
Fermi paradox
Encyclopedia

Probability
Probability is ordinarily used to describe an attitude of mind towards some proposition of whose truth we arenot certain. The proposition of interest is usually of the form "Will a specific event occur?" The attitude of mind is of the form "How certain are we that the event will occur?" The...
of the existence of extraterrestrial civilizations
Extraterrestrial life
Extraterrestrial life is defined as life that does not originate from Earth...
and the lack of evidence
Evidence
Evidence in its broadest sense includes everything that is used to determine or demonstrate the truth of an assertion. Giving or procuring evidence is the process of using those things that are either presumed to be true, or were themselves proven via evidence, to demonstrate an assertion's truth...
for, or contact with, such civilizations.
The age of the universe
Age of the universe
The age of the universe is the time elapsed since the Big Bang posited by the most widely accepted scientific model of cosmology. The best current estimate of the age of the universe is 13.75 ± 0.13 billion years within the Lambda-CDM concordance model...
and its vast number of stars suggest that unless the Earth is very atypical, extraterrestrial life should be common. In an informal discussion in 1950, the physicist
Physicist
A physicist is a scientist who studies or practices physics. Physicists study a wide range of physical phenomena in many branches of physics spanning all length scales: from sub-atomic particles of which all ordinary matter is made to the behavior of the material Universe as a whole...
Enrico Fermi
Enrico Fermi
Enrico Fermi was an Italian-born, naturalized American physicist particularly known for his work on the development of the first nuclear reactor, Chicago Pile-1, and for his contributions to the development of quantum theory, nuclear and particle physics, and statistical mechanics...
questioned why, if a multitude of advanced extraterrestrial civilizations exists in the Milky Way
Milky Way
The Milky Way is the galaxy that contains the Solar System. This name derives from its appearance as a dim un-resolved "milky" glowing band arching across the night sky...
galaxy
Galaxy
A galaxy is a massive, gravitationally bound system that consists of stars and stellar remnants, an interstellar medium of gas and dust, and an important but poorly understood component tentatively dubbed dark matter. The word galaxy is derived from the Greek galaxias , literally "milky", a...
, evidence such as spacecraft or probes
Von Neumann probe
The idea of self-replicating spacecraft has been applied — in theory — to several distinct "tasks". The particular variant of this idea applied to the idea of space exploration is known as a von Neumann probe...
is not seen. A more detailed examination of the implications of the topic began with a paper by Michael H. Hart
Michael H. Hart
Michael H. Hart is an astrophysicist who has also written three books on history and controversial articles on a variety of subjects. Hart describes himself as a Jeffersonian liberal, while his critics call him a conservative and a racial separatist.-Science:Hart, a graduate of the Bronx High...
in 1975, and it is sometimes referred to as the Fermi–Hart paradox. Other common names for the same phenomenon are Fermi's question ("Where are they?"), the Fermi Problem, the Great Silence, and silentium universi (Latin for "the silence of the universe"; the misspelling silencium universi is also common).
There have been attempts to resolve the Fermi paradox by locating evidence of extraterrestrial civilizations, along with proposals that such life could exist without human knowledge. Counterarguments suggest that intelligent extraterrestrial life
Extraterrestrial life
Extraterrestrial life is defined as life that does not originate from Earth...
does not exist or occurs so rarely or briefly that humans will never make contact with it.
Starting with Hart, a great deal of effort has gone into developing scientific theories about, and possible models of, extraterrestrial life, and the Fermi paradox has become a theoretical reference point in much of this work. The problem has spawned numerous scholarly works addressing it directly, while questions that relate to it have been addressed in fields as diverse as astronomy, biology, ecology, and philosophy. The emerging field of astrobiology
Astrobiology
Astrobiology is the study of the origin, evolution, distribution, and future of life in the universe. This interdisciplinary field encompasses the search for habitable environments in our Solar System and habitable planets outside our Solar System, the search for evidence of prebiotic chemistry,...
has brought an interdisciplinary approach to the Fermi paradox and the question of extraterrestrial life.
Basis
The Fermi paradox is a conflict between an argument of scaleScale (spatial)
Spatial scale provides a "shorthand" form for discussing relative lengths, areas, distances and sizes. A microclimate, for instance, is one which might occur in a mountain valley or near a lakeshore, whereas a megatrend is one which involves the whole planet....
and probability
Probability
Probability is ordinarily used to describe an attitude of mind towards some proposition of whose truth we arenot certain. The proposition of interest is usually of the form "Will a specific event occur?" The attitude of mind is of the form "How certain are we that the event will occur?" The...
and a lack of evidence
Evidence
Evidence in its broadest sense includes everything that is used to determine or demonstrate the truth of an assertion. Giving or procuring evidence is the process of using those things that are either presumed to be true, or were themselves proven via evidence, to demonstrate an assertion's truth...
. A more complete definition
Definition
A definition is a passage that explains the meaning of a term , or a type of thing. The term to be defined is the definiendum. A term may have many different senses or meanings...
could be stated thus:
The first aspect of the paradox, "the argument by scale", is a function of the raw numbers involved: there are an estimated 200–400 billion (2–4 ×1011) stars in the Milky Way
Milky Way
The Milky Way is the galaxy that contains the Solar System. This name derives from its appearance as a dim un-resolved "milky" glowing band arching across the night sky...
and 70 sextillion (7×1022) in the visible universe. Even if intelligent life occurs on only a minuscule percentage of planets around these stars, there might still be a great number of civilizations extant in the Milky Way galaxy
Galaxy
A galaxy is a massive, gravitationally bound system that consists of stars and stellar remnants, an interstellar medium of gas and dust, and an important but poorly understood component tentatively dubbed dark matter. The word galaxy is derived from the Greek galaxias , literally "milky", a...
alone. This argument also assumes the mediocrity principle
Mediocrity principle
The mediocrity principle is the notion in philosophy of science that there is nothing very unusual about the evolution of our solar system, the Earth, any one nation, or humans. It is a heuristic in the vein of the Copernican principle, and is sometimes used as a philosophical statement about the...
, which states that Earth is not special, but merely a typical planet
Planet
A planet is a celestial body orbiting a star or stellar remnant that is massive enough to be rounded by its own gravity, is not massive enough to cause thermonuclear fusion, and has cleared its neighbouring region of planetesimals.The term planet is ancient, with ties to history, science,...
, subject to the same laws, effects, and likely outcomes as any other world.
The second cornerstone of the Fermi paradox is a rejoinder to the argument by scale: given intelligent life's ability to overcome scarcity, and its tendency to colonize new habitats
Habitat (ecology)
A habitat is an ecological or environmental area that is inhabited by a particular species of animal, plant or other type of organism...
, it seems likely that at least some civilizations would be technologically advanced, seek out new resources in space and then colonize first their own star system
Star system
A star system or stellar system is a small number of stars which orbit each other, bound by gravitational attraction. A large number of stars bound by gravitation is generally called a star cluster or galaxy, although, broadly speaking, they are also star systems.-Binary star systems:A stellar...
and subsequently the surrounding star systems. Since there is no conclusive or certifiable evidence on Earth or elsewhere in the known universe of other intelligent life after 13.7 billion years of the universe's history, we have the conflict requiring a resolution. Some examples of which may be that intelligent life is rarer than we think, or that our assumptions about the general behavior of intelligent species are flawed.
The Fermi paradox can be asked in two ways. The first is, "Why are no aliens or their artifacts physically here?" If interstellar travel
Interstellar travel
Interstellar space travel is manned or unmanned travel between stars. The concept of interstellar travel in starships is a staple of science fiction. Interstellar travel is much more difficult than interplanetary travel. Intergalactic travel, or travel between different galaxies, is even more...
is possible, even the "slow" kind nearly within the reach of Earth technology, then it would only take from 5 million to 50 million years to colonize the galaxy. This is a relatively small amount of time on a geological scale, let alone a cosmological one
Timeline of the Big Bang
This timeline of the Big Bang describes the history of the universe according to the prevailing scientific theory of how the universe came into being, using the cosmological time parameter of comoving coordinates...
. Since there are many stars older than the Sun, or since intelligent life might have evolved earlier elsewhere, the question then becomes why the galaxy has not been colonized already. Even if colonization is impractical or undesirable to all alien civilizations, large-scale exploration of the galaxy is still possible; the means of exploration and theoretical probes involved are discussed extensively below. However, no signs of either colonization or exploration have been generally acknowledged.
The argument above may not hold for the universe as a whole, since travel times may well explain the lack of physical presence on Earth of alien inhabitants of far away galaxies. However, the question then becomes "Why do we see no signs of intelligent life?" since a sufficiently advanced civilizationThe Soviet
Soviet Union
The Soviet Union , officially the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics , was a constitutionally socialist state that existed in Eurasia between 1922 and 1991....
astronomer
Astronomer
An astronomer is a scientist who studies celestial bodies such as planets, stars and galaxies.Historically, astronomy was more concerned with the classification and description of phenomena in the sky, while astrophysics attempted to explain these phenomena and the differences between them using...
Nikolai Kardashev
Nikolai Kardashev
Nikolai Semenovich Kardashev is a Russian astrophysicist, and is the deputy director of the Russian Space Research Institute of the Russian Academy of Sciences in Moscow.Kardashev graduated from Moscow State University in 1955, following up at...
has stated that an alien civilization on Kardashev scale
Kardashev scale
The Kardashev scale is a method of measuring an advanced civilization's level of technological advancement. The scale is only theoretical and in terms of an actual civilization highly speculative; however, it puts energy consumption of an entire civilization in a cosmic perspective. It was first...
of 3 could send signals up to 10 billion light years. could potentially be observable over a significant fraction of the size of the observable universe. Even if such civilizations are rare, the scale argument indicates they should exist somewhere at some point during the history of the universe, and since they could be detected from far away over a considerable period of time, many more potential sites for their origin are within range of our observation. However, no incontrovertible signs of such civilizations have been detected.
It is unclear which version of the paradox is stronger.Let
 be the number of civilizations (per unit volume) that can be seen at a radius
be the number of civilizations (per unit volume) that can be seen at a radius  . Let
. Let  be the radius of the galaxy. So the number of civilizations we see is:
be the radius of the galaxy. So the number of civilizations we see is:
where the first integral are those in the galaxy, and the second those outside. Which integral is bigger depends on how fast N(r) decreases, which is completely unknown. This observation is due to Kardashev.
Name
In 1950, while working at Los Alamos National LaboratoryLos Alamos National Laboratory
Los Alamos National Laboratory is a United States Department of Energy national laboratory, managed and operated by Los Alamos National Security , located in Los Alamos, New Mexico...
, the physicist Enrico Fermi had a casual conversation while walking to lunch with colleagues Emil Konopinski
Emil Konopinski
Emil John Konopinski was an American nuclear scientist of Polish origin. His parents were Joseph and Sophia Sniegowska....
, Edward Teller
Edward Teller
Edward Teller was a Hungarian-American theoretical physicist, known colloquially as "the father of the hydrogen bomb," even though he did not care for the title. Teller made numerous contributions to nuclear and molecular physics, spectroscopy , and surface physics...
and Herbert York
Herbert York
Herbert Frank York was an American nuclear physicist. He held numerous research and administrative positions at various United States government and educational institutes.-Biography:...
. The men discussed a recent spate of UFO
Unidentified flying object
A term originally coined by the military, an unidentified flying object is an unusual apparent anomaly in the sky that is not readily identifiable to the observer as any known object...
reports and an Alan Dunn
Alan Dunn (cartoonist)
Alan Dunn was a cartoonist known for his work in The New Yorker. He also had architectural expertise and submitted work to Architectural Record...
cartoon facetiously blaming the disappearance of municipal trashcans on marauding aliens. They then had a more serious discussion regarding the chances
Odds
The odds in favor of an event or a proposition are expressed as the ratio of a pair of integers, which is the ratio of the probability that an event will happen to the probability that it will not happen...
of humans observing faster-than-light
Faster-than-light
Faster-than-light communications and travel refer to the propagation of information or matter faster than the speed of light....
travel by some material object within the next ten years, which Teller put at one in a million, but Fermi put closer to one in ten. The conversation shifted to other subjects, until during lunch Fermi suddenly exclaimed, "Where are they?" (alternatively, "Where is everybody?") One participant recollects that Fermi then made a series of rapid calculations using estimated figures (Fermi was known for his ability to make good estimates from first principles and minimal data, see Fermi problem
Fermi problem
In science, particularly in physics or engineering education, a Fermi problem, Fermi question, or Fermi estimate is an estimation problem designed to teach dimensional analysis, approximation, and the importance of clearly identifying one's assumptions...
