
Futile cycle
Encyclopedia
A futile cycle, also known as a substrate cycle, occurs when two metabolic pathway
s run simultaneously in opposite directions and have no overall effect other than to dissipate
energy in the form of heat
. For example, if glycolysis
and gluconeogenesis
were to be active at the same time, glucose
would be converted to pyruvate by glycolysis and then converted back to glucose by gluconeogenesis, with an overall consumption of ATP
. Futile cycles may have a role in metabolic regulation, where a futile cycle would be a system oscillating between two states and very sensitive to small changes in the activity of any of the enzyme
s involved. The cycle does generate heat, and may be used to maintain thermal homeostasis
, for example in the brown adipose tissue
of young mammal
s, or to generate heat rapidly, for example in insect
flight muscles and in hibernating animals during periodical arousal from torpor
.
It has been recently discovered that the glucose metabolism substrate cycle is not a futile cycle but a regulatory process. For example, when energy is suddenly needed, ATP is replaced by AMP, a much more reactive adenine.
and gluconeogenesis
is an example of a futile cycle, represented by the following equation:
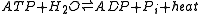
For example, during glycolysis, fructose-6-phosphate is converted to fructose-1,6-bisphosphate in a reaction catalysed
by the enzyme
phosphofructokinase 1 (PFK-1).
ATP + fructose-6-phosphate  Fructose-1,6-bisphosphate + ADP
Fructose-1,6-bisphosphate + ADP
But during gluconeogenesis (i.e. synthesis of glucose from pyruvate
and other compounds) the revese reaction takes place, being catalyzed by fructose-1,6-bisphosphatase (FBPase-1).
Fructose-1,6-bisphosphate + H2O  fructose-6-phosphate + Pi
fructose-6-phosphate + Pi
Giving an overall reaction of:
ATP + H2O  ADP + Pi + Heat
ADP + Pi + Heat
That is, hydrolysis
of ATP
without any useful metabolic work being done. Clearly, if these two reactions were allowed to proceed simultaneously at a high rate in the same cell, a large amount of chemical energy would be dissipated as heat. This uneconomical process has therefore been called a futile cycle.
Metabolic pathway
In biochemistry, metabolic pathways are series of chemical reactions occurring within a cell. In each pathway, a principal chemical is modified by a series of chemical reactions. Enzymes catalyze these reactions, and often require dietary minerals, vitamins, and other cofactors in order to function...
s run simultaneously in opposite directions and have no overall effect other than to dissipate
Dissipation
In physics, dissipation embodies the concept of a dynamical system where important mechanical models, such as waves or oscillations, lose energy over time, typically from friction or turbulence. The lost energy converts into heat, which raises the temperature of the system. Such systems are called...
energy in the form of heat
Heat
In physics and thermodynamics, heat is energy transferred from one body, region, or thermodynamic system to another due to thermal contact or thermal radiation when the systems are at different temperatures. It is often described as one of the fundamental processes of energy transfer between...
. For example, if glycolysis
Glycolysis
Glycolysis is the metabolic pathway that converts glucose C6H12O6, into pyruvate, CH3COCOO− + H+...
and gluconeogenesis
Gluconeogenesis
Gluconeogenesis is a metabolic pathway that results in the generation of glucose from non-carbohydrate carbon substrates such as lactate, glycerol, and glucogenic amino acids....
were to be active at the same time, glucose
Glucose
Glucose is a simple sugar and an important carbohydrate in biology. Cells use it as the primary source of energy and a metabolic intermediate...
would be converted to pyruvate by glycolysis and then converted back to glucose by gluconeogenesis, with an overall consumption of ATP
Adenosine triphosphate
Adenosine-5'-triphosphate is a multifunctional nucleoside triphosphate used in cells as a coenzyme. It is often called the "molecular unit of currency" of intracellular energy transfer. ATP transports chemical energy within cells for metabolism...
