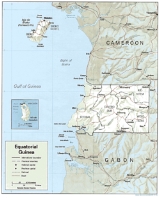
Geography of Equatorial Guinea
Encyclopedia
 |
|
| Continent Continent A continent is one of several very large landmasses on Earth. They are generally identified by convention rather than any strict criteria, with seven regions commonly regarded as continents—they are : Asia, Africa, North America, South America, Antarctica, Europe, and Australia.Plate tectonics is... |
Africa Africa Africa is the world's second largest and second most populous continent, after Asia. At about 30.2 million km² including adjacent islands, it covers 6% of the Earth's total surface area and 20.4% of the total land area... |
| Geographic coordinates | 2°00′N 10°00′E |
| Area Area Area is a quantity that expresses the extent of a two-dimensional surface or shape in the plane. Area can be understood as the amount of material with a given thickness that would be necessary to fashion a model of the shape, or the amount of paint necessary to cover the surface with a single coat... - Total - % water |
Ranked 141st 28,051 km² Negligible |
| Coastline | 296 km |
| Highest point | Pico Basile Pico Basilé Pico Basilé is the highest mountain on the island of Bioko, which is part of Equatorial Guinea. With an altitude of 9,878 ft , it is the summit of the largest and highest of three overlapping basaltic shield volcanoes which form the island. From the summit, Mt. Cameroon can be seen to the... , 3,008 m |
| Lowest point | Atlantic Ocean Atlantic Ocean The Atlantic Ocean is the second-largest of the world's oceanic divisions. With a total area of about , it covers approximately 20% of the Earth's surface and about 26% of its water surface area... , 0 m |
| Longest river | Uola River |
| Land Use - Arable land - Permanent crops - Permanent pastures - Forests and woodlands - Other |
5 % 4 % 4 % 46 % 41 % (1993 est.) |
| Climate Climate Climate encompasses the statistics of temperature, humidity, atmospheric pressure, wind, rainfall, atmospheric particle count and other meteorological elemental measurements in a given region over long periods... : |
Tropical Tropics The tropics is a region of the Earth surrounding the Equator. It is limited in latitude by the Tropic of Cancer in the northern hemisphere at approximately N and the Tropic of Capricorn in the southern hemisphere at S; these latitudes correspond to the axial tilt of the Earth... |
| add more | need ideas |
| Natural resources | petroleum Petroleum Petroleum or crude oil is a naturally occurring, flammable liquid consisting of a complex mixture of hydrocarbons of various molecular weights and other liquid organic compounds, that are found in geologic formations beneath the Earth's surface. Petroleum is recovered mostly through oil drilling... , timber Timber Timber may refer to:* Timber, a term common in the United Kingdom and Australia for wood materials * Timber, Oregon, an unincorporated community in the U.S... , small unexploited deposits of gold Gold Gold is a chemical element with the symbol Au and an atomic number of 79. Gold is a dense, soft, shiny, malleable and ductile metal. Pure gold has a bright yellow color and luster traditionally considered attractive, which it maintains without oxidizing in air or water. Chemically, gold is a... , manganese Manganese Manganese is a chemical element, designated by the symbol Mn. It has the atomic number 25. It is found as a free element in nature , and in many minerals... , uranium Uranium Uranium is a silvery-white metallic chemical element in the actinide series of the periodic table, with atomic number 92. It is assigned the chemical symbol U. A uranium atom has 92 protons and 92 electrons, of which 6 are valence electrons... |
| Environmental issues | drinking water Drinking water Drinking water or potable water is water pure enough to be consumed or used with low risk of immediate or long term harm. In most developed countries, the water supplied to households, commerce and industry is all of drinking water standard, even though only a very small proportion is actually... , desertification Desertification Desertification is the degradation of land in drylands. Caused by a variety of factors, such as climate change and human activities, desertification is one of the most significant global environmental problems.-Definitions:... |
The Republic of Equatorial Guinea
Equatorial Guinea
Equatorial Guinea, officially the Republic of Equatorial Guinea where the capital Malabo is situated.Annobón is the southernmost island of Equatorial Guinea and is situated just south of the equator. Bioko island is the northernmost point of Equatorial Guinea. Between the two islands and to the...
is located in west central Africa
Africa
Africa is the world's second largest and second most populous continent, after Asia. At about 30.2 million km² including adjacent islands, it covers 6% of the Earth's total surface area and 20.4% of the total land area...
