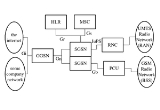
GPRS Core Network
Encyclopedia
The GPRS core network is the central part of the General Packet Radio Service
which allows 2G
, 3G
and WCDMA mobile networks
to transmit IP
packets to external networks such as the Internet
. The GPRS system is an integrated part of the GSM network switching subsystem
.
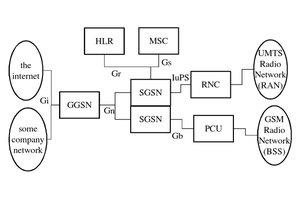 The GPRS core network provides mobility management
The GPRS core network provides mobility management
, session management
and transport
for Internet Protocol packet services in GSM and WCDMA networks. The core network also provides support for other additional functions such as billing
and lawful interception
. It was also proposed, at one stage, to support packet radio services in the US D-AMPS TDMA
system, however, in practice, all of these networks have been converted to GSM so this option has become irrelevant.
Like GSM in general, GPRS module is an open standards driven system. The standardization body is the 3GPP
.
-based protocol
of the GPRS core network. Primarily it is the protocol which allows end users of a GSM or WCDMA network to move from place to place while continuing to connect to the Internet as if from one location at the Gateway GPRS Support Node (GGSN). It does this by carrying the subscriber's data from the subscriber's current Serving GPRS Support Node (SGSN) to the GGSN which is handling the subscriber's session. Three forms of GTP are used by the GPRS core network.
GTP-U: for transfer of user data in separated tunnels for each Packet Data Protocol (PDP) context
GTP-C: for control reasons including:
GTP'
: for transfer of charging data from GSNs to the charging function.
GGSNs and SGSNs (collectively known as GSNs) listen for GTP-C messages on UDP
port 2123 and for GTP-U messages on port 2152. This communication is direct within a single network, or in the case of international roaming, via a GPRS roaming exchange
(GRX).
The Charging Gateway Function (CGF) listens to GTP' messages sent from the GSNs on TCP or UDP port 3386. The core network sends charging information to the CGF, typically including PDP context activation times and the quantity of data which the end user has transferred. However, this communication which occurs within one network is less standardized and may, depending on the vendor and configuration options, use proprietary encoding or even an entirely proprietary system.
GTP version zero supports both signalling and user data under one generic header. It can be used with UDP (User Datagram Protocol) or TCP (Transmission Control Protocol) on the registered port 3386. GTP version one is used only on UDP. The control plane protocol GTP-C (Control) using registered port 2123 and the user plane protocol GTP-U (User) using registered port 2152.
and X.25
networks.
From an external network's point of view, the GGSN is a router to a sub-network, because the GGSN ‘hides’ the GPRS infrastructure from the external network. When the GGSN receives data addressed to a specific user, it checks if the user is active. If it is, the GGSN forwards the data to the SGSN serving the mobile user, but if the mobile user is inactive, the data is discarded. On the other hand, mobile-originated packets are routed to the right network by the GGSN.
The GGSN is the anchor point that enables the mobility of the user terminal in the GPRS/UMTS networks. In essence, it carries out the role in GPRS equivalent to the Home Agent in Mobile IP
. It maintains routing necessary to tunnel the Protocol Data Unit
s (PDUs) to the SGSN that services a particular MS (Mobile Station
).
The GGSN converts the GPRS packets coming from the SGSN into the appropriate packet data protocol (PDP) format (e.g., IP or X.25) and sends them out on the corresponding packet data network. In the other direction, PDP addresses of incoming data packets are converted to the GSM address of the destination user. The readdressed packets are sent to the responsible SGSN. For this purpose, the GGSN stores the current SGSN address of the user and his or her profile in its location register. The GGSN is responsible for IP address assignment and is the default router for the connected user equipment (UE). The GGSN also performs authentication and charging functions.
Other functions include subscriber screening, IP Pool management and address mapping, QoS
and PDP context enforcement.
With LTE scenario the GGSN functionality moves to SAE
gateway (with SGSN functionality working in MME).
(EDGE) specific SGSN functions and characteristics are:
These differences in functionality have led some manufacturers to
create specialist SGSNs for each of WCDMA and GSM which do not support
the other networks, whilst other manufacturers have succeeded in
creating both together, but with a performance cost due to the compromises
required.
