
Fugacity capacity
Encyclopedia
The fugacity
capacity constant (Z) is used to help describe the concentration of a chemical in a system (usually in mol/atm*m3). Hemond and Hechner-Levy (2000) describe how to utilize the fugacity capacity to calculate the concentration
of a chemical in a system. Depending on the chemical, fugacity capacity varies. The concentration in media 'm' equals the fugacity capacity in media 'm' multiplied by the fugacity of the chemical.
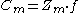
Fugacity
In chemical thermodynamics, the fugacity of a real gas is an effective pressure which replaces the true mechanical pressure in accurate chemical equilibrium calculations. It is equal to the pressure of an ideal gas which has the same chemical potential as the real gas. For example, nitrogen gas ...
capacity constant (Z) is used to help describe the concentration of a chemical in a system (usually in mol/atm*m3). Hemond and Hechner-Levy (2000) describe how to utilize the fugacity capacity to calculate the concentration
Concentration
In chemistry, concentration is defined as the abundance of a constituent divided by the total volume of a mixture. Four types can be distinguished: mass concentration, molar concentration, number concentration, and volume concentration...
of a chemical in a system. Depending on the chemical, fugacity capacity varies. The concentration in media 'm' equals the fugacity capacity in media 'm' multiplied by the fugacity of the chemical.
Sources
- Hemond HF, Fechner-Levy EJ. 2000. Chemical Fate and Transport in the Environment. Academic Press. San Diego, CA

