
Gupta-Bleuler formalism
Encyclopedia
In quantum field theory
, the Gupta–Bleuler formalism is a way of quantizing
the electromagnetic field
. The formulation is due to theoretical physicist Suraj N. Gupta
and Konrad Bleuler
.
Let's start with a single photon
first. A basis
of the one photon vector space (we'll explain why it's not a Hilbert space
below) is given by the eigenstates |k,εμ⟩ where k, the 4-momentum
is null
(k2=0) and the k0 component, the energy, is positive and εμ is the unit polarization vector and the index μ ranges from 0 to 3. So, k is uniquely determined by the spatial momentum . Using the bra-ket notation
. Using the bra-ket notation
, we equip this space with a sesquilinear form
defined by
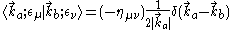
where the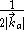 factor is to implement Lorentz covariance
factor is to implement Lorentz covariance
. We are using the +−−− metric signature
here. However, this sesquilinear form gives positive norms for spatial polarizations but negative norms for timelike polarizations. Negative probabilities are unphysical. Not to mention a physical photon only has two transverse
polarizations, not four.
If we include gauge covariance, we realize a photon can have three possible polarizations (two transverse and one longitudinal (i.e. parallel to the 4-momentum)). This is given by the restriction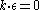 . However, the longitudinal component is merely unphysical gauge. While it would be nice to define a stricter restriction than the one given above which only leaves us with the two transverse components, it's easy to check that this can't be defined in a Lorentz covariant manner because what is transverse in one frame of reference isn't transverse anymore in another.
. However, the longitudinal component is merely unphysical gauge. While it would be nice to define a stricter restriction than the one given above which only leaves us with the two transverse components, it's easy to check that this can't be defined in a Lorentz covariant manner because what is transverse in one frame of reference isn't transverse anymore in another.
To resolve this difficulty, first look at the subspace with three polarizations. The sesquilinear form restricted to it is merely semidefinite, which is better than indefinite.
In addition, the subspace with zero norm turns out to be none other than the gauge degrees of freedom. So, define the physical Hilbert space
to be the quotient space
of the three polarization subspace by its zero norm subspace. This space has a positive definite form, making it a true Hilbert space.
This technique can be similarly extended to the bosonic Fock space
of multiparticle photons. Using the standard trick of adjoint creation and annihilation operators, but with this quotient trick, we come up with the free field
vector potential
operator valued distribution A satisfying

with the condition
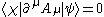
for physical states |χ⟩ and |ψ⟩ in the Fock space (it is understood that physical states are really equivalence classes of states which differ by a state of zero norm).
It should be emphasised that this is not the same thing as
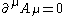
Note that if O is any gauge invariant operator,
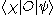
does not depend upon the choice of the representatives of the equivalence classes, and so, this quantity is well-defined.
This is not true for nongauge-invariant operators in general because the Lorenz gauge still leaves us with residual gauge degrees of freedom.
In an interacting theory of quantum electrodynamics
, the Lorenz gauge condition still applies, but A no longer satisfies the free wave equation.
Quantum field theory
Quantum field theory provides a theoretical framework for constructing quantum mechanical models of systems classically parametrized by an infinite number of dynamical degrees of freedom, that is, fields and many-body systems. It is the natural and quantitative language of particle physics and...
, the Gupta–Bleuler formalism is a way of quantizing
Quantization (physics)
In physics, quantization is the process of explaining a classical understanding of physical phenomena in terms of a newer understanding known as "quantum mechanics". It is a procedure for constructing a quantum field theory starting from a classical field theory. This is a generalization of the...
the electromagnetic field
Electromagnetic field
An electromagnetic field is a physical field produced by moving electrically charged objects. It affects the behavior of charged objects in the vicinity of the field. The electromagnetic field extends indefinitely throughout space and describes the electromagnetic interaction...
. The formulation is due to theoretical physicist Suraj N. Gupta
Suraj N. Gupta
Suraj N. Gupta is an Indian-born American theoretical physicist, notable for his contribution to quantum field theory.-Education and career:...
and Konrad Bleuler
Konrad Bleuler
Konrad Bleuler was a Swiss physicist who worked in the field of theoretical particle physics and quantum field theory. He is known for his work on the quantisation of the photon, the Gupta–Bleuler formalism.-Education and career:Bleuler was born in Herzogenbuchsee, Switzerland on 23 September 1912...
.
Let's start with a single photon
Photon
In physics, a photon is an elementary particle, the quantum of the electromagnetic interaction and the basic unit of light and all other forms of electromagnetic radiation. It is also the force carrier for the electromagnetic force...
first. A basis
Basis (linear algebra)
In linear algebra, a basis is a set of linearly independent vectors that, in a linear combination, can represent every vector in a given vector space or free module, or, more simply put, which define a "coordinate system"...
of the one photon vector space (we'll explain why it's not a Hilbert space
Hilbert space
The mathematical concept of a Hilbert space, named after David Hilbert, generalizes the notion of Euclidean space. It extends the methods of vector algebra and calculus from the two-dimensional Euclidean plane and three-dimensional space to spaces with any finite or infinite number of dimensions...
below) is given by the eigenstates |k,εμ⟩ where k, the 4-momentum
Momentum
In classical mechanics, linear momentum or translational momentum is the product of the mass and velocity of an object...
is null
Null vector
Null vector can refer to:* Null vector * A causal structure in Minkowski space...
