
Group of 77
Encyclopedia
The Group of 77 at the United Nations
is a loose coalition of developing nations, designed to promote its members' collective economic interests and create an enhanced joint negotiating capacity in the United Nations. There were 77 founding members of the organization, but the organization has since expanded to 132 member countries. Practically speaking (as of 2011), the group can be described as comprising all of UN members (along with the Palestinian Authority) excluding the following:
Argentina
holds the Chairmanship for 2011.
The group was founded on June 15, 1964 by the "Joint Declaration of the Seventy-Seven Countries" issued at the United Nations Conference on Trade and Development
(UNCTAD). The first major meeting was in Algiers in 1967, where the Charter of Algiers was adopted and the basis for permanent institutional structures was begun. There are Chapters of the Group of 77 in Rome
(FAO
), Vienna
(UNIDO
), Paris
(UNESCO
), Nairobi
(UNEP) and the Group of 24 in Washington, D.C.
(International Monetary Fund
and World Bank
).
Member nations are listed below. The years in parenthesis represent the year/s a country has presided. Countries listed in bold are also members of the G-24. See the official list of G-77 members.
 The Group of 24 (G-24) is a chapter of the G-77 that was established in 1971 to coordinate the positions of developing countries
The Group of 24 (G-24) is a chapter of the G-77 that was established in 1971 to coordinate the positions of developing countries
on international monetary and development finance issues and to ensure that their interests were adequately represented in negotiations on international monetary matters.
The Group of 24, which is officially called the Intergovernmental Group of Twenty-Four on International Monetary Affairs and Development, is not an organ of the International Monetary Fund
, but the IMF provides secretariat services for the Group. Its meetings usually take place twice a year, prior to the IMFC and Development Committee meetings, to enable developing country members to discuss agenda items beforehand.
Although membership in the G-24 is strictly limited to 24 countries, any member of the G-77 can join discussions (Mexico
is the only G-24 member that is not a G-77 member, when it left the G-77 without resigning its G-24 membership). China
has been a "special invitee" since the Gabon meetings of 1981.
Miguel Gustavo Peirano
, former Argentine
Minister of Economy
, is the current chairman of the G-24.
United Nations
The United Nations is an international organization whose stated aims are facilitating cooperation in international law, international security, economic development, social progress, human rights, and achievement of world peace...
is a loose coalition of developing nations, designed to promote its members' collective economic interests and create an enhanced joint negotiating capacity in the United Nations. There were 77 founding members of the organization, but the organization has since expanded to 132 member countries. Practically speaking (as of 2011), the group can be described as comprising all of UN members (along with the Palestinian Authority) excluding the following:
- All Council of EuropeCouncil of EuropeThe Council of Europe is an international organisation promoting co-operation between all countries of Europe in the areas of legal standards, human rights, democratic development, the rule of law and cultural co-operation...
members (with the exception of Bosnia and HerzegovinaBosnia and HerzegovinaBosnia and Herzegovina , sometimes called Bosnia-Herzegovina or simply Bosnia, is a country in Southern Europe, on the Balkan Peninsula. Bordered by Croatia to the north, west and south, Serbia to the east, and Montenegro to the southeast, Bosnia and Herzegovina is almost landlocked, except for the...
); - All Organisation for Economic Co-operation and DevelopmentOrganisation for Economic Co-operation and DevelopmentThe Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development is an international economic organisation of 34 countries founded in 1961 to stimulate economic progress and world trade...
members (with the exception of ChileChileChile ,officially the Republic of Chile , is a country in South America occupying a long, narrow coastal strip between the Andes mountains to the east and the Pacific Ocean to the west. It borders Peru to the north, Bolivia to the northeast, Argentina to the east, and the Drake Passage in the far...
); - All Commonwealth of Independent StatesCommonwealth of Independent StatesThe Commonwealth of Independent States is a regional organization whose participating countries are former Soviet Republics, formed during the breakup of the Soviet Union....
(full) members (with the exception of TajikistanTajikistanTajikistan , officially the Republic of Tajikistan , is a mountainous landlocked country in Central Asia. Afghanistan borders it to the south, Uzbekistan to the west, Kyrgyzstan to the north, and China to the east....
); - Three microstates: KiribatiKiribatiKiribati , officially the Republic of Kiribati, is an island nation located in the central tropical Pacific Ocean. The permanent population exceeds just over 100,000 , and is composed of 32 atolls and one raised coral island, dispersed over 3.5 million square kilometres, straddling the...
, PalauPalauPalau , officially the Republic of Palau , is an island nation in the Pacific Ocean, east of the Philippines and south of Tokyo. In 1978, after three decades as being part of the United Nations trusteeship, Palau chose independence instead of becoming part of the Federated States of Micronesia, a...
and TuvaluTuvaluTuvalu , formerly known as the Ellice Islands, is a Polynesian island nation located in the Pacific Ocean, midway between Hawaii and Australia. Its nearest neighbours are Kiribati, Nauru, Samoa and Fiji. It comprises four reef islands and five true atolls...
