Geography of Algeria
Encyclopedia
|
||
| Continent Continent A continent is one of several very large landmasses on Earth. They are generally identified by convention rather than any strict criteria, with seven regions commonly regarded as continents—they are : Asia, Africa, North America, South America, Antarctica, Europe, and Australia.Plate tectonics is... |
Africa Africa Africa is the world's second largest and second most populous continent, after Asia. At about 30.2 million km² including adjacent islands, it covers 6% of the Earth's total surface area and 20.4% of the total land area... |
|
| Subregion Subregion A subregion is a conceptual unit which derives from a larger region or continent and is usually based on location. Cardinal directions, such as south or southern, are commonly used to define a subregion.- United Nations subregions :... |
North Africa North Africa North Africa or Northern Africa is the northernmost region of the African continent, linked by the Sahara to Sub-Saharan Africa. Geopolitically, the United Nations definition of Northern Africa includes eight countries or territories; Algeria, Egypt, Libya, Morocco, South Sudan, Sudan, Tunisia, and... |
|
| Geographic coordinates | 28°00′N 3°00′E | |
| Area Area Area is a quantity that expresses the extent of a two-dimensional surface or shape in the plane. Area can be understood as the amount of material with a given thickness that would be necessary to fashion a model of the shape, or the amount of paint necessary to cover the surface with a single coat... - Total - Water |
Ranked 10th 2,381,740 km² 1 E12 m² To help compare orders of magnitude of different surface areas, here is a list of areas between 1 million km2 and 10 million km2. See also areas of other orders of magnitude.* Areas smaller than 1 million km2* 1,000,000 km2 is equal to:** 1 E+12 m²... 0 km2 |
|
| Coastline | 998 km | |
| Land boundaries | 6,343 km | |
| Countries bordered | Morocco Morocco Morocco , officially the Kingdom of Morocco , is a country located in North Africa. It has a population of more than 32 million and an area of 710,850 km², and also primarily administers the disputed region of the Western Sahara... 1,559 km, Mali Mali Mali , officially the Republic of Mali , is a landlocked country in Western Africa. Mali borders Algeria on the north, Niger on the east, Burkina Faso and the Côte d'Ivoire on the south, Guinea on the south-west, and Senegal and Mauritania on the west. Its size is just over 1,240,000 km² with... 1,376 km, Libya Libya Libya is an African country in the Maghreb region of North Africa bordered by the Mediterranean Sea to the north, Egypt to the east, Sudan to the southeast, Chad and Niger to the south, and Algeria and Tunisia to the west.... 982 km, Tunisia Tunisia Tunisia , officially the Tunisian RepublicThe long name of Tunisia in other languages used in the country is: , is the northernmost country in Africa. It is a Maghreb country and is bordered by Algeria to the west, Libya to the southeast, and the Mediterranean Sea to the north and east. Its area... 965 km, Niger Niger Niger , officially named the Republic of Niger, is a landlocked country in Western Africa, named after the Niger River. It borders Nigeria and Benin to the south, Burkina Faso and Mali to the west, Algeria and Libya to the north and Chad to the east... 956 km, Mauritania Mauritania Mauritania is a country in the Maghreb and West Africa. It is bordered by the Atlantic Ocean in the west, by Western Sahara in the north, by Algeria in the northeast, by Mali in the east and southeast, and by Senegal in the southwest... 463 km, Western Sahara Western Sahara Western Sahara is a disputed territory in North Africa, bordered by Morocco to the north, Algeria to the northeast, Mauritania to the east and south, and the Atlantic Ocean to the west. Its surface area amounts to . It is one of the most sparsely populated territories in the world, mainly... 42 km |
|
| Maritime claims | 32-52 nm Nautical mile The nautical mile is a unit of length that is about one minute of arc of latitude along any meridian, but is approximately one minute of arc of longitude only at the equator... |
|
| Highest point | Mount Tahat Mount Tahat Mount Tahat is the highest mountain peak in Algeria, at . Tahat is also the highest peak in the Ahaggar Mountains. Its nearest city is Tamanrasset which is located 56 km to its south.-Sources:*... , 3,003 m |
|
| Lowest point | Chott Melrhir Chott Melrhir Chott Melrhir also known as Chott Melghir or Chott Melhir is an endorheic salt lake in northeastern Algeria. It the westernmost part of a series of depressions, which extend from the Gulf of Gabès into the Sahara. They were created between Miocene and Early Pleistocene as a result of compression... , -40 m |
|
| Longest river | Chelif River, 230 km | |
| Largest inland body of water | ||
| Land Use - Arable land - Permanent crops - Other |
3.71 % 0.28 % 96.55 % (2005 est.) | |
| Irrigated Land | 5,690 km2 | |
| Climate Climate Climate encompasses the statistics of temperature, humidity, atmospheric pressure, wind, rainfall, atmospheric particle count and other meteorological elemental measurements in a given region over long periods... : |
