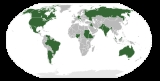
Federation
Encyclopedia
Sovereign state
A sovereign state, or simply, state, is a state with a defined territory on which it exercises internal and external sovereignty, a permanent population, a government, and the capacity to enter into relations with other sovereign states. It is also normally understood to be a state which is neither...
characterized by a union
Political union
A political union is a type of state which is composed of or created out of smaller states. Unlike a personal union, the individual states share a common government and the union is recognized internationally as a single political entity...
of partially self-governing states or regions united by a central (federal) government. In a federation, the self-governing status of the component states is typically constitutionally entrenched and may not be altered by a unilateral
Unilateralism
Unilateralism is any doctrine or agenda that supports one-sided action. Such action may be in disregard for other parties, or as an expression of a commitment toward a direction which other parties may find agreeable...
decision of the central government.
The form of government
Form of government
A form of government, or form of state governance, refers to the set of political institutions by which a government of a state is organized. Synonyms include "regime type" and "system of government".-Empirical and conceptual problems:...
or constitutional structure found in a federation is known as federalism
Federalism
Federalism is a political concept in which a group of members are bound together by covenant with a governing representative head. The term "federalism" is also used to describe a system of the government in which sovereignty is constitutionally divided between a central governing authority and...
(see also federalism as a political philosophy). It can be considered the opposite of another system, the unitary state
Unitary state
A unitary state is a state governed as one single unit in which the central government is supreme and any administrative divisions exercise only powers that their central government chooses to delegate...
. The government of Germany
Germany
Germany , officially the Federal Republic of Germany , is a federal parliamentary republic in Europe. The country consists of 16 states while the capital and largest city is Berlin. Germany covers an area of 357,021 km2 and has a largely temperate seasonal climate...
with sixteen federated Länder
States of Germany
Germany is made up of sixteen which are partly sovereign constituent states of the Federal Republic of Germany. Land literally translates as "country", and constitutionally speaking, they are constituent countries...
is an example of a federation, whereas neighboring Austria
Austria
Austria , officially the Republic of Austria , is a landlocked country of roughly 8.4 million people in Central Europe. It is bordered by the Czech Republic and Germany to the north, Slovakia and Hungary to the east, Slovenia and Italy to the south, and Switzerland and Liechtenstein to the...
and its Bundesländer
States of Austria
Austria is a federal republic made up of nine states, known in German as Länder . Since Land is also the German word for a country, the term Bundesländer is often used instead to avoid ambiguity. The Constitution of Austria uses both terms...
was a unitary state with administrative division
Administrative division
An administrative division, subnational entity, or country subdivision is a portion of a country or other political division, established for the purpose of government. Administrative divisions are each granted a certain degree of autonomy, and are required to manage themselves through their own...
s that became federated, and neighboring France
France
The French Republic , The French Republic , The French Republic , (commonly known as France , is a unitary semi-presidential republic in Western Europe with several overseas territories and islands located on other continents and in the Indian, Pacific, and Atlantic oceans. Metropolitan France...
by contrast has always been unitary.
Federations may be multi-ethnic
Ethnic group
An ethnic group is a group of people whose members identify with each other, through a common heritage, often consisting of a common language, a common culture and/or an ideology that stresses common ancestry or endogamy...
and cover a large area of territory (like extreme diversity in India
India
India , officially the Republic of India , is a country in South Asia. It is the seventh-largest country by geographical area, the second-most populous country with over 1.2 billion people, and the most populous democracy in the world...
), although neither is necessarily the case. Federations are most often founded on an original agreement between a number of sovereign
Sovereignty
Sovereignty is the quality of having supreme, independent authority over a geographic area, such as a territory. It can be found in a power to rule and make law that rests on a political fact for which no purely legal explanation can be provided...
states based on mutual concerns or interests. The initial agreements create a stability that encourages other common interests, brings the disparate territories closer, and gives them all even more common ground. At some time this is recognized and a movement is organized to merge more closely. Other times, especially when common cultural factors are at play such as ethnicity and language, some of these steps in this pattern are expedited and compressed.
The international council for federal countries, the Forum of Federations
Forum of Federations
The Forum of Federations is an international organization based in Ottawa, Canada. The Forum and its partners form a global network on federalism. It brings together elected officials, civil servants and experts in federalism from about 20 countries to learn from each other...
, is based in Ottawa
Ottawa
Ottawa is the capital of Canada, the second largest city in the Province of Ontario, and the fourth largest city in the country. The city is located on the south bank of the Ottawa River in the eastern portion of Southern Ontario...
, Canada
Canada
Canada is a North American country consisting of ten provinces and three territories. Located in the northern part of the continent, it extends from the Atlantic Ocean in the east to the Pacific Ocean in the west, and northward into the Arctic Ocean...
. It helps share best practice
Best practice
A best practice is a method or technique that has consistently shown results superior to those achieved with other means, and that is used as a benchmark...
s among countries with federal systems of government, and currently includes nine countries as partner governments.
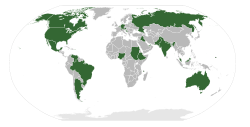
Federations and other forms of state
Federations
In a federation the component states are known as in some sense sovereign, in so far as certain powers are reserved to them that may not be exercised by the central government. However, a federation is more than a mere loose alliance of independent states. The component states of a federation usually possess no powers in relation to foreign policy and so they enjoy no independent status under international lawInternational law
Public international law concerns the structure and conduct of sovereign states; analogous entities, such as the Holy See; and intergovernmental organizations. To a lesser degree, international law also may affect multinational corporations and individuals, an impact increasingly evolving beyond...
.
Some federations are called asymmetric because some states have more autonomy than others. An example of such a federation is Malaysia, in which Sarawak
Sarawak
Sarawak is one of two Malaysian states on the island of Borneo. Known as Bumi Kenyalang , Sarawak is situated on the north-west of the island. It is the largest state in Malaysia followed by Sabah, the second largest state located to the North- East.The administrative capital is Kuching, which...
and Sabah
Sabah
Sabah is one of 13 member states of Malaysia. It is located on the northern portion of the island of Borneo. It is the second largest state in the country after Sarawak, which it borders on its southwest. It also shares a border with the province of East Kalimantan of Indonesia in the south...
entered the federation on different terms and conditions from the states of Peninsular Malaysia
Peninsular Malaysia
Peninsular Malaysia , also known as West Malaysia , is the part of Malaysia which lies on the Malay Peninsula. Its area is . It shares a land border with Thailand in the north. To the south is the island of Singapore. Across the Strait of Malacca to the west lies the island of Sumatra...
.
A federation often emerges from an initial agreement between a number of separate states. The purpose can be the will to solve mutual problems or to provide for mutual defense, or to create a nation state for an ethnicity spread over several states. The former was the case with the United States
United States
The United States of America is a federal constitutional republic comprising fifty states and a federal district...
and Switzerland
Switzerland
Switzerland name of one of the Swiss cantons. ; ; ; or ), in its full name the Swiss Confederation , is a federal republic consisting of 26 cantons, with Bern as the seat of the federal authorities. The country is situated in Western Europe,Or Central Europe depending on the definition....
, the latter with Germany
Germany
Germany , officially the Federal Republic of Germany , is a federal parliamentary republic in Europe. The country consists of 16 states while the capital and largest city is Berlin. Germany covers an area of 357,021 km2 and has a largely temperate seasonal climate...
. However, as the history of countries and nations varies, the federalism system of a state can be quite different from these models. Australia
Australia
Australia , officially the Commonwealth of Australia, is a country in the Southern Hemisphere comprising the mainland of the Australian continent, the island of Tasmania, and numerous smaller islands in the Indian and Pacific Oceans. It is the world's sixth-largest country by total area...
