Fürst-Plattner Rule
Encyclopedia
The Fürst-Plattner rule (also known as the trans-diaxial effect) describes the addition of nucleophile
s to cyclohexene
derivatives.
Epoxidation of the substituted cyclohexene gives the product where the R group
is in the pseudo-equatorial position. Nucleophilic opening of the epoxide
can occur by attack at either the 1 or 2 position. The major product formed is from attack at the 1 position due to the instability of the twist boat product formed by addition at the 2 position (disfavored by approximately 5 kcal / mol). The Fürst-Plattner rule also applies to nucleophilic additions to imine
s and halonium ion
s.
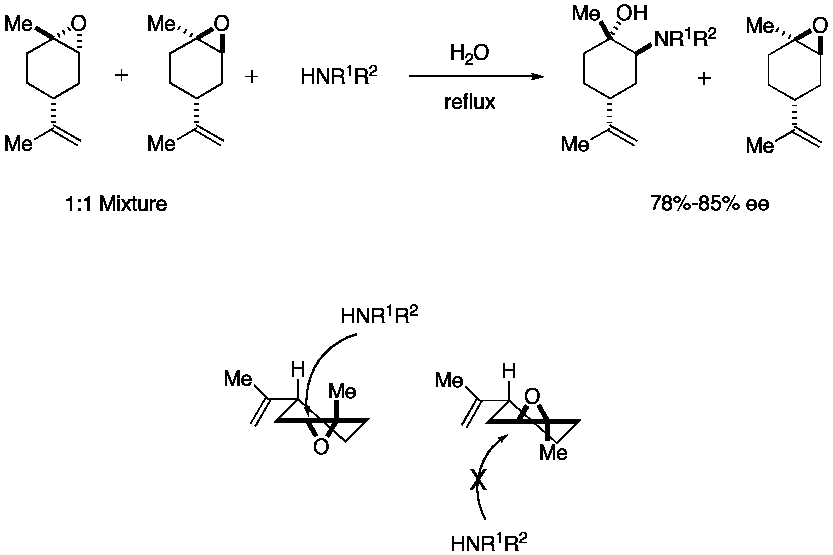
A recent example of the Fürst-Plattner rule can be seen from Chrisman et al. where limonene
is epoxidized to give a 1:1 mixture of diastereomer
s. Exposure to a nitrogen nucleophile in water at reflux provides only one ring opened product in 75-85% ee.
Nucleophile
A nucleophile is a species that donates an electron-pair to an electrophile to form a chemical bond in a reaction. All molecules or ions with a free pair of electrons can act as nucleophiles. Because nucleophiles donate electrons, they are by definition Lewis bases.Nucleophilic describes the...
s to cyclohexene
Cyclohexene
Cyclohexene is a hydrocarbon with the formula C6H10. This cycloalkene is a colorless liquid with a sharp smell. It is an intermediate in various industrial processes...
derivatives.
Epoxidation of the substituted cyclohexene gives the product where the R group
Side chain
In organic chemistry and biochemistry, a side chain is a chemical group that is attached to a core part of the molecule called "main chain" or backbone. The placeholder R is often used as a generic placeholder for alkyl group side chains in chemical structure diagrams. To indicate other non-carbon...
is in the pseudo-equatorial position. Nucleophilic opening of the epoxide
Epoxide
An epoxide is a cyclic ether with three ring atoms. This ring approximately defines an equilateral triangle, which makes it highly strained. The strained ring makes epoxides more reactive than other ethers. Simple epoxides are named from the parent compound ethylene oxide or oxirane, such as in...
can occur by attack at either the 1 or 2 position. The major product formed is from attack at the 1 position due to the instability of the twist boat product formed by addition at the 2 position (disfavored by approximately 5 kcal / mol). The Fürst-Plattner rule also applies to nucleophilic additions to imine
Imine
An imine is a functional group or chemical compound containing a carbon–nitrogen double bond, with the nitrogen attached to a hydrogen atom or an organic group. If this group is not a hydrogen atom, then the compound is known as a Schiff base...
s and halonium ion
Halonium ion
A halonium ion in organic chemistry is any onium compound containing a halogen atom carrying a positive charge. This cation has the general structure R-X+-R where X is any halogen and R any organic residue and this structure can be cyclic or an open chain molecular structure...
s.
A recent example of the Fürst-Plattner rule can be seen from Chrisman et al. where limonene
Limonene
Limonene is a colourless liquid hydrocarbon classified as a cyclic terpene. The more common D isomer possesses a strong smell of oranges. It is used in chemical synthesis as a precursor to carvone and as a renewably-based solvent in cleaning products....
is epoxidized to give a 1:1 mixture of diastereomer
Diastereomer
Diastereomers are stereoisomers that are not enantiomers.Diastereomerism occurs when two or more stereoisomers of a compound have different configurations at one or more of the equivalent stereocenters and are not mirror images of each other.When two diastereoisomers differ from each other at...
s. Exposure to a nitrogen nucleophile in water at reflux provides only one ring opened product in 75-85% ee.


