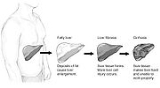
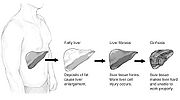
Fatty liver
Encyclopedia
Vacuole
A vacuole is a membrane-bound organelle which is present in all plant and fungal cells and some protist, animal and bacterial cells. Vacuoles are essentially enclosed compartments which are filled with water containing inorganic and organic molecules including enzymes in solution, though in certain...
s of triglyceride
Triglyceride
A triglyceride is an ester derived from glycerol and three fatty acids. There are many triglycerides, depending on the oil source, some are highly unsaturated, some less so....
fat accumulate in liver cells
Hepatocyte
A hepatocyte is a cell of the main tissue of the liver. Hepatocytes make up 70-80% of the liver's cytoplasmic mass.These cells are involved in:* Protein synthesis* Protein storage* Transformation of carbohydrates...
via the process of steatosis
Steatosis
In cellular pathology, steatosis is the process describing the abnormal retention of lipids within a cell. It reflects an impairment of the normal processes of synthesis and elimination of triglyceride fat. Excess lipid accumulates in vesicles that displace the cytoplasm...
(i.e. abnormal retention of lipids within a cell). Despite having multiple causes, fatty liver can be considered a single disease
Disease
A disease is an abnormal condition affecting the body of an organism. It is often construed to be a medical condition associated with specific symptoms and signs. It may be caused by external factors, such as infectious disease, or it may be caused by internal dysfunctions, such as autoimmune...
that occurs worldwide in those with excessive alcohol
Alcohol
In chemistry, an alcohol is an organic compound in which the hydroxy functional group is bound to a carbon atom. In particular, this carbon center should be saturated, having single bonds to three other atoms....
intake and those who are obese (with or without effects of insulin resistance
Insulin resistance
Insulin resistance is a physiological condition where the natural hormone insulin becomes less effective at lowering blood sugars. The resulting increase in blood glucose may raise levels outside the normal range and cause adverse health effects, depending on dietary conditions. Certain cell types...
). The condition is also associated with other diseases that influence fat metabolism
Metabolism
Metabolism is the set of chemical reactions that happen in the cells of living organisms to sustain life. These processes allow organisms to grow and reproduce, maintain their structures, and respond to their environments. Metabolism is usually divided into two categories...
. Morphologically it is difficult to distinguish alcoholic FLD from non alcoholic FLD and both show micro-vesicular
Vesicle (biology)
A vesicle is a bubble of liquid within another liquid, a supramolecular assembly made up of many different molecules. More technically, a vesicle is a small membrane-enclosed sack that can store or transport substances. Vesicles can form naturally because of the properties of lipid membranes , or...
and macrovesicular fatty changes at different stages.
Accumulation of fat may also be accompanied by a progressive inflammation of the liver (hepatitis
Hepatitis
Hepatitis is a medical condition defined by the inflammation of the liver and characterized by the presence of inflammatory cells in the tissue of the organ. The name is from the Greek hepar , the root being hepat- , meaning liver, and suffix -itis, meaning "inflammation"...
), called steatohepatitis
Steatohepatitis
Steatohepatitis is a type of liver disease, characterized by inflammation of the liver with concurrent fat accumulation in liver...
. By considering the contribution by alcohol, fatty liver may be termed alcoholic steatosis or non-alcoholic fatty liver disease
Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease
Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease is one cause of a fatty liver, occurring when fat is deposited in the liver not due to excessive alcohol use. It is related to insulin resistance and the metabolic syndrome and may respond to treatments originally developed for other insulin-resistant states...
(NAFLD), and the more severe forms as alcoholic steatohepatitis (part of alcoholic liver disease
Alcoholic liver disease
Alcoholic liver disease is a term that encompasses the hepatic manifestations of alcohol overconsumption, including fatty liver, alcoholic hepatitis, and chronic hepatitis with hepatic fibrosis or cirrhosis. It is the major cause of liver disease in Western countries...
) and non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH).
Causes
Fatty liver is commonly associated with alcoholAlcohol
In chemistry, an alcohol is an organic compound in which the hydroxy functional group is bound to a carbon atom. In particular, this carbon center should be saturated, having single bonds to three other atoms....
or metabolic syndrome
Metabolic syndrome
Metabolic syndrome is a combination of medical disorders that, when occurring together, increase the risk of developing cardiovascular disease and diabetes. It affects one in five people in the United States and prevalence increases with age...
