
Gliese 710
Encyclopedia
Gliese 710 is a variable
orange dwarf
star
(K7 spectral class) in the constellation
Serpens Cauda, with visual magnitude 9.66 and a mass of 0.4–0.6 solar masses.
It is currently about 63.0 light years from Earth
, but its proper motion
, distance, and radial velocity
indicate that it will approach within a very small distance—perhaps under one light year—from the Sun
within 1.4 million years, based on past and current Hipparcos
data. At closest approach it will be a first-magnitude star about as bright as Antares
. The proper motion of Gliese 710 is very small for its distance, meaning it is traveling nearly directly in our line of sight; compare for example with Arcturus.
In a time interval of ±10 million years from the present, Gliese 710 is the star whose combination of mass and close approach distance will cause the greatest gravitation
al perturbation of the Solar System
.
the hypothetical Oort cloud
enough to send a shower of comet
s into the inner Solar System, possibly causing an impact event
. However, dynamic models by García-Sánchez, et al. in 1999 indicate that the net increase in cratering rate due to the passage of Gliese 710 will be no more than 5%. They estimate that the closest approach will happen in 1,360,000 years when the star will approach within 0.337 ± 0.177 parsec
s (1.1 light-years) of the Sun.
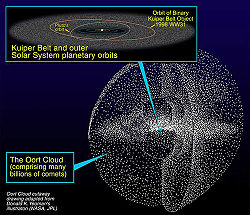 More recent calculations by Bobylev in 2010 suggest Gliese 710 has an 86 percent chance of passing through the Oort cloud, considering the Oort cloud to be a spheroid around the Sun with semiminor and semimajor axes of 80,000 and 100,000 astronomical unit
More recent calculations by Bobylev in 2010 suggest Gliese 710 has an 86 percent chance of passing through the Oort cloud, considering the Oort cloud to be a spheroid around the Sun with semiminor and semimajor axes of 80,000 and 100,000 astronomical unit
s. The distance of closest approach of Gliese 710 is difficult to compute precisely as it depends sensitively on its current position and velocity; Bobylev estimates that it will pass within 0.311 ± 0.167 pc (1.01 ± 0.54 light years) of the Sun. There is even a 1/10,000 chance of the star penetrating into the region (d < 1,000 AU) where the influence of the passing star on Kuiper belt
objects is significant.
The star with the second greatest perturbational effect in the past or future 10 million years was Algol, a triple star system that passed no closer than 9.8 light years, 7.3 million years ago, but with a considerably larger total mass of 5.8 solar masses.
Variable star
A star is classified as variable if its apparent magnitude as seen from Earth changes over time, whether the changes are due to variations in the star's actual luminosity, or to variations in the amount of the star's light that is blocked from reaching Earth...
orange dwarf
Orange dwarf
A K-type main-sequence star , also referred to orange dwarf, are main-sequence stars of spectral type K and luminosity class V. These stars are intermediate in size between red M-type main-sequence stars and yellow G-type main-sequence stars...
star
Star
A star is a massive, luminous sphere of plasma held together by gravity. At the end of its lifetime, a star can also contain a proportion of degenerate matter. The nearest star to Earth is the Sun, which is the source of most of the energy on Earth...
(K7 spectral class) in the constellation
Constellation
In modern astronomy, a constellation is an internationally defined area of the celestial sphere. These areas are grouped around asterisms, patterns formed by prominent stars within apparent proximity to one another on Earth's night sky....
Serpens Cauda, with visual magnitude 9.66 and a mass of 0.4–0.6 solar masses.
It is currently about 63.0 light years from Earth
Earth
Earth is the third planet from the Sun, and the densest and fifth-largest of the eight planets in the Solar System. It is also the largest of the Solar System's four terrestrial planets...
, but its proper motion
Proper motion
The proper motion of a star is its angular change in position over time as seen from the center of mass of the solar system. It is measured in seconds of arc per year, arcsec/yr, where 3600 arcseconds equal one degree. This contrasts with radial velocity, which is the time rate of change in...
