
Food chemistry
Encyclopedia
Food chemistry is the study of chemical processes and interactions of all biological and non-biological components of foods. The biological substances include such items as meat
, poultry
, lettuce
, beer
, and milk
as examples. It is similar to biochemistry
in its main components such as carbohydrate
s, lipid
s, and protein
, but it also includes areas such as water
, vitamin
s, minerals
, enzyme
s, food additive
s, flavor
s, and colors
. This discipline also encompasses how products change under certain food processing
techniques and ways either to enhance or to prevent them from happening. An example of enhancing a process would be to encourage fermentation of dairy
products with microorganism
s that convert lactose
to lactic acid
; an example of preventing a process would be stopping the browning on the surface of freshly cut Red Delicious
apple
s using lemon juice or other acidulated water
.
(isolated malic acid
from apples in 1785), and Sir Humphry Davy
published the first book on agricultural and food chemistry in 1813 titled Elements of Agricultural Chemistry, in a Course of Lectures for the Board of Agriculture in the United Kingdom
which would serve as a foundation for the profession worldwide, going into a fifth edition.
In 1874 the Society of Public Analysts was formed, with the aim of applying analytical methods to the benefit of the public. Its early experiments were based on bread, milk and wine.
It was also out of concern for the quality of the food supply, mainly food adulteration and contamination issues that would first stem from intentional contamination to later with chemical food additives by the 1950s. The development of colleges and universities worldwide, most notably in the United States
, would expand food chemistry as well with research of the dietary substances, most notably the Single-grain experiment
during 1907-11. Additional research by Harvey W. Wiley
at the United States Department of Agriculture
during the late 19th century would play a key factor in the creation of the United States Food and Drug Administration in 1906. The American Chemical Society
would establish their Agricultural and Food Chemistry Division in 1908 while the Institute of Food Technologists
would establish their Food Chemistry Division in 1995.
, which can encompass anywhere from 50% in meat
products to 95% in lettuce
, cabbage
, and tomato
products. It is also an excellent place for bacterial growth and food spoilage if it is not properly processed. One way this is measured in food is by water activity
which is very important in the shelf life of many foods during processing. One of the keys to food preservation
in most instances is reduce the amount of water or alter the water's characteristics to enhance shelf-life. Such methods include dehydration, freezing
, and refrigeration
.
 Comprising 75% of the biological world and 80% of all food intake for human consumption, the most common known human carbohydrate is starch
Comprising 75% of the biological world and 80% of all food intake for human consumption, the most common known human carbohydrate is starch
. The simplest version of a carbohydrate is a monosaccharide
which possesses the properties of carbon
, hydrogen
, and oxygen
in a 1:2:1 ratio under a general formula of CnH2nOn where n is a minimum of 3. Glucose
is an example of a monosaccharide as is fructose
. Combine them in the picture shown to the right and you have sucrose
, one of the more common sugar
products around.
A chain of monosaccharides form to make a polysaccharide
. Such polysaccharides include pectin
, dextran
, agar
, and xanthan.
Sugar content is commonly measured in degrees brix
.
s and to some extent is a catchall for relatively water-insoluble or nonpolar compounds of biological origin, including wax
es, fatty acid
s (including essential fatty acid
s), fatty-acid derived phospholipids, sphingolipids, glycolipids and terpenoids, such as retinoids and steroids. Some lipids are linear aliphatic molecules, while others have ring structures. Some are aromatic, while others are not. Some are flexible, while others are rigid.
Most lipids have some polar character in addition to being largely nonpolar. Generally, the bulk of their structure is nonpolar or hydrophobic ("water-fearing"), meaning that it does not interact well with polar solvents like water. Another part of their structure is polar or hydrophilic ("water-loving") and will tend to associate with polar solvents like water. This makes them amphiphilic molecules (having both hydrophobic and hydrophilic portions). In the case of cholesterol
, the polar group is a mere -OH (hydroxyl
or alcohol).
Lipids in food include the oils of such grains as corn
, soybean
, from animal
fats, and are parts of many foods such as milk, cheese
, and meat. They also act as vitamin carriers as well.
, and some sulfur
, they also may contain iron
, copper
, phosphorus
, or zinc
.
In food, proteins are essential for growth and survival and vary depending upon a person's age and physiology
(e.g., pregnancy
). Proteins in food are commonly found in peanuts
, meat, poultry
, and seafood
. They are also involved in ELISA
test for food allergy
determination.
industry use catalysts, including baking
, brewing
, dairy
, and fruit juices
, to make cheese, beer
, and bread
.
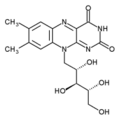 Vitamins are nutrients required in small amounts for essential metabolic reactions in the body. These are broken down in nutrition as either water
Vitamins are nutrients required in small amounts for essential metabolic reactions in the body. These are broken down in nutrition as either water
soluble (Vitamin C
) or fat
soluble (Vitamin E
). An adequate supply of vitamins can prevent diseases such as beriberi
, anemia
, and scurvy
while an overdose of vitamins can produce nausea
and vomiting
or even death
.