(diabetes, hypertension
Hypertension
Hypertension or high blood pressure is a cardiac chronic medical condition in which the systemic arterial blood pressure is elevated. What that means is that the heart is having to work harder than it should to pump the blood around the body. Blood pressure involves two measurements, systolic and...
, obesity
Obesity
Obesity is a medical condition in which excess body fat has accumulated to the extent that it may have an adverse effect on health, leading to reduced life expectancy and/or increased health problems...
and dyslipidemia
Dyslipidemia
Dyslipidemia or dyslipidaemia is an abnormal amount of lipids in the blood. In developed countries, most dyslipidemias are hyperlipidemias; that is, an elevation of lipids in the blood, often due to diet and lifestyle. The prolonged elevation of insulin levels can lead to dyslipidemia...
) but can also be due to any one of many causes:
Metabolic: Abetalipoproteinemia
Abetalipoproteinemia
Abetalipoproteinemia, or Bassen-Kornzweig syndrome, is a rare autosomal recessive disorder that interferes with the normal absorption of fat and fat-soluble vitamins from food. It is caused by a deficiency of apolipoprotein B-48 and B-100, which are used in the synthesis and exportation of...
, glycogen storage disease
Glycogen storage disease
Glycogen storage disease is the result of defects in the processing of glycogen synthesis or breakdown within muscles, liver, and other cell types. GSD has two classes of cause: genetic and acquired. Genetic GSD is caused by any inborn error of metabolism involved in these processes...
s, Weber-Christian disease, acute fatty liver of pregnancy
Acute fatty liver of pregnancy
Acute fatty liver of pregnancy is a rare life-threatening complication of pregnancy that occurs in the third trimester or the immediate period after delivery. It is thought to be caused by a disordered metabolism of fatty acids by mitochondria in the mother, caused by deficiency in the LCHAD enzyme...
, lipodystrophy
Lipodystrophy
Lipodystrophy is a medical condition characterized by abnormal or degenerative conditions of the body's adipose tissue. A more specific term, lipoatrophy is used when describing the loss of fat from one area...
Nutritional:Malnutrition
Malnutrition
Malnutrition is the condition that results from taking an unbalanced diet in which certain nutrients are lacking, in excess , or in the wrong proportions....
, total parenteral nutrition
Total parenteral nutrition
Parenteral nutrition is feeding a person intravenously, bypassing the usual process of eating and digestion. The person receives nutritional formulae that contain nutrients such as glucose, amino acids, lipids and added vitamins and dietary minerals...
, severe weight loss
Weight loss
Weight loss, in the context of medicine, health or physical fitness, is a reduction of the total body mass, due to a mean loss of fluid, body fat or adipose tissue and/or lean mass, namely bone mineral deposits, muscle, tendon and other connective tissue...
, refeeding syndrome
Refeeding syndrome
Refeeding syndrome is a syndrome consisting of metabolic disturbances that occur as a result of reinstitution of nutrition to patients who are starved or severely malnourished. Renourishment is the process of avoiding refeeding syndrome...
, jejuno-ileal bypass, gastric bypass, jejunal diverticulosis
Diverticulosis
Diverticulosis also known as "diverticular disease" is the condition of having diverticula in the colon, which are outpocketings of the colonic mucosa and submucosa through weaknesses of muscle layers in the colon wall. These are more common in the sigmoid colon, which is a common place for...
with bacterial overgrowth
Drugs and toxins:Amiodarone
Amiodarone
Amiodarone is an antiarrhythmic agent used for various types of tachyarrhythmias , both ventricular and supraventricular arrhythmias. Discovered in 1961, it was not approved for use in the United States until 1985...
, methotrexate
Methotrexate
Methotrexate , abbreviated MTX and formerly known as amethopterin, is an antimetabolite and antifolate drug. It is used in treatment of cancer, autoimmune diseases, ectopic pregnancy, and for the induction of medical abortions. It acts by inhibiting the metabolism of folic acid. Methotrexate...
, diltiazem
Diltiazem
Diltiazem is a non-dihydropyridine member of the class of drugs known as calcium channel blockers, used in the treatment of hypertension, angina pectoris, and some types of arrhythmia....