When a GPRS mobile phone sets up a PDP context, the access point
is selected. At this point an access point name
(APN) is
determined
This access point is then used in a DNS
query to a private DNS
network. This process (called APN resolution) finally gives the IP
address of the GGSN which should serve the access point. At this
point a PDP context can be activated.
present on both the Serving GPRS Support Node (SGSN) and the Gateway GPRS Support Node (GGSN) which contains the subscriber's session information when the subscriber has an active session.
When a mobile wants to use GPRS, it must first attach and then activate a PDP context.
This allocates a PDP context data structure in the SGSN that the subscriber is currently visiting and the GGSN serving the subscriber's access point. The data recorded includes
The Tunnel Endpoint ID (TEID) is a number allocated by the GSN which identifies the tunnelled data related to a particular PDP context.
Several PDP contexts may use the same IP address. The Secondary PDP Context Activation procedure may be used to activate a PDP context while reusing the PDP address and other PDP context information from an already active PDP context, but with a different QoS
profile. Note that the procedure is called secondary, not the resulting PDP contexts that have no such relationship with the one the PDP address of which they reused.
A total of 11 PDP contexts (with any combination of primary and secondary) can co-exist. NSAPI are used to differentiate the different PDP context.
s and reference points (logical points of connection which probably share a common physical connection with other reference points). Some of these names can be seen in the network structure diagram on this page.
Gb: Interface between the base station subsystem
and the SGSN the transmission protocol could be Frame Relay or IP.
Gd: Interface between the SGSN and the SMS Gateway. Can use MAP1, MAP2 or MAP3.
Ge: The interface between the SGSN and the service control point
(SCP); uses the CAP protocol.
Gf: The interface between the SGSN and the Equipment Identity Register (EIR), used for checking the mobile's equipment identity number (IMEI) against a list of reported stolen mobile phones.
Gi: IP based interface between the GGSN and a public data network (PDN) either directly to the Internet
or through a WAP gateway
.
Gmb: The interface between the GGSN and the Broadcast-Multicast Service Center (BM-SC), used for controlling MBMS bearers.
Gn: IP Based interface between SGSN and other SGSNs and (internal) GGSNs. DNS
also shares this interface. Uses the GTP Protocol.
Gp: IP based interface between internal SGSN and external GGSNs. Between the SGSN and the external GGSN, there is the border gateway (which is essentially a firewall). Also uses the GTP Protocol.
Gr: Interface between the SGSN and the HLR. Messages going through this interface uses the MAP3 protocol.
Gs: Interface between the SGSN and the MSC (VLR). Uses the BSSAP+ protocol. This interface allows paging and station availability when it performs data transfer. When the station is attached to the GPRS network, the SGSN keeps track of which routing area (RA) the station is attached to. An RA is a part of a larger location area (LA). When a station is paged this information is used to conserve network resources. When the station performs a PDP context, the SGSN has the exact BTS the station is using.
Gx: The on-line policy interface between the GGSN and the charging rules function (CRF). It is used for provisioning service data flow based on charging rules. Uses the diameter protocol.
Gy: The on-line charging interface between the GGSN and the online charging system
(OCS). Uses the diameter protocol (DCCA application
).
Gz: The off-line (CDR
-based) charging interface between the GSN and the CG. Uses GTP'.
Lg: The interface between the SGSN and the Gateway Mobile Location Center (GMLC
), used for location based services.
General Packet Radio Service
General packet radio service is a packet oriented mobile data service on the 2G and 3G cellular communication system's global system for mobile communications . GPRS was originally standardized by European Telecommunications Standards Institute in response to the earlier CDPD and i-mode...
which allows 2G
2G
2G is short for second-generation wireless telephone technology. Second generation 2G cellular telecom networks were commercially launched on the GSM standard in Finland by Radiolinja in 1991...
, 3G
3G
3G or 3rd generation mobile telecommunications is a generation of standards for mobile phones and mobile telecommunication services fulfilling the International Mobile Telecommunications-2000 specifications by the International Telecommunication Union...
and WCDMA mobile networks
Mobile telephony
Mobile telephony is the provision of telephone services to phones which may move around freely rather than stay fixed in one location. Mobile phones connect to a terrestrial cellular network of base stations , whereas satellite phones connect to orbiting satellites...
to transmit IP
Internet Protocol
The Internet Protocol is the principal communications protocol used for relaying datagrams across an internetwork using the Internet Protocol Suite...
packets to external networks such as the Internet
Internet
The Internet is a global system of interconnected computer networks that use the standard Internet protocol suite to serve billions of users worldwide...
