Geography of Mexico
Encyclopedia
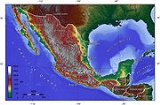
| Topographic map Topographic map A topographic map is a type of map characterized by large-scale detail and quantitative representation of relief, usually using contour lines in modern mapping, but historically using a variety of methods. Traditional definitions require a topographic map to show both natural and man-made features... of Mexico. |
|
| Area | |
| Total | 1,972,550 km2 |
| Land | 1,923,040 km2 |
| Water | 49,510 km2 |
| Latitude | 23°0' N |
| Longitude | 102°0'W |
| Borders | |
| United States | 3,141 km |
| Guatemala | 871 km |
| Belize | 251 km |
| Coastlines | 9,330 km |
| Maritime claims | |
| Contiguous zone | 24 nmi (44.4 km; 27.6 mi) |
| Economic zone | 200 nmi (370.4 km; 230.2 mi) |
| Territorial sea | 12 nmi (22.2 km; 13.8 mi) |
The geography of Mexico entails the physical
Physical geography
Physical geography is one of the two major subfields of geography. Physical geography is that branch of natural science which deals with the study of processes and patterns in the natural environment like the atmosphere, biosphere and geosphere, as opposed to the cultural or built environment, the...
and human geography
Human geography
Human geography is one of the two major sub-fields of the discipline of geography. Human geography is the study of the world, its people, communities, and cultures. Human geography differs from physical geography mainly in that it has a greater focus on studying human activities and is more...
of Mexico
Mexico
The United Mexican States , commonly known as Mexico , is a federal constitutional republic in North America. It is bordered on the north by the United States; on the south and west by the Pacific Ocean; on the southeast by Guatemala, Belize, and the Caribbean Sea; and on the east by the Gulf of...
, a country
Country
A country is a region legally identified as a distinct entity in political geography. A country may be an independent sovereign state or one that is occupied by another state, as a non-sovereign or formerly sovereign political division, or a geographic region associated with a previously...
situated in the Americas
Americas
The Americas, or America , are lands in the Western hemisphere, also known as the New World. In English, the plural form the Americas is often used to refer to the landmasses of North America and South America with their associated islands and regions, while the singular form America is primarily...
. Mexico is located at about 23° N and 102° W in the southern portion of North America
North America
North America is a continent wholly within the Northern Hemisphere and almost wholly within the Western Hemisphere. It is also considered a northern subcontinent of the Americas...
. It is also located in a region known as Middle America
Middle America (Americas)
Middle America is a region in the mid-latitudes of the Americas. In southern North America, it usually comprises Mexico, the nations of Central America, and the West Indies. The scope of the term may vary...
. From its farthest land points, Mexico is a little over 3200 km (1,988.4 mi) in length. Mexico is bounded to the North by the United States
United States
The United States of America is a federal constitutional republic comprising fifty states and a federal district...
(specifically, from West to East, by California
California
California is a state located on the West Coast of the United States. It is by far the most populous U.S. state, and the third-largest by land area...
, Arizona
Arizona
Arizona ; is a state located in the southwestern region of the United States. It is also part of the western United States and the mountain west. The capital and largest city is Phoenix...
, New Mexico
New Mexico
New Mexico is a state located in the southwest and western regions of the United States. New Mexico is also usually considered one of the Mountain States. With a population density of 16 per square mile, New Mexico is the sixth-most sparsely inhabited U.S...
, and Texas
Texas
Texas is the second largest U.S. state by both area and population, and the largest state by area in the contiguous United States.The name, based on the Caddo word "Tejas" meaning "friends" or "allies", was applied by the Spanish to the Caddo themselves and to the region of their settlement in...
), to the West and South by the Pacific Ocean
Pacific Ocean
The Pacific Ocean is the largest of the Earth's oceanic divisions. It extends from the Arctic in the north to the Southern Ocean in the south, bounded by Asia and Australia in the west, and the Americas in the east.At 165.2 million square kilometres in area, this largest division of the World...
, to the East by the Gulf of Mexico
Gulf of Mexico
The Gulf of Mexico is a partially landlocked ocean basin largely surrounded by the North American continent and the island of Cuba. It is bounded on the northeast, north and northwest by the Gulf Coast of the United States, on the southwest and south by Mexico, and on the southeast by Cuba. In...
, and to the Southeast by Belize
Belize
Belize is a constitutional monarchy and the northernmost country in Central America. Belize has a diverse society, comprising many cultures and languages. Even though Kriol and Spanish are spoken among the population, Belize is the only country in Central America where English is the official...
, Guatemala
Guatemala
Guatemala is a country in Central America bordered by Mexico to the north and west, the Pacific Ocean to the southwest, Belize to the northeast, the Caribbean to the east, and Honduras and El Salvador to the southeast...
, and the Caribbean Sea
Caribbean Sea
The Caribbean Sea is a sea of the Atlantic Ocean located in the tropics of the Western hemisphere. It is bounded by Mexico and Central America to the west and southwest, to the north by the Greater Antilles, and to the east by the Lesser Antilles....
. The Northernmost constituent of Latin America
Latin America
Latin America is a region of the Americas where Romance languages – particularly Spanish and Portuguese, and variably French – are primarily spoken. Latin America has an area of approximately 21,069,500 km² , almost 3.9% of the Earth's surface or 14.1% of its land surface area...
, it is the most populous Spanish-speaking country in the world.
Almost all of Mexico is on the North American Plate
North American Plate
The North American Plate is a tectonic plate covering most of North America, Greenland, Cuba, Bahamas, and parts of Siberia, Japan and Iceland. It extends eastward to the Mid-Atlantic Ridge and westward to the Chersky Range in eastern Siberia. The plate includes both continental and oceanic crust...