arid Arid A region is said to be arid when it is characterized by a severe lack of available water, to the extent of hindering or even preventing the growth and development of plant and animal life... to semiarid |
|
| Terrain Terrain Terrain, or land relief, is the vertical and horizontal dimension of land surface. When relief is described underwater, the term bathymetry is used... : |
mostly high plateau Plateau In geology and earth science, a plateau , also called a high plain or tableland, is an area of highland, usually consisting of relatively flat terrain. A highly eroded plateau is called a dissected plateau... and desert Desert A desert is a landscape or region that receives an extremely low amount of precipitation, less than enough to support growth of most plants. Most deserts have an average annual precipitation of less than... , mountain Mountain Image:Himalaya_annotated.jpg|thumb|right|The Himalayan mountain range with Mount Everestrect 58 14 160 49 Chomo Lonzorect 200 28 335 52 Makalurect 378 24 566 45 Mount Everestrect 188 581 920 656 Tibetan Plateaurect 250 406 340 427 Rong River... s, coastal plain Plain In geography, a plain is land with relatively low relief, that is flat or gently rolling. Prairies and steppes are types of plains, and the archetype for a plain is often thought of as a grassland, but plains in their natural state may also be covered in shrublands, woodland and forest, or... |
|
| Natural resources | petroleum Petroleum Petroleum or crude oil is a naturally occurring, flammable liquid consisting of a complex mixture of hydrocarbons of various molecular weights and other liquid organic compounds, that are found in geologic formations beneath the Earth's surface. Petroleum is recovered mostly through oil drilling... , natural gas Gas Gas is one of the three classical states of matter . Near absolute zero, a substance exists as a solid. As heat is added to this substance it melts into a liquid at its melting point , boils into a gas at its boiling point, and if heated high enough would enter a plasma state in which the electrons... , iron Iron Iron is a chemical element with the symbol Fe and atomic number 26. It is a metal in the first transition series. It is the most common element forming the planet Earth as a whole, forming much of Earth's outer and inner core. It is the fourth most common element in the Earth's crust... ore, phosphate Phosphate A phosphate, an inorganic chemical, is a salt of phosphoric acid. In organic chemistry, a phosphate, or organophosphate, is an ester of phosphoric acid. Organic phosphates are important in biochemistry and biogeochemistry or ecology. Inorganic phosphates are mined to obtain phosphorus for use in... s, uranium Uranium Uranium is a silvery-white metallic chemical element in the actinide series of the periodic table, with atomic number 92. It is assigned the chemical symbol U. A uranium atom has 92 protons and 92 electrons, of which 6 are valence electrons... , lead Lead Lead is a main-group element in the carbon group with the symbol Pb and atomic number 82. Lead is a soft, malleable poor metal. It is also counted as one of the heavy metals. Metallic lead has a bluish-white color after being freshly cut, but it soon tarnishes to a dull grayish color when exposed... , zinc Zinc Zinc , or spelter , is a metallic chemical element; it has the symbol Zn and atomic number 30. It is the first element in group 12 of the periodic table. Zinc is, in some respects, chemically similar to magnesium, because its ion is of similar size and its only common oxidation state is +2... |
|
| Natural hazards | earthquake Earthquake An earthquake is the result of a sudden release of energy in the Earth's crust that creates seismic waves. The seismicity, seismism or seismic activity of an area refers to the frequency, type and size of earthquakes experienced over a period of time... s, mudslides, flood Flood A flood is an overflow of an expanse of water that submerges land. The EU Floods directive defines a flood as a temporary covering by water of land not normally covered by water... s |
|
| Environmental issues | soil erosion, desertification Desertification Desertification is the degradation of land in drylands. Caused by a variety of factors, such as climate change and human activities, desertification is one of the most significant global environmental problems.-Definitions:... , pollution Pollution Pollution is the introduction of contaminants into a natural environment that causes instability, disorder, harm or discomfort to the ecosystem i.e. physical systems or living organisms. Pollution can take the form of chemical substances or energy, such as noise, heat or light... |
|
Algeria
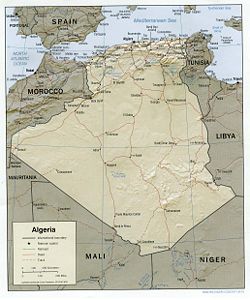
Algeria , officially the People's Democratic Republic of Algeria , also formally referred to as the Democratic and Popular Republic of Algeria, is a country in the Maghreb region of Northwest Africa with Algiers as its capital.In terms of land area, it is the largest country in Africa and the Arab...
