
Geography of Chad
Encyclopedia
Chad
is a land-locked country in north central Africa
measuring 1284000 square kilometres (495,755 sq mi), roughly three times the size of California
. Most of its ethnically and linguistically diverse population lives in the south, with densities ranging from 54 persons per square kilometers in the Logone River basin to 0.1 persons in the northern B.E.T. desert region, which is larger than France. The capital city of N'Djaména
, situated at the confluence of the Chari
and Logone Rivers, is cosmopolitan in nature, with a current population in excess of 700,000 people.
Chad has four bioclimatic zones. The northernmost Saharan zone averages less than 200 mm (7.9 in) of rainfall annually. The sparse human population is largely nomadic, with some livestock, mostly small ruminants and camels. The central Sahelian zone receives between 200 and 600 mm (7.9 and 23.6 in) rainfall and has vegetation ranging from grass/shrub steppe
to thorny, open savanna. The southern zone, often referred to as the Sudanian zone, receives between 600 and 1000 mm (23.6 and 39.4 in), with woodland savanna
and deciduous forests for vegetation. Rainfall in the Guinea zone, located in Chad's southwestern tip, ranges between 1000 and 1200 mm (39.4 and 47.2 in).
The country's topography is generally flat, with the elevation gradually rising as one moves north and east away from Lake Chad
. The highest point in Chad is Emi Koussi
, a mountain that rises 3100 m (10,171 ft) in the northern Tibesti Mountains
. The Ennedi Plateau
and the Ouaddaï highlands
in the east complete the image of a gradually sloping basin, which descends towards Lake Chad. There are also central highlands in the Guera region rising to 1500 m (4,921 ft).
Lake Chad
is the second largest lake in west Africa and is one of the most important wetlands on the continent. Home to 120 species of fish and at least that many species of birds, the lake has shrunk dramatically in the last four decades due to the increased water from an expanding population
usage and low rainfall. Bordered by Chad, Niger
, Nigeria
, and Cameroon
, Lake Chad currently covers only 1350 square kilometers, down from 25,000 square kilometers in 1963. The Chari and Logone Rivers, both of which originate in the Central African Republic and flow northward, provide most of the surface water entering Lake Chad.

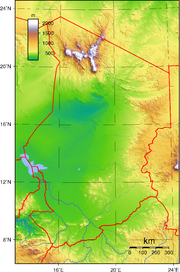 Located in north-central Africa, Chad stretches for about 1,800 kilometers from its northernmost point to its southern boundary. Except in the far northwest and south, where its borders converge, Chad's average width is about 800 kilometers. Its area of 1,284,000 square kilometers is roughly equal to the combined areas of Idaho
Located in north-central Africa, Chad stretches for about 1,800 kilometers from its northernmost point to its southern boundary. Except in the far northwest and south, where its borders converge, Chad's average width is about 800 kilometers. Its area of 1,284,000 square kilometers is roughly equal to the combined areas of Idaho
, Wyoming
, Utah
, Nevada
, and Arizona
. Chad's neighbors include Libya
to the north, Niger
and Nigeria
to the west, Sudan
to the east, Central African Republic
to the south, and Cameroon
to the southwest.
Chad exhibits two striking geographical characteristics. First, the country is landlocked. N'Djamena
, the capital, is located more than 1,100 kilometers northeast of the Atlantic Ocean
; Abéché
, a major city in the east, lies 2,650 kilometers from the Red Sea
; and Faya-Largeau
, a much smaller but strategically important center in the north, is in the middle of the Sahara Desert, 1,550 kilometers from the Mediterranean Sea
. These vast distances from the sea have had a profound impact on Chad's historical and contemporary development. The second noteworthy characteristic is that the country borders on very different parts of the African continent: North Africa
, with its Islamic culture and economic orientation toward the Mediterranean Basin
; West Africa
, with its diverse religions and cultures and its history of highly developed states and regional economies; Northeast Africa
, oriented toward the Nile Valley
and Red Sea region; and Central or Equatorial Africa, some of whose people have retained classical African religions while others have adopted Christianity
, and whose economies were part of the great Congo River
system. Although much of Chad's distinctiveness comes from this diversity of influences, since independence the diversity has also been an obstacle to the creation of a national identity.
Lake Chad, located in the southwestern part of the basin at an altitude of 282 meters, surprisingly does not mark the basin's lowest point; instead, this is found in the Bodele and Djourab regions in the north-central and northeastern parts of the country, respectively. This oddity arises because the great stationary dunes (ergs) of the Kanem region create a dam, preventing lake waters from flowing to the basin's lowest point. At various times in the past, and as late as the 1870s, the Bahr el Ghazal Depression, which extends from the northeastern part of the lake to the Djourab, acted as an overflow canal; since independence, climatic conditions have made overflows impossible.
North and northeast of Lake Chad, the basin extends for more than 800 kilometers, passing through regions characterized by great rolling dunes separated by very deep depressions. Although vegetation holds the dunes in place in the Kanem region, farther north they are bare and have a fluid, rippling character. From its low point in the Djourab, the basin then rises to the plateaus and peaks of the Tibesti Mountains in the north. The summit of this formation—as well as the highest point in the Sahara Desert—is Emi Koussi, a dormant volcano that reaches 3,414 meters above sea level.
