
Great Vowel Shift
Encyclopedia
The Great Vowel Shift was a major change in the pronunciation
of the English language
that took place in England
between 1350 and 1500.
The Great Vowel Shift was first studied by Otto Jespersen
(1860–1943), a Danish
linguist
and Anglicist
, who coined the term.
Because English spelling was becoming standardised in the 15th and 16th centuries, the Great Vowel Shift is responsible for many of the peculiarities of English spelling.
The values of the long vowels form the main difference between the pronunciation of Middle English
and Modern English
, and the Great Vowel Shift is one of the historical events marking the separation of Middle and Modern English. Prior to the Great Vowel Shift, these vowels had "continental" values much like those remaining in Italian
and liturgical Latin
. However, during the Great Vowel Shift, the two highest long vowels became diphthong
s, and the other five underwent an increase in tongue height with one of them coming to the front.
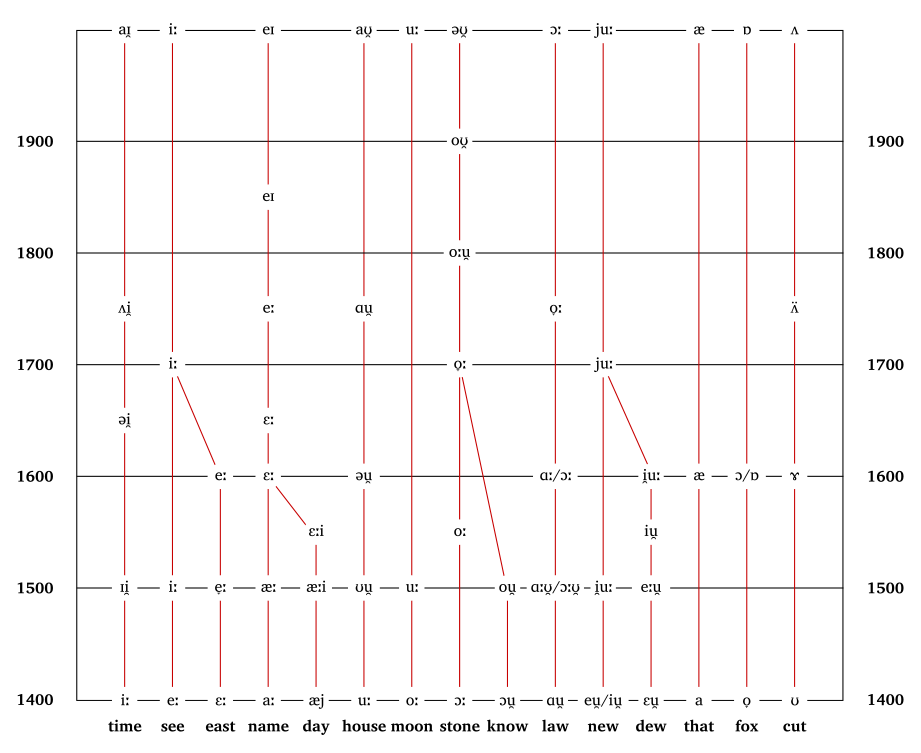
The principal changes (with the vowels shown in IPA
) are roughly as follows.
However, exceptions occur, the transitions were not always complete, and there were sometimes accompanying changes in orthography
:
This means that the vowel in the English word date was in Middle English pronounced [aː] (similar to modern non-rhotic
dart); the vowel in feet was [eː] (similar to modern fate); the vowel in wipe was [iː] (similar to modern weep); the vowel in boot was [oː] (similar to modern boat); and the vowel in house was [uː] (similar to modern whose).
The effects of the shift were not entirely uniform, and differences in degree of vowel shifting can sometimes be detected in regional dialects both in written and in spoken English. In Northern English
, the long back vowel
s remained unaffected, the long front vowel
s having undergone an earlier shift. In Scotland
, Scots
differed in its input to the Great Vowel Shift, the long vowels [iː], [eː] and [aː] shifted to [ei], [iː] and [eː] by the Middle Scots
period, [oː] had shifted to [øː] in Early Scots
and [uː] remained unaffected.