, for instance, is unique in that it came into existence as a nation by the democratic vote of the citizens of each State who voted "yes" in referendums to adopt the Australian Constitution. Brazil
Brazil
Brazil , officially the Federative Republic of Brazil , is the largest country in South America. It is the world's fifth largest country, both by geographical area and by population with over 192 million people...
on the other hand, has experienced both the federal and the unitary state through its history; some present day States of the Federation retain the borders set during Portuguese colonization (i.e. previous to the very existence of Brazilian state), whereas the latest State (Tocantins
Tocantins (state)
Tocantins is one of the states of Brazil. . The state was formed in 1988 out of the northern part of Goiás, and construction began on the capital, Palmas, in 1989, in contrast to most of the other cities in the state which date back to the Portuguese colonial period...
) was created by the 1988 Constitution, chiefly for administrative reasons.
Seven of the top ten largest countries by area are governed as federations.
Unitary states
A unitary stateUnitary state
A unitary state is a state governed as one single unit in which the central government is supreme and any administrative divisions exercise only powers that their central government chooses to delegate...
is sometimes one with only a single, centralised, national tier of government. However, unitary states often also include one or more self-governing regions. The difference between a federation and this kind of unitary state is that in a unitary state the autonomous status of self-governing regions exists by the sufferance of the central government, and may be unilaterally revoked. While it is common for a federation to be brought into being by agreement between a number of formally independent states, in a unitary state self-governing regions are often created through a process of devolution
Devolution
Devolution is the statutory granting of powers from the central government of a sovereign state to government at a subnational level, such as a regional, local, or state level. Devolution can be mainly financial, e.g. giving areas a budget which was formerly administered by central government...
, where a formerly centralised state agrees to grant autonomy to a region that was previously entirely subordinate. Thus federations are often established voluntarily from 'below' whereas devolution grants self-government from 'above'.
It is often part of the philosophy of a unitary state that, regardless of the actual status of any of its parts, its entire territory constitutes a single sovereign entity or nation-state, and that by virtue of this the central government exercises sovereignty over the whole territory as of right. In a federation, on the other hand, sovereignty is often regarded as residing notionally in the component states, or as being shared between these states and the central government.
Other forms of governance
Confederation
A confederationConfederation
A confederation in modern political terms is a permanent union of political units for common action in relation to other units. Usually created by treaty but often later adopting a common constitution, confederations tend to be established for dealing with critical issues such as defense, foreign...
, in modern political terms, is usually limited to a permanent union of sovereign states for common action in relation to other states.
In Belgium
Belgium
Belgium , officially the Kingdom of Belgium, is a federal state in Western Europe. It is a founding member of the European Union and hosts the EU's headquarters, and those of several other major international organisations such as NATO.Belgium is also a member of, or affiliated to, many...
, however, the opposite movement is under way. Belgium
Belgium
Belgium , officially the Kingdom of Belgium, is a federal state in Western Europe. It is a founding member of the European Union and hosts the EU's headquarters, and those of several other major international organisations such as NATO.Belgium is also a member of, or affiliated to, many...
was founded as a centralised state, after the French model, but has gradually been reformed into a federal state by consecutive constitutional reforms since the 1970s. Moreover, although nominally called a federal state, the country's structure already has a number of confederational traits (ex. competences are exclusive for either the federal or the state level, the treaty-making power of the Federating units without almost any possible veto of the Federal Government). At present, there is a growing movement to transform the existing federal state into a looser confederation with two or three constitutive states and/or two special regions.
By definition, the difference between a confederation and a federation is that the membership of the member state
Member state
A member state is a state that is a member of an international organisation.The World Trade Organization has members that are sovereign states and members that are not, thus WTO members are not called member states.- Worldwide :...
s in a confederation is voluntary, while the membership in a federation is not. A confederation is most likely to feature these differences over a federation: (1) No real direct powers: many confederal decisions are externalised by member-state legislation. (2) Decisions on day-to-day-matters are not taken by simple majority but by special majorities or even by consensus or unanimity (veto for every member). (3) Changes of the constitution, usually a treaty, require unanimity.
Over time these terms acquired distinct connotations leading to the present difference in definition. An example of this is the United States under the Articles of Confederation
Articles of Confederation
The Articles of Confederation, formally the Articles of Confederation and Perpetual Union, was an agreement among the 13 founding states that legally established the United States of America as a confederation of sovereign states and served as its first constitution...
. The Articles established a national government under what today would be defined as a federal system (albeit with a comparatively weaker federal government). However, Canada
Canada
Canada is a North American country consisting of ten provinces and three territories. Located in the northern part of the continent, it extends from the Atlantic Ocean in the east to the Pacific Ocean in the west, and northward into the Arctic Ocean...
, designed with a stronger central government than the U.S. in the wake of the Civil War of the latter, has always been called a Confederation by Canadians. Legal reforms, court rulings, and political compromises have somewhat decentralised Canada in practice since its formation in 1867.
Empire
An empireEmpire
The term empire derives from the Latin imperium . Politically, an empire is a geographically extensive group of states and peoples united and ruled either by a monarch or an oligarchy....
is a multi-ethnic state or group of nations with a central government established usually through coercion
Coercion
Coercion is the practice of forcing another party to behave in an involuntary manner by use of threats or intimidation or some other form of pressure or force. In law, coercion is codified as the duress crime. Such actions are used as leverage, to force the victim to act in the desired way...
(on the model of the Roman Empire
Roman Empire
The Roman Empire was the post-Republican period of the ancient Roman civilization, characterised by an autocratic form of government and large territorial holdings in Europe and around the Mediterranean....
). An empire will often include self-governing regions but these will possess autonomy only at the sufferance of the central government. On the other hand, an empire may simply consist of multiple kingdom
Monarchy
A monarchy is a form of government in which the office of head of state is usually held until death or abdication and is often hereditary and includes a royal house. In some cases, the monarch is elected...
s organised together in a federation with a high king
High king
A high king is a king who holds a position of seniority over a group of other kings, without the title of Emperor; compare King of Kings.Rulers who have been termed "high king" include:...
designated as an emperor. One example of this was Imperial Germany.
Federacy
A federacyFederacy
A federacy is a form of government where one or several substate units enjoy considerably more independence than the majority of the substate units. To some extent, such an arrangement can be considered as similar to asymmetric federalism.-Description:...
is essentially an extreme case of an asymmetric federation, either due to large differences in the level of autonomy, or the rigidity of the constitutional arrangements. The use of the term federacy
Federacy
A federacy is a form of government where one or several substate units enjoy considerably more independence than the majority of the substate units. To some extent, such an arrangement can be considered as similar to asymmetric federalism.-Description:...
is more often use to the relation between the sovereign state and its autonomous area
Autonomous area
An autonomous area or autonomous entity is an area of a country that has a degree of autonomy, or freedom from an external authority. Typically it is either geographically distinct from the rest of the country or populated by a national minority. Countries that include autonomous areas are often...
s.
Devolution
A federation differs from a devolved stateDevolution
Devolution is the statutory granting of powers from the central government of a sovereign state to government at a subnational level, such as a regional, local, or state level. Devolution can be mainly financial, e.g. giving areas a budget which was formerly administered by central government...
, such as the United Kingdom
United Kingdom
The United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern IrelandIn the United Kingdom and Dependencies, other languages have been officially recognised as legitimate autochthonous languages under the European Charter for Regional or Minority Languages...
and the Kingdom of Spain, because, in a devolved state, the central government can revoke the independence of the subunits (Scottish Parliament
Scottish Parliament
The Scottish Parliament is the devolved national, unicameral legislature of Scotland, located in the Holyrood area of the capital, Edinburgh. The Parliament, informally referred to as "Holyrood", is a democratically elected body comprising 129 members known as Members of the Scottish Parliament...
