
Geography of Djibouti
Encyclopedia
| Geography of Djibouti | |
 |
|
| Continent | Africa Africa Africa is the world's second largest and second most populous continent, after Asia. At about 30.2 million km² including adjacent islands, it covers 6% of the Earth's total surface area and 20.4% of the total land area... |
| Region | Horn of Africa Horn of Africa The Horn of Africa is a peninsula in East Africa that juts hundreds of kilometers into the Arabian Sea and lies along the southern side of the Gulf of Aden. It is the easternmost projection of the African continent... |
| Area | Ranked 149th 22,980 km2 |
| Coastline | 20 km |
| Borders | 1,016 km (Ethiopia Ethiopia Ethiopia , officially known as the Federal Democratic Republic of Ethiopia, is a country located in the Horn of Africa. It is the second-most populous nation in Africa, with over 82 million inhabitants, and the tenth-largest by area, occupying 1,100,000 km2... 337 km, Eritrea Eritrea Eritrea , officially the State of Eritrea, is a country in the Horn of Africa. Eritrea derives it's name from the Greek word Erethria, meaning 'red land'. The capital is Asmara. It is bordered by Sudan in the west, Ethiopia in the south, and Djibouti in the southeast... 113 km, Somalia Somalia Somalia , officially the Somali Republic and formerly known as the Somali Democratic Republic under Socialist rule, is a country located in the Horn of Africa. Since the outbreak of the Somali Civil War in 1991 there has been no central government control over most of the country's territory... 58 km) |
| Highest point | Mousa Ali Volcano 2,028 m |
| Lowest point | Lac Assal, −155 m |
Location
Djibouti shares 113 kilometres (70.2 mi) of border with EritreaEritrea
Eritrea , officially the State of Eritrea, is a country in the Horn of Africa. Eritrea derives it's name from the Greek word Erethria, meaning 'red land'. The capital is Asmara. It is bordered by Sudan in the west, Ethiopia in the south, and Djibouti in the southeast...
, 337 kilometres (209.4 mi) with Ethiopia
Ethiopia
Ethiopia , officially known as the Federal Democratic Republic of Ethiopia, is a country located in the Horn of Africa. It is the second-most populous nation in Africa, with over 82 million inhabitants, and the tenth-largest by area, occupying 1,100,000 km2...
and 58 kilometres (36 mi) with Somalia
Somalia
Somalia , officially the Somali Republic and formerly known as the Somali Democratic Republic under Socialist rule, is a country located in the Horn of Africa. Since the outbreak of the Somali Civil War in 1991 there has been no central government control over most of the country's territory...
(total 506 km or 314.4 mi). It also has 314 kilometres (195.1 mi) of coastline.
It has a strategic location near the world's busiest shipping lanes and close to Arabian oilfields. Djibouti is also terminus of rail traffic into Ethiopia
Ethio-Djibouti Railways
The Ethio-Djibouti Railways, also Ethio-Djibouti Railway Enterprise, is the successor of the Imperial Railway Company of Ethiopia and jointly owned by the governments of Ethiopia and Djibouti. It was formed after Djibouti gained independence in 1977 and received the French shares of the Imperial...
.
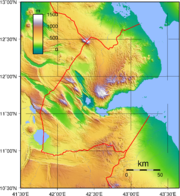
Terrain
Mountains in the center of the country separate a coastal plainCoastal plain
A coastal plain is an area of flat, low-lying land adjacent to a seacoast and separated from the interior by other features. One of the world's longest coastal plains is located in eastern South America. The southwestern coastal plain of North America is notable for its species diversity...
and a plateau
Plateau
In geology and earth science, a plateau , also called a high plain or tableland, is an area of highland, usually consisting of relatively flat terrain. A highly eroded plateau is called a dissected plateau...
. The lowest point is Lac Assal (-155 m) and the highest is Moussa Ali (2028 m or 6,653.5 ft). There is no arable land
Arable land
In geography and agriculture, arable land is land that can be used for growing crops. It includes all land under temporary crops , temporary meadows for mowing or pasture, land under market and kitchen gardens and land temporarily fallow...
, irrigation
Irrigation
Irrigation may be defined as the science of artificial application of water to the land or soil. It is used to assist in the growing of agricultural crops, maintenance of landscapes, and revegetation of disturbed soils in dry areas and during periods of inadequate rainfall...