The effect of the Great Vowel Shift may be seen very clearly in the English names of many of the letters of the alphabet. A, B, C and D are pronounced /eɪ, biː, siː, diː/ in today's English, but in contemporary French they are /a, be, se, de/. The French names (which the English names are derived from) preserve the English vowels from before the Great Vowel Shift. By contrast, the names of F, L, M, N and S (/ɛf, ɛl, ɛm, ɛn, ɛs/) remain the same in both languages, because "short" vowels were unaffected by the Shift.
, swear
, and bear
. The vowels mentioned in words like break or steak underwent the process of shortening, due to the plosives following the vowels. Obviously that happened before the great vowel shift took place. Swear and bear contain the sound [r] which was pronounced as it still is in North American, Scottish, and Irish English and other rhotic varieties. This also affected and changed the vowel quality. As a consequence, it prevented the effects of the Great Vowel Shift. Other examples are father
, which failed to become [ɛː] / ea, and broad, which failed to become [oː]. The word room retains its older medieval pronunciation as m is a labial consonant
, but its spelling makes it appear as though it was originally pronounced with [oː]. However, its Middle English spelling was roum, and was only altered after the vowel shift had taken place.
Shortening of long vowels at various stages produced further complications. ea is again a good example, shortening commonly before coronal consonant
s such as d and th, thus: dead, head, threat, wealth etc. (This is known as the bred–bread merger.) oo was shortened from [uː] to [ʊ] in many cases before k, d and less commonly t, thus book, foot, good etc. Some cases occurred before the change of [ʊ] to [ʌ]: blood, flood. Similar, yet older shortening occurred for some instances of ou: country, could.
Note that some loanword
s, such as soufflé and Umlaut, have retained a spelling from their origin language that may seem similar to the previous examples; but, since they were not a part of English at the time of the Great Vowel Shift, they are not actually exceptions to the shift.
and cultural history
. But some theories attach the cause to the mass migration to the south-east part of England after the Black Death
, where the difference in accents led to certain groups modifying their speech to allow for a standard pronunciation of vowel sounds. The different dialects and the rise of a standardised middle class in London
led to changes in pronunciation, which continued to spread out from the city.
The sudden social mobility after the Black Death may have caused the shift, with people from lower levels in society moving to higher levels (the pandemic also having hit the aristocracy). Another explanation highlights the language of the ruling class: the medieval aristocracy had spoken French, but, by the early fifteenth century, they were using English. This may have caused a change to the "prestige accent" of English, either by making pronunciation more French in style or by changing it in some other way, perhaps by hypercorrection
to something thought to be "more English" (England being at war with France for much of this period).
Another influence may have been the great political and social upheavals of the fifteenth century, which were largely contemporaneous with the Great Vowel Shift.
Because English spelling was becoming standardised in the 15th and 16th centuries, the Great Vowel Shift is responsible for many of the peculiarities of English spelling. Spellings that made sense according to Middle English pronunciation were retained in Modern English because of the adoption and use of the printing press
, which was introduced to England in the 1470s by William Caxton
and later Richard Pynson
.
and Dutch
also experienced sound changes resembling the first stage of the Great Vowel Shift. In German
, by the 15th or 16th centuries, long [iː] had changed to [aɪ], (as in Eis, 'ice') and long [uː] to [aʊ] (as in Haus, 'house'), though some Alemannic
dialects resist those changes to this day, as do Limburgish and Ripuarian
. In Dutch
, the former became [ɛi] (ijs), and the latter had earlier become [yː], which then became [œy] (huis). In German, there also was a separate [yː], which became [ɔʏ], via an intermediate similar to the Dutch. In the Polder Dutch pronunciation, the shift has actually been carried further than in Standard Dutch, with a very similar result as in German and English.
Dutch and German have, like English, also shifted common Germanic *[oː] to [uː] (German) or [u] (Dutch), as in Proto-Germanic *fōt- 'foot' > German Fuß, Dutch voet (as well as the rare secondary *[eː] to [iː] in German and [i] in Dutch). However, this similarity turns out to be superficial on closer inspection. Given the huge differences between the structures of Old English vowel phonology on one side, and that of Old Dutch and Old High German on the other, this is hardly surprising. Whereas there is no indication that English long vowels other than did anything but just move up in tongue-body position, Dutch [u] and German [uː] appear to have been raised through a process of diphthongisation.
