
Gangotri Glacier
Encyclopedia
Gangotri Glacier is located in Uttarkashi District, Uttarakhand
, India
in a region bordering China
. This glacier, source of the Ganges, is one of the largest in the Himalayas
with an estimated volume of over 27 cubic kilometers. The glacier is about 30 kilometres long (19 miles) and 2 to 4 km (1 to 2 mi) wide. Around the glacier are the peaks of the Gangotri Group
, including several peaks notable for extremely challenging climbing routes, such as Shivling
, Thalay Sagar
, Meru
, and Bhagirathi III. It flows roughly northwest, originating in a cirque
below Chaukhamba
, the highest peak of the group.
The terminus
of the Gangotri Glacier is said to resemble a cow's mouth, and the place is called Gomukh
or Gaumukh (gou, cow + mukh, face). Gomukh, which is about 18 km (11.2 mi) from the town of Gangotri, is the precise source of the Bhagirathi river, an important tributary
of the Ganges
. Gomukh is situated near the base of Shivling; in between lies the Tapovan
meadow.
The Gangotri glacier is a traditional Hindu
pilgrimage
site. Devout Hindus consider bathing in the icy waters near Gangotri town to be a holy ritual, and many make the trek to Gomukh and Tapovan
.
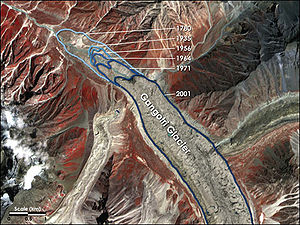
In recent times, it has been pointed out that the retreat
of the glacier has slowed significantly.
_may_28_2007.jpg)
 It is a valley-type glacier, situated in the Uttarkashi district of Garhwal Himalaya, Uttaranchal (Figure 1) and it flows to NW direction. This glacier is bound between 30°43'22"–30°55'49" (lat.) and 79°4'41"–79°16'34" (long.), extending in height from 4120 to 7000 m.a.s.l. This area is situated north of the Main Central Thrust (MCT) and is made up of bedrocks of granites, garnet mica schist, quartz biotite schist, kyanite schist, augen gneiss and banded augen gneiss.
It is a valley-type glacier, situated in the Uttarkashi district of Garhwal Himalaya, Uttaranchal (Figure 1) and it flows to NW direction. This glacier is bound between 30°43'22"–30°55'49" (lat.) and 79°4'41"–79°16'34" (long.), extending in height from 4120 to 7000 m.a.s.l. This area is situated north of the Main Central Thrust (MCT) and is made up of bedrocks of granites, garnet mica schist, quartz biotite schist, kyanite schist, augen gneiss and banded augen gneiss.
the glacier is composed of a variety of depositional features such as talus cones, snow-avalanche fans, snow-bridges, and dead ice mounds, and erosional features like pyramidal and conical peaks, serrated ridge crests, glacial troughs, smooth rock walls, crags and tails, waterfalls, rock basins, gullies and glacial lakes. All along the Gangotri glacier, several longitudinal and transverse crevasses are formed along which ice blocks have broken down. The ablation zone of the Gangotri glacier is covered by a thick pile of supraglacial moraines and is characterized by several ice sections, melting into pools of supraglacial lake
s. Because of subsidence and the fast degenerating nature of the glacier, its centre is full of supraglacial lakes. In this part of higher Himalaya, glacial melt-water dominates the fluvial system.
The total ice cover is approximately 200 km² and has about 20 km³ of ice in volume.
 NASA
NASA
, in conjunction with Scientists from United States Geological Survey
(USGS) and the National Snow and Ice Data Center
(NSIDC), is developing a global inventory of all the world's glaciers to help researchers track each glacier's history. According to them, the Gangotri glacier, currently 30.2 km long and between 0.5 to 2.5 km wide, is one of the largest in the Himalayas. This glacier has been constantly receding since measurements began in 1780. Data for 61 years (1936–96) show that the total recession of Gangotri glacier is 1147 m, with the average rate of 19 m per year. However, over the last 25 years of the 20th century it has retreated more than 850 meters (34 meters per year), and 76 meters between 1996 and 1999 (25 meters per year).
Uttarakhand
Uttarakhand , formerly Uttaranchal, is a state in the northern part of India. It is often referred to as the Land of Gods due to the many holy Hindu temples and cities found throughout the state, some of which are among Hinduism's most spiritual and auspicious places of pilgrimage and worship...
