
Gram panchayat
Encyclopedia
India
India , officially the Republic of India , is a country in South Asia. It is the seventh-largest country by geographical area, the second-most populous country with over 1.2 billion people, and the most populous democracy in the world...
. As of 2002 there were about 265,000 gram panchayats in India
India
India , officially the Republic of India , is a country in South Asia. It is the seventh-largest country by geographical area, the second-most populous country with over 1.2 billion people, and the most populous democracy in the world...
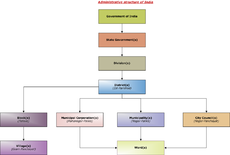
. The gram panchayat is the foundation of the Panchayat System. A gram panchayat can be set up in villages with minimum population of 300. Sometimes two or more villages are clubbed together to form group-gram panchayat when the population of the individual villages is less than 300.
Sarpanch / Chairperson
The SarpanchSarpanch
A sarpanch is a democratically elected head of a village level statutory institution of local self-government called the gram panchayat in India and Pakistan. He, together with other elected Panchas , constitute the Gram Panchayat. The Sarpanch is the focal point of contact between government...
or Chairperson is the head of the Gram Panchayat. The elected members of the Gram Panchayat elect from among themselves a Sarpanch and a Deputy Sarpanch for a term of five years. In some places the panchayat president is directly elected by village people. The Sarpanch presides over the meetings of the Gram Panchayat and supervises its working. He implements the development schemes of the village. The Deputy Sarpanch, who has the power to make his own decisions, assists the Sarpanch in his work.
The Sarpanch has the responsibilities of
- Looking after street lights, construction and repair work of the roads in the villages and also the village markets, fairs, festivals and celebrations.
- Keeping a record of births, deaths and marriages in the village.
- Looking after public health and hygiene by providing facilities for sanitationSanitationSanitation is the hygienic means of promoting health through prevention of human contact with the hazards of wastes. Hazards can be either physical, microbiological, biological or chemical agents of disease. Wastes that can cause health problems are human and animal feces, solid wastes, domestic...
and drinking water. - Providing for education.
Sources of income
The main source of income of the Gram Panchayat is the property tax levied on the buildings and the open spaces within the village.Other sources of income include professional tax, taxes on pilgrimage, animal trade, grant received from the State Government in proportion of land revenue and the grants received from the Zilla Parishad
Zilla Parishad
Zilla Parishad is a local government body at the district level in India. It looks after the administration of the rural area of the district and its office is located at the district headquarters...
.
gramsevak / gram vikas adhikari = this post is communicator in government
and village panchayat and do works for sarpanch.
this post is in maharashtra, india. he is responsible person as sarpanch.
Principles of decentralisationDr S B Sen committee, a committee appointed by the Government of Kerala
Government of Kerala
The Government of Kerala is a democratically elected body that governs the State of Kerala, India for a period of 5 years. The state government is headed by the Governor of Kerala as the nominal head of state, with a democratically elected Chief Minister as real head of the executive. The state...
in 1996, had suggested the following principles, which was later adopted by the Second Administrative Reforms Commission
Administrative Reforms Commission
The Administrative Reforms Commission or ARC is the committee appointed by the Government of India for giving recommendations for reviewing the public administration system of India. The first ARC was established on 5 January 1966...
, for local governance :-
- subsidiarity
- democratic decentralisation
- delineation of functions
- devolution of functions in real terms
- convergence
- citizen centricity
gram sabha is conducted six times in a year ...april, 1st may,15TH augest, 2octo, nov, 26 jan.