The basin's northeastern limit is the Ennedi Plateau, whose limestone bed rises in steps etched by erosion. East of the lake, the basin rises gradually to the Ouaddaï Highlands, which mark Chad's eastern border and also divide the Chad and Nile watersheds. These highland areas are part of the East Saharan montane xeric woodlands
ecoregion
.
Southeast of Lake Chad, the regular contours of the terrain are broken by the Guéra Massif, which divides the basin into its northern and southern parts. South of the lake lie the floodplains of the Chari and Logone rivers, much of which are inundated during the rainy season. Farther south, the basin floor slopes upward, forming a series of low sand and clay plateaus, called koros, which eventually climb to 615 meters above sea level. South of the Chadian border, the koros divide the Lake Chad Basin from the Ubangi-Zaire river system.
 Chad's major rivers are the Chari
Chad's major rivers are the Chari
and the Logone and their tributaries, which flow from the southeast into Lake Chad. Both river systems rise in the highlands of Central African Republic and Cameroon, regions that receive more than 1,250 millimeters of rainfall annually. Fed by rivers of Central African Republic, as well as by the Bahr Salamat, Bahr Aouk, and Bahr Sara rivers of southeastern Chad, the Chari River is about 1,200 kilometers long. From its origins near the city of Sarh, the middle course of the Chari makes its way through swampy terrain; the lower Chari is joined by the Logone River near N'Djamena. The Chari's volume varies greatly, from 17 cubic meters per second during the dry season to 340 cubic meters per second during the wettest part of the year.
The Logone River is formed by tributaries flowing from Cameroon and Central African Republic. Both shorter and smaller in volume than the Chari, it flows northeast for 960 kilometers; its volume ranges from five to eighty-five cubic meters per second. At N'Djamena the Logone empties into the Chari, and the combined rivers flow together for thirty kilometers through a large delta and into Lake Chad. At the end of the rainy season in the fall, the river overflows its banks and creates a huge floodplain in the delta.
The seventh largest lake in the world (and the fourth largest in Africa), Lake Chad
is located in the sahelian zone, a region just south of the Sahara Desert. The Chari River contributes 95 percent of Lake Chad's water, an average annual volume of 40 billion cubic meters, 95% of which is lost to evaporation. The size of the lake is determined by rains in the southern highlands bordering the basin and by temperatures in the Sahel. Fluctuations in both cause the lake to change dramatically in size, from 9,800 square kilometers in the dry season to 25,500 at the end of the rainy season. Lake Chad also changes greatly in size from one year to another. In 1870 its maximum area was 28,000 square kilometers. The measurement dropped to 12,700 in 1908. In the 1940s and 1950s, the lake remained small, but it grew again to 26,000 square kilometers in 1963. The droughts of the late 1960s, early 1970s, and mid-1980s caused Lake Chad to shrink once again, however. The only other lakes of importance in Chad are Lake Fitri, in Batha Prefecture, and Lake Iro, in the marshy southeast.
 The Saharan region covers roughly the northern third of the country, including Borkou-Ennedi-Tibesti Prefecture along with the northern parts of Kanem, Batha, and Biltine prefectures. Much of this area receives only traces of rain during the entire year; at Faya Largeau, for example, annual rainfall averages less than 30 millimetres (1.18 in). Scattered small oases and occasional wells provide water for a few date palms or small plots of millet and garden crops. In much of the north, the average daily maximum temperature is about 32 °C (89.6 °F) during January, the coolest month of the year, and about 45 °C (113 °F) during May, the hottest month. On occasion, strong winds from the northeast produce violent sandstorms. In northern Biltine Prefecture, a region called the Mortcha plays a major role in animal husbandry. Dry for nine months of the year, it receives 350 millimetres (13.8 in) or more of rain, mostly during July and August. A carpet of green springs from the desert during this brief wet season, attracting herders from throughout the region who come to pasture their cattle and camels. Because very few wells and springs have water throughout the year, the herders leave with the end of the rains, turning over the land to the antelopes, gazelles, and ostriches that can survive with little groundwater.
The Saharan region covers roughly the northern third of the country, including Borkou-Ennedi-Tibesti Prefecture along with the northern parts of Kanem, Batha, and Biltine prefectures. Much of this area receives only traces of rain during the entire year; at Faya Largeau, for example, annual rainfall averages less than 30 millimetres (1.18 in). Scattered small oases and occasional wells provide water for a few date palms or small plots of millet and garden crops. In much of the north, the average daily maximum temperature is about 32 °C (89.6 °F) during January, the coolest month of the year, and about 45 °C (113 °F) during May, the hottest month. On occasion, strong winds from the northeast produce violent sandstorms. In northern Biltine Prefecture, a region called the Mortcha plays a major role in animal husbandry. Dry for nine months of the year, it receives 350 millimetres (13.8 in) or more of rain, mostly during July and August. A carpet of green springs from the desert during this brief wet season, attracting herders from throughout the region who come to pasture their cattle and camels. Because very few wells and springs have water throughout the year, the herders leave with the end of the rains, turning over the land to the antelopes, gazelles, and ostriches that can survive with little groundwater.
The soudanian region is predominantly East Sudanian savanna
, or plains covered with a mixture of tropical or subtropical grasses and woodlands. The growth is lush during the rainy season but turns brown and dormant during the five-month dry season between November and March. Over a large part of the region, however, natural vegetation has yielded to agriculture.
, which began to enter a famine situation.