, with small parts of the Baja California Peninsula
Baja California Peninsula
The Baja California peninsula , is a peninsula in northwestern Mexico. Its land mass separates the Pacific Ocean from the Gulf of California. The Peninsula extends from Mexicali, Baja California in the north to Cabo San Lucas, Baja California Sur in the south.The total area of the Baja California...
in the northwest on the Pacific
Pacific Plate
The Pacific Plate is an oceanic tectonic plate that lies beneath the Pacific Ocean. At 103 million square kilometres, it is the largest tectonic plate....
and Cocos Plate
Cocos Plate
The Cocos Plate is an oceanic tectonic plate beneath the Pacific Ocean off the west coast of Central America, named for Cocos Island, which rides upon it.-Geology:...
s. Some geographers include the portion east of the Isthmus of Tehuantepec
Isthmus of Tehuantepec
The Isthmus of Tehuantepec is an isthmus in Mexico. It represents the shortest distance between the Gulf of Mexico and the Pacific Ocean, and prior to the opening of the Panama Canal was a major shipping route known simply as the Tehuantepec Route...
including the Yucatán Peninsula within North America
North America
North America is a continent wholly within the Northern Hemisphere and almost wholly within the Western Hemisphere. It is also considered a northern subcontinent of the Americas...
. This portion includes the five states of Campeche
Campeche
Campeche is one of the 31 states which, with the Federal District, comprise the 32 Federal Entities of Mexico. Located in Southeast Mexico, it is bordered by the states of Yucatán to the north east, Quintana Roo to the east, and Tabasco to the south west...
, Chiapas
Chiapas
Chiapas officially Estado Libre y Soberano de Chiapas is one of the 31 states that, with the Federal District, comprise the 32 Federal Entities of Mexico. It is divided in 118 municipalities and its capital city is Tuxtla Gutierrez. Other important cites in Chiapas include San Cristóbal de las...
, Tabasco
Tabasco
Tabasco officially Estado Libre y Soberano de Tabasco is one of the 31 states which, with the Federal District, comprise the 32 Federal Entities of Mexico. It is divided in 17 municipalities and its capital city is Villahermosa....
, Quintana Roo
Quintana Roo
Quintana Roo officially Estado Libre y Soberano de Quintana Roo is one of the 31 states which, with the Federal District, comprise the 32 Federal Entities of Mexico. It is divided in 10 municipalities and its capital city is Chetumal....
, and Yucatán
Yucatán
Yucatán officially Estado Libre y Soberano de Yucatán is one of the 31 states which, with the Federal District, comprise the 32 Federal Entities of Mexico. It is divided in 106 municipalities and its capital city is Mérida....
, representing 12.1% of the country's total area. Alternatively, the Trans-Mexican Volcanic Belt
Trans-Mexican volcanic belt
The Trans-Mexican Volcanic Belt also known as the Transvolcanic Belt and locally as the Sierra Nevada , is a volcanic belt that extends 900 km from west to east across central-southern Mexico...
may be said to delimit the region physiographically on the north. Geopolitically, Mexico is generally not considered part of Central America. Politically, Mexico is divided into thirty-one states and a federal district, which serves as the national capital.
As well as numerous neighbouring islands, Mexican territory includes the more remote Isla Guadalupe
Guadalupe Island
Guadalupe Island, or Isla Guadalupe is a volcanic island located 241 kilometers off the west coast of Mexico's Baja California peninsula and some 400 kilometers southwest of the city of Ensenada in Baja California state, in the Pacific Ocean...
and the Islas Revillagigedo in the Pacific Ocean
Pacific Ocean
The Pacific Ocean is the largest of the Earth's oceanic divisions. It extends from the Arctic in the north to the Southern Ocean in the south, bounded by Asia and Australia in the west, and the Americas in the east.At 165.2 million square kilometres in area, this largest division of the World...
. Mexico's total area covers 1,972,550 square kilometers, including approximately 6,000 square kilometers of islands in the Pacific Ocean, Gulf of Mexico, Caribbean Sea, and Gulf of California (see the map.) On its north, Mexico shares a 5000-kilometer border with the United States. The meandering Río Bravo del Norte (known as the Rio Grande in the United States) defines the border from Ciudad Juárez
Ciudad Juárez
Ciudad Juárez , officially known today as Heroica Ciudad Juárez, but abbreviated Juárez and formerly known as El Paso del Norte, is a city and seat of the municipality of Juárez in the Mexican state of Chihuahua. Juárez's estimated population is 1.5 million people. The city lies on the Rio Grande...
east to the Gulf of Mexico. A series of natural and artificial markers delineate the United States-Mexican border west from Ciudad Juárez to the Pacific Ocean. On its south, Mexico shares an 871 kilometer border with Guatemala and a 251-kilometer border with Belize.
Mexico has a 9,330 kilometer coastline, of which 7,338 kilometers face the Pacific Ocean and the Gulf of California, and the remaining 2,805 kilometers front the Gulf of Mexico and the Caribbean Sea. Mexico's exclusive economic zone (EEZ), which extends 200 nautical miles (370 km) off each coast, covers approximately 2.7 million square kilometers. The landmass of Mexico dramatically narrows as it moves in a southeasterly direction from the United States border and then abruptly curves northward before ending in the 500-kilometer-long Yucatán Peninsula. Indeed, the state capital of Yucatán
Yucatán
Yucatán officially Estado Libre y Soberano de Yucatán is one of the 31 states which, with the Federal District, comprise the 32 Federal Entities of Mexico. It is divided in 106 municipalities and its capital city is Mérida....
, Mérida
Mérida, Yucatán
Mérida is the capital and largest city of the Mexican state of Yucatán and the Yucatán Peninsula. It is located in the northwest part of the state, about from the Gulf of Mexico coast...
, is farther north than Mexico City
Mexico City
Mexico City is the Federal District , capital of Mexico and seat of the federal powers of the Mexican Union. It is a federal entity within Mexico which is not part of any one of the 31 Mexican states but belongs to the federation as a whole...
or Guadalajara
Guadalajara, Jalisco
Guadalajara is the capital of the Mexican state of Jalisco, and the seat of the municipality of Guadalajara. The city is located in the central region of Jalisco in the western-pacific area of Mexico. With a population of 1,564,514 it is Mexico's second most populous municipality...