, Welsh National Assembly, Northern Ireland Assembly
Northern Ireland Assembly
The Northern Ireland Assembly is the devolved legislature of Northern Ireland. It has power to legislate in a wide range of areas that are not explicitly reserved to the Parliament of the United Kingdom, and to appoint the Northern Ireland Executive...
in the case of the UK) without changing the constitution.
Associated States
A federation also differs from an associated stateAssociated state
An associated state is the minor partner in a formal, free relationship between a political territory with a degree of statehood and a nation, for which no other specific term, such as protectorate, is adopted...
, such as the Federated States of Micronesia
Federated States of Micronesia
The Federated States of Micronesia or FSM is an independent, sovereign island nation, made up of four states from west to east: Yap, Chuuk, Pohnpei and Kosrae. It comprises approximately 607 islands with c...
(in free association with the United States
United States
The United States of America is a federal constitutional republic comprising fifty states and a federal district...
) and Cook Islands
Cook Islands
The Cook Islands is a self-governing parliamentary democracy in the South Pacific Ocean in free association with New Zealand...
and Niue
Niue
Niue , is an island country in the South Pacific Ocean. It is commonly known as the "Rock of Polynesia", and inhabitants of the island call it "the Rock" for short. Niue is northeast of New Zealand in a triangle between Tonga to the southwest, the Samoas to the northwest, and the Cook Islands to...
(which form part of the Realm of New Zealand
Realm of New Zealand
The Realm of New Zealand is the entire area in which the Queen in right of New Zealand is head of state. The Realm comprises New Zealand, the Cook Islands, Niue, Tokelau and the Ross Dependency in Antarctica, and is defined by a 1983 Letters Patent constituting the office of Governor-General of New...
).
There are two kinds of associated states: in case of Micronesia, association is concluded by treaty between two sovereign states; in case of Cook Islands and Niue, association is concluded by domestic legal arrangements.
Crown dependencies
The relation between the Crown dependenciesCrown dependency
The Crown Dependencies are British possessions of the Crown, as opposed to overseas territories of the United Kingdom. They comprise the Channel Island Bailiwicks of Jersey and Guernsey in the English Channel, and the Isle of Man in the Irish Sea....
of the Isle of Man
Isle of Man
The Isle of Man , otherwise known simply as Mann , is a self-governing British Crown Dependency, located in the Irish Sea between the islands of Great Britain and Ireland, within the British Isles. The head of state is Queen Elizabeth II, who holds the title of Lord of Mann. The Lord of Mann is...
and the bailiwicks of Guernsey
Guernsey
Guernsey, officially the Bailiwick of Guernsey is a British Crown dependency in the English Channel off the coast of Normandy.The Bailiwick, as a governing entity, embraces not only all 10 parishes on the Island of Guernsey, but also the islands of Herm, Jethou, Burhou, and Lihou and their islet...
and Jersey
Jersey
Jersey, officially the Bailiwick of Jersey is a British Crown Dependency off the coast of Normandy, France. As well as the island of Jersey itself, the bailiwick includes two groups of small islands that are no longer permanently inhabited, the Minquiers and Écréhous, and the Pierres de Lecq and...
in the Channel Islands
Channel Islands
The Channel Islands are an archipelago of British Crown Dependencies in the English Channel, off the French coast of Normandy. They include two separate bailiwicks: the Bailiwick of Guernsey and the Bailiwick of Jersey...
and the United Kingdom
United Kingdom
The United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern IrelandIn the United Kingdom and Dependencies, other languages have been officially recognised as legitimate autochthonous languages under the European Charter for Regional or Minority Languages...
is very similar to a federate relation: the Islands enjoy independence from the United Kingdom, which, via The Crown, takes care of their foreign relations and defence – although the UK Parliament does have overall power to legislate for the dependencies. However, the islands are neither an incorporated part of the United Kingdom, nor are they considered to be independent or associated states. The Isle of Man
Isle of Man
The Isle of Man , otherwise known simply as Mann , is a self-governing British Crown Dependency, located in the Irish Sea between the islands of Great Britain and Ireland, within the British Isles. The head of state is Queen Elizabeth II, who holds the title of Lord of Mann. The Lord of Mann is...
does not have a monarch, per se; rather, the British Monarch
Monarchy of the United Kingdom
The monarchy of the United Kingdom is the constitutional monarchy of the United Kingdom and its overseas territories. The present monarch, Queen Elizabeth II, has reigned since 6 February 1952. She and her immediate family undertake various official, ceremonial and representational duties...
is, ex officio, Lord of Mann
Lord of Mann
The title Lord of Mann is used on the Isle of Man to refer to Queen Elizabeth II, who is the island's Lord Proprietor and head of state.-Relationship with the Crown:The title is not correctly used on its own...
(irrespective of the incumbent's sex).
Overseas territories
Overseas territories, such as the British overseas territoriesBritish overseas territories
The British Overseas Territories are fourteen territories of the United Kingdom which, although they do not form part of the United Kingdom itself, fall under its jurisdiction. They are remnants of the British Empire that have not acquired independence or have voted to remain British territories...
, are vested with varying degrees of power; some enjoy considerable independence from the sovereign state, which only takes care of their foreign relations and defence. However, they are neither considered to be part of it, nor recognised as sovereign or associated states.
Alleged de facto federations
The distinction between a federation and a unitary state is often quite ambiguous. A unitary state may closely resemble a federation in structure and, while a central government may possess the theoretical right to revoke the autonomy of a self-governing region, it may be politically difficult for it to do so in practice. The self-governing regions of some unitary states also often enjoy greater autonomy than those of some federations. For these reasons, it is sometimes argued that some modern unitary states are de factoDe facto
De facto is a Latin expression that means "concerning fact." In law, it often means "in practice but not necessarily ordained by law" or "in practice or actuality, but not officially established." It is commonly used in contrast to de jure when referring to matters of law, governance, or...
federations.
Spain
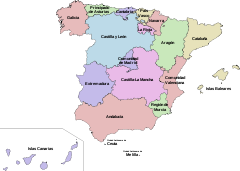
Spain
Spain , officially the Kingdom of Spain languages]] under the European Charter for Regional or Minority Languages. In each of these, Spain's official name is as follows:;;;;;;), is a country and member state of the European Union located in southwestern Europe on the Iberian Peninsula...
is suggested as one possible de facto federation as it grants more self-government to its autonomous communities than most federations allow their constituent parts. For the Spanish parliament to revoke the autonomy of regions such as Galicia, Catalonia
Catalonia
Catalonia is an autonomous community in northeastern Spain, with the official status of a "nationality" of Spain. Catalonia comprises four provinces: Barcelona, Girona, Lleida, and Tarragona. Its capital and largest city is Barcelona. Catalonia covers an area of 32,114 km² and has an...
or the Basque Country
Basque Country (autonomous community)
The Basque Country is an autonomous community of northern Spain. It includes the Basque provinces of Álava, Biscay and Gipuzkoa, also called Historical Territories....
would be a political near-impossibility, though nothing bars it legally. Additionally, some regions such as Navarre
Navarre
Navarre , officially the Chartered Community of Navarre is an autonomous community in northern Spain, bordering the Basque Country, La Rioja, and Aragon in Spain and Aquitaine in France...
or the Basque Country have full control over taxation and spending, transferring a small payment to the central government for the common services (army, foreign relations, macroeconomic policy). For example, one scholar discusses the "federal nature of Spain's government (a trend that almost no one denies)." Each autonomous community is governed by a Statute of Autonomy
Statute of Autonomy
Nominally, a Statute of Autonomy is a law hierarchically located under the constitution of a country, and over any other form of legislation...
(Estatuto de Autonomía) under the Spanish Constitution of 1978.
People's Republic of China
In the People's Republic of ChinaPeople's Republic of China
China , officially the People's Republic of China , is the most populous country in the world, with over 1.3 billion citizens. Located in East Asia, the country covers approximately 9.6 million square kilometres...
