Fibromyalgia
Encyclopedia
Fibromyalgia is a medical disorder characterized by chronic widespread pain
and allodynia
, a heightened and painful response to pressure. It is an example of a diagnosis of exclusion
. Fibromyalgia symptoms are not restricted to pain, leading to the use of the alternative term fibromyalgia syndrome for the condition. Other symptoms include debilitating fatigue, sleep disturbance, and joint stiffness
. Some patients may also report difficulty with swallowing
, bowel and bladder
abnormalities, numbness and tingling
, and cognitive dysfunction
. Fibromyalgia is frequently comorbid
with psychiatric conditions such as depression
and anxiety
and stress-related disorders such as posttraumatic stress disorder. Not all people with fibromyalgia experience all associated symptoms. Fibromyalgia is estimated to affect 2–4% of the population, with a female to male incidence ratio of approximately 9:1.
The brains of fibromyalgia patients show structural and behavioral differences from those of healthy individuals, but it is unclear whether the brain anomalies cause fibromyalgia symptoms or are the product of an unknown underlying common cause. Some research suggests that these brain anomalies may be the result of childhood stress, or prolonged or severe stress.
Historically, fibromyalgia has been considered either a musculoskeletal disease or neuropsychiatric
condition. Although there is as yet no cure for fibromyalgia, some treatments have been demonstrated by controlled clinical trial
s to be effective in reducing symptoms, including medications, behavioral interventions, patient education, and exercise. The most recent approach of a diagnosis of fibromyalgia involves pain index and a measure of key symptoms and severity.
Fibromyalgia has been recognized as a diagnosable disorder by the National Institutes of Health and the American College of Rheumatology. Fibromyalgia, a central nervous system disorder, is described as a 'central sensitisation syndrome' caused by neurobiological abnormalities which act to produce physiological pain and cognitive impairments as well as psychological symptomatology. Despite this there are some members of the medical community who do not consider fibromyalgia a disease because of a lack of abnormalities on physical examination and the absence of objective diagnostic tests.
). Other symptoms may include tingling of the skin, prolonged muscle spasms
, weakness
in the limbs, nerve pain, muscle twitching, palpitations, functional bowel disturbances, and chronic sleep disturbances
.
Many patients experience cognitive dysfunction (known as "brain fog" or "fibrofog"), which may be characterized by impaired concentration, problems with short
and long-term memory
, short-term memory consolidation, impaired speed of performance, inability to multi-task, cognitive overload, and diminished attention span
. Fibromyalgia is often associated with anxiety
, and depressive
symptoms.
Other symptoms often attributed to fibromyalgia that may possibly be due to a comorbid
disorder include myofascial pain syndrome
, also referred to as chronic myofascial pain, diffuse non-dermatomal paresthesia
s, functional bowel disturbances and irritable bowel syndrome
, genitourinary
symptoms and interstitial cystitis
, dermatological
disorders, headache
s, myoclonic twitches
, and symptomatic hypoglycemia
. Although fibromyalgia is classified based on the presence of chronic widespread pain, pain may also be localized in areas such as the shoulder
s, neck
, low back
, hips, or other areas. Many sufferers also experience varying degrees of myofascial pain and have high rates of comorbid temporomandibular joint disorder
. 20–30% of patients with rheumatoid arthritis
and systemic lupus erythematosus
may also have fibromyalgia.
The mode of inheritance is currently unknown, but it is most probably polygenic. Research has also demonstrated that fibromyalgia is potentially associated with polymorphisms of genes in the serotoninergic, dopaminergic and catecholaminergic systems. However, these polymorphisms are not specific for fibromyalgia and are associated with a variety of allied disorders (e.g. chronic fatigue syndrome
, irritable bowel syndrome
) and with depression.
may be an important precipitating factor in the development of fibromyalgia. Fibromyalgia is frequently comorbid with stress-related disorders such as chronic fatigue syndrome
, posttraumatic stress disorder, irritable bowel syndrome
and depression. A systematic review found significant association between fibromyalgia and physical and sexual abuse in both childhood and adulthood, although the quality of studies was poor.
Two studies that employed single-voxel magnetic resonance spectroscopy (1H-MRS) reported metabolic abnormalities within the hippocampal complex in patients with fibromyalgia. As the hippocampus
plays crucial roles in maintenance of cognitive functions, sleep regulation, and pain perception, it was suggested that metabolic dysfunction of the hippocampus may be implicated in the appearance of these symptoms.
Other authors have proposed that, because exposure to stressful conditions can alter the function of the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal (HPA) axis
, the development of fibromyalgia may stem from stress-induced disruption of the HPA axis.
hypothesis of fibromyalgia" proposes that the central abnormality responsible for symptoms associated with fibromyalgia is a disruption of normal dopamine-related neurotransmission. Insufficient dopamine in a part of the body is termed hypodopaminergia. Dopamine is a catecholamine
neurotransmitter
with roles in pain perception and natural analgesia. There is also strong evidence for a role of dopamine in restless leg syndrome, which is a condition found frequently in patients with fibromyalgia. Some fibromyalgia patients responded in controlled trials to pramipexole
, a dopamine agonist
that selectively stimulates dopamine D2/D3 receptors and is used to treat both Parkinson's disease
and restless leg syndrome.
, a neurotransmitter
that regulates sleep patterns, mood, concentration and pain, could be involved in the pathophysiology
of fibromyalgia-associated symptoms. In 1992, decreased serotonin metabolites in patient blood samples
and cerebrospinal fluid
were reported. However, selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs) have met with limited success in alleviating the symptoms of the disorder, while drugs with activity as mixed serotonin-norepinephrine reuptake inhibitor
s (SNRIs) have been more successful. In controlled trials funded by Eli Lily, Duloxetine
(Cymbalta), an SNRI originally used to treat depression and painful diabetic neuropathy
, was demonstrated to relieve fibromyalgia symptoms in some women, however male subjects failed to improve significantly. The Food and Drug Administration regulators approved the drug for the treatment of fibromyalgia in June 2008. However, the relevance of dysregulated serotonin metabolism to pathophysiology is a matter of debate. Complicating the analysis, one of the more effective types of medication for the treatment of the disorder (i.e. serotonin 5-HT3 antagonist
s) actually blocks some of the effects of serotonin.
, leptin
and neuropeptide Y
may be abnormal in people with fibromyalgia, but supplementing growth hormone in patients does not have large effects, and a 2007 literature review reported a need for "further study before any solid recommendations can be made". There is disagreement about the role of HGH in fibromyalgia.
to evaluate brain responses to experimental pain among fibromyalgia patients found that depressive symptoms were associated with the magnitude of clinically-induced pain response specifically in areas of the brain that participate in affective pain processing, but not in areas involved in sensory processing which indicates that the amplification of the sensory dimension of pain in fibromyalgia occurs independently of mood or emotional processes.
(NTNU) have uncovered an association between sleep problems and increased risk of fibromyalgia in 2011.
, also called Myoadenylate Deaminase Deficiency
, sometimes abbrevisted MADD
, is a quite common recessive genetic metabolic disorder that shares many of the same symptoms as Fibromyalgia. Especially fatigue, cognitive dysfunction, and enhanced sensitivity to pain. Perhaps most telling are the studies showing a positive response to Ribose
by 66% of the test subjects diagnosed with Fibromyalgia. Ribose
being a possible treatment for MADD
.
, IL-6 and IL-8
as well as corticotropin-releasing hormone
have been found in the cerebral spinal fluid of fibromyalgia suffering individuals. Increased numbers of mast cell
numbers have been found in skin biopsies of some fibromyalgia people. Quercetin
, a pharmacologically active natural product
which pocesses antiinflammatory in addition to mast cell inhibiting properties may be a useful treatment.
, which senses pressure, heat, cold, electrical and chemical stimulation. Experiments examining pain regulatory systems have shown that fibromyalgia patients display an exaggerated wind-up in response to repetitive stimulation and an absence of exercise-induced analgesic response.
(IGF-1) levels in some fibromyalgia patients have led to the theory that these patients may actually have a different, treatable syndrome, adult growth hormone deficiency
. Other abnormalities include reduced responsivity of thyrotropin and thyroid hormones to thyroid-releasing hormone, a mild elevation of prolactin levels with disinhibition of prolactin release in response to challenge and hyposecretion of adrenal androgens.
These changes might result from chronic stress, which, after being perceived and processed by the central nervous system, activates hypothalamic corticotrophin-releasing hormone neurons. Chronic overactivity of these neurons could disrupt normal function of the pituitary-adrenal axis and cause an increased stimulation of hypothalamic somatostatin secretion, which, in turn, could inhibit the secretion of other hormones.
and elements of the basal ganglia
and mid-brain (i.e., pontine nucleus). Differential activation in response to painful stimulation has also been demonstrated. Brain centers showing hyperactivation in response to noxious stimulation include such pain-related brain centers as the primary and secondary
somatosensory cortices, anterior cingulate cortex
, and insular cortex
. Patients also exhibit neural activation in brain regions associated with pain perception in response to nonpainful stimuli in such areas as the prefrontal, supplemental motor, insular, and cingulate cortices. Evidence of hippocampal disruption indicated by reduced brain metabolite ratios has been demonstrated by studies using single-voxel magnetic resonance spectroscopy (1H-MRS). A significant negative correlation was demonstrated between abnormal metabolite ratios and a validated index of the clinical severity (i.e. the Fibromyalgia Impact Questionnaire). Correlations between clinical pain severity and concentrations of the excitatory amino acid neurotransmitter glutamate within the insular cortex have also been demonstrated using 1H-MRS. An acceleration of normal age-related brain atrophy has been demonstrated using voxel-based morphometry (VBM) with areas of reduced gray matter located in the cingulate cortex, insula and parahippocampal gyrus. Grey matter loss appears to increase 9.5 times the normal rate with each year. Studies utilizing positron emission tomography
have demonstrated reduced dopamine synthesis in the brainstem and elements of the limbic cortex. A significant negative correlation between pain severity and dopamine synthesis was demonstrated within the insular cortex. A subsequent study demonstrated gross disruption of dopaminergic reactivity in response to a tonic pain stimulus within the basal ganglia
with a significant positive correlation between the defining feature of the disorder (i.e. tender point index) and dopamine D2 receptor binding potential specifically in the right putamen
. Finally, reduced availability of mu-opioid receptors in the ventral striatum
/nucleus accumbens
and cingulate cortex has been demonstrated, with a significant negative correlation between affective pain levels and receptor availability in the nucleus accumbens.