.
Physical features
Beginning approximately 50 kilometers from the United States border, the Sierra Madre OccidentalSierra Madre Occidental
The Sierra Madre Occidental is a mountain range in western Mexico.-Setting:The range runs north to south, from just south of the Sonora–Arizona border southeast through eastern Sonora, western Chihuahua, Sinaloa, Durango, Zacatecas, Nayarit, Jalisco, Aguascalientes to Guanajuato, where it joins...
extends about 1250 kilometers south to the Río Santiago, where it merges with the Cordillera Neovolcánica range that runs east-west across central Mexico. The Sierra Madre Occidental lies approximately 300 kilometers inland from the west coast of Mexico at its northern end but approaches to within fifty kilometers of the coast near the Cordillera Neovolcánica. The northwest coastal plain is the name given the lowland area between the Sierra Madre Occidental and the Gulf of California
Gulf of California
The Gulf of California is a body of water that separates the Baja California Peninsula from the Mexican mainland...
. The Sierra Madre Occidental averages 2,250 meters in elevation, with peaks reaching 3,000 meters.

Sierra Madre Oriental
The Sierra Madre Oriental is a mountain range in northeastern Mexico.-Setting:Spanning the Sierra Madre Oriental runs from Coahuila south through Nuevo León, southwest Tamaulipas, San Luis Potosí, Querétaro, and Hidalgo to northern Puebla, where it joins with the east-west running Eje Volcánico...
starts at the Big Bend region of the border with the U.S. state of Texas and continues 1,350 kilometers until reaching Cofre de Perote
Cofre de Perote
Cofre de Perote, originally Naupa-Tecutépetl , is known also as Nauhcampatépetl. Both Nahuatl names mean something like 'Place of Four Mountain' or 'Mountain of the Lord of Four Places'...
, one of the major peaks of the Cordillera Neovolcánica. As is the case with the Sierra Madre Occidental, the Sierra Madre Oriental comes progressively closer to the coastline as it approaches its southern terminus, reaching to within 75 kilometers of the Gulf of Mexico
Gulf of Mexico
The Gulf of Mexico is a partially landlocked ocean basin largely surrounded by the North American continent and the island of Cuba. It is bounded on the northeast, north and northwest by the Gulf Coast of the United States, on the southwest and south by Mexico, and on the southeast by Cuba. In...
. The northeast coastal plain extends from the eastern slope of the Sierra Madre Oriental to the Gulf of Mexico. The median elevation of the Sierra Madre Oriental is 2,200 meters, with some peaks at 3,000 meters.
The Mexican altiplano, stretching from the United States border to the Cordillera Neovolcánica, occupies the vast expanse of land between the eastern and western sierra madres. A low east-west range divides the altiplano into northern and southern sections. These two sections, previously called the Mesa del Norte and Mesa Central, are now regarded by geographers as sections of one altiplano. The northern altiplano averages 1,100 meters in elevation and continues south from the Río Bravo del Norte through the states of Zacatecas
Zacatecas
Zacatecas officially Estado Libre y Soberano de Zacatecas is one of the 31 states which, with the Federal District, comprise the 32 Federal Entities of Mexico. It is divided in 58 municipalities and its capital city is Zacatecas....
and San Luis Potosí
San Luis Potosí
San Luis Potosí officially Estado Libre y Soberano de San Luis Potosí is one of the 31 states which, with the Federal District, comprise the 32 Federal Entities of Mexico. It is divided in 58 municipalities and its capital city is San Luis Potosí....
. Various narrow, isolated ridges cross the plateaus of the northern altiplano. Numerous depressions dot the region, the largest of which is the Bolsón de Mapimí
Bolsón de Mapimí
The Bolsón de Mapimí is an endorheic river basin located in the center-north of the Mexican Plateau.It is also known as the Comarca Lagunera, and is shared by the states of Durango, Coahuila, Chihuahua, and Zacatecas...
. The southern altiplano is higher than its northern counterpart, averaging 2,000 meters in elevation. The southern altiplano contains numerous valleys originally formed by ancient lakes. Several of Mexico's most prominent cities, including Mexico City
Mexico City
Mexico City is the Federal District , capital of Mexico and seat of the federal powers of the Mexican Union. It is a federal entity within Mexico which is not part of any one of the 31 Mexican states but belongs to the federation as a whole...
and Guadalajara
Guadalajara, Jalisco
Guadalajara is the capital of the Mexican state of Jalisco, and the seat of the municipality of Guadalajara. The city is located in the central region of Jalisco in the western-pacific area of Mexico. With a population of 1,564,514 it is Mexico's second most populous municipality...
, are located in the valleys of the southern altiplano.
One other significant mountain range, the Peninsular Ranges
Peninsular Ranges
The Peninsular Ranges are a group of mountain ranges, in the Pacific Coast Ranges, which stretch from southern California in the United States to the southern tip of Mexico's Baja California peninsula; they are part of the North American Coast Ranges that run along the Pacific coast from Alaska...
, cuts across the landscape of the northern half of Mexico. A southern extension of the California coastal ranges that parallel California's coast, the Mexican portion of the Peninsular Ranges extends from the United States border to the southern tip of the Baja California Peninsula, a distance of 1,430 kilometers. Peaks in the California system range in altitude from 2,200 meters in the north to only 250 meters near La Paz in the south. Narrow lowlands are found on the Pacific Ocean and the Gulf of California sides of the mountains.The Cordillera Neovolcánica is a belt 900 kilometers long and 130 kilometers wide, extending from the Pacific Ocean to the Gulf of Mexico. The Cordillera Neovolcánica begins at the Río Grande de Santiago and continues south to Colima, where it turns east along the nineteenth parallel to the central portion of the state of Veracruz. The region is distinguished by considerable seismic activity and contains Mexico's highest volcanic peaks. This range contains three peaks exceeding 5,000 meters: Pico de Orizaba (Citlaltépetl)--the third highest mountain in North America—and Popocatépetl and Iztaccíhuatl near Mexico City. The Cordillera Neovolcánica is regarded as the geological dividing line between North America and Central America.