, a form of de facto federation has evolved without formal legislation. This has occurred as largely informal grants of power to the provinces, to handle economic affairs and implement national policies. This has resulted in a system some have termed "de facto federalism with Chinese characteristics" (in reference to Deng Xiaoping
Deng Xiaoping
Deng Xiaoping was a Chinese politician, statesman, and diplomat. As leader of the Communist Party of China, Deng was a reformer who led China towards a market economy...
's policy of socialism with Chinese characteristics). Constitutionally, the power vested in the special administrative regions of the People's Republic is granted from the Central People's Government
Central People's Government
The Central People's Government is the central government of the People's Republic of China in Beijing. According to the 1982 Constitution, "Central People's Government" is synonymous with the State Council.-History:...
, through decision by the National People's Congress
National People's Congress
The National People's Congress , abbreviated NPC , is the highest state body and the only legislative house in the People's Republic of China. The National People's Congress is held in the Great Hall of the People, Beijing, capital of the People's Republic of China; with 2,987 members, it is the...
. A Federal Republic of China, in effect the third Chinese Republic, has been proposed as a future replacement for the PRC.
European Union
The European UnionEuropean Union
The European Union is an economic and political union of 27 independent member states which are located primarily in Europe. The EU traces its origins from the European Coal and Steel Community and the European Economic Community , formed by six countries in 1958...
(EU) is based on supranational principles which are neither confederal nor federal. Robert Schuman
Robert Schuman
Robert Schuman was a noted Luxembourgish-born French statesman. Schuman was a Christian Democrat and an independent political thinker and activist...
, the initiator of the European Community system, wrote that a supranational Community like the Europe's founding European Coal and Steel Community
European Coal and Steel Community
The European Coal and Steel Community was a six-nation international organisation serving to unify Western Europe during the Cold War and create the foundation for the modern-day developments of the European Union...
lay midway between an association of States where they retained complete independence and a federation leading to a fusion of States in a super-state. The European Founding Fathers
Founding fathers of the European Union
The Founding Fathers of the European Union are a number of men who have been recognised as making a major contribution to the development of European unity and what is now the European Union. There is no official list of founding fathers or a single event defining them so some ideas vary.-Europe's...
made a Europe Declaration
Europe Declaration
The Europe Declaration was a joint statement issued by the Foreign Ministers of Germany, France, Italy, the Netherlands, Belgium, and Luxembourg at the signing of the Treaty of Paris on 18 April 1951, which created the European Coal and Steel Community....
at the time of the signing of the Treaty of Paris
Treaty of Paris (1951)
The Treaty of Paris was signed on 18 April 1951 between France, West Germany, Italy and the three Benelux countries , establishing the European Coal and Steel Community , which subsequently became part of the European Union...
on 18 April 1951 saying that Europe should be organized on a supranational foundation. They envisaged a structure quite different from a federation called the European Political Community
European Political Community
The European Political Community was proposed in 1952 as a combination of the existing European Coal and Steel Community and the proposed European Defence Community...
.
The EU is a three pillar structure of the original supranational European Economic Community
European Economic Community
The European Economic Community The European Economic Community (EEC) The European Economic Community (EEC) (also known as the Common Market in the English-speaking world, renamed the European Community (EC) in 1993The information in this article primarily covers the EEC's time as an independent...
and the nuclear non-proliferation treaty, Euratom, plus two largely intergovernmental
Intergovernmentalism
-A theory of regional integration:The theory is not applied on European integration which rejects the idea of neofunctionalism. The theory, initially proposed by Stanley Hoffmann suggests that national governments control the level and speed of European integration. Any increase in power at...
pillars dealing with External Affairs and Justice and Home Affairs. The EU is therefore not a de jure federation, although some academic observers conclude that after 50 years of institutional evolution since the Treaties of Rome it is becoming one. The European Union possesses attributes of a federal state. However, its central government is far weaker than that of most federations and the individual members are sovereign state
Sovereign state
A sovereign state, or simply, state, is a state with a defined territory on which it exercises internal and external sovereignty, a permanent population, a government, and the capacity to enter into relations with other sovereign states. It is also normally understood to be a state which is neither...
s under international law, so it is usually characterized as an unprecedented form of supra-national union. The EU has responsibility for important areas such as trade, monetary union, agriculture, fisheries. Nonetheless, EU member state
Member State of the European Union
A member state of the European Union is a state that is party to treaties of the European Union and has thereby undertaken the privileges and obligations that EU membership entails. Unlike membership of an international organisation, being an EU member state places a country under binding laws in...
s retain the right to act independently in matters of foreign policy and defense, and also enjoy a near monopoly over other major policy areas such as criminal justice and taxation. Since the Treaty of Lisbon
Treaty of Lisbon
The Treaty of Lisbon of 1668 was a peace treaty between Portugal and Spain, concluded at Lisbon on 13 February 1668, through the mediation of England, in which Spain recognized the sovereignty of Portugal's new ruling dynasty, the House of Braganza....
, Member States' right to leave the Union is codified, and the Union operates with more qualified majority voting (rather than unanimity) in many areas.
A more nuanced view has been given by the German Constitutional Court. Here the EU is defined as 'an association of sovereign national states (Staatenverbund)'. With this view, the European Union resembles more of a confederation
Confederation
A confederation in modern political terms is a permanent union of political units for common action in relation to other units. Usually created by treaty but often later adopting a common constitution, confederations tend to be established for dealing with critical issues such as defense, foreign...
.
Russian Federation
The Russian FederationRussia
Russia or , officially known as both Russia and the Russian Federation , is a country in northern Eurasia. It is a federal semi-presidential republic, comprising 83 federal subjects...
has inherited its structure from the Russian Soviet Federative Socialist Republic
Russian Soviet Federative Socialist Republic
The Russian Soviet Federative Socialist Republic , commonly referred to as Soviet Russia, Bolshevik Russia, or simply Russia, was the largest, most populous and economically developed republic in the former Soviet Union....
(RSFSR) that was one of the 15 republics of the Soviet Union
Soviet Union
The Soviet Union , officially the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics , was a constitutionally socialist state that existed in Eurasia between 1922 and 1991....
and itself was considered a federation of national territories. The RSFSR consisted of autonomous republics, which had a certain degree of autonomy, at least de jure, and of other types of administrative units (oblasts and krai
Krai
Krai or kray was a type of an administrative division in the Russian Empire and the Russian SFSR, and is one of the types of the federal subjects of modern Russia ....
s), whose status was the same as that of oblasts in other – mostly unitary – Soviet Socialist Republics. Today's Russia is defined as a federation in its Constitution (Article 5), and Russia's federal subjects
Federal subjects of Russia
Russia is a federation which, since March 1, 2008, consists of 83 federal subjects . In 1993, when the Constitution was adopted, there were 89 federal subjects listed...
, i.e., the constituent republics
Republics of Russia
The Russian Federation is divided into 83 federal subjects , 21 of which are republics. The republics represent areas of non-Russian ethnicity. The indigenous ethnic group of a republic that gives it its name is referred to as the "titular nationality"...
, oblasts
Oblasts of Russia
The Russian Federation is divided into 83 subjects , of which 46 are oblasts ....
, krais
Krais of Russia
The Russian Federation is divided into 83 subjects, of which nine are krais, or krays :#Altai Krai#Kamchatka Krai#Khabarovsk Krai#Krasnodar Krai#Krasnoyarsk Krai#Perm Krai#Primorsky Krai...
, the federal-level cities of Moscow
Moscow
Moscow is the capital, the most populous city, and the most populous federal subject of Russia. The city is a major political, economic, cultural, scientific, religious, financial, educational, and transportation centre of Russia and the continent...
and Saint Petersburg
Saint Petersburg
Saint Petersburg is a city and a federal subject of Russia located on the Neva River at the head of the Gulf of Finland on the Baltic Sea...
