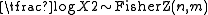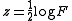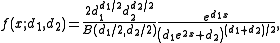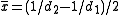Fisher's z-distribution
Encyclopedia
Fisher's z-distribution is the statistical distribution of half the logarithm
of an F distribution variate:
It was first described by Ronald Fisher
in a paper delivered at the International Mathematical Congress of 1924 in Toronto
, entitled "On a distribution yielding the error functions of several well-known statistics" (Proceedings of the International Congress of Mathematics, Toronto, 2: 805-813 (1924). Nowadays one usually uses the F distribution instead.
The probability density function
and cumulative distribution function
can be found be using the F-distribution at the value of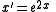 . However, the mean and variance do not follow the same transformation.
. However, the mean and variance do not follow the same transformation.
The probability density function is
where B is the beta function.
When the degrees of freedom
becomes large (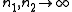 ) the distribution approach normality with mean
) the distribution approach normality with mean
and variance
Logarithm
The logarithm of a number is the exponent by which another fixed value, the base, has to be raised to produce that number. For example, the logarithm of 1000 to base 10 is 3, because 1000 is 10 to the power 3: More generally, if x = by, then y is the logarithm of x to base b, and is written...
of an F distribution variate:
It was first described by Ronald Fisher
Ronald Fisher
Sir Ronald Aylmer Fisher FRS was an English statistician, evolutionary biologist, eugenicist and geneticist. Among other things, Fisher is well known for his contributions to statistics by creating Fisher's exact test and Fisher's equation...
in a paper delivered at the International Mathematical Congress of 1924 in Toronto
Toronto
Toronto is the provincial capital of Ontario and the largest city in Canada. It is located in Southern Ontario on the northwestern shore of Lake Ontario. A relatively modern city, Toronto's history dates back to the late-18th century, when its land was first purchased by the British monarchy from...
, entitled "On a distribution yielding the error functions of several well-known statistics" (Proceedings of the International Congress of Mathematics, Toronto, 2: 805-813 (1924). Nowadays one usually uses the F distribution instead.
The probability density function
Probability density function
In probability theory, a probability density function , or density of a continuous random variable is a function that describes the relative likelihood for this random variable to occur at a given point. The probability for the random variable to fall within a particular region is given by the...
and cumulative distribution function
Cumulative distribution function
In probability theory and statistics, the cumulative distribution function , or just distribution function, describes the probability that a real-valued random variable X with a given probability distribution will be found at a value less than or equal to x. Intuitively, it is the "area so far"...
can be found be using the F-distribution at the value of
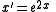 . However, the mean and variance do not follow the same transformation.
. However, the mean and variance do not follow the same transformation.The probability density function is
where B is the beta function.
When the degrees of freedom
Degrees of freedom
Degrees of freedom can mean:* Degrees of freedom , independent displacements and/or rotations that specify the orientation of the body or system...
becomes large (
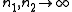 ) the distribution approach normality with mean
) the distribution approach normality with mean
and variance
Related Distribution
- If
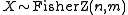 then
then 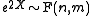 (F-distribution)
(F-distribution) - If
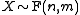 then
then