On 26 July the heat reached near record levels over Chad
and Niger
.
total:
1.284 million km²
land:
1,259,200 km²
water:
24,800 km²
Area - comparative:
Canada: smaller than the Northwest Territories
US: slightly more than three times the size of California
total:
5,968 km
border countries:
Cameroon
1,094 km, Central African Republic
1,197 km, Libya 1,055 km, Niger
1,175 km, Nigeria
87 km, Sudan
1,360 km
Coastline:
0 km (landlocked)
Maritime claims:
none (landlocked)
Elevation extremes:
lowest point:
Djourab Depression 160 m
highest point:
Emi Koussi
3,415 m
petroleum
, uranium
, natron
, kaolin, fish
(Chari River
, Logone River), gold
, limestone
, sand
and gravel
, salt
Land use:
arable land:
2.8%
permanent crops:
0.02%
other:
97.18% (2005)
Irrigated land:
300 km² (2003)
Total renewable water resources:
43 km3 (2007)
hot, dry, dusty harmattan winds occur in north; periodic droughts; locust plagues
Environment - current issues:n
inadequate supplies of potable water; improper waste disposal in rural areas contributes to soil and water pollution; desertification
Also see- 2010 Sahel drought
, the points that are farther north, south, east or west than any other location.
*Note: technically Chad does not have an easternmost point, the northern section of the border being formed by the 24° of latitude
Chad
Chad , officially known as the Republic of Chad, is a landlocked country in Central Africa. It is bordered by Libya to the north, Sudan to the east, the Central African Republic to the south, Cameroon and Nigeria to the southwest, and Niger to the west...
is a land-locked country in north central Africa
Africa
Africa is the world's second largest and second most populous continent, after Asia. At about 30.2 million km² including adjacent islands, it covers 6% of the Earth's total surface area and 20.4% of the total land area...
measuring 1284000 square kilometres (495,755 sq mi), roughly three times the size of California
California
California is a state located on the West Coast of the United States. It is by far the most populous U.S. state, and the third-largest by land area...
. Most of its ethnically and linguistically diverse population lives in the south, with densities ranging from 54 persons per square kilometers in the Logone River basin to 0.1 persons in the northern B.E.T. desert region, which is larger than France. The capital city of N'Djaména
N'Djamena
N'Djamena is the capital and largest city of Chad. A port on the Chari River, near the confluence with the Logone River, it directly faces the Cameroonian town of Kousséri, to which the city is connected by a bridge. It is also a special statute region, divided in 10 arrondissements. It is a...
, situated at the confluence of the Chari
Chari River
The Chari or Shari River is a 949-kilometer-long river of central Africa. It flows from the Central African Republic through Chad into Lake Chad, following the Cameroon border from N'Djamena, where it joins the Logone River waters....
and Logone Rivers, is cosmopolitan in nature, with a current population in excess of 700,000 people.
Chad has four bioclimatic zones. The northernmost Saharan zone averages less than 200 mm (7.9 in) of rainfall annually. The sparse human population is largely nomadic, with some livestock, mostly small ruminants and camels. The central Sahelian zone receives between 200 and 600 mm (7.9 and 23.6 in) rainfall and has vegetation ranging from grass/shrub steppe
Steppe
In physical geography, steppe is an ecoregion, in the montane grasslands and shrublands and temperate grasslands, savannas, and shrublands biomes, characterized by grassland plains without trees apart from those near rivers and lakes...
to thorny, open savanna. The southern zone, often referred to as the Sudanian zone, receives between 600 and 1000 mm (23.6 and 39.4 in), with woodland savanna
Savanna
A savanna, or savannah, is a grassland ecosystem characterized by the trees being sufficiently small or widely spaced so that the canopy does not close. The open canopy allows sufficient light to reach the ground to support an unbroken herbaceous layer consisting primarily of C4 grasses.Some...
and deciduous forests for vegetation. Rainfall in the Guinea zone, located in Chad's southwestern tip, ranges between 1000 and 1200 mm (39.4 and 47.2 in).
The country's topography is generally flat, with the elevation gradually rising as one moves north and east away from Lake Chad
Lake Chad
Lake Chad is a historically large, shallow, endorheic lake in Africa, whose size has varied over the centuries. According to the Global Resource Information Database of the United Nations Environment Programme, it shrank as much as 95% from about 1963 to 1998; yet it also states that "the 2007 ...
. The highest point in Chad is Emi Koussi
Emi Koussi
Emi Koussi is a high pyroclastic shield volcano that lies at the south end of the Tibesti Mountains in the central Sahara of northern Chad. It is the highest mountain in Chad, and the highest in the Sahara. The volcano is one of several in the Tibesti massif, and reaches 3445 m in altitude,...
, a mountain that rises 3100 m (10,171 ft) in the northern Tibesti Mountains
Tibesti Mountains
The Tibesti Mountains are a range of inactive volcanoes located on the northern edge of the Chad Basin in the Borkou- and Tibesti Region of northern Chad. The massif is one of the most prominent features of the Central-Sahara desert and covers an area of approximately 100,000 km². The northern...