. Bioko Island
Bioko
Bioko is an island 32 km off the west coast of Africa, specifically Cameroon, in the Gulf of Guinea. It is the northernmost part of Equatorial Guinea with a population of 124,000 and an area of . It is volcanic with its highest peak the Pico Basile at .-Geography:Bioko has a total area of...
lies about 40 kilometres (24.9 mi) from Cameroon
Cameroon
Cameroon, officially the Republic of Cameroon , is a country in west Central Africa. It is bordered by Nigeria to the west; Chad to the northeast; the Central African Republic to the east; and Equatorial Guinea, Gabon, and the Republic of the Congo to the south. Cameroon's coastline lies on the...
. Annobón
Annobón
Annobón may refer to:* Annobón Province* Annobonese language* Annobon people...
Island lies about 595 kilometres (370 mi) southwest of Bioko Island. The larger continental region of Rio Muni
Río Muni
Río Muni is the Continental Region of Equatorial Guinea, and comprises the mainland geographical region, covering 26,017 km².-History:Río Muni was ceded by Portugal to Spain in 1778 in the Treaty of El Pardo...
lies between Cameroon and Gabon
Gabon
Gabon , officially the Gabonese Republic is a state in west central Africa sharing borders with Equatorial Guinea to the northwest, Cameroon to the north, and with the Republic of the Congo curving around the east and south. The Gulf of Guinea, an arm of the Atlantic Ocean is to the west...
on the mainland; it includes the islands of Corisco
Corisco
Corisco, or Mandj, is a small island of Equatorial Guinea, located 29 km southwest of the Rio Muni estuary that defines the border with Gabon...
, Elobey Grande
Elobey Grande
Elobey Grande or Great Elobey is an island of Equatorial Guinea, lying at the mouth of the Mitémélé River. It is sparsely inhabited. Elobey Chico is a smaller island offshore, now uninhabited but once the colonial capital of the Rio Muni....
, Elobey Chico
Elobey Chico
Elobey Chico or Little Elobey is a small island offshore the coast of Equatorial Guinea, lying near the mouth of the Mitémélé River. The island is now uninhabited but was once de facto colonial capital of the Spanish territory of Rio Muni....
, and adjacent islets.
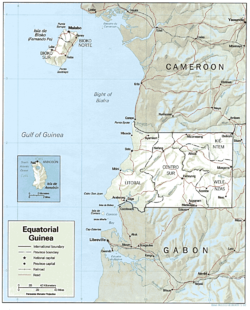
Bioko Island, called Fernando Po until the 1970s, is the largest island in the Gulf of Guinea
Gulf of Guinea
The Gulf of Guinea is the northeasternmost part of the tropical Atlantic Ocean between Cape Lopez in Gabon, north and west to Cape Palmas in Liberia. The intersection of the Equator and Prime Meridian is in the gulf....
- 2017 square kilometres (779 sq mi). It is shaped like a boot, with two large volcanic formations separated by a valley that bisects the island at its narrowest point. The 195 kilometres (121 mi) coastline is steep and rugged in the south but lower and more accessible in the north, with excellent harbors at Malabo
Malabo
Malabo is the capital of Equatorial Guinea, located on the northern coast of Bioko Island on the rim of a sunken volcano....
and Luba
Luba, Equatorial Guinea
Luba is the second largest town of Bioko in Equatorial Guinea, having a population of around 7,000 people. It lies on the west coast beneath volcanic peaks and is a port for the logging industry...
, and several scenic beaches between those towns.
On the continent, Rio Muni covers 26003 square kilometres (10,040 sq mi). The coastal plain gives way to a succession of valleys separated by low hills and spurs of the Crystal Mountains. The Rio Benito (Mbini) which divides Rio Muni in half, is unnavigable except for a 20-kilometer stretch at its estuary. Temperatures and humidity in Rio Muni are generally lower than on Bioko Island.
Annobon Island, named for its discovery on New Year's Day 1472, is a small volcanic island covering 18 square kilometres (6.9 sq mi). The coastline is abrupt except in the north; the principal volcanic cone contains a small lake. Most of the estimated 1,900 inhabitants are fisherman specializing in traditional, smallscale tuna fishing and whaling. The climate is tropical—heavy rainfall, high humidity, and frequent seasonal changes with violent windstorms.
Location:
Western Africa
Africa
Africa is the world's second largest and second most populous continent, after Asia. At about 30.2 million km² including adjacent islands, it covers 6% of the Earth's total surface area and 20.4% of the total land area...