. These criteria, which are known informally as "the ACR 1990", define fibromyalgia according to the presence of the following criteria:
The ACR criteria for classification of patients were originally established as inclusion criteria for research purposes and were not intended for clinical diagnosis but have now become the de facto diagnostic criteria in the clinical setting. It should be noted that the number of tender points that may be active at any one time may vary with time and circumstance. A controversial study done by a legal team looking to prove their client's disability based primarily on tender points and their widespread presence in non-litigious communities prompted the lead author of the ACR criteria to now question the useful validity of tender points in diagnosis. Since the ACR criteria were originally published, research with mechanical devices that exert defined pressure
indicate that diagnosis of fibromyalgia cannot be done objectively by machine and require a physician's subjective estimate of how much pressure should be exerted.
, there is no universally accepted treatment or cure for fibromyalgia, and treatment typically consists of symptom management. Developments in the understanding of the pathophysiology of the disorder have led to improvements in treatment, which include prescription medication, behavioral intervention, exercise, and alternative
and complementary medicine. Indeed, integrated treatment plans that incorporate medication, patient education, aerobic exercise and cognitive-behavioral therapy have been shown to be effective in alleviating pain and other fibromyalgia-related symptoms. In 2005, the American Pain Society produced comprehensive guidelines for patient evaluation and management.
More recently, the European League Against Rheumatism
(EULAR) issued updated treatment guidelines.
was approved in June, 2007, duloxetine
was approved in June, 2008, and milnacipran
was approved in January, 2009. Pregabalin and duloxetine have been shown to reduce pain in a substantial number of patients with fibromyalgia, but there were others who didn't benefit. Placebo-controlled trials involving a total of over 2000 patients have shown milnacipran to be significantly more effective than placebo in treating both pain and the broader syndrome of fibromyalgia.
concluded that antidepressants were "associated with improvements in pain, depression, fatigue, sleep disturbances, and health-related quality of life in patients with FMS." The authors also stated that the goal of antidepressants in fibromyalgia should be “possible symptom reduction”, and if used long term, their effects should be evaluated against side effects.
Tricyclic antidepressant
s were the most effective against pain, fatigue, and sleep problems, but have many side effects due to interaction with adrenergic, cholinergic or histaminergic receptors, and sodium channels. Selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor
s (SSRIs) and Serotonin-norepinephrine reuptake inhibitor
s (SNRIs) had lower side effects.
, a centrally acting analgesic with atypical opioid and antidepressant-like activity, is moderately effective in treating fibromyalgia pain. Long-term effectiveness and tolerability are unknown. Tramadol combined with paracetamol
provides fast, lasting relief that is more effective than either drug alone. This combination therapy has demonstrated efficacy, safety and tolerability for up to two years without the development of tolerance, in the treatment of chronic pain. It is as effective as codeine plus paracetamol but produces less sleepiness and constipation, and it is free of the toxic effects associated with non-steroidal anti-inflammatories
.
(Neurontin) and pregabalin
(Lyrica) have been tested. Gabapentin is approved for use in treatment of neuropathic pain but not fibromyalgia. Pregabalin, originally labeled for the treatment of nerve pain suffered by diabetics, has been cleared by the US Food and Drug Administration
for treatment of fibromyalgia. A randomized controlled trial
of pregabalin
450 mg/day found that 6 patients is the number needed to treat
for one patient to have a 50% reduction in pain. A Cochrane Database analysis of pregabalin use in chronic pain concluded that “A minority of patients will have substantial benefit with pregabalin, and more will have moderate benefit. Many will have no or trivial benefit, or will discontinue because of adverse events.” A meta-analysis of four trial of pregabalin in fibromyalgia found that for patients who did respond to pregabalin, there was a reduction in time off work >1 day per week.
(Mirapex) and ropinirole
(ReQuip)) resulted in some improvement in a minority of patients, but numerous side effects, including the onset of impulse control disorders like compulsive gambling and shopping, have led to concern about this approach. A trial of transdermal rotigotine
is currently ongoing.
is a muscle relaxant
medication used to relieve skeletal muscle
spasm
s and associated pain in acute
musculoskeletal conditions. It is the most well-studied drug for this application, and it also has been used off-label
for fibromyalgia treatment.
Tizanidine
(brandnames Zanaflex, Sirdalud) is a muscle relaxant centrally acting α-2 adrenergic agonist. It is used to treat the spasms, cramping, and tightness of muscles caused by medical problems such as multiple sclerosis, spastic diplegia, back pain, or certain other injuries to the spine or central nervous system. It is also prescribed off-label for some symptoms of fibromyalgia.
s (other than tramadol
) have not had randomized controlled trial
s, and "should be considered only after all other medicinal and nonmedicinal therapies have been exhausted." Despite a lack of clinical trials and the potential for addiction
and abuse
, opioids are widely used by fibromyalgia patients. An analysis of insurance claims by 52,000 fibromyalgia patients showed that 40% had received opioids in any given year (predominantly short-acting agents).
at very low dosage has been found to be effective in reducing fibromyalgia symptoms by more than 30 percent in a small controlled trial. Naltrexone, an opioid antagonist also acts at very low dosage, to inhibit microglia
cells thereby reducing proinflammatory cytokines and neurotoxic superoxides.
, a flavanoid and pharmacologically active natural compound
, which acts as an anti-inflammatory and has mast cell
inhibitory properties may be effective in the treatment of fibromyalgia.
and the 5-HT3 receptor antagonist tropisetron
. A controlled study of guaifenesin
failed to demonstrate any benefits from this treatment
.
must take place in a warm pool. Not only that, but the air temperature outside of the pool must also be heated to prevent fibromyalgia patients from getting chills and aches when out of the water. This involves a specialised pool facility, which makes this therapy more expensive and less accessible than regular swimming exercise.
members enrolled in Medicare Advantage and commercial plans compared costs and medical utilizations and found that persons with fibromyalgia used twice as much pain-related medication as those without fibromyalgia. Furthermore, the use of medications and medical necessities increased markedly across many measures once diagnosis was made.
” were applied historically to symptoms resembling those of fibromyalgia. The term fibromyalgia was coined by researcher Mohammed Yunus as a synonym for fibrositis and was first used in a scientific publication in 1981. Fibromyalgia is from the Latin
fibra (fiber) and the Greek
words myo (muscle) and algos (pain).
Historical perspectives on the development of the fibromyalgia concept note the “central importance” of a 1977 paper by Smythe and Moldofsky on fibrositis. The first clinical
, controlled study of the characteristics of fibromyalgia syndrome was published in 1981, providing support for symptom associations. In 1984, an interconnection between fibromyalgia syndrome and other similar conditions was proposed, and in 1986, trials of the first proposed medications for fibromyalgia were published.
A 1987 article in the Journal of the American Medical Association
used the term "fibromyalgia syndrome" while saying it was a "controversial condition". The American College of Rheumatology
(ACR) published its first classification criteria for fibromyalgia in 1990, although these are not strictly diagnostic criteria.
Several theories propose that fibromyalgia is a psychosomatic illness
.
Several controversial issues exist with regard to fibromyalgia that range from questions regarding the validity of the disorder as a clinical entity, to issues regarding primary pathophysiology and the potential existence of fibromyalgia subtypes.
According to Frederick Wolfe, lead author of the 1990 paper that first defined the ACR fibromyalgia classification criteria,"the large majority of physicians, sociologists, and medical historians" are skeptical about the validity of fibromyalgia as a clinical entity. Some call fibromyalgia a “non-disease” and “an over-inclusive and ultimately meaningless label.” Wolfe now questions the validity of fibromyalgia as a disease. He considers fibromyalgia a physical response to stress, depression, and economic and social anxiety, and believes the associated symptoms are a normal part of everyday life. In 2009, he wrote, "the tendency to respond with distress to physical and mental stressors is part of the human condition." Wolfe notes that, "opponents of the fibromyalgia concept argue that, as it is a non-disease, we are legitimising patients' sickness behaviour by providing a disease label."
In a study of 100 individuals identified as having fibromyalgia, physical functioning decreased slightly over time, and individuals who had been diagnosed earlier had larger numbers of reported symptoms and greater severity. However, there was also a statistically significant improvement in satisfaction with health following classification. The authors of the study concluded that the ‘fibromyalgia label’ does not have a meaningful adverse effect on clinical outcome over the long term.
The validity of fibromyalgia as a unique clinical entity is also a matter of contention because "no discrete boundary separates syndromes such as FMS, chronic fatigue syndrome, irritable bowel syndrome, or chronic muscular headaches." Because of this considerable symptomatic overlap, some researchers have proposed that fibromyalgia and other syndromes with overlapping symptoms be classified as functional somatic syndromes for some purposes.
Some researchers believe that differences in psychological and autonomic nervous system profiles among affected individuals may indicate the existence of fibromyalgia subtypes. A 2007 review divides individuals with fibromyalgia into four groups as well as “mixed types”:
Other researchers have suggested that depression may be a result of coping with the disabling impacts of a, thus far, incurable disease.
Pain
Pain is an unpleasant sensation often caused by intense or damaging stimuli such as stubbing a toe, burning a finger, putting iodine on a cut, and bumping the "funny bone."...
and allodynia
Allodynia
Allodynia is a pain due to a stimulus which does not normally provoke pain. Temperature or physical stimuli can provoke allodynia, and it often occurs after injury to a site...
, a heightened and painful response to pressure. It is an example of a diagnosis of exclusion
Diagnosis of exclusion
A diagnosis of exclusion is a medical condition reached by a process of elimination, which may be necessary if presence cannot be established with complete confidence from examination or testing...