, India
India
India , officially the Republic of India , is a country in South Asia. It is the seventh-largest country by geographical area, the second-most populous country with over 1.2 billion people, and the most populous democracy in the world...
in a region bordering China
China
Chinese civilization may refer to:* China for more general discussion of the country.* Chinese culture* Greater China, the transnational community of ethnic Chinese.* History of China* Sinosphere, the area historically affected by Chinese culture...
. This glacier, source of the Ganges, is one of the largest in the Himalayas
Himalayas
The Himalaya Range or Himalaya Mountains Sanskrit: Devanagari: हिमालय, literally "abode of snow"), usually called the Himalayas or Himalaya for short, is a mountain range in Asia, separating the Indian subcontinent from the Tibetan Plateau...
with an estimated volume of over 27 cubic kilometers. The glacier is about 30 kilometres long (19 miles) and 2 to 4 km (1 to 2 mi) wide. Around the glacier are the peaks of the Gangotri Group
Gangotri Group
The Gangotri Group of mountains is a subdivision of the Garhwal Himalaya in the northern Indian state of Uttarakhand. It rings the Gangotri Glacier, and contains peaks that are notable either for their religious significance to Hindus, for their difficult climbing routes, or both...
, including several peaks notable for extremely challenging climbing routes, such as Shivling
Shivling (Garhwal Himalaya)
Shivling is a mountain in the Gangotri Group of peaks in the western Garhwal Himalaya, near the snout of the Gangotri Glacier. It lies in the northern Indian state of Uttarakhand, south of the Hindu holy site of Gaumukh . Its name refers to its status as a sacred symbol of the God - Lord Shiva's...
, Thalay Sagar
Thalay Sagar
Thalay Sagar is a mountain in the Gangotri Group of peaks in the western Garhwal Himalaya, on the main ridge that lies south of the Gangotri Glacier. It lies in the northern Indian state of Uttarakhand, southwest of the Hindu holy site of Gaumukh...
, Meru
Meru Peak
Meru Peak is a mountain which lies in the Himalayas, in the Uttarakhand region of India. It is within the Nanda Devi National Park, and is high. It is the site of the world's highest BASE Jump from 'Earth', by Glenn Singleman and Heather Swan from a height of in June 2006.The mountain has three...
, and Bhagirathi III. It flows roughly northwest, originating in a cirque
Cirque
Cirque may refer to:* Cirque, a geological formation* Makhtesh, an erosional landform found in the Negev desert of Israel and Sinai of Egypt*Cirque , an album by Biosphere* Cirque Corporation, a company that makes touchpads...
below Chaukhamba
Chaukhamba
Chaukhamba is a mountain massif in the Gangotri Group of the Garhwal Himalaya. Its main summit, Chaukhamba I, is the highest peak in the group. It lies at the head of the Gangotri Glacier and forms the eastern anchor of the group...
, the highest peak of the group.
The terminus
Glacier terminus
A glacier terminus, or snout, is the end of a glacier at any given point in time. Although glaciers seem motionless to the observer, in reality glaciers are in endless motion and the glacier terminus is always either advancing or retreating...
of the Gangotri Glacier is said to resemble a cow's mouth, and the place is called Gomukh
Gomukh
Gomukh, the terminus or snout of the Gangotri Glacier, from where Bhagirathi River originates. The place is situated at a height of 11,500 ft. It is one of the largest in the Himalayas with an estimated volume of over 27 cubic kilometers....
or Gaumukh (gou, cow + mukh, face). Gomukh, which is about 18 km (11.2 mi) from the town of Gangotri, is the precise source of the Bhagirathi river, an important tributary
Tributary
A tributary or affluent is a stream or river that flows into a main stem river or a lake. A tributary does not flow directly into a sea or ocean...
of the Ganges
Ganges River
The Ganges or Ganga, , is a trans-boundary river of India and Bangladesh. The river rises in the western Himalayas in the Indian state of Uttarakhand, and flows south and east through the Gangetic Plain of North India into Bangladesh, where it empties into the Bay of Bengal. By discharge it...
. Gomukh is situated near the base of Shivling; in between lies the Tapovan
Tapovan
Tapovan comes from the two root words Tapasya - meaning specifically austerity, and more generally spiritual practice, and Vana, meaning forest, or wilderness...
meadow.