, expired Tetracycline, highly active antiretroviral therapy, glucocorticoids, tamoxifen
Tamoxifen
Tamoxifen is an antagonist of the estrogen receptor in breast tissue via its active metabolite, hydroxytamoxifen. In other tissues such as the endometrium, it behaves as an agonist, hence tamoxifen may be characterized as a mixed agonist/antagonist...
, environmental hepatotoxin
Hepatotoxin
A hepatotoxin is a toxic chemical substance that damages the liver.It can be a side-effect of medication, or found naturally, as microcystins, or in laboratory environments....
s (e.g., phosphorus
Phosphorus
Phosphorus is the chemical element that has the symbol P and atomic number 15. A multivalent nonmetal of the nitrogen group, phosphorus as a mineral is almost always present in its maximally oxidized state, as inorganic phosphate rocks...
, mushroom poisoning
Mushroom poisoning
Mushroom poisoning refers to harmful effects from ingestion of toxic substances present in a mushroom. These symptoms can vary from slight gastrointestinal discomfort to death. The toxins present are secondary metabolites produced in specific biochemical pathways in the fungal cells...
)
Other:Inflammatory bowel disease
Inflammatory bowel disease
In medicine, inflammatory bowel disease is a group of inflammatory conditions of the colon and small intestine. The major types of IBD are Crohn's disease and ulcerative colitis.-Classification:...
, HIV
HIV
Human immunodeficiency virus is a lentivirus that causes acquired immunodeficiency syndrome , a condition in humans in which progressive failure of the immune system allows life-threatening opportunistic infections and cancers to thrive...
, Hepatitis C especially genotype 3, and Alpha 1-antitrypsin deficiency
Pathology
Fatty change represents the intra-cytoplasmCytoplasm
The cytoplasm is a small gel-like substance residing between the cell membrane holding all the cell's internal sub-structures , except for the nucleus. All the contents of the cells of prokaryote organisms are contained within the cytoplasm...
ic accumulation of triglyceride (neutral fats). At the beginning, the hepatocytes present small fat vacuoles (liposomes) around the nucleus
Cell nucleus
In cell biology, the nucleus is a membrane-enclosed organelle found in eukaryotic cells. It contains most of the cell's genetic material, organized as multiple long linear DNA molecules in complex with a large variety of proteins, such as histones, to form chromosomes. The genes within these...
(microvesicular fatty change
Steatosis
In cellular pathology, steatosis is the process describing the abnormal retention of lipids within a cell. It reflects an impairment of the normal processes of synthesis and elimination of triglyceride fat. Excess lipid accumulates in vesicles that displace the cytoplasm...
). In this stage liver cells are filled with multiple fat droplets that do not displace the centrally located nucleus. In the late stages, the size of the vacuoles increase pushing the nucleus to the periphery of the cell giving characteristic signet ring appearance (macrovesicular fatty change). These vesicles are well delineated and optically "empty" because fats dissolve during tissue processing. Large vacuoles may coalesce and produce fatty cyst
Cyst
A cyst is a closed sac, having a distinct membrane and division on the nearby tissue. It may contain air, fluids, or semi-solid material. A collection of pus is called an abscess, not a cyst. Once formed, a cyst could go away on its own or may have to be removed through surgery.- Locations :* Acne...
s which are irreversible lesions. Macrovesicular steatosis
Steatosis
In cellular pathology, steatosis is the process describing the abnormal retention of lipids within a cell. It reflects an impairment of the normal processes of synthesis and elimination of triglyceride fat. Excess lipid accumulates in vesicles that displace the cytoplasm...
is the most common form and is typically associated with alcohol
Alcohol
In chemistry, an alcohol is an organic compound in which the hydroxy functional group is bound to a carbon atom. In particular, this carbon center should be saturated, having single bonds to three other atoms....