. The Ennedi Plateau
Ennedi Plateau
The Ennedi Plateau, located in the North-East of Chad, in the Bourkou-Ennedi-Tibesti Region, is a sandstone bulwark in the middle of the Sahara. It is assailed by the sands on all sides, that encroach the deep valleys of the Ennedi...
and the Ouaddaï highlands
Ouaddaï highlands
Ouaddaï Highlands is an area in east of Chad along the border with Sudan. The Ennedi Plateau and the Ouaddaï highlands in the east of Chad complete the image of a gradually sloping basin, which descends towards Lake Chad...
in the east complete the image of a gradually sloping basin, which descends towards Lake Chad. There are also central highlands in the Guera region rising to 1500 m (4,921 ft).
Lake Chad
Lake Chad
Lake Chad is a historically large, shallow, endorheic lake in Africa, whose size has varied over the centuries. According to the Global Resource Information Database of the United Nations Environment Programme, it shrank as much as 95% from about 1963 to 1998; yet it also states that "the 2007 ...
is the second largest lake in west Africa and is one of the most important wetlands on the continent. Home to 120 species of fish and at least that many species of birds, the lake has shrunk dramatically in the last four decades due to the increased water from an expanding population
Overpopulation
Overpopulation is a condition where an organism's numbers exceed the carrying capacity of its habitat. The term often refers to the relationship between the human population and its environment, the Earth...
usage and low rainfall. Bordered by Chad, Niger
Niger
Niger , officially named the Republic of Niger, is a landlocked country in Western Africa, named after the Niger River. It borders Nigeria and Benin to the south, Burkina Faso and Mali to the west, Algeria and Libya to the north and Chad to the east...
, Nigeria
Nigeria
Nigeria , officially the Federal Republic of Nigeria, is a federal constitutional republic comprising 36 states and its Federal Capital Territory, Abuja. The country is located in West Africa and shares land borders with the Republic of Benin in the west, Chad and Cameroon in the east, and Niger in...
, and Cameroon
Cameroon
Cameroon, officially the Republic of Cameroon , is a country in west Central Africa. It is bordered by Nigeria to the west; Chad to the northeast; the Central African Republic to the east; and Equatorial Guinea, Gabon, and the Republic of the Congo to the south. Cameroon's coastline lies on the...
, Lake Chad currently covers only 1350 square kilometers, down from 25,000 square kilometers in 1963. The Chari and Logone Rivers, both of which originate in the Central African Republic and flow northward, provide most of the surface water entering Lake Chad.
Geographical setting


Idaho
Idaho is a state in the Rocky Mountain area of the United States. The state's largest city and capital is Boise. Residents are called "Idahoans". Idaho was admitted to the Union on July 3, 1890, as the 43rd state....
, Wyoming
Wyoming
Wyoming is a state in the mountain region of the Western United States. The western two thirds of the state is covered mostly with the mountain ranges and rangelands in the foothills of the Eastern Rocky Mountains, while the eastern third of the state is high elevation prairie known as the High...
, Utah
Utah
Utah is a state in the Western United States. It was the 45th state to join the Union, on January 4, 1896. Approximately 80% of Utah's 2,763,885 people live along the Wasatch Front, centering on Salt Lake City. This leaves vast expanses of the state nearly uninhabited, making the population the...
, Nevada
Nevada
Nevada is a state in the western, mountain west, and southwestern regions of the United States. With an area of and a population of about 2.7 million, it is the 7th-largest and 35th-most populous state. Over two-thirds of Nevada's people live in the Las Vegas metropolitan area, which contains its...
, and Arizona
Arizona
Arizona ; is a state located in the southwestern region of the United States. It is also part of the western United States and the mountain west. The capital and largest city is Phoenix...
. Chad's neighbors include Libya
Libya
Libya is an African country in the Maghreb region of North Africa bordered by the Mediterranean Sea to the north, Egypt to the east, Sudan to the southeast, Chad and Niger to the south, and Algeria and Tunisia to the west....
to the north, Niger
Niger
Niger , officially named the Republic of Niger, is a landlocked country in Western Africa, named after the Niger River. It borders Nigeria and Benin to the south, Burkina Faso and Mali to the west, Algeria and Libya to the north and Chad to the east...
and Nigeria
Nigeria
Nigeria , officially the Federal Republic of Nigeria, is a federal constitutional republic comprising 36 states and its Federal Capital Territory, Abuja. The country is located in West Africa and shares land borders with the Republic of Benin in the west, Chad and Cameroon in the east, and Niger in...
to the west, Sudan
Sudan
Sudan , officially the Republic of the Sudan , is a country in North Africa, sometimes considered part of the Middle East politically. It is bordered by Egypt to the north, the Red Sea to the northeast, Eritrea and Ethiopia to the east, South Sudan to the south, the Central African Republic to the...
to the east, Central African Republic
Central African Republic
The Central African Republic , is a landlocked country in Central Africa. It borders Chad in the north, Sudan in the north east, South Sudan in the east, the Democratic Republic of the Congo and the Republic of the Congo in the south, and Cameroon in the west. The CAR covers a land area of about ,...
to the south, and Cameroon
Cameroon
Cameroon, officially the Republic of Cameroon , is a country in west Central Africa. It is bordered by Nigeria to the west; Chad to the northeast; the Central African Republic to the east; and Equatorial Guinea, Gabon, and the Republic of the Congo to the south. Cameroon's coastline lies on the...
to the southwest.
Chad exhibits two striking geographical characteristics. First, the country is landlocked. N'Djamena
N'Djamena
N'Djamena is the capital and largest city of Chad. A port on the Chari River, near the confluence with the Logone River, it directly faces the Cameroonian town of Kousséri, to which the city is connected by a bridge. It is also a special statute region, divided in 10 arrondissements. It is a...