. Fibromyalgia symptoms are not restricted to pain, leading to the use of the alternative term fibromyalgia syndrome for the condition. Other symptoms include debilitating fatigue, sleep disturbance, and joint stiffness
Joint stiffness
Joint stiffness may be either the symptom of pain on moving a joint, the symptom of loss of range of motion or the physical sign of reduced range of motion. Doctors prefer the latter two uses but patients often use the first meaning....
. Some patients may also report difficulty with swallowing
Dysphagia
Dysphagia is the medical term for the symptom of difficulty in swallowing. Although classified under "symptoms and signs" in ICD-10, the term is sometimes used as a condition in its own right. Sufferers are sometimes unaware of their dysphagia....
, bowel and bladder
Cystitis
Cystitis is a term that refers to urinary bladder inflammation that results from any one of a number of distinct syndromes. It is most commonly caused by a bacterial infection in which case it is referred to as a urinary tract infection.-Signs and symptoms:...
abnormalities, numbness and tingling
Paresthesia
Paresthesia , spelled "paraesthesia" in British English, is a sensation of tingling, burning, pricking, or numbness of a person's skin with no apparent long-term physical effect. It is more generally known as the feeling of "pins and needles" or of a limb "falling asleep"...
, and cognitive dysfunction
Cognitive dysfunction
Cognitive dysfunction is defined as unusually poor mental function, associated with confusion, forgetfulness and difficulty concentrating...
. Fibromyalgia is frequently comorbid
Comorbidity
In medicine, comorbidity is either the presence of one or more disorders in addition to a primary disease or disorder, or the effect of such additional disorders or diseases.- In medicine :...
with psychiatric conditions such as depression
Depression (mood)
Depression is a state of low mood and aversion to activity that can affect a person's thoughts, behaviour, feelings and physical well-being. Depressed people may feel sad, anxious, empty, hopeless, helpless, worthless, guilty, irritable, or restless...
and anxiety
Anxiety
Anxiety is a psychological and physiological state characterized by somatic, emotional, cognitive, and behavioral components. The root meaning of the word anxiety is 'to vex or trouble'; in either presence or absence of psychological stress, anxiety can create feelings of fear, worry, uneasiness,...
and stress-related disorders such as posttraumatic stress disorder. Not all people with fibromyalgia experience all associated symptoms. Fibromyalgia is estimated to affect 2–4% of the population, with a female to male incidence ratio of approximately 9:1.
The brains of fibromyalgia patients show structural and behavioral differences from those of healthy individuals, but it is unclear whether the brain anomalies cause fibromyalgia symptoms or are the product of an unknown underlying common cause. Some research suggests that these brain anomalies may be the result of childhood stress, or prolonged or severe stress.
Historically, fibromyalgia has been considered either a musculoskeletal disease or neuropsychiatric
Neuropsychiatry
Neuropsychiatry is the branch of medicine dealing with mental disorders attributable to diseases of the nervous system. It preceded the current disciplines of psychiatry and neurology, in as much as psychiatrists and neurologists had a common training....
condition. Although there is as yet no cure for fibromyalgia, some treatments have been demonstrated by controlled clinical trial
Clinical trial
Clinical trials are a set of procedures in medical research and drug development that are conducted to allow safety and efficacy data to be collected for health interventions...
s to be effective in reducing symptoms, including medications, behavioral interventions, patient education, and exercise. The most recent approach of a diagnosis of fibromyalgia involves pain index and a measure of key symptoms and severity.
Fibromyalgia has been recognized as a diagnosable disorder by the National Institutes of Health and the American College of Rheumatology. Fibromyalgia, a central nervous system disorder, is described as a 'central sensitisation syndrome' caused by neurobiological abnormalities which act to produce physiological pain and cognitive impairments as well as psychological symptomatology. Despite this there are some members of the medical community who do not consider fibromyalgia a disease because of a lack of abnormalities on physical examination and the absence of objective diagnostic tests.
Signs and symptoms
The defining symptoms of fibromyalgia are chronic, widespread pain, fatigue, and heightened pain in response to tactile pressure (allodyniaAllodynia
Allodynia is a pain due to a stimulus which does not normally provoke pain. Temperature or physical stimuli can provoke allodynia, and it often occurs after injury to a site...
). Other symptoms may include tingling of the skin, prolonged muscle spasms
Spasm
In medicine a spasm is a sudden, involuntary contraction of a muscle, a group of muscles, or a hollow organ, or a similarly sudden contraction of an orifice. It is sometimes accompanied by a sudden burst of pain, but is usually harmless and ceases after a few minutes...
, weakness
Muscle weakness
Muscle weakness or myasthenia is a lack of muscle strength. The causes are many and can be divided into conditions that have true or perceived muscle weakness...
in the limbs, nerve pain, muscle twitching, palpitations, functional bowel disturbances, and chronic sleep disturbances
Sleep disorder
A sleep disorder, or somnipathy, is a medical disorder of the sleep patterns of a person or animal. Some sleep disorders are serious enough to interfere with normal physical, mental and emotional functioning...
.
Many patients experience cognitive dysfunction (known as "brain fog" or "fibrofog"), which may be characterized by impaired concentration, problems with short
Short-term memory
Short-term memory is the capacity for holding a small amount of information in mind in an active, readily available state for a short period of time. The duration of short-term memory is believed to be in the order of seconds. A commonly cited capacity is 7 ± 2 elements...
and long-term memory
Long-term memory
Long-term memory is memory in which associations among items are stored, as part of the theory of a dual-store memory model. According to the theory, long term memory differs structurally and functionally from working memory or short-term memory, which ostensibly stores items for only around 20–30...
, short-term memory consolidation, impaired speed of performance, inability to multi-task, cognitive overload, and diminished attention span
Attention span
Attention span is the amount of time that a person can concentrate on a task without becoming distracted. Most educators and psychologists agree that the ability to focus one's attention on a task is crucial for the achievement of one's goals....
. Fibromyalgia is often associated with anxiety
Anxiety
Anxiety is a psychological and physiological state characterized by somatic, emotional, cognitive, and behavioral components. The root meaning of the word anxiety is 'to vex or trouble'; in either presence or absence of psychological stress, anxiety can create feelings of fear, worry, uneasiness,...
, and depressive
Clinical depression
Major depressive disorder is a mental disorder characterized by an all-encompassing low mood accompanied by low self-esteem, and by loss of interest or pleasure in normally enjoyable activities...
symptoms.
Other symptoms often attributed to fibromyalgia that may possibly be due to a comorbid
Comorbidity
In medicine, comorbidity is either the presence of one or more disorders in addition to a primary disease or disorder, or the effect of such additional disorders or diseases.- In medicine :...
disorder include myofascial pain syndrome
Myofascial pain syndrome
Myofascial pain syndrome , also known as chronic myofascial pain , is a syndrome characterized by chronic pain caused by multiple trigger points and fascial constrictions...
, also referred to as chronic myofascial pain, diffuse non-dermatomal paresthesia
Paresthesia
Paresthesia , spelled "paraesthesia" in British English, is a sensation of tingling, burning, pricking, or numbness of a person's skin with no apparent long-term physical effect. It is more generally known as the feeling of "pins and needles" or of a limb "falling asleep"...
s, functional bowel disturbances and irritable bowel syndrome
Irritable bowel syndrome
Irritable bowel syndrome is a diagnosis of exclusion. It is a functional bowel disorder characterized by chronic abdominal pain, discomfort, bloating, and alteration of bowel habits in the absence of any detectable organic cause. In some cases, the symptoms are relieved by bowel movements...
, genitourinary
Urinary system
The urinary system is the organ system that produces, stores, and eliminates urine. In humans it includes two kidneys, two ureters, the bladder and the urethra.-Kidney:...
symptoms and interstitial cystitis
Interstitial cystitis
Interstitial cystitis or bladder pain syndrome is a chronic, oftentimes severely debilitating disease of the urinary bladder...
, dermatological
Dermatology
Dermatology is the branch of medicine dealing with the skin and its diseases, a unique specialty with both medical and surgical aspects. A dermatologist takes care of diseases, in the widest sense, and some cosmetic problems of the skin, scalp, hair, and nails....
disorders, headache
Headache
A headache or cephalalgia is pain anywhere in the region of the head or neck. It can be a symptom of a number of different conditions of the head and neck. The brain tissue itself is not sensitive to pain because it lacks pain receptors. Rather, the pain is caused by disturbance of the...
s, myoclonic twitches
Myoclonus
Myoclonus is brief, involuntary twitching of a muscle or a group of muscles. It describes a medical sign and, generally, is not a diagnosis of a disease. Brief twitches are perfectly normal. The myoclonic twitches are usually caused by sudden muscle contractions; they also can result from brief...
, and symptomatic hypoglycemia
Hypoglycemia
Hypoglycemia or hypoglycæmia is the medical term for a state produced by a lower than normal level of blood glucose. The term literally means "under-sweet blood"...
. Although fibromyalgia is classified based on the presence of chronic widespread pain, pain may also be localized in areas such as the shoulder
Shoulder
The human shoulder is made up of three bones: the clavicle , the scapula , and the humerus as well as associated muscles, ligaments and tendons. The articulations between the bones of the shoulder make up the shoulder joints. The major joint of the shoulder is the glenohumeral joint, which...
s, neck
Neck
The neck is the part of the body, on many terrestrial or secondarily aquatic vertebrates, that distinguishes the head from the torso or trunk. The adjective signifying "of the neck" is cervical .-Boner anatomy: The cervical spine:The cervical portion of the human spine comprises seven boney...
, low back
Back
- People :* Adam Back, British cryptographer* Charles Back, South African winemaker* Chris Back , Australian politician* Ernst Emil Alexander Back , German physicist* Frédéric Back , Canadian animator...
, hips, or other areas. Many sufferers also experience varying degrees of myofascial pain and have high rates of comorbid temporomandibular joint disorder
Temporomandibular joint disorder
Temporomandibular joint disorder , or TMJ syndrome, is an umbrella term covering acute or chronic inflammation of the temporomandibular joint, which connects the mandible to the skull. The disorder and resultant dysfunction can result in significant pain and impairment...