. The GPRS system is an integrated part of the GSM network switching subsystem
Network Switching Subsystem
Network switching subsystem is the component of a GSM system that carries out call switching and mobility management functions for mobile phones roaming on the network of base stations...
.
General support functions

Mobility management
Mobility management is one of the major functions of a GSM ora UMTS network that allows mobile phones to work. The aim of mobility management is to track where the subscribers are, allowing calls, SMS and other mobile phone services to be delivered to them....
, session management
Session management
In human-computer interaction, session management is the process of keeping track of a user's activity across sessions of interaction with the computer system....
and transport
Transport layer
In computer networking, the transport layer or layer 4 provides end-to-end communication services for applications within a layered architecture of network components and protocols...
for Internet Protocol packet services in GSM and WCDMA networks. The core network also provides support for other additional functions such as billing
Telecommunications billing
Telecommunications billing is the process of adding together rated calls or services for a certain user or group of users, applying discounts and preparing the data for invoicing.Billing is also the name for the entire process of creating an invoice...
and lawful interception
Lawful interception
Lawful interception is obtaining communications network data pursuant to lawful authority for the purpose of analysis or evidence. Such data generally consist of signalling or network management information or, in fewer instances, the content of the communications...
. It was also proposed, at one stage, to support packet radio services in the US D-AMPS TDMA
Digital AMPS
IS-54 and IS-136 are second-generation mobile phone systems, known as Digital AMPS . It was once prevalent throughout the Americas, particularly in the United States and Canada. D-AMPS is considered end-of-life, and existing networks have mostly been replaced by GSM/GPRS or CDMA2000...
system, however, in practice, all of these networks have been converted to GSM so this option has become irrelevant.
Like GSM in general, GPRS module is an open standards driven system. The standardization body is the 3GPP
3GPP
The 3rd Generation Partnership Project is a collaboration between groups of telecommunications associations, known as the Organizational Partners...
.
GPRS tunnelling protocol (GTP)
GPRS tunnelling protocol is the defining IPInternet Protocol
The Internet Protocol is the principal communications protocol used for relaying datagrams across an internetwork using the Internet Protocol Suite...
-based protocol
Communications protocol
A communications protocol is a system of digital message formats and rules for exchanging those messages in or between computing systems and in telecommunications...
of the GPRS core network. Primarily it is the protocol which allows end users of a GSM or WCDMA network to move from place to place while continuing to connect to the Internet as if from one location at the Gateway GPRS Support Node (GGSN). It does this by carrying the subscriber's data from the subscriber's current Serving GPRS Support Node (SGSN) to the GGSN which is handling the subscriber's session. Three forms of GTP are used by the GPRS core network.
GTP-U: for transfer of user data in separated tunnels for each Packet Data Protocol (PDP) context
GTP-C: for control reasons including:
- setup and deletion of PDP contexts
- verification of GSN reachability
- updates; e.g., as subscribers move from one SGSN to another.
GTP'
GTP'
GTP is an IP based protocol used within GSM and UMTS networks. It can be used with UDP or TCP. GTP' uses the same message structure as GTP , but it is largely a separate protocol...
: for transfer of charging data from GSNs to the charging function.
GGSNs and SGSNs (collectively known as GSNs) listen for GTP-C messages on UDP
User Datagram Protocol
The User Datagram Protocol is one of the core members of the Internet Protocol Suite, the set of network protocols used for the Internet. With UDP, computer applications can send messages, in this case referred to as datagrams, to other hosts on an Internet Protocol network without requiring...
port 2123 and for GTP-U messages on port 2152. This communication is direct within a single network, or in the case of international roaming, via a GPRS roaming exchange
GPRS Roaming Exchange
A GPRS Roaming Exchange acts as a hub for GPRS connections from roaming users, removing the need for a dedicated link between each GPRS service provider...
(GRX).
The Charging Gateway Function (CGF) listens to GTP' messages sent from the GSNs on TCP or UDP port 3386. The core network sends charging information to the CGF, typically including PDP context activation times and the quantity of data which the end user has transferred. However, this communication which occurs within one network is less standardized and may, depending on the vendor and configuration options, use proprietary encoding or even an entirely proprietary system.
GTP version zero supports both signalling and user data under one generic header. It can be used with UDP (User Datagram Protocol) or TCP (Transmission Control Protocol) on the registered port 3386. GTP version one is used only on UDP. The control plane protocol GTP-C (Control) using registered port 2123 and the user plane protocol GTP-U (User) using registered port 2152.