, as well as one autonomous oblast
Autonomous oblasts of Russia
The Russian Federation is divided into 83 federal subjects, one of which is an autonomous oblast , the Jewish Autonomous Oblast....
and four autonomous (national) okrugs
Autonomous okrugs of Russia
Autonomous okrug is a type of federal subject of Russia and simultaneously a type of administrative division of some federal subjects. As of 2008, the Russian Federation is divided into 83 federal subjects, of which four are avtonomnyye okruga Autonomous okrug (district, area, region) is a...
, are equal in legal terms, save for some symbolic features allowed to republics (constitution, president, national language). Some regions (Yakutia) have concluded agreements with the Federation so as to modify the degree of their autonomy.
According to an amendment passed in December 2004, governors and presidents of Russia's constituent regions, who were previously elected by popular vote, are now proposed by the President of Russia for the approval of the local parliament Local parliaments theoretically have the authority to reject the candidate, but if this occurs three times, the parliament may be dissolved by the President and new parliamentary elections held. This lets some argue that the Russian Federation
Russia
Russia or , officially known as both Russia and the Russian Federation , is a country in northern Eurasia. It is a federal semi-presidential republic, comprising 83 federal subjects...
is not a federation in the strictest sense and that it has centralized features similar to a unitary system
Unitary state
A unitary state is a state governed as one single unit in which the central government is supreme and any administrative divisions exercise only powers that their central government chooses to delegate...
.
Internal controversy and conflict
Another common issue in federal systems is the conflict between regional and national interests, or between the interests and aspirations of different ethnic groups. In some federations the entire jurisdiction is relatively homogeneous and each constituent state resembles a miniature version of the whole; this is known as 'congruent federalism'. On the other hand, incongruent federalism exists where different states or regions possess distinct ethnic groups.
The ability of a federal government to create national institutions that can mediate differences that arise because of linguistic, ethnic, religious, or other regional differences is an important challenge. The inability to meet this challenge may lead to the secession of parts of a federation or to civil war
Civil war
A civil war is a war between organized groups within the same nation state or republic, or, less commonly, between two countries created from a formerly-united nation state....
, as occurred in United States and Switzerland. In the case of Malaysia, Singapore
Singapore
Singapore , officially the Republic of Singapore, is a Southeast Asian city-state off the southern tip of the Malay Peninsula, north of the equator. An island country made up of 63 islands, it is separated from Malaysia by the Straits of Johor to its north and from Indonesia's Riau Islands by the...
was expelled from the federation because of rising racial tension. In some cases internal conflict may lead a federation to collapse entirely, as occurred in Nigeria
Nigeria
Nigeria , officially the Federal Republic of Nigeria, is a federal constitutional republic comprising 36 states and its Federal Capital Territory, Abuja. The country is located in West Africa and shares land borders with the Republic of Benin in the west, Chad and Cameroon in the east, and Niger in...
, the Federation of Rhodesia and Nyasaland
Federation of Rhodesia and Nyasaland
The Federation of Rhodesia and Nyasaland, also known as the Central African Federation , was a semi-independent state in southern Africa that existed from 1953 to the end of 1963, comprising the former self-governing colony of Southern Rhodesia and the British protectorates of Northern Rhodesia,...
, the United Provinces of Central America and the West Indies Federation
West Indies Federation
The West Indies Federation, also known as the Federation of the West Indies, was a short-lived Caribbean federation that existed from January 3, 1958, to May 31, 1962. It consisted of several Caribbean colonies of the United Kingdom...
. Somalia
Somalia
Somalia , officially the Somali Republic and formerly known as the Somali Democratic Republic under Socialist rule, is a country located in the Horn of Africa. Since the outbreak of the Somali Civil War in 1991 there has been no central government control over most of the country's territory...
, despite its Transitional Federal Charter, Transitional Federal Parliament
Transitional Federal Parliament
The Transitional Federal Parliament of the Somali Republic is an interim Parliament of Somalia formed in neighboring Kenya in 2004.The Transitional Federal Parliament has 550 members representing Somalia's clans, Islamist opposition, representatives of citizens' groups and the Somali...
, and Transitional Federal Government
Transitional Federal Government
The Transitional Federal Government is the current internationally recognized government of the Republic of Somalia. It was established as one of the Transitional Federal Institutions of government as defined in the Transitional Federal Charter adopted in November 2004 by the Transitional...
, has a weak central government: since 1992, federal institutions have rarely controlled territory outside of parts of Mogadishu
Mogadishu
Mogadishu , popularly known as Xamar, is the largest city in Somalia and the nation's capital. Located in the coastal Benadir region on the Indian Ocean, the city has served as an important port for centuries....
(though this is changing) and the Somaliland
Somaliland
Somaliland is an unrecognised self-declared sovereign state that is internationally recognised as an autonomous region of Somalia. The government of Somaliland regards itself as the successor state to the British Somaliland protectorate, which was independent for a few days in 1960 as the State of...
region in the northwestern part of the country is autonomous.
List of federations
For a detailed list of federated units, see Federated state#List of constituents by federation. There are 27 federations as of July 2011.Contemporary
| Year Est. | Federation | Federating Units | Major Federating Units | Minor Federating Units |
|---|---|---|---|---|
 Argentina Argentina |
Provinces of Argentina Provinces of Argentina Argentina is subdivided into twenty-three provinces and one autonomous city... |
23 provinces | 1 autonomous city | |
| 1901 |  Australia Australia |
States and territories of Australia States and territories of Australia The Commonwealth of Australia is a union of six states and various territories. The Australian mainland is made up of five states and three territories, with the sixth state of Tasmania being made up of islands. In addition there are six island territories, known as external territories, and a... |
6 states | 10 territories |
 Austria Austria |
States of Austria States of Austria Austria is a federal republic made up of nine states, known in German as Länder . Since Land is also the German word for a country, the term Bundesländer is often used instead to avoid ambiguity. The Constitution of Austria uses both terms... |
9 Länder or Bundesländer | ||
 Belgium Belgium |
Divisions of Belgium | 3 Communities, 3 Regions | ||
 Bosnia and Herzegovina Bosnia and Herzegovina |
Divisions of Bosnia and Herzegovina Political divisions of Bosnia and Herzegovina The political divisions of Bosnia and Herzegovina were created by the Dayton Agreement, which recognized a second tier of government in Bosnia and Herzegovina comprising two entities—a joint Federation of Bosnia and Herzegovina and the Republika Srpska -- each presiding over roughly one half of... |
2 entities (out of which one is itself a federation, consisting of 10 cantons Cantons of the Federation of Bosnia and Herzegovina The 10 cantons of the Federation of Bosnia and Herzegovina serve as the second-level units of local autonomy of the Federation of Bosnia and Herzegovina, one of the two political entities of Bosnia and Herzegovina.... ) |
1 district | |
 Brazil Brazil |
States of Brazil | 26 states | 1 federal district and 5,561 municipalities | |
| 1867 |  Canada Canada |
Provinces and territories of Canada Provinces and territories of Canada The provinces and territories of Canada combine to make up the world's second-largest country by area. There are ten provinces and three territories... |
10 provinces | 3 territories |
 Comoros Comoros |
3 islands | |||
 Ethiopia Ethiopia |
Regions of Ethiopia Regions of Ethiopia ||Ethiopia is divided into 9 ethnically-based administrative regions and two chartered cities... |
9 regions | 2 chartered cities | |
| 1990 |  Germany Germany |