. 20–30% of patients with rheumatoid arthritis
Rheumatoid arthritis
Rheumatoid arthritis is a chronic, systemic inflammatory disorder that may affect many tissues and organs, but principally attacks synovial joints. The process produces an inflammatory response of the synovium secondary to hyperplasia of synovial cells, excess synovial fluid, and the development...
and systemic lupus erythematosus
Systemic lupus erythematosus
Systemic lupus erythematosus , often abbreviated to SLE or lupus, is a systemic autoimmune disease that can affect any part of the body. As occurs in other autoimmune diseases, the immune system attacks the body's cells and tissue, resulting in inflammation and tissue damage...
may also have fibromyalgia.
Causation hypotheses
The cause of fibromyalgia is currently unknown. However, several hypotheses have been developed including "central sensitization". This theory proposes that fibromyalgia patients have a lower threshold for pain because of increased sensitivity in the brain to pain signals.Genetic predisposition
There is evidence that genetic factors may play a role in the development of fibromyalgia. For example, there is a high aggregation of fibromyalgia in families. Using self-report of chronic widespread pain (CWP) as a surrogate marker for fibromyalgia, the Swedish Twin Registry reports:- Monozygotic twins with CWP have a 15% chance that their twin has CWP
- Dizygotic twins with CWP have a 7% chance that their twin has CWP
The mode of inheritance is currently unknown, but it is most probably polygenic. Research has also demonstrated that fibromyalgia is potentially associated with polymorphisms of genes in the serotoninergic, dopaminergic and catecholaminergic systems. However, these polymorphisms are not specific for fibromyalgia and are associated with a variety of allied disorders (e.g. chronic fatigue syndrome
Chronic fatigue syndrome
Chronic fatigue syndrome is the most common name used to designate a significantly debilitating medical disorder or group of disorders generally defined by persistent fatigue accompanied by other specific symptoms for a minimum of six months, not due to ongoing exertion, not substantially...
, irritable bowel syndrome
Irritable bowel syndrome
Irritable bowel syndrome is a diagnosis of exclusion. It is a functional bowel disorder characterized by chronic abdominal pain, discomfort, bloating, and alteration of bowel habits in the absence of any detectable organic cause. In some cases, the symptoms are relieved by bowel movements...
) and with depression.
Stress
StressStress (medicine)
Stress is a term in psychology and biology, borrowed from physics and engineering and first used in the biological context in the 1930s, which has in more recent decades become commonly used in popular parlance...
may be an important precipitating factor in the development of fibromyalgia. Fibromyalgia is frequently comorbid with stress-related disorders such as chronic fatigue syndrome
Chronic fatigue syndrome
Chronic fatigue syndrome is the most common name used to designate a significantly debilitating medical disorder or group of disorders generally defined by persistent fatigue accompanied by other specific symptoms for a minimum of six months, not due to ongoing exertion, not substantially...
, posttraumatic stress disorder, irritable bowel syndrome
Irritable bowel syndrome
Irritable bowel syndrome is a diagnosis of exclusion. It is a functional bowel disorder characterized by chronic abdominal pain, discomfort, bloating, and alteration of bowel habits in the absence of any detectable organic cause. In some cases, the symptoms are relieved by bowel movements...
and depression. A systematic review found significant association between fibromyalgia and physical and sexual abuse in both childhood and adulthood, although the quality of studies was poor.
Two studies that employed single-voxel magnetic resonance spectroscopy (1H-MRS) reported metabolic abnormalities within the hippocampal complex in patients with fibromyalgia. As the hippocampus
Hippocampus
The hippocampus is a major component of the brains of humans and other vertebrates. It belongs to the limbic system and plays important roles in the consolidation of information from short-term memory to long-term memory and spatial navigation. Humans and other mammals have two hippocampi, one in...
plays crucial roles in maintenance of cognitive functions, sleep regulation, and pain perception, it was suggested that metabolic dysfunction of the hippocampus may be implicated in the appearance of these symptoms.
Other authors have proposed that, because exposure to stressful conditions can alter the function of the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal (HPA) axis
Hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis
The hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis , also known as thelimbic-hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis and, occasionally, as the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal-gonadotropic axis, is a complex set of direct influences and feedback interactions among the hypothalamus, the pituitary gland ,...
, the development of fibromyalgia may stem from stress-induced disruption of the HPA axis.
Dopamine dysfunction (hypodopaminergia)
The "dopamineDopamine
Dopamine is a catecholamine neurotransmitter present in a wide variety of animals, including both vertebrates and invertebrates. In the brain, this substituted phenethylamine functions as a neurotransmitter, activating the five known types of dopamine receptors—D1, D2, D3, D4, and D5—and their...
hypothesis of fibromyalgia" proposes that the central abnormality responsible for symptoms associated with fibromyalgia is a disruption of normal dopamine-related neurotransmission. Insufficient dopamine in a part of the body is termed hypodopaminergia. Dopamine is a catecholamine
Catecholamine
Catecholamines are molecules that have a catechol nucleus consisting of benzene with two hydroxyl side groups and a side-chain amine. They include dopamine, as well as the "fight-or-flight" hormones adrenaline and noradrenaline released by the adrenal medulla of the adrenal glands in response to...
neurotransmitter
Neurotransmitter
Neurotransmitters are endogenous chemicals that transmit signals from a neuron to a target cell across a synapse. Neurotransmitters are packaged into synaptic vesicles clustered beneath the membrane on the presynaptic side of a synapse, and are released into the synaptic cleft, where they bind to...
with roles in pain perception and natural analgesia. There is also strong evidence for a role of dopamine in restless leg syndrome, which is a condition found frequently in patients with fibromyalgia. Some fibromyalgia patients responded in controlled trials to pramipexole
Pramipexole
Pramipexole is a non-ergoline dopamine agonist indicated for treating early-stage Parkinson's disease and restless legs syndrome...
, a dopamine agonist
Dopamine agonist
A dopamine agonist is a compound that activates dopamine receptors in the absence of dopamine. Dopamine agonists activate signaling pathways through the dopamine receptor and trimeric G-proteins, ultimately leading to changes in gene transcription.-Uses:...
that selectively stimulates dopamine D2/D3 receptors and is used to treat both Parkinson's disease
Parkinson's disease
Parkinson's disease is a degenerative disorder of the central nervous system...
and restless leg syndrome.
Abnormal serotonin metabolism
In 1975, researchers hypothesized that serotoninSerotonin
Serotonin or 5-hydroxytryptamine is a monoamine neurotransmitter. Biochemically derived from tryptophan, serotonin is primarily found in the gastrointestinal tract, platelets, and in the central nervous system of animals including humans...
, a neurotransmitter
Neurotransmitter
Neurotransmitters are endogenous chemicals that transmit signals from a neuron to a target cell across a synapse. Neurotransmitters are packaged into synaptic vesicles clustered beneath the membrane on the presynaptic side of a synapse, and are released into the synaptic cleft, where they bind to...
that regulates sleep patterns, mood, concentration and pain, could be involved in the pathophysiology
Pathophysiology
Pathophysiology is the study of the changes of normal mechanical, physical, and biochemical functions, either caused by a disease, or resulting from an abnormal syndrome...
of fibromyalgia-associated symptoms. In 1992, decreased serotonin metabolites in patient blood samples
Blood plasma
Blood plasma is the straw-colored liquid component of blood in which the blood cells in whole blood are normally suspended. It makes up about 55% of the total blood volume. It is the intravascular fluid part of extracellular fluid...
and cerebrospinal fluid
Cerebrospinal fluid
Cerebrospinal fluid , Liquor cerebrospinalis, is a clear, colorless, bodily fluid, that occupies the subarachnoid space and the ventricular system around and inside the brain and spinal cord...
were reported. However, selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs) have met with limited success in alleviating the symptoms of the disorder, while drugs with activity as mixed serotonin-norepinephrine reuptake inhibitor
Serotonin-norepinephrine reuptake inhibitor
Serotonin–norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors are a class of antidepressant drugs used in the treatment of major depression and other mood disorders...
s (SNRIs) have been more successful. In controlled trials funded by Eli Lily, Duloxetine
Duloxetine
Duloxetine is a serotonin-norepinephrine reuptake inhibitor manufactured and marketed by Eli Lilly. It is effective for major depressive disorder and has been shown to be as effective as venlafaxine for generalized anxiety disorder...
(Cymbalta), an SNRI originally used to treat depression and painful diabetic neuropathy
Diabetic neuropathy
Diabetic neuropathies are neuropathic disorders that are associated with diabetes mellitus. These conditions are thought to result from diabetic microvascular injury involving small blood vessels that supply nerves in addition to macrovascular conditions that can culminate in diabetic neuropathy...
, was demonstrated to relieve fibromyalgia symptoms in some women, however male subjects failed to improve significantly. The Food and Drug Administration regulators approved the drug for the treatment of fibromyalgia in June 2008. However, the relevance of dysregulated serotonin metabolism to pathophysiology is a matter of debate. Complicating the analysis, one of the more effective types of medication for the treatment of the disorder (i.e. serotonin 5-HT3 antagonist
5-HT3 antagonist
The 5-HT3 antagonists are a class of medications that act as receptor antagonists at the 5-HT3 receptor, a subtype of serotonin receptor found in terminals of the vagus nerve and in certain areas of the brain....
s) actually blocks some of the effects of serotonin.
Deficient growth hormone (GH) secretion
Levels of hormones under the direct or indirect control of growth hormone (GH), including IGF-1, cortisolCortisol
Cortisol is a steroid hormone, more specifically a glucocorticoid, produced by the adrenal gland. It is released in response to stress and a low level of blood glucocorticoids. Its primary functions are to increase blood sugar through gluconeogenesis; suppress the immune system; and aid in fat,...
, leptin
Leptin
Leptin is a 16 kDa protein hormone that plays a key role in regulating energy intake and energy expenditure, including appetite and metabolism. It is one of the most important adipose derived hormones...
and neuropeptide Y
Neuropeptide Y
Neuropeptide Y is a 36-amino acid peptide neurotransmitter found in the brain and autonomic nervous system."NPY has been associated with a number of physiologic processes in the brain, including the regulation of energy balance, memory and learning, and epilepsy." The main effect is increased food...
may be abnormal in people with fibromyalgia, but supplementing growth hormone in patients does not have large effects, and a 2007 literature review reported a need for "further study before any solid recommendations can be made". There is disagreement about the role of HGH in fibromyalgia.
