
Fayalite
Encyclopedia
Fayalite is the iron
-rich end-member of the olivine
solid-solution series. In common with all minerals in the olivine group
, fayalite crystallizes in the orthorhombic system (space group
Pbnm) with cell parameters a 4.82 Å, b 10.48 Å and c Å 6.09.
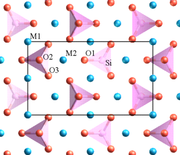 Iron rich olivine is a relatively common constituent of acidic and alkaline igneous rocks such as volcanic obsidian
Iron rich olivine is a relatively common constituent of acidic and alkaline igneous rocks such as volcanic obsidian
s, rhyolite
s, trachyte
s and phonolite
s and plutonic quartz syenite
s where it is associated with amphibole
s. Its main occurrence is in ultramafic volcanic and plutonic rocks and less commonly in felsic
plutonic rocks and rarely in granite
pegmatite
. It also occurs in lithophysae in obsidian
. It also occurs in medium-grade thermally metamorphosed
iron-rich sediments and in impure carbonate rocks.
Fayalite is stable with quartz at low pressures, whereas more magnesian olivine is not, because of the reaction olivine + quartz
= orthopyroxene. Iron stabilizes the olivine + quartz pair. The pressure and compositional dependence of the reaction can be used to calculate constraints on pressures at which assemblages of olivine + quartz formed.
Fayalite can also react with oxygen
to produce magnetite
+ quartz: the three minerals together make up the "FMQ" oxygen buffer. The reaction is used to control the fugacity
of oxygen in laboratory experiments. It can also be used to calculate the fugacity of oxygen recorded by mineral assemblages in metamorphic and igneous processes.
The name fayalite is derived from Faial
(Fayal) Island in the Azores
where it was first described in 1840.
Iron
Iron is a chemical element with the symbol Fe and atomic number 26. It is a metal in the first transition series. It is the most common element forming the planet Earth as a whole, forming much of Earth's outer and inner core. It is the fourth most common element in the Earth's crust...
-rich end-member of the olivine
Olivine
The mineral olivine is a magnesium iron silicate with the formula 2SiO4. It is a common mineral in the Earth's subsurface but weathers quickly on the surface....
solid-solution series. In common with all minerals in the olivine group
Olivine
The mineral olivine is a magnesium iron silicate with the formula 2SiO4. It is a common mineral in the Earth's subsurface but weathers quickly on the surface....
, fayalite crystallizes in the orthorhombic system (space group
Space group
In mathematics and geometry, a space group is a symmetry group, usually for three dimensions, that divides space into discrete repeatable domains.In three dimensions, there are 219 unique types, or counted as 230 if chiral copies are considered distinct...
Pbnm) with cell parameters a 4.82 Å, b 10.48 Å and c Å 6.09.

Obsidian
Obsidian is a naturally occurring volcanic glass formed as an extrusive igneous rock.It is produced when felsic lava extruded from a volcano cools rapidly with minimum crystal growth...
s, rhyolite
Rhyolite
This page is about a volcanic rock. For the ghost town see Rhyolite, Nevada, and for the satellite system, see Rhyolite/Aquacade.Rhyolite is an igneous, volcanic rock, of felsic composition . It may have any texture from glassy to aphanitic to porphyritic...
s, trachyte
Trachyte
Trachyte is an igneous volcanic rock with an aphanitic to porphyritic texture. The mineral assemblage consists of essential alkali feldspar; relatively minor plagioclase and quartz or a feldspathoid such as nepheline may also be present....
s and phonolite
Phonolite
Phonolite is a rare igneous, volcanic rock of intermediate composition, with aphanitic to porphyritic texture....
s and plutonic quartz syenite
Syenite
Syenite is a coarse-grained intrusive igneous rock of the same general composition as granite but with the quartz either absent or present in relatively small amounts Syenite is a coarse-grained intrusive igneous rock of the same general composition as granite but with the quartz either absent or...
s where it is associated with amphibole
Amphibole
Amphibole is the name of an important group of generally dark-colored rock-forming inosilicate minerals, composed of double chain tetrahedra, linked at the vertices and generally containing ions of iron and/or magnesium in their structures.-Mineralogy:...