States of Germany States of Germany Germany is made up of sixteen which are partly sovereign constituent states of the Federal Republic of Germany. Land literally translates as "country", and constitutionally speaking, they are constituent countries... |
16 Länder or Bundesländer | |
| 1950 |  India IndiaIndia India , officially the Republic of India , is a country in South Asia. It is the seventh-largest country by geographical area, the second-most populous country with over 1.2 billion people, and the most populous democracy in the world... |
States and territories of India States and territories of India India is a federal union of states comprising twenty-eight states and seven union territories. The states and territories are further subdivided into districts and so on.-List of states and territories:... |
28 States | 7 Union Territories, including a National Capital Territory |
 Iraq Iraq |
Governorates of Iraq Governorates of Iraq ||Iraq is composed of 18 provinces :#Baghdād #Salāh ad-Dīn #Diyālā #Wāsit #Maysān #Al-Basrah #Dhī Qār #Al-Muthannā #Al-Qādisiyyah... |
18 governorates, including the autonomous region of Kurdistan. | ||
 Malaysia Malaysia |
States of Malaysia States of Malaysia Malaysia is a federation which consists of thirteen states and three federal territories . Eleven states and two federal territories are located on the Malay Peninsula while the remaining two states and one federal territory are on the island of Borneo.-The states and federal territories:Malaysia... |
13 states | 3 federal territories | |
 Mexico Mexico |
States of Mexico States of Mexico The United Mexican States is a federal republic formed by 32 federal entities .According to the Constitution of 1917, the states of the federation are free and sovereign. Each state has their own congress and constitution, while the Federal District has only limited autonomy with a local Congress... |
31 states | 1 federal district | |
 Federated States of Micronesia Federated States of Micronesia |
4 states | |||
 Nepal Nepal |
Zones of Nepal Zones of Nepal Nepal is divided into 14 administrative zones , and 75 districts . The 14 administrative zones are grouped into five development regions... |
14 zones | 75 districts | |
 Nigeria Nigeria |
States of Nigeria States of Nigeria Nigeria is currently divided into 36 states and Abuja, the federal capital territory. The states are further divided into 774 Local Government Areas.... |
36 states | 1 territory | |
 Pakistan Pakistan |
Provinces and territories of Pakistan | 4 provinces | 4 federal territories including a federal capital territory | |
| 1992 |  Russia Russia |
Federal subjects of Russia Federal subjects of Russia Russia is a federation which, since March 1, 2008, consists of 83 federal subjects . In 1993, when the Constitution was adopted, there were 89 federal subjects listed... |
21 republics, 46 oblasts, 9 krais, 1 autonomous oblast, 4 autonomous okrugs, 2 federal-level cities | |
 Saint Kitts and Nevis Saint Kitts and Nevis |
Islands/parishes of Saint Kitts and Nevis Parishes of Saint Kitts and Nevis The Federation of Saint Kitts and Nevis is divided into 14 parishes. Nine parishes are located on the island of Saint Kitts and five on Nevis. The parishes are drawn like pie-slices from the ridgeline of the central mountains of both islands.... |
2 islands/14 parishes | ||
| 1910 |  South Africa South Africa |
Provinces of South Africa Provinces of South Africa South Africa is currently divided into nine provinces. On the eve of the 1994 general election, South Africa's former homelands, also known as Bantustans, were reintegrated and the four existing provinces were divided into nine. The twelfth, thirteenth and sixteenth amendments to the constitution... |
9 provinces | |
| 2011 | States of South Sudan | 10 states | ||
 Spain Spain |
Autonomous communities of Spain Autonomous communities of Spain An autonomous community In other languages of Spain:*Catalan/Valencian .*Galician .*Basque . The second article of the constitution recognizes the rights of "nationalities and regions" to self-government and declares the "indissoluble unity of the Spanish nation".Political power in Spain is... |
17 autonomous communities | 2 autonomous cities | |
 Sudan Sudan |
States of Sudan States of Sudan Below is a list of the 15 states of Sudan, organized by their original provinces during the period of Anglo-Egyptian Sudan. Arabic language versions are, as appropriate, in parentheses. States that were not provinces before 1994 are marked with . Transliterations from Arabic to English may vary;... |
15 states | ||
 Switzerland Switzerland |
Cantons of Switzerland Cantons of Switzerland The 26 cantons of Switzerland are the member states of the federal state of Switzerland. Each canton was a fully sovereign state with its own borders, army and currency from the Treaty of Westphalia until the establishment of the Swiss federal state in 1848... |
26 cantons Canton (subnational entity) A canton is a type of administrative division of a country. In general, cantons are relatively small in terms of area and population when compared to other administrative divisions such as counties, departments or provinces. Internationally the best-known cantons, and the most politically... |
||
| 1973 |  United Arab Emirates United Arab Emirates |
Emirates of the UAE Emirates of the United Arab Emirates The United Arab Emirates is composed of 7 emirates :-References:... |
7 emirate Emirate An emirate is a political territory that is ruled by a dynastic Muslim monarch styled emir.-Etymology:Etymologically emirate or amirate is the quality, dignity, office or territorial competence of any emir .... s |
|
| 1787 |  United States United States |
States of the United States U.S. state A U.S. state is any one of the 50 federated states of the United States of America that share sovereignty with the federal government. Because of this shared sovereignty, an American is a citizen both of the federal entity and of his or her state of domicile. Four states use the official title of... |
50 states | 1 federal district; 1 incorporated territory, 13 unincorporated territories |
 Venezuela Venezuela |
States of Venezuela States of Venezuela Venezuela is divided into 23 states , 1 Capital District and the Federal Dependencies that consist of a large number of Venezuelan islands... |
23 states | 1 federal district, 1 federal dependency |
Long form titles
- Federal RepublicFederal republicA federal republic is a federation of states with a republican form of government. A federation is the central government. The states in a federation also maintain the federation...
of: GermanyGermanyGermany , officially the Federal Republic of Germany , is a federal parliamentary republic in Europe. The country consists of 16 states while the capital and largest city is Berlin. Germany covers an area of 357,021 km2 and has a largely temperate seasonal climate...
, NigeriaNigeriaNigeria , officially the Federal Republic of Nigeria, is a federal constitutional republic comprising 36 states and its Federal Capital Territory, Abuja. The country is located in West Africa and shares land borders with the Republic of Benin in the west, Chad and Cameroon in the east, and Niger in...
. - Federation: RussiaRussiaRussia or , officially known as both Russia and the Russian Federation , is a country in northern Eurasia. It is a federal semi-presidential republic, comprising 83 federal subjects...
, Saint Kitts and NevisSaint Kitts and NevisThe Federation of Saint Kitts and Nevis , located in the Leeward Islands, is a federal two-island nation in the West Indies. It is the smallest sovereign state in the Americas, in both area and population.... - Federative Republic of: BrazilBrazilBrazil , officially the Federative Republic of Brazil , is the largest country in South America. It is the world's fifth largest country, both by geographical area and by population with over 192 million people...
- RepublicRepublicA republic is a form of government in which the people, or some significant portion of them, have supreme control over the government and where offices of state are elected or chosen by elected people. In modern times, a common simplified definition of a republic is a government where the head of...
of: ArgentinaArgentinaArgentina , officially the Argentine Republic , is the second largest country in South America by land area, after Brazil. It is constituted as a federation of 23 provinces and an autonomous city, Buenos Aires...
, AustriaAustriaAustria , officially the Republic of Austria , is a landlocked country of roughly 8.4 million people in Central Europe. It is bordered by the Czech Republic and Germany to the north, Slovakia and Hungary to the east, Slovenia and Italy to the south, and Switzerland and Liechtenstein to the...
, IndiaIndiaIndia , officially the Republic of India , is a country in South Asia. It is the seventh-largest country by geographical area, the second-most populous country with over 1.2 billion people, and the most populous democracy in the world...