, the capital, is located more than 1,100 kilometers northeast of the Atlantic Ocean
Atlantic Ocean
The Atlantic Ocean is the second-largest of the world's oceanic divisions. With a total area of about , it covers approximately 20% of the Earth's surface and about 26% of its water surface area...
; Abéché
Abéché
-Demographics:Demographic evolution:-References:...
, a major city in the east, lies 2,650 kilometers from the Red Sea
Red Sea
The Red Sea is a seawater inlet of the Indian Ocean, lying between Africa and Asia. The connection to the ocean is in the south through the Bab el Mandeb strait and the Gulf of Aden. In the north, there is the Sinai Peninsula, the Gulf of Aqaba, and the Gulf of Suez...
; and Faya-Largeau
Faya-Largeau
Located in the Sahara, Faya's climate is classed as hot desert on the Köppen climate classification. It experiences hot winters and very hot summers with the peak average maximum temperature reaching in May and the average minimum reaching its lowest in January at . Rainfall averages out at about...
, a much smaller but strategically important center in the north, is in the middle of the Sahara Desert, 1,550 kilometers from the Mediterranean Sea
Mediterranean Sea
The Mediterranean Sea is a sea connected to the Atlantic Ocean surrounded by the Mediterranean region and almost completely enclosed by land: on the north by Anatolia and Europe, on the south by North Africa, and on the east by the Levant...
. These vast distances from the sea have had a profound impact on Chad's historical and contemporary development. The second noteworthy characteristic is that the country borders on very different parts of the African continent: North Africa
North Africa
North Africa or Northern Africa is the northernmost region of the African continent, linked by the Sahara to Sub-Saharan Africa. Geopolitically, the United Nations definition of Northern Africa includes eight countries or territories; Algeria, Egypt, Libya, Morocco, South Sudan, Sudan, Tunisia, and...
, with its Islamic culture and economic orientation toward the Mediterranean Basin
Mediterranean Basin
In biogeography, the Mediterranean Basin refers to the lands around the Mediterranean Sea that have a Mediterranean climate, with mild, rainy winters and hot, dry summers, which supports characteristic Mediterranean forests, woodlands, and scrub vegetation...
; West Africa
West Africa
West Africa or Western Africa is the westernmost region of the African continent. Geopolitically, the UN definition of Western Africa includes the following 16 countries and an area of approximately 5 million square km:-Flags of West Africa:...
, with its diverse religions and cultures and its history of highly developed states and regional economies; Northeast Africa
Horn of Africa
The Horn of Africa is a peninsula in East Africa that juts hundreds of kilometers into the Arabian Sea and lies along the southern side of the Gulf of Aden. It is the easternmost projection of the African continent...
, oriented toward the Nile Valley
Nile
The Nile is a major north-flowing river in North Africa, generally regarded as the longest river in the world. It is long. It runs through the ten countries of Sudan, South Sudan, Burundi, Rwanda, Democratic Republic of the Congo, Tanzania, Kenya, Ethiopia, Uganda and Egypt.The Nile has two major...
and Red Sea region; and Central or Equatorial Africa, some of whose people have retained classical African religions while others have adopted Christianity
Christianity
Christianity is a monotheistic religion based on the life and teachings of Jesus as presented in canonical gospels and other New Testament writings...
, and whose economies were part of the great Congo River
Congo River
The Congo River is a river in Africa, and is the deepest river in the world, with measured depths in excess of . It is the second largest river in the world by volume of water discharged, though it has only one-fifth the volume of the world's largest river, the Amazon...
system. Although much of Chad's distinctiveness comes from this diversity of influences, since independence the diversity has also been an obstacle to the creation of a national identity.
Land
Although Chadian society is economically, socially, and culturally fragmented, the country's geography is unified by the Lake Chad Basin. Once a huge inland sea (the Pale-Chadian Sea) whose only remnant is shallow Lake Chad, this vast depression extends west into Nigeria and Niger. The larger, northern portion of the basin is bounded within Chad by the Tibesti Mountains in the northwest, the Ennedi Plateau in the northeast, the Ouaddaï Highlands in the east along the border with Sudan, the Guéra Massif in central Chad, and the Mandara Mountains along Chad's southwestern border with Cameroon. The smaller, southern part of the basin falls almost exclusively in Chad. It is delimited in the north by the Guéra Massif, in the south by highlands 250 kilometers south of the border with Central African Republic, and in the southwest by the Mandara Mountains.Lake Chad, located in the southwestern part of the basin at an altitude of 282 meters, surprisingly does not mark the basin's lowest point; instead, this is found in the Bodele and Djourab regions in the north-central and northeastern parts of the country, respectively. This oddity arises because the great stationary dunes (ergs) of the Kanem region create a dam, preventing lake waters from flowing to the basin's lowest point. At various times in the past, and as late as the 1870s, the Bahr el Ghazal Depression, which extends from the northeastern part of the lake to the Djourab, acted as an overflow canal; since independence, climatic conditions have made overflows impossible.
North and northeast of Lake Chad, the basin extends for more than 800 kilometers, passing through regions characterized by great rolling dunes separated by very deep depressions. Although vegetation holds the dunes in place in the Kanem region, farther north they are bare and have a fluid, rippling character. From its low point in the Djourab, the basin then rises to the plateaus and peaks of the Tibesti Mountains in the north. The summit of this formation—as well as the highest point in the Sahara Desert—is Emi Koussi, a dormant volcano that reaches 3,414 meters above sea level.