Psychological factors
There is strong evidence that major depression is associated with fibromyalgia, although the nature of the association is debated. A comprehensive review into the relationship between fibromyalgia and major depressive disorder (MDD) found substantial similarities in neuroendocrine abnormalities, psychological characteristics, physical symptoms and treatments between fibromyalgia and MDD, but currently available findings do not support the assumption that MDD and fibromyalgia refer to the same underlying construct or can be seen as subsidiaries of one disease concept. Indeed, the sensation of pain has at least two dimensions: a sensory dimension which processes the magnitude and location of the pain, and an affective-motivational dimension which processes the unpleasantness. Accordingly, a study that employed functional magnetic resonance imagingFunctional magnetic resonance imaging
Functional magnetic resonance imaging or functional MRI is a type of specialized MRI scan used to measure the hemodynamic response related to neural activity in the brain or spinal cord of humans or other animals. It is one of the most recently developed forms of neuroimaging...
to evaluate brain responses to experimental pain among fibromyalgia patients found that depressive symptoms were associated with the magnitude of clinically-induced pain response specifically in areas of the brain that participate in affective pain processing, but not in areas involved in sensory processing which indicates that the amplification of the sensory dimension of pain in fibromyalgia occurs independently of mood or emotional processes.
Poor sleep
Drs Paul Mork and Tom Nilsen from the Norwegian University of Science and TechnologyNorwegian University of Science and Technology
The Norwegian University of Science and Technology , commonly known as NTNU, is located in Trondheim. NTNU is the second largest of the eight universities in Norway, and, as its name suggests, has the main national responsibility for higher education in engineering and technology...
(NTNU) have uncovered an association between sleep problems and increased risk of fibromyalgia in 2011.
Adenosine monophosphate deaminase deficiency type 1
Adenosine Monophosphate Deaminase Deficiency type 1Myoadenylate deaminase deficiency
Adenosine monophosphate deaminase deficiency type 1 is also called myoadenylate deaminase deficiency. It a recessive genetic metabolic disorder that affects approximately 1–2% of populations of European descent. It appears to be considerably rarer in Asian populations...
, also called Myoadenylate Deaminase Deficiency
Myoadenylate deaminase deficiency
Adenosine monophosphate deaminase deficiency type 1 is also called myoadenylate deaminase deficiency. It a recessive genetic metabolic disorder that affects approximately 1–2% of populations of European descent. It appears to be considerably rarer in Asian populations...
, sometimes abbrevisted MADD
Myoadenylate deaminase deficiency
Adenosine monophosphate deaminase deficiency type 1 is also called myoadenylate deaminase deficiency. It a recessive genetic metabolic disorder that affects approximately 1–2% of populations of European descent. It appears to be considerably rarer in Asian populations...
, is a quite common recessive genetic metabolic disorder that shares many of the same symptoms as Fibromyalgia. Especially fatigue, cognitive dysfunction, and enhanced sensitivity to pain. Perhaps most telling are the studies showing a positive response to Ribose
Ribose
Ribose is an organic compound with the formula C5H10O5; specifically, a monosaccharide with linear form H––4–H, which has all the hydroxyl groups on the same side in the Fischer projection....
by 66% of the test subjects diagnosed with Fibromyalgia. Ribose
Ribose
Ribose is an organic compound with the formula C5H10O5; specifically, a monosaccharide with linear form H––4–H, which has all the hydroxyl groups on the same side in the Fischer projection....
being a possible treatment for MADD
Myoadenylate deaminase deficiency
Adenosine monophosphate deaminase deficiency type 1 is also called myoadenylate deaminase deficiency. It a recessive genetic metabolic disorder that affects approximately 1–2% of populations of European descent. It appears to be considerably rarer in Asian populations...
.
Neuro-immunoendocrine disorder
Evidence exists that fibromyalgia is a neuro-immunoendocrine disorder. Elevations in substance PSubstance P
In the field of neuroscience, substance P is a neuropeptide: an undecapeptide that functions as a neurotransmitter and as a neuromodulator. It belongs to the tachykinin neuropeptide family. Substance P and its closely related neuropeptide neurokinin A are produced from a polyprotein precursor...
, IL-6 and IL-8
IL-8
IL-8 can refer to:* Interleukin 8, a chemokine of the immune system* Illinois' 8th congressional district* Illinois Route 8...
as well as corticotropin-releasing hormone
Corticotropin-releasing hormone
Corticotropin-releasing hormone , originally named corticotropin-releasing factor , and also called corticoliberin, is a polypeptide hormone and neurotransmitter involved in the stress response...
have been found in the cerebral spinal fluid of fibromyalgia suffering individuals. Increased numbers of mast cell
Mast cell
A mast cell is a resident cell of several types of tissues and contains many granules rich in histamine and heparin...
numbers have been found in skin biopsies of some fibromyalgia people. Quercetin
Quercetin
Quercetin , a flavonol, is a plant-derived flavonoid found in fruits, vegetables, leaves and grains. It also may be used as an ingredient in supplements, beverages or foods.-Occurrence:...
, a pharmacologically active natural product
Nutraceutical
Nutraceutical, a portmanteau of the words “nutrition” and “pharmaceutical”, is a food or food product that reportedly provides health and medical benefits, including the prevention and treatment of disease. Health Canada defines the term as "a product isolated or purified from foods that is...
which pocesses antiinflammatory in addition to mast cell inhibiting properties may be a useful treatment.
Other hypotheses
Other hypotheses have been proposed. One of these is an aberrant immune response to intestinal bacteria.Sleep disturbances
In 1975, Moldofsky and colleagues reported the presence of anomalous alpha wave activity (typically associated with arousal states) measured by electroencephalogram (EEG) during non-rapid eye movement sleep of "fibrositis syndrome" patients. By disrupting stage IV sleep consistently in young, healthy subjects, the researchers reproduced a significant increase in muscle tenderness similar to that experienced in "neurasthenic musculoskeletal pain syndrome" but which resolved when the subjects were able to resume their normal sleep patterns.Poly-modal sensitivity
Results from studies examining responses to experimental stimulation suggest that fibromyalgia patients may have heightened sensitivity of the nociceptive systemNociception
Nociception is defined as "the neural processes of encoding and processing noxious stimuli." It is the afferent activity produced in the peripheral and central nervous system by stimuli that have the potential to damage tissue...
, which senses pressure, heat, cold, electrical and chemical stimulation. Experiments examining pain regulatory systems have shown that fibromyalgia patients display an exaggerated wind-up in response to repetitive stimulation and an absence of exercise-induced analgesic response.
Neuroendocrine disruption
Patients with fibromyalgia may have alterations of normal neuroendocrine function, characterized by mild hypocortisolemia, hyperreactivity of pituitary adrenocorticotropin hormone release in response to challenge, and glucocorticoid feedback resistance. Low insulin-like growth factor 1Insulin-like growth factor 1
Insulin-like growth factor 1 also known as somatomedin C is a protein that in humans is encoded by the IGF1 gene. IGF-1 has also been referred to as a "sulfation factor" and its effects were termed "nonsuppressible insulin-like activity" in the 1970s.IGF-1 is a hormone similar in molecular...
(IGF-1) levels in some fibromyalgia patients have led to the theory that these patients may actually have a different, treatable syndrome, adult growth hormone deficiency
Growth hormone deficiency
Growth hormone deficiency is a medical condition in which the body does not produce enough growth hormone . Growth hormone, also called somatotropin, is a polypeptide hormone which stimulates growth and cell reproduction...
. Other abnormalities include reduced responsivity of thyrotropin and thyroid hormones to thyroid-releasing hormone, a mild elevation of prolactin levels with disinhibition of prolactin release in response to challenge and hyposecretion of adrenal androgens.
These changes might result from chronic stress, which, after being perceived and processed by the central nervous system, activates hypothalamic corticotrophin-releasing hormone neurons. Chronic overactivity of these neurons could disrupt normal function of the pituitary-adrenal axis and cause an increased stimulation of hypothalamic somatostatin secretion, which, in turn, could inhibit the secretion of other hormones.
Sympathetic hyperactivity
Functional analysis of the autonomic system in patients with fibromyalgia has demonstrated disturbed activity characterized by hyperactivity of the sympathetic nervous system at baseline with reduced sympathoadrenal reactivity in response to a variety of stressors including physical exertion and mental stress. Fibromyalgia patients demonstrate lower heart rate variability, an index of sympathetic/parasympathetic balance, indicating sustained sympathetic hyperactivity, especially at night. In addition, plasma levels of neuropeptide Y, which is co-localized with norepinephrine in the sympathetic nervous system, have been reported as low in patients with fibromyalgia, while circulating levels of epinephrine and norepinephrine have been variously reported as low, normal and high. Administration of interleukin-6, a cytokine capable of stimulating the release of hypothalamic corticotropin-releasing hormone which in turn stimulates activity within the sympathetic nervous system, results in a dramatic increase in circulating norepinephrine levels and a significantly greater increase in heart rate over baseline in fibromyalgia patients as compared to healthy controls.Cerebrospinal fluid abnormalities
One of the most reproduced laboratory finding in patients with fibromyalgia is an elevation in cerebrospinal fluid levels of substance P, a putative nociceptive neurotransmitter. Metabolites for the monoamine neurotransmitters serotonin, norepinephrine, and dopamine—all of which play a role in natural analgesia—have been shown to be lower, while concentrations of endogenous opioids (i.e., endorphins and enkephalins) appear to be higher. The mean concentration of nerve growth factor, a substance known to participate in structural and functional plasticity of nociceptive pathways within the dorsal root ganglia and spinal cord, is elevated. There is also evidence for increased excitatory amino acid release within cerebrospinal fluid, with a correlation demonstrated between levels for metabolites of glutamate and nitric oxide and clinical indices of pain.Brain imaging studies
Evidence of abnormal brain involvement in fibromyalgia has been provided via functional neuroimaging. The first findings reported were decreased blood flow within the thalamusThalamus
The thalamus is a midline paired symmetrical structure within the brains of vertebrates, including humans. It is situated between the cerebral cortex and midbrain, both in terms of location and neurological connections...
and elements of the basal ganglia
Basal ganglia
The basal ganglia are a group of nuclei of varied origin in the brains of vertebrates that act as a cohesive functional unit. They are situated at the base of the forebrain and are strongly connected with the cerebral cortex, thalamus and other brain areas...
and mid-brain (i.e., pontine nucleus). Differential activation in response to painful stimulation has also been demonstrated. Brain centers showing hyperactivation in response to noxious stimulation include such pain-related brain centers as the primary and secondary
Secondary somatosensory cortex
The human secondary somatosensory cortex is a region of cerebral cortex lying mostly on the parietal operculum.Region S2 was first described by Adrian in 1940, who found that feeling in cats' feet was not only represented in the previously described primary somatosensory cortex but also in a...
somatosensory cortices, anterior cingulate cortex
Anterior cingulate cortex
The anterior cingulate cortex is the frontal part of the cingulate cortex, that resembles a "collar" form around the corpus callosum, the fibrous bundle that relays neural signals between the right and left cerebral hemispheres of the brain...
