
FDIC Enterprise Architecture Framework
Encyclopedia
FDIC Enterprise Architecture Framework is the Enterprise Architecture framework of the United States Federal Deposit Insurance Corporation
(FDIC). A lot of the current article is about the Enterprise Architecture Framework developed around 2005, and currently anno 2011 out-of-date.
is based on Federal and industry best practices, including the Chief Information Officer (CIO) Council's Federal Enterprise Architecture Framework (FEAF) and the Zachman Framework
for Enterprise Architecture. FDIC's framework has been tailored to emphasize security
. The FDIC EA framework complies with the FEAF and highlights the importance of security to all other components of the architecture.
The FDIC EA framework includes five components. The first component, the Business Architecture, focuses on FDIC's business needs. The next three components, the Data Architecture
, Applications Architecture, and Technical Infrastructure Architectures, focus on the technological capabilities that support the business and information needs. The final component, the Security Architecture
, focuses on specific aspects of interest to the Corporation that span the enterprise and must be integral parts of all other architectures.
(FEA), has been undertaken in an effort to yield significant improvements in the management and reuse of IT investments, while improving services to citizens, and facilitating business relationships internally and externally. The FEA is a business-based framework that provides the Office of Management and Budget (OMB) and Federal agencies a way to monitor, analyze, and control Federal IT investments. The FDIC first realized the value of EA in 1997, when two business executives had to reconcile data that had come from different systems for a high-profile report to the banking industry. The FDIC's first EA blueprint was published in December 2002.
In 2004 the FDIC received a 2004 Enterprise Architecture Excellence Award from the Zachman Institute for Framework Advancement (ZIFA) for its initiative to manage corporate data collaboratively. John Zachman
, an expert on enterprise architecture, founded ZIFA, a network of information professionals supporting enterprise architecture's role in helping organizations operate from a corporate perspective.
 The banking business model has become more complex, giving rise to financial instruments such as collateralized debt obligation
The banking business model has become more complex, giving rise to financial instruments such as collateralized debt obligation
s (CDOs) and structured investment vehicle
s (SIVs) to manage risk. These instruments have created greater dependencies between the domestic and international financial markets. Financial institutions must, therefore, strike a balance between regulatory, legislative and banker concerns while appropriately managing risk.
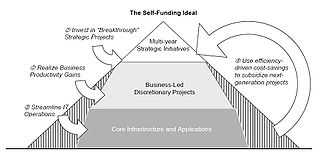
As cost savings are realized from a simplified IT environment and more efficient processes, the savings will be reinvested for IT improvements or accrue to the Corporation. This self-funding model is shown on the right.
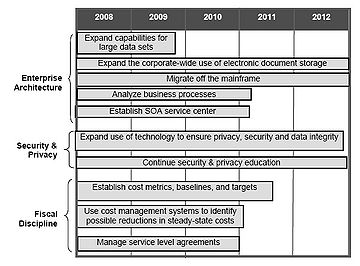 The enterprise architecture initiative will focus on simplifying the environment to ensure stable and economical performance for mission-critical applications. Simplifying the environment to decrease costs will include activities, such as decreasing the number of application systems and migrating applications off the mainframe. Efficiencies will also be gained by expanding capabilities for manipulating large data sets and storing traditional paper-based files electronically. The SOA service center will manage code (or services) for all development teams to discover and use, which will save time and costs in application development, testing and deployment.
The enterprise architecture initiative will focus on simplifying the environment to ensure stable and economical performance for mission-critical applications. Simplifying the environment to decrease costs will include activities, such as decreasing the number of application systems and migrating applications off the mainframe. Efficiencies will also be gained by expanding capabilities for manipulating large data sets and storing traditional paper-based files electronically. The SOA service center will manage code (or services) for all development teams to discover and use, which will save time and costs in application development, testing and deployment.
The organization will continue to enhance IT security and privacy programs to address new and evolving risks by improving controls over sensitive data. In some cases, technology, such as scanning outgoing e-mail for sensitive information and encrypting removable storage devices, can mitigate potential risks. The other cornerstone of mitigating risk is educating employees of emerging security and privacy issues.