.) According to this account, he then concluded that Earth should have been visited long ago and many times over.
Drake equation
While numerous theories and principles are related to the Fermi paradox, the most closely related is the Drake equationDrake equation
The Drake equation is an equation used to estimate the number of detectable extraterrestrial civilizations in the Milky Way galaxy. It is used in the fields of exobiology and the Search for ExtraTerrestrial Intelligence...
.
The equation was formulated by Dr. Frank Drake
Frank Drake
Frank Donald Drake PhD is an American astronomer and astrophysicist. He is most notable as one of the pioneers in the search for extraterrestrial intelligence, including the founding of SETI, mounting the first observational attempts at detecting extraterrestrial communications in 1961 in Project...
in 1961, a decade after the objections raised by Enrico Fermi, in an attempt to find a systematic means to evaluate the numerous probabilities involved in alien life. The speculative equation factors in: the rate of star formation
Star formation
Star formation is the process by which dense parts of molecular clouds collapse into a ball of plasma to form a star. As a branch of astronomy star formation includes the study of the interstellar medium and giant molecular clouds as precursors to the star formation process and the study of young...
in the galaxy; the fraction of stars with planets and the number per star that are habitable; the fraction of those planets which develop life, the fraction of intelligent life, and the further fraction of detectable technological intelligent life; and finally the length of time such civilizations are detectable. The fundamental problem is that the last four terms (fraction of planets with life, odds life becomes intelligent, odds intelligent life becomes detectable, and detectable lifetime of civilizations) are completely unknown. We have only one example, rendering statistical estimates impossible, and even the example we have is subject to a strong anthropic bias.
A deeper objection is that the very form of the Drake equation assumes that civilizations arise and then die out within their original solar systems. If interstellar colonization is possible, then this assumption is invalid, and the equations of population dynamics
Population dynamics
Population dynamics is the branch of life sciences that studies short-term and long-term changes in the size and age composition of populations, and the biological and environmental processes influencing those changes...
would apply instead.
The Drake equation has been used by both optimists and pessimists with wildly differing results. Dr. Carl Sagan
Carl Sagan
Carl Edward Sagan was an American astronomer, astrophysicist, cosmologist, author, science popularizer and science communicator in astronomy and natural sciences. He published more than 600 scientific papers and articles and was author, co-author or editor of more than 20 books...
, using optimistic numbers, suggested as many as one million communicating civilizations in the Milky Way
Milky Way
The Milky Way is the galaxy that contains the Solar System. This name derives from its appearance as a dim un-resolved "milky" glowing band arching across the night sky...
in 1966, though he later suggested that the actual number could be far smaller. Pessimists, such as Frank Tipler
Frank J. Tipler
Frank Jennings Tipler is a mathematical physicist and cosmologist, holding a joint appointment in the Departments of Mathematics and Physics at Tulane University. Tipler has authored books and papers on the Omega Point, which he claims is a mechanism for the resurrection of the dead. It has been...
& John D Barrow, have used pessimistic numbers and concluded that the average number of civilizations in a galaxy is much less than one.Note that, even though there is at least one civilization in our galaxy (namely our own), the average or "most likely" number of civilizations in our galaxy as described by this equation may still be smaller than one. In other words, the fact that there is at least one civilization in our galaxy does not mean that this was a likely outcome. This is an example of anthropic bias. No civilization can use itself to estimate the average number of civilizations in a galaxy, since if there was not at least one civilization the question could not arise. The Drake equation computes only the long-term average number of civilizations; even if the average number of civilizations per galaxy is less than one, there could be more than one in any given galaxy at any given time. Frank Drake himself has commented that the Drake equation is unlikely to settle the Fermi paradox; instead it is just a way of "organizing our ignorance" on the subject.
Empirical resolution attempts
One obvious way to resolve the Fermi paradox would be to find conclusive evidence of extraterrestrial intelligence. Efforts to find such evidence have been made since 1960, and several are ongoing . As human beings do not possess interstellar travelInterstellar travel
Interstellar space travel is manned or unmanned travel between stars. The concept of interstellar travel in starships is a staple of science fiction. Interstellar travel is much more difficult than interplanetary travel. Intergalactic travel, or travel between different galaxies, is even more...
capability, such searches are being remotely carried out at great distances and rely on analysis of very subtle evidence. This limits possible discoveries to civilizations which alter their environment in a detectable way, or produce effects that are observable at a distance, such as radio emissions. It is very unlikely that non-technological civilizations will be detectable from Earth in the near future.
One difficulty in searching is avoiding an overly anthropocentric viewpoint. Conjecture
Conjecture
A conjecture is a proposition that is unproven but is thought to be true and has not been disproven. Karl Popper pioneered the use of the term "conjecture" in scientific philosophy. Conjecture is contrasted by hypothesis , which is a testable statement based on accepted grounds...
on the type of evidence likely to be found often focuses on the types of activities that humans have performed, or likely would perform given more advanced technology. Intelligent aliens might avoid these "expected" activities, or perform activities totally novel to humans.
Mainstream astronomy and SETI
There are two ways that astronomy might find evidence of an extraterrestrial civilization. One is that conventional astronomers, studying stars, planets, and galaxies, might serendipitously observe some phenomenon that cannot be explained without positing an intelligent civilization as the source. This has been suspected several times. PulsarPulsar
A pulsar is a highly magnetized, rotating neutron star that emits a beam of electromagnetic radiation. The radiation can only be observed when the beam of emission is pointing towards the Earth. This is called the lighthouse effect and gives rise to the pulsed nature that gives pulsars their name...
s, when first discovered, were called LGMs (Little Green Men), because of the precise repetition of their pulses (they rival the best atomic clocks). Likewise Seyfert galaxies
Seyfert galaxy
Seyfert galaxies are a class of galaxies with nuclei that produce spectral line emission from highly ionized gas, named after Carl Keenan Seyfert, the astronomer who first identified the class in 1943...
were suspected to be industrial accidents because their enormous and directed energy output had no initial explanation. Eventually, natural explanations not involving intelligent life have been found for all such observations to date. Specifically, pulsars are now attributed to neutron stars, and Seyfert galaxies to an end-on view of the accretion onto the black holes, but the possibility of discovery remains. Proposed examples include asteroid mining that would change the appearance of debris disks around stars or large-scale use of solar power changing the light curve of planets measured near eclipse.
The other way astronomy might settle the Fermi paradox is through a search specifically dedicated to finding evidence of life.
Radio emissions

Radio telescope
A radio telescope is a form of directional radio antenna used in radio astronomy. The same types of antennas are also used in tracking and collecting data from satellites and space probes...
are presumed to be a natural advance for technological species, theoretically creating effects that might be detected over interstellar distances.
Sensitive observers of the solar system, for example, would note unusually intense radio
Radio
Radio is the transmission of signals through free space by modulation of electromagnetic waves with frequencies below those of visible light. Electromagnetic radiation travels by means of oscillating electromagnetic fields that pass through the air and the vacuum of space...
waves for a G2 star due to Earth's television and telecommunication broadcasts. In the absence of an apparent natural cause, alien observers might infer the existence of terrestrial civilization.
Therefore, the careful searching of radio emissions from space for non-natural signals may lead to the detection of alien civilizations. Such signals could be either "accidental" by-products of a civilization, or deliberate attempts to communicate, such as the Communication with Extraterrestrial Intelligence
Communication with Extraterrestrial Intelligence
Communication with extraterrestrial intelligence is a branch of the search for extraterrestrial intelligence that focuses on composing and deciphering messages that could theoretically be understood by another technological civilization. The best-known CETI experiment was the 1974 Arecibo message...
's Arecibo message
Arecibo message
The Arecibo message was broadcast into space a single time via frequency modulated radio waves at a ceremony to mark the remodeling of the Arecibo radio telescope on 16 November 1974. It was aimed at the globular star cluster M13 some 25,000 light years away because M13 was a large and close...
. A number of astronomers and observatories have attempted and are attempting to detect such evidence, mostly through the SETI
SETI
The search for extraterrestrial intelligence is the collective name for a number of activities people undertake to search for intelligent extraterrestrial life. Some of the most well known projects are run by the SETI Institute. SETI projects use scientific methods to search for intelligent life...
organization, although other approaches, such as
optical SETI, also exist.
Several decades of SETI analysis have not revealed any main sequence stars with unusually bright or meaningfully repetitive radio emissions, although there have been several candidate signals. On August 15, 1977 the "Wow! signal
Wow! signal
The Wow! signal was a strong narrowband radio signal detected by Dr. Jerry R. Ehman on August 15, 1977, while working on a SETI project at the Big Ear radio telescope of The Ohio State University then located at Ohio Wesleyan University's Perkins Observatory, Delaware, Ohio. The signal bore...
" was picked up by The Big Ear
The Big Ear
The Ohio State University Radio Observatory was a Kraus-type radio telescope located on the grounds of the Perkins Observatory at Ohio Wesleyan University from 1963 to 1998. Known as "Big Ear", the observatory was part of The Ohio State University's Search for Extraterrestrial Intelligence project...
radio telescope. However, the Big Ear only looks at each point on the sky for 72 seconds, and re-examinations of the same spot have found nothing. In 2003, Radio source SHGb02+14a
Radio source SHGb02+14a
Radio source SHGb02+14a is a source and a candidate in the Search for Extra-Terrestrial Intelligence , discovered in March 2003 by SETI@home and announced in New Scientist on September 1, 2004....
was isolated by SETI@home
SETI@home
SETI@home is an Internet-based public volunteer computing project employing the BOINC software platform, hosted by the Space Sciences Laboratory, at the University of California, Berkeley, in the United States. SETI is an acronym for the Search for Extra-Terrestrial Intelligence...
analysis, although it has largely been discounted by further study. There are numerous technical assumptions underlying SETI that may cause human beings to miss radio emissions with present search techniques; these are discussed below.
Direct planetary observation
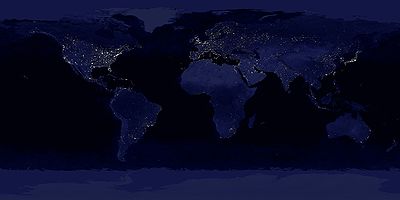
Direct evidence for the existence of life may eventually be observable, such as the detection of biotic signature gases (such as methane
Methane
Methane is a chemical compound with the chemical formula . It is the simplest alkane, the principal component of natural gas, and probably the most abundant organic compound on earth. The relative abundance of methane makes it an attractive fuel...
and oxygen
Oxygen
Oxygen is the element with atomic number 8 and represented by the symbol O. Its name derives from the Greek roots ὀξύς and -γενής , because at the time of naming, it was mistakenly thought that all acids required oxygen in their composition...
)—or even the industrial air pollution
Air pollution
Air pollution is the introduction of chemicals, particulate matter, or biological materials that cause harm or discomfort to humans or other living organisms, or cause damage to the natural environment or built environment, into the atmosphere....
of a technologically advanced civilization—in an exoplanet's atmosphere by means of spectrographic analysis
Spectroscopy
Spectroscopy is the study of the interaction between matter and radiated energy. Historically, spectroscopy originated through the study of visible light dispersed according to its wavelength, e.g., by a prism. Later the concept was expanded greatly to comprise any interaction with radiative...
. With improvements in our observational capabilities, it may eventually even be possible to detect direct evidence such as that which humanity produces (see right).