Several important mountain ranges dominate the landscape of southern and southeastern Mexico. The Sierra Madre del Sur
Sierra Madre del Sur
The Sierra Madre del Sur is a mountain range in southern Mexico, extending from southern Michoacán east through Guerrero, to the Istmo de Tehuantepec in eastern Oaxaca.-Geography:...
extends 1,200 kilometers along Mexico's southern coast from the southwestern part of the Cordillera Neovolcánica to the nearly flat isthmus of Tehuantepec
Isthmus of Tehuantepec
The Isthmus of Tehuantepec is an isthmus in Mexico. It represents the shortest distance between the Gulf of Mexico and the Pacific Ocean, and prior to the opening of the Panama Canal was a major shipping route known simply as the Tehuantepec Route...
. Mountains in this range average 2,000 meters in elevation. The range averages 100 kilometers wide, but widens to 150 kilometers in the state of Oaxaca
Oaxaca
Oaxaca , , officially Estado Libre y Soberano de Oaxaca is one of the 31 states which, along with the Federal District, comprise the 32 federative entities of Mexico. It is divided into 571 municipalities; of which 418 are governed by the system of customs and traditions...
. The narrow southwest coastal plain extends from the Sierra Madre del Sur to the Pacific Ocean
Pacific Ocean
The Pacific Ocean is the largest of the Earth's oceanic divisions. It extends from the Arctic in the north to the Southern Ocean in the south, bounded by Asia and Australia in the west, and the Americas in the east.At 165.2 million square kilometres in area, this largest division of the World...
. The Sierra Madre de Oaxaca
Sierra Madre de Oaxaca
The Sierra Madre de Oaxaca is a mountain range in southern Mexico. It begins at Pico de Orizaba and extends in a southeasterly direction for 300 km until reaching the Isthmus of Tehuantepec...
begins at Pico de Orizaba and extends in a southeasterly direction for 300 kilometers until reaching the isthmus of Tehuantepec. Peaks in the Sierra Madre de Oaxaca average 2,500 meters in elevation, with some peaks exceeding 3,000 meters. South of the isthmus of Tehuantepec, the Sierra Madre de Chiapas runs 280 kilometers along the Pacific Coast from the Oaxaca
Oaxaca
Oaxaca , , officially Estado Libre y Soberano de Oaxaca is one of the 31 states which, along with the Federal District, comprise the 32 federative entities of Mexico. It is divided into 571 municipalities; of which 418 are governed by the system of customs and traditions...
-Chiapas
Chiapas
Chiapas officially Estado Libre y Soberano de Chiapas is one of the 31 states that, with the Federal District, comprise the 32 Federal Entities of Mexico. It is divided in 118 municipalities and its capital city is Tuxtla Gutierrez. Other important cites in Chiapas include San Cristóbal de las...
border to Mexico's border with Guatemala
Guatemala
Guatemala is a country in Central America bordered by Mexico to the north and west, the Pacific Ocean to the southwest, Belize to the northeast, the Caribbean to the east, and Honduras and El Salvador to the southeast...
. Although average elevation is only 1,500 meters, one peak--Volcán de Tacuma--exceeds 4,000 meters in elevation. Finally, the Meseta Central de Chiapas extends 250 kilometers through the central part of Chiapas to Guatemala. The average height of peaks of the Meseta Central de Chiapas is 2,000 meters. The Chiapas central valley separates the Meseta Central de Chiapas and the Sierra Madre de Chiapas.
Mexico has nearly 150 rivers, two-thirds of which empty into the Pacific Ocean and the remainder of which flow into the Gulf of Mexico
Gulf of Mexico
The Gulf of Mexico is a partially landlocked ocean basin largely surrounded by the North American continent and the island of Cuba. It is bounded on the northeast, north and northwest by the Gulf Coast of the United States, on the southwest and south by Mexico, and on the southeast by Cuba. In...
or the Caribbean Sea
Caribbean Sea
The Caribbean Sea is a sea of the Atlantic Ocean located in the tropics of the Western hemisphere. It is bounded by Mexico and Central America to the west and southwest, to the north by the Greater Antilles, and to the east by the Lesser Antilles....
. Despite this apparent abundance of water, water volume is unevenly distributed throughout the country. Indeed, five rivers—the Usumacinta
Usumacinta River
The Usumacinta River is a river in southeastern Mexico and northwestern Guatemala. It is formed by the junction of the Pasión River, which arises in the Sierra de Santa Cruz and the Salinas River, also known as the Chixoy, or the Negro, which descends from the Sierra Madre de Guatemala...
, Grijalva
Grijalva River
Grijalva River, formerly known as Tabasco River. is a 480 km long river in southeastern Mexico. It is named after Juan de Grijalva who visited the area in 1518. The river rises in Chiapas highlands and flows from Chiapas to the state of Tabasco through the Sumidero Canyon into the Bay of...
, Papaloapán, Coatzacoalcos
Coatzacoalcos River
The Coatzacoalcos is a large river that feeds mainly the south part of the state of Veracruz; it originates in the Sierra de Niltepec and crosses the state of Oaxaca in the region of the Isthmus of Tehuantepec, flowing for toward the Gulf of Mexico. Tributaries include El Corte, Sarabia,...
, and Pánuco
Pánuco River
The Pánuco River is a river in Mexico that flows from the River Moctezuma in the Valley of Mexico to the Gulf of Mexico.At its source, it serves as a channel for water-drainage for Mexico City. From there, it becomes the state border between Hidalgo and Querétaro as it moves towards San Luis...