, diabetes, obesity
Obesity
Obesity is a medical condition in which excess body fat has accumulated to the extent that it may have an adverse effect on health, leading to reduced life expectancy and/or increased health problems...
and corticosteroids. Acute fatty liver of pregnancy
Acute fatty liver of pregnancy
Acute fatty liver of pregnancy is a rare life-threatening complication of pregnancy that occurs in the third trimester or the immediate period after delivery. It is thought to be caused by a disordered metabolism of fatty acids by mitochondria in the mother, caused by deficiency in the LCHAD enzyme...
and Reye's syndrome
Reye's syndrome
Reye's syndrome is a potentially fatal disease that causes numerous detrimental effects to many organs, especially the brain and liver, as well as causing a lower than usual level of blood sugar . The classic features are liver damage, aspirin use and a viral infection...
are examples of severe liver disease caused by microvesicular fatty change. The diagnosis of steatosis is made when fat in the liver exceeds 5–10% by weight.
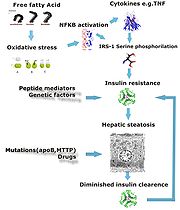
Fatty acid metabolism
Fatty acids are an important source of energy and adenosine triphosphate for many cellular organisms. Excess fatty acids, glucose, and other nutrients can be stored efficiently as fat. Triglycerides yield more than twice as much energy for the same mass as do carbohydrates or proteins. All cell...
are responsible for pathogenesis
Pathogenesis
The pathogenesis of a disease is the mechanism by which the disease is caused. The term can also be used to describe the origin and development of the disease and whether it is acute, chronic or recurrent...
of FLD which may be due to imbalance in energy consumption and its combustion resulting in lipid storage or can be a consequence of peripheral resistance to insulin, whereby the transport of fatty acids from adipose tissue
Adipose tissue
In histology, adipose tissue or body fat or fat depot or just fat is loose connective tissue composed of adipocytes. It is technically composed of roughly only 80% fat; fat in its solitary state exists in the liver and muscles. Adipose tissue is derived from lipoblasts...
to the liver is increased.
Impairment or inhibition of receptor molecules (PPAR-α
Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor
In the field of molecular biology, the peroxisome proliferator-activated receptors are a group of nuclear receptor proteins that function as transcription factors regulating the expression of genes...
, PPAR-γ
Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor
In the field of molecular biology, the peroxisome proliferator-activated receptors are a group of nuclear receptor proteins that function as transcription factors regulating the expression of genes...
and SREBP1
Sterol regulatory element binding protein
Sterol Regulatory Element-Binding Proteins are transcription factors that bind to the sterol regulatory element DNA sequence TCACNCCAC. Mammalian SREBPs are encoded by the genes SREBF1 and SREBF2. SREBPs belong to the basic-helix-loop-helix leucine zipper class of transcription factors...
) that control the enzymes responsible for the oxidation and synthesis of fatty
acids appears to contribute towards fat accumulation. In addition, alcoholism is known to damage mitochondria and other cellular structure further impairing cellular energy mechanism. On the other hand non alcoholic FLD may begin as excess of unmetabolised energy in liver cells. Hepatic steatosis is considered reversible and to some extent nonprogressive if there is cessation or removal of underlying cause.
Severe fatty liver is sometimes accompanied by inflammation
Inflammation
Inflammation is part of the complex biological response of vascular tissues to harmful stimuli, such as pathogens, damaged cells, or irritants. Inflammation is a protective attempt by the organism to remove the injurious stimuli and to initiate the healing process...
, a situation that is referred to as steatohepatitis
Steatohepatitis
Steatohepatitis is a type of liver disease, characterized by inflammation of the liver with concurrent fat accumulation in liver...
. Progression to alcoholic steatohepatitis
Steatohepatitis
Steatohepatitis is a type of liver disease, characterized by inflammation of the liver with concurrent fat accumulation in liver...
(ASH) or non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH) depend on persistence or severity of inciting cause. Pathological lesions in both conditions are similar. However, the extent of inflammatory response varies widely and does not always correlate with degree of fat accumulation. Steatosis
Steatosis
In cellular pathology, steatosis is the process describing the abnormal retention of lipids within a cell. It reflects an impairment of the normal processes of synthesis and elimination of triglyceride fat. Excess lipid accumulates in vesicles that displace the cytoplasm...
(retention of lipid
Lipid
Lipids constitute a broad group of naturally occurring molecules that include fats, waxes, sterols, fat-soluble vitamins , monoglycerides, diglycerides, triglycerides, phospholipids, and others...
) and onset of steatohepatitis may represent successive stages in FLD progression.