Lastly, in order to continue sound fiscal discipline and responsibility, the organization will establish IT baselines and metrics, study steady-state costs, manage service level agreements, and more judiciously choose new development projects. These three areas – enterprise architecture, security and privacy programs, and fiscal discipline – are shown below with the estimated time frames.
Federal Deposit Insurance Corporation
The Federal Deposit Insurance Corporation is a United States government corporation created by the Glass–Steagall Act of 1933. It provides deposit insurance, which guarantees the safety of deposits in member banks, currently up to $250,000 per depositor per bank. , the FDIC insures deposits at...
(FDIC). A lot of the current article is about the Enterprise Architecture Framework developed around 2005, and currently anno 2011 out-of-date.
Overview
The FDIC's framework for implementing its Enterprise ArchitectureEnterprise architecture
An enterprise architecture is a rigorous description of the structure of an enterprise, which comprises enterprise components , the externally visible properties of those components, and the relationships between them...
is based on Federal and industry best practices, including the Chief Information Officer (CIO) Council's Federal Enterprise Architecture Framework (FEAF) and the Zachman Framework
Zachman framework
The Zachman Framework is an Enterprise Architecture framework for enterprise architecture, which provides a formal and highly structured way of viewing and defining an enterprise...
for Enterprise Architecture. FDIC's framework has been tailored to emphasize security
Security
Security is the degree of protection against danger, damage, loss, and crime. Security as a form of protection are structures and processes that provide or improve security as a condition. The Institute for Security and Open Methodologies in the OSSTMM 3 defines security as "a form of protection...
. The FDIC EA framework complies with the FEAF and highlights the importance of security to all other components of the architecture.
The FDIC EA framework includes five components. The first component, the Business Architecture, focuses on FDIC's business needs. The next three components, the Data Architecture
Data architecture
Data Architecture in enterprise architecture is the design of data for use in defining the target state and the subsequent planning needed to achieve the target state...
, Applications Architecture, and Technical Infrastructure Architectures, focus on the technological capabilities that support the business and information needs. The final component, the Security Architecture
Security Architecture
Security provided by IT Systems can be defined as the IT system’s ability to be able to protect confidentiality and integrity of processed data, as well as to be able to provide availability of the system and data....
, focuses on specific aspects of interest to the Corporation that span the enterprise and must be integral parts of all other architectures.
History
Historically, Federal agencies have managed IT investments autonomously. Until the new millennium, there has been little incentive for agencies to partner to effectively reuse IT investments, share IT knowledge, and explore joint solutions. A collective, government-wide effort, supported by the Federal CIO Council, utilizing the Federal Enterprise ArchitectureFederal Enterprise Architecture
A federal enterprise architecture is the enterprise architecture of a federal government. It provides a common methodology for information technology acquisition, use, and disposal in the Federal government....
(FEA), has been undertaken in an effort to yield significant improvements in the management and reuse of IT investments, while improving services to citizens, and facilitating business relationships internally and externally. The FEA is a business-based framework that provides the Office of Management and Budget (OMB) and Federal agencies a way to monitor, analyze, and control Federal IT investments. The FDIC first realized the value of EA in 1997, when two business executives had to reconcile data that had come from different systems for a high-profile report to the banking industry. The FDIC's first EA blueprint was published in December 2002.
In 2004 the FDIC received a 2004 Enterprise Architecture Excellence Award from the Zachman Institute for Framework Advancement (ZIFA) for its initiative to manage corporate data collaboratively. John Zachman
John Zachman
John A. Zachman is an American business and IT consultant, early pioneer of enterprise architecture, Chief Executive Officer of Zachman International, and originator of the Zachman Framework.- Biography :...
, an expert on enterprise architecture, founded ZIFA, a network of information professionals supporting enterprise architecture's role in helping organizations operate from a corporate perspective.
FDIC EA framework
The FDIC EA framework from 2005 included five components.- Business ArchitectureBusiness architectureA business architecture is a part of an enterprise architecture related to corporate business, and the documents and diagrams that describe that architectural structure of business...