In the very earliest longer, connected Old High German and Old Dutch texts (9th cent.), the vowel [oː] is already largely written -uo-. That is, it had broken into a nucleus with a centering glide. This complex nucleus smoothed, as the term has it in Middle High German and Middle Dutch, becoming the [uː] of Modern German and the [u] of Modern Dutch around the same time as the long high vowels began to diphthongize.
The [oː] of Modern German has a variety of sources, the oldest of which is Proto-Germanic *aw, which smoothed before /t d r x/ (so rot 'red', Ohr 'ear', Floh 'flea', etc.) Elsewhere the sound was written -ou- in OHG. In Old Dutch, this sound had become -o- everywhere, explaining the difference in words such as Dutch boom and German Baum.
Pronunciation
Pronunciation refers to the way a word or a language is spoken, or the manner in which someone utters a word. If one is said to have "correct pronunciation", then it refers to both within a particular dialect....
of the English language
English language
English is a West Germanic language that arose in the Anglo-Saxon kingdoms of England and spread into what was to become south-east Scotland under the influence of the Anglian medieval kingdom of Northumbria...
that took place in England
England
England is a country that is part of the United Kingdom. It shares land borders with Scotland to the north and Wales to the west; the Irish Sea is to the north west, the Celtic Sea to the south west, with the North Sea to the east and the English Channel to the south separating it from continental...
between 1350 and 1500.
The Great Vowel Shift was first studied by Otto Jespersen
Otto Jespersen
Jens Otto Harry Jespersen or Otto Jespersen was a Danish linguist who specialized in the grammar of the English language.He was born in Randers in northern Jutland and attended Copenhagen University, earning degrees in English, French, and Latin...
(1860–1943), a Danish
Denmark
Denmark is a Scandinavian country in Northern Europe. The countries of Denmark and Greenland, as well as the Faroe Islands, constitute the Kingdom of Denmark . It is the southernmost of the Nordic countries, southwest of Sweden and south of Norway, and bordered to the south by Germany. Denmark...
linguist
Linguistics
Linguistics is the scientific study of human language. Linguistics can be broadly broken into three categories or subfields of study: language form, language meaning, and language in context....
and Anglicist
English studies
English studies is an academic discipline that includes the study of literatures written in the English language , English linguistics English studies is an academic discipline that includes the study of literatures written in the English language (including literatures from the U.K., U.S.,...
, who coined the term.
Because English spelling was becoming standardised in the 15th and 16th centuries, the Great Vowel Shift is responsible for many of the peculiarities of English spelling.
Effect
lang=enThe values of the long vowels form the main difference between the pronunciation of Middle English
Middle English
Middle English is the stage in the history of the English language during the High and Late Middle Ages, or roughly during the four centuries between the late 11th and the late 15th century....
and Modern English
Modern English
Modern English is the form of the English language spoken since the Great Vowel Shift in England, completed in roughly 1550.Despite some differences in vocabulary, texts from the early 17th century, such as the works of William Shakespeare and the King James Bible, are considered to be in Modern...
, and the Great Vowel Shift is one of the historical events marking the separation of Middle and Modern English. Prior to the Great Vowel Shift, these vowels had "continental" values much like those remaining in Italian
Italian language
Italian is a Romance language spoken mainly in Europe: Italy, Switzerland, San Marino, Vatican City, by minorities in Malta, Monaco, Croatia, Slovenia, France, Libya, Eritrea, and Somalia, and by immigrant communities in the Americas and Australia...
and liturgical Latin
Ecclesiastical Latin
Ecclesiastical Latin is the Latin used by the Latin Rite of the Catholic Church in all periods for ecclesiastical purposes...