(also called Indian Union), IraqIraqIraq ; officially the Republic of Iraq is a country in Western Asia spanning most of the northwestern end of the Zagros mountain range, the eastern part of the Syrian Desert and the northern part of the Arabian Desert....
, South AfricaSouth AfricaThe Republic of South Africa is a country in southern Africa. Located at the southern tip of Africa, it is divided into nine provinces, with of coastline on the Atlantic and Indian oceans...
, SudanSudanSudan , officially the Republic of the Sudan , is a country in North Africa, sometimes considered part of the Middle East politically. It is bordered by Egypt to the north, the Red Sea to the northeast, Eritrea and Ethiopia to the east, South Sudan to the south, the Central African Republic to the...
. - Others:
- Bolivarian Republic (VenezuelaVenezuelaVenezuela , officially called the Bolivarian Republic of Venezuela , is a tropical country on the northern coast of South America. It borders Colombia to the west, Guyana to the east, and Brazil to the south...
) - ConfederationConfederationA confederation in modern political terms is a permanent union of political units for common action in relation to other units. Usually created by treaty but often later adopting a common constitution, confederations tend to be established for dealing with critical issues such as defense, foreign...
(SwitzerlandSwitzerlandSwitzerland name of one of the Swiss cantons. ; ; ; or ), in its full name the Swiss Confederation , is a federal republic consisting of 26 cantons, with Bern as the seat of the federal authorities. The country is situated in Western Europe,Or Central Europe depending on the definition....
) - CommonwealthCommonwealthCommonwealth is a traditional English term for a political community founded for the common good. Historically, it has sometimes been synonymous with "republic."More recently it has been used for fraternal associations of some sovereign nations...
(AustraliaAustraliaAustralia , officially the Commonwealth of Australia, is a country in the Southern Hemisphere comprising the mainland of the Australian continent, the island of Tasmania, and numerous smaller islands in the Indian and Pacific Oceans. It is the world's sixth-largest country by total area...
) - Dominion (CanadaCanadaCanada is a North American country consisting of ten provinces and three territories. Located in the northern part of the continent, it extends from the Atlantic Ocean in the east to the Pacific Ocean in the west, and northward into the Arctic Ocean...
before 1982) - Federal Democratic Republic (EthiopiaEthiopiaEthiopia , officially known as the Federal Democratic Republic of Ethiopia, is a country located in the Horn of Africa. It is the second-most populous nation in Africa, with over 82 million inhabitants, and the tenth-largest by area, occupying 1,100,000 km2...
, NepalNepalNepal , officially the Federal Democratic Republic of Nepal, is a landlocked sovereign state located in South Asia. It is located in the Himalayas and bordered to the north by the People's Republic of China, and to the south, east, and west by the Republic of India...
) - Federated States (FS MicronesiaFederated States of MicronesiaThe Federated States of Micronesia or FSM is an independent, sovereign island nation, made up of four states from west to east: Yap, Chuuk, Pohnpei and Kosrae. It comprises approximately 607 islands with c...
) - Federative Republic (BrazilBrazilBrazil , officially the Federative Republic of Brazil , is the largest country in South America. It is the world's fifth largest country, both by geographical area and by population with over 192 million people...
) - Islamic Republic (PakistanPakistanPakistan , officially the Islamic Republic of Pakistan is a sovereign state in South Asia. It has a coastline along the Arabian Sea and the Gulf of Oman in the south and is bordered by Afghanistan and Iran in the west, India in the east and China in the far northeast. In the north, Tajikistan...
) - KingdomMonarchyA monarchy is a form of government in which the office of head of state is usually held until death or abdication and is often hereditary and includes a royal house. In some cases, the monarch is elected...
(BelgiumBelgiumBelgium , officially the Kingdom of Belgium, is a federal state in Western Europe. It is a founding member of the European Union and hosts the EU's headquarters, and those of several other major international organisations such as NATO.Belgium is also a member of, or affiliated to, many...
) - Union (ComorosComorosThe Comoros , officially the Union of the Comoros is an archipelago island nation in the Indian Ocean, located off the eastern coast of Africa, on the northern end of the Mozambique Channel, between northeastern Mozambique and northwestern Madagascar...
) - United Emirates (United Arab EmiratesUnited Arab EmiratesThe United Arab Emirates, abbreviated as the UAE, or shortened to "the Emirates", is a state situated in the southeast of the Arabian Peninsula in Western Asia on the Persian Gulf, bordering Oman, and Saudi Arabia, and sharing sea borders with Iraq, Kuwait, Bahrain, Qatar, and Iran.The UAE is a...
) - United Mexican States (MexicoMexicoThe United Mexican States , commonly known as Mexico , is a federal constitutional republic in North America. It is bordered on the north by the United States; on the south and west by the Pacific Ocean; on the southeast by Guatemala, Belize, and the Caribbean Sea; and on the east by the Gulf of...
) - United States (United StatesUnited StatesThe United States of America is a federal constitutional republic comprising fifty states and a federal district...
)
- Bolivarian Republic (Venezuela
- None:
- Bosnia and HerzegovinaBosnia and HerzegovinaBosnia and Herzegovina , sometimes called Bosnia-Herzegovina or simply Bosnia, is a country in Southern Europe, on the Balkan Peninsula. Bordered by Croatia to the north, west and south, Serbia to the east, and Montenegro to the southeast, Bosnia and Herzegovina is almost landlocked, except for the...
(since 1997) - CanadaCanadaCanada is a North American country consisting of ten provinces and three territories. Located in the northern part of the continent, it extends from the Atlantic Ocean in the east to the Pacific Ocean in the west, and northward into the Arctic Ocean...
(since 1982) - Malaysia
- Bosnia and Herzegovina
Defunct
- Federal Republic of CameroonCameroonCameroon, officially the Republic of Cameroon , is a country in west Central Africa. It is bordered by Nigeria to the west; Chad to the northeast; the Central African Republic to the east; and Equatorial Guinea, Gabon, and the Republic of the Congo to the south. Cameroon's coastline lies on the...
(1961–1972) - United Provinces of Central America (1823 – circa 1838)
- Confederate States of AmericaConfederate States of AmericaThe Confederate States of America was a government set up from 1861 to 1865 by 11 Southern slave states of the United States of America that had declared their secession from the U.S...
(1861–1865) - United States of ColombiaUnited States of ColombiaThe United States of Colombia was the name adopted in 1861 through the Rionegro Constitution for the nation which had been known as the Republic of New Granada since the dissolution of the federation of Gran Colombia in 1830-1831....
(1863–1886) - CzechoslovakiaCzechoslovakiaCzechoslovakia or Czecho-Slovakia was a sovereign state in Central Europe which existed from October 1918, when it declared its independence from the Austro-Hungarian Empire, until 1992...
(1969–1992) - Federated Dutch Republic (1581–1795)
- French Equatorial AfricaFrench Equatorial AfricaFrench Equatorial Africa or the AEF was the federation of French colonial possessions in Middle Africa, extending northwards from the Congo River to the Sahara Desert.-History:...
(1910–1960) - French West AfricaFrench West AfricaFrench West Africa was a federation of eight French colonial territories in Africa: Mauritania, Senegal, French Sudan , French Guinea , Côte d'Ivoire , Upper Volta , Dahomey and Niger...
(1904–1958) - Inca EmpireInca EmpireThe Inca Empire, or Inka Empire , was the largest empire in pre-Columbian America. The administrative, political and military center of the empire was located in Cusco in modern-day Peru. The Inca civilization arose from the highlands of Peru sometime in the early 13th century...
(1197–1572) - United States of Indonesia (1949–1950)
- United Kingdom of Libya (1951–1963)
- Federated Malay StatesFederated Malay StatesThe Federated Malay States was a federation of four protected states in the Malay Peninsula—Selangor, Perak, Negeri Sembilan and Pahang—established by the British government in 1895, which lasted until 1946, when they, together with the Straits Settlements and the Unfederated Malay...