Liver with extensive inflammation and high degree of steatosis often progresses to more severe forms of the disease. Hepatocyte
Hepatocyte
A hepatocyte is a cell of the main tissue of the liver. Hepatocytes make up 70-80% of the liver's cytoplasmic mass.These cells are involved in:* Protein synthesis* Protein storage* Transformation of carbohydrates...
ballooning and hepatocyte necrosis
Necrosis
Necrosis is the premature death of cells in living tissue. Necrosis is caused by factors external to the cell or tissue, such as infection, toxins, or trauma. This is in contrast to apoptosis, which is a naturally occurring cause of cellular death...
of varying degree are often present at this stage. Liver cell death and inflammatory responses lead to the activation of stellate cells
Hepatic stellate cell
Hepatic stellate cells , also known as perisinusoidal cells or Ito cells , are pericytes found in the perisinusoidal space of the liver also known as the space of Disse...
which play a pivotal role in hepatic fibrosis
Fibrosis
Fibrosis is the formation of excess fibrous connective tissue in an organ or tissue in a reparative or reactive process. This is as opposed to formation of fibrous tissue as a normal constituent of an organ or tissue...
. The extent of fibrosis varies widely. Perisinusoidal
Sinusoid (blood vessel)
A sinusoid is a small blood vessel similar to a capillary but with a fenestrated endothelium. Fenestrations are pores in the endothelial cells that greatly increase their permeability. In addition, permeability is increased by large inter-cellular clefts and fewer tight junctions...
fibrosis is most common, especially in adults, and predominates in zone 3
Hepatic lobule
A hepatic lobule is a small division of the liver defined at the histological scale. It should not be confused with the anatomic lobes of the liver , or any of the functional lobe classification systems....
around the terminal hepatic veins.
The progression to cirrhosis may be influenced by the amount of fat and degree of steatohepatitis and by a variety of other sensitizing factors. In alcoholic FLD the transition to cirrhosis related to continued alcohol consumption is well documented but the process involved in non-alcoholic FLD is less clear.
Diagnosis
| Flow chart for diagnosis, modified from |
|---|
|-
|align="center"|‡ Criteria for nonalcoholic fatty liver disease:
consumption of ethanol less than 20g/day for woman and 30g/day for man
|}
Most individuals are asymptomatic and are usually discovered incidentally because of abnormal liver function tests or hepatomegaly noted in unrelated medical condition. Elevated liver biochemistry is found in 50% of patients with simple steatosis. The serum ALT
Alanine transaminase
Alanine transaminase or ALT is a transaminase enzyme . It is also called serum glutamic pyruvic transaminase or alanine aminotransferase ....
level usually is greater than the AST
Aspartate transaminase
Aspartate transaminase , also called aspartate aminotransferase or serum glutamic oxaloacetic transaminase , is a pyridoxal phosphate -dependent transaminase enzyme . AST catalyzes the reversible transfer of an α-amino group between aspartate and glutamate and, as such, is an important enzyme in...
level in non-alcoholic variant and the opposite in alcoholic FLD ( AST:ALT more than 2:1).
Imaging studies are often obtained during evaluation process. Ultrasonography reveals a "bright" liver with increased echogenicity
Echogenicity
Echogenicity is the ability to bounce an echo, e.g. return the signal in ultrasound examinations. In other words, Echogenicity is higher when the surface bouncing the sound echo reflects increased sound waves. It could be increased by intravenously administering gas-filled microbubble contrast...
. Medical imaging
Medical imaging
Medical imaging is the technique and process used to create images of the human body for clinical purposes or medical science...
can aid in diagnosis of fatty liver; fatty livers have lower density
Density
The mass density or density of a material is defined as its mass per unit volume. The symbol most often used for density is ρ . In some cases , density is also defined as its weight per unit volume; although, this quantity is more properly called specific weight...
than spleen
Spleen
The spleen is an organ found in virtually all vertebrate animals with important roles in regard to red blood cells and the immune system. In humans, it is located in the left upper quadrant of the abdomen. It removes old red blood cells and holds a reserve of blood in case of hemorrhagic shock...
on computed tomography
Computed tomography
X-ray computed tomography or Computer tomography , is a medical imaging method employing tomography created by computer processing...