--account for 52 % of Mexico's average annual volume of surface water. All five rivers flow into the Gulf of Mexico; only the Río Pánuco is outside southeastern Mexico, which contains approximately 15 % of national territory and 12 % of the national population. In contrast, northern and central Mexico, with 47 % of the national area and almost 60 % of Mexico's population, have less than 10 % of the country's water resources.
Seismic activity
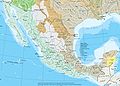
Most of the Mexican landmass rests on the westward moving North American plate. The Pacific Ocean floor off southern Mexico, however, is being carried northeast by the underlying motion of the Cocos Plate
Cocos Plate
The Cocos Plate is an oceanic tectonic plate beneath the Pacific Ocean off the west coast of Central America, named for Cocos Island, which rides upon it.-Geology:...
. Ocean floor material is relatively dense; when it strikes the lighter granite of the Mexican landmass, the ocean floor is forced under the landmass, creating the deep Middle America Trench
Middle America Trench
The Middle America Trench is a major subduction zone, an oceanic trench in the eastern Pacific Ocean off the southwestern coast of Middle America, stretching from central Mexico to Costa Rica...
that lies off Mexico's southern coast. The westward moving land atop the North American plate is slowed and crumpled where it meets the Cocos plate, creating the mountain ranges of southern Mexico. The subduction of the Cocos plate accounts for the frequency of earthquakes near Mexico's southern coast. As the rocks constituting the ocean floor are forced down, they melt, and the molten material is forced up through weaknesses in the surface rock, creating the volcanoes in the Cordillera Neovolcánica across central Mexico.
Areas of Mexico's coastline on the Gulf of California
Gulf of California
The Gulf of California is a body of water that separates the Baja California Peninsula from the Mexican mainland...
, including the Baja California Peninsula, are riding northwestward on the Pacific plate. Rather than one plate subducting, the Pacific and North American plates grind past each other, creating a slip fault that is the southern extension of the San Andreas fault
San Andreas Fault
The San Andreas Fault is a continental strike-slip fault that runs a length of roughly through California in the United States. The fault's motion is right-lateral strike-slip...
in California. Motion along this fault in the past pulled Baja California away from the coast, creating the Gulf of California. Continued motion along this fault is the source of earthquakes in western Mexico.
Mexico has a long history of destructive earthquakes and volcanic eruptions. In September 1985, an earthquake measuring 8.1 on the Richter scale and centered in the subduction zone off Acapulco killed more than 4,000 people in Mexico City, more than 300 kilometers away. Volcán de Colima, south of Guadalajara, erupted in 1994, and El Chichón, in southern Mexico, underwent a violent eruption in 1983. Parícutin
Paricutín
Parícutin is a cinder cone volcano in the Mexican state of Michoacán, close to a lava-covered village of the same name. It appears on many versions of the Seven Natural Wonders of the World...
in northwest Mexico began as puffs of smoke in a cornfield in 1943; a decade later the volcano was 424 meters high. Although dormant for decades, Popocatépetl
Popocatépetl
Popocatépetl also known as "Popochowa" by the local population is an active volcano and, at , the second highest peak in Mexico after the Pico de Orizaba...
and Iztaccíhuatl
Iztaccíhuatl
Iztaccíhuatl , is the third highest mountain in Mexico, after the Pico de Orizaba, , and Popocatépetl, . Its name is Nahuatl for "White woman"....
("smoking warrior" and "white lady," respectively, in Nahuatl
Nahuatl
Nahuatl is thought to mean "a good, clear sound" This language name has several spellings, among them náhuatl , Naoatl, Nauatl, Nahuatl, Nawatl. In a back formation from the name of the language, the ethnic group of Nahuatl speakers are called Nahua...
) occasionally send out puffs of smoke clearly visible in Mexico City, a reminder to the capital's inhabitants that volcanic activity is near. Popocatépetl showed renewed activity in 1995 and 1996, forcing the evacuation of several nearby villages and causing concern by seismologists and government officials about the effect that a large-scale eruption might have on the heavily populated region nearby.
Climate



Tropic of Cancer
The Tropic of Cancer, also referred to as the Northern tropic, is the circle of latitude on the Earth that marks the most northerly position at which the Sun may appear directly overhead at its zenith...
effectively divides the country into temperate and tropical zones. Land north of the twenty-fourth parallel experiences cooler temperatures during the winter months. South of the twenty-fourth parallel, temperatures are fairly constant year round and vary solely as a function of elevation.
Areas south of the twentieth-fourth parallel with elevations up to 1000 metres (3,281 ft) (the southern parts of both coastal plains as well as the Yucatán Peninsula
Yucatán Peninsula
The Yucatán Peninsula, in southeastern Mexico, separates the Caribbean Sea from the Gulf of Mexico, with the northern coastline on the Yucatán Channel...
), have a yearly median temperature between 24 and 28 °C (75.2 and 82.4 °F). Temperatures here remain high throughout the year, with only a 5 C-change difference between winter and summer median temperatures. Although low-lying areas north of the twentieth-fourth parallel are hot and humid during the summer, they generally have lower yearly temperature averages (from 20 to 24 °C (68 to 75.2 °F)) because of more moderate conditions during the winter.
Between 1000 and 2000 m (3,280.8 and 6,561.7 ft), one encounters yearly average temperatures between 16 and 20 °C (60.8 and 68 °F). Towns and cities at this elevation south of the twenty-fourth parallel have relatively constant, pleasant temperatures throughout the year, whereas more northerly locations experience sizeable seasonal variations. Above 2000 metres (6,562 ft), temperatures drop as low as an average yearly range between 8 and 12 °C (46.4 and 53.6 °F) in the Cordillera Neovolcánica. At 2300 metres (7,546 ft), Mexico City
Mexico City
Mexico City is the Federal District , capital of Mexico and seat of the federal powers of the Mexican Union. It is a federal entity within Mexico which is not part of any one of the 31 Mexican states but belongs to the federation as a whole...
has a yearly median temperature of 15 °C (59 °F) with pleasant summers and mild winters. Average daily highs and lows for May, the warmest month, are 26 and 12 °C (78.8 and 53.6 °F), and average daily highs and lows for January, the coldest month, are 19 and 6 °C (66.2 and 42.8 °F).