(RDI, formerly Recommended Daily Allowance (RDA)) of more than 200 mg/day are calcium
, magnesium
, and potassium
while important trace minerals (RDI less than 200 mg/day) are copper, iron, and zinc. These are found in many foods, but can also be taken in dietary supplements.
of any food
substance. It is mainly for sensory analysis
purposes. It can be used to simulate the natural color of a product as perceived by the customer, such as red dye like FD&C Red No.40 (Allura Red AC
) to ketchup
or to add unnatural colors to a product like Kellogg's
Froot Loops
. Caramel
is a natural food dye; the industrial form, caramel coloring, is the most widely-used food coloring and is found in foods from soft drink
s to soy sauce
, bread
, and pickle
s.
s and taste
s to the consumer, especially in sensory analysis. Some of these products occur naturally like salt
and sugar
, but flavor chemists (called a "flavorist
") develop many of these flavors for food products. Such artificial flavors include methyl salicylate
which creates the wintergreen
odor and lactic acid which gives milk a tart taste.
for pickling
or as an emulsifier for emulsion
mixtures like mayonnaise
. These are generally listed by "E number
" in the European Union
or GRAS
("generally recognized as safe
") by the United States
Food and Drug Administration
.
Meat
Meat is animal flesh that is used as food. Most often, this means the skeletal muscle and associated fat and other tissues, but it may also describe other edible tissues such as organs and offal...
, poultry
Poultry
Poultry are domesticated birds kept by humans for the purpose of producing eggs, meat, and/or feathers. These most typically are members of the superorder Galloanserae , especially the order Galliformes and the family Anatidae , commonly known as "waterfowl"...
, lettuce
Lettuce
Lettuce is a temperate annual or biennial plant of the daisy family Asteraceae. It is most often grown as a leaf vegetable. It is eaten either raw, notably in salads, sandwiches, hamburgers, tacos, and many other dishes, or cooked, as in Chinese cuisine in which the stem becomes just as important...
, beer
Beer
Beer is the world's most widely consumed andprobably oldest alcoholic beverage; it is the third most popular drink overall, after water and tea. It is produced by the brewing and fermentation of sugars, mainly derived from malted cereal grains, most commonly malted barley and malted wheat...
, and milk
Milk
Milk is a white liquid produced by the mammary glands of mammals. It is the primary source of nutrition for young mammals before they are able to digest other types of food. Early-lactation milk contains colostrum, which carries the mother's antibodies to the baby and can reduce the risk of many...
as examples. It is similar to biochemistry
Biochemistry
Biochemistry, sometimes called biological chemistry, is the study of chemical processes in living organisms, including, but not limited to, living matter. Biochemistry governs all living organisms and living processes...
in its main components such as carbohydrate
Carbohydrate
A carbohydrate is an organic compound with the empirical formula ; that is, consists only of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen, with a hydrogen:oxygen atom ratio of 2:1 . However, there are exceptions to this. One common example would be deoxyribose, a component of DNA, which has the empirical...
s, lipid
Lipid
Lipids constitute a broad group of naturally occurring molecules that include fats, waxes, sterols, fat-soluble vitamins , monoglycerides, diglycerides, triglycerides, phospholipids, and others...
s, and protein
Protein
Proteins are biochemical compounds consisting of one or more polypeptides typically folded into a globular or fibrous form, facilitating a biological function. A polypeptide is a single linear polymer chain of amino acids bonded together by peptide bonds between the carboxyl and amino groups of...
, but it also includes areas such as water
Water
Water is a chemical substance with the chemical formula H2O. A water molecule contains one oxygen and two hydrogen atoms connected by covalent bonds. Water is a liquid at ambient conditions, but it often co-exists on Earth with its solid state, ice, and gaseous state . Water also exists in a...
, vitamin
Vitamin
A vitamin is an organic compound required as a nutrient in tiny amounts by an organism. In other words, an organic chemical compound is called a vitamin when it cannot be synthesized in sufficient quantities by an organism, and must be obtained from the diet. Thus, the term is conditional both on...
s, minerals
Dietary mineral
Dietary minerals are the chemical elements required by living organisms, other than the four elements carbon, hydrogen, nitrogen, and oxygen present in common organic molecules. Examples of mineral elements include calcium, magnesium, potassium, sodium, zinc, and iodine...
, enzyme
Enzyme
Enzymes are proteins that catalyze chemical reactions. In enzymatic reactions, the molecules at the beginning of the process, called substrates, are converted into different molecules, called products. Almost all chemical reactions in a biological cell need enzymes in order to occur at rates...
s, food additive
Food additive
Food additives are substances added to food to preserve flavor or enhance its taste and appearance.Some additives have been used for centuries; for example, preserving food by pickling , salting, as with bacon, preserving sweets or using sulfur dioxide as in some wines...
s, flavor
Flavor
Flavor or flavour is the sensory impression of a food or other substance, and is determined mainly by the chemical senses of taste and smell. The "trigeminal senses", which detect chemical irritants in the mouth and throat as well as temperature and texture, are also very important to the overall...
s, and colors
Food coloring
Food coloring is a substance, liquid or powder, that is added to food or drink to change its color. Food coloring is used both in commercial food production and in domestic cooking...
. This discipline also encompasses how products change under certain food processing
Food processing
Food processing is the set of methods and techniques used to transform raw ingredients into food or to transform food into other forms for consumption by humans or animals either in the home or by the food processing industry...
techniques and ways either to enhance or to prevent them from happening. An example of enhancing a process would be to encourage fermentation of dairy
Dairy
A dairy is a business enterprise established for the harvesting of animal milk—mostly from cows or goats, but also from buffalo, sheep, horses or camels —for human consumption. A dairy is typically located on a dedicated dairy farm or section of a multi-purpose farm that is concerned...
products with microorganism
Microorganism
A microorganism or microbe is a microscopic organism that comprises either a single cell , cell clusters, or no cell at all...
s that convert lactose
Lactose
Lactose is a disaccharide sugar that is found most notably in milk and is formed from galactose and glucose. Lactose makes up around 2~8% of milk , although the amount varies among species and individuals. It is extracted from sweet or sour whey. The name comes from or , the Latin word for milk,...
to lactic acid
Lactic acid
Lactic acid, also known as milk acid, is a chemical compound that plays a role in various biochemical processes and was first isolated in 1780 by the Swedish chemist Carl Wilhelm Scheele. Lactic acid is a carboxylic acid with the chemical formula C3H6O3...