. However, during the Great Vowel Shift, the two highest long vowels became diphthong
Diphthong
A diphthong , also known as a gliding vowel, refers to two adjacent vowel sounds occurring within the same syllable. Technically, a diphthong is a vowel with two different targets: That is, the tongue moves during the pronunciation of the vowel...
s, and the other five underwent an increase in tongue height with one of them coming to the front.

The principal changes (with the vowels shown in IPA
International Phonetic Alphabet
The International Phonetic Alphabet "The acronym 'IPA' strictly refers [...] to the 'International Phonetic Association'. But it is now such a common practice to use the acronym also to refer to the alphabet itself that resistance seems pedantic...
) are roughly as follows.
However, exceptions occur, the transitions were not always complete, and there were sometimes accompanying changes in orthography
Orthography
The orthography of a language specifies a standardized way of using a specific writing system to write the language. Where more than one writing system is used for a language, for example Kurdish, Uyghur, Serbian or Inuktitut, there can be more than one orthography...
:
- Middle EnglishMiddle EnglishMiddle English is the stage in the history of the English language during the High and Late Middle Ages, or roughly during the four centuries between the late 11th and the late 15th century....
[aː] (ā) fronted to [æː] and then raised to [ɛː], [eː] and in many dialects diphthongised in Modern EnglishModern EnglishModern English is the form of the English language spoken since the Great Vowel Shift in England, completed in roughly 1550.Despite some differences in vocabulary, texts from the early 17th century, such as the works of William Shakespeare and the King James Bible, are considered to be in Modern...
to [eɪ] (as in make). Since Old English ā had mutated to [ɔː] in Middle English, Old English ā does not correspond to the Modern English diphthong [eɪ], but was rather formed from the lengthening of short a in open syllables. - Middle English [ɛː] raised to [eː] and then to modern English [iː] (as in beak).
- Middle English [eː] raised to Modern English [iː] (as in feet).
- Middle English [iː] diphthongised to [ɪi], which was most likely followed by [əɪ] and finally Modern English [aɪ] (as in mice).
- Middle English [ɔː] raised to [oː], and in the eighteenth century this became Modern English [oʊ] or [əʊ] (as in boat).
- Middle English [oː] raised to Modern English [uː] (as in boot).
- Middle English [uː] was diphthongised in most environments to [ʊu], and this was followed by [əʊ], and then Modern English [aʊ] (as in mouse) in the eighteenth century. Before labial consonantLabial consonantLabial consonants are consonants in which one or both lips are the active articulator. This precludes linguolabials, in which the tip of the tongue reaches for the posterior side of the upper lip and which are considered coronals...
s, this shift did not occur, and [uː] remains as in soup and room (its Middle English spelling was roum).
This means that the vowel in the English word date was in Middle English pronounced [aː] (similar to modern non-rhotic
Rhotic and non-rhotic accents
English pronunciation can be divided into two main accent groups: a rhotic speaker pronounces a rhotic consonant in words like hard; a non-rhotic speaker does not...
dart); the vowel in feet was [eː] (similar to modern fate); the vowel in wipe was [iː] (similar to modern weep); the vowel in boot was [oː] (similar to modern boat); and the vowel in house was [uː] (similar to modern whose).
The effects of the shift were not entirely uniform, and differences in degree of vowel shifting can sometimes be detected in regional dialects both in written and in spoken English. In Northern English
Northern English
Northern English is a group of dialects of the English language. It includes the North East England dialects, which are similar in some respects to Scots....
, the long back vowel
Back vowel
A back vowel is a type of vowel sound used in spoken languages. The defining characteristic of a back vowel is that the tongue is positioned as far back as possible in the mouth without creating a constriction that would be classified as a consonant. Back vowels are sometimes also called dark...
s remained unaffected, the long front vowel
Front vowel
A front vowel is a type of vowel sound used in some spoken languages. The defining characteristic of a front vowel is that the tongue is positioned as far in front as possible in the mouth without creating a constriction that would be classified as a consonant. Front vowels are sometimes also...
s having undergone an earlier shift. In Scotland
Scotland
Scotland is a country that is part of the United Kingdom. Occupying the northern third of the island of Great Britain, it shares a border with England to the south and is bounded by the North Sea to the east, the Atlantic Ocean to the north and west, and the North Channel and Irish Sea to the...