Rainfall varies widely both by location and season. Arid or semiarid conditions are encountered in the Baja California Peninsula
Baja California Peninsula
The Baja California peninsula , is a peninsula in northwestern Mexico. Its land mass separates the Pacific Ocean from the Gulf of California. The Peninsula extends from Mexicali, Baja California in the north to Cabo San Lucas, Baja California Sur in the south.The total area of the Baja California...
, the northwestern state of Sonora
Sonora
Sonora officially Estado Libre y Soberano de Sonora is one of the 31 states which, with the Federal District, comprise the 32 Federal Entities of Mexico. It is divided into 72 municipalities; the capital city is Hermosillo....
, the northern altiplano, and also significant portions of the southern altiplano. Rainfall in these regions averages between 300 and 600 mm (11.8 and 23.6 in) per year, although even less in some areas, particularly in Baja California Norte. Average rainfall totals are between 600 and 1000 mm (23.6 and 39.4 in) in most of the major populated areas of the southern altiplano, including Mexico City
Mexico City
Mexico City is the Federal District , capital of Mexico and seat of the federal powers of the Mexican Union. It is a federal entity within Mexico which is not part of any one of the 31 Mexican states but belongs to the federation as a whole...
and Guadalajara
Guadalajara, Jalisco
Guadalajara is the capital of the Mexican state of Jalisco, and the seat of the municipality of Guadalajara. The city is located in the central region of Jalisco in the western-pacific area of Mexico. With a population of 1,564,514 it is Mexico's second most populous municipality...
. Low-lying areas along the Gulf of Mexico
Gulf of Mexico
The Gulf of Mexico is a partially landlocked ocean basin largely surrounded by the North American continent and the island of Cuba. It is bounded on the northeast, north and northwest by the Gulf Coast of the United States, on the southwest and south by Mexico, and on the southeast by Cuba. In...
receive in excess of 1000 millimetres (39.4 in) of rainfall in an average year, with the wettest region being the southeastern state of Tabasco, which typically receives approximately 2000 millimetres (78.7 in) of rainfall on an annual basis. Parts of the northern altiplano, highlands and high peaks in the Sierra Madre Occidental
Sierra Madre Occidental
The Sierra Madre Occidental is a mountain range in western Mexico.-Setting:The range runs north to south, from just south of the Sonora–Arizona border southeast through eastern Sonora, western Chihuahua, Sinaloa, Durango, Zacatecas, Nayarit, Jalisco, Aguascalientes to Guanajuato, where it joins...
and the Sierra Madre Oriental
Sierra Madre Oriental
The Sierra Madre Oriental is a mountain range in northeastern Mexico.-Setting:Spanning the Sierra Madre Oriental runs from Coahuila south through Nuevo León, southwest Tamaulipas, San Luis Potosí, Querétaro, and Hidalgo to northern Puebla, where it joins with the east-west running Eje Volcánico...
occasionally receive significant snowfalls.
Mexico has pronounced wet and dry seasons. Most of the country experiences a rainy season from June to mid-October and significantly less rain during the remainder of the year. February and July generally are the driest and wettest months, respectively. Mexico City
Mexico City
Mexico City is the Federal District , capital of Mexico and seat of the federal powers of the Mexican Union. It is a federal entity within Mexico which is not part of any one of the 31 Mexican states but belongs to the federation as a whole...
, for example, receives an average of only 5 millimetre (0.196850393700787 in) of rain during February but more than 160 millimetres (6.3 in) in July. Coastal areas, especially those along the Gulf of Mexico, experience the largest amounts of rain in September. Tabasco
Tabasco
Tabasco officially Estado Libre y Soberano de Tabasco is one of the 31 states which, with the Federal District, comprise the 32 Federal Entities of Mexico. It is divided in 17 municipalities and its capital city is Villahermosa....
typically records more than 300 millimetres (11.8 in) of rain during that month. A small coastal area of northwestern coastal Mexico around Tijuana
Tijuana
Tijuana is the largest city on the Baja California Peninsula and center of the Tijuana metropolitan area, part of the international San Diego–Tijuana metropolitan area. An industrial and financial center of Mexico, Tijuana exerts a strong influence on economics, education, culture, art, and politics...
has a Mediterranean climate
Mediterranean climate
A Mediterranean climate is the climate typical of most of the lands in the Mediterranean Basin, and is a particular variety of subtropical climate...
with considerable coastal fog and a rainy season that occurs in winter.
Mexico lies squarely within the hurricane belt, and all regions of both coasts are susceptible to these storms from June through November. Hurricanes on the Pacific coast are often less violent than those affecting Mexico's eastern coastline. Several hurricanes per year strike the Caribbean
Caribbean
The Caribbean is a crescent-shaped group of islands more than 2,000 miles long separating the Gulf of Mexico and the Caribbean Sea, to the west and south, from the Atlantic Ocean, to the east and north...
and Gulf of Mexico
Gulf of Mexico
The Gulf of Mexico is a partially landlocked ocean basin largely surrounded by the North American continent and the island of Cuba. It is bounded on the northeast, north and northwest by the Gulf Coast of the United States, on the southwest and south by Mexico, and on the southeast by Cuba. In...
coastline, however, and these storms bring high winds, heavy rain, extensive damage, and occasional loss of life. Hurricane Gilbert
Hurricane Gilbert
Hurricane Gilbert was an extremely powerful Cape Verde-type hurricane that formed during the 1988 Atlantic hurricane season and created widespread destruction in the Caribbean Sea and the Gulf of Mexico. It is the second most intense hurricane ever observed in the Atlantic basin behind only...
passed directly over Cancún
Cancún
Cancún is a city of international tourism development certified by the UNWTO . Located on the northeast coast of Quintana Roo in southern Mexico, more than 1,700 km from Mexico City, the Project began operations in 1974 as Integrally Planned Center, a pioneer of FONATUR Cancún is a city of...
in September 1988, with winds in excess of 200 kilometres per hour (124 mph), producing major damage to hotels in the resort area. It then struck northeast Mexico, where flooding from the heavy rain killed dozens in the Monterrey
Monterrey
Monterrey , is the capital city of the northeastern state of Nuevo León in the country of Mexico. The city is anchor to the third-largest metropolitan area in Mexico and is ranked as the ninth-largest city in the nation. Monterrey serves as a commercial center in the north of the country and is the...
area and caused extensive damage to livestock and vegetable crops.