GPRS support nodes (GSN)
A GSN is a network node which supports the use of GPRS in the GSM core network. All GSNs should have a Gn interface and support the GPRS tunneling protocol. There are two key variants of the GSN, namely Gateway and Serving GPRS Support Node.Gateway GPRS Support Node (GGSN)
The Gateway GPRS Support Node (GGSN) is a main component of the GPRS network. The GGSN is responsible for the interworking between the GPRS network and external packet switched networks, like the InternetInternet
The Internet is a global system of interconnected computer networks that use the standard Internet protocol suite to serve billions of users worldwide...
and X.25
X.25
X.25 is an ITU-T standard protocol suite for packet switched wide area network communication. An X.25 WAN consists of packet-switching exchange nodes as the networking hardware, and leased lines, Plain old telephone service connections or ISDN connections as physical links...
networks.
From an external network's point of view, the GGSN is a router to a sub-network, because the GGSN ‘hides’ the GPRS infrastructure from the external network. When the GGSN receives data addressed to a specific user, it checks if the user is active. If it is, the GGSN forwards the data to the SGSN serving the mobile user, but if the mobile user is inactive, the data is discarded. On the other hand, mobile-originated packets are routed to the right network by the GGSN.
The GGSN is the anchor point that enables the mobility of the user terminal in the GPRS/UMTS networks. In essence, it carries out the role in GPRS equivalent to the Home Agent in Mobile IP
Mobile IP
Mobile IP is an Internet Engineering Task Force standard communications protocol that is designed to allow mobile device users to move from one network to another while maintaining a permanent IP address. Mobile IP for IPv4 is described in IETF RFC 5944, and extensions are defined in IETF RFC 4721...
. It maintains routing necessary to tunnel the Protocol Data Unit
Protocol data unit
In telecommunications, the term protocol data unit has the following meanings:#Information that is delivered as a unit among peer entities of a network and that may contain control information, address information, or data....
s (PDUs) to the SGSN that services a particular MS (Mobile Station
Mobile Station
The mobile station comprises all user equipment and software needed for communication with a mobile network.The mobile station refers to global system connected to the mobile network, i.e. mobile phone or mobile computer connected using a mobile broadband adapter. This is the terminology of 2G...
).
The GGSN converts the GPRS packets coming from the SGSN into the appropriate packet data protocol (PDP) format (e.g., IP or X.25) and sends them out on the corresponding packet data network. In the other direction, PDP addresses of incoming data packets are converted to the GSM address of the destination user. The readdressed packets are sent to the responsible SGSN. For this purpose, the GGSN stores the current SGSN address of the user and his or her profile in its location register. The GGSN is responsible for IP address assignment and is the default router for the connected user equipment (UE). The GGSN also performs authentication and charging functions.
Other functions include subscriber screening, IP Pool management and address mapping, QoS
Quality of service
The quality of service refers to several related aspects of telephony and computer networks that allow the transport of traffic with special requirements...
and PDP context enforcement.
With LTE scenario the GGSN functionality moves to SAE
System Architecture Evolution
System Architecture Evolution is the core network architecture of 3GPP's LTE wireless communication standard.SAE is the evolution of the GPRS Core Network, with some differences:* simplified architecture* all-IP Network...
gateway (with SGSN functionality working in MME).
Serving GPRS Support Node (SGSN)
A Serving GPRS Support Node (SGSN) is responsible for the delivery of data packets from and to the mobile stations within its geographical service area. Its tasks include packet routing and transfer, mobility management (attach/detach and location management), logical link management, and authentication and charging functions. The location register of the SGSN stores location information (e.g., current cell, current VLR) and user profiles (e.g., IMSI, address(es) used in the packet data network) of all GPRS users registered with this SGSN....Common SGSN Functions
- Detunnel GTP packets from the GGSN (downlink)
- Tunnel IP packets toward the GGSN (uplink)
- Carry out mobility management as Standby mode mobile moves from one Routing Area to another Routing Area
- Billing user data
GSM/EDGE specific SGSN functions
Enhanced Data Rates for GSM EvolutionEnhanced Data Rates for GSM Evolution
Enhanced Data rates for GSM Evolution is a digital mobile phone technology that allows improved data transmission rates as a backward-compatible extension of GSM...