; an example of preventing a process would be stopping the browning on the surface of freshly cut Red Delicious
Red Delicious
The Red Delicious is a clone of apple cultigen, now comprising more than 50 cultivars, that was recognized in Madison County, Iowa, United States, in 1880...
apple
Apple
The apple is the pomaceous fruit of the apple tree, species Malus domestica in the rose family . It is one of the most widely cultivated tree fruits, and the most widely known of the many members of genus Malus that are used by humans. Apple grow on small, deciduous trees that blossom in the spring...
s using lemon juice or other acidulated water
Acidulated water
Acidulated water is water where some sort of acid is added—often lemon juice, lime juice, or vinegar—to prevent cut or skinned fruits or vegetables from browning so as to maintain their appearance. Some vegetables and fruits which are often placed in acidulated water are: apples, avocados,...
.
History of food chemistry
Food chemistry's history dates back as far as the late 18th century when many famous chemists were involved in discovering chemicals important in foods, including Carl Wilhelm ScheeleCarl Wilhelm Scheele
Carl Wilhelm Scheele was a German-Swedish pharmaceutical chemist. Isaac Asimov called him "hard-luck Scheele" because he made a number of chemical discoveries before others who are generally given the credit...
(isolated malic acid
Malic acid
Malic acid is an organic compound with the formula HO2CCH2CHOHCO2H. It is a dicarboxylic acid which is made by all living organisms, contributes to the pleasantly sour taste of fruits, and is used as a food additive. Malic acid has two stereoisomeric forms , though only the L-isomer exists...
from apples in 1785), and Sir Humphry Davy
Humphry Davy
Sir Humphry Davy, 1st Baronet FRS MRIA was a British chemist and inventor. He is probably best remembered today for his discoveries of several alkali and alkaline earth metals, as well as contributions to the discoveries of the elemental nature of chlorine and iodine...
published the first book on agricultural and food chemistry in 1813 titled Elements of Agricultural Chemistry, in a Course of Lectures for the Board of Agriculture in the United Kingdom
United Kingdom
The United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern IrelandIn the United Kingdom and Dependencies, other languages have been officially recognised as legitimate autochthonous languages under the European Charter for Regional or Minority Languages...
which would serve as a foundation for the profession worldwide, going into a fifth edition.
In 1874 the Society of Public Analysts was formed, with the aim of applying analytical methods to the benefit of the public. Its early experiments were based on bread, milk and wine.
It was also out of concern for the quality of the food supply, mainly food adulteration and contamination issues that would first stem from intentional contamination to later with chemical food additives by the 1950s. The development of colleges and universities worldwide, most notably in the United States
United States
The United States of America is a federal constitutional republic comprising fifty states and a federal district...
, would expand food chemistry as well with research of the dietary substances, most notably the Single-grain experiment
Single-grain experiment
The single-grain experiment was an experiment carried out at the University of Wisconsin–Madison from May 1907 to 1911. The experiment tested if cows could survive on a single type of grain. The experiment would lead to the development of modern nutritional science.-Foundations:In 1881,...
during 1907-11. Additional research by Harvey W. Wiley
Harvey W. Wiley
Harvey Washington Wiley was a noted chemist best known for his leadership in the passage of the landmark Pure Food and Drug Act of 1906 and his subsequent work at the Good Housekeeping Institute laboratories. He was the first commissioner of the US Food and Drug Administration...
at the United States Department of Agriculture
United States Department of Agriculture
The United States Department of Agriculture is the United States federal executive department responsible for developing and executing U.S. federal government policy on farming, agriculture, and food...
during the late 19th century would play a key factor in the creation of the United States Food and Drug Administration in 1906. The American Chemical Society
American Chemical Society
The American Chemical Society is a scientific society based in the United States that supports scientific inquiry in the field of chemistry. Founded in 1876 at New York University, the ACS currently has more than 161,000 members at all degree-levels and in all fields of chemistry, chemical...
would establish their Agricultural and Food Chemistry Division in 1908 while the Institute of Food Technologists
Institute of Food Technologists
The Institute of Food Technologists or IFT is an international, non-profit professional organization for the advancement of food science and technology. It is the largest of food science organizations in the world, encompassing 22,000 members worldwide as of 2006. It is referred to as "THE Society...
would establish their Food Chemistry Division in 1995.
Water
A major component of food is waterWater
Water is a chemical substance with the chemical formula H2O. A water molecule contains one oxygen and two hydrogen atoms connected by covalent bonds. Water is a liquid at ambient conditions, but it often co-exists on Earth with its solid state, ice, and gaseous state . Water also exists in a...
, which can encompass anywhere from 50% in meat
Meat
Meat is animal flesh that is used as food. Most often, this means the skeletal muscle and associated fat and other tissues, but it may also describe other edible tissues such as organs and offal...
products to 95% in lettuce
Lettuce
Lettuce is a temperate annual or biennial plant of the daisy family Asteraceae. It is most often grown as a leaf vegetable. It is eaten either raw, notably in salads, sandwiches, hamburgers, tacos, and many other dishes, or cooked, as in Chinese cuisine in which the stem becomes just as important...