(k2=0) and the k0 component, the energy, is positive and εμ is the unit polarization vector and the index μ ranges from 0 to 3. So, k is uniquely determined by the spatial momentum
 . Using the bra-ket notation
. Using the bra-ket notationBra-ket notation
Bra-ket notation is a standard notation for describing quantum states in the theory of quantum mechanics composed of angle brackets and vertical bars. It can also be used to denote abstract vectors and linear functionals in mathematics...
, we equip this space with a sesquilinear form
Sesquilinear form
In mathematics, a sesquilinear form on a complex vector space V is a map V × V → C that is linear in one argument and antilinear in the other. The name originates from the numerical prefix sesqui- meaning "one and a half"...
defined by
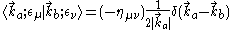
where the
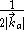 factor is to implement Lorentz covariance
factor is to implement Lorentz covarianceLorentz covariance
In standard physics, Lorentz symmetry is "the feature of nature that says experimental results are independent of the orientation or the boost velocity of the laboratory through space"...
. We are using the +−−− metric signature
Metric signature
The signature of a metric tensor is the number of positive and negative eigenvalues of the metric. That is, the corresponding real symmetric matrix is diagonalised, and the diagonal entries of each sign counted...
here. However, this sesquilinear form gives positive norms for spatial polarizations but negative norms for timelike polarizations. Negative probabilities are unphysical. Not to mention a physical photon only has two transverse
Transverse wave
A transverse wave is a moving wave that consists of oscillations occurring perpendicular to the direction of energy transfer...
polarizations, not four.
If we include gauge covariance, we realize a photon can have three possible polarizations (two transverse and one longitudinal (i.e. parallel to the 4-momentum)). This is given by the restriction
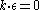 . However, the longitudinal component is merely unphysical gauge. While it would be nice to define a stricter restriction than the one given above which only leaves us with the two transverse components, it's easy to check that this can't be defined in a Lorentz covariant manner because what is transverse in one frame of reference isn't transverse anymore in another.
. However, the longitudinal component is merely unphysical gauge. While it would be nice to define a stricter restriction than the one given above which only leaves us with the two transverse components, it's easy to check that this can't be defined in a Lorentz covariant manner because what is transverse in one frame of reference isn't transverse anymore in another.To resolve this difficulty, first look at the subspace with three polarizations. The sesquilinear form restricted to it is merely semidefinite, which is better than indefinite.
In addition, the subspace with zero norm turns out to be none other than the gauge degrees of freedom. So, define the physical Hilbert space
Hilbert space
The mathematical concept of a Hilbert space, named after David Hilbert, generalizes the notion of Euclidean space. It extends the methods of vector algebra and calculus from the two-dimensional Euclidean plane and three-dimensional space to spaces with any finite or infinite number of dimensions...
to be the quotient space
Quotient space
In topology and related areas of mathematics, a quotient space is, intuitively speaking, the result of identifying or "gluing together" certain points of a given space. The points to be identified are specified by an equivalence relation...
of the three polarization subspace by its zero norm subspace. This space has a positive definite form, making it a true Hilbert space.
This technique can be similarly extended to the bosonic Fock space
Fock space
The Fock space is an algebraic system used in quantum mechanics to describe quantum states with a variable or unknown number of particles. It is named after V. A...
of multiparticle photons. Using the standard trick of adjoint creation and annihilation operators, but with this quotient trick, we come up with the free field
Free field
In classical physics, a free field is a field whose equations of motion are given by linear partial differential equations. Such linear PDE's have a unique solution for a given initial condition....
vector potential
Vector potential
In vector calculus, a vector potential is a vector field whose curl is a given vector field. This is analogous to a scalar potential, which is a scalar field whose negative gradient is a given vector field....
operator valued distribution A satisfying

with the condition
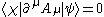
for physical states |χ⟩ and |ψ⟩ in the Fock space (it is understood that physical states are really equivalence classes of states which differ by a state of zero norm).
It should be emphasised that this is not the same thing as
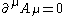
Note that if O is any gauge invariant operator,
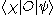
does not depend upon the choice of the representatives of the equivalence classes, and so, this quantity is well-defined.
This is not true for nongauge-invariant operators in general because the Lorenz gauge still leaves us with residual gauge degrees of freedom.
In an interacting theory of quantum electrodynamics
Quantum electrodynamics
Quantum electrodynamics is the relativistic quantum field theory of electrodynamics. In essence, it describes how light and matter interact and is the first theory where full agreement between quantum mechanics and special relativity is achieved...
, the Lorenz gauge condition still applies, but A no longer satisfies the free wave equation.
See also
- BRST formalism
- quantum gauge theoryQuantum gauge theoryIn quantum physics, in order to quantize a gauge theory, like for example Yang-Mills theory, Chern-Simons or BF model, one method is to perform a gauge fixing. This is done in the BRST and Batalin-Vilkovisky formulation...
- quantum electrodynamicsQuantum electrodynamicsQuantum electrodynamics is the relativistic quantum field theory of electrodynamics. In essence, it describes how light and matter interact and is the first theory where full agreement between quantum mechanics and special relativity is achieved...
- ξ gauge
- S. Gupta, Proc. Phys. Soc. v. A63, nr.267, p.681–691, 1950
- K. Bleuler, Helv.Phys.Acta, v.23, rn.5, p.567–586, 1950