.
Argentina
Argentina
Argentina , officially the Argentine Republic , is the second largest country in South America by land area, after Brazil. It is constituted as a federation of 23 provinces and an autonomous city, Buenos Aires...
holds the Chairmanship for 2011.
The group was founded on June 15, 1964 by the "Joint Declaration of the Seventy-Seven Countries" issued at the United Nations Conference on Trade and Development
United Nations Conference on Trade and Development
The United Nations Conference on Trade and Development was established in 1964 as a permanent intergovernmental body. It is the principal organ of the United Nations General Assembly dealing with trade, investment, and development issues....
(UNCTAD). The first major meeting was in Algiers in 1967, where the Charter of Algiers was adopted and the basis for permanent institutional structures was begun. There are Chapters of the Group of 77 in Rome
Rome
Rome is the capital of Italy and the country's largest and most populated city and comune, with over 2.7 million residents in . The city is located in the central-western portion of the Italian Peninsula, on the Tiber River within the Lazio region of Italy.Rome's history spans two and a half...
(FAO
Fão
Fão is a town in Esposende Municipality in Portugal....
), Vienna
Vienna
Vienna is the capital and largest city of the Republic of Austria and one of the nine states of Austria. Vienna is Austria's primary city, with a population of about 1.723 million , and is by far the largest city in Austria, as well as its cultural, economic, and political centre...
(UNIDO
United Nations Industrial Development Organization
The United Nations Industrial Development Organization , French/Spanish acronym ONUDI, is a specialized agency in the United Nations system, headquartered in Vienna, Austria...
), Paris
Paris
Paris is the capital and largest city in France, situated on the river Seine, in northern France, at the heart of the Île-de-France region...
(UNESCO
UNESCO
The United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization is a specialized agency of the United Nations...
), Nairobi
Nairobi
Nairobi is the capital and largest city of Kenya. The city and its surrounding area also forms the Nairobi County. The name "Nairobi" comes from the Maasai phrase Enkare Nyirobi, which translates to "the place of cool waters". However, it is popularly known as the "Green City in the Sun" and is...
(UNEP) and the Group of 24 in Washington, D.C.
Washington, D.C.
Washington, D.C., formally the District of Columbia and commonly referred to as Washington, "the District", or simply D.C., is the capital of the United States. On July 16, 1790, the United States Congress approved the creation of a permanent national capital as permitted by the U.S. Constitution....
(International Monetary Fund
International Monetary Fund
The International Monetary Fund is an organization of 187 countries, working to foster global monetary cooperation, secure financial stability, facilitate international trade, promote high employment and sustainable economic growth, and reduce poverty around the world...
and World Bank
World Bank
The World Bank is an international financial institution that provides loans to developing countries for capital programmes.The World Bank's official goal is the reduction of poverty...
).
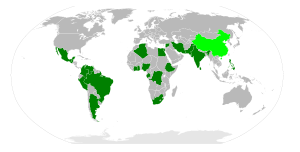
Members
On the map, founding and currently participating members (as of 2008) are shown in dark green, while founding members that have since left the organization are shown in light green. Currently participating members that joined after the foundation of the Group are shown in medium green.Member nations are listed below. The years in parenthesis represent the year/s a country has presided. Countries listed in bold are also members of the G-24. See the official list of G-77 members.
Current founding members
|
|
Other current members
|
Former members
-
 New Zealand signed the original "Joint Declaration of the Developing Countries" in October 1963, but pulled out of the group before the formation of the G-77 in 1964 (it joined the OECD in 1973).
New Zealand signed the original "Joint Declaration of the Developing Countries" in October 1963, but pulled out of the group before the formation of the G-77 in 1964 (it joined the OECD in 1973). -
 Mexico was a founding member, but left the Group after joining the OECD in 1994. It had presided over the group in 1973–1974, 1983–1984; however, it is still a member of G-24.
Mexico was a founding member, but left the Group after joining the OECD in 1994. It had presided over the group in 1973–1974, 1983–1984; however, it is still a member of G-24. -
 South Korea was a founding member, but left the Group after joining the OECD in 1996.
South Korea was a founding member, but left the Group after joining the OECD in 1996. -
 Kingdom of Yugoslavia was a founding member; by the late 1990s it was still listed on the membership list, but it was noted that it "cannot participate in the activities of G-77." It was removed from the list in late 2003. It had presided over the group in 1985–1986. Bosnia and Herzegovina is the only part of former Yugoslavia that is currently in G-77.
Kingdom of Yugoslavia was a founding member; by the late 1990s it was still listed on the membership list, but it was noted that it "cannot participate in the activities of G-77." It was removed from the list in late 2003. It had presided over the group in 1985–1986. Bosnia and Herzegovina is the only part of former Yugoslavia that is currently in G-77. -
 Cyprus was a founding member, but was no longer listed on the official membership list after its accession to the EU in 2004.