The Gangotri glacier is a traditional Hindu
Hindu
Hindu refers to an identity associated with the philosophical, religious and cultural systems that are indigenous to the Indian subcontinent. As used in the Constitution of India, the word "Hindu" is also attributed to all persons professing any Indian religion...
pilgrimage
Pilgrimage
A pilgrimage is a journey or search of great moral or spiritual significance. Typically, it is a journey to a shrine or other location of importance to a person's beliefs and faith...
site. Devout Hindus consider bathing in the icy waters near Gangotri town to be a holy ritual, and many make the trek to Gomukh and Tapovan
Tapovan
Tapovan comes from the two root words Tapasya - meaning specifically austerity, and more generally spiritual practice, and Vana, meaning forest, or wilderness...
.
In recent times, it has been pointed out that the retreat
Retreat of glaciers since 1850
The retreat of glaciers since 1850 affects the availability of fresh water for irrigation and domestic use, mountain recreation, animals and plants that depend on glacier-melt, and in the longer term, the level of the oceans...
of the glacier has slowed significantly.
_may_28_2007.jpg)
Geology

the glacier is composed of a variety of depositional features such as talus cones, snow-avalanche fans, snow-bridges, and dead ice mounds, and erosional features like pyramidal and conical peaks, serrated ridge crests, glacial troughs, smooth rock walls, crags and tails, waterfalls, rock basins, gullies and glacial lakes. All along the Gangotri glacier, several longitudinal and transverse crevasses are formed along which ice blocks have broken down. The ablation zone of the Gangotri glacier is covered by a thick pile of supraglacial moraines and is characterized by several ice sections, melting into pools of supraglacial lake
Supraglacial lake
A supraglacial lake is any pond of liquid water on the top of a glacier. Although these pools are , they may reach kilometers in diameter and be several meters deep...
s. Because of subsidence and the fast degenerating nature of the glacier, its centre is full of supraglacial lakes. In this part of higher Himalaya, glacial melt-water dominates the fluvial system.
The total ice cover is approximately 200 km² and has about 20 km³ of ice in volume.
Tributaries
This glacier has three main tributaries, namely Raktvarn (15.90 km), Chaturangi (including Kalandini bamak) (22.45 km) and Kirti (11.05 km) and more than 18 smaller tributary glaciers The Raktvarn system contains 7 tributary glaciers; among them Thelu, Swetvarn, Nilambar and Pilapani are important. Similarly the Seeta, Suralaya and Vasuki are the major tributaries which make up the Chaturangi system, while the Kirti system is made up of only three tributary glaciers. Besides these three major tributary systems, some other tributary glaciers of this area drain directly into the Gangotri glacier; among them Swachand, Miandi, Sumeru and Ghanohim are important. Four other glaciers, Maitri, Meru, Bhrigupanth and Manda drain into the river Bhagirathi. The total glacierized area of the catchment is 258.56 km², out of which the Gangotri system comprises 109.03 km², followed by Chaturangi (72.91 km²), Raktvarn (45.34 km²) and Kirti (31.28 km²). The remaining four glaciers contain 29.41 km² of glacierized area; among them maximum contribution is Bhirgupanth glacier (14.95 km²).Retreat of Gangotri Glacier

NASA
The National Aeronautics and Space Administration is the agency of the United States government that is responsible for the nation's civilian space program and for aeronautics and aerospace research...
, in conjunction with Scientists from United States Geological Survey
United States Geological Survey
The United States Geological Survey is a scientific agency of the United States government. The scientists of the USGS study the landscape of the United States, its natural resources, and the natural hazards that threaten it. The organization has four major science disciplines, concerning biology,...
(USGS) and the National Snow and Ice Data Center
National Snow and Ice Data Center
The National Snow and Ice Data Center, or NSIDC, is a United States information and referral center in support of polar and cryospheric research...
(NSIDC), is developing a global inventory of all the world's glaciers to help researchers track each glacier's history. According to them, the Gangotri glacier, currently 30.2 km long and between 0.5 to 2.5 km wide, is one of the largest in the Himalayas. This glacier has been constantly receding since measurements began in 1780. Data for 61 years (1936–96) show that the total recession of Gangotri glacier is 1147 m, with the average rate of 19 m per year. However, over the last 25 years of the 20th century it has retreated more than 850 meters (34 meters per year), and 76 meters between 1996 and 1999 (25 meters per year).
External links
- Retreat of the Gangotri Glacier, an article from NASA's Earth Observatory
- Gaumukh and Gangotri Art Photos
- Save Gangotri, highlights localized ecological damage and conservation efforts in the region
- Geomorphological evidences of retreat of the Gangotri glacier and its characteristics, A Study by Department of Geology, HNB Garhwal University
- 283 photos 1280x960 of trekking from Gangotri to Gaumukh. You can see the retreat of the Gangotri glacier on picture gomukh141.jpg