, cabbage
Cabbage
Cabbage is a popular cultivar of the species Brassica oleracea Linne of the Family Brassicaceae and is a leafy green vegetable...
, and tomato
Tomato
The word "tomato" may refer to the plant or the edible, typically red, fruit which it bears. Originating in South America, the tomato was spread around the world following the Spanish colonization of the Americas, and its many varieties are now widely grown, often in greenhouses in cooler...
products. It is also an excellent place for bacterial growth and food spoilage if it is not properly processed. One way this is measured in food is by water activity
Water activity
Water activity or aw was developed to account for the intensity with which water associates with various non-aqueous constituents and solids. Simply stated, it is a measure of the energy status of the water in a system...
which is very important in the shelf life of many foods during processing. One of the keys to food preservation
Food preservation
Food preservation is the process of treating and handling food to stop or slow down spoilage and thus allow for longer storage....
in most instances is reduce the amount of water or alter the water's characteristics to enhance shelf-life. Such methods include dehydration, freezing
Frozen food
Freezing food preserves it from the time it is prepared to the time it is eaten. Since early times, farmers, fishermen, and trappers have preserved their game and produce in unheated buildings during the winter season. Freezing food slows down decomposition by turning water to ice, making it...
, and refrigeration
Refrigeration
Refrigeration is a process in which work is done to move heat from one location to another. This work is traditionally done by mechanical work, but can also be done by magnetism, laser or other means...
.
Carbohydrates

Starch
Starch or amylum is a carbohydrate consisting of a large number of glucose units joined together by glycosidic bonds. This polysaccharide is produced by all green plants as an energy store...
. The simplest version of a carbohydrate is a monosaccharide
Monosaccharide
Monosaccharides are the most basic units of biologically important carbohydrates. They are the simplest form of sugar and are usually colorless, water-soluble, crystalline solids. Some monosaccharides have a sweet taste. Examples of monosaccharides include glucose , fructose , galactose, xylose...
which possesses the properties of carbon
Carbon
Carbon is the chemical element with symbol C and atomic number 6. As a member of group 14 on the periodic table, it is nonmetallic and tetravalent—making four electrons available to form covalent chemical bonds...
, hydrogen
Hydrogen
Hydrogen is the chemical element with atomic number 1. It is represented by the symbol H. With an average atomic weight of , hydrogen is the lightest and most abundant chemical element, constituting roughly 75% of the Universe's chemical elemental mass. Stars in the main sequence are mainly...
, and oxygen
Oxygen
Oxygen is the element with atomic number 8 and represented by the symbol O. Its name derives from the Greek roots ὀξύς and -γενής , because at the time of naming, it was mistakenly thought that all acids required oxygen in their composition...
in a 1:2:1 ratio under a general formula of CnH2nOn where n is a minimum of 3. Glucose
Glucose
Glucose is a simple sugar and an important carbohydrate in biology. Cells use it as the primary source of energy and a metabolic intermediate...
is an example of a monosaccharide as is fructose
Fructose
Fructose, or fruit sugar, is a simple monosaccharide found in many plants. It is one of the three dietary monosaccharides, along with glucose and galactose, that are absorbed directly into the bloodstream during digestion. Fructose was discovered by French chemist Augustin-Pierre Dubrunfaut in 1847...
. Combine them in the picture shown to the right and you have sucrose
Sucrose
Sucrose is the organic compound commonly known as table sugar and sometimes called saccharose. A white, odorless, crystalline powder with a sweet taste, it is best known for its role in human nutrition. The molecule is a disaccharide composed of glucose and fructose with the molecular formula...
, one of the more common sugar
Sugar
Sugar is a class of edible crystalline carbohydrates, mainly sucrose, lactose, and fructose, characterized by a sweet flavor.Sucrose in its refined form primarily comes from sugar cane and sugar beet...
products around.
A chain of monosaccharides form to make a polysaccharide
Polysaccharide
Polysaccharides are long carbohydrate molecules, of repeated monomer units joined together by glycosidic bonds. They range in structure from linear to highly branched. Polysaccharides are often quite heterogeneous, containing slight modifications of the repeating unit. Depending on the structure,...
. Such polysaccharides include pectin
Pectin
Pectin is a structural heteropolysaccharide contained in the primary cell walls of terrestrial plants. It was first isolated and described in 1825 by Henri Braconnot...
, dextran
Dextran
Dextran is a complex, branched glucan composed of chains of varying lengths...
, agar
Agar
Agar or agar-agar is a gelatinous substance derived from a polysaccharide that accumulates in the cell walls of agarophyte red algae. Throughout history into modern times, agar has been chiefly used as an ingredient in desserts throughout Asia and also as a solid substrate to contain culture medium...
, and xanthan.
Sugar content is commonly measured in degrees brix
Brix
Degrees Brix is the sugar content of an aqueous solution.One degree Brix is 1 gram of sucrose in 100 grams of solution and represents the strength of the solution as percentage by weight . If the solution contains dissolved solids other than pure sucrose, then the °Bx is only approximate the...
.