However, exoplanets are rarely directly observed (the first claim to have done so was made in 2004); rather, their existence is usually inferred from the effects they have on the star(s) they orbit. This means that usually only the mass and orbit
Orbit
In physics, an orbit is the gravitationally curved path of an object around a point in space, for example the orbit of a planet around the center of a star system, such as the Solar System...
of an exoplanet can be deduced. This information, along with the stellar classification
Stellar classification
In astronomy, stellar classification is a classification of stars based on their spectral characteristics. The spectral class of a star is a designated class of a star describing the ionization of its chromosphere, what atomic excitations are most prominent in the light, giving an objective measure...
of its sun, and educated guesses as to its composition (usually based on the mass of the planet, and its distance from its sun), allows only for rough approximations of the planetary environment.
Prior to 2009, methods for exoplanet detection
Methods of detecting extrasolar planets
Any planet is an extremely faint light source compared to its parent star. In addition to the intrinsic difficulty of detecting such a faint light source, the light from the parent star causes a glare that washes it out...
were not likely to detect life-bearing Earth-like worlds. Methods such as gravitational microlensing
Gravitational microlensing
Gravitational microlensing is an astronomical phenomenon due to the gravitational lens effect. It can be used to detect objects ranging from the mass of a planet to the mass of a star, regardless of the light they emit. Typically, astronomers can only detect bright objects that emit lots of light ...
can detect the presence of "small" worlds, potentially even smaller than the Earth, but can only detect such worlds for very brief moments of time, and no follow-up is possible. Other methods such as radial velocity, astrometry
Astrometry
Astrometry is the branch of astronomy that involves precise measurements of the positions and movements of stars and other celestial bodies. The information obtained by astrometric measurements provides information on the kinematics and physical origin of our Solar System and our Galaxy, the Milky...
, and the transit method allow prolonged observations of exoplanet effects, but only work with worlds that are many times the mass of Earth, at least when performed while looking through the atmosphere. These seem unlikely candidates to harbor Earth-like life. However, exoplanet detection and classification is a very active sub-discipline in astronomy, with 424 such planets being detected between 1988 and 2010, and the first possibly terrestrial planet
Terrestrial planet
A terrestrial planet, telluric planet or rocky planet is a planet that is composed primarily of silicate rocks or metals. Within the Solar System, the terrestrial planets are the inner planets closest to the Sun...
discovered within a star's habitable zone
Habitable zone
In astronomy and astrobiology, a habitable zone is an umbrella term for regions that are considered favourable to life. The concept is inferred from the empirical study of conditions favourable for Life on Earth...
being found in 2007. New refinements in exoplanet detection methods, and use of existing methods from space, (such as the Kepler Mission
Kepler Mission
The Kepler spacecraft is an American space observatory, the space-based portion of NASA's Kepler Mission to discover Earth-like planets orbiting other stars. The spacecraft is named in honor of the 17th-century German astronomer Johannes Kepler...
, launched in 2009) are expected to detect and characterize terrestrial-size planets, and determine if they are within the habitable zones of their stars. Such observational refinements may allow us to better gauge how common potentially habitable worlds are. Using methods like the Drake equation with this data would therefore allow a much better idea of how common life in the universe might be; this would have a profound influence over the expectations behind the Fermi paradox itself.
Probes, colonies, and other artifacts
As noted, given the size and age of the universe, and the relative rapidity at which dispersion of intelligent life can in principle occur, evidence of alien colonization attempts might plausibly be discovered. Evidence of exploration not containing extraterrestrial life, such as probes and information gathering devices, may also await discovery.Some theoretical exploration techniques such as the Von Neumann probe
Von Neumann probe
The idea of self-replicating spacecraft has been applied — in theory — to several distinct "tasks". The particular variant of this idea applied to the idea of space exploration is known as a von Neumann probe...
(a self-replicating device) could exhaustively explore a galaxy
Galaxy
A galaxy is a massive, gravitationally bound system that consists of stars and stellar remnants, an interstellar medium of gas and dust, and an important but poorly understood component tentatively dubbed dark matter. The word galaxy is derived from the Greek galaxias , literally "milky", a...
the size of the Milky Way
Milky Way
The Milky Way is the galaxy that contains the Solar System. This name derives from its appearance as a dim un-resolved "milky" glowing band arching across the night sky...
in as little as half a million years, with comparatively little investment in materials and energy relative to the results. If even a single civilization in the Milky Way attempted this, such probes could spread throughout the entire galaxy. Evidence of such probes might be found in the solar system—perhaps in the asteroid belt
Asteroid belt
The asteroid belt is the region of the Solar System located roughly between the orbits of the planets Mars and Jupiter. It is occupied by numerous irregularly shaped bodies called asteroids or minor planets...
where raw materials would be plentiful and easily accessed.
Another possibility for contact with an alien probe—one that would be trying to find human beings—is an alien Bracewell probe
Bracewell probe
A Bracewell probe is a hypothetical concept for an autonomous interstellar space probe dispatched for the express purpose of communication with one or more alien civilizations. It was proposed by Ronald N...
. Such a device would be an autonomous space probe whose purpose is to seek out and communicate with alien civilizations (as opposed to Von Neumann probes, which are usually described as purely exploratory). These were proposed as an alternative to carrying a slow speed-of-light dialogue between vastly distant neighbours. Rather than contending with the long delays a radio dialogue would suffer, a probe housing an artificial intelligence
Artificial intelligence
Artificial intelligence is the intelligence of machines and the branch of computer science that aims to create it. AI textbooks define the field as "the study and design of intelligent agents" where an intelligent agent is a system that perceives its environment and takes actions that maximize its...
would seek out an alien civilization to carry on a close range communication with the discovered civilization. The findings of such a probe would still have to be transmitted to the home civilization at light speed, but an information-gathering dialogue could be conducted in real time.
Since the 1950s, direct exploration has been carried out on a small fraction of the solar system and no evidence that it has ever been visited by alien colonists, or probes, has been uncovered. Detailed exploration of areas of the solar system where resources would be plentiful—such as the asteroid
Asteroid
Asteroids are a class of small Solar System bodies in orbit around the Sun. They have also been called planetoids, especially the larger ones...
s, the Kuiper belt
Kuiper belt
The Kuiper belt , sometimes called the Edgeworth–Kuiper belt, is a region of the Solar System beyond the planets extending from the orbit of Neptune to approximately 50 AU from the Sun. It is similar to the asteroid belt, although it is far larger—20 times as wide and 20 to 200 times as massive...
, the Oort cloud
Oort cloud
The Oort cloud , or the Öpik–Oort cloud , is a hypothesized spherical cloud of comets which may lie roughly 50,000 AU, or nearly a light-year, from the Sun. This places the cloud at nearly a quarter of the distance to Proxima Centauri, the nearest star to the Sun...
and the planetary ring systems—may yet produce evidence of alien exploration, though these regions are vast and difficult to investigate. There have been preliminary efforts in this direction in the form of the SETA and SETV projects to search for extraterrestrial artifacts or other evidence of extraterrestrial visitation within the solar system. There have also been attempts to signal, attract, or activate Bracewell probe
Bracewell probe
A Bracewell probe is a hypothetical concept for an autonomous interstellar space probe dispatched for the express purpose of communication with one or more alien civilizations. It was proposed by Ronald N...
s in Earth's local vicinity, including by scientists Robert Freitas
Robert Freitas
Robert A. Freitas Jr. is a Senior Research Fellow, one of four researchers at the nonprofit foundation Institute for Molecular Manufacturing in Palo Alto, California. He holds a 1974 Bachelor's degree majoring in both physics and psychology from Harvey Mudd College, and a 1978 Juris Doctor degree...
and Francisco Valdes. Many of the projects that fall under this umbrella are considered "fringe" science by astronomers and none of the projects has located any artifacts.
Should alien artifacts be discovered, even here on Earth, they may not be recognizable as such. The products of an alien mind and an advanced alien technology might not be perceptible or recognizable as artificial constructs. Exploratory devices in the form of bio-engineered life forms created through synthetic biology
Synthetic biology
Synthetic biology is a new area of biological research that combines science and engineering. It encompasses a variety of different approaches, methodologies, and disciplines with a variety of definitions...
would presumably disintegrate after a point, leaving no evidence; an alien information gathering system based on molecular nanotechnology
Molecular nanotechnology
Molecular nanotechnology is a technology based on the ability to build structures to complex, atomic specifications by means of mechanosynthesis. This is distinct from nanoscale materials...
could be all around us at this very moment, completely undetected. The same might be true of civilizations that actively hide their investigations from us, for possible reasons described further in this article. Also, Clarke's third law
Clarke's three laws
Clarke's Three Laws are three "laws" of prediction formulated by the British writer and scientist Arthur C. Clarke. They are:# When a distinguished but elderly scientist states that something is possible, he is almost certainly right...
suggests that an alien civilization well in advance of humanity's might have means of investigation that are not yet conceivable to human beings.
Advanced stellar-scale artifacts
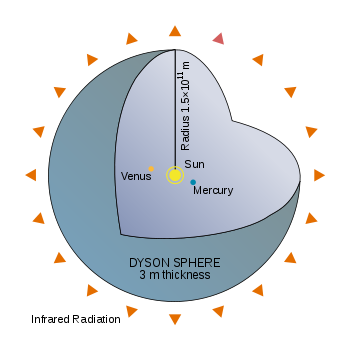
Freeman Dyson
Freeman John Dyson FRS is a British-born American theoretical physicist and mathematician, famous for his work in quantum field theory, solid-state physics, astronomy and nuclear engineering. Dyson is a member of the Board of Sponsors of the Bulletin of the Atomic Scientists...
observed that every developing human civilization constantly increases its energy consumption, and theoretically, a civilization of sufficient age would require all the energy produced by its star. The Dyson Sphere
Dyson sphere
A Dyson sphere is a hypothetical megastructure originally described by Freeman Dyson. Such a "sphere" would be a system of orbiting solar power satellites meant to completely encompass a star and capture most or all of its energy output...
was the thought experiment
Thought experiment
A thought experiment or Gedankenexperiment considers some hypothesis, theory, or principle for the purpose of thinking through its consequences...
that he derived as a solution: a shell or cloud of objects enclosing a star to harness as much radiant energy as possible. Such a feat of astroengineering
Astroengineering
Astroengineering is the construction of megastructures in space by technologically advanced beings. It is a form of megascale engineering. Typically proposed feats of astroengineering are on the scale to remake an entire stellar system....
would drastically alter the observed spectrum
Spectroscopy
Spectroscopy is the study of the interaction between matter and radiated energy. Historically, spectroscopy originated through the study of visible light dispersed according to its wavelength, e.g., by a prism. Later the concept was expanded greatly to comprise any interaction with radiative...
of the star involved, changing it at least partly from the normal emission lines of a natural stellar atmosphere
Stellar atmosphere
The stellar atmosphere is the outer region of the volume of a star, lying above the stellar core, radiation zone and convection zone. It is divided into several regions of distinct character:...
, to that of a black body radiation, probably with a peak in the infrared
Infrared
Infrared light is electromagnetic radiation with a wavelength longer than that of visible light, measured from the nominal edge of visible red light at 0.74 micrometres , and extending conventionally to 300 µm...
. Dyson himself speculated that advanced alien civilizations might be detected by examining the spectra of stars, searching for such an altered spectrum.
Since then, several other theoretical stellar-scale megastructure
Megastructure
A megastructure is a very large manmade object, though the limits of precisely how large this is vary considerably. Some apply the term to any especially large or tall building....
s have been proposed, but the central idea remains that a highly advanced civilization—Type II or greater on the Kardashev scale
Kardashev scale
The Kardashev scale is a method of measuring an advanced civilization's level of technological advancement. The scale is only theoretical and in terms of an actual civilization highly speculative; however, it puts energy consumption of an entire civilization in a cosmic perspective. It was first...
—could alter its environment enough as to be detectable from interstellar distances.