. Futile cycles may have a role in metabolic regulation, where a futile cycle would be a system oscillating between two states and very sensitive to small changes in the activity of any of the enzyme
Enzyme
Enzymes are proteins that catalyze chemical reactions. In enzymatic reactions, the molecules at the beginning of the process, called substrates, are converted into different molecules, called products. Almost all chemical reactions in a biological cell need enzymes in order to occur at rates...
s involved. The cycle does generate heat, and may be used to maintain thermal homeostasis
Homeostasis
Homeostasis is the property of a system that regulates its internal environment and tends to maintain a stable, constant condition of properties like temperature or pH...
, for example in the brown adipose tissue
Brown adipose tissue
Brown adipose tissue or brown fat is one of two types of fat or adipose tissue found in mammals....
of young mammal
Mammal
Mammals are members of a class of air-breathing vertebrate animals characterised by the possession of endothermy, hair, three middle ear bones, and mammary glands functional in mothers with young...
s, or to generate heat rapidly, for example in insect
Insect
Insects are a class of living creatures within the arthropods that have a chitinous exoskeleton, a three-part body , three pairs of jointed legs, compound eyes, and two antennae...
flight muscles and in hibernating animals during periodical arousal from torpor
Torpor
Torpor, sometimes called temporary hibernation is a state of decreased physiological activity in an animal, usually characterized by a reduced body temperature and rate of metabolism. Animals that go through torpor include birds and some mammals such as mice and bats...
.
It has been recently discovered that the glucose metabolism substrate cycle is not a futile cycle but a regulatory process. For example, when energy is suddenly needed, ATP is replaced by AMP, a much more reactive adenine.
Example
The simultaneous carrying out of glycolysisGlycolysis
Glycolysis is the metabolic pathway that converts glucose C6H12O6, into pyruvate, CH3COCOO− + H+...
and gluconeogenesis
Gluconeogenesis
Gluconeogenesis is a metabolic pathway that results in the generation of glucose from non-carbohydrate carbon substrates such as lactate, glycerol, and glucogenic amino acids....
is an example of a futile cycle, represented by the following equation:
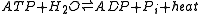
For example, during glycolysis, fructose-6-phosphate is converted to fructose-1,6-bisphosphate in a reaction catalysed
Catalysis
Catalysis is the change in rate of a chemical reaction due to the participation of a substance called a catalyst. Unlike other reagents that participate in the chemical reaction, a catalyst is not consumed by the reaction itself. A catalyst may participate in multiple chemical transformations....
by the enzyme
Enzyme
Enzymes are proteins that catalyze chemical reactions. In enzymatic reactions, the molecules at the beginning of the process, called substrates, are converted into different molecules, called products. Almost all chemical reactions in a biological cell need enzymes in order to occur at rates...
phosphofructokinase 1 (PFK-1).
 Fructose-1,6-bisphosphate + ADP
Fructose-1,6-bisphosphate + ADPBut during gluconeogenesis (i.e. synthesis of glucose from pyruvate
Pyruvic acid
Pyruvic acid is an organic acid, a ketone, as well as the simplest of the alpha-keto acids. The carboxylate ion of pyruvic acid, CH3COCOO−, is known as pyruvate, and is a key intersection in several metabolic pathways....
and other compounds) the revese reaction takes place, being catalyzed by fructose-1,6-bisphosphatase (FBPase-1).
 fructose-6-phosphate + Pi
fructose-6-phosphate + PiGiving an overall reaction of:
 ADP + Pi + Heat
ADP + Pi + HeatThat is, hydrolysis
Hydrolysis
Hydrolysis is a chemical reaction during which molecules of water are split into hydrogen cations and hydroxide anions in the process of a chemical mechanism. It is the type of reaction that is used to break down certain polymers, especially those made by condensation polymerization...
of ATP
Adenosine triphosphate
Adenosine-5'-triphosphate is a multifunctional nucleoside triphosphate used in cells as a coenzyme. It is often called the "molecular unit of currency" of intracellular energy transfer. ATP transports chemical energy within cells for metabolism...
without any useful metabolic work being done. Clearly, if these two reactions were allowed to proceed simultaneously at a high rate in the same cell, a large amount of chemical energy would be dissipated as heat. This uneconomical process has therefore been called a futile cycle.