Lipids
The term lipid comprises a diverse range of moleculeMolecule
A molecule is an electrically neutral group of at least two atoms held together by covalent chemical bonds. Molecules are distinguished from ions by their electrical charge...
s and to some extent is a catchall for relatively water-insoluble or nonpolar compounds of biological origin, including wax
Wax
thumb|right|[[Cetyl palmitate]], a typical wax ester.Wax refers to a class of chemical compounds that are plastic near ambient temperatures. Characteristically, they melt above 45 °C to give a low viscosity liquid. Waxes are insoluble in water but soluble in organic, nonpolar solvents...
es, fatty acid
Fatty acid
In chemistry, especially biochemistry, a fatty acid is a carboxylic acid with a long unbranched aliphatic tail , which is either saturated or unsaturated. Most naturally occurring fatty acids have a chain of an even number of carbon atoms, from 4 to 28. Fatty acids are usually derived from...
s (including essential fatty acid
Essential fatty acid
Essential fatty acids, or EFAs, are fatty acids that humans and other animals must ingest because the body requires them for good health but cannot synthesize them...
s), fatty-acid derived phospholipids, sphingolipids, glycolipids and terpenoids, such as retinoids and steroids. Some lipids are linear aliphatic molecules, while others have ring structures. Some are aromatic, while others are not. Some are flexible, while others are rigid.
Most lipids have some polar character in addition to being largely nonpolar. Generally, the bulk of their structure is nonpolar or hydrophobic ("water-fearing"), meaning that it does not interact well with polar solvents like water. Another part of their structure is polar or hydrophilic ("water-loving") and will tend to associate with polar solvents like water. This makes them amphiphilic molecules (having both hydrophobic and hydrophilic portions). In the case of cholesterol
Cholesterol
Cholesterol is a complex isoprenoid. Specifically, it is a waxy steroid of fat that is produced in the liver or intestines. It is used to produce hormones and cell membranes and is transported in the blood plasma of all mammals. It is an essential structural component of mammalian cell membranes...
, the polar group is a mere -OH (hydroxyl
Hydroxyl
A hydroxyl is a chemical group containing an oxygen atom covalently bonded with a hydrogen atom. In inorganic chemistry, the hydroxyl group is known as the hydroxide ion, and scientists and reference works generally use these different terms though they refer to the same chemical structure in...
or alcohol).
Lipids in food include the oils of such grains as corn
Maize
Maize known in many English-speaking countries as corn or mielie/mealie, is a grain domesticated by indigenous peoples in Mesoamerica in prehistoric times. The leafy stalk produces ears which contain seeds called kernels. Though technically a grain, maize kernels are used in cooking as a vegetable...
, soybean
Soybean
The soybean or soya bean is a species of legume native to East Asia, widely grown for its edible bean which has numerous uses...
, from animal
Animal
Animals are a major group of multicellular, eukaryotic organisms of the kingdom Animalia or Metazoa. Their body plan eventually becomes fixed as they develop, although some undergo a process of metamorphosis later on in their life. Most animals are motile, meaning they can move spontaneously and...
fats, and are parts of many foods such as milk, cheese
Cheese
Cheese is a generic term for a diverse group of milk-based food products. Cheese is produced throughout the world in wide-ranging flavors, textures, and forms....
, and meat. They also act as vitamin carriers as well.
Proteins
Proteins compose over 50% of the dry weight of an average living cell and are very complex macromolecules. They also play a fundamental role in the structure and function of cells. Consisting mainly of carbon, nitrogen, hydrogen, oxygenOxygen
Oxygen is the element with atomic number 8 and represented by the symbol O. Its name derives from the Greek roots ὀξύς and -γενής , because at the time of naming, it was mistakenly thought that all acids required oxygen in their composition...
, and some sulfur
Sulfur
Sulfur or sulphur is the chemical element with atomic number 16. In the periodic table it is represented by the symbol S. It is an abundant, multivalent non-metal. Under normal conditions, sulfur atoms form cyclic octatomic molecules with chemical formula S8. Elemental sulfur is a bright yellow...
, they also may contain iron
Iron
Iron is a chemical element with the symbol Fe and atomic number 26. It is a metal in the first transition series. It is the most common element forming the planet Earth as a whole, forming much of Earth's outer and inner core. It is the fourth most common element in the Earth's crust...
, copper
Copper
Copper is a chemical element with the symbol Cu and atomic number 29. It is a ductile metal with very high thermal and electrical conductivity. Pure copper is soft and malleable; an exposed surface has a reddish-orange tarnish...
, phosphorus
Phosphorus
Phosphorus is the chemical element that has the symbol P and atomic number 15. A multivalent nonmetal of the nitrogen group, phosphorus as a mineral is almost always present in its maximally oxidized state, as inorganic phosphate rocks...
, or zinc
Zinc
Zinc , or spelter , is a metallic chemical element; it has the symbol Zn and atomic number 30. It is the first element in group 12 of the periodic table. Zinc is, in some respects, chemically similar to magnesium, because its ion is of similar size and its only common oxidation state is +2...
.
In food, proteins are essential for growth and survival and vary depending upon a person's age and physiology
Physiology
Physiology is the science of the function of living systems. This includes how organisms, organ systems, organs, cells, and bio-molecules carry out the chemical or physical functions that exist in a living system. The highest honor awarded in physiology is the Nobel Prize in Physiology or...
(e.g., pregnancy
Pregnancy
Pregnancy refers to the fertilization and development of one or more offspring, known as a fetus or embryo, in a woman's uterus. In a pregnancy, there can be multiple gestations, as in the case of twins or triplets...
). Proteins in food are commonly found in peanuts
Peanuts
Peanuts is a syndicated daily and Sunday American comic strip written and illustrated by Charles M. Schulz, which ran from October 2, 1950, to February 13, 2000, continuing in reruns afterward...
