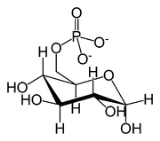
Glucose-6-phosphate
Overview
Glucose
Glucose is a simple sugar and an important carbohydrate in biology. Cells use it as the primary source of energy and a metabolic intermediate...
sugar phosphorylated on carbon 6. This compound is very common in cells
Cell (biology)
The cell is the basic structural and functional unit of all known living organisms. It is the smallest unit of life that is classified as a living thing, and is often called the building block of life. The Alberts text discusses how the "cellular building blocks" move to shape developing embryos....
as the vast majority of glucose entering a cell will become phosphorylated in this way.
Because of its prominent position in cellular chemistry
Chemistry
Chemistry is the science of matter, especially its chemical reactions, but also its composition, structure and properties. Chemistry is concerned with atoms and their interactions with other atoms, and particularly with the properties of chemical bonds....
, glucose 6-phosphate has many possible fates within the cell. It lies at the start of two major metabolic pathway
Metabolic pathway
In biochemistry, metabolic pathways are series of chemical reactions occurring within a cell. In each pathway, a principal chemical is modified by a series of chemical reactions. Enzymes catalyze these reactions, and often require dietary minerals, vitamins, and other cofactors in order to function...
s:
- GlycolysisGlycolysisGlycolysis is the metabolic pathway that converts glucose C6H12O6, into pyruvate, CH3COCOO− + H+...
- Pentose phosphate pathwayPentose phosphate pathwayThe pentose phosphate pathway is a process that generates NADPH and pentoses . There are two distinct phases in the pathway. The first is the oxidative phase, in which NADPH is generated, and the second is the non-oxidative synthesis of 5-carbon sugars...
In addition to these metabolic pathways, glucose 6-phosphate may also be converted to glycogen
Glycogen
Glycogen is a molecule that serves as the secondary long-term energy storage in animal and fungal cells, with the primary energy stores being held in adipose tissue...
or starch
Starch
Starch or amylum is a carbohydrate consisting of a large number of glucose units joined together by glycosidic bonds. This polysaccharide is produced by all green plants as an energy store...
for storage.