Environmental conditions

Biodiversity Action Plan
A Biodiversity Action Plan is an internationally recognized program addressing threatened species and habitats and is designed to protect and restore biological systems. The original impetus for these plans derives from the 1992 Convention on Biological Diversity...
to address issues of endangered species
Endangered species
An endangered species is a population of organisms which is at risk of becoming extinct because it is either few in numbers, or threatened by changing environmental or predation parameters...
and habitat
Habitat (ecology)
A habitat is an ecological or environmental area that is inhabited by a particular species of animal, plant or other type of organism...
s that merit protection.
Soil destruction is particularly pronounced in the north and northwest, with more than 60% of land considered in a total or accelerated state of erosion. Fragile because of its semiarid and arid character, the soil of the region has become increasingly damaged through excessive cattle-raising and irrigation with waters containing high levels of salinity. The result is a mounting problem of desertification throughout the region.
Mexico's vast coastline faces a different, but no less difficult, series of environmental problems. For example, inadequately regulated petroleum exploitation in the Coatzacoalcos
Coatzacoalcos
Coatzacoalcos is a major port city in the southern part of the Mexican state of Veracruz, on the Coatzacoalcos River. Coatzacoalcos comes from an indigenous word meaning "Site of the Snake" or "Where the snake hides"...
-Minatitlán
Minatitlán, Veracruz
Minatitlán is a city in southeastern Mexican state of Veracruz in the Olmec region of the state and the north of the Isthmus of Tehuantepec.In 2010 the greater metropolitan area had a population of 356,020...
zone in the Gulf of Mexico has caused serious damage to the waters and fisheries of Río Coatzacoalcos. The deadly explosion that racked a working-class neighborhood in Guadalajara in April 1992 serves as an appropriate symbol of environmental damage in Mexico. More than 1000 barrels (158,987.3 l) of gasoline seeped from a corroded Mexican Petroleum (Petróleos Mexicanos—Pemex) pipeline into the municipal sewer system, where it combined with gases and industrial residuals to produce a massive explosion that killed 190 persons and injured nearly 1,500 others.
Mexico City
Mexico City
Mexico City is the Federal District , capital of Mexico and seat of the federal powers of the Mexican Union. It is a federal entity within Mexico which is not part of any one of the 31 Mexican states but belongs to the federation as a whole...
confronts authorities with perhaps their most daunting environmental challenge. Geography and extreme population levels have combined to produce one of the world's most polluted urban areas. Mexico City sits in a valley surrounded on three sides by mountains, which serve to trap contaminants produced by the metropolitan area's 15 million residents. One government study in the late 1980s determined that nearly 5 million tons of contaminants were emitted annually in the atmosphere
Atmosphere
An atmosphere is a layer of gases that may surround a material body of sufficient mass, and that is held in place by the gravity of the body. An atmosphere may be retained for a longer duration, if the gravity is high and the atmosphere's temperature is low...
, a tenfold increase over the previous decade. Carbons and hydrocarbons from the region's more than 3 million vehicles account for approximately 80% of these contaminants, with another 15%, primarily of sulfur
Sulfur
Sulfur or sulphur is the chemical element with atomic number 16. In the periodic table it is represented by the symbol S. It is an abundant, multivalent non-metal. Under normal conditions, sulfur atoms form cyclic octatomic molecules with chemical formula S8. Elemental sulfur is a bright yellow...
and nitrogen
Nitrogen
Nitrogen is a chemical element that has the symbol N, atomic number of 7 and atomic mass 14.00674 u. Elemental nitrogen is a colorless, odorless, tasteless, and mostly inert diatomic gas at standard conditions, constituting 78.08% by volume of Earth's atmosphere...
, coming from industrial plants. The resulting dangerous mix is responsible for a wide range of respiratory illnesses. One study of twelve urban areas worldwide in the mid-1980s concluded that the residents of Mexico City had the highest levels of lead
Lead
Lead is a main-group element in the carbon group with the symbol Pb and atomic number 82. Lead is a soft, malleable poor metal. It is also counted as one of the heavy metals. Metallic lead has a bluish-white color after being freshly cut, but it soon tarnishes to a dull grayish color when exposed...
and cadmium
Cadmium
Cadmium is a chemical element with the symbol Cd and atomic number 48. This soft, bluish-white metal is chemically similar to the two other stable metals in group 12, zinc and mercury. Similar to zinc, it prefers oxidation state +2 in most of its compounds and similar to mercury it shows a low...
in their blood. The volume of pollutants from Mexico City has damaged the surrounding ecosystem
Ecosystem
An ecosystem is a biological environment consisting of all the organisms living in a particular area, as well as all the nonliving , physical components of the environment with which the organisms interact, such as air, soil, water and sunlight....
as well. For example, wastewater from Mexico City that flows north and is used for irrigation in the state of Hidalgo has been linked to congenital birth defects and high levels of gastrointestinal diseases in that state.
