
Frigorific mixture
Encyclopedia
A frigorific mixture is a mixture of two or more chemicals that reaches an equilibrium temperature that is independent of the temperature of any of its component chemicals before they are mixed. The temperature is also relatively independent of the quantities of mixtures as long as significant amounts of each original chemical are present in its pure form.
Liquid water and ice, for example form a frigorific mixture at defining 32 degrees Fahrenheit or 0 degrees Celsius. A mixture of ammonium chloride
and ice form a frigorific mixture at about -17.8 degrees Celsius or 0 degrees Fahrenheit. Other examples of frigorific mixtures include :
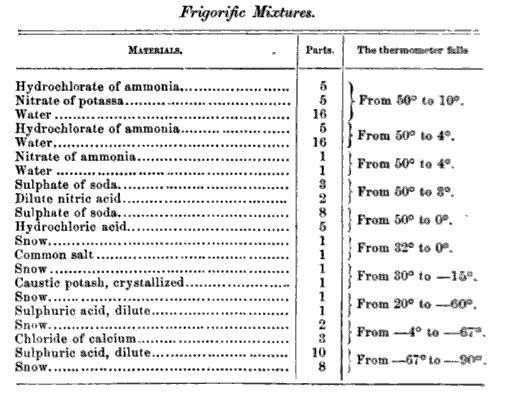
Frigorific mixtures are commonly used in laboratories as a convenient way to generate reference temperatures for calibrating thermometer
s.
They are also useful for creating cold temperatures when mechanical refrigeration is not available.
They can be used to tightly fit two parts of machined metal, for example. One part is soaked in a frigorific mixture, causing it to cool and contract. The cooled part is then placed into the second part, which has not been cooled. As the first part warms, it expands to fit tightly within the second part.
Liquid water and ice, for example form a frigorific mixture at defining 32 degrees Fahrenheit or 0 degrees Celsius. A mixture of ammonium chloride
Ammonium chloride
Ammonium chloride NH4Cl is an inorganic compound with the formula NH4Cl. It is a white crystalline salt that is highly soluble in water. Solutions of ammonium chloride are mildly acidic. Sal ammoniac is a name of natural, mineralogical form of ammonium chloride...
and ice form a frigorific mixture at about -17.8 degrees Celsius or 0 degrees Fahrenheit. Other examples of frigorific mixtures include :

Uses
The most common use of a frigorific mixture is to melt ice. When salt is placed on ice when the ambient temperature is greater than −17.8 °C (0°F), then the salt melts some of the ice and the temperature drops to −17.8. Since the mixture is colder than the ambient, heat is absorbed and the temperature rises. This causes the salt to melt more of the ice to drive the temperature down again. The process continues until all of the salt is dissolved in the melted ice. If there is enough salt present, then all of the ice will be melted.Frigorific mixtures are commonly used in laboratories as a convenient way to generate reference temperatures for calibrating thermometer
Thermometer
Developed during the 16th and 17th centuries, a thermometer is a device that measures temperature or temperature gradient using a variety of different principles. A thermometer has two important elements: the temperature sensor Developed during the 16th and 17th centuries, a thermometer (from the...
s.
They are also useful for creating cold temperatures when mechanical refrigeration is not available.
They can be used to tightly fit two parts of machined metal, for example. One part is soaked in a frigorific mixture, causing it to cool and contract. The cooled part is then placed into the second part, which has not been cooled. As the first part warms, it expands to fit tightly within the second part.