: The Business Architecture describes the activities and processes performed by the Corporation to achieve its mission and to realize its vision and goals. Developing the Business Architecture is the first step in creating an Enterprise Architecture (EA) that links the Corporation's business needs to its Information Technology (IT) environment. Maximizing IT support for these requirements will optimize Corporate performance.
- Data ArchitectureData architectureData Architecture in enterprise architecture is the design of data for use in defining the target state and the subsequent planning needed to achieve the target state...
: The Data Architecture describes the activities required to obtain and maintain data that supports the information needed by the Corporation’s major business areas. Data and information are different. Data is the foundation of information. Data is the raw material that is processed and refined to generate information. Information consists of a collection of related data that has been processed into a form that is meaningful to the recipient.
- Applications ArchitectureApplications architectureAn applications architecture describes the structure and behaviour of applications used in a business, focused on how they interact with each other and with users. It is focused on the data consumed and produced by applications rather than their internal structure...
: The Applications Architecture describes the major types of applications that manage data to produce the information needed to support the activities of the Corporation. The Applications Architecture provides a framework that enables the migration from the current applications catalog and software development environment to the target integrated applications, development and engineering environments. The target architecture promotes the use of commercial and government off-the-shelf products, consolidating applications, where applicable, and the use of emerging technologies where appropriate.
- Technical Infrastructure Architecture : The IT infrastructure provides access to application systems and office automation tools used in performance of the business processes. The Corporation places high priority on maintaining a consistent, available, and reliable technical infrastructure. The Technical Architecture describes the underlying technology for the Corporation's business, data, and application processing. It includes the technologies used for communications, data storage, application processing, and computing platforms.
- Security ArchitectureSecurity ArchitectureSecurity provided by IT Systems can be defined as the IT system’s ability to be able to protect confidentiality and integrity of processed data, as well as to be able to provide availability of the system and data....
: The Security Architecture establishes a framework for integrating safeguards into all layers of the FDIC's Enterprise Architecture. The security architecture uses a risk management and information assurance strategy that provides access control, confidentiality, integrity, and non-repudiation for the Corporation's information and systems.
Future IT development

Collateralized debt obligation
Collateralized debt obligations are a type of structured asset-backed security with multiple "tranches" that are issued by special purpose entities and collateralized by debt obligations including bonds and loans. Each tranche offers a varying degree of risk and return so as to meet investor demand...
s (CDOs) and structured investment vehicle
Structured investment vehicle
A structured investment vehicle was an operating finance company established to earn a spread between its assets and liabilities like a traditional bank...
s (SIVs) to manage risk. These instruments have created greater dependencies between the domestic and international financial markets. Financial institutions must, therefore, strike a balance between regulatory, legislative and banker concerns while appropriately managing risk.
As cost savings are realized from a simplified IT environment and more efficient processes, the savings will be reinvested for IT improvements or accrue to the Corporation. This self-funding model is shown on the right.
Five-year technology roadmap
The technology roadmap outlines the major initiatives for standardizing the IT environment and increasing IT’s efficiency and effectiveness over the next five years. The initiatives were determined by various sources including business-side IT roadmaps, executive management planning meetings, client planning sessions, and client year-end reviews. The three major initiatives identified are enterprise architecture, security and privacy programs, and fiscal discipline.
The organization will continue to enhance IT security and privacy programs to address new and evolving risks by improving controls over sensitive data. In some cases, technology, such as scanning outgoing e-mail for sensitive information and encrypting removable storage devices, can mitigate potential risks. The other cornerstone of mitigating risk is educating employees of emerging security and privacy issues.
Lastly, in order to continue sound fiscal discipline and responsibility, the organization will establish IT baselines and metrics, study steady-state costs, manage service level agreements, and more judiciously choose new development projects. These three areas – enterprise architecture, security and privacy programs, and fiscal discipline – are shown below with the estimated time frames.
Further reading
- Pallab Saha (2007). Handbook of Enterprise Systems Architecture in Practice. Chapter IX gives a detailed case study of the FDIC.
External links
- FDIC Homepage.

