand Cherokee
Jeep Grand Cherokee
The Jeep Grand Cherokee is a Mid-size SUV produced by the Jeep division of Chrysler. While some other SUVs were manufactured with body on frame construction, the Jeep Grand Cherokee has always used a unibody chassis.- Development :...
, and has since then been incorporated into comprehensive driver assistance systems by automakers worldwide.
Intelligent Light System
Intelligent Light System is a headlamp beam control system introduced in 2006 which offers five different bi-xenon light functions, each of which is suited to typical driving or weather conditions:- Country mode
- Motorway mode
- Enhanced fog lamps
- Active light function
- Cornering light function
Adaptive High beams
Adaptive highbeam assist is Mercedes-BenzMercedes-Benz
Mercedes-Benz is a German manufacturer of automobiles, buses, coaches, and trucks. Mercedes-Benz is a division of its parent company, Daimler AG...
' marketing name for a headlight control strategy that continuously automatically tailors the headlamp range so the beam just reaches other vehicles ahead, thus always ensuring maximum possible seeing range without glaring other road users.to the distance of vehicles ahead. It was first launched in the Mercedes E-class
Mercedes-Benz W212
The Mercedes-Benz W212 is a sedan sold as the ninth-generation E-Class, replacing the previous W211 model. C207 is the chassis code for the related E-Class Coupe, a replacement for the CLK-class coupe and cabriolet...
in 2009. It provides a continuous range of beam reach from a low-aimed low beam to a high-aimed high beam, rather than the traditional binary choice between low and high beams. The range of the beam can vary between 65 and 300 meters, depending on traffic conditions. In traffic, the low beam cutoff position is adjusted vertically to maximise seeing range while keeping glare out of leading and oncoming drivers' eyes. When no traffic is close enough for glare to be a problem, the system provides full high beam. Headlamps are adjusted every 40 milliseconds by a camera on the inside of the front windscreen which can determine distance to other vehicles. The S-Class
Mercedes-Benz W221
The Mercedes-Benz W221 is a chassis code of S-Class, the successor of Mercedes-Benz W220.The vehicle was unveiled in 2005 Frankfurt Motor Show.-Styling:The W221 S-Class' exterior styling is distinctly different to the W220...
, CLS-Class
Mercedes-Benz CLS-Class
The Mercedes-Benz CLS is an executive-size sedan originally launched in 2004 and based on the W211 E-Class platform and was internally designated as the C219...
and C-Class
Mercedes-Benz C-Class
The Mercedes-Benz C-Class is a compact executive car produced by the Mercedes-Benz division of Daimler AG. First introduced in 1993 as a replacement for the 190 range , the C-Class was the smallest model in the marque's lineup until the 1997 arrival of the A-Class...
also is offering the technology. In the CLS, the adaptive high beam is realised with LED headlamps - the first vehicle producing all adaptive light functions with LEDs. Since 2010 some Audi
Audi
Audi AG is a German automobile manufacturer, from supermini to crossover SUVs in various body styles and price ranges that are marketed under the Audi brand , positioned as the premium brand within the Volkswagen Group....
models with Xenon headlamps are offering a similar system; with LED headlamps it is still not available.
Glare-Free High Beam & Pixel Light
Glare-free high beam is a camera-driven dynamic lighting control strategy that selectively shades spots and slices out of the high beam pattern to protect other road users from glare, while always providing the driver with maximum seeing range. The area surrounding other road users is constantly illuminated at high beam intensity, but without the glare that would result from using uncontrolled high beams in traffic. This constantly changing beam pattern requires complex sensors, microprocessors and actuators, because the vehicles which must be shadowed out of the beam are constantly moving. The dynamic shadowing can be achieved with movable shadow masks shifted within the light path inside the headlamp. Or, the effect can be achieved by selectively darkening addressable LED emitters or reflector elements, a technique known as Pixel light.The first production vehicles with glare-free high beam are the 2011 Volkswagen Touareg
Volkswagen Touareg
The Volkswagen Touareg is a mid-size crossover SUV produced by German automaker Volkswagen since 2002. The vehicle was named after the Tuareg people, a Berber-speaking group in North Africa...
—the function is part of that vehicle's "Dynamic Light Assist" package—the Phaeton
Volkswagen Phaeton
The Volkswagen Phaeton is a full-size luxury sedan/saloon manufactured by German automaker Volkswagen, and is described by Volkswagen as their "premium class" vehicle...
, and Passat
Volkswagen Passat
The Volkswagen Passat is a large family car marketed by Volkswagen Passenger Cars through six design generations since 1973. Between the Volkswagen Golf / Volkswagen Jetta and the Volkswagen Phaeton in the current Volkswagen line-up, the Passat and its derivatives have been badged variously as...
.
Care
Headlamp systems require periodic maintenance. Sealed beamSealed beam
A sealed beam is a type of lamp that includes a reflector and filament as a single assembly, over which a front cover of clear glass, is permanently attached. Previously, automotive headlamps used a separate small bulb and reflector covered with a ribbed lens to avoid glare from the filament. This...
headlamps are modular; when the filament burns out, the entire sealed beam is replaced. Most vehicles in North America made since the late 1980s use headlamp lens-reflector assemblies that are considered a part of the car, and just the bulb is replaced when it fails. Manufacturers vary the means by which the bulb is accessed and replaced. Headlamp aim must be properly checked and adjusted frequently, for misaimed lamps are dangerous and ineffective.