, and insular cortex
Insular cortex
In each hemisphere of the mammalian brain the insular cortex is a portion of the cerebral cortex folded deep within the lateral sulcus between the temporal lobe and the frontal lobe. The cortical area overlying it towards the lateral surface of the brain is the operculum...
. Patients also exhibit neural activation in brain regions associated with pain perception in response to nonpainful stimuli in such areas as the prefrontal, supplemental motor, insular, and cingulate cortices. Evidence of hippocampal disruption indicated by reduced brain metabolite ratios has been demonstrated by studies using single-voxel magnetic resonance spectroscopy (1H-MRS). A significant negative correlation was demonstrated between abnormal metabolite ratios and a validated index of the clinical severity (i.e. the Fibromyalgia Impact Questionnaire). Correlations between clinical pain severity and concentrations of the excitatory amino acid neurotransmitter glutamate within the insular cortex have also been demonstrated using 1H-MRS. An acceleration of normal age-related brain atrophy has been demonstrated using voxel-based morphometry (VBM) with areas of reduced gray matter located in the cingulate cortex, insula and parahippocampal gyrus. Grey matter loss appears to increase 9.5 times the normal rate with each year. Studies utilizing positron emission tomography
Positron emission tomography
Positron emission tomography is nuclear medicine imaging technique that produces a three-dimensional image or picture of functional processes in the body. The system detects pairs of gamma rays emitted indirectly by a positron-emitting radionuclide , which is introduced into the body on a...
have demonstrated reduced dopamine synthesis in the brainstem and elements of the limbic cortex. A significant negative correlation between pain severity and dopamine synthesis was demonstrated within the insular cortex. A subsequent study demonstrated gross disruption of dopaminergic reactivity in response to a tonic pain stimulus within the basal ganglia
Basal ganglia
The basal ganglia are a group of nuclei of varied origin in the brains of vertebrates that act as a cohesive functional unit. They are situated at the base of the forebrain and are strongly connected with the cerebral cortex, thalamus and other brain areas...
with a significant positive correlation between the defining feature of the disorder (i.e. tender point index) and dopamine D2 receptor binding potential specifically in the right putamen
Putamen
The putamen is a round structure located at the base of the forebrain . The putamen and caudate nucleus together form the dorsal striatum. It is also one of the structures that comprises the basal ganglia. Through various pathways, the putamen is connected to the substantia nigra and globus pallidus...
. Finally, reduced availability of mu-opioid receptors in the ventral striatum
Ventral striatum
The ventral striatum is generally considered that part of the striatum that is connectionally associated with limbic structures, such as the amygdala, hippocampus, midline thalamus, and certain regions of the prefrontal cortex...
/nucleus accumbens
Nucleus accumbens
The nucleus accumbens , also known as the accumbens nucleus or as the nucleus accumbens septi , is a collection of neurons and forms the main part of the ventral striatum...
and cingulate cortex has been demonstrated, with a significant negative correlation between affective pain levels and receptor availability in the nucleus accumbens.
Diagnosis
There is no single test that can fully diagnose fibromyalgia and there is debate over what should be considered essential diagnostic criteria and whether an objective diagnosis is possible. In most cases, patients with fibromyalgia symptoms may also have laboratory test results that appear normal and many of their symptoms may mimic those of other rheumatic conditions such as arthritis or osteoporosis. In general, most doctors diagnose patients with a process called differential diagnosis, which means that doctors consider all of the possible things that might be wrong with the patient based on the patient's symptoms, gender, age, geographic location, medical history and other factors. They then narrow down the diagnosis to the most likely one. The most widely accepted set of classification criteria for research purposes was elaborated in 1990 by the Multicenter Criteria Committee of the American College of RheumatologyAmerican College of Rheumatology
The American College of Rheumatology is an organization of and for physicians, health professionals, and scientists that advances rheumatology through programs of education, research, advocacy and practice support that foster excellence in the care of people with arthritis and rheumatic and...
. These criteria, which are known informally as "the ACR 1990", define fibromyalgia according to the presence of the following criteria:
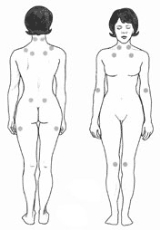
- A history of widespread pain lasting more than three months—affecting all four quadrants of the body, i.e., both sides, and above and below the waist.
- Tender points—there are 18 designated possible tender points (although a person with the disorder may feel pain in other areas as well). The patient must feel pain at 11 or more of these points for fibromyalgia to be considered.
The ACR criteria for classification of patients were originally established as inclusion criteria for research purposes and were not intended for clinical diagnosis but have now become the de facto diagnostic criteria in the clinical setting. It should be noted that the number of tender points that may be active at any one time may vary with time and circumstance. A controversial study done by a legal team looking to prove their client's disability based primarily on tender points and their widespread presence in non-litigious communities prompted the lead author of the ACR criteria to now question the useful validity of tender points in diagnosis. Since the ACR criteria were originally published, research with mechanical devices that exert defined pressure
Dolorimeter
A dolorimeter is an instrument used to measure pain threshold and pain tolerance. Dolorimetry has been defined as "the measurement of pain sensitivity or pain intensity." There are several kinds of dolorimeter that have been developed...
indicate that diagnosis of fibromyalgia cannot be done objectively by machine and require a physician's subjective estimate of how much pressure should be exerted.
Treatment
As with many other medically unexplained syndromesMedically unexplained physical symptoms
Medically unexplained physical symptoms or medically unexplained symptoms are patient symptoms for which the treating physician, other healthcare providers, and research scientists have found no medical cause...
, there is no universally accepted treatment or cure for fibromyalgia, and treatment typically consists of symptom management. Developments in the understanding of the pathophysiology of the disorder have led to improvements in treatment, which include prescription medication, behavioral intervention, exercise, and alternative
Alternative medicine
Alternative medicine is any healing practice, "that does not fall within the realm of conventional medicine." It is based on historical or cultural traditions, rather than on scientific evidence....
and complementary medicine. Indeed, integrated treatment plans that incorporate medication, patient education, aerobic exercise and cognitive-behavioral therapy have been shown to be effective in alleviating pain and other fibromyalgia-related symptoms. In 2005, the American Pain Society produced comprehensive guidelines for patient evaluation and management.
More recently, the European League Against Rheumatism
European League Against Rheumatism
The is an international organisation in the field of rheumatology. The society publishes a medical journal, the Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases, and organises an annual scientific meeting, the Annual European Congress of Rheumatology....
(EULAR) issued updated treatment guidelines.
Psychological/behavioural therapies
Cognitive behavioural therapy (CBT) and related psychological/behavioral therapies are evidence-based treatments which have shown to be moderately effective in randomized controlled trials. The greatest benefit occurs when CBT is used along with exercise.Pharmaceutical
There are three medications that have been approved by the FDA for treatment of Fibromyalgia. PregabalinPregabalin
Pregabalin is an anticonvulsant drug used for neuropathic pain and as an adjunct therapy for partial seizures with or without secondary generalization in adults. It has also been found effective for generalized anxiety disorder and is approved for this use in the European Union. It was designed...
was approved in June, 2007, duloxetine
Duloxetine
Duloxetine is a serotonin-norepinephrine reuptake inhibitor manufactured and marketed by Eli Lilly. It is effective for major depressive disorder and has been shown to be as effective as venlafaxine for generalized anxiety disorder...
was approved in June, 2008, and milnacipran
Milnacipran
Milnacipran is a serotonin–norepinephrine reuptake inhibitor used in the clinical treatment of fibromyalgia...
was approved in January, 2009. Pregabalin and duloxetine have been shown to reduce pain in a substantial number of patients with fibromyalgia, but there were others who didn't benefit. Placebo-controlled trials involving a total of over 2000 patients have shown milnacipran to be significantly more effective than placebo in treating both pain and the broader syndrome of fibromyalgia.
Antidepressants
A 2009 meta-analysis in the Journal of the American Medical AssociationJournal of the American Medical Association
The Journal of the American Medical Association is a weekly, peer-reviewed, medical journal, published by the American Medical Association. Beginning in July 2011, the editor in chief will be Howard C. Bauchner, vice chairman of pediatrics at Boston University’s School of Medicine, replacing ...
concluded that antidepressants were "associated with improvements in pain, depression, fatigue, sleep disturbances, and health-related quality of life in patients with FMS." The authors also stated that the goal of antidepressants in fibromyalgia should be “possible symptom reduction”, and if used long term, their effects should be evaluated against side effects.
Tricyclic antidepressant
Tricyclic antidepressant
Tricyclic antidepressants are heterocyclic chemical compounds used primarily as antidepressants. The TCAs were first discovered in the early 1950s and were subsequently introduced later in the decade; they are named after their chemical structure, which contains three rings of atoms...
s were the most effective against pain, fatigue, and sleep problems, but have many side effects due to interaction with adrenergic, cholinergic or histaminergic receptors, and sodium channels. Selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor
Selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor
Selective serotonin re-uptake inhibitors or serotonin-specific reuptake inhibitor are a class of compounds typically used as antidepressants in the treatment of depression, anxiety disorders, and some personality disorders. The efficacy of SSRIs is disputed...
s (SSRIs) and Serotonin-norepinephrine reuptake inhibitor
Serotonin-norepinephrine reuptake inhibitor
Serotonin–norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors are a class of antidepressant drugs used in the treatment of major depression and other mood disorders...
s (SNRIs) had lower side effects.