comprises 2,381,741 square kilometers of land, more than four-fifths of which is desert, in northern Africa
Africa
Africa is the world's second largest and second most populous continent, after Asia. At about 30.2 million km² including adjacent islands, it covers 6% of the Earth's total surface area and 20.4% of the total land area...
, between Morocco
Morocco
Morocco , officially the Kingdom of Morocco , is a country located in North Africa. It has a population of more than 32 million and an area of 710,850 km², and also primarily administers the disputed region of the Western Sahara...
and Tunisia
Tunisia
Tunisia , officially the Tunisian RepublicThe long name of Tunisia in other languages used in the country is: , is the northernmost country in Africa. It is a Maghreb country and is bordered by Algeria to the west, Libya to the southeast, and the Mediterranean Sea to the north and east. Its area...
. It is the largest country in Africa. Its Arabic name, Al Jazair (the islands), derives from the name of the capital Algiers
Algiers
' is the capital and largest city of Algeria. According to the 1998 census, the population of the city proper was 1,519,570 and that of the urban agglomeration was 2,135,630. In 2009, the population was about 3,500,000...
(Al Jazair in Arabic), after the small islands formerly found in its harbor. It has a long Mediterranean coastline, most of which is more properly termed the Alboran Sea
Alboran Sea
|300px|thumb|]]The Alboran Sea is the westernmost portion of the Mediterranean Sea, lying between Spain on the north and Morocco and Algeria on the south...
, which is the westernmost element of the Mediterranean Sea. The northern portion, an area of mountains, valleys, and plateaus between the Mediterranean Sea and the Sahara Desert, forms an integral part of the section of North Africa known as the Maghreb
Maghreb
The Maghreb is the region of Northwest Africa, west of Egypt. It includes five countries: Morocco, Algeria, Tunisia, Libya, and Mauritania and the disputed territory of Western Sahara...
. This area includes Morocco
Morocco
Morocco , officially the Kingdom of Morocco , is a country located in North Africa. It has a population of more than 32 million and an area of 710,850 km², and also primarily administers the disputed region of the Western Sahara...
, Tunisia
Tunisia
Tunisia , officially the Tunisian RepublicThe long name of Tunisia in other languages used in the country is: , is the northernmost country in Africa. It is a Maghreb country and is bordered by Algeria to the west, Libya to the southeast, and the Mediterranean Sea to the north and east. Its area...
, and the northwestern portion of Libya
Libya
Libya is an African country in the Maghreb region of North Africa bordered by the Mediterranean Sea to the north, Egypt to the east, Sudan to the southeast, Chad and Niger to the south, and Algeria and Tunisia to the west....
known historically as Tripolitania
Tripolitania
Tripolitania or Tripolitana is a historic region and former province of Libya.Tripolitania was a separate Italian colony from 1927 to 1934...
.
Geographic coordinates: 28°N 3°E
Size and boundaries
Land boundaries:total: 6,343 km
border countries: Libya
Libya
Libya is an African country in the Maghreb region of North Africa bordered by the Mediterranean Sea to the north, Egypt to the east, Sudan to the southeast, Chad and Niger to the south, and Algeria and Tunisia to the west....
982 km, Mali
Mali
Mali , officially the Republic of Mali , is a landlocked country in Western Africa. Mali borders Algeria on the north, Niger on the east, Burkina Faso and the Côte d'Ivoire on the south, Guinea on the south-west, and Senegal and Mauritania on the west. Its size is just over 1,240,000 km² with...
1,376 km, Mauritania
Mauritania
Mauritania is a country in the Maghreb and West Africa. It is bordered by the Atlantic Ocean in the west, by Western Sahara in the north, by Algeria in the northeast, by Mali in the east and southeast, and by Senegal in the southwest...