, distance, and radial velocity
Radial velocity
Radial velocity is the velocity of an object in the direction of the line of sight . In astronomy, radial velocity most commonly refers to the spectroscopic radial velocity...
indicate that it will approach within a very small distance—perhaps under one light year—from the Sun
Sun
The Sun is the star at the center of the Solar System. It is almost perfectly spherical and consists of hot plasma interwoven with magnetic fields...
within 1.4 million years, based on past and current Hipparcos
Hipparcos
Hipparcos was a scientific mission of the European Space Agency , launched in 1989 and operated between 1989 and 1993. It was the first space experiment devoted to precision astrometry, the accurate measurement of the positions of celestial objects on the sky...
data. At closest approach it will be a first-magnitude star about as bright as Antares
Antares
Antares is a red supergiant star in the Milky Way galaxy and the sixteenth brightest star in the nighttime sky . Along with Aldebaran, Spica, and Regulus it is one of the four brightest stars near the ecliptic...
. The proper motion of Gliese 710 is very small for its distance, meaning it is traveling nearly directly in our line of sight; compare for example with Arcturus.
In a time interval of ±10 million years from the present, Gliese 710 is the star whose combination of mass and close approach distance will cause the greatest gravitation
Gravitation
Gravitation, or gravity, is a natural phenomenon by which physical bodies attract with a force proportional to their mass. Gravitation is most familiar as the agent that gives weight to objects with mass and causes them to fall to the ground when dropped...
al perturbation of the Solar System
Solar System
The Solar System consists of the Sun and the astronomical objects gravitationally bound in orbit around it, all of which formed from the collapse of a giant molecular cloud approximately 4.6 billion years ago. The vast majority of the system's mass is in the Sun...
.
Computing and details of the closest approach
Gliese 710 has the potential to perturbPerturbation (astronomy)
Perturbation is a term used in astronomy in connection with descriptions of the complex motion of a massive body which is subject to appreciable gravitational effects from more than one other massive body....
the hypothetical Oort cloud
Oort cloud
The Oort cloud , or the Öpik–Oort cloud , is a hypothesized spherical cloud of comets which may lie roughly 50,000 AU, or nearly a light-year, from the Sun. This places the cloud at nearly a quarter of the distance to Proxima Centauri, the nearest star to the Sun...
enough to send a shower of comet
Comet
A comet is an icy small Solar System body that, when close enough to the Sun, displays a visible coma and sometimes also a tail. These phenomena are both due to the effects of solar radiation and the solar wind upon the nucleus of the comet...
s into the inner Solar System, possibly causing an impact event
Impact event
An impact event is the collision of a large meteorite, asteroid, comet, or other celestial object with the Earth or another planet. Throughout recorded history, hundreds of minor impact events have been reported, with some occurrences causing deaths, injuries, property damage or other significant...
. However, dynamic models by García-Sánchez, et al. in 1999 indicate that the net increase in cratering rate due to the passage of Gliese 710 will be no more than 5%. They estimate that the closest approach will happen in 1,360,000 years when the star will approach within 0.337 ± 0.177 parsec
Parsec
The parsec is a unit of length used in astronomy. It is about 3.26 light-years, or just under 31 trillion kilometres ....
s (1.1 light-years) of the Sun.

Astronomical unit
An astronomical unit is a unit of length equal to about or approximately the mean Earth–Sun distance....
s. The distance of closest approach of Gliese 710 is difficult to compute precisely as it depends sensitively on its current position and velocity; Bobylev estimates that it will pass within 0.311 ± 0.167 pc (1.01 ± 0.54 light years) of the Sun. There is even a 1/10,000 chance of the star penetrating into the region (d < 1,000 AU) where the influence of the passing star on Kuiper belt
Kuiper belt
The Kuiper belt , sometimes called the Edgeworth–Kuiper belt, is a region of the Solar System beyond the planets extending from the orbit of Neptune to approximately 50 AU from the Sun. It is similar to the asteroid belt, although it is far larger—20 times as wide and 20 to 200 times as massive...
objects is significant.
The star with the second greatest perturbational effect in the past or future 10 million years was Algol, a triple star system that passed no closer than 9.8 light years, 7.3 million years ago, but with a considerably larger total mass of 5.8 solar masses.
External links
- SolStation.com
- VizieR variable star database
- Wikisky image of HD 168442 (Gliese 710)