The basin's northeastern limit is the Ennedi Plateau, whose limestone bed rises in steps etched by erosion. East of the lake, the basin rises gradually to the Ouaddaï Highlands, which mark Chad's eastern border and also divide the Chad and Nile watersheds. These highland areas are part of the East Saharan montane xeric woodlands
East Saharan montane xeric woodlands
The East Saharan montane xeric woodlands is an ecoregion of central Africa, a number of high mountains in the middle of the huge area of savanna on the edge of the Sahara Desert.-Location and description:...
ecoregion
Ecoregion
An ecoregion , sometimes called a bioregion, is an ecologically and geographically defined area that is smaller than an ecozone and larger than an ecosystem. Ecoregions cover relatively large areas of land or water, and contain characteristic, geographically distinct assemblages of natural...
.
Southeast of Lake Chad, the regular contours of the terrain are broken by the Guéra Massif, which divides the basin into its northern and southern parts. South of the lake lie the floodplains of the Chari and Logone rivers, much of which are inundated during the rainy season. Farther south, the basin floor slopes upward, forming a series of low sand and clay plateaus, called koros, which eventually climb to 615 meters above sea level. South of the Chadian border, the koros divide the Lake Chad Basin from the Ubangi-Zaire river system.
Water systems
Permanent streams do not exist in northern or central Chad. Following infrequent rains in the Ennedi Plateau and Ouaddaï Highlands, water may flow through depressions called enneris and wadis. Often the result of flash floods, such streams usually dry out within a few days as the remaining puddles seep into the sandy clay soil. The most important of these streams is the Batha, which in the rainy season carries water west from the Ouaddaï Highlands and the Guéra Massif to Lake Fitri.
Chari River
The Chari or Shari River is a 949-kilometer-long river of central Africa. It flows from the Central African Republic through Chad into Lake Chad, following the Cameroon border from N'Djamena, where it joins the Logone River waters....
and the Logone and their tributaries, which flow from the southeast into Lake Chad. Both river systems rise in the highlands of Central African Republic and Cameroon, regions that receive more than 1,250 millimeters of rainfall annually. Fed by rivers of Central African Republic, as well as by the Bahr Salamat, Bahr Aouk, and Bahr Sara rivers of southeastern Chad, the Chari River is about 1,200 kilometers long. From its origins near the city of Sarh, the middle course of the Chari makes its way through swampy terrain; the lower Chari is joined by the Logone River near N'Djamena. The Chari's volume varies greatly, from 17 cubic meters per second during the dry season to 340 cubic meters per second during the wettest part of the year.
The Logone River is formed by tributaries flowing from Cameroon and Central African Republic. Both shorter and smaller in volume than the Chari, it flows northeast for 960 kilometers; its volume ranges from five to eighty-five cubic meters per second. At N'Djamena the Logone empties into the Chari, and the combined rivers flow together for thirty kilometers through a large delta and into Lake Chad. At the end of the rainy season in the fall, the river overflows its banks and creates a huge floodplain in the delta.
The seventh largest lake in the world (and the fourth largest in Africa), Lake Chad
Lake Chad
Lake Chad is a historically large, shallow, endorheic lake in Africa, whose size has varied over the centuries. According to the Global Resource Information Database of the United Nations Environment Programme, it shrank as much as 95% from about 1963 to 1998; yet it also states that "the 2007 ...
is located in the sahelian zone, a region just south of the Sahara Desert. The Chari River contributes 95 percent of Lake Chad's water, an average annual volume of 40 billion cubic meters, 95% of which is lost to evaporation. The size of the lake is determined by rains in the southern highlands bordering the basin and by temperatures in the Sahel. Fluctuations in both cause the lake to change dramatically in size, from 9,800 square kilometers in the dry season to 25,500 at the end of the rainy season. Lake Chad also changes greatly in size from one year to another. In 1870 its maximum area was 28,000 square kilometers. The measurement dropped to 12,700 in 1908. In the 1940s and 1950s, the lake remained small, but it grew again to 26,000 square kilometers in 1963. The droughts of the late 1960s, early 1970s, and mid-1980s caused Lake Chad to shrink once again, however. The only other lakes of importance in Chad are Lake Fitri, in Batha Prefecture, and Lake Iro, in the marshy southeast.