However, such constructs may be more difficult to detect than originally thought. Dyson spheres might have different emission spectra depending on the desired internal environment; life based on high-temperature reactions may require a high temperature environment, with resulting "waste radiation" in the visible spectrum, not the infrared. Additionally, a variant of the Dyson sphere has been proposed which would be difficult to observe from any great distance; a Matrioshka brain
Matrioshka brain
A matrioshka brain is a hypothetical megastructure proposed by Robert Bradbury, based on the Dyson sphere, of immense computational capacity. It is an example of a Class B stellar engine, employing the entire energy output of a star to drive computer systems...
is a series of concentric spheres, each radiating less energy per area than its inner neighbour. The outermost sphere of such a structure could be close to the temperature of the interstellar background radiation, and thus be all but invisible.
There have been some preliminary attempts to find evidence of the existence of Dyson sphere
Dyson sphere
A Dyson sphere is a hypothetical megastructure originally described by Freeman Dyson. Such a "sphere" would be a system of orbiting solar power satellites meant to completely encompass a star and capture most or all of its energy output...
s or other large Type-II or Type-III Kardashev scale
Kardashev scale
The Kardashev scale is a method of measuring an advanced civilization's level of technological advancement. The scale is only theoretical and in terms of an actual civilization highly speculative; however, it puts energy consumption of an entire civilization in a cosmic perspective. It was first...
artifacts that would alter the spectra of their core stars. These surveys have not located anything yet, though they are still incomplete. Similarly, direct observation of thousands of galaxies has shown no explicit evidence of artificial construction or modifications.
Explaining the paradox theoretically
Certain theoreticians accept that the apparent absence of evidence proves the absence of extraterrestrials and attempt to explain why. Others offer possible frameworks in which the silence may be explained without ruling out the possibility of such life, including assumptions about extraterrestrial behaviour and technology. Each of these hypothesized explanations is essentially an argument for decreasing the value of one or more of the terms in the Drake equationDrake equation
The Drake equation is an equation used to estimate the number of detectable extraterrestrial civilizations in the Milky Way galaxy. It is used in the fields of exobiology and the Search for ExtraTerrestrial Intelligence...
. The arguments are not, in general, mutually exclusive. For example, it could be that both life is rare, and technical civilizations are short lived, or many other combinations of the explanations below.
Few, if any, other civilizations currently exist
One explanation is that the human civilization is alone (or very nearly so) in the galaxy. Several theories along these lines have been proposed, explaining why intelligent life might be either very rare, or very short lived. Implications of these hypotheses are examined as the Great Filter.No other civilizations have arisen
Those who believe that extraterrestrial intelligent life does not exist argue that the conditions needed for lifeLife
Life is a characteristic that distinguishes objects that have signaling and self-sustaining processes from those that do not, either because such functions have ceased , or else because they lack such functions and are classified as inanimate...
—or at least complex life—to evolve are rare or even unique to Earth. This is known as the Rare Earth hypothesis, which attempts to resolve the Fermi paradox by rejecting the mediocrity principle
Mediocrity principle
The mediocrity principle is the notion in philosophy of science that there is nothing very unusual about the evolution of our solar system, the Earth, any one nation, or humans. It is a heuristic in the vein of the Copernican principle, and is sometimes used as a philosophical statement about the...
, and asserting that Earth is not typical, but unusual or even unique. While a unique Earth has historically been assumed on philosophical or religious grounds, the Rare Earth Hypothesis
Hypothesis
A hypothesis is a proposed explanation for a phenomenon. The term derives from the Greek, ὑποτιθέναι – hypotithenai meaning "to put under" or "to suppose". For a hypothesis to be put forward as a scientific hypothesis, the scientific method requires that one can test it...
uses quantifiable and statistical arguments to argue that multicellular life is exceedingly rare in the universe because Earth-like planets are themselves exceedingly rare and/or many improbable coincidences have converged to make complex life on Earth
Life on Earth
Life on Earth: A Natural History by David Attenborough is a television natural history series made by the BBC in association with Warner Bros. and Reiner Moritz Productions...
possible. It is possible that complex life may evolve through other mechanisms than those found specifically here on Earth, but the fact that in the history of life on the Earth only one species has developed a civilization to the point of being capable of space flight and radio technology; or, more basically, abstract ideas such as music, art, or religion lends more credence to the idea of technologically advanced civilizations being rare in the universe.
For example, the emergence of intelligence may have been an evolutionary accident. Geoffrey Miller
Geoffrey Miller (evolutionary psychologist)
Geoffrey F. Miller , Associate Professor of Psychology at the University of New Mexico, is an American evolutionary psychologist.Miller is a 1987 graduate of Columbia University, where he earned a B.A. in biology and psychology. He received his PhD in cognitive psychology from Stanford University...
proposes that human intelligence is the result of runaway sexual selection
Sexual selection
Sexual selection, a concept introduced by Charles Darwin in his 1859 book On the Origin of Species, is a significant element of his theory of natural selection...
, which takes unpredictable directions. Steven Pinker
Steven Pinker
Steven Arthur Pinker is a Canadian-American experimental psychologist, cognitive scientist, linguist and popular science author...
, in his book How the Mind Works
How the Mind Works
How the Mind Works is a book by Canadian-American cognitive scientist Steven Pinker, published in 1997. The book attempts to explain some of the human mind's poorly understood functions and quirks in evolutionary terms...
, cautions that the idea that evolution of life (once it has reached a certain minimum complexity) is bound to produce intelligent beings, relies on the fallacy of the "ladder of evolution": As evolution
Evolution
Evolution is any change across successive generations in the heritable characteristics of biological populations. Evolutionary processes give rise to diversity at every level of biological organisation, including species, individual organisms and molecules such as DNA and proteins.Life on Earth...
does not strive for a goal but just happens, it uses the adaptation
Adaptation
An adaptation in biology is a trait with a current functional role in the life history of an organism that is maintained and evolved by means of natural selection. An adaptation refers to both the current state of being adapted and to the dynamic evolutionary process that leads to the adaptation....
most useful for a given ecological niche
Ecological niche
In ecology, a niche is a term describing the relational position of a species or population in its ecosystem to each other; e.g. a dolphin could potentially be in another ecological niche from one that travels in a different pod if the members of these pods utilize significantly different food...
, and the fact that, on Earth, this led to language-capable sentience only once so far may suggest that this adaptation is only rarely a good choice and hence by no means a sure endpoint of the evolution of a tree of life
Tree of life (science)
Charles Darwin proposed that phylogeny, the evolutionary relatedness among species through time, was expressible as a metaphor he termed the Tree of Life...
.
Another theory along these lines is that even if the conditions needed for life
Life
Life is a characteristic that distinguishes objects that have signaling and self-sustaining processes from those that do not, either because such functions have ceased , or else because they lack such functions and are classified as inanimate...
might be common in the universe, that the formation of life itself, a complex array of molecules that are capable simultaneously of reproduction, of extraction of base components from the environment, and of obtaining energy in a form that life can use to maintain the reaction (or the initial abiogenesis
Abiogenesis
Abiogenesis or biopoesis is the study of how biological life arises from inorganic matter through natural processes, and the method by which life on Earth arose...
on a potential life-bearing planet), might ultimately be very rare.
Additionally, in the nondirectional meandering from initial life to humans, other low-probability happenings may have been the transition from prokaryotic
Prokaryote
The prokaryotes are a group of organisms that lack a cell nucleus , or any other membrane-bound organelles. The organisms that have a cell nucleus are called eukaryotes. Most prokaryotes are unicellular, but a few such as myxobacteria have multicellular stages in their life cycles...
cells to eukaryotic
Eukaryote
A eukaryote is an organism whose cells contain complex structures enclosed within membranes. Eukaryotes may more formally be referred to as the taxon Eukarya or Eukaryota. The defining membrane-bound structure that sets eukaryotic cells apart from prokaryotic cells is the nucleus, or nuclear...
cells (with separate nucleus, organelles, specialization, and a cytoskeleton allowing the cell to take on different shapes) and the transition from single-cellular life to multicellular life
Multicellular organism
Multicellular organisms are organisms that consist of more than one cell, in contrast to single-celled organisms. Most life that can be seen with the the naked eye is multicellular, as are all animals and land plants.-Evolutionary history:Multicellularity has evolved independently dozens of times...
, which was recorded in the Cambrian Explosion
Cambrian explosion
The Cambrian explosion or Cambrian radiation was the relatively rapid appearance, around , of most major phyla, as demonstrated in the fossil record, accompanied by major diversification of other organisms, including animals, phytoplankton, and calcimicrobes...
of 530 mya when significant numbers of organisms had evolved hard body parts, although multicellular life perhaps first started to evolve a couple of hundred million years before that. For most of Earth's history, there have only been single-celled creatures.
And there are many other potential branching points. For example, perhaps the transition from ocean creatures to land-dwelling creatures crucially depends on an unusually large moon and significant tides.
It is also possible that intelligence is common, but industrial civilization is not. For example, the rise of industrialism on Earth was driven by the presence of convenient energy sources such as fossil fuels. If such energy sources are rare or nonexistent elsewhere, then it may be far more difficult for an intelligent race to advance technologically to the point where we could communicate with them. There may also be other unique factors on which our civilization is dependent. Or, on a water world, where the intelligent creatures are something like dolphins, it may be difficult to build fire and forge metals.
Another possibility is that Earth is the first planet in the Milky Way on which industrial civilization has arisen. However, critics note that according to current understanding, many Earth-like planets were created many billions of years prior to Earth, so this explanation requires repudiation of the mediocrity principle
Mediocrity principle
The mediocrity principle is the notion in philosophy of science that there is nothing very unusual about the evolution of our solar system, the Earth, any one nation, or humans. It is a heuristic in the vein of the Copernican principle, and is sometimes used as a philosophical statement about the...
.
Insofar as the Rare Earth Hypothesis privileges life on Earth and its process of formation, it is a variant of the anthropic principle
Anthropic principle
In astrophysics and cosmology, the anthropic principle is the philosophical argument that observations of the physical Universe must be compatible with the conscious life that observes it. Some proponents of the argument reason that it explains why the Universe has the age and the fundamental...
. The variant of the anthropic principle states the universe seems uniquely suited towards developing human intelligence. This philosophical stance opposes not only the mediocrity principle
Mediocrity principle
The mediocrity principle is the notion in philosophy of science that there is nothing very unusual about the evolution of our solar system, the Earth, any one nation, or humans. It is a heuristic in the vein of the Copernican principle, and is sometimes used as a philosophical statement about the...
, but also the wider Copernican principle
Copernican principle
In physical cosmology, the Copernican principle, named after Nicolaus Copernicus, states that the Earth is not in a central, specially favored position. More recently, the principle has been generalized to the relativistic concept that humans are not privileged observers of the universe...
, which suggests there is no privileged location in the universe.
Opponents dismiss both Rare Earth and the anthropic principle as tautological
Tautology (logic)
In logic, a tautology is a formula which is true in every possible interpretation. Philosopher Ludwig Wittgenstein first applied the term to redundancies of propositional logic in 1921; it had been used earlier to refer to rhetorical tautologies, and continues to be used in that alternate sense...
—if a condition must exist in the universe
Universe
The Universe is commonly defined as the totality of everything that exists, including all matter and energy, the planets, stars, galaxies, and the contents of intergalactic space. Definitions and usage vary and similar terms include the cosmos, the world and nature...
for human life to arise, then the universe must already meet that condition, as human life exists—and as an unimaginative argument. According to this analysis, the Rare Earth hypothesis confuses a description of how life on Earth arose with a uniform conclusion of how life must arise. While the probability of the specific conditions on Earth being widely replicated is low, we do not know what complex life may require in order to evolve.
It is the nature of intelligent life to destroy itself
This is the argument that technological civilizations may usually or invariably destroy themselves before or shortly after developing radio or space flight technology. Possible means of annihilation include nuclear warNuclear warfare
Nuclear warfare, or atomic warfare, is a military conflict or political strategy in which nuclear weaponry is detonated on an opponent. Compared to conventional warfare, nuclear warfare can be vastly more destructive in range and extent of damage...