(EDGE) specific SGSN functions and characteristics are:
- Maximum data rate of approx. 60 kbit/s (150 kbit/s for EDGE) per subscriber
- Connect via frame relayFrame relayFrame Relay is a standardized wide area network technology that specifies the physical and logical link layers of digital telecommunications channels using a packet switching methodology...
or IPInternet ProtocolThe Internet Protocol is the principal communications protocol used for relaying datagrams across an internetwork using the Internet Protocol Suite...
to the Packet Control Unit using the Gb protocol stack - Accept uplink data to form IP packets
- Encrypt down-link data, decrypt up-link data
- Carry out mobility management to the level of a cell for connected mode mobiles
WCDMA specific SGSN functions
- Carry up to about 42 Mbit/s traffic downlink and 5.8 Mbit/s traffic uplink (HSPA+)
- Tunnel/detunnel downlink/uplink packets toward the radio network controllerRadio Network ControllerThe Radio Network Controller is a governing element in the UMTS radio access network and is responsible for controlling the Node Bs that are connected to it. The RNC carries out radio resource management, some of the mobility management functions and is the point where encryption is done before...
(RNC) - Carry out mobility management to the level of an RNC for connected mode mobiles
These differences in functionality have led some manufacturers to
create specialist SGSNs for each of WCDMA and GSM which do not support
the other networks, whilst other manufacturers have succeeded in
creating both together, but with a performance cost due to the compromises
required.
Access point
An access point is:- An IP network to which a mobile can be connected
- A set of settings which are used for that connection
- A particular option in a set of settings in a mobile phone
When a GPRS mobile phone sets up a PDP context, the access point
is selected. At this point an access point name
Access Point Name
Access Point Name is a computer protocol that typically allows a user's computer to access the Internet using the mobile phone network.On a technical level it is a configurable network identifier used by a mobile device when connecting to a GSM carrier...
(APN) is
determined
- Example: aricenttechnologies.mnc012.mcc345.gprs
- Example: Internet
- Example: mywap
- Example: hcl.cisco.ggsn
This access point is then used in a DNS
Domain name system
The Domain Name System is a hierarchical distributed naming system for computers, services, or any resource connected to the Internet or a private network. It associates various information with domain names assigned to each of the participating entities...
query to a private DNS
network. This process (called APN resolution) finally gives the IP
address of the GGSN which should serve the access point. At this
point a PDP context can be activated.
PDP Context
The packet data protocol (PDP; e.g., IP, X.25, FrameRelay) context is a data structureData structure
In computer science, a data structure is a particular way of storing and organizing data in a computer so that it can be used efficiently.Different kinds of data structures are suited to different kinds of applications, and some are highly specialized to specific tasks...
present on both the Serving GPRS Support Node (SGSN) and the Gateway GPRS Support Node (GGSN) which contains the subscriber's session information when the subscriber has an active session.
When a mobile wants to use GPRS, it must first attach and then activate a PDP context.
This allocates a PDP context data structure in the SGSN that the subscriber is currently visiting and the GGSN serving the subscriber's access point. The data recorded includes
- Subscriber's IP addressIP addressAn Internet Protocol address is a numerical label assigned to each device participating in a computer network that uses the Internet Protocol for communication. An IP address serves two principal functions: host or network interface identification and location addressing...
- Subscriber's IMSIInternational Mobile Subscriber IdentityAn International Mobile Subscriber Identity or IMSI is a unique identification associated with all GSM and UMTS network mobile phone users. It is stored as a 64 bit field in the SIM inside the phone and is sent by the phone to the network...
- Subscriber's
- Tunnel Endpoint ID (TEID) at the GGSN
- Tunnel Endpoint ID (TEID) at the SGSN
-
The Tunnel Endpoint ID (TEID) is a number allocated by the GSN which identifies the tunnelled data related to a particular PDP context.
Several PDP contexts may use the same IP address. The Secondary PDP Context Activation procedure may be used to activate a PDP context while reusing the PDP address and other PDP context information from an already active PDP context, but with a different QoS
Quality of service
The quality of service refers to several related aspects of telephony and computer networks that allow the transport of traffic with special requirements...
profile. Note that the procedure is called secondary, not the resulting PDP contexts that have no such relationship with the one the PDP address of which they reused.
A total of 11 PDP contexts (with any combination of primary and secondary) can co-exist. NSAPI are used to differentiate the different PDP context.
Reference points and interfaces
Within the GPRS core network standards there are a number of interfaceNetwork interface device
In telecommunications, a Network Interface Device is a device that serves as the demarcation point between the carrier's local loop and the customer's premises wiring....
s and reference points (logical points of connection which probably share a common physical connection with other reference points). Some of these names can be seen in the network structure diagram on this page.