, meat, poultry
Poultry
Poultry are domesticated birds kept by humans for the purpose of producing eggs, meat, and/or feathers. These most typically are members of the superorder Galloanserae , especially the order Galliformes and the family Anatidae , commonly known as "waterfowl"...
, and seafood
Seafood
Seafood is any form of marine life regarded as food by humans. Seafoods include fish, molluscs , crustaceans , echinoderms . Edible sea plants, such as some seaweeds and microalgae, are also seafood, and are widely eaten around the world, especially in Asia...
. They are also involved in ELISA
ELISA
Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay , is a popular format of a "wet-lab" type analytic biochemistry assay that uses one sub-type of heterogeneous, solid-phase enzyme immunoassay to detect the presence of a substance in a liquid sample."Wet lab" analytic biochemistry assays involves detection of an...
test for food allergy
Food allergy
A food allergy is an adverse immune response to a food protein. They are distinct from other adverse responses to food, such as food intolerance, pharmacological reactions, and toxin-mediated reactions....
determination.
Enzymes
Enzymes are biochemical catalysts used in converting processes from one substance to another. They are also involved in reducing the amount of time and energy required to complete a chemical process. Many aspects of the foodFood
Food is any substance consumed to provide nutritional support for the body. It is usually of plant or animal origin, and contains essential nutrients, such as carbohydrates, fats, proteins, vitamins, or minerals...
industry use catalysts, including baking
Baking
Baking is the technique of prolonged cooking of food by dry heat acting by convection, and not by radiation, normally in an oven, but also in hot ashes, or on hot stones. It is primarily used for the preparation of bread, cakes, pastries and pies, tarts, quiches, cookies and crackers. Such items...
, brewing
Brewing
Brewing is the production of beer through steeping a starch source in water and then fermenting with yeast. Brewing has taken place since around the 6th millennium BCE, and archeological evidence suggests that this technique was used in ancient Egypt...
, dairy
Dairy
A dairy is a business enterprise established for the harvesting of animal milk—mostly from cows or goats, but also from buffalo, sheep, horses or camels —for human consumption. A dairy is typically located on a dedicated dairy farm or section of a multi-purpose farm that is concerned...
, and fruit juices
Juice
Juice is the liquid that is naturally contained in fruit or vegetable tissue.Juice is prepared by mechanically squeezing or macerating fruit or vegetable flesh without the application of heat or solvents. For example, orange juice is the liquid extract of the fruit of the orange tree...
, to make cheese, beer
Beer
Beer is the world's most widely consumed andprobably oldest alcoholic beverage; it is the third most popular drink overall, after water and tea. It is produced by the brewing and fermentation of sugars, mainly derived from malted cereal grains, most commonly malted barley and malted wheat...
, and bread
Bread
Bread is a staple food prepared by cooking a dough of flour and water and often additional ingredients. Doughs are usually baked, but in some cuisines breads are steamed , fried , or baked on an unoiled frying pan . It may be leavened or unleavened...
.
Vitamins

Water
Water is a chemical substance with the chemical formula H2O. A water molecule contains one oxygen and two hydrogen atoms connected by covalent bonds. Water is a liquid at ambient conditions, but it often co-exists on Earth with its solid state, ice, and gaseous state . Water also exists in a...
soluble (Vitamin C
Vitamin C
Vitamin C or L-ascorbic acid or L-ascorbate is an essential nutrient for humans and certain other animal species. In living organisms ascorbate acts as an antioxidant by protecting the body against oxidative stress...
) or fat
Fat
Fats consist of a wide group of compounds that are generally soluble in organic solvents and generally insoluble in water. Chemically, fats are triglycerides, triesters of glycerol and any of several fatty acids. Fats may be either solid or liquid at room temperature, depending on their structure...
soluble (Vitamin E
Vitamin E
Vitamin E is used to refer to a group of fat-soluble compounds that include both tocopherols and tocotrienols. There are many different forms of vitamin E, of which γ-tocopherol is the most common in the North American diet. γ-Tocopherol can be found in corn oil, soybean oil, margarine and dressings...
). An adequate supply of vitamins can prevent diseases such as beriberi
Beriberi
Beriberi is a nervous system ailment caused by a thiamine deficiency in the diet. Thiamine is involved in the breakdown of energy molecules such as glucose and is also found on the membranes of neurons...
, anemia
Anemia
Anemia is a decrease in number of red blood cells or less than the normal quantity of hemoglobin in the blood. However, it can include decreased oxygen-binding ability of each hemoglobin molecule due to deformity or lack in numerical development as in some other types of hemoglobin...
, and scurvy
Scurvy
Scurvy is a disease resulting from a deficiency of vitamin C, which is required for the synthesis of collagen in humans. The chemical name for vitamin C, ascorbic acid, is derived from the Latin name of scurvy, scorbutus, which also provides the adjective scorbutic...
while an overdose of vitamins can produce nausea
Nausea
Nausea , is a sensation of unease and discomfort in the upper stomach with an involuntary urge to vomit. It often, but not always, precedes vomiting...
and vomiting
Vomiting
Vomiting is the forceful expulsion of the contents of one's stomach through the mouth and sometimes the nose...
or even death
Death
Death is the permanent termination of the biological functions that sustain a living organism. Phenomena which commonly bring about death include old age, predation, malnutrition, disease, and accidents or trauma resulting in terminal injury....
.