Climate
The Lake Chad Basin embraces a great range of tropical climates from north to south, although most of these climates tend to be dry. Apart from the far north, most regions are characterized by a cycle of alternating rainy and dry seasons. In any given year, the duration of each season is determined largely by the positions of two great air masses—a maritime mass over the Atlantic Ocean to the southwest and a much drier continental mass. During the rainy season, winds from the southwest push the moister maritime system north over the African continent where it meets and slips under the continental mass along a front called the "intertropical convergence zone". At the height of the rainy season, the front may reach as far as Kanem Prefecture. By the middle of the dry season, the intertropical convergence zone moves south of Chad, taking the rain with it. This weather system contributes to the formation of three major regions of climate and vegetation.Saharan region

Sahelian region
The semiarid sahelian zone, or Sahel, forms a belt about 500 kilometres (311 mi) wide that runs from Lac and Chari-Baguirmi prefectures eastward through Guéra, Ouaddaï, and northern Salamat prefectures to the Sudanese frontier. The climate in this transition zone between the desert and the southern soudanian zone is divided into a rainy season (from June to early September) and a dry period (from October to May). In the northern Sahel, thorny shrubs and acacia trees grow wild, while date palms, cereals, and garden crops are raised in scattered oases. Outside these settlements, nomads tend their flocks during the rainy season, moving southward as forage and surface water disappear with the onset of the dry part of the year. The central Sahel is characterized by drought-resistant grasses and small woods. Rainfall is more abundant there than in the Saharan region. For example, N'Djamena records a maximum annual average rainfall of 580 millimetres (22.8 in), while Ouaddaï Prefecture receives just a bit less. During the hot season, in April and May, maximum temperatures frequently rise above 40 °C (104 °F). In the southern part of the Sahel, rainfall is sufficient to permit crop production on unirrigated land, and millet and sorghum are grown. Agriculture is also common in the marshlands east of Lake Chad and near swamps or wells. Many farmers in the region combine subsistence agriculture with the raising of cattle, sheep, goats, and poultry.Soudanian region
The humid soudanian zone includes the southern prefectures of Mayo-Kebbi, Tandjilé, Logone Occidental, Logone Oriental, Moyen-Chari, and southern Salamat. Between April and October, the rainy season brings between 750 and 1250 mm (29.5 and 49.2 in) of precipitation. Temperatures are high throughout the year. Daytime readings in Moundou, the major city in the southwest, range from 27 °C (80.6 °F) in the middle of the cool season in January to about 40 °C (104 °F) in the hot months of March, April, and May.The soudanian region is predominantly East Sudanian savanna
East Sudanian savanna
The East Sudanian Savanna is a hot, dry, tropical savanna ecoregion of central Africa.-Location and description:This is the eastern half of the broad savanna belt which runs east and west across Africa, this section lying east of the Cameroon Highlands...
, or plains covered with a mixture of tropical or subtropical grasses and woodlands. The growth is lush during the rainy season but turns brown and dormant during the five-month dry season between November and March. Over a large part of the region, however, natural vegetation has yielded to agriculture.
2010 drought
On 22 June, the temperature reached 47.6 °C (117.7 °F) in Faya, breaking a record set in 1961 at the same location. Similar temperature rises were also reported in NigerNiger
Niger , officially named the Republic of Niger, is a landlocked country in Western Africa, named after the Niger River. It borders Nigeria and Benin to the south, Burkina Faso and Mali to the west, Algeria and Libya to the north and Chad to the east...
, which began to enter a famine situation.
On 26 July the heat reached near record levels over Chad
Chad
Chad , officially known as the Republic of Chad, is a landlocked country in Central Africa. It is bordered by Libya to the north, Sudan to the east, the Central African Republic to the south, Cameroon and Nigeria to the southwest, and Niger to the west...
and Niger
Niger
Niger , officially named the Republic of Niger, is a landlocked country in Western Africa, named after the Niger River. It borders Nigeria and Benin to the south, Burkina Faso and Mali to the west, Algeria and Libya to the north and Chad to the east...
.
Area
Area:total:
1.284 million km²
land:
1,259,200 km²
water:
24,800 km²
Area - comparative:
Canada: smaller than the Northwest Territories
Northwest Territories
The Northwest Territories is a federal territory of Canada.Located in northern Canada, the territory borders Canada's two other territories, Yukon to the west and Nunavut to the east, and three provinces: British Columbia to the southwest, and Alberta and Saskatchewan to the south...
US: slightly more than three times the size of California
California
California is a state located on the West Coast of the United States. It is by far the most populous U.S. state, and the third-largest by land area...
Boundaries
Land boundaries:total:
5,968 km
border countries:
Cameroon
Cameroon
Cameroon, officially the Republic of Cameroon , is a country in west Central Africa. It is bordered by Nigeria to the west; Chad to the northeast; the Central African Republic to the east; and Equatorial Guinea, Gabon, and the Republic of the Congo to the south. Cameroon's coastline lies on the...
1,094 km, Central African Republic
Central African Republic
The Central African Republic , is a landlocked country in Central Africa. It borders Chad in the north, Sudan in the north east, South Sudan in the east, the Democratic Republic of the Congo and the Republic of the Congo in the south, and Cameroon in the west. The CAR covers a land area of about ,...
1,197 km, Libya 1,055 km, Niger
Niger
Niger , officially named the Republic of Niger, is a landlocked country in Western Africa, named after the Niger River. It borders Nigeria and Benin to the south, Burkina Faso and Mali to the west, Algeria and Libya to the north and Chad to the east...
1,175 km, Nigeria
Nigeria
Nigeria , officially the Federal Republic of Nigeria, is a federal constitutional republic comprising 36 states and its Federal Capital Territory, Abuja. The country is located in West Africa and shares land borders with the Republic of Benin in the west, Chad and Cameroon in the east, and Niger in...
87 km, Sudan
Sudan
Sudan , officially the Republic of the Sudan , is a country in North Africa, sometimes considered part of the Middle East politically. It is bordered by Egypt to the north, the Red Sea to the northeast, Eritrea and Ethiopia to the east, South Sudan to the south, the Central African Republic to the...