, biological warfare
Biological warfare
Biological warfare is the use of biological toxins or infectious agents such as bacteria, viruses, and fungi with intent to kill or incapacitate humans, animals or plants as an act of war...
or accidental contamination, nanotechnological catastrophe
Grey goo
Grey goo is a hypothetical end-of-the-world scenario involving molecular nanotechnology in which out-of-control self-replicating robots consume all matter on Earth while building more of themselves, a scenario known as ecophagy .Self-replicating machines of the macroscopic variety were originally...
, ill-advised physics experiments,An example of fears of civilization-destroying physics experiments. This particular fear (particle colliders creating black holes, destroying the false vacuum, etc.) is discounted among scientists, since cosmic rays of much higher energy have been striking the Earth and moon for eons (NYT article, Technical report). a badly programmed super-intelligence, or a Malthusian catastrophe
Malthusian catastrophe
A Malthusian catastrophe was originally foreseen to be a forced return to subsistence-level conditions once population growth had outpaced agricultural production...
after the deterioration of a planet's ecosphere. This general theme is explored both in fiction and in mainstream scientific theorizing. Indeed, there are probabilistic arguments which suggest that human extinction may occur sooner rather than later. In 1966 Sagan
Carl Sagan
Carl Edward Sagan was an American astronomer, astrophysicist, cosmologist, author, science popularizer and science communicator in astronomy and natural sciences. He published more than 600 scientific papers and articles and was author, co-author or editor of more than 20 books...
and Shklovskii
Iosif Shklovsky
Iosif Samuilovich Shklovsky was a Soviet astronomer and astrophysicist...
suggested that technological civilizations will either tend to destroy themselves within a century of developing interstellar communicative capability or master their self-destructive tendencies and survive for billion-year timescales. Self-annihilation may also be viewed in terms of thermodynamics: insofar as life is an ordered system that can sustain itself against the tendency to disorder, the "external transmission" or interstellar communicative phase may be the point at which the system becomes unstable and self-destructs.
From a Darwinian
Charles Darwin
Charles Robert Darwin FRS was an English naturalist. He established that all species of life have descended over time from common ancestry, and proposed the scientific theory that this branching pattern of evolution resulted from a process that he called natural selection.He published his theory...
perspective, self-destruction would be a paradoxical outcome of evolutionary success. The evolutionary psychology
Evolutionary psychology
Evolutionary psychology is an approach in the social and natural sciences that examines psychological traits such as memory, perception, and language from a modern evolutionary perspective. It seeks to identify which human psychological traits are evolved adaptations, that is, the functional...
that developed during the competition for scarce resources over the course of human evolution has left the species subject to aggressive, instinctual drives. These compel humanity to consume resources, extend longevity, and to reproduce—in part, the very motives that led to the development of technological society. It seems likely that intelligent extraterrestrial life would evolve in a similar fashion and thus face the same possibility of self-destruction. And yet, to provide a good answer to Fermi's Question, self-destruction by technological species would have to be a near universal occurrence.
This argument does not require the civilization to entirely self-destruct, only to become once again non-technological. In other ways it could persist and even thrive according to evolutionary standards, which postulate producing offspring as the sole goal of life—not "progress", be it in terms of technology or even intelligence.
It is the nature of intelligent life to destroy others
Another possibility is that an intelligent species beyond a certain point of technological capability will destroy other intelligence as it appears, as is exemplified by the theorised extermination of Neanderthals by early man. The idea that someone, or something, is destroying intelligent life in the universe has been well explored in science fictionScience fiction
Science fiction is a genre of fiction dealing with imaginary but more or less plausible content such as future settings, futuristic science and technology, space travel, aliens, and paranormal abilities...
and scientific literature. A species might undertake such extermination out of expansionist motives, paranoia, or simple aggression. In 1981, cosmologist Edward Harrison
Edward Robert Harrison
Edward R. Harrison was a British astronomer and cosmologist, who spent much of his career at the University of Massachusetts and University of Arizona...
argued that such behavior would be an act of prudence: an intelligent species that has overcome its own self-destructive tendencies might view any other species bent on galactic expansion as a kind of virus. It has also been suggested that a successful alien species would be a superpredator, as is Homo sapiens.
This hypothesis requires at least one civilization to have arisen in the past, and the first civilization would not have faced this problem. However, it could still be that Earth is alone now. Like exploration, the extermination of other civilizations might be carried out with self-replicating spacecraft. Under such a scenario, even if a civilization that created such machines were to disappear, the probes could outlive their creators, destroying civilizations far into the future.
If true, this argument reduces the number of visible civilizations in two ways—by destroying some civilizations, and forcing others to remain quiet, under fear of discovery (see They choose not to interact with us) so we would see no signs of them.
Life is periodically destroyed by naturally occurring events
On Earth, there have been numerous major extinction events that destroyed the majority of complex species alive at the time. The extinction of the dinosaurs is the best known example. These are believed to be caused by events such as impact from a large meteorite, massive volcanic eruptions, or astronomical events such as gamma ray burstGamma ray burst
Gamma-ray bursts are flashes of gamma rays associated with extremely energetic explosions that have been observed in distant galaxies. They are the most luminous electromagnetic events known to occur in the universe. Bursts can last from ten milliseconds to several minutes, although a typical...
s. It may be the case that such extinction events are common throughout the universe and periodically destroy intelligent life (or at least destroy their civilizations) before the species is able to develop the technology to communicate with other species.
Human beings were created alone
Religious and philosophical speculation about extraterrestrial intelligent life long predates modern scientific inquiry into the subject. The Greek philosopher EpicurusEpicurus
Epicurus was an ancient Greek philosopher and the founder of the school of philosophy called Epicureanism.Only a few fragments and letters remain of Epicurus's 300 written works...
(4th century BC) suggested that there may be other inhabited worlds. Some religious thinkers, including the Jewish rationalist commentator Rabbi Hasdai Crescas
Hasdai Crescas
Hasdai ben Judah Crescas was a Jewish philosopher and a renowned halakhist...
(c. 1340–1410/1411) and the Christian philosopher Nicholas of Cusa
Nicholas of Cusa
Nicholas of Kues , also referred to as Nicolaus Cusanus and Nicholas of Cusa, was a cardinal of the Catholic Church from Germany , a philosopher, theologian, jurist, mathematician, and an astronomer. He is widely considered one of the great geniuses and polymaths of the 15th century...
(1401–1464), also put forward their views of the possibility of such extraterrestrial intelligence. On the other hand, some strains within Western religious traditions claim that human beings are unique in the divine plan and counsel against belief in intelligent life on other worlds.
Religious reasons for doubting the existence of extraterrestrial intelligent life resemble some forms of the Rare Earth Hypothesis
Rare Earth hypothesis
In planetary astronomy and astrobiology, the Rare Earth hypothesis argues that the emergence of complex multicellular life on Earth required an improbable combination of astrophysical and geological events and circumstances...
. The argument here would be a teleological form of the strong anthropic principle
Anthropic principle
In astrophysics and cosmology, the anthropic principle is the philosophical argument that observations of the physical Universe must be compatible with the conscious life that observes it. Some proponents of the argument reason that it explains why the Universe has the age and the fundamental...
: the universe was designed for the express purpose of creating human (and only human) intelligence. This argument presupposes that a prior advanced intelligence existed in order to create human life, which might pose the question whether that intelligence was the only one to exist before it created us, but the perspective is a philosophical and abstract one.
Inflation theory and the Youngness Argument
Cosmologist Alan GuthAlan Guth
Alan Harvey Guth is an American theoretical physicist and cosmologist. Guth has researched elementary particle theory...
proposed a multi-verse solution to the Fermi Paradox. In this theory, using the synchronous gauge probability distribution, young universes exceedingly outnumber older ones (by a factor of e1037 for every second of age). Therefore, averaged over all universes, universes with civilizations will almost always have just one, the first to develop. However, Guth notes "Perhaps this argument explains why SETI has not found any signals from alien civilizations, but I find it more plausible that it is merely a symptom that the synchronous gauge probability distribution is not the right one."
Notably, however, in the interest of this topic, SETI
SETI
The search for extraterrestrial intelligence is the collective name for a number of activities people undertake to search for intelligent extraterrestrial life. Some of the most well known projects are run by the SETI Institute. SETI projects use scientific methods to search for intelligent life...
received at least one questionably intelligent signal known as the Wow! signal
Wow! signal
The Wow! signal was a strong narrowband radio signal detected by Dr. Jerry R. Ehman on August 15, 1977, while working on a SETI project at the Big Ear radio telescope of The Ohio State University then located at Ohio Wesleyan University's Perkins Observatory, Delaware, Ohio. The signal bore...
in 1977.
They do exist, but we see no evidence
It may be that technological extraterrestrial civilizations exist, but that human beings cannot communicate with them because of constraints: problems of scale or of technology; because they do not wish to communicate or their nature is simply too alien for meaningful communication, or perhaps even be recognized as technology.Intelligent civilizations are too far apart in space or time

Bracewell probe
A Bracewell probe is a hypothetical concept for an autonomous interstellar space probe dispatched for the express purpose of communication with one or more alien civilizations. It was proposed by Ronald N...
. In this case at least one partner in the exchange may obtain meaningful information. Alternatively, a civilization may simply broadcast its knowledge, and leave it to the receiver to make what they may of it. This is similar to the transmission of information from ancient civilizations to the present, and humanity has undertaken similar activities like the Arecibo message
Arecibo message
The Arecibo message was broadcast into space a single time via frequency modulated radio waves at a ceremony to mark the remodeling of the Arecibo radio telescope on 16 November 1974. It was aimed at the globular star cluster M13 some 25,000 light years away because M13 was a large and close...
, which could transfer information about Earth's intelligent species, even if it never yields a response (or does not yield a response in time for humanity to receive it). It is also possible that archaeological
Archaeology
Archaeology, or archeology , is the study of human society, primarily through the recovery and analysis of the material culture and environmental data that they have left behind, which includes artifacts, architecture, biofacts and cultural landscapes...
evidence of past civilizations may be detected through deep space observations—especially if they left behind large artifacts such as Dyson sphere
Dyson sphere
A Dyson sphere is a hypothetical megastructure originally described by Freeman Dyson. Such a "sphere" would be a system of orbiting solar power satellites meant to completely encompass a star and capture most or all of its energy output...
s.
The problem of distance is compounded by the fact that timescales affording a "window of opportunity" for detection or contact might be quite small. Advanced civilizations may periodically arise and fall throughout our galaxy
Galaxy
A galaxy is a massive, gravitationally bound system that consists of stars and stellar remnants, an interstellar medium of gas and dust, and an important but poorly understood component tentatively dubbed dark matter. The word galaxy is derived from the Greek galaxias , literally "milky", a...
, but this may be such a rare event, relatively speaking, that the odds of two or more such civilizations existing at the same time are low. There may have been intelligent civilizations in the galaxy before the emergence of intelligence on Earth, and there may be intelligent civilizations after its extinction, but it is possible that human beings are the only intelligent civilization in existence now. The term "now" is somewhat complicated by the finite speed of light
Speed of light
The speed of light in vacuum, usually denoted by c, is a physical constant important in many areas of physics. Its value is 299,792,458 metres per second, a figure that is exact since the length of the metre is defined from this constant and the international standard for time...
and the nature of spacetime
Spacetime
In physics, spacetime is any mathematical model that combines space and time into a single continuum. Spacetime is usually interpreted with space as being three-dimensional and time playing the role of a fourth dimension that is of a different sort from the spatial dimensions...
under relativity. Assuming that an extraterrestrial intelligence is not able to travel to our vicinity at faster-than-light
Faster-than-light
Faster-than-light communications and travel refer to the propagation of information or matter faster than the speed of light....
speeds, in order to detect an intelligence 1,000 light-years distant, that intelligence will need to have been active 1,000 years ago. Strictly speaking, only the portions of the universe lying within the past light cone
Light cone
A light cone is the path that a flash of light, emanating from a single event and traveling in all directions, would take through spacetime...
of Earth need be considered, since any civilizations outside it could not be detected.