463 km, Morocco 1,559 km, Niger
Niger
Niger , officially named the Republic of Niger, is a landlocked country in Western Africa, named after the Niger River. It borders Nigeria and Benin to the south, Burkina Faso and Mali to the west, Algeria and Libya to the north and Chad to the east...
956 km, Tunisia 965 km, Western Sahara
Western Sahara
Western Sahara is a disputed territory in North Africa, bordered by Morocco to the north, Algeria to the northeast, Mauritania to the east and south, and the Atlantic Ocean to the west. Its surface area amounts to . It is one of the most sparsely populated territories in the world, mainly...
42 km
Area - comparative: roughly 3.5 times the size of Texas
Coastline: 998 km
Maritime claims:
exclusive fishing zone: 32–52 nmi (59.3–96.3 km)
territorial sea: 12 nmi (22.2 km)
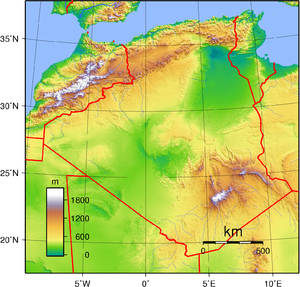
Tell Atlas, High Plateaus and the Saharan Atlas
Stretching from the Moroccan border the Tell AtlasTell Atlas
The Tell Atlas is a mountain chain over 1,500 kilometers in length, belonging to the Atlas mountain ranges in North Africa, stretching from Morocco, through Algeria to Tunisia. It parallels the Mediterranean coast...
, including the Djebel Babor
Djebel Babor
Djebel Babor is a mountainous landform in Algeria. A prominent feature of this area is the Djebel Babor Nature Reserve, which is known for birdwatching and as one of the few relict habitats for the endangered Barbary Macaque, Macaca sylvanus.-References:...
formation, is the dominant northwestern mountain range. Stretching more than 600 kilometers eastward from the Moroccan border, the High Plateaus (often referred to by their French name Hauts Plateaux) consist of undulating, steppe-like plains lying between the Tell and Saharan Atlas
Saharan Atlas
The Saharan Atlas of Algeria is the eastern portion of the Atlas Mountains. Not as tall as the Grand Atlas of Morocco they are far more imposing than the Tell Atlas range that runs closer to the coast. The tallest peak in the range is the high Djebel Aissa....
ranges. The plateaus average between 1,100 and 1,300 meters in elevation in the west, dropping to 400 meters in the east. So dry that they are sometimes thought of as part of the Sahara, the plateaus are covered by alluvial debris formed when the mountains eroded. An occasional ridge projects through the alluvial cover to interrupt the monotony of the landscape.
Higher and more continuous than the Tell Atlas, the Sahara Atlas range is formed of three massifs: the Ksour near the Moroccan border, the Amour, and the Oulad Nail south of Algiers
Algiers
' is the capital and largest city of Algeria. According to the 1998 census, the population of the city proper was 1,519,570 and that of the urban agglomeration was 2,135,630. In 2009, the population was about 3,500,000...
. The mountains, which receive more rainfall than those of the High Plateaus, include some good grazing land. Watercourses on the southern slopes of these massifs disappear into the desert but supply the wells of numerous oases along the northern edge of the desert, of which Biskra
Biskra
Biskra is the capital city of Biskra province, Algeria. In 2007, its population was recorded as 207,987.During Roman times the town was called Vescera, though this may have been simply a Latin transliteration of the native name. Around 200 AD under Septimius Severus' reign, it was seized by the...
, Laghouat
Laghouat
Laghouat is the capital city of the Laghouat Province, Algeria, 400 km south of the Algerian capital Algiers in the Atlas Mountains. As of 2005, the population of the city was 126,291 inhabitants. Nearby, in Hassi R'Mel, there is the largest natural gas reserve in Africa.The city was founded in...
, and Béchar
Béchar
Béchar , formerly known as Colomb-Béchar, is a capital city of Béchar Province, Algeria. The area is controlled by Algeria, though claims have also been made on it by Morocco. In 1998 the city had a population of 134,954....
are the most prominent.
