
Fatigue limit
Encyclopedia
Cyclic stress
Cyclic stress in engineering refers to an internal distribution of forces that changes over time in a repetitive fashion. As an example, consider one of the large wheels used to drive an aerial lift such as a ski lift. The wire cable wrapped around the wheel exerts a downward force on the wheel...
that can be applied to the material without causing fatigue failure
Fatigue (material)
'In materials science, fatigue is the progressive and localized structural damage that occurs when a material is subjected to cyclic loading. The nominal maximum stress values are less than the ultimate tensile stress limit, and may be below the yield stress limit of the material.Fatigue occurs...
. Ferrous
Ferrous
Ferrous , in chemistry, indicates a divalent iron compound , as opposed to ferric, which indicates a trivalent iron compound ....
alloys and titanium
Titanium
Titanium is a chemical element with the symbol Ti and atomic number 22. It has a low density and is a strong, lustrous, corrosion-resistant transition metal with a silver color....
alloys have a distinct limit, an amplitude below which there appears to be no number of cycles that will cause failure. Other structural metals such as aluminium
Aluminium
Aluminium or aluminum is a silvery white member of the boron group of chemical elements. It has the symbol Al, and its atomic number is 13. It is not soluble in water under normal circumstances....
and copper
Copper
Copper is a chemical element with the symbol Cu and atomic number 29. It is a ductile metal with very high thermal and electrical conductivity. Pure copper is soft and malleable; an exposed surface has a reddish-orange tarnish...
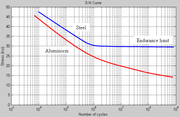
, do not have a distinct limit and will eventually fail even from small stress amplitudes. In these cases, a number of cycles (usually 107) is chosen to represent the fatigue life of the material.
Definitions
The ASTMASTM International
ASTM International, known until 2001 as the American Society for Testing and Materials , is an international standards organization that develops and publishes voluntary consensus technical standards for a wide range of materials, products, systems, and services...
defines fatigue strength, SNf, as the value of stress at which failure occurs after Nf cycles, and fatigue limit, Sf, as the limiting value of stress at which failure occurs as Nf becomes very large. ASTM does not define endurance limit, the stress value below which the material will withstand many number of load cycles, but implies that it is similar to fatigue limit.
Some authors use endurance limit, Se, for the stress below which failure never occurs, even for an indefinitely large number of loading cycles, as in the case of steel
Steel
Steel is an alloy that consists mostly of iron and has a carbon content between 0.2% and 2.1% by weight, depending on the grade. Carbon is the most common alloying material for iron, but various other alloying elements are used, such as manganese, chromium, vanadium, and tungsten...
; and fatigue limit or fatigue strength, Sf, for the stress at which failure occurs after a specified number of loading cycles, such as 500 million, as in the case of aluminium. Other authors do not differentiate between the expressions even if they do differentiate between the two types of materials.
Typical values
Typical values of the limit (Se) for steels are 1/2 the ultimate tensile strength, to a maximum of 100 ksi (690 MPaPascal (unit)
The pascal is the SI derived unit of pressure, internal pressure, stress, Young's modulus and tensile strength, named after the French mathematician, physicist, inventor, writer, and philosopher Blaise Pascal. It is a measure of force per unit area, defined as one newton per square metre...
). For iron, aluminium, and copper alloys, Se is typically 0.4 times the ultimate tensile strength. Maximum typical values for irons are 24 ksi (165 MPa), aluminums 19 ksi (131 MPa), and coppers 14 ksi (96.5 MPa).
Note that these values are for smooth "un-notched" test specimens. The endurance limit for notched specimens (and thus for many practical design situations) is significantly lower.
History
The concept of endurance limit was introduced in 1870 by August WöhlerAugust Wöhler
August Wöhler was a German engineer, best remembered for his systematic investigations of metal fatigue.Born in the town of Soltau, the son of local teacher Georg Heinrich Wöhler showed early mathematical ability and won a scholarship to study at the Technische Hochschule in Hannover, under the...
. However, recent research suggests that endurance limits do not actually exist, that if enough stress cycles are performed, even the smallest stress will eventually produce fatigue failure.