, permanent crop
Permanent crop
A permanent crop is one produced from plants which last for many seasons, rather than being replanted after each harvest.As used in The World Factbook land use statistics the term comprises land cultivated for crops like citrus, olives, coffee, and rubber; it includes land under flowering shrubs,...
s, and negligible forest
Forest
A forest, also referred to as a wood or the woods, is an area with a high density of trees. As with cities, depending where you are in the world, what is considered a forest may vary significantly in size and have various classification according to how and what of the forest is composed...
cover. (What little forest, is in the Goda Mountains
Goda Mountains
The Goda Mountains lie northwest of the Gulf of Tadjoura, Afar region in Djibouti. They rise to above sea level and are the nation's largest vegetated area...
, especially in the Day Forest National Park
Day Forest National Park
Day Forest National Park is a national park in Djibouti. It protects an important forest island in a sea of semi-desert, with at least four known endemic plant species, which include: Juniperus procera, Olea africana, Buxus hildebrantii, and Tarchonanthus camphoratus...
.) 9% of the country is permanent pasture
Pasture
Pasture is land used for grazing. Pasture lands in the narrow sense are enclosed tracts of farmland, grazed by domesticated livestock, such as horses, cattle, sheep or swine. The vegetation of tended pasture, forage, consists mainly of grasses, with an interspersion of legumes and other forbs...
land (1993 est). Therefore most of Djibouti has been described as part of the Ethiopian xeric grasslands and shrublands
Ethiopian xeric grasslands and shrublands
The Ethiopian xeric grasslands and shrublands ecoregion is a semi-desert strip on or near the Red Sea and the Gulf of Oman coasts in Eritrea, Ethiopia, Djibouti and Somaliland.-Location and description:...
ecoregion
Ecoregion
An ecoregion , sometimes called a bioregion, is an ecologically and geographically defined area that is smaller than an ecozone and larger than an ecosystem. Ecoregions cover relatively large areas of land or water, and contain characteristic, geographically distinct assemblages of natural...
except for a strip along the Red Sea
Red Sea
The Red Sea is a seawater inlet of the Indian Ocean, lying between Africa and Asia. The connection to the ocean is in the south through the Bab el Mandeb strait and the Gulf of Aden. In the north, there is the Sinai Peninsula, the Gulf of Aqaba, and the Gulf of Suez...
coast is part of the Eritrean coastal desert
Eritrean coastal desert
The Eritrean coastal desert ecoregion is a a harsh sand and gravel strip along the southern part of the coast of Eritrea and the Red Sea coast of Djibouti...
, noted as an important migration route for birds of prey.
Environment
Natural hazards include earthquakeEarthquake
An earthquake is the result of a sudden release of energy in the Earth's crust that creates seismic waves. The seismicity, seismism or seismic activity of an area refers to the frequency, type and size of earthquakes experienced over a period of time...
s, drought
Drought
A drought is an extended period of months or years when a region notes a deficiency in its water supply. Generally, this occurs when a region receives consistently below average precipitation. It can have a substantial impact on the ecosystem and agriculture of the affected region...
s, and occasional cyclonic disturbances
Cyclone
In meteorology, a cyclone is an area of closed, circular fluid motion rotating in the same direction as the Earth. This is usually characterized by inward spiraling winds that rotate anticlockwise in the Northern Hemisphere and clockwise in the Southern Hemisphere of the Earth. Most large-scale...
from the Indian Ocean
Indian Ocean
The Indian Ocean is the third largest of the world's oceanic divisions, covering approximately 20% of the water on the Earth's surface. It is bounded on the north by the Indian Subcontinent and Arabian Peninsula ; on the west by eastern Africa; on the east by Indochina, the Sunda Islands, and...
, which bring heavy rains and flash floods. Natural resource
Natural resource
Natural resources occur naturally within environments that exist relatively undisturbed by mankind, in a natural form. A natural resource is often characterized by amounts of biodiversity and geodiversity existent in various ecosystems....
s include geothermal energy. Inadequate supplies of potable water and desertification
Desertification
Desertification is the degradation of land in drylands. Caused by a variety of factors, such as climate change and human activities, desertification is one of the most significant global environmental problems.-Definitions:...
are current issues.