A related argument holds that other civilizations exist, and are transmitting and exploring, but their signals and probes simply have not arrived yet. However, critics have noted that this is unlikely, since it requires that humanity's advancement has occurred at a very special point in time, while the Milky Way
Milky Way
The Milky Way is the galaxy that contains the Solar System. This name derives from its appearance as a dim un-resolved "milky" glowing band arching across the night sky...
is in transition from empty to full. This is a tiny fraction of the life of a galaxy under ordinary assumptions and calculations resulting from them, so the likelihood that we're in the midst of this transition is considered low in the paradox. Work on the theory of Neocatastrophism
Neocatastrophism
Neocatastrophism is the theory that life-exterminating events such as gamma-ray bursts have acted as a galactic regulation mechanism in the Milky Way upon the emergence of complex life in its habitable zone...
, wherein galactic and even super-galactic dynamics are seen as possibly frequently injurious to extant biospheres in a way that is roughly analogous to the way geological
Geology
Geology is the science comprising the study of solid Earth, the rocks of which it is composed, and the processes by which it evolves. Geology gives insight into the history of the Earth, as it provides the primary evidence for plate tectonics, the evolutionary history of life, and past climates...
and climatological
Climate
Climate encompasses the statistics of temperature, humidity, atmospheric pressure, wind, rainfall, atmospheric particle count and other meteorological elemental measurements in a given region over long periods...
catastrophes have occasionally set back biological
Biology
Biology is a natural science concerned with the study of life and living organisms, including their structure, function, growth, origin, evolution, distribution, and taxonomy. Biology is a vast subject containing many subdivisions, topics, and disciplines...
developments on Earth
Earth
Earth is the third planet from the Sun, and the densest and fifth-largest of the eight planets in the Solar System. It is also the largest of the Solar System's four terrestrial planets...
, might be given as a partial, if not full, resolution to the paradox, as advanced species might well be fragile to major events at a pace that would argue against a short transition.
It is too expensive to spread physically throughout the galaxy
Many assumptions about the ability of an alien culture to colonize other stars are based on the idea that interstellar travel is technologically feasible. While the current understanding of physics rules out the possibility of faster than light travel, it appears that there are no major theoretical barriers to the construction of "slow" interstellar ships. This idea underlies the concept of the Von Neumann probe
Von Neumann probe
The idea of self-replicating spacecraft has been applied — in theory — to several distinct "tasks". The particular variant of this idea applied to the idea of space exploration is known as a von Neumann probe...
and the Bracewell probe
Bracewell probe
A Bracewell probe is a hypothetical concept for an autonomous interstellar space probe dispatched for the express purpose of communication with one or more alien civilizations. It was proposed by Ronald N...
as evidence of extraterrestrial intelligence.
It is possible, however, that present scientific knowledge cannot properly gauge the feasibility and costs of such interstellar colonization. Theoretical barriers may not yet be understood and the cost of materials and energy for such ventures may be so high as to make it unlikely that any civilization could afford to attempt it. Even if interstellar travel and colonization are possible, they may be difficult, leading to a colonization model based on percolation theory
Percolation theory
In mathematics, percolation theory describes the behavior of connected clusters in a random graph. The applications of percolation theory to materials science and other domains are discussed in the article percolation.-Introduction:...
. Colonization efforts may not occur as an unstoppable rush, but rather as an uneven tendency to "percolate" outwards, within an eventual slowing and termination of the effort given the enormous costs involved and the fact that colonies will inevitably develop a culture and civilization of their own. Colonization may thus occur in "clusters," with large areas remaining uncolonized at any one time.
A similar argument holds that interstellar physical travel may be possible, but is much more expensive than interstellar communication. Furthermore, to an advanced civilization, travel itself may be replaced by communication, through mind uploading and similar technologies. Therefore the first civilization may have physically explored or colonized the galaxy, but subsequent civilizations find it cheaper, faster, and easier to travel and get information through contacting existing civilizations rather than physically exploring or traveling themselves. In this scenario, since there is little or no physical travel, and directed communications are hard to see except to the intended receiver, there could be many technical and interacting civilizations with few signs visible across interstellar distances.
Human beings have not been searching long enough
Humanity's ability to detect and comprehend intelligent extraterrestrial life has existed for only a very brief period—from 1937 onwards, if the invention of the radio telescope
Radio telescope
A radio telescope is a form of directional radio antenna used in radio astronomy. The same types of antennas are also used in tracking and collecting data from satellites and space probes...
is taken as the dividing line—and Homo sapiens is a geologically recent species. The whole period of modern human existence to date (about 200,000 years
Human evolution
Human evolution refers to the evolutionary history of the genus Homo, including the emergence of Homo sapiens as a distinct species and as a unique category of hominids and mammals...
) is a very brief period on a cosmological scale, while radio
Radio
Radio is the transmission of signals through free space by modulation of electromagnetic waves with frequencies below those of visible light. Electromagnetic radiation travels by means of oscillating electromagnetic fields that pass through the air and the vacuum of space...
transmissions have only been propagated since 1895. Thus it remains possible that human beings have neither been searching long enough to find other intelligences, nor been in existence long enough to be found.
One million years ago there would have been no humans for any extraterrestrial emissaries to meet. For each further step back in time, there would have been increasingly fewer indications to such emissaries that intelligent life would develop on Earth. In a large and already ancient universe, a space-faring alien species may well have had many other more promising worlds to visit and revisit. Even if alien emissaries visited in more recent times, they may have been interpreted by early human cultures as supernatural
Supernatural
The supernatural or is that which is not subject to the laws of nature, or more figuratively, that which is said to exist above and beyond nature...
entities.
This hypothesis is more plausible if alien civilizations tend to stagnate or die out, rather than expand. In addition, "the probability of a site never being visited, even [with an] infinite time limit, is a non-zero value." Thus, even if intelligent life expands elsewhere, it remains statistically possible that such extraterrestrial life might never discover Earth.
Humans are not listening properly
There are some assumptions that underlie the SETI
SETI
The search for extraterrestrial intelligence is the collective name for a number of activities people undertake to search for intelligent extraterrestrial life. Some of the most well known projects are run by the SETI Institute. SETI projects use scientific methods to search for intelligent life...
search programs that may cause searchers to miss signals that are present. For example, the radio searches to date would completely miss highly compressed
Data compression
In computer science and information theory, data compression, source coding or bit-rate reduction is the process of encoding information using fewer bits than the original representation would use....
data streams (which would be almost indistinguishable from "white noise
White noise
White noise is a random signal with a flat power spectral density. In other words, the signal contains equal power within a fixed bandwidth at any center frequency...
" to anyone who did not understand the compression algorithm). Extraterrestrials might also use frequencies that scientists have decided are unlikely to carry signals, or do not penetrate our atmosphere, or use modulation
Modulation
In electronics and telecommunications, modulation is the process of varying one or more properties of a high-frequency periodic waveform, called the carrier signal, with a modulating signal which typically contains information to be transmitted...
strategies that are not being looked for. The signals might be at a datarate that is too fast for our electronics to handle, or too slow to be recognised as attempts at communication. "Simple" broadcast techniques might be employed, but sent from non-main sequence
Main sequence
The main sequence is a continuous and distinctive band of stars that appears on plots of stellar color versus brightness. These color-magnitude plots are known as Hertzsprung–Russell diagrams after their co-developers, Ejnar Hertzsprung and Henry Norris Russell...
stars which are searched with lower priority; current programs assume that most alien life will be orbiting Sun-like stars.
The greatest problem is the sheer size of the radio search needed to look for signals (effectively spanning the entire visible universe), the limited amount of resources committed to SETI, and the sensitivity of modern instruments. SETI estimates, for instance, that with a radio telescope as sensitive as the Arecibo Observatory
Arecibo Observatory
The Arecibo Observatory is a radio telescope near the city of Arecibo in Puerto Rico. It is operated by SRI International under cooperative agreement with the National Science Foundation...
, Earth's television and radio broadcasts would only be detectable at distances up to 0.3 light years. Clearly detecting an Earth type civilization at great distances is difficult. A signal is much easier to detect if the signal energy is limited to either a narrow range of frequencies (Narrowband
Narrowband
In radio, narrowband describes a channel in which the bandwidth of the message does not significantly exceed the channel's coherence bandwidth. It is a common misconception that narrowband refers to a channel which occupies only a "small" amount of space on the radio spectrum.The opposite of...
transmissions), and/or directed at a specific part of the sky. Such signals can be detected at ranges of hundreds to tens of thousands of light-years distance. However this means that detectors must be listening to an appropriate range of frequencies, and be in that region of space to which the beam is being sent. Many SETI searches, starting with the venerable Project Cyclops
Project Cyclops
Project Cyclops was a 1971 NASA project that investigated how SETI should be conducted. As a NASA product the report is in the public domain. The project team created a design for coordinating large numbers of radio telescopes to search for Earth-like radio signals at a distance of up to 1000...
, go so far as to assume that extraterrestrial civilizations will be broadcasting a deliberate signal (like the Arecibo message
Arecibo message
The Arecibo message was broadcast into space a single time via frequency modulated radio waves at a ceremony to mark the remodeling of the Arecibo radio telescope on 16 November 1974. It was aimed at the globular star cluster M13 some 25,000 light years away because M13 was a large and close...
), in order to be found.
Thus to detect alien civilizations through their radio emissions, Earth observers either need more sensitive instruments or must hope for fortuitous circumstances: that the broadband radio emissions of alien radio technology are much stronger than our own; that one of SETI's programs is listening to the correct frequencies from the right regions of space; or that aliens are sending focused transmissions such as the Arecibo message in our general direction.
Civilizations only broadcast detectable radio signals for a brief period of time
It may be that alien civilizations are detectable through their radio emissions for only a short time, reducing the likelihood of spotting them. There are two possibilities in this regard: civilizations outgrow radio through technological advance or, conversely, resource depletion cuts short the time in which a species broadcasts.
The first idea, that civilizations advance beyond radio
Radio
Radio is the transmission of signals through free space by modulation of electromagnetic waves with frequencies below those of visible light. Electromagnetic radiation travels by means of oscillating electromagnetic fields that pass through the air and the vacuum of space...
, is based in part on the "fiber optic
Optical fiber
An optical fiber is a flexible, transparent fiber made of a pure glass not much wider than a human hair. It functions as a waveguide, or "light pipe", to transmit light between the two ends of the fiber. The field of applied science and engineering concerned with the design and application of...
objection": the use of high power radio with low-to-medium gain (i.e., non-directional) antennas for long-distance transmission is wasteful of spectrum, yet this "waste" is precisely what makes these systems conspicuous at interstellar distances. Humans are moving to directional or guided transmission channels such as electrical cables, optical fibers, narrow-beam microwave
Microwave
Microwaves, a subset of radio waves, have wavelengths ranging from as long as one meter to as short as one millimeter, or equivalently, with frequencies between 300 MHz and 300 GHz. This broad definition includes both UHF and EHF , and various sources use different boundaries...
and laser
Laser
A laser is a device that emits light through a process of optical amplification based on the stimulated emission of photons. The term "laser" originated as an acronym for Light Amplification by Stimulated Emission of Radiation...
s, and conventional radio with non-directional antennas is increasingly reserved for low-power, short-range applications such as cell phones
Mobile phone
A mobile phone is a device which can make and receive telephone calls over a radio link whilst moving around a wide geographic area. It does so by connecting to a cellular network provided by a mobile network operator...
and Wi-Fi
Wi-Fi
Wi-Fi or Wifi, is a mechanism for wirelessly connecting electronic devices. A device enabled with Wi-Fi, such as a personal computer, video game console, smartphone, or digital audio player, can connect to the Internet via a wireless network access point. An access point has a range of about 20...
networks. These signals are far less detectable from space. Analog television, developed in the mid-twentieth century, contains strong carriers
Carrier wave
In telecommunications, a carrier wave or carrier is a waveform that is modulated with an input signal for the purpose of conveying information. This carrier wave is usually a much higher frequency than the input signal...
to aid reception and demodulation. Carriers are spectral lines that are very easily detected yet do not convey any information beyond their highly artificial nature. Nearly every SETI project is looking for carriers for just this reason, and UHF TV carriers are the most conspicuous and artificial signals from Earth that could be detected at interstellar distances. But advances in technology are replacing analog TV with digital television
Digital television
Digital television is the transmission of audio and video by digital signals, in contrast to the analog signals used by analog TV...
which uses spectrum more efficiently precisely by eliminating or reducing components such as carriers that make them so conspicuous. Using our own experience as an example, we could set the date of radio-visibility for Earth as December 12, 1901, when Guglielmo Marconi
Guglielmo Marconi
Guglielmo Marconi was an Italian inventor, known as the father of long distance radio transmission and for his development of Marconi's law and a radio telegraph system. Marconi is often credited as the inventor of radio, and indeed he shared the 1909 Nobel Prize in Physics with Karl Ferdinand...
sent radio signals from Cornwall, England, to Newfoundland, Canada. Visibility is now ending, or at least becoming orders of magnitude more difficult, as analog TV is being phased out
Digital television transition
The digital television transition is the process in which analog television broadcasting is converted to and replaced by digital television. This primarily involves both TV stations and over-the-air viewers; however it also involves content providers like TV networks, and cable television...