Beginning in the mid-1980s, the government enacted numerous antipollution policies in Mexico City with varied degrees of success. Measures such as vehicle emissions inspections, the introduction of unleaded gasoline, and the installation of catalytic converters on new vehicles helped reduce pollution generated by trucks and buses. In contrast, one of the government's most prominent actions, the No Driving Day program, may have inadvertently contributed to higher pollution levels. Under the program, metropolitan area residents were prohibited from driving their vehicles one day each work week based on the last number of their license plate. However, those with the resources to do so purchased additional automobiles to use on the day their principal vehicle was prohibited from driving, thus adding to the region's vehicle stock. Thermal inversions reached such dangerous levels at various times in the mid-1990s that the government declared pollution emergencies, necessitating sharp temporary cutbacks in vehicle use and industrial production.
General indicators
Climate: varies from tropical to desert.Terrain: high, rugged mountains; low coastal plains; high plateaus; desert.
Elevation extremes:
- lowest point: Laguna Salada -10 m
- highest point: Pico de OrizabaPico de OrizabaThe Pico de Orizaba, or Citlaltépetl , is a stratovolcano, the highest mountain in Mexico and the third highest in North America. It rises above sea level in the eastern end of the Trans-Mexican Volcanic Belt, on the border between the states of Veracruz and Puebla...
volcano 5,610 m
Natural resources: petroleum
Petroleum
Petroleum or crude oil is a naturally occurring, flammable liquid consisting of a complex mixture of hydrocarbons of various molecular weights and other liquid organic compounds, that are found in geologic formations beneath the Earth's surface. Petroleum is recovered mostly through oil drilling...
, silver
Silver
Silver is a metallic chemical element with the chemical symbol Ag and atomic number 47. A soft, white, lustrous transition metal, it has the highest electrical conductivity of any element and the highest thermal conductivity of any metal...
, copper
Copper
Copper is a chemical element with the symbol Cu and atomic number 29. It is a ductile metal with very high thermal and electrical conductivity. Pure copper is soft and malleable; an exposed surface has a reddish-orange tarnish...
, gold
Gold
Gold is a chemical element with the symbol Au and an atomic number of 79. Gold is a dense, soft, shiny, malleable and ductile metal. Pure gold has a bright yellow color and luster traditionally considered attractive, which it maintains without oxidizing in air or water. Chemically, gold is a...
, lead
Lead
Lead is a main-group element in the carbon group with the symbol Pb and atomic number 82. Lead is a soft, malleable poor metal. It is also counted as one of the heavy metals. Metallic lead has a bluish-white color after being freshly cut, but it soon tarnishes to a dull grayish color when exposed...
, zinc
Zinc
Zinc , or spelter , is a metallic chemical element; it has the symbol Zn and atomic number 30. It is the first element in group 12 of the periodic table. Zinc is, in some respects, chemically similar to magnesium, because its ion is of similar size and its only common oxidation state is +2...
, natural gas
Natural gas
Natural gas is a naturally occurring gas mixture consisting primarily of methane, typically with 0–20% higher hydrocarbons . It is found associated with other hydrocarbon fuel, in coal beds, as methane clathrates, and is an important fuel source and a major feedstock for fertilizers.Most natural...
and timber
Timber
Timber may refer to:* Timber, a term common in the United Kingdom and Australia for wood materials * Timber, Oregon, an unincorporated community in the U.S...
.
Land use:
- arable land: 12%
- permanent crops: 1%
- permanent pastures: 39%
- forests and woodland: 26%
- other: 22% (1993 est.)
Irrigated land: 61,000 km2 (1993 est.)
Natural hazards: Tsunami
Tsunami
A tsunami is a series of water waves caused by the displacement of a large volume of a body of water, typically an ocean or a large lake...
s along the Pacific coast, volcano
Volcano
2. Bedrock3. Conduit 4. Base5. Sill6. Dike7. Layers of ash emitted by the volcano8. Flank| 9. Layers of lava emitted by the volcano10. Throat11. Parasitic cone12. Lava flow13. Vent14. Crater15...
es and destructive earthquake
Earthquake
An earthquake is the result of a sudden release of energy in the Earth's crust that creates seismic waves. The seismicity, seismism or seismic activity of an area refers to the frequency, type and size of earthquakes experienced over a period of time...
s in the center and south, and hurricanes on the Gulf of Mexico and Caribbean coasts.
Environment – current issues: Natural fresh water resources scarce and polluted in north, inaccessible and poor quality in center and extreme southeast; raw sewage and industrial effluents polluting rivers in urban areas; deforestation
Deforestation
Deforestation is the removal of a forest or stand of trees where the land is thereafter converted to a nonforest use. Examples of deforestation include conversion of forestland to farms, ranches, or urban use....
; widespread erosion
Erosion
Erosion is when materials are removed from the surface and changed into something else. It only works by hydraulic actions and transport of solids in the natural environment, and leads to the deposition of these materials elsewhere...
; desertification
Desertification
Desertification is the degradation of land in drylands. Caused by a variety of factors, such as climate change and human activities, desertification is one of the most significant global environmental problems.-Definitions:...
; serious air pollution in the national capital
Mexico City
Mexico City is the Federal District , capital of Mexico and seat of the federal powers of the Mexican Union. It is a federal entity within Mexico which is not part of any one of the 31 Mexican states but belongs to the federation as a whole...
and urban centers along the US-Mexico border.
Environment – international agreements: Party to: Biodiversity, Climate Change, Desertification, Endangered Species, Hazardous Wastes, Law of the Sea
Law of the sea
Law of the sea may refer to:* United Nations Convention on the Law of the Sea* Admiralty law* The Custom of the Sea...
, Marine Dumping, Marine Life Conservation, Nuclear Test Ban, Ozone Layer Protection, Ship Pollution, Wetlands, Whaling and Kyoto Protocol
Kyoto Protocol
The Kyoto Protocol is a protocol to the United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change , aimed at fighting global warming...
.
See also
- 4000 meter peaks of Mexico
- Geology of North America
- Mountain peaks of MexicoMountain peaks of MexicoThis article comprises three sortable tables of the major mountain peaks of Mexico.Topographic elevation is the vertical distance above the reference geoid, a precise mathematical model of the Earth's sea level as an equipotential gravitational surface. Topographic prominence is the elevation...

