
Glottal consonant
Encyclopedia
Glottal consonants, also called laryngeal consonant
s, are consonant
s articulated with the glottis
. Many phoneticians consider them, or at least the so-called fricative
, to be transitional states of the glottis without a point of articulation as other consonants have; in fact, some do not consider them to be consonants at all. However, glottal consonants behave as typical consonants in many languages. For example, in Arabic
, most words are formed from a root C-C-C consisting of three consonants, which are inserted into templates such as /CaːCiC/ or /maCCuːC/. The glottal consonants /h/ and /ʔ/ can occupy any of the three root consonant slots, just like "normal" consonants such as /k/ or /n/.
:
) without a specific place of articulation. [h] is a voiceless transition. [ɦ] is a breathy-voiced
transition, and could be transcribed as [h̤].
The glottal stop
occurs in many languages. Often all vocalic onsets are preceded by a glottal stop, for example in German
. The Hawaiian language
writes the glottal stop as an opening single quote ‘. Some alphabets use diacritic
s for the glottal stop, such as hamza <ء> in the Arabic alphabet
; in many languages of Mesoamerica
, the Latin letter is used for glottal stop, while in Maltese
, the letter
Laryngeal consonant
A laryngeal consonant is generally synonymous with a glottal consonant; that is, with , , and .Besides the glottis , the larynx includes the epiglottis and aryepiglottic folds, though epiglottal and aryepiglottal consonants are usually counted as radical rather than as laryngeal...
s, are consonant
Consonant
In articulatory phonetics, a consonant is a speech sound that is articulated with complete or partial closure of the vocal tract. Examples are , pronounced with the lips; , pronounced with the front of the tongue; , pronounced with the back of the tongue; , pronounced in the throat; and ,...
s articulated with the glottis
Glottis
The glottis is defined as the combination of the vocal folds and the space in between the folds .-Function:...
. Many phoneticians consider them, or at least the so-called fricative
Fricative consonant
Fricatives are consonants produced by forcing air through a narrow channel made by placing two articulators close together. These may be the lower lip against the upper teeth, in the case of ; the back of the tongue against the soft palate, in the case of German , the final consonant of Bach; or...
, to be transitional states of the glottis without a point of articulation as other consonants have; in fact, some do not consider them to be consonants at all. However, glottal consonants behave as typical consonants in many languages. For example, in Arabic
Arabic language
Arabic is a name applied to the descendants of the Classical Arabic language of the 6th century AD, used most prominently in the Quran, the Islamic Holy Book...
, most words are formed from a root C-C-C consisting of three consonants, which are inserted into templates such as /CaːCiC/ or /maCCuːC/. The glottal consonants /h/ and /ʔ/ can occupy any of the three root consonant slots, just like "normal" consonants such as /k/ or /n/.
Glottal consonant in IPA
Glottal consonants in the International Phonetic AlphabetInternational Phonetic Alphabet
The International Phonetic Alphabet "The acronym 'IPA' strictly refers [...] to the 'International Phonetic Association'. But it is now such a common practice to use the acronym also to refer to the alphabet itself that resistance seems pedantic...