Tramadol
TramadolTramadol
Tramadol hydrochloride is a centrally acting synthetic opioid analgesic used in treating moderate pain. The drug has a wide range of applications, including treatment for restless legs syndrome and fibromyalgia...
, a centrally acting analgesic with atypical opioid and antidepressant-like activity, is moderately effective in treating fibromyalgia pain. Long-term effectiveness and tolerability are unknown. Tramadol combined with paracetamol
Paracetamol
Paracetamol INN , or acetaminophen USAN , is a widely used over-the-counter analgesic and antipyretic . It is commonly used for the relief of headaches and other minor aches and pains and is a major ingredient in numerous cold and flu remedies...
provides fast, lasting relief that is more effective than either drug alone. This combination therapy has demonstrated efficacy, safety and tolerability for up to two years without the development of tolerance, in the treatment of chronic pain. It is as effective as codeine plus paracetamol but produces less sleepiness and constipation, and it is free of the toxic effects associated with non-steroidal anti-inflammatories
Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug
Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, usually abbreviated to NSAIDs or NAIDs, but also referred to as nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory agents/analgesics or nonsteroidal Anti-inflammatory medicines , are drugs with analgesic and antipyretic effects and which have, in higher doses, anti-inflammatory...
.
Anti-seizure medication
The anti-seizure drugs gabapentinGabapentin
Gabapentin is a pharmaceutical drug, specifically a GABA analogue. It was originally developed for the treatment of epilepsy, and currently is also used to relieve neuropathic pain...
(Neurontin) and pregabalin
Pregabalin
Pregabalin is an anticonvulsant drug used for neuropathic pain and as an adjunct therapy for partial seizures with or without secondary generalization in adults. It has also been found effective for generalized anxiety disorder and is approved for this use in the European Union. It was designed...
(Lyrica) have been tested. Gabapentin is approved for use in treatment of neuropathic pain but not fibromyalgia. Pregabalin, originally labeled for the treatment of nerve pain suffered by diabetics, has been cleared by the US Food and Drug Administration
Food and Drug Administration
The Food and Drug Administration is an agency of the United States Department of Health and Human Services, one of the United States federal executive departments...
for treatment of fibromyalgia. A randomized controlled trial
Randomized controlled trial
A randomized controlled trial is a type of scientific experiment - a form of clinical trial - most commonly used in testing the safety and efficacy or effectiveness of healthcare services or health technologies A randomized controlled trial (RCT) is a type of scientific experiment - a form of...
of pregabalin
Pregabalin
Pregabalin is an anticonvulsant drug used for neuropathic pain and as an adjunct therapy for partial seizures with or without secondary generalization in adults. It has also been found effective for generalized anxiety disorder and is approved for this use in the European Union. It was designed...
450 mg/day found that 6 patients is the number needed to treat
Number needed to treat
The number needed to treat is an epidemiological measure used in assessing the effectiveness of a health-care intervention, typically a treatment with medication. The NNT is the average number of patients who need to be treated to prevent one additional bad outcome...
for one patient to have a 50% reduction in pain. A Cochrane Database analysis of pregabalin use in chronic pain concluded that “A minority of patients will have substantial benefit with pregabalin, and more will have moderate benefit. Many will have no or trivial benefit, or will discontinue because of adverse events.” A meta-analysis of four trial of pregabalin in fibromyalgia found that for patients who did respond to pregabalin, there was a reduction in time off work >1 day per week.
Dopamine agonists
Dopamine agonists (e.g. pramipexolePramipexole
Pramipexole is a non-ergoline dopamine agonist indicated for treating early-stage Parkinson's disease and restless legs syndrome...
(Mirapex) and ropinirole
Ropinirole
Ropinirole is a non-ergoline dopamine agonist. It is manufactured by GlaxoSmithKline , Cipla and Sun Pharmaceutical. It is used in the treatment of Parkinson's disease...
(ReQuip)) resulted in some improvement in a minority of patients, but numerous side effects, including the onset of impulse control disorders like compulsive gambling and shopping, have led to concern about this approach. A trial of transdermal rotigotine
Rotigotine
Rotigotine is a non-ergoline dopamine agonist indicated for the treatment of Parkinson's disease and restless legs syndrome in Europe and the United States...
is currently ongoing.
Muscle relaxants
CyclobenzaprineCyclobenzaprine
Cyclobenzaprine is a muscle relaxant medication used to relieve skeletal muscle spasms and associated pain in acute musculoskeletal conditions. It is the most well-studied drug for this application, and it also has been used off-label for fibromyalgia treatment.- Mechanism of action :The mechanism...
is a muscle relaxant
Muscle relaxant
A muscle relaxant is a drug which affects skeletal muscle function and decreases the muscle tone. It may be used to alleviate symptoms such as muscle spasms, pain, and hyperreflexia. The term "muscle relaxant" is used to refer to two major therapeutic groups: neuromuscular blockers and spasmolytics...
medication used to relieve skeletal muscle
Skeletal muscle
Skeletal muscle is a form of striated muscle tissue existing under control of the somatic nervous system- i.e. it is voluntarily controlled. It is one of three major muscle types, the others being cardiac and smooth muscle...
spasm
Spasm
In medicine a spasm is a sudden, involuntary contraction of a muscle, a group of muscles, or a hollow organ, or a similarly sudden contraction of an orifice. It is sometimes accompanied by a sudden burst of pain, but is usually harmless and ceases after a few minutes...
s and associated pain in acute
Acute (medicine)
In medicine, an acute disease is a disease with either or both of:# a rapid onset, as in acute infection# a short course ....
musculoskeletal conditions. It is the most well-studied drug for this application, and it also has been used off-label
Off-label use
Off-label use is the practice of prescribing pharmaceuticals for an unapproved indication or in an unapproved age group, unapproved dose or unapproved form of administration...
for fibromyalgia treatment.
Tizanidine
Tizanidine
Tizanidine is a drug that is used as a muscle relaxant. It is a centrally acting α2 adrenergic agonist. It is used to treat the spasms, cramping, and tightness of muscles caused by medical problems such as multiple sclerosis, spastic diplegia, back pain, or certain other injuries to the spine or...
(brandnames Zanaflex, Sirdalud) is a muscle relaxant centrally acting α-2 adrenergic agonist. It is used to treat the spasms, cramping, and tightness of muscles caused by medical problems such as multiple sclerosis, spastic diplegia, back pain, or certain other injuries to the spine or central nervous system. It is also prescribed off-label for some symptoms of fibromyalgia.
Opioids
According to a 2004 review of fibromyalgia treatment studies, opioidOpioid
An opioid is a psychoactive chemical that works by binding to opioid receptors, which are found principally in the central and peripheral nervous system and the gastrointestinal tract...
s (other than tramadol
Tramadol
Tramadol hydrochloride is a centrally acting synthetic opioid analgesic used in treating moderate pain. The drug has a wide range of applications, including treatment for restless legs syndrome and fibromyalgia...
) have not had randomized controlled trial
Randomized controlled trial
A randomized controlled trial is a type of scientific experiment - a form of clinical trial - most commonly used in testing the safety and efficacy or effectiveness of healthcare services or health technologies A randomized controlled trial (RCT) is a type of scientific experiment - a form of...
s, and "should be considered only after all other medicinal and nonmedicinal therapies have been exhausted." Despite a lack of clinical trials and the potential for addiction
Substance dependence
The section about substance dependence in the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders does not use the word addiction at all. It explains:...
and abuse
Substance abuse
A substance-related disorder is an umbrella term used to describe several different conditions associated with several different substances .A substance related disorder is a condition in which an individual uses or abuses a...
, opioids are widely used by fibromyalgia patients. An analysis of insurance claims by 52,000 fibromyalgia patients showed that 40% had received opioids in any given year (predominantly short-acting agents).
Naltrexone
NaltrexoneNaltrexone
Naltrexone is an opioid receptor antagonist used primarily in the management of alcohol dependence and opioid dependence. It is marketed in generic form as its hydrochloride salt, naltrexone hydrochloride, and marketed under the trade names Revia and Depade...
at very low dosage has been found to be effective in reducing fibromyalgia symptoms by more than 30 percent in a small controlled trial. Naltrexone, an opioid antagonist also acts at very low dosage, to inhibit microglia
Microglia
Microglia are a type of glial cell that are the resident macrophages of the brain and spinal cord, and thus act as the first and main form of active immune defense in the central nervous system . Microglia constitute 20% of the total glial cell population within the brain...
cells thereby reducing proinflammatory cytokines and neurotoxic superoxides.
Quercetin
QuercetinQuercetin
Quercetin , a flavonol, is a plant-derived flavonoid found in fruits, vegetables, leaves and grains. It also may be used as an ingredient in supplements, beverages or foods.-Occurrence:...
, a flavanoid and pharmacologically active natural compound
Nutraceutical
Nutraceutical, a portmanteau of the words “nutrition” and “pharmaceutical”, is a food or food product that reportedly provides health and medical benefits, including the prevention and treatment of disease. Health Canada defines the term as "a product isolated or purified from foods that is...
, which acts as an anti-inflammatory and has mast cell
Mast cell
A mast cell is a resident cell of several types of tissues and contains many granules rich in histamine and heparin...
inhibitory properties may be effective in the treatment of fibromyalgia.
Investigational medications
Investigational medications include cannabinoidsCannabinoids
Cannabinoids are a class of chemical compounds that include the phytocannabinoids , and chemical compounds that mimic the actions of phytocannabinoids or have a similar structure...
and the 5-HT3 receptor antagonist tropisetron
Tropisetron
Tropisetron is a serotonin 5-HT3 receptor antagonist used mainly as an antiemetic to treat nausea and vomiting following chemotherapy, although it has been used experimentally as an analgesic in cases of fibromyalgia. The drug is available in a 5 mg oral preparation or in 2 mg...