(CT) and fat appears bright in T1-weighted
Relaxation (NMR)
In nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy and magnetic resonance imaging the term relaxation describes several processes by which nuclear magnetization prepared in a non-equilibrium state return to the equilibrium distribution. In other words, relaxation describes how fast spins "forget" the...
magnetic resonance images
Magnetic resonance imaging
Magnetic resonance imaging , nuclear magnetic resonance imaging , or magnetic resonance tomography is a medical imaging technique used in radiology to visualize detailed internal structures...
(MRIs). No medical imagery, however, is able to distinguish simple steatosis from advanced NASH
Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease
Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease is one cause of a fatty liver, occurring when fat is deposited in the liver not due to excessive alcohol use. It is related to insulin resistance and the metabolic syndrome and may respond to treatments originally developed for other insulin-resistant states...
. Histological
Histology
Histology is the study of the microscopic anatomy of cells and tissues of plants and animals. It is performed by examining cells and tissues commonly by sectioning and staining; followed by examination under a light microscope or electron microscope...
diagnosis by liver biopsy
Liver biopsy
Liver biopsy is the biopsy from the liver. It is a medical test that is done to aid diagnosis of liver disease, to assess the severity of known liver disease, and to monitor the progress of treatment.-History:...
is sought when assessment of severity is indicated.
Treatment
The treatment of fatty liver depends on what is causing it, and generally, treating the underlying cause will reverse the process of steatosis if implemented at early stage.Complication
Up to 10% of cirrhotic alcoholic FLD will develop hepatocellular carcinomaHepatocellular carcinoma
Hepatocellular carcinoma is the most common type of liver cancer. Most cases of HCC are secondary to either a viral hepatitide infection or cirrhosis .Compared to other cancers, HCC is quite a rare tumor in the United States...
. Overall incidence of liver cancer in non-alcoholic FLD has not yet been quantified, but the association is well established.
Epidemiology
The prevalence of FLD in the general population ranges from 10% to 24% in various countries. However, the condition is observed in up to 75% of obese people, 35% of whom will progress to non-alcoholic FLDNon-alcoholic fatty liver disease
Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease is one cause of a fatty liver, occurring when fat is deposited in the liver not due to excessive alcohol use. It is related to insulin resistance and the metabolic syndrome and may respond to treatments originally developed for other insulin-resistant states...
, despite no evidence of excessive alcohol consumption. FLD is the most common cause of abnormal liver function test in the US. "Fatty livers occur in 33% of European-Americans, 45% of Hispanic-Americans, and 24% of African-Americans."
See also
- SteatosisSteatosisIn cellular pathology, steatosis is the process describing the abnormal retention of lipids within a cell. It reflects an impairment of the normal processes of synthesis and elimination of triglyceride fat. Excess lipid accumulates in vesicles that displace the cytoplasm...
- SteatohepatitisSteatohepatitisSteatohepatitis is a type of liver disease, characterized by inflammation of the liver with concurrent fat accumulation in liver...
- Non-alcoholic fatty liver diseaseNon-alcoholic fatty liver diseaseNon-alcoholic fatty liver disease is one cause of a fatty liver, occurring when fat is deposited in the liver not due to excessive alcohol use. It is related to insulin resistance and the metabolic syndrome and may respond to treatments originally developed for other insulin-resistant states...
- Metabolic syndromeMetabolic syndromeMetabolic syndrome is a combination of medical disorders that, when occurring together, increase the risk of developing cardiovascular disease and diabetes. It affects one in five people in the United States and prevalence increases with age...
- Alcoholic liver diseaseAlcoholic liver diseaseAlcoholic liver disease is a term that encompasses the hepatic manifestations of alcohol overconsumption, including fatty liver, alcoholic hepatitis, and chronic hepatitis with hepatic fibrosis or cirrhosis. It is the major cause of liver disease in Western countries...
- CirrhosisCirrhosisCirrhosis is a consequence of chronic liver disease characterized by replacement of liver tissue by fibrosis, scar tissue and regenerative nodules , leading to loss of liver function...
- Focal fatty liverFocal fatty liverFocal fatty liver is localised or patchy process of lipid accumulation in the liver. It is likely to have different pathogenesis than non-alcoholic steatohepatitis which is a diffuse process. FFL may result from altered venous flow to liver, tissue hypoxia and malabsorption of lipoproteins...