Cyprus was a founding member, but was no longer listed on the official membership list after its accession to the EU in 2004. -
 Malta was admitted to the Group in 1976, but was no longer listed on the official membership list after its accession to the EU in 2004.
Malta was admitted to the Group in 1976, but was no longer listed on the official membership list after its accession to the EU in 2004. -
 Palau joined the Group in 2002, but withdrew in 2004, having decided that it could best pursue its environmental interests through the Alliance of Small Island StatesAlliance of Small Island StatesAlliance of Small Island States is an intergovernmental organization of low-lying coastal and small Island countries. Established in 1990, the main purpose of the alliance is to consolidate the voices of Small Island Developing States to address global warming...
Palau joined the Group in 2002, but withdrew in 2004, having decided that it could best pursue its environmental interests through the Alliance of Small Island StatesAlliance of Small Island StatesAlliance of Small Island States is an intergovernmental organization of low-lying coastal and small Island countries. Established in 1990, the main purpose of the alliance is to consolidate the voices of Small Island Developing States to address global warming...
. -
 Kingdom of Romania was admitted to the Group in 1976, but was no longer listed on the official membership list after its accession to the EU in 2007.
Kingdom of Romania was admitted to the Group in 1976, but was no longer listed on the official membership list after its accession to the EU in 2007.
Group of 24

Developing country
A developing country, also known as a less-developed country, is a nation with a low level of material well-being. Since no single definition of the term developing country is recognized internationally, the levels of development may vary widely within so-called developing countries...
on international monetary and development finance issues and to ensure that their interests were adequately represented in negotiations on international monetary matters.
The Group of 24, which is officially called the Intergovernmental Group of Twenty-Four on International Monetary Affairs and Development, is not an organ of the International Monetary Fund
International Monetary Fund
The International Monetary Fund is an organization of 187 countries, working to foster global monetary cooperation, secure financial stability, facilitate international trade, promote high employment and sustainable economic growth, and reduce poverty around the world...
, but the IMF provides secretariat services for the Group. Its meetings usually take place twice a year, prior to the IMFC and Development Committee meetings, to enable developing country members to discuss agenda items beforehand.
Although membership in the G-24 is strictly limited to 24 countries, any member of the G-77 can join discussions (Mexico
Mexico
The United Mexican States , commonly known as Mexico , is a federal constitutional republic in North America. It is bordered on the north by the United States; on the south and west by the Pacific Ocean; on the southeast by Guatemala, Belize, and the Caribbean Sea; and on the east by the Gulf of...
is the only G-24 member that is not a G-77 member, when it left the G-77 without resigning its G-24 membership). China
China
Chinese civilization may refer to:* China for more general discussion of the country.* Chinese culture* Greater China, the transnational community of ethnic Chinese.* History of China* Sinosphere, the area historically affected by Chinese culture...
has been a "special invitee" since the Gabon meetings of 1981.
Miguel Gustavo Peirano
Miguel Gustavo Peirano
Miguel Gustavo Peirano is an Argentine economist, and former Minister of Economy and Production of Argentina. He was appointed by President Néstor Kirchner on July 16, 2007, in place of Felisa Miceli....
, former Argentine
Argentina
Argentina , officially the Argentine Republic , is the second largest country in South America by land area, after Brazil. It is constituted as a federation of 23 provinces and an autonomous city, Buenos Aires...
Minister of Economy
Economy of Argentina
This article provides an overview of the Economic history of Argentina.-Emergence into the world economy:Prior to the 1880s, Argentina was a relatively isolated backwater, dependent on the wool, leather and hide industry for both the greater part of its foreign exchange and the generation of...
, is the current chairman of the G-24.
See also
- Non-Aligned MovementNon-Aligned MovementThe Non-Aligned Movement is a group of states considering themselves not aligned formally with or against any major power bloc. As of 2011, the movement had 120 members and 17 observer countries...
- Third WorldThird WorldThe term Third World arose during the Cold War to define countries that remained non-aligned with either capitalism and NATO , or communism and the Soviet Union...
- South-South CooperationSouth-South CooperationSouth-South Cooperation is a term historically used by policymakers and academics to describe the exchange of resources, technology, and knowledge between developing countries, also known as countries of the global South.- History :...
- G20 developing nationsG20 developing nationsThe G20 is a bloc of developing nations established on 20 August 2003. Distinct and separate from the G-20 major economies, the group emerged at the 5th Ministerial WTO conference, held in Cancún, Mexico, from 10 September to 14 September 2003...
- Politics of global warmingPolitics of global warmingThe politics of global warming have involved corporate lobbying, funding of special interest groups and public relations campaigns by the oil and coal industries which have affected policy decisions and legislation worldwide...


































































































































