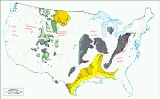
Geologic province
Encyclopedia
A geologic or geomorphic province is a spatial entity with common geologic
or geomorphic
attributes. A province may include a single dominant structural element such as a basin
or a fold belt
, or a number of contiguous related elements. Adjoining provinces may be similar in structure but be considered separate due to differing histories.
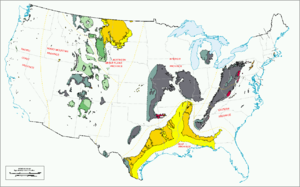 Some studies classify provinces based upon mineral resources, such as mineral
Some studies classify provinces based upon mineral resources, such as mineral
deposits. There are a particularly large number of provinces identified worldwide for petroleum
and other mineral fuels, such as the Niger Delta petroleum province
.
Geology
Geology is the science comprising the study of solid Earth, the rocks of which it is composed, and the processes by which it evolves. Geology gives insight into the history of the Earth, as it provides the primary evidence for plate tectonics, the evolutionary history of life, and past climates...
or geomorphic
Geomorphology
Geomorphology is the scientific study of landforms and the processes that shape them...
attributes. A province may include a single dominant structural element such as a basin
Basin (geology)
A structural basin is a large-scale structural formation of rock strata formed by tectonic warping of previously flat lying strata. Structural basins are geological depressions, and are the inverse of domes. Some elongated structural basins are also known as synclines...
or a fold belt
Fold (geology)
The term fold is used in geology when one or a stack of originally flat and planar surfaces, such as sedimentary strata, are bent or curved as a result of permanent deformation. Synsedimentary folds are those due to slumping of sedimentary material before it is lithified. Folds in rocks vary in...
, or a number of contiguous related elements. Adjoining provinces may be similar in structure but be considered separate due to differing histories.
Geologic provinces by origin
Geologic provinces based on origin:- ShieldShield (geology)A shield is generally a large area of exposed Precambrian crystalline igneous and high-grade metamorphic rocks that form tectonically stable areas. In all cases, the age of these rocks is greater than 570 million years and sometimes dates back 2 to 3.5 billion years...
- PlatformPlatform (geology)In geology, a platform is a continental area covered by relatively flat or gently tilted, mainly sedimentary strata, which overlie a basement of consolidated igneous or metamorphic rocks of an earlier deformation...
(shield covered with sediment) - Orogen
- Island arcIsland arcAn island arc is a type of archipelago composed of a chain of volcanoes which alignment is arc-shaped, and which are situated parallel and close to a boundary between two converging tectonic plates....
- Continental arc
- ForearcForearcA forearc or forarc, also called arc-trench gap is a depression in the sea floor located between a subduction zone and an associated volcanic arc. It is typically filled with sediments from the adjacent landmass and the island arc in addition to trapped oceanic crustal material...
- Island arc
- Basin
- CratonCratonA craton is an old and stable part of the continental lithosphere. Having often survived cycles of merging and rifting of continents, cratons are generally found in the interiors of tectonic plates. They are characteristically composed of ancient crystalline basement rock, which may be covered by...
ic basin - Foredeep basin
- Craton
- Large igneous provinceLarge igneous provinceA Large Igneous Province is an extremely large accumulation of igneous rocks—intrusive, extrusive, or both—in the earth's crust...
- Extended crustCrust (geology)In geology, the crust is the outermost solid shell of a rocky planet or natural satellite, which is chemically distinct from the underlying mantle...
- Rifted margin
- RiftRiftIn geology, a rift or chasm is a place where the Earth's crust and lithosphere are being pulled apart and is an example of extensional tectonics....
- Northern Cordilleran Volcanic ProvinceNorthern Cordilleran volcanic provinceThe Northern Cordilleran Volcanic Province , formerly known as the Stikine Volcanic Belt, is a geologic province defined by the occurrence of Miocene to Holocene volcanoes in the Pacific Northwest of North America...
- Northern Cordilleran Volcanic Province
Geologic provinces by resources

Mineral
A mineral is a naturally occurring solid chemical substance formed through biogeochemical processes, having characteristic chemical composition, highly ordered atomic structure, and specific physical properties. By comparison, a rock is an aggregate of minerals and/or mineraloids and does not...
deposits. There are a particularly large number of provinces identified worldwide for petroleum
Petroleum
Petroleum or crude oil is a naturally occurring, flammable liquid consisting of a complex mixture of hydrocarbons of various molecular weights and other liquid organic compounds, that are found in geologic formations beneath the Earth's surface. Petroleum is recovered mostly through oil drilling...
and other mineral fuels, such as the Niger Delta petroleum province
Niger Delta province
The Niger Delta province is a geologic province in the Niger Delta of West Africa also known as the Niger Delta Basin. The province contains one petroleum system, the "Tertiary Niger Delta Petroleum System" , the majority of which lies within the borders of Nigeria, with suspected or proven...
.