Northeastern Algeria
Eastern Algeria consists of a massive area extensively dissected into mountains, plains, and basins. It differs from the western portion of the country in that its prominent topographic features do not parallel the coast. In its southern sector, the steep cliffs and long ridges of the Aurès MountainsAurès Mountains
The Aurès , or Aurea, refers to an Amazigh language-speaking region in East Algeria, as well as an extension of the Atlas mountain range that lies to the east of the Saharan Atlas in eastern Algeria and northwestern Tunisia...
create an almost impenetrable refuge that has played an important part in the history of the Maghrib since Roman
Ancient Rome
Ancient Rome was a thriving civilization that grew on the Italian Peninsula as early as the 8th century BC. Located along the Mediterranean Sea and centered on the city of Rome, it expanded to one of the largest empires in the ancient world....
times. Near the northern coast, the Petite Kabylie Mountains are separated from the Grande Kabylie range at the eastward limits of the Tell by the Soummam River. The coast is predominantly mountainous in the far eastern part of the country, but limited plains provide hinterlands for the port cities of Bejaïa, Skikda, and Annaba. In the interior of the region, extensive high plains mark the region around Sétif
Sétif
Sétif |Colonia]]) is a town in northeastern Algeria. It is the capital of Sétif Province and it has a population of 239,195 inhabitants as of the 1998 census. Setif is located to the east of Algiers and is the second most important Wilaya after the country's capital. It is 1,096 meters above sea...
and Constantine
Constantine, Algeria
Constantine is the capital of Constantine Province in north-eastern Algeria. It was the capital of the same-named French département until 1962. Slightly inland, it is about 80 kilometres from the Mediterranean coast, on the banks of Rhumel river...
; these plains were developed during the French colonial period as the principal centers of grain cultivation. Near Constantine, salt marshes offer seasonal grazing grounds to seminomadic sheep herders.
The Sahara
The Algerian portion of the Sahara extends south of the Saharan Atlas for 1,500 kilometers to the Niger and Mali frontiers. The desert is an otherworldly place, scarcely considered an integral part of the country. Far from being covered wholly by sweeps of sand, however, it is a region of great diversity. Immense areas of sand dunes called areg (sing., erg) occupy about one-quarter of the territory. The largest such region is the Grand Erg Oriental
Grand Erg Oriental
The Grand Erg Oriental is a large erg in the Sahara desert. Situated for the most part in Saharan lowlands of northeast Algeria, the Grand Erg Oriental covers an area some 600 km wide by 200 km north to south...
(Great Eastern Erg), where enormous dunes two to five meters high are spaced about 40 meters apart. Much of the remainder of the desert is covered by rocky platforms called humud (sing., hamada), and almost the entire southeastern quarter is taken up by the high, complex mass of the Ahaggar and Tassili n'Ajjer
Tassili n'Ajjer
Tassili n'Ajjer is a mountain range in the Algerian section of the Sahara Desert. It is a vast plateau in south-east Algeria at the borders of Libya, Niger and Mali, covering an area of 72,000 sq...
highlands, some parts of which reach more than 2,000 meters. Surrounding the Ahaggar are sandstone plateaus, cut into deep gorges by ancient rivers, and to the west a desert of pebbles stretches to the Mali frontier.
The desert consists of readily distinguishable northern and southern sectors, the northern sector extending southward a little less than half the distance to the Niger
Niger
Niger , officially named the Republic of Niger, is a landlocked country in Western Africa, named after the Niger River. It borders Nigeria and Benin to the south, Burkina Faso and Mali to the west, Algeria and Libya to the north and Chad to the east...
and Mali
Mali
Mali , officially the Republic of Mali , is a landlocked country in Western Africa. Mali borders Algeria on the north, Niger on the east, Burkina Faso and the Côte d'Ivoire on the south, Guinea on the south-west, and Senegal and Mauritania on the west. Its size is just over 1,240,000 km² with...
frontiers. The north, less arid than the south, supports most of the few persons who live in the region and contains most of the desert's oases. Sand dunes are the most prominent features of this area's topography, but between the desert areas of the Grand Erg Oriental and the Grand Erg Occidental
Grand Erg Occidental
The Grand Erg Occidental is the second largest erg in northern Algeria, behind the Grand Erg Oriental. This true desert region receives less than 25 cm of rainfall per year. It contains no human villages and there are no roads through it....