, Scots
Scots language
Scots is the Germanic language variety spoken in Lowland Scotland and parts of Ulster . It is sometimes called Lowland Scots to distinguish it from Scottish Gaelic, the Celtic language variety spoken in most of the western Highlands and in the Hebrides.Since there are no universally accepted...
differed in its input to the Great Vowel Shift, the long vowels [iː], [eː] and [aː] shifted to [ei], [iː] and [eː] by the Middle Scots
Middle Scots
Middle Scots was the Anglic language of Lowland Scotland in the period from 1450 to 1700. By the end of the 13th century its phonology, orthography, accidence, syntax and vocabulary had diverged markedly from Early Scots, which was virtually indistinguishable from early Northumbrian Middle English...
period, [oː] had shifted to [øː] in Early Scots
Early Scots
Early Scots describes the emerging literary language of the Northern Middle English speaking parts of Scotland in the period before 1450. The northern forms of Middle English descended from Northumbrian Old English...
and [uː] remained unaffected.
The effect of the Great Vowel Shift may be seen very clearly in the English names of many of the letters of the alphabet. A, B, C and D are pronounced /eɪ, biː, siː, diː/ in today's English, but in contemporary French they are /a, be, se, de/. The French names (which the English names are derived from) preserve the English vowels from before the Great Vowel Shift. By contrast, the names of F, L, M, N and S (/ɛf, ɛl, ɛm, ɛn, ɛs/) remain the same in both languages, because "short" vowels were unaffected by the Shift.
Exceptions
Not all words underwent certain phases of the Great Vowel Shift. ea in particular did not take the step to [iː] in several words, such as great, break, steakSteak
A steak is a cut of meat . Most are cut perpendicular to the muscle fibers, improving the perceived tenderness of the meat. In North America, steaks are typically served grilled, pan-fried, or broiled. The more tender cuts from the loin and rib are cooked quickly, using dry heat, and served whole...
, swear
Swear
Swear or Swearing may refer to:*Oath*Profanity*The Swear, a band*"Swear" , a 1980s pop song by Tim Scott and later covered by Sheena Easton*"Swear", a j-pop song by Alan from the album "My Life"...
, and bear
Bear
Bears are mammals of the family Ursidae. Bears are classified as caniforms, or doglike carnivorans, with the pinnipeds being their closest living relatives. Although there are only eight living species of bear, they are widespread, appearing in a wide variety of habitats throughout the Northern...
. The vowels mentioned in words like break or steak underwent the process of shortening, due to the plosives following the vowels. Obviously that happened before the great vowel shift took place. Swear and bear contain the sound [r] which was pronounced as it still is in North American, Scottish, and Irish English and other rhotic varieties. This also affected and changed the vowel quality. As a consequence, it prevented the effects of the Great Vowel Shift. Other examples are father
Father
A father, Pop, Dad, or Papa, is defined as a male parent of any type of offspring. The adjective "paternal" refers to father, parallel to "maternal" for mother...
, which failed to become [ɛː] / ea, and broad, which failed to become [oː]. The word room retains its older medieval pronunciation as m is a labial consonant
Labial consonant
Labial consonants are consonants in which one or both lips are the active articulator. This precludes linguolabials, in which the tip of the tongue reaches for the posterior side of the upper lip and which are considered coronals...
, but its spelling makes it appear as though it was originally pronounced with [oː]. However, its Middle English spelling was roum, and was only altered after the vowel shift had taken place.
Shortening of long vowels at various stages produced further complications. ea is again a good example, shortening commonly before coronal consonant
Coronal consonant
Coronal consonants are consonants articulated with the flexible front part of the tongue. Only the coronal consonants can be divided into apical , laminal , domed , or subapical , as well as a few rarer orientations, because only the front of the tongue has such...
s such as d and th, thus: dead, head, threat, wealth etc. (This is known as the bred–bread merger.) oo was shortened from [uː] to [ʊ] in many cases before k, d and less commonly t, thus book, foot, good etc. Some cases occurred before the change of [ʊ] to [ʌ]: blood, flood. Similar, yet older shortening occurred for some instances of ou: country, could.