. And so, if our experience is typical, a civilization remains radio-visible for approximately a hundred years. So a civilization may have been very visible from 1325 to 1483, but we were just not listening at that time. This is essentially the solution, "Everyone is listening, no one is sending."
More hypothetically, advanced alien civilizations evolve beyond broadcasting at all in the electromagnetic spectrum and communicate by principles of physics we don't yet understand. Some scientists have hypothesized that advanced civilizations may send neutrino
Neutrino
A neutrino is an electrically neutral, weakly interacting elementary subatomic particle with a half-integer spin, chirality and a disputed but small non-zero mass. It is able to pass through ordinary matter almost unaffected...
signals. If such signals exist they could be detectable by neutrino detector
Neutrino detector
A neutrino detector is a physics apparatus designed to study neutrinos. Because neutrinos are only weakly interacting with other particles of matter, neutrino detectors must be very large in order to detect a significant number of neutrinos. Neutrino detectors are often built underground to isolate...
s that are now under construction. If stable wormholes could be created and used for communications then interstellar broadcasts would become largely redundant. Thus it may be that other civilizations would only be detectable for a relatively short period of time between the discovery of radio and the switch to more efficient technologies.
One counter to this argument is that although broadcast communication may become difficult to detect, other uses for radio such as radar and power transmission cannot be replaced by low power technologies or fiber optics. These will potentially remain visible even after broadcast emission are replaced by less observable technology.
A different argument is that resource depletion will soon result in a decline in technological capability. Human civilization has been capable of interstellar radio communication for only a few decades and is already rapidly depleting fossil fuels and confronting possible problems such as peak oil
Peak oil
Peak oil is the point in time when the maximum rate of global petroleum extraction is reached, after which the rate of production enters terminal decline. This concept is based on the observed production rates of individual oil wells, projected reserves and the combined production rate of a field...
. It may only be a few more decades before energy becomes too expensive, and the necessary electronics and computers too difficult to manufacture, for us to continue the search. If the same conditions regarding energy supplies hold true for other civilizations, then radio technology may be a short-lived phenomenon. Unless two civilizations happen to be near each other and develop the ability to communicate at the same time it would be virtually impossible for any one civilization to "talk" to another.
Critics of the resource depletion argument point out that alternate energy sources exist, such as solar power, which are renewable and have enormous potential relative to technical barriers. For depletion of fossil fuels to end the "technological phase" of a civilization, some form of technological regression would have to invariably occur, preventing the exploitation of renewable energy
Renewable energy
Renewable energy is energy which comes from natural resources such as sunlight, wind, rain, tides, and geothermal heat, which are renewable . About 16% of global final energy consumption comes from renewables, with 10% coming from traditional biomass, which is mainly used for heating, and 3.4% from...
sources.
They tend to experience a technological singularity
Another possibility is that technological civilizations invariably experience a technological singularity
Technological singularity
Technological singularity refers to the hypothetical future emergence of greater-than-human intelligence through technological means. Since the capabilities of such an intelligence would be difficult for an unaided human mind to comprehend, the occurrence of a technological singularity is seen as...
and attain a posthuman
Posthuman
Posthuman may refer to:*Posthuman, a hypothetical future being whose basic capacities so radically exceed those of present humans as to be no longer human by our current standards...
(or more properly, post-biological) character. Theoretical civilizations of this sort may have altered drastically enough to render communication impossible. The intelligences of a post-singularity civilization might require more information exchange than is possible through interstellar communication, for example. Or perhaps any information humanity might provide would appear elementary, and thus they do not try to communicate, any more than human beings attempt to talk to ants—even though we do ascribe a form of intelligence to them.
Even more extreme forms of post-singularity have been suggested, particularly in fiction: beings that divest themselves of physical form, create massive artificial virtual environments, transfer themselves into these environments through mind uploading, and exist totally within virtual worlds, ignoring the external physical universe. Surprisingly early treatments, such as Lewis Padgett
Lewis Padgett
Lewis Padgett was the joint pseudonym of the science fiction authors and spouses Henry Kuttner and C. L. Moore, taken from their mothers' maiden names. They also used the pseudonyms Lawrence O'Donnell and C. H...
's short story Mimsy were the Borogoves
Mimsy Were the Borogoves
"Mimsy Were the Borogoves" is a science fiction short story by Lewis Padgett that was originally published in the February 1943 issue of Astounding Science Fiction Magazine...
(1943), suggest a migration of advanced beings out of the presently known physical universe into a different and presumably more agreeable alternative one.
A further argument, suggested by Charles Stross
Charles Stross
Charles David George "Charlie" Stross is a British writer of science fiction, Lovecraftian horror and fantasy. He was born in Leeds.Stross specialises in hard science fiction and space opera...
in Accelerando
Accelerando (novel)
Accelerando is a 2005 science fiction novel consisting of a series of interconnected short stories by British author Charles Stross. As well as normal hardback and paperback editions, it was released as a free e-book under the Creative Commons attribution-noncommercial-no derivatives license...
, is that although advanced virtual civilizations - possibly en route developmentally to a Matrioshka Brain
Matrioshka brain
A matrioshka brain is a hypothetical megastructure proposed by Robert Bradbury, based on the Dyson sphere, of immense computational capacity. It is an example of a Class B stellar engine, employing the entire energy output of a star to drive computer systems...
- could engage in travel to other star systems, they choose not to. This is not due to a lack of curiosity, but more through a set of energy-information economic choices, whereby in an information market predicated on available solar energy and planetary matter for building more computing capacity, the most successful virtual intelligences have to remain central to the star. Energy and proximity (and therefore wireless communication bandwidth and speed) are much greater closer to the matter and energy sources of the star, and larger planets, and so to be successful requires intra-solar-system focus. In this scenario, economic incentives to travel out of the solar system are inhibited.
One version of this perspective, which makes predictions for future SETI findings of transcension "fossils" and includes a variation of the Zoo hypothesis below, has been proposed by singularity scholar John Smart
John Smart (futurist)
John Smart is a futurist and scholar of accelerating change. He is founder and president of the Acceleration Studies Foundation, an organization that does “outreach, education, research, and advocacy with respect to issues of accelerating change.”. Smart has an MS in futures studies from the...
.
They are too alien
Another possibility is that human theoreticians have underestimated how much alien life might differ from that on Earth. Aliens may be psychologically unwilling to attempt to communicate with human beings. Perhaps human mathematics
Mathematics
Mathematics is the study of quantity, space, structure, and change. Mathematicians seek out patterns and formulate new conjectures. Mathematicians resolve the truth or falsity of conjectures by mathematical proofs, which are arguments sufficient to convince other mathematicians of their validity...
is parochial to Earth and not shared by other life, though others argue this can only apply to abstract math since the math associated with physics must be similar (in results, if not in methods.)
Physiology might also cause a communication barrier. In Contact
Contact (novel)
Contact is a science fiction novel written by Carl Sagan and published in 1985. It deals with the theme of contact between humanity and a more technologically advanced, extraterrestrial life form. It ranked No. 7 on the 1985 U.S. bestseller list....
, Carl Sagan briefly speculated that an alien species might have a thought process orders of magnitude slower (or faster) than humans. Such a species could conceivably speak so slowly that it requires years to say even a simple phrase like "Hello". A message broadcast by that species might well seem like random background noise to humans, and therefore go undetected.
They are non-technological
It is not clear that a civilization of intelligent beings must be technological. If alien species do not develop technology, because it is difficult in its environment, because it chooses not to, or for any other reason, they will be very hard for human beings to detect. Intelligence alone, as opposed to life, is not necessarily visible across interstellar distances. While there are remote sensing techniques which could perhaps detect life-bearing planets, none of them has any ability to distinguish intelligent but non-technical life from non-intelligent life. Not even any theoretical methods for doing so have been proposed, short of an actual physical visit by an astronaut or probe. This is sometimes referred to as the "algae vs. alumnae" problem.
The evidence is being suppressed
It is theoretically possible that SETI groups are not reporting positive detections, or governments have been blocking extraterrestrial signals or suppressing publication of detections, perhaps in response to National Security and Trade Interests from the potential use of advanced extraterrestrial technology or weapons. It has been suggested that the detection of an extraterrestrial radio signal or technology could well be the most highly classified military information that exists. Claims that this has already happened are common in the popular press, but the scientists involved report the opposite experience – the press becomes informed and interested in a potential detection even before a signal can be confirmed.
They choose not to interact with us
In these scenarios, alien civilizations exist that are technically capable of contacting Earth, but explicitly choose not to do so.This is the official position of the Earth today; we listen (SETI
SETI
The search for extraterrestrial intelligence is the collective name for a number of activities people undertake to search for intelligent extraterrestrial life. Some of the most well known projects are run by the SETI Institute. SETI projects use scientific methods to search for intelligent life...
), but except for a few small efforts, do not explicitly transmit
Active SETI
Active SETI is the attempt to send messages to intelligent aliens. Active SETI messages are usually in the form of radio signals. Physical messages like that of the Pioneer plaque may also be considered an active SETI message...
.
Of course if all, or even most, civilizations act the same way, the galaxy could be full of civilizations eager for contact, but everyone is listening and no-one is transmitting. This is the so-called SETI Paradox.
They don't agree among themselves
The official earth policy among the SETI community is "No response to a signal or other evidence of extraterrestrial intelligence should be sent until appropriate international consultations have taken place.". However, given the possible impact of any reply it may be very difficult to obtain any consensus on "Who speaks for Earth?" and "What should we say?". Other civilizations might suffer from this same lack of consensus, and therefore send no messages at all.
Earth is purposely isolated (The zoo hypothesis)
It is possible that the belief that alien races would communicate with the human species is merely an assumption, and that alien civilizations may not wish to communicate, even if they have the technical ability. A particular reason that alien civilizations may choose not to communicate is the so-called Zoo hypothesis: the idea that alien civilizations avoid contact with Earth so as not to interfere with our development, or to preserve an isolated "zoo or wilderness area". It may be helpful for some readers to think of this as aliens following their own version of Star Trek's Prime Directive
Prime Directive
In the universe of Star Trek, the Prime Directive, Starfleet's General Order #1, is the most prominent guiding principle of the United Federation of Planets...
.
Many other reasons that an alien race might avoid contact have been proposed. Aliens might only choose to allow contact once the human race has passed certain ethical, political, or technological standards, e.g., ending poverty/war or being able to master interstellar travel. They may not want to interfere with our natural independent progress,For an example from popular culture, see the Prime Directive of Star Trek
Star Trek
Star Trek is an American science fiction entertainment franchise created by Gene Roddenberry. The core of Star Trek is its six television series: The Original Series, The Animated Series, The Next Generation, Deep Space Nine, Voyager, and Enterprise...
or the Earth may have been set up as an explicit experiment that contact would ruin.
