Fasciola gigantica
Overview
Fasciola gigantica is a parasitic flatworm
of the class
Trematoda
, which causes tropical fascioliasis
. It is regarded as one of the most important single platyhelminth infections of ruminants in Asia
and Africa
. Estimates of infection
rates are as high as 80-100% in some countries.
Fasciola gigantica causes outbreaks in tropical areas of southern Asia, Southeast Asia, and Africa. The geographical distribution of Fasciola gigantica overlaps with Fasciola hepatica
in many African and Asian countries and sometimes in the same country, although in such cases the ecological requirement of the flukes and their snail host are distinct.
Infection is most prevalent in regions with intensive sheep and cattle production.
In Egypt Fasciola gigantica exist in domestic animals since the times of the pharaoh
s.
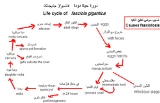
The life cycle of Fasciola gigantica is as follows: eggs (transported with feces) → eggs hatchs → miracidium
→ miracidium infect snail intermediate host → (parthenogenesis
in 24 hours) sporocyst
→ redia
→ daughter redia → cercaria → (gets outside the snail and forms sporocyst) → metacercaria → infection of the host → adult stage produces eggs.
As with other trematodes, Fasciola develop in a mollusca
n intermediate host
.
Flatworm
The flatworms, known in scientific literature as Platyhelminthes or Plathelminthes are a phylum of relatively simple bilaterian, unsegmented, soft-bodied invertebrate animals...
of the class
Class (biology)
In biological classification, class is* a taxonomic rank. Other well-known ranks are life, domain, kingdom, phylum, order, family, genus, and species, with class fitting between phylum and order...
Trematoda
Trematoda
Trematoda is a class within the phylum Platyhelminthes that contains two groups of parasitic flatworms, commonly referred to as "flukes".-Taxonomy and biodiversity:...
, which causes tropical fascioliasis
Fascioliasis
Fasciolosis also known as Fascioliasis, Fasciolasis, distomatosis and liver rot, is an important helminth disease caused by two trematodes Fasciola hepatica and Fasciola gigantica. This disease belongs to the plant-borne trematode zoonoses. In Europe, the Americas and Oceania only F...
. It is regarded as one of the most important single platyhelminth infections of ruminants in Asia
Asia
Asia is the world's largest and most populous continent, located primarily in the eastern and northern hemispheres. It covers 8.7% of the Earth's total surface area and with approximately 3.879 billion people, it hosts 60% of the world's current human population...
and Africa
Africa
Africa is the world's second largest and second most populous continent, after Asia. At about 30.2 million km² including adjacent islands, it covers 6% of the Earth's total surface area and 20.4% of the total land area...
. Estimates of infection
Infection
An infection is the colonization of a host organism by parasite species. Infecting parasites seek to use the host's resources to reproduce, often resulting in disease...
rates are as high as 80-100% in some countries.
Fasciola gigantica causes outbreaks in tropical areas of southern Asia, Southeast Asia, and Africa. The geographical distribution of Fasciola gigantica overlaps with Fasciola hepatica
Fasciola hepatica
Fasciola hepatica, also known as the common liver fluke or sheep liver fluke, is a parasitic flatworm of the class Trematoda, phylum Platyhelminthes that infects the livers of various mammals, including humans. The disease caused by the fluke is called fascioliasis . F...
in many African and Asian countries and sometimes in the same country, although in such cases the ecological requirement of the flukes and their snail host are distinct.
Infection is most prevalent in regions with intensive sheep and cattle production.
In Egypt Fasciola gigantica exist in domestic animals since the times of the pharaoh
Pharaoh
Pharaoh is a title used in many modern discussions of the ancient Egyptian rulers of all periods. The title originates in the term "pr-aa" which means "great house" and describes the royal palace...
s.
The life cycle of Fasciola gigantica is as follows: eggs (transported with feces) → eggs hatchs → miracidium
Miracidium
Trematodes are small parasitic flatworms that use vertebrates as their definitive host, and molluscs as their intermediate host. In order to accomplish this, they have several varied lifecyle stages....
→ miracidium infect snail intermediate host → (parthenogenesis
Parthenogenesis
Parthenogenesis is a form of asexual reproduction found in females, where growth and development of embryos occur without fertilization by a male...
in 24 hours) sporocyst
Trematode lifecycle stages
Trematodes are small parasitic flatworms that use vertebrates as their definitive host, and molluscs as their intermediate host. In order to accomplish this, they have several varied lifecyle stages....
→ redia
Trematode lifecycle stages
Trematodes are small parasitic flatworms that use vertebrates as their definitive host, and molluscs as their intermediate host. In order to accomplish this, they have several varied lifecyle stages....
→ daughter redia → cercaria → (gets outside the snail and forms sporocyst) → metacercaria → infection of the host → adult stage produces eggs.
As with other trematodes, Fasciola develop in a mollusca
Mollusca
The Mollusca , common name molluscs or mollusksSpelled mollusks in the USA, see reasons given in Rosenberg's ; for the spelling mollusc see the reasons given by , is a large phylum of invertebrate animals. There are around 85,000 recognized extant species of molluscs. Mollusca is the largest...
n intermediate host
Intermediate host
A secondary host or intermediate host is a host that harbors the parasite only for a short transition period, during which some developmental stage is completed. For trypanosomes, the cause of sleeping sickness, humans are the primary host, while the tsetse fly is the secondary host...
.