Over time, the headlamp lens can deteriorate. It can become pitted due to abrasion of road sand and pebbles, and can crack, admitting water into the headlamp. "Plastic" (polycarbonate
Polycarbonate
PolycarbonatePhysical PropertiesDensity 1.20–1.22 g/cm3Abbe number 34.0Refractive index 1.584–1.586FlammabilityV0-V2Limiting oxygen index25–27%Water absorption – Equilibrium0.16–0.35%Water absorption – over 24 hours0.1%...
) lenses can become cloudy and discoloured. This is due to oxidation of the painted-on lens hardcoat by ultraviolet light from the sun and the headlamp bulbs. If it is minor, it can be polished out using a reputable brand of a car polish that is intended for restoring the shine to chalked paint. In more advanced stages, the deterioration extends through the actual plastic material, rendering the headlamp useless and necessitating complete replacement. Sanding or aggressively polishing the lenses, or plastic headlight restoration
Plastic headlight restoration
Plastic headlight restoration is the act of refinishing aged headlights that have succumbed to headlamp oxidation and other environmental hazards of travel, weather, and exposure to caustic chemicals...
, can buy some time, but doing so removes the protective coating from the lens, which when so stripped will deteriorate faster and more severely.
The reflector, made out of vapourised aluminum deposited in an extremely thin layer on a metal, glass or plastic substrate, can become dirty, oxidised, or burnt, and lose its specularity
Specular reflection
Specular reflection is the mirror-like reflection of light from a surface, in which light from a single incoming direction is reflected into a single outgoing direction...
. This can happen if water enters the headlamp, if bulbs of higher than specified wattage are installed, or simply with age and use. Reflectors thus degraded, if they cannot be cleaned, must be replaced.
Lens cleaners

Federal Motor Vehicle Safety Standard 108
Federal Motor Vehicle Safety Standard 108 regulates all automotive lighting, signalling and reflective devices in the United States. Like all other Federal Motor Vehicle Safety Standards, FMVSS 108 is administered by the United States Department of Transportation's National Highway Traffic Safety...
does not require lens cleaners on any headlamps, though they are permitted. Lens cleaning systems come in two main varieties: a small motor-driven wiper blade or brush conceptually similar to those used on the windshield of the car, or a fixed or pop-up high-pressure sprayer which cleans the lenses with a spray of windshield washer fluid. Some cars with retractable headlamps, such as the original Mazda Miata have a squeegee
Squeegee
A squeegee, squilgee or sometimes squimjim, is an onomatopoeically named tool with a flat, smooth rubber blade, used to remove or control the flow of liquid on a flat surface...
at the front of the lamp recess which automatically wipes the lenses as they are raised or lowered. The effectiveness of this depends on the lamps’ being wet from rain, since there are no headlamp washers.
See also
- Headlight flashingHeadlight flashingHeadlight flashing refers to the act of either briefly switching on the headlights of a car, or of momentarily switching between a headlight's high beams and low beams, in an effort to communicate with another driver or drivers...
- Automotive lightingAutomotive lightingThe lighting system of a motor vehicle consists of lighting and signalling devices mounted or integrated to the front, sides, rear, and in some cases the top of the motor vehicle...
- Automotive lamp typesAutomotive lamp typesA modern vehicle uses different kinds of lamps for multiple purposes: illumination for the driver to be able to drive in dark conditions, illumination to be seen and lights for information displays. Types of these lamps vary depending on the purpose and different car manufacturers and models use...
- Automotive night visionAutomotive night visionAn automotive night vision system is a system to increase a vehicle driver's perception and seeing distance in darkness or poor weather beyond the reach of the vehicle's headlights...
- Hidden headlampsHidden headlampsHidden headlamps, also commonly known as pop-up headlamps or headlights, are an automotive styling feature that conceals an automobile's headlamps when they are not in use...
- FogFogFog is a collection of water droplets or ice crystals suspended in the air at or near the Earth's surface. While fog is a type of stratus cloud, the term "fog" is typically distinguished from the more generic term "cloud" in that fog is low-lying, and the moisture in the fog is often generated...
- World Forum for Harmonization of Vehicle RegulationsWorld Forum for Harmonization of Vehicle RegulationsThe World Forum for Harmonization of Vehicle Regulations is a working party of the United Nations Economic Commission for Europe...
- Non-glaring headlamp
- Lighting-up timeLighting-up timeIn the United Kingdom there is a legally enforced lighting-up time, defined as from one half-hour after sunset to one half-hour before sunrise, during which all motor vehicles on unlit public roads must use their headlights....
- Twilight SentinelTwilight SentinelOn an automobile, Twilight Sentinel is a device on General Motors' cars that senses outside light and turns the exterior lights on and off depending on lighting conditions....