(Great Western Erg) and extending north to the Atlas Saharien are plateaus, including a complex limestone structure called the M'zab
M'zab
The M'zab or Mzab, , is a region of the northern Sahara, in the Ghardaïa wilaya, an administrative division similar to a province, of Algeria...
where the M'zabite Berbers
Berber people
Berbers are the indigenous peoples of North Africa west of the Nile Valley. They are continuously distributed from the Atlantic to the Siwa oasis, in Egypt, and from the Mediterranean to the Niger River. Historically they spoke the Berber language or varieties of it, which together form a branch...
have settled. The southern zone of the Sahara is almost totally arid and is inhabited only by the Tuareg nomads and, recently, by oil camp workers. Barren rock predominates, but in some parts of Ahaggar and Tassili n'Ajjer alluvial deposits permit garden farming.
Climate and hydrology

Northern Algeria is in the temperate zone and enjoys a mild, Mediterranean climate. It lies within approximately the same latitudes as southern California and has somewhat similar climatic conditions. Its broken topography, however, provides sharp local contrasts in both prevailing temperatures and incidence of rainfall. Year-to-year variations in climatic conditions are also common.
In the Tell, temperatures in summer average between 21 and 24 °C (69.8 and 75.2 °F) and in winter drop to 10 to 12 °C (50 to 53.6 °F). Winters are not cold, but the humidity is high and houses are seldom adequately heated. In eastern Algeria, the average temperatures are somewhat lower, and on the steppes of the High Plateaus winter temperatures hover only a few degrees above freezing. A prominent feature of the climate in this region is the sirocco, a dusty, choking south wind blowing off the desert, sometimes at gale force. This wind also occasionally reaches into the coastal Tell.
In Algeria only a relatively small corner of the Sahara lies across the Tropic of Cancer in the torrid zone, but even in winter, midday desert temperatures can be very hot. After sunset, however, the clear, dry air permits rapid loss of heat, and the nights are cool to chilly. Enormous daily ranges in temperature are recorded.
Rainfall is fairly abundant along the coastal part of the Tell, ranging from 400 to 670 mm (15.7 to 26.4 in) annually, the amount of precipitation increasing from west to east. Precipitation is heaviest in the northern part of eastern Algeria, where it reaches as much as 1000 mm (39.4 in) in some years. Farther inland the rainfall is less plentiful. Prevailing winds that are easterly and northeasterly in summer change to westerly and northerly in winter and carry with them a general increase in precipitation from September to December, a decrease in the late winter and spring months, and a near absence of rainfall during the summer months.
Terrain
Clearing of land for agricultural use and cutting of timber over the centuries have severely reduced the once bountiful forest wealth. Forest fires have also taken their toll. In the higher and wetter portions of the Tell Atlas, cork oak and Aleppo pine grow in thick soils. At lower levels on thinner soils, drought-resistant shrubs predominate. The grapevine is indigenous to the coastal lowlands, and grasses and scrub cover the High Plateaus. On the Saharan Atlas, little survives of the once extensive forests of Atlas cedar that have been exploited for fuel and timber since antiquity.The forest reserves in Algeria were severely reduced during the colonial period. In 1967 it was calculated that the country's forested area extended over no more than 24,000 square kilometres of terrain, of which 18,000 km2 were overgrown with brushwood and scrub. By contrast, woodlands in 1830 had covered 50,000 km2. In the mid-1970s, however, the government embarked on a vast reforestation program to help control erosion, which was estimated to affect 100,000 cubic meters of arable land annually. Among projects was one to create a barrage vert (green barrier) more or less following the ridge line of the Saharan Atlas and extending from Morocco to the Tunisian frontier in a zone 1,500 kilometers long and up to twenty kilometers wide.
The barrage vert consists principally of Aleppo pine, a species that can thrive in areas of scanty rainfall. It is designed to restore a damaged ecological balance and to halt the northern encroachment of the Sahara. By the early 1980s, the desert had already penetrated the hilly gap between the Saharan Atlas and the Aurès Mountains as far as the town of Bou Saâda, a point well within the High Plateaus region. The barrage vert project was ended in the late 1980s because of lack of funds.
Statistics
Elevation extremes:lowest point: Chott Melrhir
Chott Melrhir
Chott Melrhir also known as Chott Melghir or Chott Melhir is an endorheic salt lake in northeastern Algeria. It the westernmost part of a series of depressions, which extend from the Gulf of Gabès into the Sahara. They were created between Miocene and Early Pleistocene as a result of compression...
-40 m
highest point: Mount Tahat
Mount Tahat
Mount Tahat is the highest mountain peak in Algeria, at . Tahat is also the highest peak in the Ahaggar Mountains. Its nearest city is Tamanrasset which is located 56 km to its south.-Sources:*...