Interfaces in the GPRS network
Ga: The interface serves the CDRs (accounting records) which are written in the GSN and sent to the charging gateway (CG). This interface uses a GTP-based protocol, with modifications that supports CDRs (Called GTP' or GTP prime).Gb: Interface between the base station subsystem
Base Station Subsystem
The base station subsystem is the section of a traditional cellular telephone network which is responsible for handling traffic and signaling between a mobile phone and the network switching subsystem...
and the SGSN the transmission protocol could be Frame Relay or IP.
Gd: Interface between the SGSN and the SMS Gateway. Can use MAP1, MAP2 or MAP3.
Ge: The interface between the SGSN and the service control point
Service Control Point
A service control point is a standard component of the Intelligent Network telephone system which is used to control the service. Standard SCPs in the telecom industry today are deployed using SS7, Sigtran or SIP technologies. The SCP queries the service data point which holds the actual...
(SCP); uses the CAP protocol.
Gf: The interface between the SGSN and the Equipment Identity Register (EIR), used for checking the mobile's equipment identity number (IMEI) against a list of reported stolen mobile phones.
Gi: IP based interface between the GGSN and a public data network (PDN) either directly to the Internet
Internet
The Internet is a global system of interconnected computer networks that use the standard Internet protocol suite to serve billions of users worldwide...
or through a WAP gateway
WAP gateway
A WAP gateway sits between mobile devices using the WAP protocol and the World Wide Web, passing pages from one to the other much like a proxy. This translates pages into a form suitable for the mobiles, for instance using the Wireless Markup Language...
.
Gmb: The interface between the GGSN and the Broadcast-Multicast Service Center (BM-SC), used for controlling MBMS bearers.
Gn: IP Based interface between SGSN and other SGSNs and (internal) GGSNs. DNS
Domain name system
The Domain Name System is a hierarchical distributed naming system for computers, services, or any resource connected to the Internet or a private network. It associates various information with domain names assigned to each of the participating entities...
also shares this interface. Uses the GTP Protocol.
Gp: IP based interface between internal SGSN and external GGSNs. Between the SGSN and the external GGSN, there is the border gateway (which is essentially a firewall). Also uses the GTP Protocol.
Gr: Interface between the SGSN and the HLR. Messages going through this interface uses the MAP3 protocol.
Gs: Interface between the SGSN and the MSC (VLR). Uses the BSSAP+ protocol. This interface allows paging and station availability when it performs data transfer. When the station is attached to the GPRS network, the SGSN keeps track of which routing area (RA) the station is attached to. An RA is a part of a larger location area (LA). When a station is paged this information is used to conserve network resources. When the station performs a PDP context, the SGSN has the exact BTS the station is using.
Gx: The on-line policy interface between the GGSN and the charging rules function (CRF). It is used for provisioning service data flow based on charging rules. Uses the diameter protocol.
Gy: The on-line charging interface between the GGSN and the online charging system
Online charging system
Online charging system is a system allowing a Communications service provider to charge their customers, in real time, based on service usage-Unified charging engine for all services:...
(OCS). Uses the diameter protocol (DCCA application
Diameter Credit-Control Application
Diameter Credit-Control Application, is a networking protocol for Diameter application used toimplement real-time credit-control for a variety of end user services.It is an IETF standard defined in RFC 4006.- Purpose :...
).
Gz: The off-line (CDR
Call detail record
A call detail record , also known as call data record, is a data record produced by a telephone exchange or other telecommunications equipment documenting the details of a phone call that passed through the facility or device...
-based) charging interface between the GSN and the CG. Uses GTP'.
Lg: The interface between the SGSN and the Gateway Mobile Location Center (GMLC
GMLC
The Gateway Mobile Location Centre contains functionality required to support LCS . In one PLMN , there may be more than one GMLC. The GMLC is the first node an external LCS client accesses in a GSM or UMTS network. The GMLC may request routing information from the HLR or HSS...
), used for location based services.
See also
- Base station subsystemBase Station SubsystemThe base station subsystem is the section of a traditional cellular telephone network which is responsible for handling traffic and signaling between a mobile phone and the network switching subsystem...
- Packet control unit
- Network switching subsystemNetwork Switching SubsystemNetwork switching subsystem is the component of a GSM system that carries out call switching and mobility management functions for mobile phones roaming on the network of base stations...