Minerals
Dietary minerals in foods are large and diverse with many required to function while other trace elements can be hazardous if consumed in excessive amounts. Bulk minerals with a Reference Daily IntakeReference Daily Intake
The Reference Daily Intake or Recommended Daily Intake is the daily intake level of a nutrient that is considered to be sufficient to meet the requirements of 97–98% of healthy individuals in every demographic in the United States .The RDI is used to determine the Daily Value of foods,...
(RDI, formerly Recommended Daily Allowance (RDA)) of more than 200 mg/day are calcium
Calcium
Calcium is the chemical element with the symbol Ca and atomic number 20. It has an atomic mass of 40.078 amu. Calcium is a soft gray alkaline earth metal, and is the fifth-most-abundant element by mass in the Earth's crust...
, magnesium
Magnesium
Magnesium is a chemical element with the symbol Mg, atomic number 12, and common oxidation number +2. It is an alkaline earth metal and the eighth most abundant element in the Earth's crust and ninth in the known universe as a whole...
, and potassium
Potassium
Potassium is the chemical element with the symbol K and atomic number 19. Elemental potassium is a soft silvery-white alkali metal that oxidizes rapidly in air and is very reactive with water, generating sufficient heat to ignite the hydrogen emitted in the reaction.Potassium and sodium are...
while important trace minerals (RDI less than 200 mg/day) are copper, iron, and zinc. These are found in many foods, but can also be taken in dietary supplements.
Color
Food coloring is added to change the colorColor
Color or colour is the visual perceptual property corresponding in humans to the categories called red, green, blue and others. Color derives from the spectrum of light interacting in the eye with the spectral sensitivities of the light receptors...
of any food
Food
Food is any substance consumed to provide nutritional support for the body. It is usually of plant or animal origin, and contains essential nutrients, such as carbohydrates, fats, proteins, vitamins, or minerals...
substance. It is mainly for sensory analysis
Sensory analysis
Sensory analysis is a scientific discipline that applies principles of experimental design and statistical analysis to the use of human senses for the purposes of evaluating consumer products. The discipline requires panels of human assessors, on whom the products are tested, and recording the...
purposes. It can be used to simulate the natural color of a product as perceived by the customer, such as red dye like FD&C Red No.40 (Allura Red AC
Allura Red AC
Allura Red AC is a red azo dye that goes by several names including: Allura Red, Food Red 17, C.I. 16035, FD&C Red 40, 2-naphthalenesulfonic acid, 6-hydroxy-5--, disodium salt, and disodium 6-hydroxy-5--2-naphthalenesulfonate. It is used as a food dye and has the E number E129...
) to ketchup
Ketchup
Ketchup is a sweet-and-tangy condiment typically made from tomatoes, vinegar, sugar or high-fructose corn syrup and an assortment of...
or to add unnatural colors to a product like Kellogg's
Kellogg Company
Kellogg Company , is a producer of cereal and convenience foods, including cookies, crackers, toaster pastries, cereal bars, fruit-flavored snacks, frozen waffles, and vegetarian foods...
Froot Loops
Froot Loops
Froot Loops is a brand of breakfast cereal produced by Kellogg's and sold in Hungary, Mexico, Canada, New Zealand, Australia, the United States, South Korea, Philippines, Thailand, Germany, The Middle East, The Caribbean, South Africa, Latin America, Sweden and Finland...
. Caramel
Caramel
Caramel is a beige to dark-brown confection made by heating any of a variety of sugars. It is used as a flavoring in puddings and desserts, as a filling in bonbons, and as a topping for ice cream, custard and coffee....
is a natural food dye; the industrial form, caramel coloring, is the most widely-used food coloring and is found in foods from soft drink
Soft drink
A soft drink is a non-alcoholic beverage that typically contains water , a sweetener, and a flavoring agent...
s to soy sauce
Soy sauce
Soy sauce is a condiment produced by fermenting soybeans with Aspergillus oryzae or Aspergillus sojae molds, along with water and salt...
, bread
Bread
Bread is a staple food prepared by cooking a dough of flour and water and often additional ingredients. Doughs are usually baked, but in some cuisines breads are steamed , fried , or baked on an unoiled frying pan . It may be leavened or unleavened...
, and pickle
Pickling
Pickling, also known as brining or corning is the process of preserving food by anaerobic fermentation in brine to produce lactic acid, or marinating and storing it in an acid solution, usually vinegar . The resulting food is called a pickle. This procedure gives the food a salty or sour taste...
s.
Flavors
Flavor in food is important in how food smellOlfaction
Olfaction is the sense of smell. This sense is mediated by specialized sensory cells of the nasal cavity of vertebrates, and, by analogy, sensory cells of the antennae of invertebrates...
s and taste
Taste
Taste is one of the traditional five senses. It refers to the ability to detect the flavor of substances such as food, certain minerals, and poisons, etc....
s to the consumer, especially in sensory analysis. Some of these products occur naturally like salt
Salt
In chemistry, salts are ionic compounds that result from the neutralization reaction of an acid and a base. They are composed of cations and anions so that the product is electrically neutral...
and sugar
Sugar
Sugar is a class of edible crystalline carbohydrates, mainly sucrose, lactose, and fructose, characterized by a sweet flavor.Sucrose in its refined form primarily comes from sugar cane and sugar beet...
, but flavor chemists (called a "flavorist
Flavorist
A flavorist, also known as flavor chemist, is someone who uses chemistry to engineer artificial and natural flavors. The tools and materials used by flavorists are almost the same as that used by perfumers with the exception that flavorists seek to mimic or modify both the olfactory and gustation...
