
Global meteoric water line
Encyclopedia
The Global Meteoric Water Line is an equation defined by the geochemist Harmon Craig
that states the average relationship between hydrogen
and oxygen
isotope ratios in natural terrestrial waters, expressed as a worldwide average.
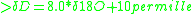
A meteoric water line can also be calculated for a given area, and used as a baseline within that area. Kinetic fractionation
will cause the isotope ratios to vary between localities within that area. This relationship is used within the field of isotope hydrology
. Craig's original assertion is that the isotopic enrichments, relative to ocean
water, display a linear correlation over the entire range for waters which have not undergone excessive evaporation
.
Harmon Craig
Harmon Craig was an American geochemist.Craig studied geology and chemistry at the University of Chicago, where he earned a Ph.D. under Nobel Laureate Harold Urey with a thesis on carbon isotope geochemistry in 1951. He remained at the University of Chicago as a research associate at the Enrico...
that states the average relationship between hydrogen
Hydrogen
Hydrogen is the chemical element with atomic number 1. It is represented by the symbol H. With an average atomic weight of , hydrogen is the lightest and most abundant chemical element, constituting roughly 75% of the Universe's chemical elemental mass. Stars in the main sequence are mainly...
and oxygen
Oxygen
Oxygen is the element with atomic number 8 and represented by the symbol O. Its name derives from the Greek roots ὀξύς and -γενής , because at the time of naming, it was mistakenly thought that all acids required oxygen in their composition...
isotope ratios in natural terrestrial waters, expressed as a worldwide average.
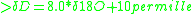
A meteoric water line can also be calculated for a given area, and used as a baseline within that area. Kinetic fractionation
Kinetic fractionation
Kinetic fractionation is a process that separates stable isotopes from each other by their mass during unidirectional processes.One naturally occurring example of kinetic fractionation is the evaporation of seawater to form clouds...
will cause the isotope ratios to vary between localities within that area. This relationship is used within the field of isotope hydrology
Isotope hydrology
Isotope hydrology is a field of hydrology that uses isotopic dating to estimate the age and origins of water and of movement within the hydrologic cycle. The techniques are used for water-use policy, mapping aquifers, conserving water supplies, and controlling pollution...
. Craig's original assertion is that the isotopic enrichments, relative to ocean
Ocean
An ocean is a major body of saline water, and a principal component of the hydrosphere. Approximately 71% of the Earth's surface is covered by ocean, a continuous body of water that is customarily divided into several principal oceans and smaller seas.More than half of this area is over 3,000...
water, display a linear correlation over the entire range for waters which have not undergone excessive evaporation
Evaporation
Evaporation is a type of vaporization of a liquid that occurs only on the surface of a liquid. The other type of vaporization is boiling, which, instead, occurs on the entire mass of the liquid....
.

