G-code
Overview
Numerical control
Numerical control refers to the automation of machine tools that are operated by abstractly programmed commands encoded on a storage medium, as opposed to controlled manually via handwheels or levers, or mechanically automated via cams alone...
(CNC) programming language
Programming language
A programming language is an artificial language designed to communicate instructions to a machine, particularly a computer. Programming languages can be used to create programs that control the behavior of a machine and/or to express algorithms precisely....
, which has many implementation
Implementation
Implementation is the realization of an application, or execution of a plan, idea, model, design, specification, standard, algorithm, or policy.-Computer Science:...
s. Used mainly in automation
Automation
Automation is the use of control systems and information technologies to reduce the need for human work in the production of goods and services. In the scope of industrialization, automation is a step beyond mechanization...
, it is part of computer-aided engineering
Computer-aided engineering
Computer-aided engineering is the broad usage of computer software to aid in engineering tasks. It includes computer-aided design , computer-aided analysis , computer-integrated manufacturing , computer-aided manufacturing , material requirements planning , and computer-aided planning .- Overview...
. G-code is sometimes called G programming language. (The names of the language are explained at "Etymology".)
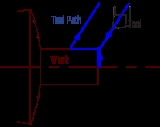
In fundamental terms, G-code is a language in which people tell computerized machine tool
Machine tool
A machine tool is a machine, typically powered other than by human muscle , used to make manufactured parts in various ways that include cutting or certain other kinds of deformation...
s what to make and how to make it. The "what" and "how" are mostly defined by instructions on where to move to, how fast to move, and through what path to move.
The first implementation of numerical control was developed at the MIT Servomechanisms Laboratory in the early 1950s.