3,003 m
Extreme Points
Northernmost Point - Cap Bougaroûn, Skikda
Skikda
Skikda is a city in north eastern Algeria and a port on the Gulf of Stora, the ancient Sinus Numidicus. It was known as Philippeville until the end of the Algerian War of Independence in 1962...
province
Easternmost Point - Tripoint
Tripoint
A tripoint, or trijunction , is a geographical point at which the borders of three countries or subnational entities meet....
with Libya
Libya
Libya is an African country in the Maghreb region of North Africa bordered by the Mediterranean Sea to the north, Egypt to the east, Sudan to the southeast, Chad and Niger to the south, and Algeria and Tunisia to the west....
and Niger
Niger
Niger , officially named the Republic of Niger, is a landlocked country in Western Africa, named after the Niger River. It borders Nigeria and Benin to the south, Burkina Faso and Mali to the west, Algeria and Libya to the north and Chad to the east...
, Tamanghasset
Tamanghasset
Tamanrasset is an oasis city and capital of Tamanrasset Province in southern Algeria, in the Ahaggar Mountains. It is the chief city of the Algerian Tuareg...
province
Southernmost Point - unnamed location on the border with Mali
Mali
Mali , officially the Republic of Mali , is a landlocked country in Western Africa. Mali borders Algeria on the north, Niger on the east, Burkina Faso and the Côte d'Ivoire on the south, Guinea on the south-west, and Senegal and Mauritania on the west. Its size is just over 1,240,000 km² with...
, Adrar province
Westernmost Point - N/A
Natural resources: petroleum, natural gas, iron ore, phosphates, uranium, lead, zinc
Land use:
arable land: 3.17%
permanent crops: 0.28%
other: 96.55% (2005)
Irrigated land: 5,690 km2 (2003)
Natural hazards: mountainous areas subject to severe earthquakes; mudslides and floods in rainy season
Total renewable water resources: 14.3 km3 (1997)
Freshwater withdrawal (domestic/industrial/agricultural)
total: 6.07 km3/yr (22%/13%/65%)
per capita: 185 m3/yr (2000)
Environment - current issues: soil erosion from overgrazing and other poor farming practices; desertification; dumping of raw sewage, petroleum refining wastes, and other industrial effluents is leading to the pollution of rivers and coastal waters; Mediterranean Sea, in particular, becoming polluted from oil wastes, soil erosion, and fertilizer runoff; inadequate supplies of potable water
Environment - international agreements:
party to: Biodiversity, Climate Change, Desertification, Endangered Species, Environmental Modification, Hazardous Wastes, Law of the Sea, Ozone Layer Protection, Ship Pollution, Wetlands signed, but not ratified: Nuclear Test Ban
Protected areas
Algeria has a number of protected areas including National Parks and nature reserves. An example of such a protected area is the Djebel Babor Nature ReserveDjebel Babor Nature Reserve
The Djebel Babor Nature Reserve is a protected area in Algeria. The reserve is within the Djebel Babor Mountains. Much of this area is forested with Mediterranean conifer and mixed forests. This reserve offers one of the few remaining disjunctive habitats for the endangered Barbary Macaque, Macaca...
within the Djebel Babor Mountains; the Djebel Babor is also one of the few relict habitats for the endangered Barbary Macaque
Barbary Macaque
The Barbary Macaque , or Common macaque, is a macaque with no tail. Found in the Atlas Mountains of Algeria and Morocco with a small population, of unknown origin, in Gibraltar, the Barbary Macaque is one of the best-known Old World monkey species. Besides humans, they are the only primates that...
, Macaca sylvanus.
The National Parks in Algeria are: Ahaggar
Ahaggar Mountains
The Ahaggar Mountains , also known as the Hoggar, are a highland region in central Sahara, or southern Algeria, along the Tropic of Cancer. They are located about 1,500 km south of the capital, Algiers and just west of Tamanghasset. The region is largely rocky desert with an average...
, Belezma, Chréa
Chréa National Park
The Chréa National Park ' is one of the smallest national parks of Algeria. It is located in Blida Province, named after Chréa, a town near this park...
, Djurdjura
Djurdjura National Park
The national park of Djurdjura ' is one of the national parks of Algeria. It is located in Kabylia, named after the Djurdjura mountain chain. Nearby cities include Tizi Ouzou and Bouïra...