:
| IPA | Description | Example | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Language | Orthography | IPA | Meaning | ||
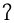 |
voiceless glottal stop Glottal stop The glottal stop, or more fully, the voiceless glottal plosive, is a type of consonantal sound used in many spoken languages. In English, the feature is represented, for example, by the hyphen in uh-oh! and by the apostrophe or [[ʻokina]] in Hawaii among those using a preservative pronunciation of... |
Hawaiian Hawaiian language The Hawaiian language is a Polynesian language that takes its name from Hawaii, the largest island in the tropical North Pacific archipelago where it developed. Hawaiian, along with English, is an official language of the state of Hawaii... |
‘okina | [ʔo.ˈki.na] | ‘okina Okina The okina, also called by several other names , is a unicameral consonant letter used within the Latin script to mark the phonetic glottal stop, as it is used in many Polynesian languages.- Geographic names in the United States :... |
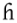 |
breathy voiced glottal "fricative" | Czech Czech language Czech is a West Slavic language with about 12 million native speakers; it is the majority language in the Czech Republic and spoken by Czechs worldwide. The language was known as Bohemian in English until the late 19th century... |
Praha | [ˈpra.ɦa] | Prague Prague Prague is the capital and largest city of the Czech Republic. Situated in the north-west of the country on the Vltava river, the city is home to about 1.3 million people, while its metropolitan area is estimated to have a population of over 2.3 million... |
 |
voiceless glottal "fricative" Voiceless glottal fricative The voiceless glottal transition, commonly called a "fricative", is a type of sound used in some spoken languages which patterns like a fricative or approximant consonant phonologically, but often lacks the usual phonetic characteristics of a consonant... |
English English language English is a West Germanic language that arose in the Anglo-Saxon kingdoms of England and spread into what was to become south-east Scotland under the influence of the Anglian medieval kingdom of Northumbria... |
hat | [ˈhæt] | hat Hat A hat is a head covering. It can be worn for protection against the elements, for ceremonial or religious reasons, for safety, or as a fashion accessory. In the past, hats were an indicator of social status... |
Characteristics
The "fricatives" are not true fricatives. This is a historical usage of the word. They instead represent transitional states of the glottis (phonationPhonation
Phonation has slightly different meanings depending on the subfield of phonetics. Among some phoneticians, phonation is the process by which the vocal folds produce certain sounds through quasi-periodic vibration. This is the definition used among those who study laryngeal anatomy and physiology...
) without a specific place of articulation. [h] is a voiceless transition. [ɦ] is a breathy-voiced
Breathy voice
Breathy voice is a phonation in which the vocal cords vibrate, as they do in normal voicing, but are held further apart, so that a larger volume of air escapes between them. This produces an audible noise...
transition, and could be transcribed as [h̤].
The glottal stop
Glottal stop
The glottal stop, or more fully, the voiceless glottal plosive, is a type of consonantal sound used in many spoken languages. In English, the feature is represented, for example, by the hyphen in uh-oh! and by the apostrophe or [[ʻokina]] in Hawaii among those using a preservative pronunciation of...
occurs in many languages. Often all vocalic onsets are preceded by a glottal stop, for example in German
German language
German is a West Germanic language, related to and classified alongside English and Dutch. With an estimated 90 – 98 million native speakers, German is one of the world's major languages and is the most widely-spoken first language in the European Union....
. The Hawaiian language
Hawaiian language
The Hawaiian language is a Polynesian language that takes its name from Hawaii, the largest island in the tropical North Pacific archipelago where it developed. Hawaiian, along with English, is an official language of the state of Hawaii...
writes the glottal stop as an opening single quote ‘. Some alphabets use diacritic
Diacritic
A diacritic is a glyph added to a letter, or basic glyph. The term derives from the Greek διακριτικός . Diacritic is both an adjective and a noun, whereas diacritical is only an adjective. Some diacritical marks, such as the acute and grave are often called accents...
s for the glottal stop, such as hamza <ء> in the Arabic alphabet
Arabic alphabet
The Arabic alphabet or Arabic abjad is the Arabic script as it is codified for writing the Arabic language. It is written from right to left, in a cursive style, and includes 28 letters. Because letters usually stand for consonants, it is classified as an abjad.-Consonants:The Arabic alphabet has...
; in many languages of Mesoamerica
Mesoamerica
Mesoamerica is a region and culture area in the Americas, extending approximately from central Mexico to Belize, Guatemala, El Salvador, Honduras, Nicaragua, and Costa Rica, within which a number of pre-Columbian societies flourished before the Spanish colonization of the Americas in the 15th and...
, the Latin letter
Maltese language
Maltese is the national language of Malta, and a co-official language of the country alongside English,while also serving as an official language of the European Union, the only Semitic language so distinguished. Maltese is descended from Siculo-Arabic...
, the letter
is used instead.
Because the glottis is necessarily closed for the glottal stop, it cannot be voiced.