Djibouti is a party to international agreements on Biodiversity, Climate Change, Desertification, Endangered Species, Law of the Sea
Law of the sea
Law of the sea may refer to:* United Nations Convention on the Law of the Sea* Admiralty law* The Custom of the Sea...
, Ozone Layer Protection, Ship Pollution.
Maritime claims
- contiguous zone: 24 nmi (44.4 km; 27.6 mi)
- exclusive economic zone: 200 nmi (370.4 km; 230.2 mi)
- territorial sea: 12 nmi (22.2 km; 13.8 mi)
Extreme points
This is a list of the extreme points of DjiboutiDjibouti
Djibouti , officially the Republic of Djibouti , is a country in the Horn of Africa. It is bordered by Eritrea in the north, Ethiopia in the west and south, and Somalia in the southeast. The remainder of the border is formed by the Red Sea and the Gulf of Aden at the east...
, the points that are farther north, south, east or west than any other location.
- Northern-most point - Ras Doumera, Obock RegionObock RegionThe Obock Region is one of the six Regions of Djibouti. The Region borders the Red Sea and Gulf of Aden to the east and south, Eritrea to the north, and the Tadjoura Region to the west....
- Northern-most point (mainland) - the point at which the border with EritreaEritreaEritrea , officially the State of Eritrea, is a country in the Horn of Africa. Eritrea derives it's name from the Greek word Erethria, meaning 'red land'. The capital is Asmara. It is bordered by Sudan in the west, Ethiopia in the south, and Djibouti in the southeast...
enters the Red SeaRed SeaThe Red Sea is a seawater inlet of the Indian Ocean, lying between Africa and Asia. The connection to the ocean is in the south through the Bab el Mandeb strait and the Gulf of Aden. In the north, there is the Sinai Peninsula, the Gulf of Aqaba, and the Gulf of Suez...
, Obock RegionObock RegionThe Obock Region is one of the six Regions of Djibouti. The Region borders the Red Sea and Gulf of Aden to the east and south, Eritrea to the north, and the Tadjoura Region to the west.... - Eastern-most point - unnamed section of the Red SeaRed SeaThe Red Sea is a seawater inlet of the Indian Ocean, lying between Africa and Asia. The connection to the ocean is in the south through the Bab el Mandeb strait and the Gulf of Aden. In the north, there is the Sinai Peninsula, the Gulf of Aqaba, and the Gulf of Suez...
coast north of Ras Bir, Obock RegionObock RegionThe Obock Region is one of the six Regions of Djibouti. The Region borders the Red Sea and Gulf of Aden to the east and south, Eritrea to the north, and the Tadjoura Region to the west.... - Southern-most point - unnamed location on the border with EthiopiaEthiopiaEthiopia , officially known as the Federal Democratic Republic of Ethiopia, is a country located in the Horn of Africa. It is the second-most populous nation in Africa, with over 82 million inhabitants, and the tenth-largest by area, occupying 1,100,000 km2...
west of the town of As Ela, Dikhil RegionDikhil RegionThe Dikhil Region is one of the six Regions of Djibouti. The Region borders the Tadjoura Region to the north-west, the Arta Region to the north-east, the Ali Sabieh Region to the east, and Ethiopia to the west and south.... - Western-most point - unnamed location on the border with EthiopiaEthiopiaEthiopia , officially known as the Federal Democratic Republic of Ethiopia, is a country located in the Horn of Africa. It is the second-most populous nation in Africa, with over 82 million inhabitants, and the tenth-largest by area, occupying 1,100,000 km2...
immediately east of the Ethiopian town of AfamboAfamboAfambo is one of the 29 woredas in the Afar Region of Ethiopia. It is named after Lake Afambo, located at the border of this woreda with Asayita, near the international border with Djibouti. Part of the Administrative Zone 1, Afambo is bordered on the south by the Somali Region, on the west by...
, Dikhil RegionDikhil RegionThe Dikhil Region is one of the six Regions of Djibouti. The Region borders the Tadjoura Region to the north-west, the Arta Region to the north-east, the Ali Sabieh Region to the east, and Ethiopia to the west and south....