, bordering the Bight of Biafra, between Cameroon
Cameroon
Cameroon, officially the Republic of Cameroon , is a country in west Central Africa. It is bordered by Nigeria to the west; Chad to the northeast; the Central African Republic to the east; and Equatorial Guinea, Gabon, and the Republic of the Congo to the south. Cameroon's coastline lies on the...
and Gabon
Gabon
Gabon , officially the Gabonese Republic is a state in west central Africa sharing borders with Equatorial Guinea to the northwest, Cameroon to the north, and with the Republic of the Congo curving around the east and south. The Gulf of Guinea, an arm of the Atlantic Ocean is to the west...
.
Boundaries
Equatorial Guinea's land boundaries total 539 km. It borders CameroonCameroon
Cameroon, officially the Republic of Cameroon , is a country in west Central Africa. It is bordered by Nigeria to the west; Chad to the northeast; the Central African Republic to the east; and Equatorial Guinea, Gabon, and the Republic of the Congo to the south. Cameroon's coastline lies on the...
(189 km) in the north and Gabon
Gabon
Gabon , officially the Gabonese Republic is a state in west central Africa sharing borders with Equatorial Guinea to the northwest, Cameroon to the north, and with the Republic of the Congo curving around the east and south. The Gulf of Guinea, an arm of the Atlantic Ocean is to the west...
(350 km) in the east and south.
Maritime claims:
exclusive economic zone:
200 nmi (370.4 km; 230.2 mi)
territorial sea:
12 nmi (22.2 km; 13.8 mi)
Climate
The climate of both the continental region and the islands is typically equatorial, with high temperatures, heavy rainfall, and much cloud cover most of the year. Local variations are due to differences in altitude and proximity to the sea. The wet seasons in the continental region are from February to June and from September to December. Rainfall is higher on the coast than inland. In Bata the rainiest months are September, October, and November, with rainfall averaging more than 94 in (2,388 mm) a year. At Calatrava, farther south on the coast, it sometimes reaches 180 in (4,572 mm). Inland, however, rainfall diminishes; MikomesengMicomeseng
Micomeseng is a city in Equatorial Guinea. It is located in Kié-Ntem Province and has a population of 5813....
, for example, receives only about 58 in (1,473 mm). The average annual temperature is about 79 °F (26.1 °C) and is fairly constant throughout the year. The temperature maxima are somewhat lower than in Bioko. The relative humidity, however, is higher than in Bioko. Bioko has a rather debilitating climate. The so-called dry season lasts from November to March, and the rest of the year is rainy. The average annual temperature of about 77 °F (25 °C) varies little throughout the year. Afternoon temperatures reach the high 80s °F (low 30s °C) and drop to only about 70 °F (21.1 °C) at night. Most of the time the sky is cloudy and overcast. Extreme rainfall occurs in the south, with rain brought by monsoon winds amounting to about 450 in (11,430 mm) a year around San Antonio de Ureca.
Terrain
Coastal plains rise to interior hills; islands are volcanicIrrigated land:
NA km²
Natural hazards:
violent windstorms, flash floods
Environment - current issues:
tap water is not potable; desertification
Environment - international agreements:
party to:
Biodiversity, Desertification, Endangered Species, Law of the Sea, Ship Pollution
signed, but not ratified:
none of the selected agreements
Geography - note:
insular and continental regions rather widely separated
Extreme points
This is a list of the extreme points of Equatorial GuineaEquatorial Guinea
Equatorial Guinea, officially the Republic of Equatorial Guinea where the capital Malabo is situated.Annobón is the southernmost island of Equatorial Guinea and is situated just south of the equator. Bioko island is the northernmost point of Equatorial Guinea. Between the two islands and to the...
, the points that are farther north, south, east or west than any other location.
- Northern-most point - Punta Europa, Bioko Island
- Eastern-most point - the eastern section of the border with GabonGabonGabon , officially the Gabonese Republic is a state in west central Africa sharing borders with Equatorial Guinea to the northwest, Cameroon to the north, and with the Republic of the Congo curving around the east and south. The Gulf of Guinea, an arm of the Atlantic Ocean is to the west...
* - Southern-most point - A Dyibó, AnnobónAnnobónAnnobón may refer to:* Annobón Province* Annobonese language* Annobon people...
Island - Western-most point - Punta Dyiscoj, AnnobónAnnobónAnnobón may refer to:* Annobón Province* Annobonese language* Annobon people...
Island
- Note: technically Equatorial Guinea does not have an eastern-most point as its eastern border is formed by a straight line between the 11° and 12° of latitude
See also
- Equatorial GuineaEquatorial GuineaEquatorial Guinea, officially the Republic of Equatorial Guinea where the capital Malabo is situated.Annobón is the southernmost island of Equatorial Guinea and is situated just south of the equator. Bioko island is the northernmost point of Equatorial Guinea. Between the two islands and to the...