s. Its main occurrence is in ultramafic volcanic and plutonic rocks and less commonly in felsic
Felsic
The word "felsic" is a term used in geology to refer to silicate minerals, magma, and rocks which are enriched in the lighter elements such as silicon, oxygen, aluminium, sodium, and potassium....
plutonic rocks and rarely in granite
Granite
Granite is a common and widely occurring type of intrusive, felsic, igneous rock. Granite usually has a medium- to coarse-grained texture. Occasionally some individual crystals are larger than the groundmass, in which case the texture is known as porphyritic. A granitic rock with a porphyritic...
pegmatite
Pegmatite
A pegmatite is a very crystalline, intrusive igneous rock composed of interlocking crystals usually larger than 2.5 cm in size; such rocks are referred to as pegmatitic....
. It also occurs in lithophysae in obsidian
Obsidian
Obsidian is a naturally occurring volcanic glass formed as an extrusive igneous rock.It is produced when felsic lava extruded from a volcano cools rapidly with minimum crystal growth...
. It also occurs in medium-grade thermally metamorphosed
Metamorphic rock
Metamorphic rock is the transformation of an existing rock type, the protolith, in a process called metamorphism, which means "change in form". The protolith is subjected to heat and pressure causing profound physical and/or chemical change...
iron-rich sediments and in impure carbonate rocks.
Fayalite is stable with quartz at low pressures, whereas more magnesian olivine is not, because of the reaction olivine + quartz
Quartz
Quartz is the second-most-abundant mineral in the Earth's continental crust, after feldspar. It is made up of a continuous framework of SiO4 silicon–oxygen tetrahedra, with each oxygen being shared between two tetrahedra, giving an overall formula SiO2. There are many different varieties of quartz,...
= orthopyroxene. Iron stabilizes the olivine + quartz pair. The pressure and compositional dependence of the reaction can be used to calculate constraints on pressures at which assemblages of olivine + quartz formed.
Fayalite can also react with oxygen
Oxygen
Oxygen is the element with atomic number 8 and represented by the symbol O. Its name derives from the Greek roots ὀξύς and -γενής , because at the time of naming, it was mistakenly thought that all acids required oxygen in their composition...
to produce magnetite
Magnetite
Magnetite is a ferrimagnetic mineral with chemical formula Fe3O4, one of several iron oxides and a member of the spinel group. The chemical IUPAC name is iron oxide and the common chemical name is ferrous-ferric oxide. The formula for magnetite may also be written as FeO·Fe2O3, which is one part...
+ quartz: the three minerals together make up the "FMQ" oxygen buffer. The reaction is used to control the fugacity
Fugacity
In chemical thermodynamics, the fugacity of a real gas is an effective pressure which replaces the true mechanical pressure in accurate chemical equilibrium calculations. It is equal to the pressure of an ideal gas which has the same chemical potential as the real gas. For example, nitrogen gas ...
of oxygen in laboratory experiments. It can also be used to calculate the fugacity of oxygen recorded by mineral assemblages in metamorphic and igneous processes.
The name fayalite is derived from Faial
Faial Island
Faial Island , also known in English as Fayal, is a Portuguese island of the Central Group of the Azores....
(Fayal) Island in the Azores
Azores
The Archipelago of the Azores is composed of nine volcanic islands situated in the middle of the North Atlantic Ocean, and is located about west from Lisbon and about east from the east coast of North America. The islands, and their economic exclusion zone, form the Autonomous Region of the...
where it was first described in 1840.
See also
- ForsteriteForsteriteForsterite is the magnesium rich end-member of the olivine solid solution series. Forsterite crystallizes in the orthorhombic system with cell parameters a 4.75 Å , b 10.20 Å and c 5.98 Å .Forsterite is associated with igneous and metamorphic rocks and has also been found in meteorites...
, (Mg2SiO4), the magnesiumMagnesiumMagnesium is a chemical element with the symbol Mg, atomic number 12, and common oxidation number +2. It is an alkaline earth metal and the eighth most abundant element in the Earth's crust and ninth in the known universe as a whole...
-rich end-member of the olivineOlivineThe mineral olivine is a magnesium iron silicate with the formula 2SiO4. It is a common mineral in the Earth's subsurface but weathers quickly on the surface....
solid-solution series.