(1896–1946) - Federation of MalayaFederation of MalayaThe Federation of Malaya is the name given to a federation of 11 states that existed from 31 January 1948 until 16 September 1963. The Federation became independent on 31 August 1957...
(1948–1963) - Mali FederationMali FederationThe Mali Federation was a country in West Africa. It was formed by a union between Senegal and the Sudanese Republic...
(1959–1960) - New Granada (1855–1886)
- Polish-Lithuanian CommonwealthPolish-Lithuanian CommonwealthThe Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth was a dualistic state of Poland and Lithuania ruled by a common monarch. It was the largest and one of the most populous countries of 16th- and 17th‑century Europe with some and a multi-ethnic population of 11 million at its peak in the early 17th century...
(1569–1795) - Federation of Rhodesia and NyasalandFederation of Rhodesia and NyasalandThe Federation of Rhodesia and Nyasaland, also known as the Central African Federation , was a semi-independent state in southern Africa that existed from 1953 to the end of 1963, comprising the former self-governing colony of Southern Rhodesia and the British protectorates of Northern Rhodesia,...
(1953–1963) - Federation of South ArabiaFederation of South ArabiaThe Federation of South Arabia was an organization of states under British protection in what would become South Yemen. It was formed on 4 April 1962 from the 15 protected states of the Federation of Arab Emirates of the South. On 18 January 1963 it was merged with the crown colony of Aden...
(1962–1967) - Union of Soviet Socialist RepublicsSoviet UnionThe Soviet Union , officially the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics , was a constitutionally socialist state that existed in Eurasia between 1922 and 1991....
(1922–1991) - Federal Republic of SpainFirst Spanish RepublicThe First Spanish Republic was the political regime that existed in Spain between the parliamentary proclamation on 11 February 1873 and 29 December 1874 when General Arsenio Martínez-Campos's pronunciamento marked the beginning of the Bourbon Restoration in Spain...
(1873–1874) - UgandaUgandaUganda , officially the Republic of Uganda, is a landlocked country in East Africa. Uganda is also known as the "Pearl of Africa". It is bordered on the east by Kenya, on the north by South Sudan, on the west by the Democratic Republic of the Congo, on the southwest by Rwanda, and on the south by...
(1962–1967) - West Indies FederationWest Indies FederationThe West Indies Federation, also known as the Federation of the West Indies, was a short-lived Caribbean federation that existed from January 3, 1958, to May 31, 1962. It consisted of several Caribbean colonies of the United Kingdom...
(1958–1962) - Socialist Federal Republic of YugoslaviaSocialist Federal Republic of YugoslaviaThe Socialist Federal Republic of Yugoslavia was the Yugoslav state that existed from the abolition of the Yugoslav monarchy until it was dissolved in 1992 amid the Yugoslav Wars. It was a socialist state and a federation made up of six socialist republics: Bosnia and Herzegovina, Croatia,...
(1943–1992) - Federal Republic of Yugoslavia (1992–2003)
Some of the proclaimed Arab federations were confederations de facto
De facto
De facto is a Latin expression that means "concerning fact." In law, it often means "in practice but not necessarily ordained by law" or "in practice or actuality, but not officially established." It is commonly used in contrast to de jure when referring to matters of law, governance, or...
.
See also
- Anti-Federalist
- Capital city
- Corporative federalismCorporative federalismCorporative federalism, not to be confused with the 'cooperative federalism' of the New Deal, is a system of federalism not based on the common federalist idea of relative land area or nearest spheres of influence for governance, but on fiduciary jurisdiction to corporate personhood, where groups...
- Constitutional economicsConstitutional economicsConstitutional economics is a research program in economics and constitutionalism that has been described as extending beyond the definition of 'the economic analysis of constitutional law' in explaining the choice "of alternative sets of legal-institutional-constitutional rules that constrain the...
- Political economyPolitical economyPolitical economy originally was the term for studying production, buying, and selling, and their relations with law, custom, and government, as well as with the distribution of national income and wealth, including through the budget process. Political economy originated in moral philosophy...
- Rule according to higher lawRule according to higher lawThe rule according to a higher law means that no written law may be enforced by the government unless it conforms with certain unwritten, universal principles of fairness, morality, and justice...
- European UnionEuropean UnionThe European Union is an economic and political union of 27 independent member states which are located primarily in Europe. The EU traces its origins from the European Coal and Steel Community and the European Economic Community , formed by six countries in 1958...
- European Coal and Steel CommunityEuropean Coal and Steel CommunityThe European Coal and Steel Community was a six-nation international organisation serving to unify Western Europe during the Cold War and create the foundation for the modern-day developments of the European Union...
- FederacyFederacyA federacy is a form of government where one or several substate units enjoy considerably more independence than the majority of the substate units. To some extent, such an arrangement can be considered as similar to asymmetric federalism.-Description:...
- Federalism in AustraliaFederalism in AustraliaOn 1 January 1901 the Australian nation emerged as a federation. The model of Australian federalism adheres closely to the original model of the United States of America.- Federal features in the Australian Constitution :...
- FederalistFederalistThe term federalist describes several political beliefs around the world. Also, it may refer to the concept of federalism or the type of government called a federation...
- The Federalist Papers
- Federal monarchy
- Federated state
- Federation of AustraliaFederation of AustraliaThe Federation of Australia was the process by which the six separate British self-governing colonies of New South Wales, Queensland, South Australia, Tasmania, Victoria and Western Australia formed one nation...
- FoederatiFoederatiFoederatus is a Latin term whose definition and usage drifted in the time between the early Roman Republic and the end of the Western Roman Empire...
- Indian Union
- International organisationInternational organizationAn intergovernmental organization, sometimes rendered as an international governmental organization and both abbreviated as IGO, is an organization composed primarily of sovereign states , or of other intergovernmental organizations...
- MiędzymorzeMiedzymorzeMiędzymorze was a plan, pursued after World War I by Polish leader Józef Piłsudski, for a federation, under Poland's aegis, of Central and Eastern European countries...
(Intermarum) - Multinational stateMultinational stateA multinational state is a sovereign state which is viewed as comprising two or more nations. Such a state contrasts with a nation-state where a single nation comprises the bulk of the population...
- Neo-functionalismNeofunctionalismNeofunctionalism is a theory of regional integration, building on the work of Ernst B. Haas, an American political scientist and also Leon Lindberg, an American political scientist...
- New federalismNew FederalismNew Federalism is a political philosophy of devolution, or the transfer of certain powers from the United States federal government back to the states...
- Regional stateRegional stateIn political geography, a regional state is a state more centralized than a federation, but less centralized than an unitary state. Regional states include federations in which power has become more centralized, and unitary states in which some power has been devolved to regional governments...
- Supranationalism
- Supranational unionSupranational unionSupranationalism is a method of decision-making in multi-national political communities, wherein power is transferred or delegated to an authority by governments of member states. The concept of supranational union is sometimes used to describe the European Union, as a new type of political entity...
- Unitary stateUnitary stateA unitary state is a state governed as one single unit in which the central government is supreme and any administrative divisions exercise only powers that their central government chooses to delegate...
- United Federation of PlanetsUnited Federation of PlanetsThe United Federation of Planets, also known as "The Federation" is a fictional interplanetary federal republic depicted in the Star Trek television series and motion pictures...
- World Federalist MovementWorld Federalist MovementThe World Federalist Movement is a global citizens movement with member and associate organizations around the world. The WFM International Secretariat is based in New York City across from the United Nations headquarters...
- Centre for Studies on FederalismCentre for Studies on FederalismThe Centre for Studies on Federalism was established in November 2000 with the primary purpose of studying and researching the theory and practice of Federalism both as a political doctrine and in its implementation in the institutional systems of the Modern state...