Note that some loanword
Loanword
A loanword is a word borrowed from a donor language and incorporated into a recipient language. By contrast, a calque or loan translation is a related concept where the meaning or idiom is borrowed rather than the lexical item itself. The word loanword is itself a calque of the German Lehnwort,...
s, such as soufflé and Umlaut, have retained a spelling from their origin language that may seem similar to the previous examples; but, since they were not a part of English at the time of the Great Vowel Shift, they are not actually exceptions to the shift.
History
The exact causes of the shift are continuing mysteries in linguisticsLinguistics
Linguistics is the scientific study of human language. Linguistics can be broadly broken into three categories or subfields of study: language form, language meaning, and language in context....
and cultural history
Cultural history
The term cultural history refers both to an academic discipline and to its subject matter.Cultural history, as a discipline, at least in its common definition since the 1970s, often combines the approaches of anthropology and history to look at popular cultural traditions and cultural...
. But some theories attach the cause to the mass migration to the south-east part of England after the Black Death
Black Death
The Black Death was one of the most devastating pandemics in human history, peaking in Europe between 1348 and 1350. Of several competing theories, the dominant explanation for the Black Death is the plague theory, which attributes the outbreak to the bacterium Yersinia pestis. Thought to have...
, where the difference in accents led to certain groups modifying their speech to allow for a standard pronunciation of vowel sounds. The different dialects and the rise of a standardised middle class in London
London
London is the capital city of :England and the :United Kingdom, the largest metropolitan area in the United Kingdom, and the largest urban zone in the European Union by most measures. Located on the River Thames, London has been a major settlement for two millennia, its history going back to its...
led to changes in pronunciation, which continued to spread out from the city.
The sudden social mobility after the Black Death may have caused the shift, with people from lower levels in society moving to higher levels (the pandemic also having hit the aristocracy). Another explanation highlights the language of the ruling class: the medieval aristocracy had spoken French, but, by the early fifteenth century, they were using English. This may have caused a change to the "prestige accent" of English, either by making pronunciation more French in style or by changing it in some other way, perhaps by hypercorrection
Hypercorrection
In linguistics or usage, hypercorrection is a non-standard usage that results from the over-application of a perceived rule of grammar or a usage prescription...
to something thought to be "more English" (England being at war with France for much of this period).
Another influence may have been the great political and social upheavals of the fifteenth century, which were largely contemporaneous with the Great Vowel Shift.
Because English spelling was becoming standardised in the 15th and 16th centuries, the Great Vowel Shift is responsible for many of the peculiarities of English spelling. Spellings that made sense according to Middle English pronunciation were retained in Modern English because of the adoption and use of the printing press
Printing press
A printing press is a device for applying pressure to an inked surface resting upon a print medium , thereby transferring the ink...
, which was introduced to England in the 1470s by William Caxton
William Caxton
William Caxton was an English merchant, diplomat, writer and printer. As far as is known, he was the first English person to work as a printer and the first to introduce a printing press into England...
and later Richard Pynson
Richard Pynson
Richard Pynson was one of the first printers of English books. The 500 books he printed were influential in the standardisation of the English language...
.
Other languages
GermanGerman language
German is a West Germanic language, related to and classified alongside English and Dutch. With an estimated 90 – 98 million native speakers, German is one of the world's major languages and is the most widely-spoken first language in the European Union....
and Dutch
Dutch language
Dutch is a West Germanic language and the native language of the majority of the population of the Netherlands, Belgium, and Suriname, the three member states of the Dutch Language Union. Most speakers live in the European Union, where it is a first language for about 23 million and a second...
also experienced sound changes resembling the first stage of the Great Vowel Shift. In German
German phonology
This article is about the phonology of the German language based on standard German. It deals with current phonology and phonetics as well as with historical developments thereof, including geographical variants .Since German is a pluricentric language, there are a number of different...
