
Goff-Gratch equation
Encyclopedia
The Goff–Gratch equation is one (arguably the first reliable) amongst many equations that have been proposed to estimate the saturation water vapor pressure
at a given temperature.
Another similar equation based on more recent data is the Arden Buck equation
.
in 1988, with further corrections in 2000.
where:
Similarly, the equation for the saturation water vapor pressure over ice is:
where:
Vapour pressure of water
The vapour pressure of water is the pressure at which steam is saturated. At higher pressures water would condense. Vapour pressure is a function of temperature...
at a given temperature.
Another similar equation based on more recent data is the Arden Buck equation
Arden Buck Equation
The Arden Buck equations are a group of empirical correlations that relate the saturation vapor pressure to temperature for moist air. The curve fits have been optimized for more accuracy than the Goff–Gratch equation in the range −80 to 50°C....
.
Historical note
This equation is named after the authors of the original scientific article who described how to calculate the saturation water vapor pressure above a flat free water surface as a function of temperature (Goff and Gratch, 1946). Goff (1957) later revised his formula, and the latter was recommended for use by the World Meteorological OrganizationWorld Meteorological Organization
The World Meteorological Organization is an intergovernmental organization with a membership of 189 Member States and Territories. It originated from the International Meteorological Organization , which was founded in 1873...
in 1988, with further corrections in 2000.
Equations
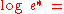
The original Goff–Gratch (1946) equation reads as follows: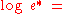 |
 |
|
 |
||
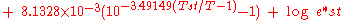 |
where:
- log refers to the logarithm in base 10
- e* is the saturation water vapor pressure (hPaPascal (unit)The pascal is the SI derived unit of pressure, internal pressure, stress, Young's modulus and tensile strength, named after the French mathematician, physicist, inventor, writer, and philosopher Blaise Pascal. It is a measure of force per unit area, defined as one newton per square metre...
) - T is the absolute air temperature in kelvinKelvinThe kelvin is a unit of measurement for temperature. It is one of the seven base units in the International System of Units and is assigned the unit symbol K. The Kelvin scale is an absolute, thermodynamic temperature scale using as its null point absolute zero, the temperature at which all...
s - Tst is the steam-point (i.e. boiling pointBoiling pointThe boiling point of an element or a substance is the temperature at which the vapor pressure of the liquid equals the environmental pressure surrounding the liquid....
at 1 atm.) temperature (373.15 K) - e*st is e* at the steam-point pressure (1 atm = 1013.25 hPa)
Similarly, the equation for the saturation water vapor pressure over ice is:
 |
 |
 |
where:
- log stands for the logarithm in base 10
- e*i is the saturation water vapor pressure over ice (hPa)
- T is the air temperature (K)
- T0 is the ice-point (triple pointTriple pointIn thermodynamics, the triple point of a substance is the temperature and pressure at which the three phases of that substance coexist in thermodynamic equilibrium...
) temperature (273.16 K) - e*i0 is e* at the ice-point pressure (6.1173 hPa)
External links
- http://cires.colorado.edu/~voemel/vp.html
- Free Windows Program, Moisture Units Conversion Calculator w/Goff-Gratch equation - PhyMetrix