1,360 km
Coastline:
0 km (landlocked)
Maritime claims:
none (landlocked)
Elevation extremes:
lowest point:
Djourab Depression 160 m
highest point:
Emi Koussi
Emi Koussi
Emi Koussi is a high pyroclastic shield volcano that lies at the south end of the Tibesti Mountains in the central Sahara of northern Chad. It is the highest mountain in Chad, and the highest in the Sahara. The volcano is one of several in the Tibesti massif, and reaches 3445 m in altitude,...
3,415 m
Land use and resources
Natural resources:petroleum
Petroleum
Petroleum or crude oil is a naturally occurring, flammable liquid consisting of a complex mixture of hydrocarbons of various molecular weights and other liquid organic compounds, that are found in geologic formations beneath the Earth's surface. Petroleum is recovered mostly through oil drilling...
, uranium
Uranium
Uranium is a silvery-white metallic chemical element in the actinide series of the periodic table, with atomic number 92. It is assigned the chemical symbol U. A uranium atom has 92 protons and 92 electrons, of which 6 are valence electrons...
, natron
Natron
Natron is a naturally occurring mixture of sodium carbonate decahydrate and about 17% sodium bicarbonate along with small quantities of household salt and sodium sulfate. Natron is white to colourless when pure, varying to gray or yellow with impurities...
, kaolin, fish
Fish
Fish are a paraphyletic group of organisms that consist of all gill-bearing aquatic vertebrate animals that lack limbs with digits. Included in this definition are the living hagfish, lampreys, and cartilaginous and bony fish, as well as various extinct related groups...
(Chari River
Chari River
The Chari or Shari River is a 949-kilometer-long river of central Africa. It flows from the Central African Republic through Chad into Lake Chad, following the Cameroon border from N'Djamena, where it joins the Logone River waters....
, Logone River), gold
Gold
Gold is a chemical element with the symbol Au and an atomic number of 79. Gold is a dense, soft, shiny, malleable and ductile metal. Pure gold has a bright yellow color and luster traditionally considered attractive, which it maintains without oxidizing in air or water. Chemically, gold is a...
, limestone
Limestone
Limestone is a sedimentary rock composed largely of the minerals calcite and aragonite, which are different crystal forms of calcium carbonate . Many limestones are composed from skeletal fragments of marine organisms such as coral or foraminifera....
, sand
Sand
Sand is a naturally occurring granular material composed of finely divided rock and mineral particles.The composition of sand is highly variable, depending on the local rock sources and conditions, but the most common constituent of sand in inland continental settings and non-tropical coastal...
and gravel
Gravel
Gravel is composed of unconsolidated rock fragments that have a general particle size range and include size classes from granule- to boulder-sized fragments. Gravel can be sub-categorized into granule and cobble...
, salt
Salt
In chemistry, salts are ionic compounds that result from the neutralization reaction of an acid and a base. They are composed of cations and anions so that the product is electrically neutral...
Land use:
arable land:
2.8%
permanent crops:
0.02%
other:
97.18% (2005)
Irrigated land:
300 km² (2003)
Total renewable water resources:
43 km3 (2007)
Environmental issues
Natural hazards:hot, dry, dusty harmattan winds occur in north; periodic droughts; locust plagues
Environment - current issues:n
inadequate supplies of potable water; improper waste disposal in rural areas contributes to soil and water pollution; desertification
Desertification
Desertification is the degradation of land in drylands. Caused by a variety of factors, such as climate change and human activities, desertification is one of the most significant global environmental problems.-Definitions:...
Also see- 2010 Sahel drought
Extreme points
This is a list of the extreme points of ChadChad
Chad , officially known as the Republic of Chad, is a landlocked country in Central Africa. It is bordered by Libya to the north, Sudan to the east, the Central African Republic to the south, Cameroon and Nigeria to the southwest, and Niger to the west...
, the points that are farther north, south, east or west than any other location.
- Northernmost point - an unnamed location on the border with LibyaLibyaLibya is an African country in the Maghreb region of North Africa bordered by the Mediterranean Sea to the north, Egypt to the east, Sudan to the southeast, Chad and Niger to the south, and Algeria and Tunisia to the west....
, Borkou-Ennedi-Tibesti region - Easternmost point - the northern section of the Chad-Sudan borderBorderBorders define geographic boundaries of political entities or legal jurisdictions, such as governments, sovereign states, federated states and other subnational entities. Some borders—such as a state's internal administrative borders, or inter-state borders within the Schengen Area—are open and...
, Borkou-Ennedi-Tibesti region * - Southernmost point - unnamed location on the border with Central Africa Republic at a confluence in the Lébé river, Logone OrientalLogone OrientalLogone Oriental may refer to:* Logone Oriental Prefecture* Logone Oriental Region...
region - Westernmost point - unnamed location west of the town of Kanirom and immediately north of Lake ChadLake ChadLake Chad is a historically large, shallow, endorheic lake in Africa, whose size has varied over the centuries. According to the Global Resource Information Database of the United Nations Environment Programme, it shrank as much as 95% from about 1963 to 1998; yet it also states that "the 2007 ...
, Lac RegionLac RegionLac is one of the 22 regions of Chad and its capital is Bol. It is composed by the former Lac Prefecture.- Subdivisions :The region of Lac is divided in 2 departments:- Demography :The population of this region has 248,226 inhabitants ....
*Note: technically Chad does not have an easternmost point, the northern section of the border being formed by the 24° of latitude