, by the 15th or 16th centuries, long [iː] had changed to [aɪ], (as in Eis, 'ice') and long [uː] to [aʊ] (as in Haus, 'house'), though some Alemannic
Alemannic German
Alemannic is a group of dialects of the Upper German branch of the Germanic language family. It is spoken by approximately ten million people in six countries: Switzerland, Germany, Austria, Liechtenstein, France and Italy...
dialects resist those changes to this day, as do Limburgish and Ripuarian
Ripuarian
Ripuarian is a German dialect group, part of the West Central German language group....
. In Dutch
Dutch phonology
Dutch is a Germanic language and as such has a similar phonology to other Germanic languages...
, the former became [ɛi] (ijs), and the latter had earlier become [yː], which then became [œy] (huis). In German, there also was a separate [yː], which became [ɔʏ], via an intermediate similar to the Dutch. In the Polder Dutch pronunciation, the shift has actually been carried further than in Standard Dutch, with a very similar result as in German and English.
Dutch and German have, like English, also shifted common Germanic *[oː] to [uː] (German) or [u] (Dutch), as in Proto-Germanic *fōt- 'foot' > German Fuß, Dutch voet (as well as the rare secondary *[eː] to [iː] in German and [i] in Dutch). However, this similarity turns out to be superficial on closer inspection. Given the huge differences between the structures of Old English vowel phonology on one side, and that of Old Dutch and Old High German on the other, this is hardly surprising. Whereas there is no indication that English long vowels other than did anything but just move up in tongue-body position, Dutch [u] and German [uː] appear to have been raised through a process of diphthongisation.
In the very earliest longer, connected Old High German and Old Dutch texts (9th cent.), the vowel [oː] is already largely written -uo-. That is, it had broken into a nucleus with a centering glide. This complex nucleus smoothed, as the term has it in Middle High German and Middle Dutch, becoming the [uː] of Modern German and the [u] of Modern Dutch around the same time as the long high vowels began to diphthongize.
The [oː] of Modern German has a variety of sources, the oldest of which is Proto-Germanic *aw, which smoothed before /t d r x/ (so rot 'red', Ohr 'ear', Floh 'flea', etc.) Elsewhere the sound was written -ou- in OHG. In Old Dutch, this sound had become -o- everywhere, explaining the difference in words such as Dutch boom and German Baum.
See also
- Chain shiftChain shiftIn phonology, a chain shift is a phenomenon in which several sounds move stepwise along a phonetic scale. The sounds involved in a chain shift can be ordered into a "chain" in such a way that, after the change is complete, each phoneme ends up sounding like what the phoneme before it in the chain...
- History of the English languageHistory of the English languageEnglish is a West Germanic language that originated from the Anglo-Frisian dialects brought to Britain by Germanic invaders from various parts of what is now northwest Germany and the Netherlands. Initially, Old English was a diverse group of dialects, reflecting the varied origins of the...
- International Phonetic AlphabetInternational Phonetic AlphabetThe International Phonetic Alphabet "The acronym 'IPA' strictly refers [...] to the 'International Phonetic Association'. But it is now such a common practice to use the acronym also to refer to the alphabet itself that resistance seems pedantic...
- Phonological history of English vowelsPhonological history of English vowelsIn the history of English phonology, there were many diachronic sound changes affecting vowels, especially involving phonemic splits and mergers.-Great Vowel Shift and Trisyllabic laxing:...
External links
- Great Vowel Shift website, Furman UniversityFurman UniversityFurman University is a selective, private, coeducational, liberal arts college in Greenville, South Carolina, United States. Furman is one of the oldest, and more selective private institutions in South Carolina...
- "What is the Great Vowel Shift?" from the same site
- "The Great Vowel Shift" page from the Geoffrey ChaucerGeoffrey ChaucerGeoffrey Chaucer , known as the Father of English literature, is widely considered the greatest English poet of the Middle Ages and was the first poet to have been buried in Poet's Corner of Westminster Abbey...
section of the Harvard UniversityHarvard UniversityHarvard University is a private Ivy League university located in Cambridge, Massachusetts, United States, established in 1636 by the Massachusetts legislature. Harvard is the oldest institution of higher learning in the United States and the first corporation chartered in the country...
website