") develop many of these flavors for food products. Such artificial flavors include methyl salicylate
Methyl salicylate
Methyl salicylate is a natural product of many species of plants. Some of the plants which produce it are called wintergreens, hence the common name.-Botanical background:...
which creates the wintergreen
Wintergreen
Wintergreen is a group of plants. Wintergreen once commonly referred to plants that continue photosynthesis throughout the winter...
odor and lactic acid which gives milk a tart taste.
Food additives
Food additives are substances added to food for preserving flavors, or improving taste or appearance. These processes are as old as adding vinegarVinegar
Vinegar is a liquid substance consisting mainly of acetic acid and water, the acetic acid being produced through the fermentation of ethanol by acetic acid bacteria. Commercial vinegar is produced either by fast or slow fermentation processes. Slow methods generally are used with traditional...
for pickling
Pickling
Pickling, also known as brining or corning is the process of preserving food by anaerobic fermentation in brine to produce lactic acid, or marinating and storing it in an acid solution, usually vinegar . The resulting food is called a pickle. This procedure gives the food a salty or sour taste...
or as an emulsifier for emulsion
Emulsion
An emulsion is a mixture of two or more liquids that are normally immiscible . Emulsions are part of a more general class of two-phase systems of matter called colloids. Although the terms colloid and emulsion are sometimes used interchangeably, emulsion is used when both the dispersed and the...
mixtures like mayonnaise
Mayonnaise
Mayonnaise, , often abbreviated as mayo, is a sauce. It is a stable emulsion of oil, egg yolk and either vinegar or lemon juice, with many options for embellishment with other herbs and spices. Lecithin in the egg yolk is the emulsifier. Mayonnaise varies in color but is often white, cream, or pale...
. These are generally listed by "E number
E number
E numbers are number codes for food additives that have been assessed for use within the European Union . They are commonly found on food labels throughout the European Union. Safety assessment and approval are the responsibility of the European Food Safety Authority...
" in the European Union
European Union
The European Union is an economic and political union of 27 independent member states which are located primarily in Europe. The EU traces its origins from the European Coal and Steel Community and the European Economic Community , formed by six countries in 1958...
or GRAS
Gras
Gras is a commune in the Ardèche department in southern France.-Population:-References:*...
("generally recognized as safe
Generally recognized as safe
Generally recognized as safe is an American Food and Drug Administration designation that a chemical or substance added to food is considered safe by experts, and so is exempted from the usual Federal Food, Drug, and Cosmetic Act food additive tolerance requirements.-History:On January 1, 1958,...
") by the United States
United States
The United States of America is a federal constitutional republic comprising fifty states and a federal district...
Food and Drug Administration
Food and Drug Administration
The Food and Drug Administration is an agency of the United States Department of Health and Human Services, one of the United States federal executive departments...
.
See also
- Dietary supplementDietary supplementA dietary supplement, also known as food supplement or nutritional supplement, is a preparation intended to supplement the diet and provide nutrients, such as vitamins, minerals, fiber, fatty acids, or amino acids, that may be missing or may not be consumed in sufficient quantities in a person's diet...
- Food and Bioprocess Technology (journal)
- Food Chemistry (journal)Food Chemistry (journal)Food Chemistry is a peer-reviewed scientific journal. It was established in 1976 and is published 24 times a year by Elsevier....
- Food engineeringFood engineeringFood engineering is a multidisciplinary field of applied physical sciences which combines science, microbiology, and engineering education for food and related industries. Food engineering includes, but is not limited to, the application of agricultural engineering, mechanical engineering and...
- Food fortificationFood fortificationFood fortification or enrichment is the process of adding micronutrients to food. It can be purely a commercial choice to provide extra nutrients in a food, or sometimes it is a public health policy which aims to reduce numbers of people with dietary deficiencies in a population.Diets that lack...
- Food microbiologyFood microbiologyFood microbiology is the study of the microorganisms that inhabit, create, or contaminate food. Of major importance is the study of microorganisms causing food spoilage. "Good" bacteria, however, such as probiotics, are becoming increasingly important in food science...
- Food packagingFood packagingFood packaging is packaging for food. It requires protection, tampering resistance, and special physical, chemical, or biological needs. It also shows the product that is labeled to show any nutrition information on the food being consumed....
- Food preservationFood preservationFood preservation is the process of treating and handling food to stop or slow down spoilage and thus allow for longer storage....
- Food rheologyFood rheologyFood rheology is the study of the rheological properties of food, that is, the consistency and flow of food under tightly specified conditions. The consistency, degree of fluidity, and other mechanical properties are important in understanding how long food can be stored, how stable it will...
- Food safetyFood safetyFood safety is a scientific discipline describing handling, preparation, and storage of food in ways that prevent foodborne illness. This includes a number of routines that should be followed to avoid potentially severe health hazards....
- Food scienceFood scienceFood science is a study concerned with all technical aspects of foods, beginning with harvesting or slaughtering, and ending with its cooking and consumption, an ideology commonly referred to as "from field to fork"...
- Food storageFood storageFood storage is both a traditional domestic skill and is important industrially. Food is stored by almost every human society and by many animals...
- Food supplements
- Food technologyFood technologyFood technology, is a branch of food science which deals with the actual production processes to make foods.-Early history of food technology:...
- NutraceuticalNutraceuticalNutraceutical, a portmanteau of the words “nutrition” and “pharmaceutical”, is a food or food product that reportedly provides health and medical benefits, including the prevention and treatment of disease. Health Canada defines the term as "a product isolated or purified from foods that is...
- Nutrification (also called food enrichment or fortification)