These ideas are perhaps most plausible if there is a single alien civilization within contact range, or there is a relatively universal cultural or legal policy amongst more advanced lifeforms necessitating isolation with respect to civilizations at Earth-like stages of development. If there is a plurality of alien cultures, however, this theory may break down under the uniformity of motive
Uniformity of motive
In astrobiology, the Uniformity of Motive theory suggests that any civilization in the universe would go through similar technological steps in their development...
flaw: all it takes is a single culture or civilization to decide to act contrary to the imperative within our range of detection for it to be abrogated, and the probability of such a violation increases with the number of civilizations. This idea, and many others, becomes more plausible if we estimate that our galaxy has only a relatively small number of civilizations, or that all civilizations tend to evolve similar cultural values in regard to contact, or that all civilizations follow the lead of some particularly distinguished civilization (a hegemony
Hegemony
Hegemony is an indirect form of imperial dominance in which the hegemon rules sub-ordinate states by the implied means of power rather than direct military force. In Ancient Greece , hegemony denoted the politico–military dominance of a city-state over other city-states...
).
A related idea is that the perceived universe is a simulated reality
Simulated reality
Simulated reality is the proposition that reality could be simulated—perhaps by computer simulation—to a degree indistinguishable from "true" reality. It could contain conscious minds which may or may not be fully aware that they are living inside a simulation....
. The planetarium hypothesis
Planetarium hypothesis
The planetarium hypothesis, conceived in 2001 by Stephen Baxter, attempts to provide a solution to the Fermi paradox by holding that our astronomical observations represent an illusion, created by a Type III civilization capable of manipulating matter and energy on galactic scales...
holds that beings may have simulated a universe for us that appears to be empty of other life, by design. The simulation argument by Bostrom
Nick Bostrom
Nick Bostrom is a Swedish philosopher at the University of Oxford known for his work on existential risk and the anthropic principle. He holds a PhD from the London School of Economics...
holds that although such a simulation may contain other life, such life cannot be much in advance of us since a far more advanced civilization may be correspondingly hard to simulate. If we treat this matter literally, then the truth is entirely inaccessible, there being an infinite regress
Infinite regress
An infinite regress in a series of propositions arises if the truth of proposition P1 requires the support of proposition P2, the truth of proposition P2 requires the support of proposition P3, .....
problem (See Simulated reality
Simulated reality
Simulated reality is the proposition that reality could be simulated—perhaps by computer simulation—to a degree indistinguishable from "true" reality. It could contain conscious minds which may or may not be fully aware that they are living inside a simulation....
).
It is dangerous to communicate
An alien civilization might feel it is too dangerous to communicate, either for us or for them. After all, when very different civilizations have met on Earth, the results have often been disastrous for one side or the other, and the same may well apply to interstellar contact. Even contact at a safe distance could lead to infection by computer code or even ideas themselves (see meme
Meme
A meme is "an idea, behaviour or style that spreads from person to person within a culture."A meme acts as a unit for carrying cultural ideas, symbols or practices, which can be transmitted from one mind to another through writing, speech, gestures, rituals or other imitable phenomena...
).
Perhaps prudent civilizations actively hide not only from us but from everyone, out of fear of other civilizations.
The Fermi paradox itself is what prevents communication
Perhaps the Fermi paradox itself—or the alien equivalent of it—is the ultimate reason for any civilization to avoid contact with other civilizations, even if no other obstacles existed. From any one civilization's point of view, it would be unlikely for them to be the first ones to make first contact and therefore likely for them to face the same possibly fatal problems that supposedly prevented the earlier civilizations from contacting them. So perhaps every civilization keeps quiet because of the possibility that there is a real reason for others to do so.
They are here unobserved
It may be that intelligent alien life forms not only exist, but are already present here on Earth. They are not detected because they do not wish it, human beings are technically unable to, or because societies refuse to admit to the evidence. Several variations of this idea have been proposed:Carl Sagan
Carl Sagan
Carl Edward Sagan was an American astronomer, astrophysicist, cosmologist, author, science popularizer and science communicator in astronomy and natural sciences. He published more than 600 scientific papers and articles and was author, co-author or editor of more than 20 books...
and Iosif Shklovsky
Iosif Shklovsky
Iosif Samuilovich Shklovsky was a Soviet astronomer and astrophysicist...
argued for serious consideration of "paleocontact" with extraterrestrials in the early historical era, and for examination of myths and religious lore for evidence of such contact. Sagan and Shklovsky noted that many or most religions were founded by men who claimed contact with supernatural entities who bestowed wisdom, guidance and technology, citing the fish-god Oannes as a particularly salient example. On this hypothesis, there is in fact ample evidence of alien visitation – it is simply not recognized as such.
It is possible that a life form technologically advanced enough to travel to Earth might also be sufficiently advanced to exist here undetected. In this view, the aliens have arrived on Earth, or in our solar system, and are observing the planet, while concealing their presence. Observation could conceivably be conducted in a number of ways that would be very difficult to detect. For example, a complex system of microscopic monitoring devices constructed via molecular nanotechnology
Molecular nanotechnology
Molecular nanotechnology is a technology based on the ability to build structures to complex, atomic specifications by means of mechanosynthesis. This is distinct from nanoscale materials...
could be deployed on Earth and remain undetected, or sophisticated instruments could conduct passive monitoring from elsewhere.
UFO researchers note that the Fermi Paradox arose within the context of a wave of UFO reports, yet Fermi, Teller, York and Konopinski apparently dismissed the possibility that flying saucers might be extraterrestrial – despite contemporary US Air Force investigations that judged a small portion of UFO reports as inexplicable by contemporary technology. (Mainstream scientific publications have occasionally addressed the possibility of extraterrestrial contact, but the scientific community in general has given little serious attention to claims of unidentified flying objects.) Given that UFO investigators argue compelling evidence supports the reality of UFOs as anomalies
Anomalistics
Anomalistics is the use of scientific methods to evaluate anomalies , with the aim of finding a rational explanation. The term itself was coined in 1973 by Drew University anthropologist Roger W...
, but that extant UFO evidence does not support an extraterrestrial origin, it is suggested that closer examination of UFO data may confirm or falsify the Fermi paradox and/or the extraterrestrial hypothesis
Extraterrestrial hypothesis
The extraterrestrial hypothesis is the hypothesis that some unidentified flying objects are best explained as being extraterrestrial life or non-human aliens from other planets occupying physical spacecraft visiting Earth.-Etymology:...
of UFO origins: “Any refusal of interest [by mainstream scientists] in investigating the UFO phenomenon, using an ETI [extraterrestrial intelligence] concept as one working hypothesis, should surely be astonishing.”
This extraterrestrial hypothesis was jokingly suggested in response to Fermi's paradox by his fellow physicist, Leó Szilárd
Leó Szilárd
Leó Szilárd was an Austro-Hungarian physicist and inventor who conceived the nuclear chain reaction in 1933, patented the idea of a nuclear reactor with Enrico Fermi, and in late 1939 wrote the letter for Albert Einstein's signature that resulted in the Manhattan Project that built the atomic bomb...
, who suggested to Fermi that extraterrestrials "are already among us—but they call themselves Hungarians", a humorous reference to the peculiar Hungarian language
Hungarian language
Hungarian is a Uralic language, part of the Ugric group. With some 14 million speakers, it is one of the most widely spoken non-Indo-European languages in Europe....
, unrelated to most other languages spoken in Europe.See, for example, George Marx's 1995 lecture, "Conflicts and Creativity – The Hungarian Lesson", which was based on his 1994 book, The Voice of the Martians, Roland Eötvös Physical Society ISBN 9630574276, and his article
See also
- Fermi problemFermi problemIn science, particularly in physics or engineering education, a Fermi problem, Fermi question, or Fermi estimate is an estimation problem designed to teach dimensional analysis, approximation, and the importance of clearly identifying one's assumptions...
- Anthropic principleAnthropic principleIn astrophysics and cosmology, the anthropic principle is the philosophical argument that observations of the physical Universe must be compatible with the conscious life that observes it. Some proponents of the argument reason that it explains why the Universe has the age and the fundamental...
- Interstellar travelInterstellar travelInterstellar space travel is manned or unmanned travel between stars. The concept of interstellar travel in starships is a staple of science fiction. Interstellar travel is much more difficult than interplanetary travel. Intergalactic travel, or travel between different galaxies, is even more...
- Rare Earth HypothesisRare Earth hypothesisIn planetary astronomy and astrobiology, the Rare Earth hypothesis argues that the emergence of complex multicellular life on Earth required an improbable combination of astrophysical and geological events and circumstances...
- The Drake Equation
- Zoo hypothesisZoo hypothesisThe zoo hypothesis is one of a number of suggestions that have been advanced in response to the Fermi paradox, regarding the apparent absence of evidence in support of the existence of advanced extraterrestrial life...
Further reading
- Ben Zuckerman and Michael H. Hart, Extraterrestrials: Where Are They? ISBN 0-521-44803-4 Amazon
- Evolving the Alien: The Science of Extraterrestrial Life
- Documentary "Overcome the Great Silence!"
External links
- SMBC
- Interstellar Radio Messages
- Exotic Civilizations: Possible Answer to Fermi's Paradox by Paul Hughes
- Introduction and Drake equations for the Fermi paradox
- So much space, so little time: why aliens haven't found us yet by Ian Sample,The Guardian January 18, 2007
- The Possibilities of FTL: Or Fermi's Paradox Reconsidered by F.E. Freiheit IV
- Fermi's Paradox (i.e. Where are They?) by James Schombert
- Life in the Universe, by Eric SchulmanEric SchulmanEric Schulman is an American astronomer and science humorist. Schulman received his bachelor's degree from UCLA and his PhD from the University of Michigan. He is the author of A Briefer History of Time: From the Big Bang to the Big Mac and has been a member of the editorial board of the Annals of...
, MercuryMercury (magazine)Mercury is a science magazine that features articles and columns about astronomy for a general audience. It is the bi-monthly magazine of the Astronomical Society of the Pacific and was first published in 1972....
Magazine (May/June to November/December 2000) - Answering the Fermi Paradox: Exploring the Mechanisms of Universal Transcension by John SmartJohn Smart (futurist)John Smart is a futurist and scholar of accelerating change. He is founder and president of the Acceleration Studies Foundation, an organization that does “outreach, education, research, and advocacy with respect to issues of accelerating change.”. Smart has an MS in futures studies from the...
- Extraterrestrial Intelligence in the Solar System: Resolving the Fermi Paradox, which argues that our observations are incomplete, and There Is No Fermi Paradox, arguing that the paradox is based on a logical flaw, both by Robert FreitasRobert FreitasRobert A. Freitas Jr. is a Senior Research Fellow, one of four researchers at the nonprofit foundation Institute for Molecular Manufacturing in Palo Alto, California. He holds a 1974 Bachelor's degree majoring in both physics and psychology from Harvey Mudd College, and a 1978 Juris Doctor degree...
- Fermi Paradox debate Astrobiology Magazine July 2002. Michael Meyer, Frank Drake, Christopher McKay, Donald Brownlee, & David Grinspoon.
- The Fermi Paradox: Back With a Vengeance by George DvorskyGeorge DvorskyGeorge P. Dvorsky is a transhumanist futurist, and author of the Sentient Developments blog. Dvorsky is a co-founder and president of the Toronto Transhumanist Association, and currently serves on the board of directors for Humanity+ and the Institute for Ethics and Emerging Technologies...
. - Virtual Reality Could Explain the Fermi Paradox by Michael Graham Richard
- A list of possible answers to the Fermi paradox (with references to published works discussing some of these options) by Anders SandbergAnders SandbergAnders Sandberg is a researcher, science debater, futurist, transhumanist, and author. He was born in Solna, Sweden. He holds a Ph.D...

