Hammurabi
Overview
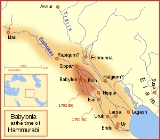
Babylon
Babylon was an Akkadian city-state of ancient Mesopotamia, the remains of which are found in present-day Al Hillah, Babil Province, Iraq, about 85 kilometers south of Baghdad...
(that is, of the First Babylonian Dynasty
First Babylonian Dynasty
The chronology of the first dynasty of Babylonia is debated as there is a Babylonian King List A and a Babylonian King List B. In this chronology, the regnal years of List A are used due to their wide usage...
) from 1792 BC to 1750 BC middle chronology (1728 BC – 1686 BC short chronology) He became the first king of the Babylonian Empire
Babylonia
Babylonia was an ancient cultural region in central-southern Mesopotamia , with Babylon as its capital. Babylonia emerged as a major power when Hammurabi Babylonia was an ancient cultural region in central-southern Mesopotamia (present-day Iraq), with Babylon as its capital. Babylonia emerged as...
following the abdication of his father, Sin-Muballit
Sin-Muballit
Sin-Muballit was the father of Hammurabi. He was the fifth king of the first dynasty of Babylonia, reigning c. 1748 to 1729 BC. His son Hammurabi greatly expanded the Babylonian kingdom. Sin-Muballit succeeded Apil-Sin. No inscriptions for either king are known. In Sin-Muballit's 13th year, he...
, extending Babylon's control over Mesopotamia
Mesopotamia
Mesopotamia is a toponym for the area of the Tigris–Euphrates river system, largely corresponding to modern-day Iraq, northeastern Syria, southeastern Turkey and southwestern Iran.Widely considered to be the cradle of civilization, Bronze Age Mesopotamia included Sumer and the...
by winning a series of wars against neighboring kingdoms. Although his empire controlled all of Mesopotamia at the time of his death, his successors were unable to maintain his empire.
Hammurabi is known for the set of laws called Hammurabi's Code
Code of Hammurabi
The Code of Hammurabi is a well-preserved Babylonian law code, dating to ca. 1780 BC . It is one of the oldest deciphered writings of significant length in the world. The sixth Babylonian king, Hammurabi, enacted the code, and partial copies exist on a human-sized stone stele and various clay...
, one of the first written codes of law
Civil code
A civil code is a systematic collection of laws designed to comprehensively deal with the core areas of private law. A jurisdiction that has a civil code generally also has a code of civil procedure...
in recorded history
Recorded history
Recorded history is the period in history of the world after prehistory. It has been written down using language, or recorded using other means of communication. It starts around the 4th millennium BC, with the invention of writing.-Historical accounts:...
.
Unanswered Questions