. A controlled study of guaifenesin
Guaifenesin
Guaifenesin INN or guaiphenesin , also glyceryl guaiacolate, is an expectorant drug sold over the counter and usually taken by mouth to assist the bringing up of phlegm from the airways in acute respiratory tract infections.-History:Similar medicines derived from the guaiac tree were in use as a...
failed to demonstrate any benefits from this treatment
Guaifenesin protocol
Guaifenesin protocol is an experimental, alternative treatment for fibromyalgia proposed in the 1990s by R. Paul St. Amand. The proposed treatment involves three parts: titrating to the proper guaifenesin dosage, avoiding salicylates, and following a low-carbohydrate diet if the patient is...
.
Physical treatments
Exercise improves fitness and sleep and may reduce pain and fatigue in some people with fibromyalgia. In particular, there is strong evidence that cardiovascular exercise is effective for some patients. Long-term aquatic-based exercise has been proven beneficial as it combines cardiovascular exercise with resistance training. However, due to the cold sensitivities of people with fibromyalgia syndrome, aquatic therapyAquatic therapy
Definition of Aquatic Therapy: A therapeutic procedure which attempts to improve function through the application of aquatic therapeutic exercises. These procedures require constant attendance of a therapist educated in performing aquatic therapeutic exercises. [1, 2] Common synonyms: Aquatic...
must take place in a warm pool. Not only that, but the air temperature outside of the pool must also be heated to prevent fibromyalgia patients from getting chills and aches when out of the water. This involves a specialised pool facility, which makes this therapy more expensive and less accessible than regular swimming exercise.
Combination therapy
In the majority of the literature on therapy options for fibromyalgia, an overwhelming amount of studies echo the same sentiment: that the optimal intervention for fibromyalgia would include a treatment package, consisting of appropriate medications in combination with non-pharmacological treatments including physical exercise and cognitive behaviour therapy. Unfortunately, although the majority of fibromyalgia treatment reviews recommend this multi-treatment approach, very few actually study the interactive benefits of combining the therapy options, with many stating that ‘more research needs to be done.’ By adding parts of each of the three therapy options (drug therapy, exercise, and cognitive-behavioural therapy), fibromyalgia patients and clinicians have the ability to create individualised treatment packages that suit the patient’s particular needs. Because not everyone with fibromyalgia experiences the same co-morbidities and secondary symptoms, it’s important to have treatment options that are adaptive and personalized, not a ‘one size fits all’ treatment.Costs of fibromyalgia
Patients with fibromyalgia have higher health care costs and utilization. A study of almost 20,000 HumanaHumana
Humana Inc. , founded in 1961 in Louisville, Kentucky, is a Fortune 100 company that markets and administers health insurance. With a customer base of over 11.5 million in the United States, the company is the largest Fortune 100 company headquartered in the Commonwealth of Kentucky, and has a...
members enrolled in Medicare Advantage and commercial plans compared costs and medical utilizations and found that persons with fibromyalgia used twice as much pain-related medication as those without fibromyalgia. Furthermore, the use of medications and medical necessities increased markedly across many measures once diagnosis was made.
Prognosis
Although in itself neither degenerative nor fatal, the chronic pain of fibromyalgia is pervasive and persistent. Most fibromyalgia patients report that their symptoms do not improve over time. An evaluation of 332 consecutive new fibromyalgia patients found that disease-related factors such as pain and psychological factors such as work status, helplessness, education, and coping ability had an independent and significant relationship to FM symptom severity and function.Epidemiology
Fibromyalgia is seen in about 2% of the general population and affects more females than males, with a ratio of 9:1 by ACR criteria. It is most commonly diagnosed in individuals between the ages of 20 and 50, though onset can occur in childhood.History
Many names, including “muscular rheumatism”, “fibrositis”, “psychogenic rheumatism”, and “neurastheniaNeurasthenia
Neurasthenia is a psycho-pathological term first used by George Miller Beard in 1869 to denote a condition with symptoms of fatigue, anxiety, headache, neuralgia and depressed mood...
” were applied historically to symptoms resembling those of fibromyalgia. The term fibromyalgia was coined by researcher Mohammed Yunus as a synonym for fibrositis and was first used in a scientific publication in 1981. Fibromyalgia is from the Latin
Latin
Latin is an Italic language originally spoken in Latium and Ancient Rome. It, along with most European languages, is a descendant of the ancient Proto-Indo-European language. Although it is considered a dead language, a number of scholars and members of the Christian clergy speak it fluently, and...
fibra (fiber) and the Greek
Greek language
Greek is an independent branch of the Indo-European family of languages. Native to the southern Balkans, it has the longest documented history of any Indo-European language, spanning 34 centuries of written records. Its writing system has been the Greek alphabet for the majority of its history;...
words myo (muscle) and algos (pain).
Historical perspectives on the development of the fibromyalgia concept note the “central importance” of a 1977 paper by Smythe and Moldofsky on fibrositis. The first clinical
Clinical trial
Clinical trials are a set of procedures in medical research and drug development that are conducted to allow safety and efficacy data to be collected for health interventions...
, controlled study of the characteristics of fibromyalgia syndrome was published in 1981, providing support for symptom associations. In 1984, an interconnection between fibromyalgia syndrome and other similar conditions was proposed, and in 1986, trials of the first proposed medications for fibromyalgia were published.
A 1987 article in the Journal of the American Medical Association
Journal of the American Medical Association
The Journal of the American Medical Association is a weekly, peer-reviewed, medical journal, published by the American Medical Association. Beginning in July 2011, the editor in chief will be Howard C. Bauchner, vice chairman of pediatrics at Boston University’s School of Medicine, replacing ...
used the term "fibromyalgia syndrome" while saying it was a "controversial condition". The American College of Rheumatology
American College of Rheumatology
The American College of Rheumatology is an organization of and for physicians, health professionals, and scientists that advances rheumatology through programs of education, research, advocacy and practice support that foster excellence in the care of people with arthritis and rheumatic and...
(ACR) published its first classification criteria for fibromyalgia in 1990, although these are not strictly diagnostic criteria.
Controversies
Fibromyalgia continues to be a disputed diagnosis. Many members of the medical community do not consider fibromyalgia a disease because of a lack of abnormalities on physical examination, and the absence of objective diagnostic tests.Several theories propose that fibromyalgia is a psychosomatic illness
Psychosomatic illness
Psychosomatic medicine is an interdisciplinary medical field studying the relationships of social, psychological, and behavioral factors on bodily processes and well-being in humans and animals...
.
Several controversial issues exist with regard to fibromyalgia that range from questions regarding the validity of the disorder as a clinical entity, to issues regarding primary pathophysiology and the potential existence of fibromyalgia subtypes.
According to Frederick Wolfe, lead author of the 1990 paper that first defined the ACR fibromyalgia classification criteria,"the large majority of physicians, sociologists, and medical historians" are skeptical about the validity of fibromyalgia as a clinical entity. Some call fibromyalgia a “non-disease” and “an over-inclusive and ultimately meaningless label.” Wolfe now questions the validity of fibromyalgia as a disease. He considers fibromyalgia a physical response to stress, depression, and economic and social anxiety, and believes the associated symptoms are a normal part of everyday life. In 2009, he wrote, "the tendency to respond with distress to physical and mental stressors is part of the human condition." Wolfe notes that, "opponents of the fibromyalgia concept argue that, as it is a non-disease, we are legitimising patients' sickness behaviour by providing a disease label."
In a study of 100 individuals identified as having fibromyalgia, physical functioning decreased slightly over time, and individuals who had been diagnosed earlier had larger numbers of reported symptoms and greater severity. However, there was also a statistically significant improvement in satisfaction with health following classification. The authors of the study concluded that the ‘fibromyalgia label’ does not have a meaningful adverse effect on clinical outcome over the long term.
The validity of fibromyalgia as a unique clinical entity is also a matter of contention because "no discrete boundary separates syndromes such as FMS, chronic fatigue syndrome, irritable bowel syndrome, or chronic muscular headaches." Because of this considerable symptomatic overlap, some researchers have proposed that fibromyalgia and other syndromes with overlapping symptoms be classified as functional somatic syndromes for some purposes.
Some researchers believe that differences in psychological and autonomic nervous system profiles among affected individuals may indicate the existence of fibromyalgia subtypes. A 2007 review divides individuals with fibromyalgia into four groups as well as “mixed types”:
- "extreme sensitivity to pain but no associated psychiatric conditions" (may respond to medications that block the 5-HT3 receptor)
- "fibromyalgia and comorbid, pain-related depression" (may respond to antidepressants)
- "depression with concomitant fibromyalgia syndrome" (may respond to antidepressants)
- "fibromyalgia due to somatization" (may respond to psychotherapy).
Other researchers have suggested that depression may be a result of coping with the disabling impacts of a, thus far, incurable disease.
External links
- Fibromyalgia Topics A-Z from the National Fibromyalgia AssociationNational Fibromyalgia AssociationNational Fibromyalgia Association is a United States nonprofit organization founded to support persons with fibromyalgia and other chronic pain illnesses.-Mission:...
- Fibromyalgia Professional Resource Center from the National Fibromyalgia Association
- Fibromyalgia Continuing Medical Education Program FAME Project, Unihealth Foundation grant
- American College of Rheumatology Fibromyalgia factsheet
- Living with Fibromyalgia: Two Drugs Approved at US Food and Drug AdministrationFood and Drug AdministrationThe Food and Drug Administration is an agency of the United States Department of Health and Human Services, one of the United States federal executive departments...
- Questions and Answers About Fibromyalgia by the National Institute of Arthritis and Musculoskeletal and Skin DiseasesNational Institute of Arthritis and Musculoskeletal and Skin DiseasesThe National Institute of Arthritis and Musculoskeletal and Skin Diseases, or NIAMS, is an institute of the National Institutes of Health, an agency of the United States Department of Health and Human Services...
- Arthritis - Types - Fibromyalgia by the CDC
- Fibromyalgia Treatment Guidelines Published by US Department of Health & Human Resources