, El Kala
El Kala National Park
The national park of El Ka la ' is one of the national parks of Algeria, in the extreme north-east of the country...
, Gouraya
Gouraya National Park
The national park of Gouraya ' is one of the coastal national parks of Algeria. It is located in Béjaïa Province, near the town of Sidi Touati.The park is located 30 kilometers north-east of Jijel...
, Tassili n'Ajjer
Tassili n'Ajjer
Tassili n'Ajjer is a mountain range in the Algerian section of the Sahara Desert. It is a vast plateau in south-east Algeria at the borders of Libya, Niger and Mali, covering an area of 72,000 sq...
, Taza
Taza National Park
The national park of Taza ' is one of the smaller national national parks of Algeria. It is located in Jijel Province, named after Taza, a town near this park....
, Théniet El Had
Théniet El Had National Park
The Théniet El Had National Park is one of the 10 national parks of Algeria. It is located in Tissemsilt Province, named after Théniet El Haâd, a town near this park. It has several forests, and it is located in the foothills of the highest peak of the Ouarsenis, a mountain chain in the Tell...
, and Tlemcen
Tlemcen National Park
The Tlemcen National Park ' is one of the more recent national parks of Algeria. It is located in Tlemcen Province, named after Tlemcen, a city near this park...
.
Extreme points
This is a list of the extreme points of AlgeriaAlgeria
Algeria , officially the People's Democratic Republic of Algeria , also formally referred to as the Democratic and Popular Republic of Algeria, is a country in the Maghreb region of Northwest Africa with Algiers as its capital.In terms of land area, it is the largest country in Africa and the Arab...
, the points that are farther north, south, east or west than any other location.
- Northernmost point – Cap Takouch, Annaba ProvinceAnnaba ProvinceAnnaba is a small province in the north-eastern corner of Algeria. Its capital, Annaba is Algeria's main port for mineral exports.-Administrative divisions:The province is divided into 6 districts and 12 municipalities.The districts are:...
- Easternmost point – the tripointTripointA tripoint, or trijunction , is a geographical point at which the borders of three countries or subnational entities meet....
with NigerNigerNiger , officially named the Republic of Niger, is a landlocked country in Western Africa, named after the Niger River. It borders Nigeria and Benin to the south, Burkina Faso and Mali to the west, Algeria and Libya to the north and Chad to the east...
and LibyaLibyaLibya is an African country in the Maghreb region of North Africa bordered by the Mediterranean Sea to the north, Egypt to the east, Sudan to the southeast, Chad and Niger to the south, and Algeria and Tunisia to the west....
, Tamanghasset ProvinceTamanghasset ProvinceTamanrasset or Tamanghasset is the largest province in Algeria. It was named after its province seat: Tamanrasset. The Province has two national parks, more than any other in Algeria. They are: Tassili n'Ajjer National Park and Ahaggar National Park... - Southernmost point – unnamed location on the border with MaliMaliMali , officially the Republic of Mali , is a landlocked country in Western Africa. Mali borders Algeria on the north, Niger on the east, Burkina Faso and the Côte d'Ivoire on the south, Guinea on the south-west, and Senegal and Mauritania on the west. Its size is just over 1,240,000 km² with...
east of the Malian village of In-Abalen, Adrar ProvinceAdrar ProvinceAdrar is a province in southwestern Algeria, named after its capital Adrar. It is the second-largest province, with an area of 427,368 km²... - Westernmost point - the western section of the border with MoroccoMoroccoMorocco , officially the Kingdom of Morocco , is a country located in North Africa. It has a population of more than 32 million and an area of 710,850 km², and also primarily administers the disputed region of the Western Sahara...
/Western SaharaWestern SaharaWestern Sahara is a disputed territory in North Africa, bordered by Morocco to the north, Algeria to the northeast, Mauritania to the east and south, and the Atlantic Ocean to the west. Its surface area amounts to . It is one of the most sparsely populated territories in the world, mainly...
, Tindouf ProvinceTindouf ProvinceTindouf, also written Tinduf, is the westernmost province of Algeria, having a population of 58,193 as of the 2008 census. Despite the barren landscape, Tindouf is a resource-rich province, with important quantities of iron ore located in the Gara Djebilet area close to the border with Mali...
*
- *Note: Algeria does not have a westernmost point, the border being formed by a line of longitude